автордың кітабын онлайн тегін оқу A Book of North Wales
TRANSCRIBER’S NOTES:
—Obvious print and punctuation errors were corrected.
—The transcriber of this project created the book cover image using the front cover of the original book. The image is placed in the public domain.
A BOOK OF
NORTH WALES
UNIFORM WITH THIS VOLUME
By S. BARING-GOULD
A BOOK OF DARTMOOR
A BOOK OF THE WEST—TWO VOLUMES
VOL. I. DEVON VOL. II. CORNWALL
A BOOK OF BRITTANY
By F. J. SNELL
A BOOK OF EXMOOR

CONWAY CASTLE
A BOOK OF
NORTH WALES
BY S. BARING-GOULD
WITH FORTY-NINE ILLUSTRATIONS
METHUEN & CO.
36 ESSEX STREET W.C.
LONDON
1903
PREFACE
CONCERNING the purpose and scope of this little book I have but to repeat what I have said in the prefaces to my other works of the same nature—A Book of the West, A Book of Dartmoor, A Book of Brittany—that it is not intended as a Guide, but merely as an introduction to North Wales, for the use of intending visitors, that they may know something of the history of that delightful land they are about to see.
Welsh history is a puzzle to most Englishmen; accordingly I have made an attempt to simplify it sufficiently for the visitor to grasp its outlines. Without a knowledge of the history of a country in which one travels more than half its interest is lost.
I have to return my warmest thanks to kind friends who have helped me with information, notably the Rev. J. Fisher, B.D., of Cefn, S. Asaph; Mr. J. E. Griffith, of Bryn Dinas, Bangor; the Rev. E. Evans, of Llansadwrn; Mr. C. H. Jones, of the Public Library, Welshpool; Mr. A. Foulkes-Roberts, of Denbigh; Mr. D. R. Daniel, of Four Crosses, Chwilog; and Mr. R. Williams, of Celynog, Newtown. I am also much indebted to Mr. R. J. Lloyd Price, of Rhiwlas, for kindly allowing me to reproduce the portrait of Catherine of Berain in his possession; and to Mr. Prys-Jones, of Bryn-Tegid, Pontypridd, for sending me a photograph of the painting. But, indeed, everywhere in Wales I have met with general kindness and hospitality; and if I have failed to interest readers in the country and people the fault is all mine. It is a glorious country, and its people delightful.
S. BARING-GOULD
Lew Trenchard, N. Devon
May 17th, 1903
CONTENTS
Chapter PageI.
The Welsh People 1II.
The English Conquest 12III.
Anglesey 22IV.
Holyhead 46V.
Bangor and Carnarvon 63VI.
Snowdon 90VII.
Lleyn 106VIII.
Conway 125IX.
S. Asaph 145X.
Denbigh 163XI.
Llangollen 183XII.
Dolgelley 205XIII.
Harlech 231XIV.
Welshpool 244XV.
Newtown 271XVI.
Machynlleth 291ILLUSTRATIONS
FULL PAGE Conway Castle FrontispieceFrom a photograph by Messrs. F. Frith and Co.
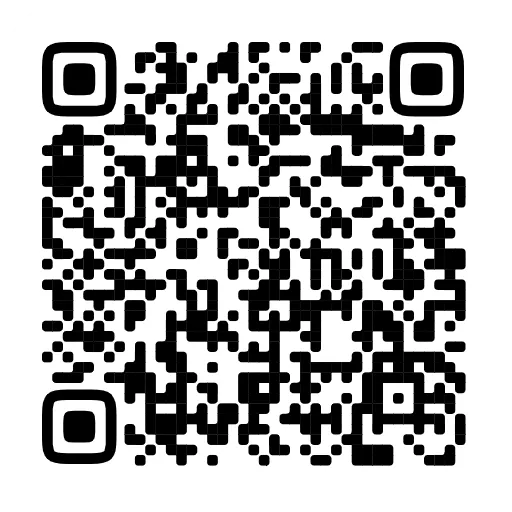
Welsh Women To face page 8From a photograph by Messrs. F. Frith and Co.
Holyhead at Rhoscolyn ” 22From a photograph by Messrs. F. Frith and Co.
South Stack Light, Holyhead ” 46From a photograph by Messrs. F. Frith and Co.
South Stack Bridge ” 59From a photograph by Messrs. Valentine and Sons, Ltd.
Carnarvon Castle ” 74From a photograph by Messrs. Valentine and Sons, Ltd.
Nant Bridge, Carnarvon ” 80From a photograph by Messrs. Valentine and Sons, Ltd.
Bethesda ” 85From a photograph by Messrs. F. Frith and Co.
Snowdon ” 90From a photograph by Messrs. Valentine and Sons, Ltd.
Aberglaslyn Pass ” 95From a photograph by Messrs. Valentine and Sons, Ltd.
Llanberis ” 99From a photograph by Messrs. Valentine and Sons, Ltd.
Beddgelert ” 102From a photograph by Messrs. Valentine and Sons, Ltd.
Capel Curig ” 105From a photograph by Messrs. Valentine and Sons, Ltd.
Conway Castle ” 125From a photograph by Messrs. Valentine and Sons, Ltd.
Plas Mawr, Exterior ” 129From a photograph by Messrs. F. Frith and Co.
Plas Mawr, Court ” 130From a photograph by Messrs. F. Frith and Co.
Catherine of Berain ” 146From a painting.
Ruthin Castle ” 163From a photograph by Messrs. Valentine and Sons, Ltd.
Llangollen Bridge ” 183From a photograph by Messrs. Valentine and Sons, Ltd.
Berwyn ” 184From a photograph by Messrs. Valentine and Sons, Ltd.
Berwyn, from Castell Dinas Bran ” 187From a photograph by Messrs. F. Frith and Co.
The Ladies of Llangollen ” 188From an old print.
The Pillar of Eliseg ” 190From a photograph by Messrs. Valentine and Sons, Ltd.
Vale Crucis Abbey ” 191From a photograph by Messrs. Valentine and Sons, Ltd.
Vale Crucis Abbey from within ” 195From a photograph by Messrs. Valentine and Sons, Ltd.
Cader Idris ” 205From a photograph by Messrs. F. Frith and Co.
Cader Idris ” 206From a photograph by Messrs. F. Frith and Co.
Torrent Walk, Dolgelley ” 208From a photograph by Messrs. Valentine and Sons, Ltd.
Null, Torrent Walk ” 209From a photograph by Messrs. Valentine and Sons, Ltd.
Cader Idris ” 210From a photograph by Messrs. F. Frith and Co.
Pistyll-y-Cain ” 216From a photograph by Messrs. Valentine and Sons, Ltd.
Lyn-y-Groes, Dolgelley ” 224From a photograph by Messrs. Valentine and Sons, Ltd.
Halfway House, Dolgelley ” 226From a photograph by Messrs. Valentine and Sons, Ltd.
Harlech Castle ” 231From a photograph by Messrs. Valentine and Sons, Ltd.
Church, Montgomery ” 246From a photograph by F. Bligh Bond, Esq.,
f.r.i.b.a. Powis Castle ” 256From a photograph by Messrs. Valentine and Sons, Ltd.
Owen Glyndwr’s Parliament House, Machynlleth ” 291From a photograph by Messrs. Valentine and Sons, Ltd.
Old Bridge, Dinas Mawddwy ” 300From a photograph by Messrs. F. Frith and Co.
