автордың кітабын онлайн тегін оқу Introduction to the Science of Sociology
INTRODUCTION TO THE SCIENCE OF SOCIOLOGY
THE UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO PRESS
CHICAGO, ILLINOIS
THE BAKER & TAYLOR COMPANY
NEW YORK
THE CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS
LONDON
THE MARUZEN-KABUSHIKI-KAISHA
TOKYO, OSAKA, KYOTO, FUKUOKA, SENDAI
THE MISSION BOOK COMPANY
SHANGHAI
INTRODUCTION TO THE SCIENCE OF SOCIOLOGY
By
Robert E. Park and Ernest W. Burgess
THE UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO PRESS
CHICAGO, ILLINOIS
Copyright 1921 By The University of Chicago
All rights Reserved
Published September 1921
PREFACE
The materials upon which this book is based have been collected from a wide range of sources and represent the observation and reflection of men who have seen life from very different points of view. This was necessary in order to bring into the perspective of a single volume the whole wide range of social organization and human life which is the subject-matter of a science of society.
At the same time an effort has been made to bring this material within the limits of a very definite series of sociological conceptions which suggest, at any rate, where they do not clearly exhibit, the fundamental relations of the parts to one another and to the concepts and contents of the volume as a whole.
The Introduction to the Science of Sociology is not conceived as a mere collection of materials, however, but as a systematic treatise. On the other hand, the excerpts which make up the body of the book are not to be regarded as mere illustrations. In the context in which they appear, and with the headings which indicate their place in the volume, they should enable the student to formulate for himself the principles involved. An experience of some years, during which this book has been in preparation, has demonstrated the value to the teacher of a body of materials that are interesting in themselves and that appeal to the experience of the student. If students are invited to take an active part in the task of interpretation of the text, if they are encouraged to use the references in order to extend their knowledge of the subject-matter and to check and supplement classroom discussion by their personal observation, their whole attitude becomes active rather than passive. Students gain in this way a sense of dealing at first hand with a subject-matter that is alive and with a science that is in the making. Under these conditions sociology becomes a common enterprise in which all members of the class participate; to which, by their observation and investigation, they can and should make contributions.
The first thing that students in sociology need to learn is to observe and record their own observations; to read, and then to select and record the materials which are the fruits of their readings; to organize and use, in short, their own experience. The whole organization of this volume may be taken as an illustration of a method, at once tentative and experimental, for the collection, classification, and interpretation of materials, and should be used by students from the very outset in all their reading and study.
Social questions have been endlessly discussed, and it is important that they should be. What the student needs to learn, however, is how to get facts rather than formulate opinions. The most important facts that sociologists have to deal with are opinions (attitudes and sentiments), but until students learn to deal with opinions as the biologists deal with organisms, that is, to dissect them—reduce them to their component elements, describe them, and define the situation (environment) to which they are a response—we must not expect very great progress in sociological science.
It will be noticed that every single chapter, except the first, falls naturally into four parts; (1) the introduction, (2) the materials, (3) investigations and problems, and (4) bibliography. The first two parts of each chapter are intended to raise questions rather than to answer them. The last two, on the other hand, should outline or suggest problems for further study. The bibliographies have been selected mainly to exhibit the recognized points of view with regard to the questions raised, and to suggest the practical problems that grow out of, and are related to, the subject of the chapter as a whole.
The bibliographies, which accompany the chapters, it needs to be said, are intended to be representative rather than authoritative or complete. An attempt has been made to bring together literature that would exhibit the range, the divergence, the distinctive character of the writings and points of view upon a single topic. The results are naturally subject to criticism and revision.
A word should be said in regard to chapter i. It seemed necessary and important, in view of the general vagueness and uncertainty in regard to the place of sociology among the sciences and its relation to the other social sciences, particularly to history, to state somewhere, clearly and definitely, what, from the point of view of this volume, sociology is. This resulted finally in the imposition of a rather formidable essay upon what is in other respects, we trust, a relatively concrete and intelligible book. Under these circumstances we suggest that, unless the reader is specially interested in the matter, he begin with the chapter on "Human Nature," and read the first chapter last.
The editors desire to express their indebtedness to Dr. W. I. Thomas for the point of view and the scheme of organization of materials which have been largely adopted in this book.[1] They are also under obligations to their colleagues, Professor Albion W. Small, Professor Ellsworth Faris, and Professor Leon C. Marshall, for constant stimulus, encouragement, and assistance. They wish to acknowledge the co-operation and the courtesy of their publishers, all the more appreciated because of the difficult technical task involved in the preparation of this volume. In preparing copy for publication and in reading proof, invaluable service was rendered by Miss Roberta Burgess.
Finally the editors are bound to express their indebtedness to the writers and publishers who have granted their permission to use the materials from which this volume has been put together. Without the use of these materials it would not have been possible to exhibit the many and varied types of observation and reflection which have contributed to present-day knowledge of social life. In order to give this volume a systematic character it has been necessary to tear these excerpts from their contexts and to put them, sometimes, into strange categories. In doing this it will no doubt have happened that some false impressions have been created. This was perhaps inevitable and to be expected. On the other hand these brief excerpts offered here will serve, it is hoped, as an introduction to the works from which they have been taken, and, together with the bibliographies which accompany them, will serve further to direct and stimulate the reading and research of students. The co-operation of the following publishers, organizations and journals, in giving, by special arrangement, permission to use selections from copyright material, was therefore distinctly appreciated by the editors:
D. Appleton & Co.; G. Bell & Sons; J. F. Bergmann; Columbia University Press; George H. Doran Co.; Duncker und Humblot; Duffield & Co.; Encyclopedia Americana Corporation; M. Giard et Cie; Ginn & Co.; Harcourt, Brace & Co.; Paul B. Hoeber; Houghton Mifflin Co.; Henry Holt & Co.; B. W. Huebsch; P. S. King & Son; T. W. Laurie, Ltd.; Longmans, Green & Co.; John W. Luce & Co.; The Macmillan Co.; A. C. McClurg & Co.; Methuen & Co.; John Murray; Martinus Nijhoff; Open Court Publishing Co.; Oxford University Press; G. P. Putnam's Sons; Rütten und Loening; Charles Scribner's Sons; Frederick A. Stokes & Co.; W. Thacker & Co.; University of Chicago Press; University Tutorial Press, Ltd.; Wagnerische Univ. Buchhandlung; Walter Scott Publishing Co.; Williams & Norgate; Yale University Press; American Association for International Conciliation; American Economic Association; American Sociological Society; Carnegie Institution of Washington; American Journal of Psychology; American Journal of Sociology; Cornhill Magazine; International Journal of Ethics; Journal of Abnormal Psychology; Journal of Delinquency; Nature; Pedagogical Seminary; Popular Science Monthly; Religious Education; Scientific Monthly; Sociological Review; World's Work; Yale Review.
Chicago
June 18, 1921
FOOTNOTES:
[1] See Source Book for Social Origins. Ethnological materials, psychological standpoint, classified and annotated bibliographies for the interpretation of savage society (Chicago, 1909).
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Chapter I. Sociology and the Social Sciences
PAGE
I. Sociology and "Scientific" History 1
II. Historical and Sociological Facts 6
III. Human Nature and Law 12
IV. History, Natural History, and Sociology 16
V. The Social Organism: Humanity or Leviathan? 24
VI. Social Control and Schools of Thought 27
VII. Social Control and the Collective Mind 36
VIII. Sociology and Social Research 43
Representative Works in Systematic Sociology and Methods of Sociological Research 57
Topics for Written Themes 60
Questions for Discussion 60
Chapter II. Human Nature
I. Introduction
1. Human Interest in Human Nature 64
2. Definition of Human Nature 65
3. Classification of the Materials 68
II. Materials
A. The Original Nature of Man
1. Original Nature Defined. Edward L. Thorndike 73
2. Inventory of Original Tendencies. Edward L. Thorndike 75
3. Man Not Born Human. Robert E. Park 76
4. The Natural Man. Milicent W. Shinn 82
5. Sex Differences. Albert Moll 85
6. Racial Differences. C. S. Myers 89
7. Individual Differences. Edward L. Thorndike 92
B. Human Nature and Social Life
1. Human Nature and Its Remaking. W. E. Hocking 95
2. Human Nature, Folkways, and the Mores. William G. Sumner 97
3. Habit and Custom, the Individual and the General Will. Ferdinand Tönnies 100
4. The Law, Conscience, and the General Will. Viscount Haldane 102
C. Personality and the Social Self
1. The Organism as Personality. Th. Ribot 108
2. Personality as a Complex. Morton Prince 110
3. The Self as the Individual's Conception of His Rôle. Alfred Binet 113
4. The Natural Person versus the Social and Conventional Self. L. G. Winston 117
5. The Divided Self and Moral Consciousness. William James 119
6. Personality of Individuals and of Peoples. W. v. Bechterew 123
D. Biological and Social Heredity
1. Nature and Nurture. J. Arthur Thomson 126
2. Inheritance of Original Nature. C. B. Davenport 128
3. Inheritance of Acquired Nature: Tradition. Albert G. Keller 134
4. Temperament, Tradition, and Nationality. Robert E. Park 135
III. Investigations and Problems
1. Conceptions of Human Nature Implicit in Religious and Political Doctrines 139
2. Literature and the Science of Human Nature 141
3. Research in the Field of Original Nature 143
4. The Investigation of Human Personality 143
5. The Measurement of Individual Differences 145
Selected Bibliography 147
Topics for Written Themes 154
Questions for Discussion 155
Chapter III. Society and the Group
I. Introduction
1. Society, the Community, and the Group 159
2. Classification of the Materials 162
II. Materials
A. Society and Symbiosis
1. Definition of Society. Alfred Espinas 165
2. Symbiosis (literally "living together"). William M. Wheeler 167
3. The Taming and the Domestication of Animals. P. Chalmers Mitchell 170
B. Plant Communities and Animal Societies
1. Plant Communities. Eugenius Warming 173
2. Ant Society. William E. Wheeler 180
C. Human Society
1. Social Life. John Dewey 182
2. Behavior and Conduct. Robert E. Park 185
3. Instinct and Character. L. T. Hobhouse 190
4. Collective Representation and Intellectual Life. Émile Durkheim 193
D. The Social Group
1. Definition of the Group. Albion W. Small 196
2. The Unity of the Social Group. Robert E. Park 198
3. Types of Social Groups. S. Sighele 200
4. Esprit de Corps, Morale, and Collective Representations of Social Groups. William E. Hocking 205
III. Investigations and Problems
1. The Scientific Study of Societies 210
2. Surveys of Communities 211
3. The Group as a Unit of Investigation 212
4. The Study of the Family 213
Selected Bibliography 217
Topics for Written Themes 223
Questions for Discussion 224
Chapter IV. Isolation
I. Introduction
1. Geological and Biological Conceptions of Isolation 226
2. Isolation and Segregation 228
3. Classification of the Materials 230
II. Materials
A. Isolation and Personal Individuality
1. Society and Solitude. Francis Bacon 233
2. Society in Solitude. Jean Jacques Rousseau 234
3. Prayer as a Form of Isolation. George Albert Coe. 235
4. Isolation, Originality, and Erudition. T. Sharper Knowlson 237
B. Isolation and Retardation
1. Feral Men. Maurice H. Small 239
2. From Solitude to Society. Helen Keller 243
3. Mental Effects of Solitude. W. H. Hudson 245
4. Isolation and the Rural Mind. C. J. Galpin 247
5. The Subtler Effects of Isolation. W. I. Thomas. 249
C. Isolation and Segregation
1. Segregation as a Process. Robert E. Park 252
2. Isolation as a Result of Segregation. L. W. Crafts and E. A. Doll 254
D. Isolation and National Individuality
1. Historical Races as Products of Isolation. N. S. Shaler 257
2. Geographical Isolation and Maritime Contact. George Grote 260
3. Isolation as an Explanation of National Differences. William Z. Ripley 264
4. Natural versus Vicinal Location in National Development. Ellen C. Semple 268
III. Investigations and Problems
1. Isolation in Anthropogeography and Biology 269
2. Isolation and Social Groups 270
3. Isolation and Personality 271
Bibliography: Materials for the Study of Isolation 273
Topics for Written Themes 277
Questions for Discussion 278
Chapter V. Social Contacts
I. Introduction
1. Preliminary Notions of Social Contact 280
2. The Sociological Concept of Contact 281
3. Classification of the Materials 282
II. Materials
A. Physical Contact and Social Contact
1. The Frontiers of Social Contact. Albion W. Small 288
2. The Land and the People. Ellen C. Semple 289
3. Touch and Social Contact. Ernest Crawley 291
B. Social Contact in Relation to Solidarity and to Mobility
1. The In-Group and the Out-Group. W. G. Sumner. 293
2. Sympathetic Contacts versus Categoric Contacts. N. S. Shaler 294
3. Historical Continuity and Civilization. Friedrich Ratzel 298
4. Mobility and the Movement of Peoples. Ellen C. Semple 301
C. Primary and Secondary Contacts
1. Village Life in America (from the Diary of a Young Girl). Caroline C. Richards 305
2. Secondary Contacts and City Life. Robert E. Park. 311
3. Publicity as a Form of Secondary Contact. Robert E. Park 315
4. From Sentimental to Rational Attitudes. Werner Sombart 317
5. The Sociological Significance of the "Stranger." Georg Simmel 322
III. Investigations and Problems
1. Physical Contacts 327
2. Touch and the Primary Contacts of Intimacy 329
3. Primary Contacts of Acquaintanceship 330
4. Secondary Contacts 331
Bibliography: Materials for the Study of Social Contacts 332
Topics for Written Themes 336
Questions for Discussion 336
Chapter VI. Social Interaction
I. Introduction
1. The Concept of Interaction 339
2. Classification of the Materials 341
II. Materials
A. Society as Interaction
1. The Mechanistic Interpretation of Society. Ludwig Gumplowicz 346
2. Social Interaction as the Definition of the Group in Time and Space. Georg Simmel 348
B. The Natural Forms of Communication
1. Sociology of the Senses: Visual Interaction. Georg Simmel 356
2. The Expression of the Emotions. Charles Darwin 361
3. Blushing. Charles Darwin 365
4. Laughing. L. Dugas 370
C. Language and the Communication of Ideas
1. Intercommunication in the Lower Animals. C. Lloyd Morgan 375
2. The Concept as the Medium of Human Communication. F. Max Müller 379
3. Writing as a Form of Communication. Charles H. Judd 381
4. The Extension of Communication by Human Invention. Carl Bücher 385
D. Imitation
1. Definition of Imitation. Charles H. Judd 390
2. Attention, Interest, and Imitation. G. F. Stout 391
3. The Three Levels of Sympathy. Th. Ribot 394
4. Rational Sympathy. Adam Smith 397
5. Art, Imitation, and Appreciation. Yrjö Hirn 401
E. Suggestion
1. A Sociological Definition of Suggestion. W. v. Bechterew 408
2. The Subtler Forms of Suggestion. Albert Moll 412
3. Social Suggestion and Mass or "Corporate" Action. W. v. Bechterew 415
III. Investigations and Problems
1. The Process of Interaction 420
2. Communication 421
3. Imitation 423
4. Suggestion 424
Selected Bibliography 425
Topics for Written Themes 431
Questions for Discussion 431
Chapter VII. Social Forces
I. Introduction
1. Sources of the Notion of Social Forces 435
2. History of the Concept of Social Forces 436
3. Classification of the Materials 437
II. Materials
A. Trends, Tendencies, and Public Opinion
1. Social Forces in American History. A. M. Simons 443
2. Social Tendencies as Social Forces. Richard T. Ely 444
3. Public Opinion and Legislation in England. A. V. Dicey 445
B. Interests, Sentiments, and Attitudes
1. Social Forces and Interaction. Albion W. Small 451
2. Interests. Albion W. Small 454
3. Social Pressures. Arthur F. Bentley 458
4. Idea-Forces. Alfred Fouillée 461
5. Sentiments. William McDougall 464
6. Social Attitudes. Robert E. Park 467
C. The Four Wishes: A Classification of Social Forces
1. The Wish, the Social Atom. Edwin B. Holt 478
2. The Freudian Wish. John B. Watson 482
3. The Person and His Wishes. W. I. Thomas 488
III. Investigations and Problems
1. Popular Notions of Social Forces 491
2. Social Forces and History 493
3. Interests, Sentiments, and Attitudes as Social Forces 494
4. Wishes and Social Forces 497
Selected Bibliography 498
Topics for Written Themes 501
Questions for Discussion 502
Chapter VIII. Competition
I. Introduction
1. Popular Conceptions of Competition 505
2. Competition a Process of Interaction 507
3. Classification of the Materials 511
II. Materials
A. The Struggle for Existence
1. Different Forms of the Struggle for Existence. J. Arthur Thomson 513
2. Competition and Natural Selection. Charles Darwin 515
3. Competition, Specialization, and Organization. Charles Darwin 519
4. Man: An Adaptive Mechanism. George W. Crile 522
B. Competition and Segregation
1. Plant Migration, Competition, and Segregation. F. E. Clements 526
2. Migration and Segregation. Carl Bücher 529
3. Demographic Segregation and Social Selection. William Z. Ripley 534
4. Inter-racial Competition and Race Suicide. Francis A. Walker 539
C. Economic Competition
1. Changing Forms of Economic Competition. John B. Clark 544
2. Competition and the Natural Harmony of Individual Interests. Adam Smith 550
3. Competition and Freedom. Frédéric Bastiat 551
4. Money and Freedom. Georg Simmel 552
III. Investigations and Problems
1. Biological Competition 553
2. Economic Competition 554
3. Competition and Human Ecology 558
4. Competition and the "Inner Enemies": the Defectives, the Dependents, and the Delinquents 559
Selected Bibliography 562
Topics for Written Themes 562
Questions for Discussion 563
Chapter IX. Conflict
I. Introduction
1. The Concept of Conflict 574
2. Classification of the Materials 576
II. Materials
A. Conflict as Conscious Competition
1. The Natural History of Conflict. W. I. Thomas 579
2. Conflict as a Type of Social Interaction. Georg Simmel 582
3. Types of Conflict Situations. Georg Simmel 586
B. War, Instincts, and Ideals
1. War and Human Nature. William A. White 594
2. War as a Form of Relaxation. G. T. W. Patrick 598
3. The Fighting Animal and the Great Society. Henry Rutgers Marshall 600
C. Rivalry, Cultural Conflicts, and Social Organization
1. Animal Rivalry. William H. Hudson 604
2. The Rivalry of Social Groups. George E. Vincent 605
3. Cultural Conflicts and the Organization of Sects. Franklin H. Giddings 610
D. Racial Conflicts
1. Social Contacts and Race Conflict. Robert E. Park 616
2. Conflict and Race Consciousness. Robert E. Park 623
3. Conflict and Accommodation. Alfred H. Stone 631
III. Investigations and Problems
1. The Psychology and Sociology of Conflict, Conscious Competition, and Rivalry 638
2. Types of Conflict 639
3. The Literature of War 641
4. Race Conflict 642
5. Conflict Groups 643
Selected Bibliography 645
Topics for Written Themes 660
Questions for Discussion 661
Chapter X. Accommodation
I. Introduction
1. Adaptation and Accommodation 663
2. Classification of the Materials 666
II. Materials
A. Forms of Accommodation
1. Acclimatization. Daniel G. Brinton 671
2. Slavery Defined. H. J. Nieboer 674
3. Excerpts from the Journal of a West India Slave Owner. Matthew G. Lewis 677
4. The Origin of Caste in India. John C. Nesfield 681
5. Caste and the Sentiments of Caste Reflected in Popular Speech. Herbert Risley 684
B. Subordination and Superordination
1. The Psychology of Subordination and Superordination. Hugo Münsterberg 688
2. Social Attitudes in Subordination: Memories of an Old Servant. An Old Servant 692
3. The Reciprocal Character of Subordination and Superordination. Georg Simmel 695
4. Three Types of Subordination and Superordination. Georg Simmel 697
C. Conflict and Accommodation
1. War and Peace as Types of Conflict and Accommodation. Georg Simmel 703
2. Compromise and Accommodation. Georg Simmel 706
D. Competition, Status, and Social Solidarity
1. Personal Competition, Social Selection, and Status. Charles H. Cooley 708
2. Personal Competition and the Evolution of Individual Types. Robert E. Park 712
3. Division of Labor and Social Solidarity. Émile Durkheim 714
III. Investigations and Problems
1. Forms of Accommodation 718
2. Subordination and Superordination 721
3. Accommodation Groups 721
4. Social Organization 723
Selected Bibliography 725
Topics for Written Themes 732
Questions for Discussion 732
Chapter XI. Assimilation
I. Introduction
1. Popular Conceptions of Assimilation 734
2. The Sociology of Assimilation 735
3. Classification of the Materials 737
II. Materials
A. Biological Aspects of Assimilation
1. Assimilation and Amalgamation. Sarah E. Simons 740
2. The Instinctive Basis of Assimilation. W. Trotter 742
B. The Conflict and Fusion of Cultures
1. The Analysis of Blended Cultures. W. H. R. Rivers 746
2. The Extension of Roman Culture in Gaul. John H. Cornyn 751
3. The Competition of the Cultural Languages. E. H. Babbitt 754
4. The Assimilation of Races. Robert E. Park 756
C. Americanization as a Problem in Assimilation
1. Americanization as Assimilation 762
2. Language as a Means and a Product of Participation 763
3. Assimilation and the Mediation of Individual Differences 766
III. Investigations and Problems
1. Assimilation and Amalgamation 769
2. The Conflict and Fusion of Cultures 771
3. Immigration and Americanization 772
Selected Bibliography 775
Topics for Written Themes 783
Questions for Discussion 783
Chapter XII. Social Control
I. Introduction
1. Social Control Defined 785
2. Classification of the Materials 787
II. Materials
A. Elementary Forms of Social Control
1. Control in the Crowd and the Public. Lieut. J. S. Smith 800
2. Ceremonial Control. Herbert Spencer 805
3. Prestige. Lewis Leopold 807
4. Prestige and Status in South East Africa. Maurice S. Evans 811
5. Taboo. W. Robertson Smith 812
B. Public Opinion
1. The Myth. Georges Sorel 816
2. The Growth of a Legend. Fernand van Langenhove 819
3. Ritual, Myth, and Dogma. W. Robertson Smith 822
4. The Nature of Public Opinion. A. Lawrence Lowell 826
5. Public Opinion and the Mores. Robert E. Park 829
6. News and Social Control. Walter Lippmann 834
7. The Psychology of Propaganda. Raymond Dodge 837
C. Institutions
1. Institutions and the Mores. W. G. Sumner 841
2. Common Law and Statute Law. Frederic J. Stimson 843
3. Religion and Social Control. Charles A. Ellwood 846
III. Investigations and Problems
1. Social Control and Human Nature 848
2. Elementary Forms of Social Control 849
3. Public Opinion and Social Control 850
4. Legal Institutions and Law 851
Selected Bibliography 854
Topics for Written Themes 862
Questions for Discussion 862
Chapter XIII. Collective Behavior
I. Introduction
1. Collective Behavior Defined 865
2. Social Unrest and Collective Behavior 866
3. The Crowd and the Public 867
4. Crowds and Sects 870
5. Sects and Institutions 872
6. Classification of the Materials 874
II. Materials
A. Social Contagion
1. An Incident in a Lancashire Cotton Mill 878
2. The Dancing Mania of the Middle Ages. J. F. C. Hecker 879
B. The Crowd
1. The "Animal" Crowd 881
a) The Flock. Mary Austin 881
b) The Herd. W. H. Hudson 883
c) The Pack. Ernest Thompson Seton 886
2. The Psychological Crowd. Gustave Le Bon 887
3. The Crowd Defined. Robert E. Park 893
C. Types of Mass Movements
1. Crowd Excitements and Mass Movements: The Klondike Rush. T. C. Down 895
2. Mass Movements and the Mores: The Woman's Crusade. Annie Wittenmyer 898
3. Mass Movements and Revolution
a) The French Revolution. Gustave Le Bon 905
b) Bolshevism. John Spargo 909
4. Mass Movements and Institutions: Methodism. William E. H. Lecky 915
III. Investigations and Problems
1. Social Unrest 924
2. Psychic Epidemics 926
3. Mass Movements 927
4. Revivals, Religious and Linguistic 929
5. Fashion, Reform, and Revolution 933
Selected Bibliography 934
Topics for Written Themes 951
Questions for Discussion 951
Chapter XIV. Progress
I. Introduction
1. Popular Conceptions of Progress 953
2. The Problem of Progress 956
3. History of the Concept of Progress 958
4. Classification of the Materials 962
II. Materials
A. The Concept of Progress
1. The Earliest Conception of Progress. F. S. Marvin 965
2. Progress and Organization. Herbert Spencer 966
3. The Stages of Progress. Auguste Comte 968
4. Progress and the Historical Process. Leonard T. Hobhouse 969
B. Progress and Science
1. Progress and Happiness. Lester F. Ward 973
2. Progress and Prevision. John Dewey 975
3. Progress and the Limits of Scientific Prevision. Arthur J. Balfour 977
4. Eugenics as a Science of Progress. Francis Galton 979
C. Progress and Human Nature
1. The Nature of Man. George Santayana 983
2. Progress and the Mores. W. G. Sumner 983
3. War and Progress. James Bryce 984
4. Progress and the Cosmic Urge
a) The Élan Vitale. Henri Bergson 989
b) The Dunkler Drang. Arthur Schopenhauer 994
III. Investigations and Problems
1. Progress and Social Research 1000
2. Indices of Progress 1002
Selected Bibliography 1004
Topics for Written Themes 1010
Questions for Discussion 1010
[1] See Source Book for Social Origins. Ethnological materials, psychological standpoint, classified and annotated bibliographies for the interpretation of savage society (Chicago, 1909).
The editors desire to express their indebtedness to Dr. W. I. Thomas for the point of view and the scheme of organization of materials which have been largely adopted in this book.[1] They are also under obligations to their colleagues, Professor Albion W. Small, Professor Ellsworth Faris, and Professor Leon C. Marshall, for constant stimulus, encouragement, and assistance. They wish to acknowledge the co-operation and the courtesy of their publishers, all the more appreciated because of the difficult technical task involved in the preparation of this volume. In preparing copy for publication and in reading proof, invaluable service was rendered by Miss Roberta Burgess.
History has not become, as Comte believed it must, an exact science, and sociology has not taken its place in the social sciences. It is important, however, for understanding the mutations which have taken place in sociology since Comte to remember that it had its origin in an effort to make history exact. This, with, to be sure, considerable modifications, is still, as we shall see, an ambition of the science.
Natural law, as the term is used here, is any statement which describes the behavior of a class of objects or the character of a class of acts. For example, the classic illustration of the so-called "universal proposition" familiar to students of formal logic, "all men are mortal," is an assertion in regard to a class of objects we call men. This is, of course, simply a more formal way of saying that "men die." Such general statements and "laws" get meaning only when they are applied to particular cases, or, to speak again in the terms of formal logic, when they find a place in a syllogism, thus: "Men are mortal. This is a man." But such syllogisms may always be stated in the form of a hypothesis. If this is a man, he is mortal. If a is b, a is also c. This statement, "Human nature is a product of social contact," is a general assertion familiar to students of sociology. This law or, more correctly, hypothesis, applied to an individual case explains the so-called feral man. Wild men, in the proper sense of the word, are not the so-called savages, but the men who have never been domesticated, of which an individual example is now and then discovered.
What has been said simply serves to emphasize the instrumental character of the abstract sciences. History and geography, all of the concrete sciences, can and do measurably enlarge our experience of life. Their very purpose is to arouse new interests and create new sympathies; to give mankind, in short, an environment so vast and varied as will call out and activate all his instincts and capacities.
Historically sociology has had its origin in history. It owes its existence as a science to the attempt to apply exact methods to the explanation of historical facts. In the attempt to achieve this, however, it has become something quite different from history. It has become like psychology with which it is most intimately related, a natural and relatively abstract science, and auxiliary to the study of history, but not a substitute for it. The whole matter may be summed up in this general statement: history interprets, natural science explains. It is upon the interpretation of the facts of experience that we formulate our creeds and found our faiths. Our explanations of phenomena, on the other hand, are the basis for technique and practical devices for controlling nature and human nature, man and the physical world.
Of such a society as this it may indeed be said, that it "exists for the benefit of its members, not its members for the benefit of society. It has ever to be remembered that great as may be the efforts made for the prosperity of the body politic, yet the claims of the body politic are nothing in themselves, and become something only in so far as they embody the claims of its component individuals."[30]
Historically, sociology has had its origin in history. History has been and is the great mother science of all the social sciences. Of history it may be said nothing human is foreign to it. Anthropology, ethnology, folklore, and archaeology have grown up largely, if not wholly, to complete the task which history began and answer the questions which historical investigation first raised. In history and the sciences associated with it, i.e., ethnology, folklore, and archaeology, we have the concrete records of that human nature and experience which sociology has sought to explain. In the same sense that history is the concrete, sociology is the abstract, science of human experience and human nature.
As a matter of fact, many, if not most, of our present social problems have their source and origin in the transition of great masses of the population—the immigrants, for example—out of a society based on primary group relationships into the looser, freer, and less controlled existence of life in great cities.