Llanegryn ” 308From a photograph by F. Bligh Bond, Esq.,
f.r.i.b.a.WELSH WOMEN
HOLYHEAD, AT RHOSCOLYN
SOUTH STACK LIGHT, HOLYHEAD
SOUTH STACK BRIDGE
CARNARVON CASTLE
NANT BRIDGE, CARNARVON
BETHESDA
SNOWDEN, FROM BWLCH GLAS
ABERGLASLYN PASS
LLANBERIS
BEDDGELERT
CAPEL CURIG
CONWAY CASTLE
PLAS MAWR, CONWAY
PLAS MAWR, CONWAY
CATHERINE OF BERAIN
RUTHIN CASTLE
LLANGOLLEN
BERWYN
BERWYN FROM CASTELL DINAS BRAN
THE LADIES OF LLANGOLLEN
THE PILLAR OF ELISEG
VALE CRUCIS ABBEY
VALE CRUCIS ABBEY
CADER IDRIS
CADER IDRIS
THE TORRENT WALK, DOLGELLEY
MILL, TORRENT WALK, DULGELLEY
CADER IDRIS
PISTYLL-Y-CAIN, DOLGELLEY
TYN-Y-GROES, DOLGELLEY
HALFWAY HOUSE, DOLGELLEY
HARLECH CASTLE
CHURCH, MONTGOMERY
POWIS CASTLE
OWEN GLYNDWR’S HOUSE, MACHYNLLETH
OLD BRIDGE, DINAS MAWDDWY
LLANEGRYN
IN THE TEXT Page Serigi. A Statue at Caergybi 25 S. Seiriol. Stained Glass, Penmon 31 Holy Well, Penmon 35 Base of Shrine, Llaneilian 39 Cross at Llanbadrig 41 S. Cybi. Statue, South Doorway, Caergybi 53 Doorway, S. Cybi’s Well 111 Bronwen’s Urn 235 Tyssilio’s Ring at Saint-Suliac 264 Gildas. A sixteenth-century Statue at Locminé 279
SERIGI. A STATUE AT CAERGYBI
S. SEIRIOL. STAINED GLASS, PENMON
HOLY WELL, PENMON
BASE OF SHRINE, LLANEILIAN
CROSS AT LLANBADRIG
S. CYBI. STATUE, SOUTH DOORWAY, CAERGYBI
DOORWAY, S. CYBI’S WELL
BRONWEN’S URN
TYSSILIO’S RING AT SAINT-SULIAC
A FIFTEENTH-CENTURY STATUE AT LOCMINÉ
NORTH WALES
CHAPTER I
THE WELSH PEOPLE
General characteristics—The Iberian race—Linguistic survivals—Brython and Goidel—Roman conquest—Irish occupation of Wales—Their expulsion by Cunedda—Saxon occupation of Britain—Causes of subjection of the Celtic races—The Celt in the Englishman of to-day—Divisions of Wales.
IT cannot be said that the Welsh have any very marked external characteristics to distinguish them from the English. But there is certainly among them a greater prevalence of dark hair and eyes, and they are smaller in build. This is due to the Iberian blood flowing in the stock which occupied the mountain land from a time before history began, at least in these isles. It is a stock so enduring, that although successive waves of conquest and migration have passed over the land, and there has been an immense infiltration of foreign blood, yet it asserts itself as one of predominant and indestructible vitality.
Moreover, although the language is Celtic, that is to say, the vocabulary is so, yet the grammar reveals the fact that it is an acquired tongue. It is a comparatively easy matter for a subjugated people to adopt the language of its masters, so far as to accept the words they employ, but it is another matter altogether to acquire their construction of sentences. The primeval population belonged to what is called the Hamitic stock, represented by ancient Egyptian and modern Berber. This people at a vastly remote period spread over all Western Europe, and it forms the subsoil of the French nation at the present day.
The constant relations that existed between the Hebrews and the Egyptians had the effect of carrying into the language of the former a number of Hamitic words. Moreover, the Sons of Israel were brought into daily contact with races of the same stock on their confines in Gilead and Moab, and the consequence is that sundry words of this race are found in both Hebrew and Welsh. This was noticed by the Welsh scholar Dr. John Davies, of Mallwyd, who in 1621 drew up a Welsh Grammar, and it is repeated by Thomas Richards in his Welsh-English Dictionary in 1753. He says: “It hath been observed, that our Language hath not a great many Marks of the original Simplicity of the Hebrew, but that a vast Number of Words are found therein, that either exactly agree with, or may be very naturally derived from, that Mother-language of Mankind.”
The fact is that these words, common to both, belong radically to neither, but are borrowed from the tongue of the Hamitic people.
This original people, which for convenience we will call Iberian, migrated at some unknown period from Asia, and swept round Europe, whilst a second branch colonised the Nile basin and Northern Africa, and a third streamed east and occupied China and Japan.
The master idea in the religion of this people was the cult of ancestors, and the rude stone monuments, menhirs, cromlechs, and kistvaens they have left everywhere, where they have been, all refer to commemoration of the sacred dead. The obelisk in Egypt is the highly refined menhir, and the elaborate, ornamented tombs of the Nile valley are the expression of the same veneration for the dead, and belief in the after life connected with the tomb, that are revealed in the construction of the dolmen and kistvaen.
This same people occupied Ireland. It was a dusky, short-statured race, with long heads, and was mild and unwarlike in character.
Then came rushing from the East great hordes of fair-haired, round-headed men, with blue eyes. Their original homes were perhaps the Alps, but more probably Siberia. This new race was the Celt. It was divided into two branches, the Goidels and the Brythons, and the Goidels came first. Considerable difference as well as affinity exists between the dialects spoken by each. Where a Brython or Britton would speak of his head as “pen,” the Goidel or Gael would call it “ceann,” pronouncing the c hard, as k. So “five” in Manx is “queig,” but in Welsh “pump.” A like difference was found in Italy, where the Roman would name a man Quinctius (Fifth), but a Samnite would call him Pontius.
The Gael is now represented by the Irish, the Manx, and the Highlander: the Britton, so far as language goes, by the Welsh and Breton.
Where such names are found as Penmon in Anglesey, Pentire in Cornwall, Pen-y-gent in Yorkshire, there we know that the Britton lived long enough to give names to places. But where we find Kenmare, Kentire, Kinnoul, there we know that the Gael was at home.
Now we find it asserted that the Goidels overran Wales before they swept into Ireland, and that the Brittons penetrated as a wedge into Powys between two masses of Goidels.
But the place-names in North and South Wales are purely British, and not Gaelic. That the latter were at one time in both North and South Wales is indubitable, but they were not there long enough to stamp the mountains and rivers, the headlands and lakes, with names in their tongue. That was done by the Brittons who overflowed the whole of Wales from north to south.
Owing to the weakness of Britain, that had been in part Romanised, and which was ill-defended by a few legions, the island became a prey to invaders. It was fallen upon from all sides.
The Irish or Scots, as they were then called, poured down upon the western coast; the Picts broke over the wall from the north, and the Scandinavians and Germans invaded the east and north-east.
In 240 the Irish king Cormac MacAirt invaded Britain and assumed a nominal sovereignty over it. It was probably about this time that the Irish Gaels effected a lodgment on the coast of Wales and occupied Anglesey and all the northern fringe of the fair lands by the sea and the whole of Southern Wales.
That they were in the land we know, not only from the testimony of Welsh ancient writers, but from the number of inscribed stones they have left behind them, some with the Ogam script, bearing distinctly Irish names. All these inscribed stones belong to the period after the occupation from Ireland, and none go back to an earlier date, and give any grounds for supposing that the original population of North and South Wales were Gaels. The Scots or Irish held these parts till an event took place which led to their expulsion.