(9) Revue internationale de sociologie. Paris, M. Giard et Cie., 1893-.
Poetry, drama, and the plastic arts are interesting and significant only so far as they reveal in new and ever changing circumstances the unchanging characteristics of a fundamental human nature. Illustrations of this naïve and unreflecting interest in the study of mankind are familiar enough in the experience and observation of any of us. Intellectual interest in, and the scientific observation of, human traits and human behavior have their origin in this natural interest and unreflective observation by man of his fellows. History, ethnology, folklore, all the comparative studies of single cultural traits, i.e., of language, of religion, and of law, are but the more systematic pursuit of this universal interest of mankind in man.
Human nature is not something existing separately in the individual, but a group nature or primary phase of society, a relatively simple and general condition of the social mind. It is something more, on the one hand, than the mere instinct that is born in us—though that enters into it—and something less, on the other, than the more elaborate development of ideas and sentiments that makes up institutions. It is the nature which is developed and expressed in those simple, face-to-face groups that are somewhat alike in all societies; groups of the family, the playground, and the neighborhood. In the essential similarity of these is to be found the basis, in experience, for similar ideas and sentiments in the human mind. In these, everywhere, human nature comes into existence. Man does not have it at birth; he cannot acquire it except through fellowship, and it decays in isolation.[55]
Historically, the scientific interest in the question of biological and social inheritance has concerned itself with the rather sterile problem of the weight to be attached on the one hand to physical heredity and on the other to social heritage. The selection, "Temperament, Tradition, and Nationality" suggests that a more important inquiry is to determine how the behavior patterns and the culture of a racial group or a social class are determined by the interaction of original nature and the social tradition. According to this conception, racial temperament is an active selective agency, determining interest and the direction of attention. The group heritages on the other hand represent a detached external social environment, a complex of stimuli, effective only in so far as they call forth responses. The culture of a group is the sum total and organization of the social heritages which have acquired a social meaning because of racial temperament and of the historical life of the group.
A typical reflex, or instinct, or capacity, as a whole, includes the ability to be sensitive to a certain situation, the ability to make a certain response, and the existence of a bond or connection whereby that response is made to that situation. For instance, the young chick is sensitive to the absence of other members of his species, is able to peep, and is so organized that the absence of other members of the species makes him peep. But the tendency to be sensitive to a certain situation may exist without the existence of a connection therewith of any further exclusive response, and the tendency to make a certain response may exist without the existence of a connection limiting that response exclusively to any single situation. The three-year-old child is by inborn nature markedly sensitive to the presence and acts of other human beings, but the exact nature of his response varies. The original tendency to cry is very strong, but there is no one situation to which it is exclusively bound. Original nature seems to decide that the individual will respond somehow to certain situations more often than it decides just what he will do, and to decide that he will make certain responses more often than it decides just when he will make them. So, for convenience in thinking about man's unlearned equipment, this appearance of multiple response to one same situation and multiple causation of one same response may be taken roughly as the fact.
I. Sensory capacities
II. Original attentiveness
III. Gross bodily control
IV. Food getting and habitation
A. Food getting
1. Eating. 2. Reaching, grasping, putting into the mouth.
3. Acquisition and possession. 4. Hunting (a) a small
escaping object, (b) a small or moderate-sized object not of
offensive mien, moving away from or past him. 5. Possible
specialized tendencies. 6. Collecting and hoarding.
7. Avoidance and repulsion. 8. Rivalry and co-operation
B. Habitation
1. Responses to confinement. 2. Migration and domesticity
V. Fear, fighting, and anger
A. Fear
1. Unpleasant expectation and dread. 2. Anxiety and
worry. 3. Dislike and avoidance. 4. Shock. 5. Flight,
paralysis, etc.
B. Fighting
1. Escape from restraint. 2. Overcoming a moving obstacle.
3. Counter-attack. 4. Irrational response to pain.
5. Combat in rivalry. 6. Resentment of presence of other
males in courtship. 7. Angry behavior at persistent
thwarting.
C. Anger
VI. Responses to the behavior of other human beings
A. Motherly behavior
B. Filial behavior
C. Responses to presence, approval, and scorn of men
1. Gregariousness. 2. Attention to human beings. 3. Attention-getting.
4. Responses to approval and scorn.
5. Responses by approval and scorn
D. Mastering and submissive behavior
1. Display. 2. Shyness. 3. Self-conscious behavior
E. Other social instincts
1. Sex behavior. 2. Secretiveness. 3. Rivalry. 4. Co-operation.
5. Suggestibility and opposition. 6. Envious
and jealous behavior. 7. Greed. 8. Ownership. 9. Kindliness.
10. Teasing, tormenting, and bullying
F. Imitation
1. General imitativeness. 2. Imitation of particular forms
of behavior
VII. Original satisfiers and annoyers
VIII. Minor bodily movements and cerebral connections
A. Vocalization
B. Visual exploration
C. Manipulation
D. Other possible specializations
1. Constructiveness. 2. Cleanliness. 3. Adornment and art
E. Curiosity and mental control
1. Curiosity. 2. The instinct of multiform mental activity.
3. The instinct of multiform physical activity.
4. The instinct of workmanship and the desire for excellence
F. Play
IX. The emotions and their expression
X. Consciousness, learning, and remembering
These views in the radical form in which they are expressed by Loeb and Watson have naturally enough been the subject of considerable controversy, both on scientific and sentimental grounds. They seem to reduce human behavior to a system of chemical and physical reactions, and rob life of all its spiritual values. On the other hand, it must be remembered that human beings, like other forms of nature, have this mechanical aspect and it is precisely the business of natural science to discover and lay them bare. It is only thus that we are able to gain control over ourselves and of others. It is a matter of common experience that we do form habits and that education and social control are largely dependent upon our ability to establish habits in ourselves and in others. Habit is, in fact, a characteristic example of just what is meant by "mechanism," in the sense in which it is here used. It is through the fixation of habit that we gain that control over our "original nature," which lifts us above the brutes and gives human nature its distinctive character as human. Character is nothing more than the sum and co-ordination of those mechanisms which we call habit and which are formed on the basis of the inherited and instinctive tendencies and dispositions which we share in so large a measure with the lower animals.
Our baby was at this time in a way aware of the difference between companionship and solitude. In the latter days of the first month she would lie contentedly in the room with people near by, but would fret if left alone. But by the end of the month she was apt to fret when she was laid down on a chair or lounge, and to become content only when taken into the lap. This was not yet distinct memory and desire, but it showed that associations of pleasure had been formed with the lap, and that she felt a vague discomfort in the absence of these.
Criminological experiences appear also to confirm the notion of an inherited sexual differentiation, in children as well as in adults. According to various statistics, embracing not only the period of childhood, but including as well the period of youth, we learn that girls constitute one-fifth only of the total number of youthful criminals. A number of different explanations have been offered to account for this disproportion. Thus, for instance, attention has been drawn to the fact that a girl's physical weakness renders her incapable of attempting violent assaults upon the person, and this would suffice to explain why it is that girls so rarely commit such crimes. In the case of offenses for which bodily strength is less requisite, such as fraud, theft, etc., the number of youthful female offenders is proportionately larger, although here also they are less numerous than males of corresponding age charged with the like offenses. It has been asserted that in the law courts girls find more sympathy than boys, and that for this reason the former receive milder sentences than the latter; hence it results that in appearance merely the criminality of girls is less than that of boys. Others, again, refer the differences in respect of criminality between the youthful members of the two sexes to the influences of education and general environment. Morrison, however, maintains that all these influences combined are yet insufficient to account for the great disproportion between the sexes, and insists that there exists in youth as well as in adult life a specific sexual differentiation, based, for the most part, upon biological differences of a mental and physical character.
The answer to this question brings me to the second point of difference which I have mentioned—the difference in variability. I have already alluded to the divergencies in temperament to be found among the members of every primitive community. But well marked as are these and other individual differences, I suspect that they are less prominent among primitive than among more advanced peoples. This difference in variability, if really existent, is probably the outcome of more frequent racial admixture and more complex social environment in civilized communities. In another sense, the variability of the savage is indicated by the comparative data afforded by certain psychological investigations. A civilized community may not differ much from a primitive one in the mean or average of a given character, but the extreme deviations which it shows from that mean will be more numerous and more pronounced. This kind of variability has probably another source. The members of a primitive community behave toward the applied test in the simplest manner, by the use of a mental process which we will call A, whereas those of a more advanced civilization employ other mental processes, in addition to A, say B, C, D, or E, each individual using them in different degrees for the performance of one and the same test. Finally, there is in all likelihood a third kind of variability, whose origin is ultimately environmental, which is manifested by extremes of nervous instability. Probably the exceptionally defective and the exceptional genius are more common among civilized than among primitive peoples.
The differences exist at birth and commonly increase with progress toward maturity. Individuality is already clearly manifest in children of school age. The same situation evokes widely differing responses; the same task is done at differing speeds and with different degrees of success; the same treatment produces differing results. There can be little doubt that of a thousand ten-year-olds taken at random, some will be four times as energetic, industrious, quick, courageous, or honest as others, or will possess four times as much refinement, knowledge of arithmetic, power of self-control, sympathy, or the like. It has been found that among children of the same age and, in essential respects, of the same home training and school advantages, some do in the same time six times as much, or do the same amount with only one-tenth as many errors.
What, to be explicit, is the possible future of measures dealing with divorce, with war, with political corruption, with prostitution, with superstition? Enthusiastic idealism is too precious an energy to be wasted if we can spare it false efforts by recognizing those permanent ingredients of our being indicated by the words pugnacity, greed, sex, fear. Machiavelli was not inclined to make little of what an unhampered ruler could do with his subjects; yet he saw in such passions as these a fixed limit to the power of the Prince. "It makes him hated above all things to be rapacious, and to be violator of the property and women of his subjects, from both of which he must abstain." And if Machiavelli's despotism meets its master in the undercurrents of human instinct, governments of less determined stripe, whether of states or of persons, would hardly do well to treat these ultimate data with less respect.
Custom is the product of concurrent action through time. We find it existent and in control at the extreme reach of our investigations. Whence does it begin, and how does it come to be? How can it give guidance "at the outset"? All mass actions seem to begin because the mass wants to act together. The less they know what it is right and best to do, the more open they are to suggestion from an incident in nature, or from a chance act of one, or from the current doctrines of ghost fear. A concurrent drift begins which is subject to later correction. That being so, it is evident that instinctive action, under the guidance of traditional folkways, is an operation of the first importance in all societal matters. Since the custom never can be antecedent to all action, what we should desire most is to see it arise out of the first actions, but, inasmuch as that is impossible, the course of the action after it is started is our field of study. The origin of primitive customs is always lost in mystery, because when the action begins the men are never conscious of historical action or of the historical importance of what they are doing. When they become conscious of the historical importance of their acts, the origin is already far behind.
As a rule, opinions (mental attitudes) are dependent upon habit, by which they are conditioned and circumscribed. Yet, of course, opinions can also detach themselves from habit, and rise above it, and this is done successfully when they become general opinions, principles, convictions. As such they gain strength which may even break down and overcome habit. Faith, taken in the conventional religious sense of assurance of things hoped for, is a primitive form of will. While in general habit and opinion on the whole agree, there is nevertheless in their relations the seeds of conflict and struggle. Thought continually tends to become the dominating element of the mind, and man thereby becomes the more human.
There is, according to this view, a General Will with which the will of the good citizen is in accord. He feels that he would despise himself were his private will not in harmony with it. The notion of the reality of such a will is no new one. It is as old as the Greeks, for whom the moral order and the city state were closely related; and we find it in modern books in which we do not look for it. Jean Jacques Rousseau is probably best known to the world by the famous words in which he begins the first chapter of the Social Contract: "Man is born free, and everywhere he is in chains. Those who think themselves to be the masters of others cease not to be greater slaves than the people they govern." He goes on in the next paragraph to tell us that if he were only to consider force and the effects of it, he would say that if a nation was constrained to obey and did obey, it did well, but that whenever it could throw off its yoke and did throw it off, it acted better. His words, written in 1762, became a text for the pioneers of the French Revolution. But they would have done well to read further into the book. As Rousseau goes on, we find a different conception. He passes from considering the fiction of a social contract to a discussion of the power over the individual of the General Will, by virtue of which a people becomes a people. This General Will, the Volonté Générale, he distinguishes from the Volonté de Tous, which is a mere numerical sum of individual wills. These particular wills do not rise above themselves. The General Will, on the other hand, represents what is greater than the individual volition of those who compose the society of which it is the will. On occasions, this higher will is more apparent than at other times. But it may, if there is social slackness, be difficult to distinguish from a mere aggregate of voices, from the will of a mob. What is interesting is that Rousseau, so often associated with doctrine of quite another kind, should finally recognize the bond of a General Will as what really holds the community together. For him, as for those who have had a yet clearer grasp of the principle, in willing the General Will we not only realize our true selves but we may rise above our ordinary habit of mind. We may reach heights which we could not reach, or which at all events most of us could not reach, in isolation. There are few observers who have not been impressed with the wonderful unity and concentration of purpose which an entire nation may display—above all, in a period of crisis. We see it in time of war, when a nation is fighting for its life or for a great cause. We have marvelled at the illustrations with which history abounds of the General Will rising to heights of which but few of the individual citizens in whom it is embodied have ever before been conscious even in their dreams.
The unity of the ego, in a psychological sense, is, therefore, the cohesion, during a given time, of a certain number of clear states of consciousness, accompanied by others less clear, and by a multitude of physiological states which, without being accompanied by consciousness like the others, yet operate as much as, and even more than, the former. Unity, in fact, means co-ordination. The conclusion to be drawn from the above remarks is namely this, that the consensus of consciousness being subordinate to the consensus of the organism, the problem of the unity of the ego is, in its ultimate form, a biological problem. To biology pertains the task of explaining, if it can, the genesis of organisms and the solidarity of their component parts. Psychological interpretation can only follow in its wake.
In fact, the total of our complexes, which, regarded as a whole and in view of their reaction to the environment, their behavior under the various conditions of social life, their aptitudes, feeling-tones, "habits," and faculties, we term character and personality, are in large part predetermined by the mental experiences of the past and the vestiges of memory which have been left as residual from these experiences. We are the offspring of our past.
On the other hand, everything that is inconsistent with the suggestion gets inhibited and leaves the subject's consciousness. As has been said, alterations of personality imply phenomena of amnesia. In order that the subject may assume the fictitious personality he must begin by forgetting his true personality. The infinite number of memories that represent his past experience and constitute the basis of his normal ego are for the time being effaced, because these memories are inconsistent with the ideal of the suggestion.
In society the difference is more marked. I seem to be a combination chaperone and protégée. The older appears at ease, the younger shy and awkward—she has never made her début. If one addresses a remark to her she is thrown into utter confusion until the older rushes to the rescue. My sympathy is with the younger, however, for even to this day I, the combination, can scarce resist the temptation to say nothing when there is nothing to say.
Thus the thoughts by which I meditated upon thee were like the efforts of one who would awake, but being overpowered with sleepiness is soon asleep again. Often does a man when heavy sleepiness is on his limbs defer to shake it off, and though not approving it, encourage it; even so I was sure it was better to surrender to thy love than to yield to my own lusts, yet, though the former course convinced me, the latter pleased and held me bound. There was naught in me to answer thy call, "Awake, thou sleeper," but only drawling, drowsy words, "Presently; yes, presently; wait a little while." But the "presently" had no "present," and the "little while" grew long. For I was afraid thou wouldst hear me too soon, and heal me at once of my disease of lust, which I wished to satiate rather than to see extinguished. With what lashes of words did I not scourge my own soul. Yet it shrank back; it refused, though it had no excuse to offer. I said within myself: "Come, let it be done now," and as I said it, I was on the point of the resolve. I all but did it, yet I did not do it. And I made another effort, and almost succeeded, yet I did not reach it, and did not grasp it, hesitating to die to death, and live to life; and the evil to which I was so wonted held me more than the better life I had not tried.
The importance of personality in the historic life of peoples is manifest in periods when social conditions accelerate the movement of social life. Personality, like every other force, reaches its maximum when it encounters resistance, in conflict and in rivalry—when it fights—hence its great value in friendly rivalry of nations in industry and culture, and especially in periods of natural calamities or of enemies from without. Since the fruits of individual development contribute to the common fund of social values, it is clear that societies and peoples which, other things being equal, possess the most advanced and active personalities contribute most to the enrichment of civilization. It does not seem necessary to demonstrate that the pacific competition of nations and their success depends on the development of the personalities which compose them. A nation weak in the development of individualities, of social units which compose it, could not defend itself against the exploitation of nations composed of personalities with a superior development.
In the development of "character," much depends upon early nurture, education, and surrounding influences generally, but how the individual reacts to these must largely depend on his inheritance. Truly the individual himself makes his own character, but he does so by his habitual adjustment of his (hereditarily determined) constitution to surrounding influences. Nurture supplies the stimulus for the expression of the moral inheritance, and how far the inheritance can express itself is limited by the nurture-stimuli available just as surely as the result of nurture is conditioned by the hereditarily determined nature on which it operates. It may be urged that character, being a product of habitual modes of feeling, thinking, and acting, cannot be spoken of as inherited, but bodily character is also a product dependent upon vital experience. It seems to us as idle to deny that some children are "born good" or "born bad," as it is to deny that some children are born strong and others weak, some energetic and others "tired" or "old." It may be difficult to tell how far the apparently hereditary goodness or badness of disposition is due to the nutritive influences of the mother, both before and after birth, and we must leave it to the reader's experience and observation to decide whether we are right or wrong in our opinion that quite apart from maternal nutritive influence there is a genuine inheritance of kindly disposition, strong sympathy, good humor, and good will. The further difficulty that the really organic character may be half-concealed by nurture-effects, or inhibited by the external heritage of custom and tradition, seems less serious, for the selfishness of an acquired altruism is as familiar as honor among thieves.
The sociological conclusion is: Prevent the feeble-minded, drunkards, paupers, sex-offenders, and criminalistic from marrying their like or cousins or any person belonging to a neuropathic strain. Practically it might be well to segregate such persons during the reproductive period for one generation. Then the crop of defectives will be reduced to practically nothing.
Tradition is, in a sense and if such a comparison were profitable, more conservative than heredity. There is in the content of tradition an invariability which could not exist if it were a dual composite, as is the constitution of the germ-plasm. Here we must recall certain essential qualities of the mores which we have hitherto viewed from another angle. Tradition always looks to the folkways as constituting the matter to be transmitted. But the folkways, after the concurrence in their practice has been established, come to include a judgment that they conduce to societal and, indeed, individual welfare. This is where they come to be properly called mores. They become the prosperity-policy of the group, and the young are reared up under their sway, looking to the older as the repositories of precedent and convention. But presently the older die, and in conformity with the ideas of the time, they become beings of a higher power toward whom the living owe duty, and whose will they do not wish to cross. The sanction of ghost-fear is thus extended to the mores, which, as the prosperity-policy of the group, have already taken on a stereotyped character. They thus become in an even higher degree "uniform, universal in a group, imperative, invariable. As time goes on, they become more and more arbitrary, positive, and imperative. If asked why they act in a certain way in certain cases, primitive people always answer that it is because they and their ancestors always have done so." Thus the transmission of the mores comes to be a process embodying the greatest conservatism and the least likelihood of change. This situation represents an adaption of society to life-conditions; it would seem that because of the rapidity of succession of variations there is need of an intensely conserving force (like ethnocentrism or religion) to preserve a certain balance and poise in the evolutionary movement.
When the physical unity of a group is perpetuated by the succession of parents and children, the racial temperament, including fundamental attitudes and values which rest in it, is preserved intact. When, however, society grows and is perpetuated by immigration and adaptation, there ensues, as a result of miscegenation, a breaking up of the complex of the biologically inherited qualities which constitute the temperament of the race. This again initiates changes in the mores, traditions, and eventually in the institutions of the community. The changes which proceed from modification in the racial temperament will, however, modify but slightly the external forms of the social traditions, but they will be likely to change profoundly their content and meaning. Of course other factors, individual competition, the formation of classes, and especially the increase of communication, all co-operate to complicate the whole situation and to modify the effects which would be produced by racial factors working in isolation.
Comte's notion that every scientific discipline must pass through a theological and metaphysical stage before it assumed the character of a positive science seems to be true as far as sociology is concerned. Machiavelli shocked the moral sense of his time, if not the moralists of all time, when he proposed to accept human nature as it is as a basis for political science. Herbert Spencer insisted upon the futility of expecting "golden conduct from leaden instincts." To the utopian social reformers of his day he pointed out a series of welfare measures in England in which the outcome was the direct opposite of the results desired.
After all that may be said for the experimental novel, however, its primary aim, like that of history, is appreciation and understanding, not generalization and abstract formulas. Insight and sympathy, the mystical sense of human solidarity, expressed in the saying "to comprehend all is to forgive all," this fiction has to give. And these are materials which the sociologist cannot neglect. As yet there is no autobiography or biography of an egocentric personality so convincing as George Meredith's The Egoist. The miser is a social type; but there are no case studies as sympathetic and discerning as George Eliot's Silas Marner. Nowhere in social science has the technique of case study developed farther than in criminology; yet Dostoévsky's delineation of the self-analysis of the murderer in Crime and Punishment dwarfs all comparison outside of similar studies in fiction. The function of the so-called psychological or sociological novel stops, however, with its presentation of the individual incident or case; it is satisfied by the test of its appeal to the experience of the reader. The scientific study of human nature proceeds a step farther; it seeks generalizations. From the case studies of history and of literature it abstracts the laws and principles of human behavior.
Autobiography and biography provide source material for the study both of the subjective life and of the social rôle of the person. Three great autobiographies which have inspired the writing of personal narratives are themselves representative of the different types: Caesar's Commentaries, with his detached impersonal description of his great exploits; the Confessions of St. Augustine, with his intimate self-analysis and intense self-reproach, and the less well-known De Vita Propria Liber by Cardan. This latter is a serious attempt at scientific self-examination. Recently, attention has been directed to the accumulation of autobiographical and biographical materials which are interpreted from the point of view of psychiatry and psychoanalysis. The study Der Fall Otto Weininger by Dr. Ferdinand Probst is a representative monograph of this type. The outstanding example of this method and its use for sociological interpretation is "Life Record of an Immigrant" contained in the third volume of Thomas and Znaniecki, The Polish Peasant. In connection with the Recreation Survey of the Cleveland Foundation and the Americanization Studies of the Carnegie Corporation, the life-history has been developed as part of the technique of investigation.
This survey indicates the present status of attempts to define and measure differences in original and human nature. A knowledge of individual differences is important in every field of social control. It is significant that these tests have been devised to meet problems of policies and of administration in medicine, in industry, in education, and in penal and reformatory institutions. Job analysis, personnel administration, ungraded rooms, classes for exceptional children, vocational guidance, indicate fields made possible by the development of tests for measuring individual differences.
(7) Hollingworth, Leta S. "Variability as Related to Sex Differences in Achievement," American Journal of Sociology, XIX (1913-14), 510-30. [Bibliography.]
22. Mental Inferiority and Crime
The term social group has come into use with the attempts of students to classify societies. Societies may be classified with reference to the rôle which they play in the organization and life of larger social groups or societies. The internal organization of any given social group will be determined by its external relation to other groups in the society of which it is a part as well as by the relations of individuals within the group to one another. A boys' gang, a girls' clique, a college class, or a neighborhood conforms to this definition quite as much as a labor union, a business enterprise, a political party, or a nation. One advantage of the term "group" lies in the fact that it may be applied to the smallest as well as to the largest forms of human association.
To society the most alien relations of two living beings which can be produced are those of the predator and his prey. In general, the predator is bulkier than his prey, since he overcomes him and devours him. Yet smaller ones sometimes attack larger creatures, consuming them, however, by instalments, and letting them live that they themselves may live on them as long as possible. In such a case they are forced to remain for a longer or a shorter time attached to the body of their victim, carried about by it wherever the vicissitudes of its life lead them. Such animals have received the name of parasites. Parasitism forms the line inside of which our subject begins; for if one can imagine that the parasite, instead of feeding on the animal from whom he draws his subsistence, is content to live on the remains of the other's meals, one will find himself in the presence, not yet of an actual society, but of half the conditions of a society; that is to say, a relation between two beings such that, all antagonism ceasing, one of the two is useful to the other. Such is commensalism. However, this association does not yet offer the essential element of all society, co-operation. There is co-operation when the commensal is not less useful to his host than the latter is to the commensal himself, when the two are concerned in living in a reciprocal relation and in developing their double activity in corresponding ways toward a single and an identical goal. One has given to this mode of activity the name of mutualism. Domestication is only one form of it. Parasitism, commensalism, mutualism, exist with animals among the different species.
It is convenient to follow the European writers, von Hagens, Forel, Wasmann, and others, in grouping all the cases of social symbiosis under two heads, the compound nests and the mixed colonies. Different species of ants or of ants and termites are said to form compound nests when their galleries are merely contiguous or actually interpenetrate and open into one another, although the colonies which inhabit them bring up their respective offspring in different apartments. In mixed colonies, on the other hand, which, in a state of nature, can be formed only by species of ants of close taxonomic affinities, the insects live together in a single nest and bring up their young in common. Although each of these categories comprises a number of dissimilar types of social symbiosis, and although it is possible, under certain circumstances, as will be shown in the sequel, to convert a compound nest into a mixed colony, the distinction is nevertheless fundamental. It must be admitted, however, that both types depend in last analysis on the dependent, adoption-seeking instincts of the queen ant and on the remarkable plasticity which enables allied species and genera to live in very close proximity to one another. By a strange paradox these peculiarities have been produced in the struggle for existence, although this struggle is severer among different species of ants than between ants and other organisms. As Forel says: "The greatest enemies of ants are other ants, just as the greatest enemies of men are other men."
When wild animals become tame, they are really extending or transferring to human beings the confidence and affection they naturally give their mothers, and this view will be found to explain more facts about tameness than any other. Every creature that would naturally enjoy maternal, or it would be better to say parental, care, as the father sometimes shares in or takes upon himself the duty of guarding the young, is ready to transfer its devotion to other animals or to human beings, if the way be made easy for it, and if it be treated without too great violation of its natural instincts. The capacity to be tamed is greatest in those animals that remain longest with their parents and that are most intimately associated with them. The capacity to learn new habits is greatest in those animals which naturally learn most from their parents, and in which the period of youth is not merely a period of growing, a period of the awakening of instincts, but a time in which a real education takes place. These capacities of being tamed and of learning new habits are greater in the higher mammals than in the lower mammals, in mammals than in birds, and in birds than in reptiles. They are very much greater in very young animals, where dependence on the parents is greatest, than in older animals, and they gradually fade away as the animal grows up, and are least of all in fully grown and independent creatures of high intelligence.
Woodhead has suggested the term complementary association to denote a community of species that live together in harmony, because their rhizomes occupy different depths in the soil; for example, he described an "association" in which Holcus mollis is the "surface plant," Pteris aquilina has deeper-seated rhizomes, and Scilla festalis buries its bulbs at the greatest depth. The photophilous parts of these plants are "seasonably complementary." The opposite extreme is provided by competitive associations, composed of species that are battling with each other.
An ant society, therefore, may be regarded as little more than an expanded family, the members of which co-operate for the purpose of still further expanding the family and detaching portions of itself to found other families of the same kind. There is thus a striking analogy, which has not escaped the philosophical biologist, between the ant colony and the cell colony which constitutes the body of a Metazoan animal; and many of the laws that control the cellular origin, development, growth, reproduction, and decay of the individual Metazoan, are seen to hold good also of the ant society regarded as an individual of a higher order. As in the case of the individual animal, no further purpose of the colony can be detected than that of maintaining itself in the face of a constantly changing environment till it is able to reproduce other colonies of a like constitution. The queen-mother of the ant colony displays the generalized potentialities of all the individuals, just as the Metazoan egg contains in potentia all the other cells of the body. And, continuing the analogy, we may say that since the different castes of the ant colony are morphologically specialized for the performance of different functions, they are truly comparable with the differentiated tissues of the Metazoan body.
Not only is social life identical with communication, but all communication (and hence all genuine social life) is educative. To be a recipient of a communication is to have an enlarged and changed experience. One shares in what another has thought and felt, and in so far, meagerly or amply, has his own attitude modified. Nor is the one who communicates left unaffected. Try the experiment of communicating, with fulness and accuracy, some experience to another, especially if it be somewhat complicated, and you will find your own attitude toward your experience changing; otherwise you resort to expletives and ejaculations. The experience has to be formulated in order to be communicated. To formulate requires getting outside of it, seeing it as another would see it, considering what points of contact it has with the life of another so that it may be got into such form that he can appreciate its meaning. Except in dealing with commonplaces and catch phrases one has to assimilate, imaginatively, something of another's experience in order to tell him intelligently of one's own experience. All communication is like art. It may fairly be said, therefore, that any social arrangement that remains vitally social, or vitally shared, is educative to those who participate in it. Only when it becomes cast in a mold and runs in a routine way does it lose its educative power.
No doubt all these activities have their beginnings in, and are founded upon, forms of behavior of which we may find the rudiments in the lower animals. But there is in all distinctively human activities a conventional, one might almost say a contractual, element which is absent in action of other animals. Human actions are more often than not controlled by a sense or understanding of what they look like or appear to be to others. This sense and understanding gets itself embodied in some custom or ceremonial observance. In this form it is transmitted from generation to generation, becomes an object of sentimental respect, gets itself embodied in definite formulas, is an object not only of respect and reverence but of reflection and speculation as well. As such it constitutes the mores, or moral customs, of a group and is no longer to be regarded as an individual possession.
In human society, then, the conditions regulating conduct are from the first greatly modified. Instinct, becoming vague and more general, has evolved into "character," while the intelligence finds itself confronted with customs to which it has to accommodate conduct. But how does custom arise? Let us first consider what custom is. It is not merely a habit of action; but it implies also a judgment upon action, and a judgment stated in general and impersonal terms. It would seem to imply a bystander or third party. If A hits B, B probably hits back. It is his "habit" so to do. But if C, looking on, pronounces that it was or was not a fair blow, he will probably appeal to the "custom" of the country—the traditional rules of fighting, for instance—as the ground of his judgment. That is, he will lay down a rule which is general in the sense that it would apply to other individuals under similar conditions, and by it he will, as an impartial third person, appraise the conduct of the contending parties. The formation of such rules, resting as it does on the power of framing and applying general conceptions, is the prime differentia of human morality from animal behavior. The fact that they arise and are handed on from generation to generation makes social tradition at once the dominating factor in the regulation of human conduct. Without such rules we can scarcely conceive society to exist, since it is only through the general conformity to custom that men can understand each other, that each can know how the other will act under given circumstances, and without this amount of understanding the reciprocity, which is the vital principle of society, disappears.
The collective consciousness is the highest form of the psychic life, since it is the consciousness of the consciousnesses. Being placed outside of and above individual and local contingencies, it sees things only in their permanent and essential aspects, which it crystallizes into communicable ideas. At the same time that it sees from above, it sees farther; at every moment of time, it embraces all known reality; that is why it alone can furnish the mind with the molds which are applicable to the totality of things and which make it possible to think of them. It does not create these molds artificially; it finds them within itself; it does nothing but become conscious of them. They translate the ways of being which are found in all the stages of reality but which appear in their full clarity only at the summit, because the extreme complexity of the psychic life which passes there necessitates a greater development of consciousness. Collective representations also contain subjective elements, and these must be progressively rooted out if we are to approach reality more closely. But howsoever crude these may have been at the beginning, the fact remains that with them the germ of a new mentality was given, to which the individual could never have raised himself by his own efforts; by them the way was opened to a stable, impersonal and organized thought which then had nothing to do except to develop its nature.
In effect, the groups to which we belong might be as separate and independent of us as the streets and buildings of a city are from the population. If the inhabitants should migrate in a body, the streets and buildings would remain. This is not true of human groups, but their reaction upon the persons who compose them is no less real and evident. We are in large part what our social set, our church, our political party, our business and professional circles are. This has always been the case from the beginning of the world, and will always be the case. To understand what society is, either in its larger or its smaller parts, and why it is so, and how far it is possible to make it different, we must invariably explain groups on the one hand, no less than individuals on the other. There is a striking illustration in Chicago at present (summer, 1905). Within a short time a certain man has made a complete change in his group-relations. He was one of the most influential trade-union leaders in the city. He has now become the executive officer of an association of employers. In the elements that are not determined by his group-relationships he is the same man that he was before. Those are precisely the elements, however, that may be canceled out of the social problem. All the elements in his personal equation that give him a distinct meaning in the life of the city are given to him by his membership in the one group or the other. Till yesterday he gave all his strength to organizing labor against capital. Now he gives all his strength to the service of capital against labor.
In the case of human societies we discover not merely organically inherited adaptation, which characterizes animal societies, but, in addition, a great body of habits and accommodations which are transmitted in the form of social inheritance. Something that corresponds to social tradition exists, to be sure, in animal societies. Animals learn by imitation from one another, and there is evidence that this social tradition varies with changes in environment. In man, however, association is based on something more than habits or instinct. In human society, largely as a result of language, there exists a conscious community of purpose. We have not merely folkways, which by an extension of that term might be attributed to animals, but we have mores and formal standards of conduct.
The bond which unites all the citizens of a state is language and nationality. Above the state there are only the crowds determined by race, which comprise many states. And these are, like the states and like the classes, human aggregates which in a moment could be transformed into violent crowds. But then, and justly, because their evolution and their organization are more developed, their mobs are called armies, and their violences are called wars, and they have the seal of legitimacy unknown in other crowds. In this order of ideas war could be defined as the supreme form of collective crimes.
Crowds are capable of doing reasonless things upon impulse and of adopting creeds without reflection. But an army is not a crowd; still less is a nation a crowd. A mob or crowd is an unorganized group of people governed by less than the average individual intelligence of its members. Armies and nations are groups of people so organized that they are controlled by an intelligence higher than the average. The instincts that lend, and must lend, their immense motive-power to the great purposes of war are the servants, not the masters, of that intelligence.
Modern sociology's chief inheritance from Comte and Spencer was a problem in logic: What is a society?
More recently the impact of social problems has led to the intensive study of modern communities. The monumental work of Charles Booth, Life and Labour of the People in London, is a comprehensive description of conditions of social life in terms of the community. In the United States, interest in community study is chiefly represented by the social-survey movement which received impetus from the Pittsburgh Survey of 1907. For sociological research of greater promise than the survey are the several monographs which seek to make a social analysis of the community, as Williams, An American Town, or Galpin, The Social Anatomy of an Agricultural Community. With due recognition of these auspicious beginnings, it must be confessed that there is no volume upon human communities comparable with several works upon plant and animal communities.
The first written accounts of conflict groups were quite naturally of the propagandist type both by their defenders and by their opponents. Histories of nationalities, for example, originated in the patriotic motive of national glorification. With the acceptance of objective standards of historical criticism the ground was prepared for the sociological study of nationalities as conflict groups. A school of European sociologists represented by Gumplowicz, Ratzenhofer, and Novicow stressed conflict as the characteristic behavior of social groups. Beginnings, as indicated in the bibliography, have been made of the study of various conflict groups as gangs, labor unions, parties, and sects.
(10) Du Bois, W. E. B. The Negro American Family. Atlanta, 1908. [Bibliography.]
5. Animal Communities, or Studies in Animal Ecology.
The biological use of the term "isolation" introduces a new emphasis. Separation may be spatial, but its effects are increasingly structural and functional. Indeed, spatial isolation was a factor in the origin of species because of specialized organic adaptation to varied geographic conditions. In other words, the structure of the species, its habits of life, and its original and acquired responses, tend to isolate it from other species.
The life-history of any group when analyzed is found to incorporate within it elements of isolation as well as of social contact. Membership in a group makes for increasing contacts within the circle of participants, but decreasing contacts with persons without. Isolation is for this reason a factor in the preservation of individuality and unity. The esprit de corps and morale of the group is in large part maintained by the fixation of attention upon certain collective representations to the exclusion of others. The memories and sentiments of the members have their source in common experiences of the past from which non-members are isolated. This natural tendency toward exclusive experiences is often reinforced by conscious emphasis upon secrecy. Primitive and modern secret societies, sororities, and fraternities have been organized around the principle of isolation. Secrecy in a society, like reserve in an individual, protects it from a disintegrating publicity. The family has its "skeleton in the closet," social groups avoid the public "washing of dirty linen"; the community banishes from consciousness, if it can, its slums, and parades its parks and boulevards. Every individual who has any personality at all maintains some region of privacy.
This circular effect of the processes of competition, selection, and segregation, from isolation to isolation, may be found everywhere in modern western society. Individual variants with criminalistic tendencies exiled from villages and towns through the process of selection form a segregated group in city areas popularly called "breeding places of crime." The tribe of Pineys, Tin Town, The Village of a Thousand Souls, are communities made up by adverse selection of feeble-minded individuals, outcasts of the competitive struggle of intelligent, "high-minded" communities. The result is the formation of a criminal type and of a feeble-minded caste. These slums and outcast groups are in turn isolated from full and free communication with the progressive outside world.
It had been hard for him that spake it to have put more truth and untruth together in few words than in that speech: "Whosoever is delighted in solitude is either a wild beast or a god." For it is most true that a natural and secret hatred and aversation towards society in any man hath somewhat of the savage beast; but it is most untrue that it should have any character at all of the divine nature except it proceed, not out of a pleasure in solitude, but out of a love and desire to sequester a man's self for a higher conversation, such as is found to have been falsely and feignedly in some of the heathen, as Epimenides the Candian, Numa the Roman, Empedocles the Sicilian, and Apollonius of Tyana; and truly and really in divers of the ancient hermits and Holy Fathers of the Church. But little do men perceive what solitude is, and how far it extendeth. For a crowd is not company, and faces are but a gallery of pictures, and talk but a tinkling cymbal, where there is no love. The Latin adage meeteth with it a little: Magna civitas magna solitudo ("A great town is a great solitude"), because in a great town friends are scattered, so that there is not that fellowship, for the most part, which is in less neighborhoods. But we may go further, and affirm most truly that it is a mere and miserable solitude to want true friends, without which the world is but a wilderness; and, even in this sense also of solitude, whosoever in the frame of his nature and affections is unfit for friendship, he taketh it of the beast and not from humanity.
The wild spot of the forest [selected by Rousseau for his solitary walks and meditations] could not long remain a desert to my imagination. I soon peopled it with beings after my own heart, and, dismissing opinion, prejudice, and all factitious passions, I brought to these sanctuaries of nature men worthy of inhabiting them. I formed with these a charming society, of which I did not feel myself unworthy. I made a golden age according to my fancy, and, filling up these bright days with all the scenes of my life that had left the tenderest recollections, and with all that my heart still longed for, I affected myself to tears over the true pleasures of humanity—pleasure so delicious, so pure, and yet so far from men! Oh, if in these moments any ideas of Paris, of the age, and of my little author vanity, disturbed my reveries, with what contempt I drove them instantly away, to give myself up entirely to the exquisite sentiments with which my soul was filled. Yet, in the midst of all this, I confess the nothingness of my chimeras would sometimes appear, and sadden me in a moment.
The values of prayer in sickness, distress, and doubt are by no means measurable by the degree to which the primary causes thereof are made to disappear. There is a real conquest of trouble, even while trouble remains. It is sometimes a great source of strength, also, merely to realize that one is fully understood. The value of having some friend or helper from whom I reserve no secrets has been rendered more impressive than ever by the Freud-Jung methods of relieving mental disorders through (in part) a sort of mental house-cleaning, or bringing into the open the patient's hidden distresses and even his most intimate and reticent desires. Into the psychology of the healings that are brought about by this psychoanalysis we need not go, except to note that one constant factor appears to be the turning of a private possession into a social possession, and particularly the consciousness that another understands. I surmise that we shall not be far from the truth here if we hold that, as normal experience has the ego-alter form, so the continuing possession of one's self in one's developing experience requires development of this relation. We may, perhaps, go as far as to believe that the bottling up of any experience as merely private is morbid. But, however this may be, there are plenty of occasions when the road to poise, freedom, and joy is that of social sharing. Hence the prayer of confession, not only because it helps us to see ourselves as we are, but also because it shares our secrets with another, has great value for organizing the self. In this way we get relief from the misjudgments of others, also, and from the mystery that we are to ourselves, for we lay our case, as it were, before a judge who does not err. Thus prayer has value in that it develops the essentially social form of personal self-realization.
But let us take other names with different associations—e.g., Plato, Charlemagne, Caesar, Shakespeare, Napoleon, Bismarck. Can it be said of any one of these that he owed one-third of his distinction to what he learned from manuscripts or books? We do know, indeed, that Bismarck was a wide reader, but it was on the selective principle as a student of history and affairs. His library grew under the influence of the controlling purpose of his life—i.e., the unification of Germany, so that there was no vague distribution of energy. Of Shakespeare's reading we know less, but there is no evidence that he was a collector of books or that he was a student after the manner of the men of letters of his day. The best way to estimate him as a reader is to judge him by the references in his plays, and these do not show an acquaintance with literature so extensive as it is intensive. The impression he made on Ben Johnson, an all-round scholar, was not one of learning—quite otherwise. The qualities that impressed the author of Timber, or Discoveries upon Men and Matter, were Shakespeare's "open and free nature," his "excellent fancy, brave notions, and gentle expressions wherein he flowed with that facility that sometimes it was necessary he should be stopped." And, true to himself, Ben Jonson immediately adds: "Sufflaminandus erat, as Augustus said of Haterius." Shakespeare, when in the company of kindred spirits, showed precisely the kind of talk we should expect—not Latin and Greek or French and Italian quotations, not a commentary on books past or present, but a stream of conversation marked by brilliant fancy, startling comparison, unique contrast, and searching pathos, wherein life, not literature, was the chief subject.
i) Peter of Hanover. Found in the woods of Hanover; food—buds, barks, roots, frogs, eggs of birds, and anything else that he could get out of doors; had a habit of wandering away in the spring; always went to bed as soon as he had his supper; was unable to walk in shoes at first, and it was long before he would tolerate a covering for his head. Although Queen Caroline furnished him a teacher, he could never learn to speak; he became docile, but remained stoical in manner; he learned to do farm work willingly unless he was compelled to do it; his sense of hearing and of smell was acute, and before changes in the weather he was sullen and irritable; he lived to be nearly seventy years old.[103]
We walked down the path to the well-house, attracted by the fragrance of the honeysuckle with which it was covered. Some one was drawing water and my teacher placed my hand under the spout. As the cool stream gushed over one hand she spelled into the other the word water, first slowly, then rapidly. I stood still, my whole attention fixed upon the motions of her fingers. Suddenly I felt a misty consciousness as of something forgotten—a thrill of returning thought; and somehow the mystery of language was revealed to me. I knew then that "w-a-t-e-r" meant the wonderful cool something that was flowing over my hand. That living word awakened my soul, gave it light, hope, joy, set it free! There were barriers still, it is true, but barriers that could in time be swept away.
Not once nor twice nor thrice, but day after day I returned to this solitude, going to it in the morning as if to attend a festival, and leaving it only when hunger and thirst and the westering sun compelled me. And yet I had no object in going—no motive which could be put into words; for, although I carried a gun, there was nothing to shoot—the shooting was all left behind in the valley. Sometimes I would pass an entire day without seeing one mammal and perhaps not more than a dozen birds of any size. The weather at that time was cheerless, generally with a gray film of cloud spread over the sky, and a bleak wind, often cold enough to make my bridle hand quite numb. At a slow pace, which would have seemed intolerable in other circumstances, I would ride about for hours at a stretch. On arriving at a hill, I would slowly ride to its summit, and stand there to survey the prospect. On every side it stretched away in great undulations, wild and irregular. How gray it all was! Hardly less so near at hand than on the haze-wrapped horizon, where the hills were dim and the outline blurred by distance. Descending from my outlook, I would take up my aimless wanderings again, and visit other elevations to gaze on the same landscape from another point; and so on for hours; and at noon I would dismount and sit or lie on my folded poncho for an hour or longer. One day, in these rambles, I discovered a small grove composed of twenty or thirty trees, growing at a convenient distance apart, that had evidently been resorted to by a herd of deer or other wild animals. This grove was on a hill differing in shape from other hills in its neighborhood; and after a time I made a point of finding and using it as a resting-place every day at noon. I did not ask myself why I made choice of that one spot, sometimes going miles out of my way to sit there, instead of sitting down under any one of the millions of trees and bushes on any other hillside. I thought nothing at all about it, but acted unconsciously. Only afterward it seemed to me that, after having rested there once, each time I wished to rest again the wish came associated with the image of that particular clump of trees, with polished stems and clean bed of sand beneath; and in a short time I formed a habit of returning, animal-like, to repose at that same spot.
Occasions must be created, plans must be made, to bring people together in a wholesale manner so as to facilitate this interchange of community acquaintance. Especially is it necessary for rural children to know many more children. The one-room district school has proved its value in making the children of the neighborhood acquainted with one another. One of the large reasons for the consolidated and centralized school is the increased size of territorial unit, with more children to know one another and mingle together. Intervisiting of district schools—one school, teachers and pupils, playing host to a half-dozen other schools, with some regularity, using plays and games, children's readiest means of getting acquainted—is a successful means of extending acquaintance under good auspices.
Obviously obstacles which discourage one race may stimulate another. Even the extreme measures in Russia and Roumania against the Jew have not isolated him. He has resources and traditions and technique of his own, and we have even been borrowers from him.
The people of the original East London have now overflowed and crossed the Lea, and spread themselves over the marshes and meadows beyond. This population has created new towns which were formerly rural villages, West Ham, with a population of nearly 300,000; East Ham, with 90,000; Stratford, with its "daughters," 150,000; and other "hamlets" similarly overgrown. Including these new populations we have an aggregate of nearly two millions of people. The population is greater than that of Berlin or Vienna, or St. Petersburg, or Philadelphia.
This factor of natural selection has not to our knowledge been given adequate consideration in any published investigation on delinquency. But if our estimate of its effects is at all justified, then most examinations of juvenile delinquents, especially in reform and industrial schools, have disclosed proportions of mental defectives distinctly in excess of the original proportion previously existent among the entire mass of all offenders. The reports of these examinations have given rise to quite erroneous impressions concerning the extent of criminality among the feeble-minded and its relation to the whole volume of crime, and have consequently led to inaccurate deductions. The feeble-minded are undoubtedly more prone to commit crime than are the average normals; but through disregard of the influences of this factor of natural selection, as well as of others, both the proportion of crime committed by mental defectives and the true proportion of mental defectives among delinquents and criminals have very often been exaggerated.
This fixity of race characteristics has enabled the several national varieties of men to go forth from their nurseries, carrying the qualities bred in their earlier conditions through centuries of life in other climes. The Gothic blood of Italy and of Spain still keeps much of its parent strength; the Aryan's of India, though a world apart in its conditions from those which gave it character in its cradle, is still, in many of its qualities, distinctly akin to that of the home people. Moor, Hun and Turk—all the numerous folk we find in the present condition of the world so far from their cradle-lands—are still to a great extent what their primitive nurture made them. On this rigidity which comes to mature races in the lower life as well as in man, depends the vigor with which they do their appointed work.
We may remark, first, that their position made them at once mountaineers and mariners, thus supplying them with great variety of objects, sensations, and adventures; next, that each petty community, nestled apart amidst its own rocks, was sufficiently severed from the rest to possess an individual life and attributes of its own, yet not so far as to subtract it from the sympathies of the remainder; so that an observant Greek, commercing with a great diversity of half-countrymen, whose language he understood, and whose idiosyncrasies he could appreciate, had access to a larger mass of social and political experience than any other man in so unadvanced an age could personally obtain. The Phœnician, superior to the Greek on shipboard, traversed wider distances and saw a greater number of strangers, but had not the same means of intimate communion with a multiplicity of fellows in blood and language. His relations, confined to purchase and sale, did not comprise that mutuality of action and reaction which pervaded the crowd at a Grecian festival. The scene which here presented itself was a mixture of uniformity and variety highly stimulating to the observant faculties of a man of genius—who at the same time, if he sought to communicate his own impressions, or to act upon this mingled and diverse audience, was forced to shake off what was peculiar to his own town or community, and to put forth matter in harmony with the feelings of all. It is thus that we may explain, in part, that penetrating apprehension of human life and character, and that power of touching sympathies common to all ages and nations, which surprises us so much in the unlettered authors of the old epic. Such periodical intercommunion of brethren habitually isolated from each other was the only means then open of procuring for the bard a diversified range of experience and a many-colored audience; and it was to a great degree the result of geographical causes. Perhaps among other nations such facilitating causes might have been found, yet without producing any results comparable to the Iliad and Odyssey. But Homer was nevertheless dependent upon the conditions of his age, and we can at least point out those peculiarities in early Grecian society without which Homeric excellence would never have existed—the geographical position is one, the language another.
Appeal to the social geography of other countries, wherein the ethnic balance of power is differently distributed, may be directed against almost any of the phenomena we have instanced in France as seemingly of racial derivation. In the case either of suicide or divorce, if we turn from France to Italy or Germany, we instantly perceive all sorts of contradictions. The ethnic type, which is so immune from propensity to self-destruction or domestic disruption in France, becomes in Italy most prone to either mode of escape from temporary earthly ills. For each phenomenon culminates in frequency in the northern half of the latter country, stronghold of the Alpine race. Nor is there an appreciable infusion of Teutonism, physically speaking, herein, to account for the change of heart. Of course, it might be urged that this merely shows that the Mediterranean race of southern Italy is as much less inclined to the phenomenon than the Alpine race in these respects, as it in turn lags behind the Teuton. For it must be confessed that even in Italy neither divorce nor suicide is so frequent anywhere as in Teutonic northern France. Well, then, turn to Germany. Compare its two halves in these respects again. The northern half of the empire is most purely Teutonic by race; the southern is not distinguishable ethnically, as we have sought to prove, from central France. Bavaria, Baden, and Würtemberg are scarcely more Teutonic by race than Auvergne. Do we find differences in suicide, for example, following racial boundaries here? Far from it; for Saxony is its culminating center; and Saxony, as we know, is really half-Slavic at heart, as is also eastern Prussia. Suicide should be most frequent in Schleswig-Holstein and Hanover, if racial causes were appreciably operative. The argument, in fact, falls to pieces of its own weight, as Durkheim has shown. His conclusion is thus stated:
A people has, therefore, a twofold location, an immediate one, based upon their actual territory, and a mediate or vicinal one, growing out of its relations to the countries nearest them. The first is a question of the land under their feet; the other, of the neighbors about them. The first or natural location embodies the complex of local geographic conditions which furnish the basis for their tribal or national existence. This basis may be a peninsula, island, archipelago, an oasis, an arid steppe, a mountain system, or a fertile lowland. The stronger the vicinal location, the more dependent is the people upon the neighboring states, but the more potent the influence which it can, under certain circumstances, exert upon them. Witness Germany in relation to Holland, France, Austria, and Poland. The stronger the natural location, on the other hand, the more independent is the people and the more strongly marked is the national character. This is exemplified in the people of mountain lands like Switzerland, Abyssinia, and Nepal; of peninsulas like Korea, Spain, and Scandinavia; and of islands like England and Japan. Today we stand amazed at that strong primordial brand of the Japanese character which nothing can blur or erase.
A systematic treatise upon isolation as a sociological concept remains to be written. The idea of isolation as a tool of investigation has been fashioned with more precision in geography and in biology than in sociology.
The literature upon isolated peoples ranges from investigations of arrest of cultural development as, for example, the natives of Australia, the Mountain Whites of the southern states, or the inhabitants of Pitcairn Island to studies of hermit nations, of caste systems as in India, or of outcast groups such as feeble-minded "tribes" or hamlets, fraternities of criminals, and the underworld of commercialized prostitution. Special research in dialects, in folklore, and in provincialism shows how spatial isolation fixes differences in speech, attitudes, folkways, and mores which, in turn, enforce isolation even when geographic separation has disappeared.
Psychiatry and psychoanalysis in probing mental life and personality have related certain mental and social abnormalities to isolation from social contact. Studies of paranoia and of egocentric personalities have resulted in the discovery of the only or favorite child complex. The exclusion of the boy or girl in the one-child family from the give and take of democratic relations with brothers and sisters results, according to the theory advanced, in a psychopathic personality of the self-centered type. A contributing cause of homosexuality, it is said by psychoanalysts, is the isolation during childhood from usual association with individuals of the same sex. Research in dementia praecox discloses a symptom and probably a cause of this mental malady to be the withdrawal of the individual from normal social contacts and the substitution of an imaginary for a real world of persons and events. Dementia praecox has been related by one psychoanalyst to the "shut-in" type of personality.
(5) ——. The Blind. Their condition and the work being done for them in the United States. New York, 1919.
10. Isolation and Prestige.
The frontiers of social contact are farther extended to the widest horizons, by commerce. The economists, for example, include in their conception of society the intricate and complex maze of relations created by the competition and co-operation of individuals and societies within the limits of a world-wide economy. This inclusion of unconscious as well as conscious reciprocal influences in the concept of social relations brings into "contact" the members of a village missionary society with the savages of the equatorial regions of Africa; or the pale-faced drug addict, with the dark-skinned Hindu laborers upon the opium fields of Benares; or the man gulping down coffee at the breakfast table, with the Java planter; the crew of the Pacific freighter and its cargo of spices with the American wholesaler and retailer in food products. In short, everyone is in a real, though concealed and devious, way in contact with every other person in the world. Contacts of this type, remote from the familiar experiences of everyday life, have reality to the intellectual and the mystic and are appreciated by the masses only when co-operation breaks down, or competition becomes conscious and passes into conflict.
The use of the term "contact" in sociology is not a departure from, but a development of, its customary significance. In the preceding chapter the point was made that the distinction between isolation and contact is not absolute but relative. Members of a society spatially separate, but socially in contact through sense perception and through communication of ideas, may be thereby mobilized to collective behavior. Sociological interest in this situation lies in the fact that the various kinds of social contacts between persons and groups determine behavior. The student of problems of American society, for example, realizes the necessity of understanding the mutual reactions involved in the contacts of the foreign and the native-born, of the white and the negro, and of employers and employees. In other words, contact, as the first stage of social interaction, conditions and controls the later stages of the process.
In the first place, we want to indicate, not the essence of the social, but the location, the sphere, the extent, of the social. If we can agree where it is, we may then proceed to discover what it is. The social, then, is the term next beyond the individual. Assuming, for the sake of analysis, that our optical illusion, "the individual," is an isolated and self-sufficient fact, there are many sorts of scientific problems that do not need to go beyond this fact to satisfy their particular terms. Whether the individual can ever be abstracted from his conditions and remain himself is not a question that we need here discuss. At all events, the individual known to our experience is not isolated. He is connected in various ways with one or more individuals. The different ways in which individuals are connected with each other are indicated by the inclusive term "contact." Starting, then, from the individual, to measure him in all his dimensions and to represent him in all his phases, we find that each person is what he is by virtue of the existence of other persons, and by virtue of an alternating current of influence between each person and all the other persons previously or at the same time in existence. The last native of Central Africa around whom we throw the dragnet of civilization, and whom we inoculate with a desire for whiskey, adds an increment to the demand for our distillery products, and affects the internal revenue of the United States, and so the life-conditions of every member of our population. This is what we mean by "contact." So long as that African tribe is unknown to the outside world, and the world to it, so far as the European world is concerned, the tribe might as well not exist. The moment the tribe comes within touch of the rest of the world, the aggregate of the world's contacts is by so much enlarged; the social world is by so much extended. In other words, the realm of the social is the realm of circuits of reciprocal influence between individuals and the groups which individuals compose. The general term "contact" is proposed to stand for this realm, because it is a colorless word that may mark boundaries without prejudging contents. Wherever there is physical or spiritual contact between persons, there is inevitably a circuit of exchange of influence. The realm of the social is the realm constituted by such exchange. It extends from the producing of the baby by the mother, and the simultaneous producing of the mother by the baby, to the producing of merchant and soldier by the world-powers, and the producing of the world-powers by merchant and soldier.
Most systems of sociology treat man as if he were in some way detached from the earth's surface; they ignore the land basis of society. The anthropogeographer recognizes the various social forces, economic and psychologic, which sociologists regard as the cement of societies; but he has something to add. He sees in the land occupied by a primitive tribe or a highly organized state the underlying material bond holding society together, the ultimate basis of their fundamental social activities, which are therefore derivatives from the land. He sees the common territory exercising an integrating force—weak in primitive communities where the group has established only a few slight and temporary relations with its soil, so that this low social complex breaks up readily like its organic counterpart, the low animal organism found in an amœba; he sees it growing stronger with every advance in civilization involving more complex relations to the land—with settled habitations, with increased density of population, with a discriminating and highly differentiated use of the soil, with the exploitation of mineral resources, and, finally, with that far-reaching exchange of commodities and ideas which means the establishment of varied extra-territorial relations. Finally, the modern society or state has grown into every foot of its own soil, exploited its every geographic advantage, utilized its geographic location to enrich itself by international trade, and, when possible, to absorb outlying territories by means of colonies. The broader this geographic base, the richer, more varied, its resources, and the more favorable its climate to their exploitation, the more numerous and complex are the connections which the members of a social group can establish with it, and through it with each other; or, in other words, the greater may be its ultimate historical significance.
In the next place, there are the facts, first, that an element of thought inheres in all sensation, while sensation conditions thought; and secondly, that there is a close connection of all the senses, both in origin—each of them being a modification of the one primary sense of touch—and in subsequent development, where the specialized organs are still co-ordinated through tactile sensation, in the sensitive surface of organism. Again, and here we see the genesis of ideas of contact, it is by means of the tactile sensibility of the skin and membranes of sense-organs, forming a sensitized as well as a protecting surface, that the nervous system conveys to the brain information about the external world, and this information is in its original aspect the response to impact. Primitive physics, no less than modern, recognizes that contact is a modified form of a blow. These considerations show that contact not only plays an important part in the life of the soul but must have had a profound influence on the development of ideas, and it may now be assumed that ideas of contact have been a universal and original constant factor in human relations and that they are so still. The latter assumption is to be stressed, because we find that the ideas which lie beneath primitive taboo are still a vital part of human nature, though mostly emptied of their religious content; and also because, as I hold, ceremonies and etiquette, such as still obtain, could not possess such vitality as they do unless there were a living psychological force behind them, such as we find in elementary ideas which come straight from functional processes.