The incursions of the Picts had made residence in the land between the Roman walls, i.e. from the Clyde to Solway Firth, altogether unendurable, and a chief there named Cunedda, with his sons and a great host of followers, descended on North Wales to wrest it from the Irish. This they succeeded in doing. Cunedda and his sons were Brittons. After a series of contests they drove the Irish first out of Gwynedd, and then out of Anglesey. Finally they turned them bag and baggage out of South Wales as well. Thenceforth the Gaels never again obtained a foothold for any length of time in Wales.
Ceredig, son of Cunedda, gave his name to Ceredigion or Cardigan; Meirion, grandson of Cunedda, has bequeathed his to Merioneth.
The contest began between 400 and 450, and the complete sweeping out of the Gael was not accomplished till the beginning of the following century. But by this time the invasion of Britain by the Jute, Angle, and Saxon had begun on a large scale, and as the Teutonic warriors advanced, burning and slaying, they rolled back the unfortunate Brittons westward.
After the whole of Eastern Britain had been taken and occupied, the line of demarcation between Celt and Teuton ran from the Firth of Forth along the backbone of the Pennine Range to the Forest of Arden, and thence to Salisbury and to the sea by Christchurch. But the invaders pressed on. In 577 the Brittons were defeated at Deorham, near Bath, and those of Wales were cut off from their brethren in Devon and Cornwall. In 607 they met with a signal reverse at Chester, and they thenceforth were separated from the Brittons in Strathclyde. Still the unsatiated Anglo-Saxons pressed on, and the Brittons finally retained only the mountains of Wales as their last refuge. Many, indeed, fled over the sea and occupied and colonised Armorica, to which they gave the name of Lesser Britain or Brittany.
The borderland was the scene of bloody skirmishes for centuries. Till 784 Shrewsbury had been accounted the capital of the British kingdom of Powys, but then Offa took the city and advanced the English frontier to the Wye. He then constructed a dyke or bank with a moat that ran from the estuary of the Dee to the mouth of the Wye, as a limit beyond which no Welshman might pass.
Mona received an English colony under Egbert, and acquired its new name of Anglesey. Some time after the battles of Deorham and Chester the refugees began to call themselves Cymry.
The name implies “compatriots,” and well describes those of the same blood from all parts of Britain, now united in a common overthrow, and in a common resolution to hold for ever their mountain fastnesses to which they had been driven.
We may halt to inquire how it was that this great and heroic people, to which belong some of the finest qualities that are found in man, a people in some respects more gifted than that which dispossessed it, should have been so completely routed by invaders from across the stormy North Sea. The Gaul had been of precisely the same Brythonic stock, and he had allowed himself to be buffeted by Cæsar and brought to his knees. Cæsar was sharp-witted enough to detect at a glance the defects in character and in political organisation of the Gauls, and to take advantage of them. Cæsar could always reckon on tribal jealousies, and consequently on setting one clan against another; and there was not a tribe in which there were not traitors, who, offended in their self-esteem, were ready to betray those of their own race and household, to wipe off some petty slight, to avenge some personal grudge. Precisely the same cause led to the ruin of the Brittons when opposed to Germanic invaders, and, as we shall see in the sequel, the same cause again acted throughout the long struggle with the English kings.
The divisions in Wales opened the door for Norman and English adventurers to come in and possess the land, and for the monarch to obtain an ever-strengthening grip on the land.
A brother was always ready to go over to the foe to gain some mean advantage; one sept was ever prepared to side with the national foe if it thought thereby to humble another sept, or to acquire through this means a few more cows and a little more pasture.
When Jute, Angle, or Saxon crossed the North Sea they were in the same political condition as were the Welsh; they also were tribally organised. But they quickly learned the lesson never to be taken to heart and acted on by the Britton, that of subordination of individual interests to the common good. The English kingdoms became consolidated into one; the British chieftains remained to the end disunited.
In feudal France province was opposed to province, in much the same way, till the strong hand of Richelieu consolidated the monarchy.
Even in Armorica, Lesser Britain, to which crowds of refugees had escaped, the lesson was not acquired. Attacked from the east by the Franks, ravaged along the sea-coast by the Northmen, they could not combine. The princes turned their swords against each other in the face of the common foe.
Alan Barbetorte, godson of Athelstan, had not been fostered in England without having drunk in that which made England strong. When he returned to Armorica he succeeded in forcing his countrymen to combine in a supreme effort to hurl the pirates back into the sea, and naturally enough succeeded, by so doing, in freeing the land from them. But after his death all went back into the same condition of internal jealousies and strife. Throughout the Middle Ages Brittany was a battlefield, the dukes and counts flying at each other’s throat, some calling themselves partisans of the English, some of the French, but all seeking personal aggrandisement only.

WELSH WOMEN
Not till 1490 did peace and unity reign in Brittany, just five years after Henry Tudor became King of England, and put a stop to the strife in Wales. The late Mr. Green, in his The Making of England, laid stress on the important part that the Latin Church played in promoting the unity of the English race. But neither in France nor in Germany, there least of all, did it serve this end, and it was probably less the work of the Church that England became one than the peculiar genius of the Anglo-Saxon race. For a while we see it divided into three great forces—the Northumbrian, the Mercian, and the West Saxon—contending for the mastery, but each actuated by the dominating belief that so only could England thrive and shake off her enemies.
Mr. Green perhaps overrates the Anglo-Saxon, and thinks that the Britton disappeared from the soil before him as he advanced. At first, indeed, those who landed from their German keels proceeded to ruthless extermination. But as they advanced they ceased to do so; they were not themselves inclined to till the soil, they were content to spare their captives on condition that they became their slaves, and they certainly kept the women for themselves. Gildas, a contemporary, says that “some, being taken in the mountains, were murdered in great numbers; others, constrained by famine, yielded themselves up to be enthralled by their foes; others, again, escaped beyond the seas.”
The English of to-day are a mixed race, and there is certainly a great deal more of British and Iberian blood in our veins than some have supposed. The Anglo-Saxon possessed rare qualities, perseverance, tenacity, and power of organisation; yet some of the higher qualities of our race, the searching intellect, the bright imagination, and idealism, are due to the spark of living fire entering into the somewhat heavy lump of the Germanic nature through contact with the Celt.
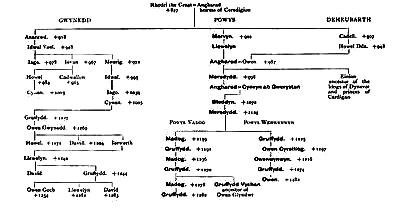
Wales was formed into three main divisions—Gwynedd, Powys, and Deheubarth—but in this volume we have only to do with the two former. Each had its independent prince, but as according to Welsh custom every principality was divided up among all the sons of a prince on his death, this led to endless subdivisions, to fraternal quarrels, and fratricides. Moreover, the boundaries were incessantly shifting. The king of Gwynedd was recognised as the Gwledig, or Over-King, and the supremacy remained in the family of Maelgwn till 817, when it died out with Cynon Tyndaethwy. His daughter Esyllt married Mervyn Vrych, king of Powys, who by this means united both portions of North Wales under his sceptre.
Rhodri the Great, son and successor of Mervyn, moreover, acquired South Wales by his marriage with Angharad, daughter of Meurig, king of Ceredigion. Thus by a series of marriages all Wales was united under one sovereign and an unrivalled opportunity offered for consolidation, and sturdy united opposition to encroachment from England. Unhappily the chance was allowed to slip. On the death of Rhodri, Wales was divided among his three sons (877): Anarawd obtained Gwynedd, Cadell became king of Deheubarth, and Mervyn was placed in possession of Powys. In 1229 Powys was subdivided into Powys Vadog and Powys Wenwynwyn. In addition to the main divisions there were a number of small principalities, whose princes were engaged in incessant strife with one another and with the sovereign who claimed supreme rule over them. They sided now with the English, then those in Gwynedd would throw in their lot with the princes of the south. It was these intestine divisions, never appeased, that exhausted the strength of the country and made way for the conquest by the English.