The conception of "primitive society" which we ought to form is that of small groups scattered over a territory. The size of the groups is determined by the conditions of the struggle for existence. The internal organization of each group corresponds to its size. A group of groups may have some relation to each other (kin, neighborhood, alliance, connubium, and commercium) which draws them together and differentiates them from others. Thus a differentiation arises between ourselves, the we-group, or in-group, and everybody else, or the others-groups, out-groups. The insiders in a we-group are in a relation of peace, order, law, government, and industry, to each other. Their relation to all outsiders, or others-groups, is one of war and plunder, except so far as agreements have modified it. If a group is exogamic, the women in it were born abroad somewhere. Other foreigners who might be found in it are adopted persons, guest-friends, and slaves.
It is easy to see how by means of sympathy we can at once pass the gulf which separates man from man. All the devices of the ages in the way of dumb or spoken language fail to win across the void, and leave the two beings apart; but with a step the sympathetic spirit passes the gulf. In this strange feature we have the completion of the series of differences between the inorganic and the organic groups of individualities. In the lower or non-living isolations there is no reason why the units should do more than mechanically interact. All their service in the realm can be best effected by their remaining forever completely apart. But when we come to the organic series, the units begin to have need of understanding their neighbors, in order that they may form those beginnings of the moral order which we find developing among the members even of the lowliest species. Out of this sympathetic accord arises the community, which we see in its simple beginnings in the earlier stages of life; it grows with the advance in the scale of being, and has its supreme success in man. Human society, the largest of all organic associations, requires that its units be knit together in certain common purposes and understandings, and the union can only be made effective by the ways of sympathy—by the instinctive conviction of essential kinship.
The reasons why they do not make use of these gifts are of many kinds. Lower intellectual endowment is often placed in the first rank. That is a convenient but not quite fair explanation. Among the savage races of today we find great differences in endowments. We need not dispute that in the course of development races of even slightly higher endowments have got possession of more and more means of culture, and gained steadiness and security for their progress, while the less endowed remained behind. But external conditions, in respect to their furthering or hindering effects, can be more clearly recognized and estimated; and it is juster and more logical to name them first. We can conceive why the habitations of the savage races are principally to be found on the extreme borders of the inhabited world, in the cold and hot regions, in remote islands, in secluded mountains, in deserts. We understand their backward condition in parts of the earth which offer so few facilities for agriculture and cattle-breeding as Australia, the Arctic regions, or the extreme north and south of America. In the insecurity of incompletely developed resources we can see the chain which hangs heavily on their feet and confines their movements within a narrow space. As a consequence their numbers are small, and from this again results the small total amount of intellectual and physical accomplishment, the rarity of eminent men, the absence of the salutary pressure exercised by surrounding masses on the activity and forethought of the individual, which operates in the division of society into classes, and the promotion of a wholesome division of labor. A partial consequence of this insecurity of resources is the instability of natural races. A nomadic strain runs through them all, rendering easier to them the utter incompleteness of their unstable political and economical institutions, even when an indolent agriculture seems to tie them to the soil. Thus it often comes about that, in spite of abundantly provided and well-tended means of culture, their life is desultory, wasteful of power, unfruitful. This life has no inward consistency, no secure growth; it is not the life in which the germs of civilization first grew up to the grandeur in which we frequently find them at the beginnings of what we call history. It is full rather of fallings-away from civilization and dim memories from civilized spheres which in many cases must have existed long before the commencement of history as we have it.
Throughout the life of any people, from its fetal period in some small locality to its well-rounded adult era marked by the occupation and organization of a wide national territory, gradations in area mark gradations of development. And this is true, whether we consider the compass of their commercial exchanges, the scope of their maritime ventures, the extent of their linguistic area, the measure of their territorial ambitions, or the range of their intellectual interests and human sympathies. From land to ethics, the rule holds good. Peoples in the lower stages of civilization have contracted spatial ideas, desire and need at a given time only a limited territory, though they may change that territory often; they think in small linear terms, have a small horizon, a small circle of contact with others, a small range of influence, only tribal sympathies; they have an exaggerated conception of their own size and importance, because their basis of comparison is fatally limited. With a mature, widespread people like the English or French, all this is different; they have made the earth their own, so far as possible.
1860, Sunday.—Frankie Richardson asked me to go with her to teach a class in the colored Sunday School on Chapel Street this afternoon. I asked Grandmother if I could go and she said she never noticed that I was particularly interested in the colored race and she said she thought I only wanted an excuse to get out for a walk Sunday afternoon. However, she said I could go just this once. When we got up as far as the Academy, Mr. Noah T. Clarke's brother, who is one of the teachers, came out and Frank said he led the singing at the Sunday school and she said she would give me an introduction to him, so he walked up with us and home again. Grandmother said that when she saw him opening the gate for me, she understood my zeal in missionary work. "The dear little lady," as we often call her, has always been noted for her keen discernment and wonderful sagacity and loses none of it as she advances in years. Some one asked Anna the other day if her Grandmother retained all her faculties and Anna said, "Yes, indeed, to an alarming degree." Grandmother knows that we think she is a perfect angel even if she does seem rather strict sometimes. Whether we are seven or seventeen we are children to her just the same, and the Bible says, "Children obey your parents in the Lord for this is right." We are glad that we never will seem old to her. I had the same company home from church in the evening. His home is in Naples.
Gray wrote the "Elegy in a Country Churchyard" before the existence of the modern city.
In spite, however, of the industry with which newspapers pursue facts of personal intelligence and human interest, they cannot compete with the village gossips as a means of social control. For one thing, the newspaper maintains some reservations not recognized by gossip, in the matters of personal intelligence. For example, until they run for office or commit some other overt act that brings them before the public conspicuously, the private life of individual men or women is a subject that is for the newspaper taboo. It is not so with gossip, partly because in a small community no individual is so obscure that his private affairs escape observation and discussion; partly because the field is smaller. In small communities there is a perfectly amazing amount of personal information afloat among the individuals who compose them.
Yet results such as these are not achieved by strangers merely because they happen to be strangers. Place a negro in a new environment; will he build railways and invent labor-saving machines? Hardly. There must be a certain fitness; it must be in the blood. In short, other forces beside that of being merely a stranger in a strange land are bound to co-operate before the total result can be fully accounted for. There must be a process of selection, making the best types available, and the ethical and moral factor, too, counts for much. Nevertheless, the migrations themselves were a very powerful element in the growth of capitalism.
On the other hand, there is a sort of strangeness, in which this very connection on the basis of a general quality embracing the parties is precluded. The relation of the Greeks to the Barbarians is a typical example; so are all the cases in which the general characteristics which one takes as peculiarly and merely human are disallowed to the other. But here the expression "the stranger" has no longer any positive meaning. The relation with him is a non-relation. He is not a member of the group itself. As such he is much more to be considered as near and far at the same moment, seeing that the foundation of the relation is now laid simply on a general human similarity. Between these two elements there occurs, however, a peculiar tension, since the consciousness of having only the absolutely general in common has exactly the effect of bringing into particular emphasis that which is not common. In the case of strangers according to country, city, or race, the individual characteristics of the person are not perceived; but attention is directed to his alien extraction which he has in common with all the members of his group. Therefore the strangers are perceived, not indeed as individuals, but chiefly as strangers of a certain type. Their remoteness is no less general than their nearness.
The Spirit of Youth and the City Streets
In psychoanalysis, a rapidly growing literature is accessible to sociologists upon the nature and the effects of the intimate contacts of sex and family life. Indeed, the Freudian concept of the libido may be translated for sociological purposes into the desire for response. The intensity of the sentiments of love and hate that cement and disrupt the family is indicated in the analyses of the so-called "family romance." Life histories reveal the natural tendencies toward reciprocal affection of mother and son or father and daughter, and the mutual antagonism of father and son or mother and daughter.
Two of the best sociological statements of primary contacts are to be found in Professor Cooley's analysis of primary groups in his book Social Organization and in Shaler's exposition of the sympathetic way of approach in his volume The Neighbor. A mass of descriptive material for the further study of the primary contacts is available from many sources. Studies of primitive peoples indicate that early social organizations were based upon ties of kinship and primary group contacts. Village life in all ages and with all races exhibits absolute standards and stringent primary controls of behavior. The Blue Laws of Connecticut are little else than primary-group attitudes written into law. Common law, the traditional code of legal conduct sanctioned by the experience of primary groups, may be compared with statute law, which is an abstract prescription for social life in secondary societies. Here also should be included the consideration of programs and projects for community organization upon the basis of primary contacts, as for example, Ward's The Social Center.
Naturally enough, sympathetic and arresting pictures of city life have come from residents of settlements as in Jane Addam's Twenty Years at Hull House, Robert Wood's The City Wilderness, Lillian Wald's The House on Henry Street and Mrs. Simkhovitch's The City Worker's World. Georg Simmel has made the one outstanding contribution to a sociology or, perhaps better, a social philosophy of the city in his paper "The Great City and Cultural Life."
(24) Hasanovitz, Elizabeth. One of Them. Chapters from a passionate autobiography. Boston, 1918.
Imitation and suggestion are both mechanisms of social interaction in which an individual or group is controlled by another individual or group. The distinction between the two processes is now clear. The characteristic mark of imitation is the tendency, under the influence of copies socially presented, to build up mechanisms of habits, sentiments, ideals, and patterns of life. The process of suggestion, as differentiated from imitation in social interaction, is to release under the appropriate social stimuli mechanisms already organized, whether instincts, habits, or sentiments. The other differences between imitation and suggestion grow out of this fundamental distinction. In imitation attention is alert, now on the copy and now on the response. In suggestion the attention is either absorbed in, or distracted from, the stimulus. In imitation the individual is self conscious; the subject in suggestion is unconscious of his behavior. In imitation the activity tends to reproduce the copy; in suggestion the response may be like or unlike the copy.
This principle may be very simply stated: Every stronger ethnic or social group strives to subjugate and make serviceable to its purposes every weaker element which exists or may come within the field of its influence. This thesis of the relation of heterogeneous ethnic and social elements to each other, with all the consequences proceeding from it, contains within it the key to the solution of the entire riddle of the natural process of human history. We shall see this thesis illustrated ever and everywhere in the past and the present in the interrelations of heterogeneous ethnic and social elements and become convinced of its universal validity. In this latter relation it does not correspond at all to such natural laws, as, for example, attraction and gravitation or chemical affinity, or to the laws of vegetable and animal life. In order better to conceive of this social natural law in its general validity, we must study it in its different consequences and in the various forms which it assumes according to circumstances and conditions.
g) Continuity through group honor.—The sociological significance of honor as a form of cohesion is extraordinarily great. Through the appeal to honor, society secures from its members the kind of conduct conducive to its own preservation, particularly within the spheres of conduct intermediate between the purview of the criminal code, on the one hand, and the field of purely personal morality, on the other. By the demands upon its members contained in the group standard of honor the group preserves its unified character and its distinctness from the other groups within the same inclusive association. The essential thing is the specific idea of honor in narrow groups—family honor, officers' honor, mercantile honor, yes, even the "honor among thieves." Since the individual belongs to various groups, the individual may, at the same time, be under the demands of several sorts of honor which are independent of each other. One may preserve his mercantile honor, or his scientific honor as an investigator, who has forfeited his family honor, and vice versa; the robber may strictly observe the requirements of thieves' honor after he has violated every other; a woman may have lost her womanly honor and in every other respect be most honorable, etc. Thus honor consists in the relation of the individual to a particular circle, which in this respect manifests its separateness, its sociological distinctness, from other groups.
Social life in the large city as compared with the towns shows a great preponderance of occasions to see rather than to hear people. One explanation lies in the fact that the person in the town is acquainted with nearly all the people he meets. With these he exchanges a word or a glance, and their countenance represents to him not merely the visible but indeed the entire personality. Another reason of especial significance is the development of public means of transportation. Before the appearance of omnibuses, railroads, and street cars in the nineteenth century, men were not in a situation where for periods of minutes or hours they could or must look at each other without talking to one another. Modern social life increases in ever growing degree the rôle of mere visual impression which always characterizes the preponderant part of all sense relationship between man and man, and must place social attitudes and feelings upon an entirely changed basis. The greater perplexity which characterizes the person who only sees, as contrasted with the one who only hears, brings us to the problems of the emotions of modern life: the lack of orientation in the collective life, the sense of utter lonesomeness, and the feeling that the individual is surrounded on all sides by closed doors.
We have seen that the study of the theory of expression confirms to a certain limited extent the conclusion that man is derived from some lower animal form, and supports the belief of the specific or subspecific unity of the several races; but as far as my judgment serves, such confirmation was hardly needed. We have also seen that expression in itself, or the language of the emotions, as it has sometimes been called, is certainly of importance for the welfare of mankind. To understand, as far as is possible, the source or origin of the various expressions which may be hourly seen on the faces of the men around us, not to mention our domesticated animals, ought to possess much interest for us. From these several causes we may conclude that the philosophy of our subject has well deserved that attention which it has already received from several excellent observers, and that it deserves still further attention, especially from any able physiologist.
We have seen that in all parts of the world persons who feel shame for some moral delinquency are apt to avert, bend down, or hide their faces, independently of any thought about their personal appearance. The object can hardly be to conceal their blushes, for the face is thus averted or hidden under circumstances which exclude any desire to conceal shame, as when guilt is fully confessed and repented of. It is, however, probable that primeval man before he had acquired much moral sensitiveness would have been highly sensitive about his personal appearance, at least in reference to the other sex, and he would consequently have felt distress at any depreciatory remarks about his appearance; and this is one form of shame. And as the face is the part of the body which is most regarded, it is intelligible that any one ashamed of his personal appearance would desire to conceal this part of his body. The habit, having been thus acquired, would naturally be carried on when shame from strictly moral causes was felt; and it is not easy otherwise to see why under these circumstances there should be a desire to hide the face more than any other part of the body.
In fact, the self-love at which one laughs is, as we have said, harmless. Besides it is often a natural failing, a weakness, not a vice. Even if it were a vice, the jester would not be justified in laughing at it, for it does not appear that he himself is exempt. On the contrary, his vanity is magnified when that of others is upon the rack. Finally the humiliation caused by laughter is not a chastisement which one accepts but a torture to which one submits; it is a feeling of resentment, of bitterness, not a wholesome sense of shame, nor one from which anyone is likely to profit. Laughter may then have a social use; but it is not an act of justice. It is a quick and summary police measure which will not stand too close a scrutiny but which it would be imprudent either to condemn or to approve without reserve. Society is established and organized according to natural laws which seem to be modeled on those of reason, but self-loves discipline themselves, they enter into conflict and hold each other in check.
From the many anecdotes of dogs calling others to their assistance or bringing others to those who feed them or treat them kindly, we may indeed infer the existence of a social tendency and of the suggestive effects of behavior, but we cannot derive conclusive evidence of anything like descriptive communication.
The fact that every word is originally a predicate—that names, though signs of individual conceptions, are all, without exception, derived from general ideas—is one of the most important discoveries in the science of language. It was known before that language is the distinguishing characteristic of man; it was known also that the having of general ideas is that which puts a perfect distinction betwixt man and brutes; but that these two were only different expressions of the same fact was not known till the theory of roots had been established as preferable to the theories both of onomatopoicia and of interjections. But, though our modern philosophy did not know it, the ancient poets and framers of language must have known it. For in Greek, language is logos, but logos means also reason, and alogon was chosen as the name and the most proper name, for brute. No animal, so far as we know, thinks and speaks except man. Language and thought are inseparable. Words without thought are dead sounds; thoughts without words are nothing. To think is to speak low; to speak is to think aloud. The word is the thought incarnate.
The ideational associations which appear in developed language could never have reached the elaborate form which they have at present if there had not been social co-operation. The tendency of the individual when left to himself is to drop back into the direct adjustments which are appropriate to his own life. He might possibly develop articulation to a certain extent for his own sake, but the chief impulse to the development of language comes through intercourse with others. As we have seen, the development of the simplest forms of communication, as in animals, is a matter of social imitation. Writing is also an outgrowth of social relations. It is extremely doubtful whether even the child of civilized parents would ever have any sufficient motive for the development of writing, if it were not for the social encouragement he receives.
Each number of a great journal which appears today is a marvel of economic division of labor, capitalistic organization, and mechanical technique; it is an instrument of intellectual and economic intercourse, in which the potencies of all other instruments of commerce—the railway, the post, the telegraph, and the telephone—are united as in a focus.
This general doctrine of Tarde has been elaborated by a number of recent writers. Royce calls attention to the fundamental importance of imitation as a means of social inheritance. The same doctrine is taken up by Baldwin in his Mental Development in the Child and Race, and in Social and Ethical Interpretations. With these later writers, imitation takes on a significance which is somewhat technical and broader than the significance which it has either with Tarde or in the ordinary use of the term. Baldwin uses the term to cover that case in which an individual repeats an act because he has himself gone through the act. In such a case one imitates himself and sets up what Baldwin terms a circular reaction. The principle of imitation is thus introduced into individual psychology as well as into general social psychology, and the relation between the individual's acts and his own imagery is brought under the same general principle as the individual's responses to his social environment. The term "imitation" in this broader sense is closely related to the processes of sympathy.
b) Learning by imitation.—Let us now turn to the other side of the question. Let us consider the case in which the power of performing an action is acquired in and by the process of imitation itself. Here there is a general rule which is obvious when once it is pointed out. It is part of the still more general rule that "to him that hath shall be given." Our power of imitating the activity of another is strictly proportioned to our pre-existing power of performing the same general kind of action independently. For instance, one devoid of musical faculty has practically no power of imitating the violin playing of Joachim. Imitation may develop and improve a power which already exists, but it cannot create it. Consider the child beginning for the first time to write in a copybook. He learns by imitation; but it is only because he has already some rudimentary ability to make such simple figures as pothooks that the imitative process can get a start. At the outset, his pothooks are very unlike the model set before him. Gradually he improves; increased power of independent production gives step by step increased power of imitation, until he approaches too closely the limits of his capacity in this direction to make any further progress of an appreciable kind.
In passing from the emotional to the intellectual phase, sympathy gains in extent and stability. In fact, emotional sympathy requires some analogy in temperament or nature; it can scarcely be established between the timid and the daring, between the cheerful and the melancholic; it may be extended to all human beings and to the animals nearest us, but not beyond them. On the contrary, it is the special attribute of intelligence to seek resemblances or analogies everywhere, to unify; it embraces the whole of nature. By the law of transfer (which we have already studied) sympathy follows this invading march and comprehends even inanimate objects, as in the case of the poet, who feels himself in communion with the sea, the woods, the lakes, or the mountains. Besides, intellectual sympathy participates in the relative fixity of representation; we find a simple instance of this in animal societies, such as those of the bees, where unity or sympathy among the members is only maintained by the perception or representation of the queen.
But whatever may be the cause of sympathy, or however it may be excited, nothing pleases us more than to observe in other men a fellow-feeling with all the emotions of our own breast; nor are we ever so much shocked as by the appearance of the contrary. Those who are fond of deducing all our sentiments from certain refinements of self-love think themselves at no loss to account, according to their own principles, both for this pleasure and for this pain. Man, say they, conscious of his own weakness and of the need which he has for the assistance of others, rejoices whenever he observes that they adopt his own passions because he is then assured of that assistance and grieves whenever he observes the contrary, because he is then assured of their opposition. But both the pleasure and the pain are always felt so instantaneously, and often upon such frivolous occasions, that it seems evident that neither of them can be derived from any such self-interested consideration. A man is mortified when, after having endeavored to divert the company, he looks round and sees that nobody laughs at his jests but himself. On the contrary, the mirth of the company is highly agreeable to him and he regards this correspondence of their sentiments with his own as the greatest applause.
The more conscious our craving for retroaction from sympathisers, the more there must also be developed in us a conscious endeavor to cause the feeling to be appropriated by as many as possible and as completely as possible. The expressional impulse is not satisfied by the resonance which an occasional public, however sympathetic, is able to afford. Its natural aim is to bring more and more sentient beings under the influence of the same emotional state. It seeks to vanquish the refractory and arouse the indifferent. An echo, a true and powerful echo—that is what it desires with all the energy of an unsatisfied longing. As a result of this craving the expressional activities lead to artistic production. The work of art presents itself as the most effective means by which the individual is enabled to convey to wider and wider circles of sympathisers an emotional state similar to that by which he is himself dominated.
Now and then, especially in the French writers, one will find besides "suggestion" the term "psychic contagion," under which, however, nothing further than involuntary imitation is to be understood (compare A. Vigouroux and P. Juquelier, La contagion mentale, Paris, 1905). If one takes up the conception of suggestion in a wider sense, and considers by it the possibility of involuntary suggestion in the way of example and imitation, one will find that the conceptions of suggestion and of psychic contagion depend upon each other most intimately, and to a great extent are not definitely to be distinguished from each other. In any case, it is to be maintained that a strict boundary between psychic contagion and suggestion does not always exist, a fact which Vigouroux and Juquelier in their paper have rightly emphasized.
Anyone who has done critical work in the domain of hypnotism after the manner insisted on by the Nancy school cannot help considering Stumpf's method of investigation erroneous from the very outset. A first source of error that had to be considered was that someone present—it might have been Herr v. Osten or it might have been anyone else—unintentionally had given the horse a sign when to stop tapping. It cannot be considered sufficient, as stated in Stumpf's report, that Herr v. Osten did not know the answer; no one should be present who knows it. This is the first condition to be fulfilled when making such experiments. Anybody who has been engaged in training hypnotized subjects knows that these insignificant signs constitute one of the chief sources of error. Some of the leading modern investigators in the domain of hypnotism—Charcot and Heidenhain, for instance—were misled by them at the time they thought they had discovered new physical reflexes in hypnosis. But in 1904, by which time suggestion had been sufficiently investigated to prevent such an occurrence, a psychologist should not have fallen into an error that had been sufficiently made more than twenty years previously. But the main point is this: signs that are imperceptible to others are nevertheless perceived by a subject trained to do so, no matter whether that subject be a human being or an animal.
Many, it is well known, are still inclined to deny the individual personality any influence upon the course of historic events. The individual is to them only an expression of the views of the mass, an embodiment of the epoch, something, therefore, that cannot actively strike at the course of history; he is much rather himself heaved up out of the mass by historic events, which, unaffected by the individual, proceed in the courses they have themselves chosen.
In sociology, Gumplowicz arrived at the notions of a "natural social process" and of "reciprocal action of heterogeneous elements" in his study of the conflict of races. Ratzenhofer, Simmel, and Small place the social process and socialization central in their systems of sociology. Cooley's recent book The Social Process is an intimate and sympathetic exposition of "interaction" and the "social process." "Society is a complex of forms or processes each of which is living and growing by interaction with the others, the whole being so unified that what takes place in one part affects all the rest. It is a vast tissue of reciprocal activity, differentiated into innumerable systems, some of them quite distinct, others not readily traceable, and all interwoven to such a degree that you see different systems according to the point of view you take."[154]
The significance for social life of the extension of communication through inventions has impressed ethnologists, historians, and sociologists. The ethnologist determines the beginnings of ancient civilization by the invention of writing. Historians have noted and emphasized the relation of the printing press to the transition from medieval to modern society. Graham Wallas in his Great Society interprets modern society as a creation of the machine and of the artificial means of communication.
In this unwarranted extension of the concept of imitation Tarde undeniably had committed the unpardonable sin of science, i.e., he substituted for the careful study and patient observation of imitative behavior, easy and glittering generalizations upon uniformities in society. Contributions to an understanding of the actual process of imitation came from psychologists. Baldwin brought forward the concept of circular reaction to explain the interrelation of stimulus and response in imitation. He also indicated the place of imitation in personal development in his description of the dialectic of personal growth where the self develops in a process of give-and-take with other selves. Dewey, Stout, Mead, Henderson, and others, emphasizing the futility of the mystical explanation of imitation by imitation, have pointed out the influence of interest and attention upon imitation as a learning process. Mead, with keen analysis of the social situation, interprets imitation as the process by which the person practices rôles in social life. The studies of Thorndike may be mentioned as representative of the important experimental research upon this subject.
From the study of hypnotism to observation upon the rôle of suggestion in social life was a short step. Binet, Sidis, Münsterberg have formulated psychological definitions of suggestion and indicated its significance for an understanding of so-called crowd phenomena in human behavior. Bechterew in his monograph Die Bedeutung der Suggestion im Sozialen Leben has presented an interpretation of distinct value for sociological research. At the present time there are many promising developments in the study of suggestion in special fields, such as advertising, leadership, politics, religion.
(14) Cooley, Charles. Human Nature and the Social Order. Chap. ii. New York, 1902.
"The result," he states, "is a disgrace to our modern civilization. It is one of the worst communities I ever saw."
From the point of view and for the purposes of reformers social forces were conceived as embodied in institutions. For the purposes of the historian they are merely tendencies which combine to define the general trend of historical change. The logical motive, which has everywhere guided science in formulating its conceptions, is here revealed in its most naïve and elementary form. Natural science invariably seeks to describe change in terms of process, that is to say, in terms of interaction of tendencies. These tendencies are what science calls forces.
The fundamental value for social research of the classification inheres in the fact that the wishes in one class cannot be substituted for wishes in another. The desire for response and affection cannot be satisfied by fame and recognition or only partially so. The wholesome individual is he who in some form or other realizes all the four fundamental wishes. The security and permanence of any society or association depends upon the extent to which it permits the individuals who compose it to realize their fundamental wishes. The restless individual is the individual whose wishes are not realized even in dreams.
In this work I have sought to begin at the origin of each line of social progress. I have first endeavored to describe the steps in mechanical progress, then the social classes brought into prominence by the mechanical changes, then the struggle by which these new classes sought to gain social power, and, finally, the institutions which were created or the alterations made in existing institutions as a consequence of the struggle or as a result of the victory of a new class.
A counter-current here means a body of opinion, belief, or sentiment more or less directly opposed to the dominant opinion of a particular era. Counter-currents of this kind have generally been supplied by the survival of ideas or convictions which are gradually losing their hold upon a given generation, and particularly the youthful part thereof. This kind of "conservatism" which prompts men to retain convictions which are losing their hold upon the mass of the world is found, it should be remarked, as much among the adherents of one religious or political creed as of another. Any Frenchman who clung to Protestantism during the reign of Louis the Fourteenth; any north-country squire who in the England of the eighteenth century adhered to the Roman Catholicism of his fathers; Samuel Johnson, standing forth as a Tory and a High Churchman amongst Whigs and Free Thinkers; the Abbé Gregoire, retaining in 1830 the attitude and the beliefs of a bishop of that constitutional church of France whereof the claims have been repudiated at once by the Church and by the State; James Mill, who, though the leader in 1832 of philosophic Radicals, the pioneers as they deemed themselves of democratic progress, was in truth the last "of the eighteenth century"—these are each and all of them examples of that intellectual and moral conservatism which everywhere, and especially in England, has always been a strong force. The past controls the present.
Every desire that any man harbors is a force making or marring, strengthening or weakening, the structure and functions of the society of which he is a part. What the human desires are, what their relations are to each other, what their peculiar modifications are under different circumstances—these are questions of detail which must be answered in general by social psychology, and in particular by specific analysis of each social situation. The one consideration to be urged at this point is that the concept "social forces" has a real content. It represents reality. There are social forces. They are the desires of persons. They range in energy from the vagrant whim that makes the individual a temporary discomfort to his group, to the inbred feelings that whole races share. It is with these subtle forces that social arrangements and the theories of social arrangements have to deal.
We need to emphasize, in addition, several considerations about these interests which are the motors of all individual and social action. First, there is a subjective and an objective aspect of them all. It would be easy to use terms of these interests in speculative arguments in such a way as to shift the sense fallaciously from the one aspect to the other; e.g., moral conduct, as an actual adjustment of the person in question with other persons, is that person's "interest," in the objective sense. On the other hand, we are obliged to think of something in the person himself impelling him, however unconsciously, toward that moral conduct, i.e., interest as "unsatisfied capacity" in the subjective sense. So with each of the other interests. The fact that these two senses of the term are always concerned must never be ignored; but, until we reach refinements of analysis which demand use for these discriminations, they may be left out of sight. Second, human interests pass more and more from the latent, subjective, unconscious state to the active, objective, conscious form. That is, before the baby is self-conscious, the baby's essential interest in bodily well-being is operating in performance of the organic functions. A little later the baby is old enough to understand that certain regulation of his diet, certain kinds of work or play, will help to make and keep him well and strong. Henceforth there is in him a co-operation of interest in the fundamental sense, and interest in the derived, secondary sense, involving attention and choice. If we could agree upon the use of terms, we might employ the word "desire" for this development of interest; i.e., physiological performance of function is, strictly speaking, the health interest; the desires which men actually pursue within the realm of bodily function may be normal or perverted, in an infinite scale of variety. So with each of the other interests. Third, with these qualifications provided for, resolution of human activities into pursuit of differentiated interests becomes the first clue to the combination that unlocks the mysteries of society. For our purposes in this argument we need not trouble ourselves very much about nice metaphysical distinctions between the aspects of interest, because we have mainly to do with interests in the same sense in which the man of affairs uses the term. The practical politician looks over the lobby at Washington and he classifies the elements that compose it. He says: "Here is the railroad interest, the sugar interest, the labor interest, the army interest, the canal interest, the Cuban interest, etc." He uses the term "interest" essentially in the sociological sense but in a relatively concrete form, and he has in mind little more than variations of the wealth interest. He would explain the legislation of a given session as the final balance between these conflicting pecuniary interests. He is right, in the main; and every social action is, in the same way, an accommodation of the various interests which are represented in the society concerned.
It lies almost on the surface that a legislature which is a class agency will produce results in accordance with the class pressure behind it. Its existence has been established by struggle, and its life is a continual struggle against the representatives of the opposite class. Of course there will be an immense deal of argument to be heard on both sides, and the argument will involve the setting forth of "reasons" in limitless number. It is indeed because of the advantages (in group terms, of course) of such argument as a technical means of adjustment that the legislative bodies survive. Argument under certain conditions is a greater labor-saver than blows, and in it the group interests more fully unfold themselves. But beneath all the argument lies the strength. The arguments go no farther than the strength goes. What the new Russian duma will get, if it survives, will be what the people it solidly represents are strong enough to make it get, and no more and no less, with bombs and finances, famine and corruption funds alike in the scale.
The philosophers of the seventeenth century, with Descartes and Pascal, considered sentiments and passions as indistinct thoughts, as "thoughts, as it were, in process of precipitation." This is true. Beneath all our sentiments lies a totality of imperfectly analyzed ideas, a swelling stream of crowded and indistinct reasons by the momentum of which we are carried away and swept along. Inversely, sentiments underlie all our ideas; they smoulder in the dying embers of abstractions. Even language has a power because it arouses all the sentiments which it condenses in a formula; the mere names "honor" and "duty" arouse infinite echoes in the consciousness. At the name of "honor" alone, a legion of images is on the point of surging up; vaguely, as with eyes open in the dark, we see all the possible witnesses of our acts, from father and mother to friends and fellow-countrymen; further, if our imagination is vivid enough, we can see those great ancestors who did not hesitate under similar circumstances. "We must; forward!" We feel that we are enrolled in an army of gallant men; the whole race, in its most heroic representatives, is urging us on. There is a social and even a historical element beneath moral ideas. Besides, language, a social product, is also a social force. The pious mind goes farther still; duty is personified as a being—the living Good whose voice we hear.
When any one of the emotions is strongly or repeatedly excited by a particular object, there is formed the rudiment of a sentiment. Suppose that a child is thrown into the company of some person given to frequent outbursts of violent anger, say, a violent-tempered father who is otherwise indifferent to the child and takes no further notice of him than to threaten, scold, and, perhaps, beat him. At first the child experiences fear at each exhibition of violence, but repetition of these incidents very soon creates the habit of fear, and in the presence of his father, even in his mildest moods, the child is timorous; that is to say, the mere presence of the father throws the child's fear-disposition into a condition of sub-excitement, which increases on the slightest occasion until it produces all the subjective and objective manifestations of fear. As a further stage, the mere idea of the father becomes capable of producing the same effects as his presence; this idea has become associated with the emotion; or, in stricter language, the psychophysical disposition whose excitement involves the rise to consciousness of this idea, has become associated or intimately connected with the psychophysical disposition whose excitement produces the bodily and mental symptoms of fear. Such an association constitutes a rudimentary sentiment that we can only call a sentiment of fear.
Sentiments were first defined and distinguished from the emotions by Shand, who conceived of them as organizations of the emotions about some particular object or type of object. Maternal love, for example, includes the emotions of fear, anger, joy, or sorrow, all organized about the child. This maternal love is made up of innate tendencies but is not itself a part of original nature. It is the mother's fostering care of the child which develops her sentiments toward it, and the sentiment attaches to any object that is bound up with the life of the child. The cradle is dear to the mother because it is connected with her occupation in caring for the child. The material fears for its welfare, her joy in its achievements, her anger with those who injure or even disparage it, are all part of the maternal sentiment.
It is this objective reference of a process of release that is significant. The mere reflex does not refer to anything beyond itself; if it drives an organism in a certain direction, it is only as a rocket ignited at random shoots off in some direction, depending on how it happened to lie. But specific response is not merely in some random direction, it is toward an object, and if this object is moved, the responding organism changes its direction and still moves after it. And the objective reference is that the organism is moving with reference to some object or fact of the environment. For the organism, while a very interesting mechanism in itself, is one whose movements turn on objects outside of itself, much as the orbit of the earth turns upon the sun; and these external, and sometimes very distant, objects are as much constituents of the behavior process as is the organism which does the turning. It is this pivotal outer object, the object of specific response, which seems to me to have been overneglected.
A few illustrations may help in understanding how thwarted tendencies may lay the basis for the so-called unfulfilled wish which later appears in the dream. One individual becomes a psychologist in spite of his strong interest in becoming a medical man, because at the time it was easier for him to get the training along psychological lines. Another pursues a business career, when, if he had had his choice, he would have become a writer of plays. Sometimes on account of the care of a mother or of younger brothers and sisters, a young man cannot marry, even though the mating instinct is normal; such a course of action necessarily leaves unfulfilled wishes and frustrated impulses in its train. Again a young man will marry and settle down when mature consideration would show that his career would advance much more rapidly if he were not burdened with a family. Again, an individual marries and without even admitting to himself that his marriage is a failure he gradually shuts himself off from any emotional expression—protects himself from the married state by sublimating his natural domestic ties, usually in some kind of engrossing work, but often in questionable ways—by hobbies, speed manias, and excesses of various kinds. In connection with this it is interesting to note that the automobile, quite apart from its utilitarian value, is coming to be a widely used means of repression or wish sublimation. I have been struck by the enormously increasing number of women drivers. Women in the present state of society have not the same access to absorbing kinds of works that men have (which will shortly come to be realized as a crime far worse than that of the Inquisition). Hence their chances of normal sublimation are limited. For this reason women seek an outlet by rushing to the war as nurses, in becoming social workers, pursuing aviation, etc. Now if I am right in this analysis these unexercised tendencies to do things other than we are doing are never quite got rid of. We cannot get rid of them unless we could build ourselves over again so that our organic machinery would work only along certain lines and only for certain occupations. Since we cannot completely live these tendencies down, we are all more or less "unadjusted" and ill adapted. These maladjustments are exhibited whenever the brakes are off, that is, whenever our higher and well-developed habits of speech and action are dormant, as in sleep, in emotional disturbances, etc.
The individual's attitude toward the totality of his attitudes constitutes his conscious "personality." The conscious personality represents the conception of self, the individual's appreciation of his own character.
"Sentiment" was used by French writers, Ribot, Binet, and others, as a general term for the entire field of affective life. A. F. Shand in two articles in Mind, "Character and the Emotions" and "Ribot's Theory of the Passions," has made a distinct contribution by distinguishing the sentiments from the emotions. Shand pointed out that the sentiment, as a product of social experience, is an organization of emotions around the idea of an object. McDougall in his Social Psychology adopted Shand's definition and described the organization of typical sentiments, as love and hate.
(1) White, W. A. Mechanisms of Character Formation. An introduction to psychoanalysis. New York, 1916.
3. The Concept of Social Forces in Recent Studies of the Local Community.
The more fundamental objection is that in giving freedom to economic competition society has sacrificed other fundamental interests that are not directly involved in the economic process. In any case economic freedom exists in an order that has been created and maintained by society. Economic competition, as we know it, presupposes the existence of the right of private property, which is a creation of the state. It is upon this premise that the more radical social doctrines, communism and socialism, seek to abolish competition altogether.
The situation is different in the so-called animal societies. Animals are adapted in part to the situation of competition, but in part also to the situation of co-operation. With the animal, maternal instinct, gregariousness, sex attraction restrict competition to a greater or less extent among individuals of the same family, herd, or species. In the case of the ant community competition is at a minimum and co-operation at a maximum.
b) Struggle between foes.—In the locust swarm and in the rats' combats there is competition between fellows of the same or nearly related species, but the struggle for existence includes much wider antipathies. We see it between foes of entirely different nature, between carnivores and herbivores, between birds of prey and small mammals. In both these cases there may be a stand-up fight, for instance between wolf and stag, or between hawk and ermine; but neither the logic nor the biology of the process is different when all the fight is on one side. As the lemmings, which have overpopulated the Scandinavian valleys, go on the march they are followed by birds and beasts of prey, which thin their ranks. Moreover, the competition between species need not be direct; it will come to the same result if both types seek after the same things. The victory will be with the more effective and the more prolific.
It is good thus to try in imagination to give to any one species an advantage over another. Probably in no single instance should we know what to do. This ought to convince us of our ignorance on the mutual relations of all organic beings, a conviction as necessary as it is difficult to acquire. All that we can do is to keep steadily in mind that each organic being is striving to increase in a geometrical ratio; that each at some period of its life, during some season of the year, during each generation or at intervals, has to struggle for life and to suffer great destruction. When we reflect on this struggle, we may console ourselves with the full belief that the war of nature is not incessant, that no fear is felt, that death is generally prompt, and that the vigorous, the healthy, and the happy survive and multiply.
Although organization, on the whole, may have advanced and may be still advancing throughout the world, yet the scale will always present many degrees of perfection; for the high advancement of certain whole classes, or of certain members of each class, does not at all necessarily lead to the extinction of those groups with which they do not enter into close competition. In some cases, lowly organized forms appear to have been preserved to the present day from inhabiting confined or peculiar stations, where they have been subjected to less severe competition and where their scanty numbers have retarded the chance of favorable variations arising.
The same measure applies within the human species—the number of nervous reactions of the artist, the financier, the statesman, the scientist, being invariably greater than the reactions of the stolid savage. That man alone of all animals should have achieved the degree of versatility sufficient for such advance is no more remarkable than that the elephant should have evolved a larger trunk and tusks than the boar; that the legs of the deer should be fleeter than those of the ox; that the wings of the swallow should outfly those of the bat. Each organism, in evolving the combination of characters commensurate with safety in its particular environment, has touched the limit of both its necessity and its power to "advance." There exists abundant and reliable evidence of the fact that wherever man has been subjected to the stunting influences of an unchanging environment fairly favorable to life, he has shown no more disposition to progress than the most stolid animals. Indeed, he has usually retrograded. The need to fight for food and home has been the spur that has ever driven man forward to establish the manifold forms of physical and mental life which make up human existence today. Like the simple adaptive mechanisms of the plant by which it gets air, and of the animal by which it overcomes its rivals in battle, the supremely differentiated functions of thought and human relations are the outcome of the necessity of the organism to become adapted to entities in its environment.
The reaction of a community is usually more than the sum of the reactions of the component species and individuals. It is the individual plant which produces the reaction, though the latter usually becomes recognizable through the combined action of the group. In most cases the action of the group accumulates or emphasizes an effect which would otherwise be insignificant or temporary. A community of trees casts less shade than the same number of isolated individuals, but the shade is constant and continuous, and hence controlling. The significance of the community reaction is especially well shown in the case of leaf mold and duff. The leaf litter is again only the total of the fallen leaves of all the individuals but its formation is completely dependent upon the community. The reaction of plants upon wind-borne sand and silt-laden waters illustrates the same fact.
If these considerations show that by no means the majority of internal migrations find their objective point in the cities, they at the same time prove that the trend toward the great centers of population can, in itself be looked upon as having an extensive social and economic importance. It produces an alteration in the distribution of population throughout the state; and at its originating and objective points it gives rise to difficulties which legislative and executive authority has hitherto labored, usually with but very moderate success, to overcome. It transfers large numbers of persons almost directly from a sphere of life where barter predominates into one where money and credit exchange prevail, thereby affecting the social conditions of life and the social customs of the manual laboring classes in a manner to fill the philanthropist with grave anxiety.
From the preceding formidable array of testimony it appears that the tendency of urban populations is certainly not toward the pure blond, long-headed, and tall Teutonic type. The phenomenon of urban selection is something more complex than a mere migration of a single racial element in the population toward the cities. The physical characteristics of townsmen are too contradictory for ethnic explanations alone. To be sure, the tendencies are slight; we are not even certain of their universal existence at all. We are merely watching for their verification or disproof. There is, however, nothing improbable in the phenomena we have noted. Naturalists have always turned to the environment for the final solution of many of the great problems of nature. In this case we have to do with one of the most sudden and radical changes of environment known to man. Every condition of city life, mental as well as physical, is at the polar extreme from those which prevail in the country. To deny that great modifications in human structure and functions may be effected by a change from one to the other is to gainsay all the facts of natural history.
If the foregoing views are true, or contain any considerable degree of truth, foreign immigration into this country has, from the time it first assumed large proportions, amounted, not to a reinforcement of our population, but to a replacement of native by foreign stock. That if the foreigners had not come the native element would long have filled the places the foreigners usurped, I entertain not a doubt. The competency of the American stock to do this it would be absurd to question, in the face of such a record as that for 1790 to 1830. During the period from 1830 to 1860 the material conditions of existence in this country were continually becoming more and more favorable to the increase of population from domestic sources. The old man-slaughtering medicine was being driven out of civilized communities; houses were becoming larger; the food and clothing of the people were becoming ampler and better. Nor was the cause which, about 1840 or 1850, began to retard the growth of population here to be found in the climate which Mr. Clibborne stigmatizes so severely. The climate of the United States has been benign enough to enable us to take the English shorthorn and greatly to improve it, as the re-exportation of that animal to England at monstrous prices abundantly proves; to take the English race-horse and to improve him to a degree of which the startling victories of Parole, Iroquois, and Foxhall afford but a suggestion; to take the Englishman and to improve him, too, adding agility to his strength, making his eye keener and his hand steadier, so that in rowing, in riding, in shooting, and in boxing, the American of pure English stock is today the better animal. No! Whatever were the causes which checked the growth of the native population, they were neither physiological nor climatic. They were mainly social and economic; and chief among them was the access of vast hordes of foreign immigrants, bringing with them a standard of living at which our own people revolted.
The rewards of professional life are gauged primarily by character and native endowment, and are, to this extent, open to the children of workmen. New barriers, however, arise here in the ampler education which, as time advances, is demanded of persons in these pursuits; and these barriers give to a part of the fourth and highest class in the scheme that we are criticising a permanent basis of existence. Another variety of labor retains a pre-eminence based on native adaptations and special opportunities. It is the work of the employer himself. It is an organizing and directing function, and in large industries is performed only in part by the owners. A portion of this work is committed to hired assistants. Strictly speaking, the entrepreneur, or employer, of a great establishment is not one man, but many, who work in a collective capacity, and who receive a reward that, taken in the aggregate, constitutes the "wages of superintendence." To some members of this administrative body the returns come in the form of salaries, while to others they come partly in the form of dividends; but if we regard their work in its entirety, and consider their wages in a single sum, we must class it with entrepreneur's profits rather than with ordinary wages. It is a different part of the product from the sum distributed among day laborers; and this fact separates the administrative group from the class considered in our present inquiry. Positions of the higher sort are usually gained either through the possession of capital or through relations to persons who possess it. Though clerkships of the lower grade demand no attainments which the children of workmen cannot gain, and though promotion to the higher grades is still open, the tendency of the time is to make the transition from the ranks of labor to those of administration more and more difficult. The true laboring class is merging its subdivisions, while it is separating more sharply from the class whose interests, in test questions, place them on the side of capital.
Every individual is continually exerting himself to find out the most advantageous employment for whatever capital he can command. It is his own advantage, indeed, and not that of the society, which he has in view. But the study of his own advantage naturally, or rather necessarily, leads him to prefer that employment which is most advantageous to the society.
What, after all, is competition? Is it something that exists and acts of itself, like the cholera? No, competition is simply the absence of oppression. In reference to the matters that interest me, I prefer to choose for myself and I do not want anyone else to choose for me against my will; that's all. And if anyone undertakes to substitute his judgment for mine in matters that concern me I shall demand the privilege of substituting my wishes for his in matters which concern him. What guaranty is there that this arrangement will improve matters? It is evident that competition is liberty. To destroy liberty of action is to destroy the possibility and consequently the faculty of choosing, judging, comparing; it is to kill intelligence, to kill thought, to kill man himself. Whatever the point of departure, there is where modern reforms always end; in order to improve society it is necessary to annihilate the individual, upon the assumption that the individual is the source of all evil, and as if the individual was not likewise the source of all good.
The independence of the person of the concrete objects, in which he has a mere money interest, is reflected, likewise, in his independence, in his personal relations, of the other individuals with whom he is connected by an exclusive money interest. This has produced one of the most effective cultural formations—one which makes it possible for individuals to take part in an association whose objective aim it will promote, use, and enjoy without this association bringing with it any further personal connection or imposing any further obligation. Money has brought it about that one individual may unite himself with others without being compelled to surrender any of his personal freedom or reserve. That is the fundamental and unspeakably significant difference between the medieval form of organization which made no difference between the association of men as men and the association of men as members of an organization. The medieval form or organization united equally in one circle the entire business, religious, political, and friendly interests of the individuals who composed it.
The conception of competition has had a twofold origin: in the notions (a) of the struggle for existence and (b) of the struggle for livelihood. Naturally, then, the concept of competition has had a parallel development in biology and in economics. The growth of the notion in these two fields of thought, although parallel, is not independent. Indeed, the fruitful process of interaction between the differing formulations of the concept in biology and economics is a significant illustration of the cross-fertilization of the sciences. Although Malthus was a political economist, his principle of population is essentially biological rather than economic. He is concerned with the struggle for existence rather than for livelihood. Reacting against the theories of Condorcet and of Godwin concerning the natural equality, perfectability, and inevitable progress of man, Malthus in 1798 stated the dismal law that population tends to increase in geometrical progression and subsistence in arithmetical progression. In the preface to the second edition of his Essay on the Principle of Population Malthus acknowledged his indebtedness to "Hume, Wallace, Dr. Adam Smith and Dr. Price." Adam Smith no doubt anticipated and perhaps suggested to Malthus his thesis in such passages in the Wealth of Nations as, "Every species of animals naturally multiplies in proportion to the means of their subsistence," "The demand for men necessarily regulates the production of men." These statements of the relation of population to food supply, however, are incidental to Smith's general theories of economics; the contribution of Malthus lay in taking this principle out of its limited context, giving it the character of scientific generalization, and applying it to current theories and programs of social reform.
The full meaning of this change in law and opinion can only be fully understood, however, when it is considered in connection with the growth of communication, economic organization, and cities, all of which have so increased the mutual interdependence of all members of society as to render illusory and unreal the old freedoms and liberties which the system of laissez faire was supposed to guarantee.
The literature of criminology has sought an answer to the enigma of the criminal. The writings of the European criminologists run the gamut of explanation from Lombroso, who explained crime as an inborn tendency of the criminal, to Tarde, who defines the criminal as a purely social product.
(4) ——. Darwinism. An exposition of the theory of natural selection with some of its applications. Chap. iv, "The Struggle for Existence," pp. 14-40; chap. v, "Natural Selection by Variation and Survival of the Fittest," pp. 102-25. 3d ed. London, 1901.
In general, then, one may say competition becomes conscious and personal in conflict. In the process of transition competitors are transformed into rivals and enemies. In its higher forms, however, conflict becomes impersonal—a struggle to establish and maintain rules of justice and a moral order. In this case the welfare not merely of individual men but of the community is involved. Such are the struggles of political parties and religious sects. Here the issues are not determined by the force and weight of the contestants immediately involved, but to a greater or less extent, by the force and weight of public opinion of the community, and eventually by the judgment of mankind.
A more positive factor in racial antagonism is the conflict of cultures: the unwillingness of one race to enter into personal competition with a race of a different or inferior culture. This turns out, in the long run, to be the unwillingness of a people or a class occupying a superior status to compete on equal terms with a people of a lower status. Race conflicts like wars are fundamentally the struggles of racial groups for status. In this sense and from this point of view the struggles of the European nationalities and the so-called "subject peoples" for independence and self-determination are actually struggles for status in the family of nations.
Gladiatorial shows, bear baiting, bull fighting, dog and cock fighting, and prize fighting afford an opportunity to gratify the interest in conflict. The spectator has by suggestion emotional reactions analogous to those of the combatant, but without personal danger; and vicarious contests between slaves, captives, and animals, whose blood and life are cheap, are a pleasure which the race allowed itself until a higher stage of morality was reached. Pugilism is the modification of the fight in a slightly different way. The combatants are members of society, not slaves or captives, but the conflict is so qualified as to safeguard their lives, though injury is possible and is actually planned. The intention to do hurt is the point to which society and the law object. But the prize fight is a fight as far as it goes, and the difficulties which men will surmount to "pull off" and to witness these contests are sufficient proof of their fascination. A football game is also a fight, with the additional qualification that no injury is planned, and with an advantage over the prize fight in the fact that it is not a single-handed conflict, but an organized mêlée—a battle where the action is more massive and complex and the strategic opportunities are multiplied. It is a fact of interest in this connection that, unless appearances are deceptive, altogether the larger number of visitors to a university during the year are visitors to the football field. It is the only phase of university life which appeals directly and powerfully to the instincts, and it is consequently the only phase of university life which appeals equally to the man of culture, the artist, the business man, the man about town, the all-round sport, and, in fact, to all the world.
A struggle for struggle's sake seems to have its natural basis in a certain formal impulse of hostility, which forces itself sometimes upon psychological observation, and in various forms. In the first place, it appears as that natural enmity between man and man which is often emphasized by skeptical moralists. The argument is: Since there is something not wholly displeasing to us in the misfortune of our best friends, and, since the presupposition excludes, in this instance, conflict of material interests, the phenomenon must be traced back to an a priori hostility, to that homo homini lupus, as the frequently veiled, but perhaps never inoperative, basis of all our relationships.
A most interesting symptom of this correlation was presented by the boycotting of the Berlin breweries by the labor body in the year 1894. This was one of the most intense local struggles of the last decade. It was carried on by both sides with extraordinary energy, yet without any personal offensiveness on either side toward the other, although the stimulus was close at hand. Indeed, two of the party leaders, in the midst of the struggle, published their opinions about it in the same journal. They agreed in their formulation of the objective facts, and disagreed in a partisan spirit only in the practical conclusions drawn from the facts. Inasmuch as the struggle eliminated everything irrelevantly personal, and thereby restricted antagonism quantitatively, facilitating an understanding about everything personal, producing a recognition of being impelled on both sides by historical necessities, this common basis did not reduce but rather increased, the intensity, the irreconcilability, and the obstinate consistency of the struggle.
War is an example of ambivalency on the grandest scale. That is, it is at once potent for the greatest good and the greatest evil: in the very midst of death it calls for the most intense living; in the face of the greatest renunciation it offers the greatest premium; for the maximum of freedom it demands the utmost giving of one's self; in order to live at one's best it demands the giving of life itself. "No man has reached his ethical majority who would not die if the real interests of the community could thus be furthered. What would the world be without the values that have been bought at the price of death?" In this sense the great creative force, love, and the supreme negation, death, become one. That the larger life of the race should go forward to greater things, the smaller life of the individual must perish. In order that man shall be born again, he must first die.
Our present society tends more and more in its outward form in time of peace toward the Chautauqua plan, but meanwhile striving and passion burn in the brain of the human units, till the time comes when they find this insipid life unendurable. They resort to amusement crazes, to narcotic drugs, to political strife, to epidemics of crime, and finally to war. The alcohol question well illustrates the tendencies we are pointing out. Science and hygiene have at last shown beyond all question that alcohol, whether in large or smaller doses, exerts a damaging effect upon both mind and body. It lessens physical and mental efficiency, shortens life, and encourages social disorder. In spite of this fact and, what is still more amazing, in spite of the colossal effort now being put forth to suppress by legislative means the traffic in liquor, the per capita consumption of alcoholic drinks in the United States increases from year to year. From a per capita consumption of four gallons in 1850, it has steadily risen to nearly twenty-five gallons in 1913.
But the very existence of an ideal is indicative of a tendency, on the part of the man who entertains it, to modify his characteristic activities. Thus it appears that we have in the very existence of this ideal of peace the evidence that we may look for a change in man's nature, the result of which will be that we shall no longer be warranted in describing him as a fighting animal.
This masterful or domineering temper, so common among social mammals, is the cause of the persecution of the sick and weakly. When an animal begins to ail he can no longer hold his own; he ceases to resent the occasional ill-natured attacks made on him; his non-combative condition is quickly discovered, and he at once drops down to a place below the lowest; it is common knowledge in the herd that he may be buffeted with impunity by all, even by those that have hitherto suffered buffets but have given none. But judging from my own observation, this persecution is not, as a rule, severe, and is seldom fatal.
A national group is to be thought of as an inclusive unity with a fundamental character, upon the basis of which a multitude of groups compete with and rival each other. It is the task of the nation to control and to utilize this group struggle, to keep it on as high a plane as possible, to turn it to the common account. Government gets its chief meaning from the rivalry of groups to grasp political power in their own interests. Aristocracy and democracy may be interpreted in terms of group antagonism, the specialized few versus the undifferentiated many. The ideal merges the two elements of efficiency and solidarity in one larger group within which mutual confidence and emulation take the place of conflict. Just as persons must be disciplined into serving their groups, groups must be subordinated to the welfare of the nation. It is in conflict or competition with other nations that a country becomes a vivid unity to the members of constituent groups. It is rivalry which brings out the sense of team work, the social consciousness.
Whether the mental and moral traits of women are inherent and therefore permanent, or whether they are but passing effects of circumscribed experience and therefore possibly destined to be modified, is immaterial for my present purpose. It is not certain that either the biologist or the psychologist is prepared to answer the question. It is certain that the sociologist is not. It is enough for the analysis that I am making now if we can say that, as a merely descriptive fact, women thus far in the history of the race have generally been more instinctive, more intuitive of subjective states, more emotional, more conservative than men; and that men, more generally than women, have been intuitive of objective relations, inclined therefore to break with instinct and to rely on the later-developed reasoning processes of the brain, and willing, consequently, to take chances, to experiment, and to innovate.
In conclusion, I may perhaps say in a word what seems to me the practical bearing of Mr. Steiner's book. Race prejudice is a mechanism of the group mind which acts reflexly and automatically in response to its proper stimulus. That stimulus seems to be, in the cases where I have met it, unrestricted competition of peoples with different standards of living. Racial animosities and the so-called racial misunderstandings that grow out of them cannot be explained or argued away. They can only be affected when there has been a readjustment of relations and an organization of interests in such a way as to bring about a larger measure of co-operation and a lesser amount of friction and conflict. This demands something more than a diplomacy of kind words. It demands a national policy based on an unflinching examination of the facts.
After a race has achieved in this way its moral independence, assimilation, in the sense of copying, will still continue. Nations and races borrow from those whom they fear as well as from those whom they admire. Materials taken over in this way, however, are inevitably stamped with the individuality of the nationalities that appropriate them. These materials will contribute to the dignity, to the prestige, and to the solidarity of the nationality which borrows them, but they will no longer inspire loyalty to the race from which they are borrowed. A race which has attained the character of a nationality may still retain its loyalty to the state of which it is a part, but only in so far as that state incorporates, as an integral part of its organization, the practical interests, the aspirations and ideals of that nationality.
And with this dawning consciousness of race there is likewise coming an appreciation of the limitations and restrictions which hem in its unfolding and development. One of the best indices to the possibilities of increased racial friction is the Negro's own recognition of the universality of the white man's racial antipathy toward him. This is the one clear note above the storm of protest against the things that are, that in his highest aspirations everywhere the white man's "prejudice" blocks the colored man's path. And the white man may with possible profit pause long enough to ask the deeper significance of the Negro's finding of himself. May it not be only part of a general awakening of the darker races of the earth? Captain H. A. Wilson, of the English army, says that through all Africa there has penetrated in some way a vague confused report that far off somewhere, in the unknown, outside world, a great war has been fought between a white and a yellow race, and won by the yellow man. And even before the Japanese-Russian conflict, "Ethiopianism" and the cry of "Africa for the Africans" had begun to disturb the English in South Africa. It is said time and again that the dissatisfaction and unrest in India are accentuated by the results of this same war. There can be no doubt in the mind of any man who carefully reads American Negro journals that their rejoicing over the Japanese victory sounded a very different note from that of the white American. It was far from being a mere expression of sympathy with a people fighting for national existence against a power which had made itself odious to the civilized world by its treatment of its subjects. It was, instead, a quite clear cry of exultation over the defeat of a white race by a dark one. The white man is no wiser than the ostrich if he refuses to see the truth that in the possibilities of race friction the Negro's increasing consciousness of race is to play a part scarcely less important than the white man's racial antipathies, prejudices, or whatever we may elect to call them.
Emulation and rivalry represent conflict at higher social levels, where competition has been translated into forms that inure to the survival and success of the group. Research in this field, fragmentary as it is, confirms the current impression of the stimulation of effort in the person through conscious competition with his fellows. Adler's theory of "psychic compensation" is based on the observation that handicapped individuals frequently excel in the very fields in which they are apparently least qualified to compete. Demosthenes, for example, became a great orator in spite of the fact that he stuttered. Ordahl presents the only comprehensive survey of the literature in this field.