CHAPTER II
THE ENGLISH CONQUEST
The contest with the Saxons—William the Conqueror—The Norman invasion of Wales—The castles—The Welsh kingdoms—Rhodri the Great—Llewelyn the Great—The last Llewelyn—Edward I.’s treatment of the Welsh.
THROUGHOUT the reigns of the Saxon kings the Welsh had to maintain a contest, on the one hand with the English, and on the other with the Danes and Northmen hovering round the coast.
The Vikings, who carried devastation through England, did not overlook Wales. Wherever we find camps of a certain description, there we know that either Saxon or Dane has been.
These camps consist of earthen tumps or bell-shaped mounds, usually hollowed out in the middle, and with base-courts attached, protected by a palisade, and the top of the tump was crowned with a tower-like structure of timber.
At times the Welsh were in league with one of the kings of the Heptarchy against another; at others they were in league with the Danes against the English, and when not so engaged were fighting one another.
When William the Conqueror had subjugated England he was determined not to leave Wales to its independence.
But the conquest of Wales was not executed by one master mind. Wales was given over to a number of Norman adventurers to carry out the conquest in their own way, under no control, with the result that it was conducted with barbarity, lawlessness, wanton destruction, and spasmodically. In England, after the battle of Hastings, the Conqueror set to work to consolidate the kingdom under his sceptre, and blood ceased to flow. In Wales, in the north, the Earl of Chester and Robert of Rhuddlan fought and conquered for themselves in Gwynedd. In like manner the Earl of Shrewsbury raided in Powys from his fortress at Montgomery. In the south the Earl of Hereford carried sword and fire into Deheubarth. Frightful cruelties were committed. Ordericus Vitalis, as he records the glory of “the warlike marquess,” or Lord Marcher, Robert of Rhuddlan, is forced to admit with honest indignation that his deeds were such as no Christian warrior ought to commit against his fellow-Christians.
Seeing the importance of Shrewsbury, William built a strong castle there. Chester, Worcester, Hereford, and Gloucester were made into fortresses, and everything was prepared for advance.
In the reign of William Rufus, Deganwy, the old residence of the kings of Gwynedd, above the mouth of the Conway, was seized and fortified, and the Welsh king had to remove to Aberffraw, in Anglesey.
“The conquest which now began,” says Mr. Freeman, “that which we call either the English or Norman conquest of Britain, differed from the Norman conquest of England. It wrought far less change than the landing at Ebbfleet; it wrought far more change than the landing at Pevensey.
“The Britton of these lands, which in the Red King’s day were still British, was gradually conquered; he was brought gradually under English rule and English law, but he was neither exterminated nor enslaved, nor wholly assimilated. He still abides in his ancient land, still speaking his ancient tongue.
“The English or Norman conquest of Wales was not due to a national migration like the English conquest of Britain, nor was it a conquest wrought under the guise of an elaborate legal fiction, like the Norman conquest of England.”
The process pursued was this. The Norman barons advanced with their armed men along the shore, and up the basins of the rivers, till they gained some point of vantage controlling the neighbourhood, and there they erected castles of stone. This was an art they had acquired in Normandy, where stone was abundant and easily quarried. It was one to which the Brittons were strange. By degrees they forced their way further; they seized the whole sea-board. They strangled the valleys by gripping them where they opened out; they controlled the fertile pasture and arable land from their strongholds. Towns sprang up under the shelter of the castles, and English mechanics and traders were encouraged to settle in them.
The Welsh had never been city builders or dwellers in cities. They had suffered the old Roman towns to fall into decay, the walls to crumble into shapeless heaps of ruins. They lived in scattered farms, and every farmer had his hafod, or summer residence, as well as his hendre, or winter and principal home. Only the retainers of a prince dwelt about him in his palace, or caer. And now they saw strongly walled and fortified towns starting up at commanding points on the roads and beside all harbours. The arteries of traffic, the very pores of the land, were occupied by foreigners.
As Freeman further observes:—
“Wales is, as everyone knows, pre-eminently the land of castles. Through those districts with which we are specially concerned, castles great and small, or the ruins or traces of castles, meet us at every step. The churches, mostly small and plain, might themselves, with their fortified towers, almost count as castles. The towns, almost all of English foundation, were mostly small; they were military colonies rather than seats of commerce. As Wales had no immemorial cities like Exeter and Lincoln, so she had no towns which sprung up into greatness in later times, like Bristol, Norwich, and Coventry. Every memorial of former days which we see in the British land reminds us of how long warfare remained the daily business alike of the men in that land and of the strangers who had made their way into it at the sword’s point.”
Through the reigns of the Plantagenet kings the oppression and cruelties to which the Welsh were subjected drove them repeatedly to reprisals. At times they were successful.
During the commotions caused by the misrule of King John and the incapacity of Henry III. the Welsh took occasion to stretch their limbs and recover some of the lands that had been wrested from them, and to throw down the castles that were an incubus upon them.
There were three Welsh kingdoms, or principalities. Gwynedd, roughly conterminous with the counties of Anglesey, Carnarvon, Merioneth, and parts of Denbigh and Flint. Powys, sadly shrunken, still comprised Montgomeryshire and Radnor and a portion of Denbigh. The third principality, Deheubarth or Dynevor, composed of Pembrokeshire, Cardiganshire, Carmarthenshire, and Glamorgan. Brecknock was claimed as part of it, but was an enclave in which the Normans had firmly established themselves. Monmouthshire also belonged to Deheubarth.
The king of Gwynedd claimed supremacy as head over the rest, and although this was allowed as a theory, if practically asserted it always met with armed resistance. But this was not all that went to weaken the Welsh opposition. Each prince who left sons carved up his principality into portions for each, and as the brothers were mutually jealous and desirous of acquiring each other’s land, this led to incessant strife and intrigue with the enemy in the heart of each of the three principalities. A great opportunity had offered. Rhodri the Great had united all Wales in his own hands, as mentioned already. But the union lasted only for his life; all flew apart once more at his death in 877, and that just at the moment when unity was of paramount importance.
Llewelyn ab Iorwerth, surnamed “the Great,” was king of Gwynedd at the beginning of the thirteenth century, and he had sufficient wit to see that the only salvation for Wales was to be found in its reunion, and he attempted to achieve this. As Powys was obstructive, he had to fight Gwenwynwyn its king, then to subject Lleyn and Merioneth.
In 1202 Llewelyn was firmly established in Gwynedd, and he married Joan, the daughter of King John, who proceeded to reinstate Gwenwynwyn in Powys. In 1211 this prince sided with Llewelyn against John, who, furious at this act of ingratitude, hanged twenty-eight Welsh hostages at Nottingham.
Llewelyn now turned his attention to the conquest of South Wales. He stormed one castle after another, and obtained recognition as prince of Dynevor. But in 1216 the false and fickle Gwenwynwyn abandoned the Welsh side and went over to that of the English. After some fighting Llewelyn submitted to Henry III. at Worcester in 1218.
His grandson, another Llewelyn, was also an able man, but he lacked just that essential faculty of being able to detect the changes of the sky and the signs of the times, and that ruined him.
In 1256 Llewelyn was engaged in war against the English. He had done homage to Henry III. in 1247, but the unrest in England caused by the feeble rule and favouritism of Henry had resulted in the revolt of the barons. Llewelyn took advantage of this condition of affairs to recover Deganwy Castle and to subdue Ceredigion. Then he drove the unpatriotic son of Gwenwynwyn out of Powys. The same year he entered South Wales, and was everywhere victorious. Brecon was brought under his rule, and the castles held by the English were taken and burned. But Llewelyn’s great difficulty lay with his own people, though his power was used for the recovery of Wales from English domination.
In 1265 he had received the oaths of fealty throughout Wales, which was now once more an independent principality. But he made at this point a fatal mistake. He did not appreciate the strength and determination of Edward I., the son of the feeble Henry, and in place of making favourable terms with him he intrigued against him with some revolted barons.
But Edward was a man of different metal from his father, and he declared war against Llewelyn, and in 1277 invaded Wales.
Three formidable armies poured in, and Llewelyn was driven to take refuge among the wilds of Snowdon, where he was starved into submission. All might have gone smoothly thenceforth had Edward been just. But he was ungenerous and harsh. He suffered his officials to treat the Welsh with such brutality that their condition became intolerable. Appeals for redress that were made to him were contemptuously set aside, and the Welsh princes and people felt that it would be better to die with honour than to be treated as slaves.
A general revolt broke out. In 1282 Llewelyn took the castles of Flint, Rhuddlan, and Hawarden in the north, and Prince Gruffydd rose against the English in the south.
Edward I. resolved on completely and irretrievably crushing Wales under his heel. He entered it with a large army, and again drove Llewelyn into the fastnesses of Snowdon. Llewelyn thence moved south to join forces with the Welsh of Dyved, leaving his brother David to hold the king back in North Wales.
The place appointed for the junction was near Builth, in Brecknock, but he was betrayed into a trap and was surrounded and slain, and his head sent to Edward, who was at Conway.
Edward ordered that his gallant adversary’s body should be denied a Christian burial, and forwarded the head to London, where, crowned in mockery with ivy leaves, it was set in the pillory in Cheapside. Nor was that all: he succeeded in securing the person of David, had him tried for high treason, hanged, drawn, and quartered. Llewelyn’s daughter was forced to assume the veil. Thus ended the line of Cunedda, and Llewelyn is regarded as the last of the kings of Wales.
Edward was at Carnarvon when his second son Edward was born, 1301, and soon after he proclaimed him Prince of Wales.
It has been fondly supposed that this was a tactful and gracious act of the king to reconcile the Welsh to the English Crown. It was nothing of the kind. His object was to assure the Crown lands of Gwynedd to his son.
“Edward’s brutal treatment of the remains of Llewelyn, who, though a rebel according to the laws of the king’s nation, was slain in honourable war, and his utter want of magnanimity in dealing with David were long remembered among the Cymry, and helped to keep alive the hatred with which the Welsh-speaking people for several generations more regarded the English.”[1]
The principality of Wales indeed remained, but in a new and alien form, and all was over for ever with the royal Cymric line.
PEDIGREE OF THE PRINCES OF GWYNEDD AND OF POWYS
[1] Rhys and Brynmor Jones, The Welsh People, p. 342.
CHAPTER III
ANGLESEY
The “Mother of Wales”—Agricola—Invades Môn—Mines—Caswallon Long-hand—Drives out the Irish—Conquest by Edwin—Aberffraw—Characteristics of Anglesey—Plas Llanfair—Llandyssilio—Llansadwrn—Inscribed stone of Sadwrn—Prophecy—Beaumaris—Bulkeley monuments—Penmon—Church of S. Seiriol—Old gallows—Puffin Isle—Maelgwn Gwynedd—Gildas—Loss of the Rothesay Castle—Tin Sylwy—English and Welsh inscriptions—Monument of Iestyn—His story—The Three Leaps—Amlwch—Llaneilian—John Jones—Llanbadrig—The witches of Llanddona—Goronwy Owen—Lewis Morris.
ANGLESEY is called the “Mother of Wales,” apparently because of its fertility and as supplying the mountain districts of the Principality with corn.
It has not the rugged beauty of the greater portion of Wales—there is, however, some bold coast scenery on the north and the west—but it possesses one great charm, the magnificent prospects it affords of the Snowdon chain and group and of the heights of Lleyn. Its Welsh name is Môn, which was Latinised into Mona, and it did not acquire that of Anglesey till this was given to it by King Egbert in 828. We first hear of it in A.D. 78, when the Roman general Cn. Julius Agricola was sent into Britain. He at once marched against the Ordovices, who occupied Powys.

HOLYHEAD, AT RHOSCOLYN
As represented by Tacitus, Agricola was a Roman of the purest type, a man sincere, faithful, and affectionate in his domestic relations, and gracious in his behaviour to all men. He was upright in his dealings, a fine soldier, an able general, but inflexible in his dealings with the enemies of Rome. The ancient Roman was filled with the conviction that the gods had predestined the City on the Seven Hills to rule all nations and languages, and that such as resisted were to be treated as the enemies of the gods. No mercy was to be accorded to them. Much of the same principle actuated the generals of the Republic and the Empire as did the followers of the Prophet. With one it was Rome, with the other Islam, or the sword.
The Ordovices had been most stubborn in their opposition, and most difficult to restrain within bounds. In a short but decisive campaign Agricola so severely chastised them that his biographer says that he almost literally exterminated them. This is certainly an exaggeration, but it implies the hewing to pieces of the chiefs and free men capable of bearing the sword who fell into his hands. Cæsar had treated the Cadurci, after their gallant stand at Uxellodunum, in the same way, and again the Veneti of Armorica, without a shadow of compunction. Whatsoever people opposed Rome was guilty of a capital crime, and must be dealt with accordingly. Agricola now pushed on to the Menai Straits, beyond which he could see the undulating land of Mona, the shore lined with Britons in paint, and brandishing their weapons, whilst behind them were ranged the Druids and bards inciting them to victory with their incantations and songs.
We can determine with some confidence the spot where Agricola stood contemplating the last stronghold of the Briton and its defenders. It was at Dinorwic, where now plies a ferry.
He waited till the strong current of the tide had run to exhaustion and left a long stretch of sand on the further side. The Britons seeing that he was without ships feared nothing.
But they were speedily convinced of their mistake. Agricola’s auxiliaries, probably natives of the low lands at the mouth of the Rhine, had no fear of the water, plunged in, and gallantly swam across the channel.
A massacre ensued; the island was subjugated, and Roman remains found on it in several places testify that the conquerors of the world planted troops there in camp to keep Mona in complete control. They worked the copper mines near Amlwch.
SERIGI. A STATUE AT CAERGYBI
As the Roman power failed in Britain, Mona became the stronghold of the invading Gwyddyl or Irish; they held it, and erected on its commanding heights their stone-walled fortresses, and it was not till the time of Caswallon Long-hand, grandson of Cunedda, that they were dislodged. He fought them in a series of battles, drove them from their strong castles faced with immense slabs of granite, such as Tin Sylwy, swept them together into Holy Island, then broke in on their last remaining fortress. According to legend, Caswallon was obliged to fasten his Britons together with horse-hobbles, to constrain them to fight by taking away from them the chance of escape by running away. With his own hand he slew Serigi, the Irish chief, near the entrance to the camp, and those of the Gwyddyl who did not escape in their boats were put to the sword. By an odd freak much like ours in glorifying De Wet and Lucas Meyer, the Welsh agreed to consider their late enemy as a martyr, and a chapel was erected where he fell, and he is figured, very shock-headed and bearing the short sword wherewith he was killed, in a niche of the doorway of the church which now stands in the midst of the old Gwyddyl fortress.