The history of discussion, however, is the history of freedom—freedom, at any rate, of thought and of speech. It is only when peace and freedom have been established that discussion is practicable or possible. A number of histories have been written in recent years describing the rise of rationalism, as it is called, and the rôle of discussion and agitation in social life. Draper's History of the Intellectual Development of Europe and Lecky's History of the Rise and Influence of the Spirit of Rationalism in Europe are among the earlier works in this field. Robertson's History of Free Thought is mainly a survey of religious skepticism but contains important and suggestive references to the natural processes by which abstract thought has arisen out of the cultural contacts and conflicts among peoples, which conquest and commerce have brought into the same universe of discourse. What we seem to have in these works are materials for the study of the communal processes through which thought is formulated. Once formulated it becomes a permanent factor in the life of the group. The rôle of discussion in the communal process will be considered later in connection with the newspaper, the press agent, propaganda, and the various factors and mechanisms determining the formation of public opinion.
Psychological studies of war have explained war either as an expression of instinct or as a reversion to a primordial animal-human type of behavior. Patrick, who is representative of this latter school, interprets war as a form of relaxation. G. W. Crile has offered a mechanistic interpretation of war and peace based on studies of the chemical changes which men undergo in warfare. Crile comes to the conclusion, however, that war is an action pattern, fixed in the social heredity of the national group, and not a type of behavior determined biologically.
With the tremendous extension of communication and growth of commerce, the world is today a great community in a sense that could not have been understood a century ago. But the world, if it is now one community, is not yet one society. Commerce has created an economic interdependence, but contact and communication have not resulted in either a political or a cultural solidarity. Indeed, the first evidences of the effects of social contacts appear to be disruptive rather than unifying. In every part of the world in which the white and colored races have come into intimate contact, race problems have presented the most intractable of all social problems.
The natural history of the state from the tribe to the modern nation has been that of a political society based on conflict. Franz Oppenheimer maintains the thesis in his book The State: Its History and Development Viewed Sociologically, that conquest has been the historical basis of the state. The state is, in other words, an organization of groups that have been in conflict, i.e., classes and castes; or of groups that are in conflict, i.e., political parties.
(9) Le Bon, Gustave. The Psychology of Peoples. London, 1898.
13. War as an Action Pattern, Biological or Social?
d) Competition, status, and social solidarity.—Under the title "Competition, Status, and Social Solidarity" selections are introduced in the materials which emphasize the relation of competition to accommodation. Up to this point in the materials only the relations of conflict to accommodation have been considered. Status has been described as an effect of conflict. But it is clear that economic competition frequently becomes conscious and so passes over into some of the milder forms of conflict. Aside from this it is evident that competition in so far as it determines the vocation of the individual, determines indirectly also his status, since it determines the class of which he is destined to be a member. In the same way competition is indirectly responsible for the organization of society in so far as it determines the character of the accommodations and understandings which are likely to exist between conflict groups. Social types as well as status are indirectly determined by competition, since most of them are vocational. The social types of the modern city, as indicated by the selection on "Personal Competition and the Evolution of Individual Types," are an outcome of the division of labor. Durkheim points out that the division of labor in multiplying the vocations has increased and not diminished the unity of society. The interdependence of differentiated individuals and groups has made possible a social solidarity that otherwise would not exist.
It is possible that more extended researches may enable ethnographers to map out, in this sense, the distribution of our species; but the secular alterations in meteorologic conditions, combined with the migratory habits of most early communities, must greatly interfere with a rigid application of these principles in ethnography.
Recapitulating, we may define a slave in the ordinary sense of the word as a man who is the property of another, politically and socially at a lower level than the mass of the people, and performing compulsory labor.
On my former visit to Jamaica, I found on my estate a poor woman nearly one hundred years old, and stone blind. She was too infirm to walk, but two young negroes brought her on their backs to the steps of my house, in order, as she said, that she might at least touch massa, although she could not see him. When she had kissed my hand, "that was enough," she said: "now me hab once kiss a massa's hand, me willing to die tomorrow, me no care." She had a woman appropriated to her service and was shown the greatest care and attention; however, she did not live many months after my departure. There was also a mulatto, about thirty years of age, named Bob, who had been almost deprived of the use of his limbs by the horrible cocoa-bay, and had never done the least work since he was fifteen. He was so gentle and humble and so fearful, from the consciousness of his total inability of soliciting my notice, that I could not help pitying the poor fellow; and whenever he came in my way I always sought to encourage him by little presents and other trifling marks of favor. His thus unexpectedly meeting with distinguishing kindness, where he expected to be treated as a worthless incumbrance, made a strong impression on his mind.
All these classes had been in existence for centuries before any such thing as caste was known on Indian soil; and the only thing that was needed to convert them into castes, such as they now are, was that the Brāhman, who possessed the highest of all functions—the priestly—should set the example. This he did by establishing for the first time the rule that no child, either male or female, could inherit the name and status of Brāhman, unless he or she was of Brāhman parentage on both sides. By the establishment of this rule the principle of marriage unionship was superadded to that of functional unionship; and it was only by the combination of these two principles that a caste in the strict sense of the term could or can be formed. The Brāhman, therefore, as the Hindu books inform us, was "the first-born of castes." When the example had thus been set by an arrogant and overbearing priesthood, whose pretensions it was impossible to put down, the other hereditary classes followed in regular order downward, partly in imitation and partly in self-defence. Immediately behind the Brāhman came the Kshatriya, the military chieftain or landlord. He therefore was the "second-born of castes." Then followed the bankers or upper trading classes (the Agārwal, Khattri, etc.); the scientific musician and singer (Kathak); the writing or literary class (Kāyasth); the bard or genealogist (Bhāt); and the class of inferior nobles (Taga and Bhuinhār) who paid no rent to the landed aristocracy. These, then, were the third-born of castes. Next in order came those artisan classes, who were coeval with the age and art of metallurgy; the metallurgic classes themselves; the middle trading classes; the middle agricultural classes, who placed themselves under the protection of the Kshatriya and paid him rent in return (Kurmi, Kāchhi, Māli, Tāmboli); and the middle serving classes, such as Napit and Baidya, who attended to the bodily wants of their equals and superiors. These, then, were the fourth-born of castes; and their rank in the social scale has been determined by the fact that their manners and notions are farther removed than those of the preceding castes from the Brāhmanical ideal. Next came the inferior artisan classes, those who preceded the age and art of metallurgy (Teli, Kumhār, Kalwār, etc.); the partly nomad and partly agricultural classes (Jāt, Gūjar, Ahir, etc.); the inferior serving classes, such as Kahār; and the inferior trading classes, such as Bhunja. These, then, were the fifth-born of castes, and their mode of life is still farther removed from the Brāhmanical ideal than that of the preceding. The last-born, and therefore the lowest, of all the classes are those semisavage communities, partly tribes and partly castes, whose function consists in hunting or fishing, or in acting as butcher for the general community, or in rearing swine and fowls, or in discharging the meanest domestic services, such as sweeping and washing, or in practicing the lowest of human arts, such as basket-making, hide-tanning, etc. Thus throughout the whole series of Indian castes a double test of social precedence has been in active force, the industrial and the Brāhmanical; and these two have kept pace together almost as evenly as a pair of horses harnessed to a single carriage. In proportion as the function practiced by any given caste stands high or low in the scale of industrial development, in the same proportion does the caste itself, impelled by the general tone of society by which it is surrounded, approximate more nearly or more remotely to the Brāhmanical idea of life. It is these two criteria combined which have determined the relative ranks of the various castes in the Hindu social scale.
In the west of India, Mahārs and Dheds hold much the same place as the Dom. In the walled villages of the Marāthā country the Mahār is the scavenger, watchman, and gate-keeper. His presence pollutes; he is not allowed to live in the village; and his miserable shanty is huddled up against the wall outside. But he challenges the stranger who comes to the gate, and for this and other services he is allowed various perquisites, among them that of begging for broken victuals from house to house. He offers old blankets to his god, and his child's playthings are bones. The Dhed's status is equally low. If he looks at a water jar he pollutes its contents; if you run up against him by accident, you must go off and bathe. If you annoy a Dhed he sweeps up the dust in your face. When he dies, the world is so much the cleaner. If you go to the Dheds' quarter you find there nothing but a heap of bones.
The superficial counterpart is the desire for self-display with all its variations of vanity and boastfulness. From the most bashful submission to the most ostentatious self-assertion, from the self-sacrifice of motherly love to the pugnaciousness of despotic egotism, the social psychologist can trace the human impulses through all the intensities of the human energies which interfere with equality in the group. Each variation has its emotional background and its impulsive discharge. Within normal limits they are all equally useful for the biological existence of the group and through the usefulness for the group ultimately serviceable to its members. Only through superordination and subordination does the group receive the inner firmness which transforms the mere combination of men into working units. They give to human society that strong and yet flexible organization which is the necessary condition for its successful development.
A great deal more could easily be written, and we hope some old servant may also speak out in favor of domestic service, and so let it be again what it has been, and when both will look on each other as they ought, for there has always been master and servant, and we have the number of servants, or near the number, given here by one who knows, 1,330,783 female domestic servants at the last census in 1911, and so the domestic service is the largest single industry that is; there are more people employed as domestic servants than any other class of employment. Before closing this book the writer would ask that a kinder interest may be taken in girls who may have at one time been in disgrace; many of them have no homes and we might try to help them into situations. This appeal is from the old housekeeper and so from one who has had many a talk with young girls for their good; but they have often been led far astray. We ought to give them the chance again, by trying to get them situations, and if the lady is not her friend, nor the housekeeper, we pity her.
Still farther; the concept "law" seems to connote that he who gives the law is in so far unqualifiedly superior. Apart from those cases in which the law is instituted by those who will be its subjects, there appears in lawgiving as such no sign of spontaneity on the part of the subject of the law. It is, nevertheless, very interesting to observe how the Roman conception of law makes prominent the reciprocity between the superior and the subordinate elements. Thus lex means originally "compact," in the sense, to be sure, that the terms of the same are fixed by the proponent, and the other party can accept or reject it only en bloc. The lex publica populi Romani meant originally that the king proposed and the people accepted the same. Thus even here, where the conception itself seems to express the complete one-sidedness of the superior, the nice social instinct of the Romans pointed in the verbal expression to the co-operation of the subordinate. In consequence of like feeling of the nature of socialization the later Roman jurists declared that the societas leonina is not to be regarded as a social compact. Where the one absolutely controls the other, that is, where all spontaneity of the subordinate is excluded, there is no longer any socialization.
We now turn to the second sociological question raised by the case of subordination to an impersonal ideal principle. How does this subordination affect the reciprocal relation of the persons thus subordinated in common? The development of the position of the pater familias among the Aryans exhibits this process clearly. The power of the pater familias was originally unlimited and entirely subjective; that is, his momentary desire, his personal advantage, was permitted to give the decision upon all regulations. But this arbitrary power gradually became limited by a feeling of responsibility. The unity of the domestic group, embodied in the spiritus familiaris, grew into the ideal power, in relation to which the lord of the whole came to regard himself as merely an obedient agent. Accordingly it follows that morals and custom, instead of subjective preference, determine his acts, his decisions, his judicial judgments; that he no longer behaves as though he were absolute lord of the family property, but rather the manager of it in the interest of the whole; that his position bears more the character of an official station than that of an unlimited right. Thus the relation between superiors and inferiors is placed upon an entirely new basis. The family is thought of as standing above all the individual members. The guiding patriarch himself is, like every other member, subordinate to the family idea. He may give directions to the other members of the family only in the name of the higher ideal unity.
The simplest and most radical sort of passage from war to peace is victory—a quite unique phenomenon in life, of which there are, to be sure, countless individual forms and measures, which, however, have no resemblance to any of the otherwise mentioned forms which may occur between persons. Victory is a mere watershed between war and peace; when considered absolutely, only an ideal structure which extends itself over no considerable time. For so long as struggle endures there is no definitive victor, and when peace exists a victory has been gained but the act of victory has ceased to exist. Of the many shadings of victory, through which it qualifies the following peace, I mention here merely as an illustration the one which is brought about, not exclusively by the preponderance of the one party, but, at least in part, through the resignation of the other. This confession of inferiority, this acknowledgment of defeat, or this consent that victory shall go to the other party without complete exhaustion of the resources and chances for struggle, is by no means always a simple phenomenon. A certain ascetic tendency may also enter in as a purely individual factor, the tendency to self-humiliation and to self-sacrifice, not strong enough to surrender one's self from the start without a struggle, but emerging so soon as the consciousness of being vanquished begins to take possession of the soul; or another variation may be that of finding its supreme charm in the contrast to the still vital and active disposition to struggle. Still further, there is impulse to the same conclusion in the feeling that it is worthier to yield rather than to trust to the last moment in the improbable chance of a fortunate turn of affairs. To throw away this chance and to elude at this price the final consequences that would be involved in utter defeat—this has something of the great and noble qualities of men who are sure, not merely of their strengths, but also of their weaknesses, without making it necessary for them in each case to make these perceptibly conscious. Finally, in this voluntariness of confessed defeat there is a last proof of power on the part of the agent; the latter has of himself been able to act. He has therewith virtually made a gift to the conqueror. Consequently, it is often to be observed in personal conflicts that the concession of the one party, before the other has actually been able to compel it, is regarded by the latter as a sort of insult, as though this latter party were really the weaker, to whom, however, for some reason or other, there is made a concession without its being really necessary. Behind the objective reasons for yielding "for the sake of sweet peace" a mixture of these subjective motives is not seldom concealed. The latter may not be entirely without visible consequences, however, for the further sociological attitude of the parties. In complete antithesis with the end of strife by victory is its ending by compromise. One of the most characteristic ways of subdividing struggles is on the basis of whether they are of a nature which admits of compromise or not.
In distinction from the objective character of accommodation of struggle through compromise, we should notice that conciliation is a purely subjective method of avoiding struggle. I refer here not to that sort of conciliation which is the consequence of a compromise or of any other adjournment of struggle but rather to the reasons for this adjournment. The state of mind which makes conciliation possible is an elementary attitude which, entirely apart from objective grounds, seeks to end struggle, just as, on the other hand, a disposition to quarrel, even without any real occasion, promotes struggle. Probably both mental attitudes have been developed as matters of utility in connection with certain situations; at any rate, they have been developed psychologically to the extent of independent impulses, each of which is likely to make itself felt where the other would be more practically useful. We may even say that in the countless cases in which struggle is ended otherwise than in the pitiless consistency of the exercise of force, this quite elementary and unreasoned tendency to conciliation is a factor in the result—a factor quite distinct from weakness, or good fellowship; from social morality or fellow-feeling. This tendency to conciliation is, in fact, a quite specific sociological impulse which manifests itself exclusively as a pacificator, and is not even identical with the peaceful disposition in general. The latter avoids strife under all circumstances, or carries it on, if it is once undertaken, without going to extremes, and always with the undercurrents of longing for peace. The spirit of conciliation, however, manifests itself frequently in its full peculiarity precisely after complete surrender to the struggle, after the conflicting energies have exercised themselves to the full in the conflict.
Throughout history there has been a struggle between the principles of status and competition regarding the part that each should play in the social system. Generally speaking the advantage of status is in its power to give order and continuity. As Gibbon informs us, "The superior prerogative of birth, when it has obtained the sanction of time and popular opinion, is the plainest and least invidious of all distinctions among mankind," and he is doubtless right in ascribing the confusion of the later Roman Empire largely to the lack of an established rule for the transmission of imperial authority. The chief danger of status is that of suppressing personal development, and so of causing social enfeeblement, rigidity, and ultimate decay. On the other hand, competition develops the individual and gives flexibility and animation to the social order, its danger being chiefly that of disintegration in some form or other. The general tendency in modern times has been toward the relative increase of the free or competitive principle, owing to the fact that the rise of other means of securing stability has diminished the need for status. The latter persists, however, even in the freest countries, as the method by which wealth is transmitted, and also in social classes, which, so far as they exist at all, are based chiefly upon inherited wealth and the culture and opportunities that go with it. The ultimate reason for this persistence—without very serious opposition—in the face of the obvious inequalities and limitations upon liberty that it perpetuates is perhaps the fact that no other method of transmission has arisen that has shown itself capable of giving continuity and order to the control of wealth.
The effect of the vocations and the division of labor is to produce, in the first instance, not social groups but vocational types—the actor, the plumber, and the lumber-jack. The organizations, like the trade and labor unions, which men of the same trade or profession form are based on common interests. In this respect they differ from forms of association like the neighborhood, which are based on contiguity, personal association, and the common ties of humanity. The different trades and professions seem disposed to group themselves in classes, that is to say, the artisan, business, and professional classes. But in the modern democratic state the classes have as yet attained no effective organization. Socialism, founded on an effort to create an organization based on "class consciousness," has never succeeded in creating more than a political party.
Nevertheless, the customs and code of a profession are imperative. They oblige the individual to act in accordance with ends which to him are not his own, to make concessions, to consent to compromises, to take account of interests superior to his own. The consequence is that, even where the society rests most completely upon the division of labor, it does not disintegrate into a dust of atoms, between which there can exist only external and temporary contacts. Every function which one individual exercises is invariably dependent upon functions exercised by others and forms with them a system of interdependent parts. It follows that, from the nature of the task one chooses, corresponding duties follow. Because we fill this or that domestic or social function, we are imprisoned in a net of obligations from which we do not have the right to free ourselves. There is especially one organ toward which our state of dependencies is ever increasing—the state. The points at which we are in contact with it are multiplying. So are the occasions in which it takes upon itself to recall us to a sense of the common solidarity.
Adjustments of personal and social relations in the past have been made unreflectively and with a minimum of personal and social consciousness. The extant literature reveals rather an insistent demand for these accommodations than any systematic study of the processes by which the accommodations take place. Simmel's observation upon subordination and superordination is almost the only attempt that has been made to deal with the subject from the point of view of sociology.
In the field of castes the work of research is well under way. The caste system of India has been the subject of careful examination and analysis. Sighele points out that the prohibition of intermarriage observed in its most rigid and absolute form is a fundamental distinction of the caste. If this be regarded as the fundamental criterion, the Negro race in the United States occupies the position of a caste. The prostitute, in America, until recently constituted a separate caste. With the systematic breaking up of the segregated vice districts in our great cities prostitution, as a caste, seems to have disappeared. The place of the prostitute seems to have been occupied by the demimondaine who lives on the outskirts of society but who is not by any means an outcast.
In the bibliography of this chapter is given a list of references to certain of the experiments in community organization. Students should study this literature in the light of the more fundamental studies of types of social groups and studies of individual communities listed in an earlier bibliography.[240] It is at once apparent that the rural community has been more carefully studied than has the urban community. Yet more experiments in community organization have been tried out in the city than in the country. Reports upon social-center activities, upon community councils, and other types of community organization have tended to be enthusiastic rather than factual and critical. The most notable experiment of community organization, the Social Unit Plan, tried out in Cincinnati, was what the theatrical critics call a succès d'estime, but after the experiment had been tried it was abandoned. Control of conditions of community life is not likely to meet with success unless based on an appreciation and understanding of human nature on the one hand, and of the natural or ecological organization of community life on the other.
(7) National Social Unit Organization, Bulletins 1, 2, 2a, 3, 4, 5. Cincinnati, 1917-19.
Assimilation, as popularly conceived in the United States, was expressed symbolically some years ago in Zangwill's dramatic parable of The Melting Pot. William Jennings Bryan has given oratorical expression to the faith in the beneficent outcome of the process: "Great has been the Greek, the Latin, the Slav, the Celt, the Teuton, and the Saxon; but greater than any of these is the American, who combines the virtues of them all."
As social contact initiates interaction, assimilation is its final perfect product. The nature of the social contacts is decisive in the process. Assimilation naturally takes place most rapidly where contacts are primary, that is, where they are the most intimate and intense, as in the area of touch relationship, in the family circle and in intimate congenial groups. Secondary contacts facilitate accommodations, but do not greatly promote assimilation. The contacts here are external and too remote.
c) Americanization as a problem of assimilation.—Any consideration of policies, programs, and methods of Americanization gain perspective when related to the sociology of assimilation. The "Study of Methods of Americanization," of the Carnegie Corporation, defines Americanization as "the participation of the immigrant in the life of the community in which he lives." From this standpoint participation is both the medium and the goal of assimilation. Participation of the immigrant in American life in any area of life prepares him for participation in every other. What the immigrant and the alien need most is an opportunity for participation. Of first importance, of course, is the language. In addition he needs to know how to use our institutions for his own benefit and protection. But participation, to be real, must be spontaneous and intelligent, and that means, in the long run, that the immigrant's life in America must be related to the life he already knows. Not by the suppression of old memories, but by their incorporation in his new life is assimilation achieved. The failure of conscious, coercive policies of denationalization in Europe and the great success of the early, passive phase of Americanization in this country afford in this connection an impressive contrast. It follows that assimilation cannot be promoted directly, but only indirectly, that is, by supplying the conditions that make for participation.
The process of assimilation is of a psychological rather than of a biological nature, and refers to the growing alike in character, thoughts, and institutions, rather than to the blood-mingling brought about by intermarriage. The intellectual results of the process of assimilation are far more lasting than the physiological. Thus in France today, though nineteen-twentieths of the blood is that of the aboriginal races, the language is directly derived from that imposed by the Romans in their conquest of Gaul. Intermarriage, the inevitable result to a greater or less extent of race contact, plays its part in the process of assimilation, but mere mixture of races will not cause assimilation. Moreover, assimilation is possible, partially at least, without intermarriage. Instances of this are furnished by the partial assimilation of the Negro and the Indian of the United States. Thinkers are beginning to doubt the great importance once attributed to intermarriage as a factor in civilization. Says Mayo-Smith, "It is not in unity of blood but in unity of institutions and social habits and ideals that we are to seek that which we call nationality," and nationality is the result of assimilation.
Manifestations relatively more simple are shown in the dislike of being conspicuous, in shyness, and in stage fright. It is, however, sensitiveness to the behavior of the herd which has the most important effects upon the structure of the mind of the gregarious animal. This sensitiveness is, as Sidis has clearly seen, closely associated with the suggestibility of the gregarious animal, and therefore with that of man. The effect of it will clearly be to make acceptable those suggestions which come from the herd, and those only. It is of especial importance to note that this suggestibility is not general, and that it is only herd suggestions which are rendered acceptable by the action of instinct.
If the development of social structure is thus to be taken as a guide to assist the process of analysis, it is evident that there will be involved a logical process of considerable complexity in which there will be the danger of arguing in a circle. If, however, the analysis of culture is to be the primary task of the anthropologist, it is evident that the logical methods of the science will attain a complexity far exceeding those hitherto in vogue. I believe that the only logical process which will in general be found possible will be the formulation of hypothetical working schemes into which the facts can be fitted, and that the test of such schemes will be their capacity to fit in with themselves, or, as we generally express it, "explain" new facts as they come to our knowledge. This is the method of other sciences which deal with conditions as complex as those of human society. In many other sciences these new facts are discovered by experiment. In our science they must be found by exploration, not only of the cultures still existent in living form, but also of the buried cultures of past ages.
The introduction of Christianity gave additional impulse to the study of Latin, which soon became the official language of the Christian church; and it was taught everywhere by the priests to the middle and upper classes, and they also encouraged the masses to learn it. It seemed as if this was destined to maintain the prestige of Latin as the official language of the country. But in reality it hastened its downfall by making it more and more the language of the illiterate masses. Soon the rural districts furnished priests who spoke their own Roman tongue; and the struggle to rehabilitate the literary Latin among the masses was abandoned. The numerous French dialects of Latin had already begun to assume shape when the decline of the Roman Empire brought the Germanic tribes down upon Gaul and introduced a new element into the Romanic speech, which had already worked its will upon the tongue of the Caesars. Under its influence the loose Latin construction disappeared; articles and prepositions took the place of the inflectional terminations brought to a high state of artificial perfection in Latin; and the wholesale suppression of unaccented syllables had so contracted the Latin words that they were often scarcely recognizable. The modification of vowel sounds increased the efficacy of the disguise assumed by Latin words masquerading in the Romanic dialects throughout Gaul; and the Celtic and other native words in current use to designate the interests and occupations of the masses helped to differentiate the popular speech from the classical Latin. Already Celtic, as a spoken tongue, had almost entirely disappeared from the cities; and even in the rural districts it had fallen into a certain amount of neglect, as the lingua franca of the first centuries of Roman occupation, reaching out in every direction, became the ever-increasing popular speech.
The most striking illustration of this is the fact of domestic slavery. Slavery has been, historically, the usual method by which peoples have been incorporated into alien groups. When a member of an alien race is adopted into the family as a servant or as a slave, and particularly when that status is made hereditary, as it was in the case of the Negro after his importation to America, assimilation followed rapidly and as a matter of course.
The Americanization Study has assumed that the fundamental condition of what we call "Americanization" is the participation of the immigrant in the life of the community in which he lives. The point here emphasized is that patriotism, loyalty, and common sense are neither created nor transmitted by purely intellectual processes. Men must live and work and fight together in order to create that community of interest and sentiment which will enable them to meet the crises of their common life with a common will.
It is important also that every individual should share as fully as possible a fund of knowledge, experience, sentiments, and ideals common to the whole community and himself contribute to this fund. It is for this reason that we maintain and seek to maintain freedom of speech and free schools. The function of literature, including poetry, romance, and the newspaper, is to enable all to share victoriously and imaginatively in the inner life of each. The function of science is to gather up, classify, digest, and preserve, in a form in which they may become available to the community as a whole, the ideas, inventions, and technical experience of the individuals composing it. Thus not merely the possession of a common language but the wide extension of the opportunities for education become conditions of Americanization.
Defining the situation with reference to the participation of the immigrant is of course not solving the problem of immigration. This involves an analysis of the whole significance of the qualitative and quantitative character of a population, with reference to any given values—standards of living, individual level of efficiency, liberty and determinism, etc. We have, for instance, in America a certain level of culture, depending, let us say as a minimum, on the perpetuation of our public-school system. But, if by some conceivable lusus naturae the birth rate was multiplied a hundred fold, or by some conceivable cataclysm a hundred million African blacks were landed annually on our eastern coast and an equal number of Chinese coolies on our western coast, then we should have neither teachers enough nor buildings enough nor material resources enough to impart even the three R's to a fraction of the population, and the outlook of democracy, so far as it is dependent upon participation, would become very dismal. On the other hand, it is conceivable that certain immigrant populations in certain numbers, with their special temperaments, endowments, and social heritages, would contribute positively and increasingly to our stock of civilization. These are questions to be determined, but certainly if the immigrant is admitted on any basis whatever the condition of his Americanization is that he shall have the widest and freest opportunity to contribute in his own way to the common fund of knowledge, ideas, and ideals which makes up the culture of our common country. It is only in this way that the immigrant can "participate" in the fullest sense of the term.
Historical cases of the assimilation of one group by another are frequent. Kaindl's investigations of the German settlements in the Carpathian lands are particularly instructive. The story of the manner in which the early German settlers in Cracow, Galicia, were Polonized mainly under the influence of the Polish nobility, is all the more interesting when it is contrasted with the German colonists in the Siebenbürgen, which have remained strongholds of the German language and culture in the midst of a population of Roumanian peasants for nearly eight hundred years. Still more interesting are the recent attempts of the Prussians to Germanize the former province of Posen, now reunited to Poland. Prussia's policy of colonization of German peasants in Posen failed for several reasons, but it failed finally because the German peasant, finding himself isolated in the midst of a Polish community, either gave up the land the government had acquired for him and returned to his native German province, or identified himself with the Polish community and was thus lost to the cause of German nationalism. The whole interesting history of that episode is related in Bernard's Die Polenfrage, which is at the same time an account of the organization of an autonomous Polish community within the limits of a German state.
The problem of origin is the first and often the most perplexing problem which the study of primitive cultures presents.[248] Was a given cultural trait, i.e., a weapon, a tool, or a myth, borrowed or invented? For example, there are several independent centers of origin and propagation of the bow and arrow. Writing approached or reached perfection in at least five different, widely separated regions. Other problems of acculturation which have been studied include the following: the degree and order of transmissibility of different cultural traits; the persistence or the immunity against change of different traits; the modification of cultural traits in the process of transmission; the character of social contacts between cultural groups; the distance that divides cultural levels; and the rôle of prestige in stimulating imitation and copying.
Materials valuable for the study of certain immigrant communities, assembled for quite other purposes, are contained in the almanacs, yearbooks, and local histories of the various immigrant communities. The most interesting of these are the Jewish Communal Register of New York and the studies made by the Norwegian Lutheran Church in America under the direction of O. M. Norlie.[249]
(11) Steiner, Edward A. From Alien to Citizen. The story of my life in America. New York, 1914.
During the past seventy years the various tribes, races, and nationalities of mankind have been examined in detail by the students of ethnology, and a comparison of the results shows that the fundamental patterns of life and behavior are everywhere the same, whether among the ancient Greeks, the modern Italians, the Asiatic Mongols, the Australian blacks, or the African Hottentots. All have a form of family life, moral and legal regulations, a religious system, a form of government, artistic practices, and so forth. An examination of the moral code of any given group, say the African Kaffirs, will disclose many identities with that of any other given group, say the Hebrews. All groups have such "commandments" as "Honor thy father and mother," "Thou shalt not kill," "Thou shalt not steal." Formerly it was assumed that this similarity was the result of borrowing between groups. When Bastian recorded a Hawaiian myth resembling the one of Orpheus and Eurydice, there was speculation as to how this story had been carried so far from Greece. But it is now recognized that similarities of culture are due, in the main, not to imitation, but to parallel development. The nature of man is everywhere essentially the same and tends to express itself everywhere in similar sentiments and institutions.[251]
The increasing interest in the natural history of the law and of legal institutions, and the increasing disposition to interpret it in sociological terms, from the point of view of its function, is another evidence of the same tendency.