Caswallon set up his residence on the hill above Llaneilian, where the foundations may still be traced—a spot whence in the declining day the mountains of Wicklow may be seen, the Isle of Man stands out to the north, and in clear weather Helvellyn may be distinguished on the rim of the blue sea.
Edwin, king of Northumbria, conquered both Mona and the Isle of Man in 625. The place of his landing is still pointed out at Lleiniog, near Beaumaris, and a mound of the Anglo-Saxon type remains to show where was his first camp. Here also Hugh the Fat, Earl of Chester, was killed by the arrow of Magnus Barefoot. But of this more presently. Driven from Deganwy, on the Conway, the kings of Gwynedd made their residence at Aberffraw, in Mona. Of that palace there are but scanty traces.
There is something remarkable in the character of Anglesey. The bold mountains of Wales come to an abrupt fall at the Menai Straits, and thence the island stretches west in low undulation rising nowhere to any considerable elevation, and scored across with depressions from north to south, feeble and imperfect replicas of the Menai Straits. One is the furrow occupied by the Malldraeth morass and sands, but this does not cut completely across the island. The other is more thorough; it severs Holy Island from the main body of Môn, but it is so narrow that it has been bridged at Penybont and the railway crosses it on a causeway at Valley.
Anglesey does not impress the visitor as being so fertile as has been supposed. There are long stretches of morass and moor strewn with pools. But perhaps Môn was first called the “Mother of Wales” because to it, as to a mother’s lap, retreated the Cymry when beaten, wounded, and sore before their oppressors. If so, it soon ceased to be their place of refuge, but formed a point d’appui for their enemies, whence to strike at them from the rear.
Mona, as already said, does not present us with very striking scenery, except on the coast, but it teems with interest in other ways. It is dotted with monuments of the primeval inhabitants—cromlechs and meini-hirion (the plural of maen-hir). It possesses very well preserved camps of the Gwyddyl invaders. It was first the sanctuary and school of the Druids, and after that, of their spiritual successors, the Saints. The slope of Mona towards the east is well timbered and studded with mansions, the park of Plas Newydd, the residence of the Marquess of Anglesey, Plas Llanfair, and the palace of the Bishop of Bangor. This prelate had his residence near the Cathedral, but this has been sold, and a lordly mansion has been given to him on the Straits, where he can turn his back on his Anglesey clergy, and say to the rest, “Between us and you there is a great gulf fixed.” The beautiful suspension bridge erected by Telford crosses the Straits at their sweetest spot. Here the channel is broken by a little island occupied by the graveyard and church of Llandyssilio. The church is of no architectural interest. It was founded by Tyssilio, one of the sons of Brochwel Ysgythrog, prince of Powys, when he ran away from Meifod to escape the blandishment of an over-affectionate sister-in-law.
Llansadwrn Church, beautifully situated and carefully restored, contains the tombstone of its patron saint. This is a small block, now broken, that was found under the wall of the north transept, and is now let into the side of the chancel. It bears the inscription: Hic Beatu(s) Saturninus Se(pultus I)acit. Et Sua Sa(ncta) Coniux. P(ax). The knight was an Armorican prince, and the brother of S. Illtyd, founder of Llantwit Major, in Glamorganshire. Sadwrn and his wife Canna, who was his cousin, left Armorica, owing probably to some family unpleasantness. After his death she married again, and became the mother of Elian the Pilgrim, of whom we shall have something to say presently. In the very interesting church of Beaumaris is a tomb the sides of which are decorated with delicately carved figures of Anglesey saints, and among these are two that may be taken to represent Sadwrn and his wife. He is shown in armour, his sword sheathed, and holding a pilgrim’s staff in his left hand, whilst giving a benediction with the right.
When the tubular bridge for the railway was built it was considered that a prophecy made by a Welsh bard had been fulfilled, wherein he spoke of rising from his bed in Mona, of breakfasting in Chester, of lunching in Ireland, and of returning to sup in Mona. But the required speed to Ireland has not yet been attained. Another meaning or interpretation has been put on the words of Robyn Ddu. He was living at Holyhead when he wrote the lines in question, and there were two boats by the quay, one from Chester and the other from Dublin, and he breakfasted with the captain at his table in the first boat, took his midday meal in the cabin of the second, and returned to his own quarters to sup and sleep.
Beaumaris is a sleepy little place, only waking to life when the bathing season sets in. The castle was erected by Edward I., and took its name from its situation on the Fair Marsh. It is not a particularly striking building, and is far gone in ruin.
The church, however, which is of the same period, and due to Edward I., is worth a visit. The side aisles contain five two-light Decorated windows. The chancel is Late Perpendicular, with a very poor east window containing some fragments of stained glass. The arcade of the church is Perpendicular. In the vestry are Bulkeley monuments, removed at the Dissolution from Penmon. From Beaumaris a delightful excursion may be made to Penmon, which was a great nursery of saints for Gwynedd. It would be hard to find anywhere a sweeter or sunnier spot. The hills fold around the little dell in which lies the church, shutting off the gales from north and east and west, and open only to the south to let in the sun.
Unhappily a marble quarry is close by, and is eating into one of the arms that is wrapped lovingly about the old site, and will in time eat its way through.
In the combe, among ancient walnut and chestnut trees and flowering elder, are some relics of the monastery and its Norman priory church. The foundation of the cloister may be traced. The church is cruciform, and is aisleless. The south transept contains rich Norman arcades, and the arch into this transept is of the same period and of equal richness. A square font in the nave, covered with interlaced and key work, is the base of an old Celtic cross. A Norman doorway on the south side gives admission to the nave. This has knotwork and a monster biting its tail in the tympanum. The chancel is three steps below the level of the nave. A fine cross is in the south transept, taken out of the ruins of the priory, where it had served as lintel to a mediæval window.
S. Seiriol, the founder, is represented in stained glass of the fifteenth century in a window of the south transept, and a bishop, probably S. Elian, in one of the north transept. Near the church is the holy well of the saint, gushing forth from under a rock, and filling what was once the priory fishpond. The well is now in request mainly by such as desire to know what is in store for them in their love affairs, by dropping in pins and forming wishes.
About a mile distant, on a height where the rock comes to the surface, are four holes—the sockets for a pair of gallows, as the Prior of Penmon had seigneurial rights, and could hang misdoers.
Just off the coast is Ynys Seiriol, or Puffin Island, with the tower and ruins of a church on it. Hither retreated the monks of the first Celtic monastery to die and to be buried, and the soil is dense with their bones. The rabbits turn them up when burrowing. Here, according to tradition, Maelgwn, king of Gwynedd, was buried in 547. He was son of Caswallon, who drove the Irish out of Anglesey. Maelgwn was a remarkable man, tall and noble of countenance, and a masterful prince. He incurred the wrath of the ecclesiastics because he had once been a monk and had thrown aside the cowl. He was not particularly scrupulous about the rights of sanctuary claimed by the saints, and he was imperious in requisitioning meals of them when hunting in their neighbourhood.

S. SEIRIOL. STAINED GLASS, PENMON
He was, however, large-hearted and liberal, and when Caw, a prince of Strathclyde, and his sons came helter-skelter into Gwynedd, flying from the Picts, he generously received them and gave them lands in Anglesey.
Somewhat later, Gildas the historian, one of the sons of Caw, when himself safe in Brittany, wrote his venomous letter on the Destruction of Britain, and thus indecently and ungratefully attacked Maelgwn, the protector of his family:—
“Thou island dragon, first in wickedness, exceeding others in power and in malice, liberal in giving, but more prompt in sin, strong in arms, but stronger in what destroys the soul, why dost thou wallow in such a black pool of crimes? Why dost thou lade thy neck with such loads of heavy crimes? Thy conversion once on a time brought as much joy as now thy accursed reversion to thy disgusting vomit, like a sick dog, has caused sorrow. Thy ears are not given to listen to sacred hymns, but to the bawling of a rascally crew howling out lies and frothing phlegm, bespattering everyone round about.”
Probably Maelgwn was not a good man, but the family of Gildas owed every yard of land it possessed to his munificence. By a word only does Gildas allude to their indebtedness to him; not an indication appears of loving pity—all is scurrilous abuse of the most insulting description. He was a sixth-century counterpart of Mr. Cutcliffe Hyne’s Captain Owen Kettle, a curious combination of narrow religiousness and foulmouthedness. No wonder that in Brittany his symbol is a snarling cur. And the meanness of the man is conspicuous throughout. So long as his own skin was safe from the lash it deserved, he gave no thought to his kinsmen living under the protection of Maelgwn and other princes against whom he inveighed—with what unpleasant consequences to them we shall see presently.
At Ruys, in the Morbihan, is a very beautiful marble statue of him, set up by his tomb a few years ago. It represents a young monk with angelic face, and a mouth in which butter would not melt. It is too funny for words to look at that idealised portrait and read the Destruction of Britain.
And now the bones of Maelgwn lie in Ynys Seiriol. In 1897 some excavations were made on the island by Mr. Harold Hughes, who says:—
“On removing the debris of centuries”—near the ruined church—“with the aid of pick and shovel we have succeeded in making a considerable clearing immediately to the east of the structure. We discovered at about four feet from the surface an ancient tomb. Beneath the rough clay, worn slabs, and covered with shingle from the shore, lay within a narrow inclosure, with feet to the east, the skeleton of a man. Although portions of the skeleton had crumbled away, many fragments remained, and these, after much difficulty, I pieced together.”
Was this, one may ask, the tomb of the famous Maelgwn Gwynedd?
From the island a reef runs into the sea, called the Causeway of Seiriol, and it is supposed that it was constructed by the saint as a means of communication with Penmaen Mawr. It disappears under the Dutchman’s Bank, a sandy stretch that obstructs the entrance to the Menai Straits. Hereon, in 1831, the Rothesay Castle was cast, when a hundred lives were lost. Miss Martineau, in her History of the Thirty Years’ Peace, tells a striking story of this wreck:—
“Two men, strangers to each other, found themselves holding on to the same plank, which, it soon appeared, would support only one. Each desired the other to hold on, the one because his companion was old, the other because his companion was young, and they quitted their grasp at the same moment. By extraordinary accidents both were saved, each without the knowledge of the other, and they met on the shore in great surprise. Few greetings in the course of human life can be so sweet and moving as must have been that of these two heroes.”
The country for some distance west of Penmon is commanded by Tin Sylwy or Bwrdd Arthur as it is also called. It rises 500 feet above the sea and is crowned by a fortification. The wall is of stone unset in mortar, faced within and without with slabs set on end, and within the area are faint traces of cytiau or circular huts of stone, such as are traditionally attributed to the Irish. Some excavations have been made here, but not on an extensive scale, and Roman coins and Samian ware have been found; but the extant walling assuredly belongs to the Gwyddyl invasion and occupation. Below the camp, between it and the church of Llanfihangel, is a holy well. In the graveyard may be noticed a token of a change of feeling towards the Welsh tongue. To the date 1860, or thereabouts, the inscriptions on the tombstones are in English, after that date in Welsh.
There is nothing in the church of Llaniestyn but the very curious carved slab with a full-length figure of the saint who founded the church. One very similar and of the same period, the reign of Edward III., is in Llanbabo Church. Iestyn was a son of Geraint, the heroic king of Devon and Cornwall, who fell at Langport, in Somersetshire, fighting against invaders, about the year 522. Iestyn was buried here. He seems to have travelled, and it is probably of him that a pretty story is told.

HOLY WELL, PENMON
He had gone to Brittany, and had found a deserted habitation at Plestin, of which he took possession. The hut had been constructed by an Irish settler named Efflam, who had departed on a pilgrimage. On his return Efflam found his cell in the occupation of a stranger. The question arose as to which should have it. This they decided to determine in the following manner. Both seated themselves in the cabin. The day was overcast, but the clouds were breaking, and the sun was nearing its setting. He on whom it first shone should retain the hovel. Presently the clouds parted, and a golden ray shot in through the little window and blazed on Efflam’s upturned face. Then Iestyn rose, bowed, and withdrew, and ended his days in Mona. It is by an artist’s licence that on the monument Iestyn is represented wearing a crown. He was, indeed, a king’s son, but he never bore the royal circlet.
The somewhat similar monument is at Llanbabo, in the north-west of the island. Pabo, after long and stubborn fighting against the Picts in North Britain, was driven to take refuge in Wales, and was kindly received by the prince of Powys. He bears the title of “The Pillar of Britain.”
On the north coast is Pentraeth, at the head of Red Wharf Bay, and here may be seen the Three Leaps, by which hangs a tale.
Einion, son of Gwalchmai, was lord of Trefeilir. Now there was a young lady named Angharad, daughter of Ednyfed Fychan, who was so beautiful, and was an heiress of so much, that she had many suitors. As she professed herself unable to decide among such an embarras de richesses of nice young men, her father proposed that she should marry the youth who could jump the furthest. She agreed. When the suitors came to try their powers, Einion surpassed the rest, for with a hop, skip, and a jump he covered fifty feet. The hop, skip, and jump are marked by three stones, which remain to this day in the dingle of Plas Gwyn. So Einion became the husband of Angharad.
His happiness was of short duration, for he was summoned by Owen Gwynedd to assist in driving the Flemings out of South Wales, who had been settled there by Henry I. This was in 1137. Einion was away for a good many years, constantly engaged in fighting, and when he did return to Trefeilir he found that on that day his wife had given her hand to another suitor, supposing that Einion was dead. Einion remained without and sent a servant within to summon her to come forth, and then, striking his harp, he sang a lay of reproach that has been preserved. Then he entered the house and ejected the gentleman who had presumed to invade his premises.
The Parys Mountain rises to the height of 420 feet, and is pretty completely honeycombed with mines, as it is an almost solid lump of copper. It has been worked continually since the times of the Romans, and had probably been quarried at in the Bronze Age before that.
The little town of Amlwch is dominated by this mountain. It consists of two parts, the town proper and the port, and a considerable manufacture of chemical manures is carried on in it. Altogether Amlwch is in itself not a particularly attractive place. It has many spots of interest about it, and from it can be reached Bull Bay, where there are good sands, and the place is growing in favour. To the east the adjoining parish is Llaneilian, that possesses a quaint and interesting church, which, however, has suffered cruelly from unintelligent “restoration.” Like the majority of Welsh village churches, it has no side aisles; it is a cross church, with battlements and a western tower, covered from top to bottom in a panoply of slates. At the “restoration” the old oak seats were cast forth to make room for deal benches in preference, and the fine rood-screen with its loft had all the dainty tracery stripped from its panels and openings and destroyed, so that now it is a mere skeleton.
There is a curious little chapel at the south-east end of the church, differently orientated, and with a covered passage to it from the chancel.
This chapel has a well-preserved and good carved oak roof, which the present rector has saved from destruction by damp. Here is the base of the shrine of S. Elian. It is of wood, and the panels were formerly carved, but the tracery is gone. Into this people crawled, and if they succeeded in turning themselves about within, believed that they would get cured of any disease they might have, or, according to another version, would have their lives extended by five years.