A week or so later we landed in England. A marked change had come over the men since the day we left Halifax. Then most of us regarded the whole war, or our part in it, as more or less of a lark. On landing we were still for a lark, but something else had come into our consciousness. We were soldiers fighting for a cause—a cause clear cut and well defined—the saving of the world from a militarily mad country without a conscience. At our camp in England we saw those boys of the first division who had stood in their trenches in front of Ypres one bright April morning and watched with great curiosity a peculiar looking bank of fog roll toward them from the enemy's line. It rolled into their trenches, and in a second those men were choking and gasping for breath. Their lungs filled with the rotten stuff, and they were dying by dozens in the most terrible agony, beating off even as they died a part of the "brave" Prussian army as it came up behind those gas clouds; came up with gas masks on and bayonets dripping with the blood of men lying on the ground fighting, true, but for breath. A great army, that Prussian army! And what a "glorious" victory! Truly should the Hun be proud! So far as I am concerned, Germany did not lose the war at the battle of the Marne, at the Aisne, or at the Yser. She lost it there at Ypres, on April 22, 1915. It is no exaggeration when I say our eagerness to work, to complete our training, to learn how to kill, so we could take our places in the line, and help fight off those mad people, grew by the hour. They stiffened our backs and made us fighting mad. We saw what they had done to our boys from Canada; they and their gas. The effect on our battalion was the effect on the whole army, and, I am quite sure, on the rest of the world. They put themselves beyond the pale. They compelled the world to look on them as mad dogs, and to treat them as mad dogs. We trained in England until August, when we went to France. To all outward appearances we were still happy, carefree soldiers, all out for a good time. We were happy! We were happy we were there, and down deep there was solid satisfaction, not on account of the different-colored books that were issuing from every chancellory in Europe, but from a feeling rooted in white men's hearts, backed by the knowledge of Germany's conduct, that we were there in a righteous cause. Our second stop in our march toward the line was a little village which had been occupied by the Boches in their mad dash toward Paris. Our billet was a farm just on the edge of the village. The housewife permitted us in her kitchen to do our cooking, at the same time selling us coffee. We stayed there two or three days and became quite friendly with her, even if she did scold us for our muddy boots. Two pretty little kiddies played around the house, got in the way, were scolded and spanked and in the next instant loved to death by Madame. Then she would parade them before a picture of a clean-cut looking Frenchman in the uniform of the army, and say something about "après la guerre." In a little crib to one side of the room was a tiny baby, neglected by Madame, except that she bathed and fed it. The neglect was so pronounced that our curiosity was aroused. The explanation came through the estaminet gossip, and later from Madame herself. A Hun captain of cavalry had stayed there a few days in August, '14, and not only had he allowed his detachment full license in the village, but had abused his position in the house in the accustomed manner of his bestial class. As Madame told us her story; how her husband had rushed off to his unit with the first call for reserves, leaving her alone with two children, and how the blond beast had come, our fists clenched and we boiled with rage. That is German war! but it is not all. What will be the stories that come out of what is now occupied France? This Frenchwoman's story was new to us then, but, like other things in the war, as we moved through the country it became common enough, with here and there a revolting detail more horrible than anything we had heard before.
Yet another indication of primordialism may be named. This species of control establishes itself anew with every fresh relation among individuals. Even between intimates greetings signifying continuance of respect begin each renewal of intercourse. And in the presence of a stranger, say in a railway carriage, a certain self-restraint, joined with some small act like the offer of a newspaper, shows the spontaneous rise of a propitiatory behavior such as even the rudest of mankind are not without. So that the modified forms of action caused in men by the presence of their fellows constitute that comparatively vague control out of which other more definite controls are evolved—the primitive undifferentiated kind of government from which the political and religious governments are differentiated, and in which they ever continue immersed.
In every stage of the development of savage peoples we come across classical examples of mock kings—of the "primus inter pares," "duces ex virtute," not "ex nobilitate reges"—of rational and valued leaders. The savages of Chile elect as their chief the man who is able to carry the trunk of a tree farthest. In other places, military prowess, command of words, crafts, a knowledge of spells are the causal sources of the usually extremely trifling homage due to the chieftain. "Savage hordes in the lowest stage of civilization are organized, like troops of monkeys, on the basis of authority. The strongest old male by virtue of his strength acquires a certain ascendancy, which lasts as long as his physical strength is superior to that of every other male...."
In no other land under the British flag, except, perhaps, in the Far East, certainly in none of the great self-governing colonies with which we rank ourselves, is the position of white man qua white man so high, his status so impugnable, as in South East Africa. Differing in much else, the race instinct binds the whites together to demand recognition as a member of the ruling and inviolable caste, even for the poorest, the degraded of their race. And this position connotes freedom from all manual and menial toil; without hesitation the white man demands this freedom, without question the black man accedes and takes up the burden, obeying the race command of one who may be his personal inferior. It is difficult to convey to one who has never known this distinction the way in which the very atmosphere is charged with it in South East Africa. A white oligarchy, every member of the race an aristocrat; a black proletariat, every member of the race a server; the line of cleavage as clear and deep as the colours. The less able and vigorous of our race, thus protected, find here an ease, a comfort, a recognition to which their personal worth would never entitle them in a homogeneous white population.
Holy and unclean things have this in common, that in both cases certain restrictions lie on men's use of and contact with them, and that the breach of these restrictions involves supernatural dangers. The difference between the two appears, not in their relation to man's ordinary life, but in their relation to the gods. Holy things are not free to man, because they pertain to the gods; uncleanness is shunned, according to the view taken in the higher Semitic religions, because it is hateful to the god, and therefore not to be tolerated in his sanctuary, his worshippers, or his land. But that this explanation is not primitive can hardly be doubted when we consider that the acts that cause uncleanness are exactly the same which among savage nations place a man under taboo, and that these acts are often involuntary, and often innocent, or even necessary to society. The savage, accordingly, imposes a taboo on a woman in childbed, or during her courses, and on the man who touches a corpse, not out of any regard for the gods, but simply because birth and everything connected with the propagation of the species on the one hand, and disease and death on the other, seem to him to involve the action of superhuman agencies of a dangerous kind. If he attempts to explain, he does so by supposing that on these occasions spirits of deadly power are present; at all events the persons involved seem to him to be sources of mysterious danger, which has all the characters of an infection and may extend to other people unless due precautions are observed. This is not scientific, but it is perfectly intelligible, and forms the basis of a consistent system of practice; whereas, when the rules of uncleanness are made to rest on the will of the gods, they appear altogether arbitrary and meaningless. The affinity of such taboos with laws of uncleanness comes out most clearly when we observe that uncleanness is treated like a contagion, which has to be washed away or otherwise eliminated by physical means. Take the rules about the uncleanness produced by the carcases of vermin in Lev. 11:32 ff.; whatever they touch must be washed; the water itself is then unclean, and can propagate the contagion; nay, if the defilement affect an (unglazed) earthen pot, it is supposed to sink into the pores, and cannot be washed out, so that the pot must be broken. Rules like this have nothing in common with the spirit of Hebrew religion; they can only be remains of a primitive superstition, like that of the savage who shuns the blood of uncleanness, and such like things, as a supernatural and deadly virus. The antiquity of the Hebrew taboos, for such they are, is shown by the way in which many of them reappear in Arabia; cf. for example Deut. 21:12, 13, with the Arabian ceremonies for removing the impurity of widowhood. In the Arabian form the ritual is of purely savage type; the danger to life that made it unsafe for a man to marry the woman was transferred in the most materialistic way to an animal, which it was believed generally died in consequence, or to a bird.
To solve this question, we are no longer compelled to argue learnedly about the future; we are not obliged to indulge in lofty reflections about philosophy, history, or economics; we are not on the plane of theories, and we can remain on the level of observable facts. We have to question men who take a very active part in the real revolutionary movement amidst the proletariat, men who do not aspire to climb into the middle class and whose mind is not dominated by corporative prejudices. These men may be deceived about an infinite number of political, economical, or moral questions; but their testimony is decisive, sovereign, and irrefutable when it is a question of knowing what are the ideas which most powerfully move them and their comrades, which most appeal to them as being identical with their socialistic conceptions, and thanks to which their reason, their hopes, and their way of looking at particular facts seem to make but one indivisible unity.
The legendary stories have thus attained the last stage of their elaboration and completed their diffusion. They have penetrated not only into the purlieus of the cities but into distant countries; into centers of education as among the popular classes. Wounded convalescents and soldiers on leave at home for a time have told them to the city man and to the peasant. Both have found them in letters from the front; both have read them in journals and books, both have listened to the warnings of the government and to the imperial word. The schoolteacher has mixed these episodes with his teaching; he has nourished with them infantile imaginations. Scholars have read the text of them in their classbooks and have enacted them in the games inspired by the war; they have told them at home in the family circle, giving them the authority attached to the master's word.
The traditional usages of religion had grown up gradually in the course of many centuries, and reflected habits of thought characteristic of very diverse stages of man's intellectual and moral development. No one conception of the nature of the gods could possibly afford the clue to all parts of that motley complex of rites and ceremonies which the later paganism had received by inheritance, from a series of ancestors in every state of culture from pure savagery upwards. The record of the religious thought of mankind, as it is embodied in religious institutions, resembles the geological record of the history of the earth's crust; the new and the old are preserved side by side or rather layer upon layer. The classification of ritual formations in their proper sequence is the first step towards their explanation, and that explanation itself must take the form, not of a speculative theory, but of a rational life-history.
One more remark must be made before quitting the subject of the relation of public opinion to the opinion of the majority. The late Gabriel Tarde, with his habitual keen insight, insisted on the importance of the intensity of belief as a factor in the spread of opinions. There is a common impression that public opinion depends upon and is measured by the mere number of persons to be found on each side of a question; but this is far from accurate. If 49 per cent of a community feel very strongly on one side, and 51 per cent are lukewarmly on the other, the former opinion has the greater public force behind it and is certain to prevail ultimately, if it does not at once.
It is probably not the business of the universities to agitate reforms nor to attempt directly to influence public opinion in regard to current issues. To do this is to relax its critical attitude, lessen its authority in matters of fact, and jeopardize its hard-won academic freedom. When a university takes over the function of a political party or a church it ceases to perform its function as a university.
Few episodes in recent history are more poignant than that of the British prime minister, sitting at the breakfast table with that morning's paper before him, protesting that he cannot do the sensible thing in regard to Russia because a powerful newspaper proprietor has drugged the public. That incident is a photograph of the supreme danger which confronts popular government. All other dangers are contingent upon it, for the news is the chief source of the opinion by which government now proceeds. So long as there is interposed between the ordinary citizen and the facts a news organization determining by entirely private and unexamined standards, no matter how lofty, what he shall know, and hence what he shall believe, no one will be able to say that the substance of democratic government is secure. The theory of our constitution, says Mr. Justice Holmes, is that truth is the only ground upon which men's wishes safely can be carried out. In so far as those who purvey the news make of their own beliefs a higher law than truth, they are attacking the foundations of our constitutional system. There can be no higher law in journalism than to tell the truth and shame the devil.
The second social danger is the tendency to overload and level down every great human incentive in the pursuit of relatively trivial ends. To become blasé is the inevitable penalty of emotional exploitation. I believe there may well be grave penalties in store for the reckless commercialized exploitation of human emotions in the cheap sentimentalism of our moving pictures. But there are even graver penalties in store for the generation that permits itself to grow morally blasé. One of our social desiderata, it seems to me, is the protection of the great springs of human action from destructive exploitation for selfish, commercial, or other trivial ends.
Acts of legislation come out of the mores. In low civilization all societal regulations are customs and taboos, the origin of which is unknown. Positive laws are impossible until the stage of verification, reflection, and criticism is reached. Until that point is reached there is only customary law, or common law. The customary law may be codified and systematized with respect to some philosophical principles, and yet remain customary. The codes of Manu and Justinian are examples. Enactment is not possible until reverence for ancestors has been so much weakened that it is no longer thought wrong to interfere with traditional customs by positive enactment. Even then there is reluctance to make enactments, and there is a stage of transition during which traditional customs are extended by interpretation to cover new cases and to prevent evils. Legislation, however, has to seek standing ground on the existing mores, and it soon becomes apparent that legislation, to be strong, must be consistent with the mores. Things which have been in the mores are put under police regulation and later under positive law. It is sometimes said that "public opinion" must ratify and approve police regulations, but this statement rests on an imperfect analysis. The regulations must conform to the mores, so that the public will not think them too lax or too strict. The mores of our urban and rural populations are not the same; consequently legislation about intoxicants which is made by one of these sections of the population does not succeed when applied to the other. The regulation of drinking-places, gambling-places, and disorderly houses has passed through the above-mentioned stages. It is always a question of expediency whether to leave a subject under the mores, or to make a police regulation for it, or to put it into the criminal law. Betting, horse racing, dangerous sports, electric cars, and vehicles are cases now of things which seem to be passing under positive enactment and out of the unformulated control of the mores. When an enactment is made there is a sacrifice of the elasticity and automatic self-adaptation of custom, but an enactment is specific and is provided with sanctions. Enactments come into use when conscious purposes are formed, and it is believed that specific devices can be framed by which to realize such purposes in the society. Then also prohibitions take the place of taboos, and punishments are planned to be deterrent rather than revengeful. The mores of different societies, or of different ages, are characterized by greater of less readiness and confidence in regard to the use of positive enactments for the realization of societal purposes.
I am quite sure that all the American people when they think of law in the sense I am now speaking of, even when they are not thinking necessarily of statute law, do mean, nevertheless, a law which is enforced by somebody with power, somebody with a big stick. They mean a law, an ordinance, an order or dictate addressed to them by a sovereign, or at least by a power of some sort, and they mean an ordinance which if they break they are going to suffer for, either in person or in property. In other words, they have a notion of law as a written command addressed by the sovereign to the subject, or at least by one of the departments of government to the citizen. Now that, I must caution you, is in the first place rather a modern notion of law, quite modern in England; it is really Roman, and was not law as it was understood by our Anglo-Saxon ancestors. He did not think of law as a thing written, addressed to him by the king. Neither did he necessarily think of it as a thing which had any definite punishment attached or any code attached, any "sanction," as we call it, or thing which enforces the law; a penalty or fine or imprisonment. There are just as good "sanctions" for law outside of the sanctions that our people usually think of as there are inside of them, and often very much better; for example, the sanction of a strong custom. Take any example you like; there are many states where marriage between blacks and whites is not made unlawful but where practically it is made tremendously unlawful by the force of public opinion [mores]. Take the case of debts of honor, so called, debts of gambling; they are paid far more universally than ordinary commercial debts, even by the same people; but there is no law enforcing them—there is no sanction for the collection of gambling debts. And take any custom that grows up. We know how strong our customs in college are. Take the mere custom of a club table; no one dares or ventures to supplant the members at that table. That kind of sanction is just as good a law as a law made by statute and imposing five or ten dollars' penalty or a week's imprisonment. And judges or juries recognize those things as laws, just as much as they do statute laws; when all other laws are lacking, our courts will ask what is the "custom of the trade." These be laws, and are often better enforced than the statute law; the rules of the New York Stock Exchange are better enforced than the laws of the state legislature. Now all our early Anglo-Saxon law was law of that kind. For the law was but universal custom, and that custom had no sanction; but for breach of the custom anybody could make personal attack, or combine with his friends to make attack, on the person who committed the breach, and then, when the matter was taken up by the members of both tribes, and finally by the witenagemot as a judicial court, the question was, what the law was. That was the working of the old Anglo-Saxon law, and it was a great many centuries before the notion of law changed from that in their minds. And this "unwritten law" perdures in the minds of many of the people today.
There is no necessity, however, for the social control which religion exerts being of a non-progressive kind. The values which religion universalizes and makes absolute may as easily be values which are progressive as those which are static. In a static society which emphasizes prohibitions and the conservation of mere habit or custom, religion will also, of course, emphasize the same things; but in a progressive society religion can as easily attach its sanctions to social ideals and standards beyond the existing order as to those actually realized. Such an idealistic religion will, however, have the disadvantages of appealing mainly to the progressive and idealizing tendencies of human nature rather than to its conservative and reactionary tendencies. Necessarily, also, it will appeal more strongly to those enlightened classes in society who are leading in social progress rather than to those who are content with things as they are. This is doubtless the main reason why progressive religions are exceedingly rare in human history, taking it as a whole, and have appeared only in the later stages of cultural evolution.
Society, so far as it can be distinguished from the individuals that compose it, performs for those individuals the function of a mind. Like mind in the individual man, society is a control organization. Evidence of mind in the animal is the fact that it can make adjustments to new conditions. The evidence that any group of persons constitutes a society is the fact that the group is able to act with some consistency, and as a unit. It follows that the literature on social control, in the widest extension of that term, embraces most that has been written and all that is fundamental on the subject of society. In chapter ii, "Human Nature," and the later chapters on "Interaction" and its various forms, "Conflict," "Accommodation," and "Assimilation," points of view and literature which might properly be included in an adequate study of social control have already been discussed. The present chapter is concerned mainly with ceremonial, public opinion, and law, three of the specific forms in which social control has universally found expression.
The materials upon ceremony, social ritual, and fashion are large in comparison with the attempts at a systematic study of the phenomena. Herbert Spencer's chapter on "Ceremonial Government," while it interprets social forms from the point of view of the individual rather than of the group, is still the only adequate survey of the materials in this special field.
Public opinion, "the fourth estate" as Burke called it, has been appreciated, but not studied. The old Roman adage, Vox populi, vox dei, is a recognition of public opinion as the ultimate seat of authority. Public opinion has been elsewhere identified with the "general will." Rousseau conceived the general will to be best expressed through a plebiscite at which a question was presented without the possibilities of the divisive effects of public discussion. The natural impulses of human nature would make for more uniform and beneficial decisions than the calculated self-interest that would follow discussion and deliberation. English liberals like John Stuart Mill, of the latter half of the nineteenth century, looked upon freedom of discussion and free speech as the breath of life of a free society, and that tradition has come down to us a little shaken by recent experience, but substantially intact.
(11) Continental Legal History Series. Published under the auspices of the Association of American Law Schools. 11 vols. Boston, 1912-.
The amount of individual eccentricity or deviation from normal and accepted modes of behavior which a community will endure without comment and without protest will vary naturally enough with the character of the community. A cosmopolitan community like New York City can and does endure a great deal in the way of individual eccentricity that a smaller city like Boston would not tolerate. In any case, and this is the point of these observations, even in the most casual relations of life, people do not behave in the presence of others as if they were living alone like Robinson Crusoe, each on his individual island. The very fact of their consciousness of each other tends to maintain and enforce a great body of convention and usage which otherwise falls into abeyance and is forgotten. Collective behavior, then, is the behavior of individuals under the influence of an impulse that is common and collective, an impulse, in other words, that is the result of social interaction.
The isolation, territorial and cultural, under which alone it is possible to maintain an organization which corresponds to Sumner's description, has disappeared within comparatively recent times from all the more inhabitable portions of the earth. In place of it there has come, and with increasing rapidity is coming, into existence a society which includes within its limits the total population of the earth and is so intimately bound together that the speculation of a grain merchant in Chicago may increase the price of bread in Bombay, while the act of an assassin in a provincial town in the Balkans has been sufficient to plunge the world into a war which changed the political map of three continents and cost the lives, in Europe alone, of 8,500,000 combatants.
Sects, and that is what characterizes and distinguishes them from secular institutions, at least, have had their origin in movements that aimed to reform the mores—movements that sought to renovate and renew the inner life of the community. They have wrought upon society from within outwardly. Revolutionary and reform movements, on the contrary, have been directed against the outward fabric and formal structure of society. Revolutionary movements in particular have assumed that if the existing structure could be destroyed it would then be possible to erect a new moral order upon the ruins of the old social structures.
Crusades are reformatory and religious. This was true at any rate of the early crusades, inspired by Peter the Hermit, whatever may have been the political purposes of the popes who encouraged them. It was the same motive that led the people of the Middle Ages to make pilgrimages which led them to join the crusades. At bottom it was an inner restlessness, that sought peace in great hardship and inspiring action, which moved the masses.
At a cotton manufactory at Hodden Bridge, in Lancashire, a girl, on the fifteenth of February, 1787, put a mouse into the bosom of another girl, who had a great dread of mice. The girl was immediately thrown into a fit, and continued in it with the most violent convulsions for twenty-four hours. On the following day three more girls were seized in the same manner; and on the seventeenth, six more. By this time the alarm was so great that the whole work, in which 200 or 300 were employed, was totally stopped, and an idea prevailed that a particular disease had been introduced by a bag of cotton opened in the house. On Sunday, the eighteenth, Dr. St. Clare was sent for from Preston; before he arrived three more were seized, and during that night and the morning of the nineteenth, eleven more, making in all twenty-four. Of these, twenty-one were young women, two were girls of about ten years of age, and one man, who had been much fatigued with holding the girls. Three of the number lived about two miles from the place where the disorder first broke out, and three at another factory in Clitheroe, about five miles distant, which last and two more were infected entirely from report, not having seen the other patients, but, like them and the rest of the country, strongly impressed with the idea of the plague being caught from the cotton. The symptoms were anxiety, strangulation, and very strong convulsions; and these were so violent as to last without any intermission from a quarter of an hour to twenty-four hours, and to require four or five persons to prevent the patients from tearing their hair and dashing their heads against the floor or walls. Dr. St. Clare had taken with him a portable electrical machine, and by electric shocks the patients were universally relieved without exception. As soon as the patients and the country were assured that the complaint was merely nervous, easily cured, and not introduced by the cotton, no fresh person was affected. To dissipate their apprehension still further, the best effects were obtained by causing them to take a cheerful glass and join in a dance. On Tuesday, the twentieth, they danced, and the next day were all at work, except two or three, who were much weakened by their fits.
A few months after this dancing malady had made its appearance at Aix-la-Chapelle, it broke out at Cologne, where the number of those possessed amounted to more than five hundred; and about the same time at Metz, the streets of which place are said to have been filled with eleven hundred dancers. Peasants left their plows, mechanics their workshops, housewives their domestic duties, to join the wild revels, and this rich commercial city became the scene of the most ruinous disorder. Secret desires were excited and but too often found opportunities for wild enjoyment; and numerous beggars, stimulated by vice and misery, availed themselves of this new complaint to gain a temporary livelihood. Girls and boys quitted their parents, and servants their masters, to amuse themselves at the dances of those possessed, and greedily imbibed the poison of mental infection. Above a hundred unmarried women were seen raving about in consecrated and unconsecrated places, and the consequences were soon perceived. Gangs of idle vagabonds, who understood how to imitate to the life the gestures and convulsions of those really affected, roved from place to place seeking maintenance and adventures, and thus, wherever they went, spreading this disgusting spasmodic disease like a plague; for in maladies of this kind the susceptible are infected as easily by the appearance as by the reality. At last it was found necessary to drive away these mischievous guests, who were equally inaccessible to the exorcisms of the priests and the remedies of the physicians. It was not, however, until after four months that the Rhenish cities were able to suppress these impostures, which had so alarmingly increased the original evil. In the meantime, when once called into existence, the plague crept on and found abundant food in the tone of thought which prevailed in the fourteenth and fifteenth centuries, and even, though in a minor degree, throughout the sixteenth and seventeenth, causing a permanent disorder of the mind, and exhibiting, in those cities to whose inhabitants it was a novelty, scenes as strange as they were detestable.
In sudden attacks from several quarters, or inexplicable man-thwarting of their instincts, the flock-mind teaches them to turn a solid front, revolving about in the smallest compass with the lambs in their midst, narrowing and indrawing until they perish by suffocation. So they did in the intricate defiles of Red Rock, where Carrier lost 250 in '74, and at Poison Springs, as Narcisse Duplin told me, where he had to choose between leaving them to the deadly waters, or, prevented from the spring, made witless by thirst, to mill about until they piled up and killed threescore in their midst. By no urgency of the dogs could they be moved forward or scattered until night fell with coolness and returning sanity. Nor does the imperfect gregariousness of man always save us from ill-considered rushes or strangulous in-turnings of the social mass. Notwithstanding there are those who would have us to be flock-minded.
The animals that had forced their way into the center of the mass to the spot where the blood was, pawed the earth, and dug it up with their horns, and trampled each other down in their frantic excitement. It was terrible to see and hear them. The action of those on the border of the living mass, in perpetually moving round in a circle with dolorous bellowings, was like that of the women in an Indian village when a warrior dies, and all night they shriek and howl with simulated grief, going round and round the dead man's hut in an endless procession.
An instance in point was related to me by Mr. Gordon Wright of Carberry, Manitoba. During the winter of 1865 he was logging at Sturgeon Lake, Ontario. One Sunday he and some companions strolled out on the ice of the lake to look at the logs there. They heard the hunting-cry of wolves, then a deer (a female) darted from the woods to the open ice. Her sides were heaving, her tongue out, and her legs cut by the slight crust of the snow. Evidently she was hard pressed. She was coming toward them, but one of the men gave a shout which caused her to sheer off. A minute later six timber wolves appeared galloping on her trail, heads low, tails horizontal, and howling continuously. They were uttering their hunting-cry, but as soon as they saw her they broke into a louder, different note, left the trail and made straight for her. Five of the wolves were abreast and one that seemed much darker was behind. Within half a mile they overtook her and pulled her down, all seemed to seize her at once. For a few minutes she bleated like a sheep in distress; after that the only sound was the snarling and the crunching of the wolves as they feasted. Within fifteen minutes nothing was left of the deer but hair and some of the larger bones, and the wolves fighting among themselves for even these. Then they scattered, each going a quarter of a mile or so, no two in the same direction, and those that remained in view curled up there on the open lake to sleep. This happened about ten in the morning within three hundred yards of several witnesses.
The conclusion to be drawn from what precedes is that the crowd is always intellectually inferior to the isolated individual, but that, from the point of view of feelings and of the acts these feelings provoke, the crowd may, according to circumstances, be better or worse than the individual. All depends on the nature of the suggestion to which the crowd is exposed. This is the point that has been completely misunderstood by writers who have only studied crowds from the criminal point of view. Doubtless a crowd is often criminal, but also it is often heroic. It is crowds rather than isolated individuals that may be induced to run the risk of death to secure the triumph of a creed or an idea, that may be fired with enthusiasm for glory and honor, that are led on—almost without bread and without arms, as in the age of the Crusades—to deliver the tomb of Christ from the infidel, or, as in '93, to defend the fatherland. Such heroism is without doubt somewhat unconscious, but it is of such heroism that history is made. Were peoples only to be credited with the great actions performed in cold blood, the annals of the world would register but few of them.
Of the 6,000 people who went in this fall, 200 at the most got over to the Dawson Route by the White Pass, and perhaps 700 by the Chilcoot. There were probably 1,000 camped at Lake Bennett, and all the rest, except the 1,500 remaining on the coast, had returned home to wait till midwinter or the spring before venturing up again. The question of which was the best trail was still undecided, and men vehemently debated it every day with the assistance of the most powerful language at their command.
A short time after, on a dying-bed, this four days' liquor-dealer sent for some of these women, telling them their songs and prayers had never ceased to ring in his ears, and urging them to pray again in his behalf; so he passed away.
The religious forms rapidly assumed by the Revolution explain its power of expansion and the prestige which it possessed and has retained. Few historians have understood that this great monument ought to be regarded as the foundation of a new religion. The penetrating mind of Tocqueville, I believe, was the first to perceive as much. He wrote:
Finally, if we would understand why millions of people in all lands have turned away from old ideals, old loyalties, and old faiths to bolshevism, with something of the passion and frenzy characteristic of great messianic movements, we must take into account the intense spiritual agony and hunger which the Great War has brought into the lives of civilized men. The old gods are dead and men are everywhere expectantly waiting for the new gods to arise. The aftermath of the war is a spiritual cataclysm such as civilized mankind has never before known. The old religions and moralities are shattered and men are waiting and striving for new ones. It is a time suggestive of the birth of new religions. Man cannot live as yet without faith, without some sort of religion. The heart of the world today is strained with yearning for new and living faiths to replace the old faiths which are dead. Were some persuasive fanatic to arise proclaiming himself to be a new Messiah, and preaching the religion of action, the creation of a new society, he would find an eager, soul-hungry world already predisposed to believe.