A painting of S. Elian by an Italian artist of the seventeenth century is kept in the church, but it is devoid of merit and is in bad preservation. There is also a pair of wooden gefail gwn, or dog-tongs, bearing the date 1748.
Above Llaneilian rises the hill on which was Caswallon’s llys, or court. The story goes that Caswallon promised to Elian as much land as a stag he was hunting could run round in the day, and the deer’s spring, a leap over a rent in the rocks, is shown to this day, but it is not any longer in the parish of the saint.
BASE OF SHRINE, LLANEILIAN
A late rector of Llaneilian, John Jones, who died in 1870, and had been curate of the parish for twenty years and after that rector for thirty-three, kept his harper and also a pack of hounds.
To the west of Amlwch, in a bold situation, is Llanbadrig. The church was founded, not by the Apostle of the Irish, but by a namesake who lived later and was a member of S. Cybi’s monastery at Holyhead. According to legend, when he was on his way back from Iona, where he had visited S. Columba, his frail boat was wrecked on Ynys Badrig, or the Middle Mouse, an islet off the coast. Patrick succeeded in making his way to the land, drank of a fountain near the shore, and scrambled up the rock, in which the marks of his feet are still to be seen, to where is the church which he planted on the edge of the precipice in commemoration of his providential escape.
Within the church is a very rude cross that may well date from the time of S. Patrick. The niche at the east end of the chancel that now contains a representation of “Salvator Mundi” has twisted serpents on the pedestal, and formerly contained a figure of the patron saint, who was confounded with the Apostle of Ireland.
The parish of Llanddona is in evil repute, as a nest of witches. The story goes that a boat came ashore in Red Wharf Bay without rudder or oars, containing women and men in a condition of great destitution. They were Irish. Now it was a common custom in Ireland to punish malefactors by putting them in a wicker-work coracle, covered by a single hide, without allowing them oars or rudder. So when S. Patrick converted Maughold, the robber, he bade him drift oarless on the sea, his feet chained together. He was swept by the winds and waves to the Isle of Man, and eventually became bishop there. Now when the good people of Llanddona saw this boat come ashore thus unprovided with the necessary apparatus for its guidance, they concluded that those on board were criminals, and would have nothing to do with them. They would have sent them adrift again had not a spring of clear water burst forth on the sands where the coracle had come ashore. The spring still flows. This was decisive as a token that Heaven accepted the punishment of the crew, and desired them to rest where they had landed.
CROSS AT LLANBADRIG
So these strangers remained, and were suffered to build cottages, but for generations they continued apart from the Welsh inhabitants, and they maintained their evil propensities. The men lived by smuggling, and the women supported themselves by the exercise of witchcraft. It was not possible to overcome the smugglers in a fray, for they carried about with them a black fly tied in a knot of their kerchief, and the moment that the knot was undone the fly flew at the eyes of their opponents and blinded them. The women, old and young, were dreaded for the power they possessed of cursing those who refused them whatsoever they asked—a fowl, a loaf of bread, eggs, part of a pig. If this were denied them, they would imprecate the most awful curses, of which here is one:—
“May he wander for ages
And find at each step a stile,
And at every stile find a fall,
And at every fall a broken bone;
Not the largest, nor the least bone,
But the chief neck bone, each time.”
If the Llanddona witches attended a market, and bid for anything, no one ventured to bid against them. But are not most Welsh girls witches?—witches, however, that win and do not revolt like those of Llanddona.
On the further side of Red Wharf Bay, where, by the way, there is an hotel, and where lodgings may be had, is Llanfair Mathafarn Eithaf. There are three parishes of the name of Llanfair in the island. Llanfair means the Llan or Church of S. Mary, the M in combination becoming f, as Llanfihangel signifies the Church of Mi[chael] the Angel.
This Llanfair Mathafarn was the birthplace of Goronwy Owen, the poet. He was born in 1722 of extremely poor parents, went to Oxford through help of Edward Wynne, of Bodewryd. Subsequently Mr. Wynne despatched him to Jesus College, Oxford, and maintained him there. From an early age he gave indications of poetic genius, and he proved himself to be a ripe scholar in the classic tongues.
He was ordained in 1745, and his great ambition was to obtain a Welsh curacy and settle down in it. Lewis Morris did his best for him, but all he could get was a temporary appointment to his native parish Llanfair, where the curacy chanced to be vacant. But he had been there only three weeks when he received notice from the Bishop of Bangor that he must turn out to make way for a young clergyman of large independent fortune; so Goronwy was obliged to depart. He sought curacies in Wales, but could get no bishop to touch him with the ends of his fingers, as he had no connections and no fortune. That he was deeply pious, earnest, a scholar, an eloquent Welsh preacher, and a poet of singular merit counted as nothing. Unhappily, though Goronwy was a genius, he was given to drink, and could never remain long anywhere. At length he obtained a curacy at Oswestry, and there he married. From Oswestry he was removed to Donnington, in Shropshire, where his rector was a Scotchman and an absentee, but being a Douglas, rich and with the means of pushing himself, having neglected his duties as parish priest, he managed to get himself nominated and consecrated Bishop of Salisbury. Lewis Morris did his best to save the poet from his unfortunate vice, but failed.
At Donnington poor Goronwy Owen not only acted as curate to the great absentee rector, but also as master of the grammar school, and received twenty-six pounds as his stipend. Thence he shifted, first into Cheshire and then to Northolt, near London. In 1756 he was living in a garret in town vainly soliciting employment in his sacred calling, and undergoing with his family the utmost privations. His Welsh accent in English stood in his way, and his brilliant Welsh qualifications were not wanted in Wales. But, indeed, poor Goronwy, with all his gifts, was not the man to do much spiritual work.
At length Lewis Morris obtained for Goronwy Owen the mastership of a Government school at Williamsburg, in Virginia. Thither he went, and there he died about the year 1770.
As Lewis Morris has been mentioned in connection with poor Goronwy Owen, a few words must be devoted to him.
“Lewis Morris,” says George Borrow, “was born at a place called Trev y Beirdd, in Anglesey, in the year 1700. Anglesey, or Mona, has given birth to many illustrious men, but few, upon the whole, entitled to more honourable mention than himself. From a humble situation in life, for he served an apprenticeship to a cooper at Holyhead, he raised himself by his industry and talents to affluence and distinction, became a landed proprietor in the county of Cardigan, and inspector of the royal domains and mines in Wales. Perhaps a man more generally accomplished never existed; he was a first-rate mechanic, an expert navigator, a great musician, both in theory and practice, and a poet of singular excellence. Of him it was said, and with truth, that he could build a ship and sail it, frame a harp and make it speak, write an ode and set it to music. Though self-taught, he was confessedly the best Welsh scholar of his age, and was well versed in those cognate dialects of the Welsh—the Cornish, Armoric, Highland Gaelic, and Irish.... It was he who first told his countrymen that there was a youth in Anglesey whose genius, if properly encouraged, promised fair to rival that of Milton; one of the most eloquent letters ever written is one by him, in which he discants upon the beauties of certain poems of Goronwy Owen, the latent genius of whose boyhood he had observed, whom he had clothed, educated, and assisted up to the period when he was ordained a minister of the Church, and whom he finally rescued from a state bordering on starvation in London, procuring for him an honourable appointment in the New World.”
Lewis Morris made a collection of Welsh MSS., consisting of about eighty volumes, which are now in the British Museum. He died in 1765 and was buried at Llanbadarn Vawr, in Cardiganshire.