But with all its divisions and defects the movement was unquestionably effecting a great moral revolution in England. It was essentially a popular movement, exercising its deepest influence over the lower and middle classes. Some of its leaders were men of real genius, but in general the Methodist teacher had little sympathy with the more educated of his fellow-countrymen. To an ordinarily cultivated mind there was something extremely repulsive in his tears and groans and amorous ejaculations, in the coarse and anthropomorphic familiarity and the unwavering dogmatism with which he dealt with the most sacred subjects, in the narrowness of his theory of life and his utter insensibility to many of the influences that expand and embellish it, in the mingled credulity and self-confidence with which he imagined that the whole course of nature was altered for his convenience. But the very qualities that impaired his influence in one sphere enhanced it in another. His impassioned prayers and exhortations stirred the hearts of multitudes whom a more decorous teaching had left absolutely callous. The supernatural atmosphere of miracles, judgments, and inspirations in which he moved, invested the most prosaic life with a halo of romance. The doctrines he taught, the theory of life he enforced, proved themselves capable of arousing in great masses of men an enthusiasm of piety which was hardly surpassed in the first days of Christianity, of eradicating inveterate vice, of fixing and directing impulsive and tempestuous natures that were rapidly hastening toward the abyss. Out of the profligate slave-dealer, John Newton, Methodism formed one of the purest and most unselfish of saints. It taught criminals in Newgate to mount the gallows in an ecstasy of rapturous devotion. It planted a fervid and enduring religious sentiment in the midst of the most brutal and most neglected portions of the population, and whatever may have been its vices or its defects, it undoubtedly emancipated great numbers from the fear of death, and imparted a warmer tone to the devotion and a greater energy to the philanthropy of every denomination both in England and the colonies.
Some years ago John Graham Brooks wrote a popular treatise on the labor situation in the United States. He called the volume Social Unrest. The term was, even at that time, a familiar one. Since then the word unrest, in both its substantive and adjective forms, has gained wide usage. We speak in reference to the notorious disposition of the native American to move from one part of the country to another, of his restless blood, as if restlessness was a native American trait transmitted in the blood. We speak more often of the "restless age," as if mobility and the desire for novelty and new experience were peculiarly characteristic of the twentieth century. We use the word to describe conditions in different regions of social life in such expressions as "political," "religious," and "labor" unrest, and in every case the word is used in a sense that indicates change, but change that menaces the existing order. Finally, we speak of the "restless woman," as of a peculiar modern type, characteristic of the changed status of women in general in the modern world. In all these different uses we may observe the gradual unfolding of the concept which seems to have been implicit in the word as it was first used. It is the concept of an activity in response to some urgent organic impulse which the activity, however, does not satisfy. It is a diagnostic symptom, a symptom of what Graham Wallas calls "balked disposition." It is a sign that in the existing situation some one or more of the four wishes—security, new experience, recognition, and response—has not been and is not adequately realized. The fact that the symptom is social, that it is contagious, is an indication that the situations that provoke it are social, that is to say, general in the community or the group where the unrest manifests itself.[313] The materials in which the term unrest is used in the sense indicated are in the popular discussions of social questions. The term is not defined but it is frequently used in connection with descriptions of conditions which are evidently responsible for it. Labor strikes are evidences of social unrest, and the literature already referred to in the chapter on "Conflict"[1] shows the conditions under which unrest arises, is provoked and exploited in labor situations. The relation of unrest to routine and fatigue has been the subject of a good deal of discussion and some investigation. The popular conception is that labor unrest is due to the dull driving routine of machine industry. The matter needs further study. The actual mental experiences of the different sexes, ages, temperamental and mental types under the influence of routine would add a much needed body of fact to our present psychology of the worker.
Social epidemics, however, are evidence of a social disintegration due to more fundamental and widespread disorders. The literature has recorded the facts but writers have usually interpreted the phenomena in medical rather than sociological terms. Stoll, in his very interesting but rather miscellaneous collection of materials upon primitive life, disposes of the phenomena by giving them another name. His volume is entitled Suggestion and Hypnotism in Folk Psychology.[314] Friedmann, in his monograph, Über Wahnideen im Völkerleben, is disposed as a psychiatrist to treat the whole matter as a form of "social" insanity.
In this field there is room for investigation and study, for almost all attempts thus far made to put advertising on a scientific basis have been made by students of individual rather than social psychology.
Fashion is distinguished from reform by the fact that the changes it introduces are wholly irrational if not at the same time wholly unpredictable. Reform, on the other hand, is nothing if not rational. It achieves its ends by agitation and discussion. Attempts have been made to introduce fashions by agitation, but they have not succeeded. On the other hand, reform is itself a fashion and has largely absorbed in recent years the interest that was formerly bestowed on party politics.
(16) Le Bon, Gustave. The World in Revolt. A psychological study of our times. Translated from the French by Bernard Miall. New York, 1921.
Already this century has witnessed the first municipalized street railways and telephones in American cities; a national epidemic of street paving and cleaning; the quadrupling of electric lighting service and the national appropriation of display lighting; a successful crusade against dirt of all kinds—smoke, flies, germs,—and the diffusion of constructive provisions for health like baths, laundries, comfort stations, milk stations, school nurses and open air schools; fire prevention; the humanizing of the police and the advent of the policewomen; the transforming of some municipal courts into institutions for the prevention of crime and the cure of offenders; the elaboration of the school curriculum to give every child a complete education from the kindergarten to the vocational course in school or university or shop; municipal reference libraries; the completion of park systems in most large cities and the acceptance of the principle that the smallest city without a park and playground is not quite civilized; the modern playground movement giving organized and directed play to young and old; the social center; the democratic art museum; municipal theaters; the commission form of government; the city manager; home rule for cities; direct legislation—a greater advance than the whole nineteenth century compassed.[326]
The modern man finds this idea quite as stimulating to him as the idea of progress was to his ancestor of the Renaissance or the idea of providence to his medieval forebears. For while he does not blindly believe nor feel optimistically certain things will come about all right, yet he is nerved to square his shoulders, to think, to contrive, and to exert himself to the utmost in his effort to conquer the difficulties ahead, and to control the forces of nature and man. The idea of providence was not merely a generalization on life, it was a force that inspired hope. The idea of progress was likewise not merely a concept, it was also an energizing influence in a time of great intellectual activity. The idea that the forces of nature can be controlled in the service of man, differs from the others, but is also a dynamic potency that seems to be equally well adapted to the twentieth century.
It is not necessary for the students of sociology to discuss the merits of these different doctrines. We may accept them as human documents. They throw light, at any rate, upon the idea of progress, and upon all the other fundamental ideas in which men have sought to formulate their common hopes and guide their common life.
Fire was first learned from lightning and the friction of trees, and cooking from the softening and ripening of things by the sun. Then men of genius invented improved methods of life, the building of cities and private property in lands and cattle. But gold gave power to the wealthy and destroyed the sense of contentment in simple happiness. It must always be so whenever men allow themselves to become the slaves of things which should be their dependents and instruments.
In respect to that progress which individual organisms display in the course of their evolution, this question has been answered by the Germans. The investigations of Wolff, Goethe, and von Baer have established the truth that the series of changes gone through during the development of a seed into a tree, or an ovum into an animal, constitute an advance from homogeneity of structure to heterogeneity of structure. In its primary stage, every germ consists of a substance that is uniform throughout, both in texture and chemical composition. The first step is the appearance of a difference between two parts of this substance; or, as the phenomenon is called in physiological language, a differentiation. Each of these differentiated divisions presently begins itself to exhibit some contrast of parts; and by and by these secondary differentiations become as definite as the original one. This process is continuously repeated—is simultaneously going on in all parts of the growing embryo; and by endless differentiations of this sort there is finally produced that complex combination of tissues and organs constituting the adult animal or plant. This is the history of all organisms whatever. It is settled beyond dispute that organic progress consists in a change from the homogeneous to the heterogeneous.
If we regard the course of human development from the highest scientific point of view, we shall perceive that it consists in educing more and more the characteristic faculties of humanity, in comparison with those of animality; and especially with those which man has in common with the whole organic kingdom. It is in this philosophical sense that the most eminent civilization must be pronounced to be fully accordant with nature, since it is, in fact, only a more marked manifestation of the chief properties of our species, properties which, latent at first, can come into play only in that advanced state of social life for which they are exclusively destined. The whole system of biological philosophy indicates the natural progression. We have seen how, in the brute kingdom, the superiority of each race is determined by the degree of preponderance of the animal life over the organic. In like manner we see that our social evolution is only the final term of a progression which has continued from the simplest vegetables and most insignificant animals, up through the higher reptiles to the birds and the mammifers, and still on to the carnivorous animals and monkeys, the organic characteristics retiring and the animal prevailing more and more, till the intellectual and moral tend toward the ascendancy which can never be fully obtained, even in the highest state of human perfection that we can conceive of. This comparative estimate affords us the scientific view of human progression, connected, as we see it is, with the whole course of animal advancement, of which it is itself the highest degree. The analysis of our social progress proves indeed that, while the radical dispositions of our nature are necessarily invariable, the highest of them are in a continuous state of relative development, by which they rise to be preponderant powers of human existence, though the inversion of the primitive economy can never be absolutely complete. We have seen that this is the essential character of the social organism in a statical view; but it becomes much more marked when we study its variations in their gradual succession.
We are not to conclude that physical heredity is of no importance to the social order; it must be obvious that the better the qualities of the individuals constituting a race, the more easily they will fit themselves into good social traditions, the more readily they will advance those traditions to a still higher point of excellence, and the more stoutly they would resist deterioration. The qualities upon which the social fabric calls must be there, and the more readily they are forthcoming, the more easily the social machine will work. Hence social progress necessarily implies a certain level of racial development, and its advance may always be checked by the limitations of the racial type. Nevertheless, if we look at human history as a whole, we are impressed with the stability of the great fundamental characteristics of human nature and the relatively sweeping character and often rapid development of social change.
It would involve a great fallacy to deduce from this the conclusion that civilization begets misery or reduces the happiness of mankind. Against this gross but popular mistake may be cited the principle before introduced, which is unanimously accepted by biologists, that an organism is perfect in proportion as its organs are numerous and varied. This is because, the more organs there are, the greater is the capacity for enjoyment. For this enjoyment is quantitative as well as qualitative, and the greater the number of faculties, the greater is the possible enjoyment derivable from their normal exercise. To say that primitive man is happier than enlightened man, is equivalent to saying that an oyster or a polyp enjoys more than an eagle or an antelope. This could be true only on the ground that the latter, in consequence of their sensitive organisms, suffer more than they enjoy; but if to be happy is to escape from all feeling, then it were better to be stones or clods, and destitute of conscious sensibility. If this be the happiness which men should seek, then is the Buddhist in the highest degree consistent when he prays for the promised Nirvâna, or annihilation. But this is not happiness—it is only the absence of it. For happiness can only be increased by increasing the capacity for feeling, or emotion, and, when this is increased, the capacity for suffering is likewise necessarily increased, and suffering must be endured unless sufficient sagacity accompanies it to prevent this consequence. And that is the truest progress which, while it indefinitely multiplies and increases the facilities for enjoyment, furnishes at the same time the most effective means of preventing discomfort, and, as nearly all suffering is occasioned by the violation of natural laws through ignorance of or error respecting those laws, therefore that is the truest progress which succeeds in overcoming ignorance and error.
There is at any time a sufficient amount of kindly impulses possessed by man to enable him to live in amicable peace with all his fellows; and there is at any time a sufficient equipment of bellicose impulses to keep him in trouble with his fellows. An intensification of the exhibition of one may accompany an intensification of the display of the other, the only difference being that social arrangements cause the kindly feelings to be displayed toward one set of fellows and the hostile impulses toward another set. Thus, as everybody knows, the hatred toward the foreigner characterizing peoples now at war is attended by an unusual manifestation of mutual affection and love within each warring group. So characteristic is this fact that that man was a good psychologist who said that he wished that this planet might get into war with another planet, as that was the only effective way he saw of developing a world-wide community of interest in this globe's population.
We habitually talk as if a self-governing or free community was one which managed its own affairs. In strictness, no community manages its own affairs, or by any possibility could manage them. It manages but a narrow fringe of its affairs, and that in the main by deputy. It is only the thinnest surface layer of law and custom, belief and sentiment, which can either be successfully subjected to destructive treatment, or become the nucleus of any new growth—a fact which explains the apparent paradox that so many of our most famous advances in political wisdom are nothing more than the formal recognition of our political impotence.
5. Persistence in setting forth the national importance of Eugenics. There are three stages to be passed through. Firstly, it must be made familiar as an academic question, until its exact importance has been understood and accepted as a fact; secondly, it must be recognised as a subject whose practical development deserves serious consideration; and thirdly, it must be introduced into the national conscience, like, a new religion. It has, indeed, strong claims to become an orthodox religious tenet of the future, for Eugenics cooperates with the workings of Nature by securing that humanity shall be represented by the fittest races. What Nature does blindly, slowly, and ruthlessly, man may do providently, quickly, and kindly. I see no impossibility in Eugenics becoming a religious dogma among mankind, but its details must first be worked out sedulously in the study. The first and main point is to secure the general intellectual acceptance of Eugenics as a hopeful and most important study. Then let its principles work into the heart of the nation, who will gradually give practical effect to them in ways that we may not wholly foresee.
What now are some of the leading features in the mores of civilized society at the present time? Undoubtedly they are monogamy, anti-slavery, and democracy. All people now are more nervous than anybody used to be. Social ambition is great and is prevalent in all classes. The idea of class is unpopular and is not understood. There is a superstitious yearning for equality. There is a decided preference for city life, and a stream of population from the country into big cities. These are facts of the mores of the time. Our societies are almost unanimous in their response if there is any question raised on these matters.
The future progress of mankind is to be sought, not through the strifes and hatreds of the nations, but rather by their friendly co-operation in the healing and enlightening works of peace and in the growth of a spirit of friendship and mutual confidence which may remove the causes of war.
Consciousness is distinct from the organism it animates, although it must undergo its vicissitudes. As the possible actions which a state of consciousness indicates are at every instant beginning to be carried out in the nervous centres, the brain underlies at every instant the motor indications of the state of consciousness; but the interdependency of consciousness and brain is limited to this; the destiny of consciousness is not bound up on that account with the destiny of cerebral matter. Finally, consciousness is essentially free; it is freedom itself; but it cannot pass through matter without settling on it, without adapting itself to it: this adaptation is what we call intellectuality; and the intellect, turning itself back towards active, that is to say, free, consciousness, naturally makes it enter into the conceptual forms into which it is accustomed to see matter fit. It will therefore always perceive freedom in the form of necessity; it will always neglect the part of novelty or of creation inherent in the free act; it will always substitute for action itself an imitation artificial, approximative, obtained by compounding the old with the old and the same with the same. Thus, to the eyes of a philosophy that attempts to reabsorb intellect in intuition, many difficulties vanish or become light. But such a doctrine does not only facilitate speculation; it gives us also more power to act and to live. For, with it, we feel ourselves no longer isolated in humanity, humanity no longer seems isolated in the nature that it dominates. As the smallest grain of dust is bound up with our entire solar system, drawn along with it in that undivided movement of descent which is materiality itself, so all organized beings, from the humblest to the highest, from the first origins of life to the time in which we are, and in all places, as in all times, do but evidence a single impulsion, the inverse of the movement of matter, and in itself indivisible. All the living hold together, and all yield to the same tremendous push. The animal takes its stand on the plant, man bestrides animality, and the whole of humanity, in space and in time, is one immense army galloping beside and before and behind each of us in an overwhelming charge able to beat down every resistance and clear the most formidable obstacles, perhaps even death.
The law of motivation only extends to the particular actions, not to willing as a whole and in general. It depends upon this, that if we conceive of the human race and its action as a whole and universally, it does not present itself to us, as when we contemplate the particular actions, as a play of puppets who are pulled after the ordinary manner by threads outside them; but from this point of view, as puppets that are set in motion by internal clockwork. For if, as we have done above, one compares the ceaseless, serious, and laborious striving of men with what they gain by it, nay, even with what they ever can gain, the disproportion we have pointed out becomes apparent, for one recognizes that that which is to be gained, taken as the motive power, is entirely insufficient for the explanation of that movement and that ceaseless striving. What, then, is a short postponement of death, a slight easing of misery or deferment of pain, a momentary stilling of desire, compared with such an abundant and certain victory over them all as death? What could such advantages accomplish taken as actual moving causes of a human race, innumerable because constantly renewed, which unceasingly moves, strives, struggles, grieves, writhes, and performs the whole tragi-comedy of the history of the world, nay, what says more than all, perseveres in such a mock-existence as long as each one possibly can? Clearly this is all inexplicable if we seek the moving causes outside the figures and conceive the human race as striving, in consequence of rational reflection, or something analogous to this (as moving threads), after those good things held out to it, the attainment of which would be a sufficient reward for its ceaseless cares and troubles. The matter being taken thus, everyone would rather have long ago said, "Le jeu ne vaut pas la chandelle," and have gone out. But, on the contrary, everyone guards and defends his life, like a precious pledge entrusted to him under heavy responsibility, under infinite cares and abundant misery, even under which life is tolerable. The wherefore and the why, the reward for this, certainly he does not see; but he has accepted the worth of that pledge without seeing it, upon trust and faith, and does not know what it consists in. Hence I have said that these puppets are not pulled from without, but each bears in itself the clockwork from which its movements result. This is the will to live, manifesting itself as an untiring machine, an irrational tendency, which has not its sufficient reason in the external world. It holds the individuals firmly upon the scene, and is the primum mobile of their movements; while the external objects, the motives, only determine their direction in the particular case; otherwise the cause would not be at all suitable to the effect. For, as every manifestation of a force of nature has a cause, but the force of nature itself none, so every particular act of will has a motive, but the will in general has none: indeed at bottom these two are one and the same. The will, as that which is metaphysical, is everywhere the boundary-stone of every investigation, beyond which it cannot go. We often see a miserable figure, deformed and shrunk with age, want, and disease, implore our help from the bottom of his heart for the prolongation of an existence, the end of which would necessarily appear altogether desirable if it were an objective judgment that determined here. Thus instead of this it is the blind will, appearing as the tendency to life, the love of life, and the sense of life; it is the same which makes the plants grow. This sense of life may be compared to a rope which is stretched above the puppet show of the world of men, and on which the puppets hang by invisible threads, while apparently they are supported only by the ground beneath them (the objective value of life). But if the rope becomes weak the puppet sinks; if it breaks the puppet must fall, for the ground beneath it only seemed to support it: i.e., the weakening of that love of life shows itself as hypochondria, spleen, melancholy: its entire exhaustion as the inclination to suicide. And as with the persistence in life, so is it also with its action and movement. This is not something freely chosen; but while everyone would really gladly rest, want and ennui are the whips that keep the top spinning. Therefore everything is in continual strain and forced movement, and the course of the world goes on, to use an expression of Aristotle's (De coelo ii. 13), "ου φυσει, αλλα βια" (motu, non naturali sed molento). Men are only apparently drawn from in front; really they are pushed from behind; it is not life that tempts them on, but necessity that drives them forward. The law of motivation is, like all causality, merely the form of the phenomenon.
Progress may be considered as the addition to the sum of accumulated experience, tradition, and technical devices organized for social efficiency. This is at once a definition of progress and of civilization, in which civilization is the sum of social efficiencies and progress consists of the units (additions) of which it is composed. Defined in these terms, progress turns out to be a relative, local, temporal, and secular phenomenon. It is possible, theoretically at least, to compare one community with another with respect to their relative efficiency and their relative progress in efficiency, just as we can compare one institution with another in respect to its efficiency and progress. It is even possible to measure the progress of humanity in so far as humanity can be said to be organized for social action.
(16) Morgan, Alexander. Education and Social Progress. Chaps. vi, ix-xxi. London and New York, 1916.
CHAPTER I
SOCIOLOGY AND THE SOCIAL SCIENCES[2]
I. SOCIOLOGY AND "SCIENTIFIC" HISTORY
Sociology first gained recognition as an independent science with the publication, between 1830 and 1842, of Auguste Comte's Cours de philosophie positive. Comte did not, to be sure, create sociology. He did give it a name, a program, and a place among the sciences.
Comte's program for the new science proposed an extension to politics and to history of the positive methods of the natural sciences. Its practical aim was to establish government on the secure foundation of an exact science and give to the predictions of history something of the precision of mathematical formulae.
We have to contemplate social phenomena as susceptible of prevision, like all other classes, within the limits of exactness compatible with their higher complexity. Comprehending the three characteristics of political science which we have been examining, prevision of social phenomena supposes, first, that we have abandoned the region of metaphysical idealities, to assume the ground of observed realities by a systematic subordination of imagination to observation; secondly, that political conceptions have ceased to be absolute, and have become relative to the variable state of civilization, so that theories, following the natural course of facts, may admit of our foreseeing them; and, thirdly, that permanent political action is limited by determinate laws, since, if social events were always exposed to disturbance by the accidental intervention of the legislator, human or divine, no scientific prevision of them would be possible. Thus, we may concentrate the conditions of the spirit of positive social philosophy on this one great attribute of scientific prevision.[3]
Comte proposed, in short, to make government a technical science and politics a profession. He looked forward to a time when legislation, based on a scientific study of human nature, would assume the character of natural law. The earlier and more elementary sciences, particularly physics and chemistry, had given man control over external nature; the last science, sociology, was to give man control over himself.
Men were long in learning that Man's power of modifying phenomena can result only from his knowledge of their natural laws; and in the infancy of each science, they believed themselves able to exert an unbounded influence over the phenomena of that science.... Social phenomena are, of course, from their extreme complexity, the last to be freed from this pretension: but it is therefore only the more necessary to remember that the pretension existed with regard to all the rest, in their earliest stage, and to anticipate therefore that social science will, in its turn, be emancipated from the delusion.... It [the existing social science] represents the social action of Man to be indefinite and arbitrary, as was once thought in regard to biological, chemical, physical, and even astronomical phenomena, in the earlier stages of their respective sciences.... The human race finds itself delivered over, without logical protection, to the ill-regulated experimentation of the various political schools, each one of which strives to set up, for all future time, its own immutable type of government. We have seen what are the chaotic results of such a strife; and we shall find that there is no chance of order and agreement but in subjecting social phenomena, like all others, to invariable natural laws, which shall, as a whole, prescribe for each period, with entire certainty, the limits and character of political action: in other words, introducing into the study of social phenomena the same positive spirit which has regenerated every other branch of human speculation.[4]
In the present anarchy of political opinion and parties, changes in the existing social order inevitably assume, he urged, the character, at the best, of a mere groping empiricism; at the worst, of a social convulsion like that of the French Revolution. Under the direction of a positive, in place of a speculative or, as Comte would have said, metaphysical science of society, progress must assume the character of an orderly march.
It was to be expected, with the extension of exact methods of investigation to other fields of knowledge, that the study of man and of society would become, or seek to become, scientific in the sense in which that word is used in the natural sciences. It is interesting, in this connection, that Comte's first name for sociology was social physics. It was not until he had reached the fourth volume of his Positive Philosophy that the word sociological is used for the first time.
Comte, if he was foremost, was not first in the search for a positive science of society, which would give man that control over men that he had over external nature. Montesquieu, in his The Spirit of Laws, first published in 1747, had distinguished in the organization of society, between form, "the particular structure," and the forces, "the human passions which set it in motion." In his preface to this first epoch-making essay in what Freeman calls "comparative politics," Montesquieu suggests that the uniformities, which he discovered beneath the wide variety of positive law, were contributions not merely to a science of law, but to a science of mankind.
I have first of all considered mankind; and the result of my thoughts has been, that amidst such an infinite diversity of laws and manners, they are not solely conducted by the caprice of fancy.[5]
Hume, likewise, put politics among the natural sciences.[6] Condorcet wanted to make history positive.[7] But there were, in the period between 1815 and 1840 in France, conditions which made the need of a new science of politics peculiarly urgent. The Revolution had failed and the political philosophy, which had directed and justified it, was bankrupt. France, between 1789 and 1815, had adopted, tried, and rejected no less than ten different constitutions. But during this period, as Saint-Simon noted, society, and the human beings who compose society, had not changed. It was evident that government was not, in any such sense as the philosophers had assumed, a mere artefact and legislative construction. Civilization, as Saint-Simon conceived it, was a part of nature. Social change was part of the whole cosmic process. He proposed, therefore, to make politics a science as positive as physics. The subject-matter of political science, as he conceived it, was not so much political forms as social conditions. History had been literature. It was destined to become a science.[8]
Comte called himself Saint-Simon's pupil. It is perhaps more correct to say Saint-Simon formulated the problem for which Comte, in his Positive Philosophy, sought a solution. It was Comte's notion that with the arrival of sociology the distinction which had so long existed, and still exists, between philosophy, in which men define their wishes, and natural science, in which they describe the existing order of nature, would disappear. In that case ideals would be defined in terms of reality, and the tragic difference between what men want and what is possible would be effaced. Comte's error was to mistake a theory of progress for progress itself. It is certainly true that as men learn what is, they will adjust their ideals to what is possible. But knowledge grows slowly.
Man's knowledge of mankind has increased greatly since 1842. Sociology, "the positive science of humanity," has moved steadily forward in the direction that Comte's program indicated, but it has not yet replaced history. Historians are still looking for methods of investigation which will make history "scientific."
No one who has watched the course of history during the last generation can have felt doubt of its tendency. Those of us who read Buckle's first volume when it appeared in 1857, and almost immediately afterwards, in 1859, read the Origin of Species and felt the violent impulse which Darwin gave to the study of natural laws, never doubted that historians would follow until they had exhausted every possible hypothesis to create a science of history. Year after year passed, and little progress has been made. Perhaps the mass of students are more skeptical now than they were thirty years ago of the possibility that such a science can be created. Yet almost every successful historian has been busy with it, adding here a new analysis, a new generalization there; a clear and definite connection where before the rupture of idea was absolute; and, above all, extending the field of study until it shall include all races, all countries, and all times. Like other branches of science, history is now encumbered and hampered by its own mass, but its tendency is always the same, and cannot be other than what it is. That the effort to make history a science may fail is possible, and perhaps probable; but that it should cease, unless for reasons that would cause all science to cease, is not within the range of experience. Historians will not, and even if they would they can not, abandon the attempt. Science itself would admit its own failure if it admitted that man, the most important of all its subjects, could not be brought within its range.[9]
Since Comte gave the new science of humanity a name and a point of view, the area of historical investigation has vastly widened and a number of new social sciences have come into existence—ethnology, archaeology, folklore, the comparative studies of cultural materials, i.e., language, mythology, religion, and law, and in connection with and closely related with these, folk-psychology, social psychology, and the psychology of crowds, which latter is, perhaps, the forerunner of a wider and more elaborate political psychology. The historians have been very much concerned with these new bodies of materials and with the new points of view which they have introduced into the study of man and of society. Under the influences of these sciences, history itself, as James Harvey Robinson has pointed out, has had a history. But with the innovations which the new history has introduced or attempted to introduce, it does not appear that there have been any fundamental changes in method or ideology in the science itself.
Fifty years have elapsed since Buckle's book appeared, and I know of no historian who would venture to maintain that we had made any considerable advance toward the goal he set for himself. A systematic prosecution of the various branches of social science, especially political economy, sociology, anthropology, and psychology, is succeeding in explaining many things; but history must always remain, from the standpoint of the astronomer, physicist, or chemist, a highly inexact and fragmentary body of knowledge.... History can no doubt be pursued in a strictly scientific spirit, but the data we possess in regard to the past of mankind are not of a nature to lend themselves to organization into an exact science, although, as we shall see, they may yield truths of vital importance.[10]
History has not become, as Comte believed it must, an exact science, and sociology has not taken its place in the social sciences. It is important, however, for understanding the mutations which have taken place in sociology since Comte to remember that it had its origin in an effort to make history exact. This, with, to be sure, considerable modifications, is still, as we shall see, an ambition of the science.
II. HISTORICAL AND SOCIOLOGICAL FACTS
Sociology, as Comte conceived it, was not, as it has been characterized, "a highly important point of view," but a fundamental science, i.e., a method of investigation and "a body of discoveries about mankind."[11] In the hierarchy of the sciences, sociology, the last in time, was first in importance. The order was as follows: mathematics, astronomy, physics, chemistry, biology including psychology, sociology. This order represented a progression from the more elementary to the more complex. It was because history and politics were concerned with the most complex of natural phenomena that they were the last to achieve what Comte called the positive character. They did this in sociology.
Many attempts have been made before and since Comte to find a satisfactory classification of the sciences. The order and relation of the sciences is still, in fact, one of the cardinal problems of philosophy. In recent years the notion has gained recognition that the difference between history and the natural sciences is not one of degree, but of kind; not of subject-matter merely, but of method. This difference in method is, however, fundamental. It is a difference not merely in the interpretation but in the logical character of facts.
Every historical fact, it is pointed out, is concerned with a unique event. History never repeats itself. If nothing else, the mere circumstance that every event has a date and location would give historical facts an individuality that facts of the abstract sciences do not possess. Because historical facts always are located and dated, and cannot therefore be repeated, they are not subject to experiment and verification. On the other hand, a fact not subject to verification is not a fact for natural science. History, as distinguished from natural history, deals with individuals, i.e., individual events, persons, institutions. Natural science is concerned, not with individuals, but with classes, types, species. All the assertions that are valid for natural science concern classes. An illustration will make this distinction clear.
Sometime in October, 1838, Charles Darwin happened to pick up and read Malthus' book on Population. The facts of "the struggle for existence," so strikingly presented in that now celebrated volume, suggested an explanation of a problem which had long interested and puzzled him, namely, the origin of species.
This is a statement of a historical fact, and the point is that it is not subject to empirical verification. It cannot be stated, in other words, in the form of a hypothesis, which further observation of other men of the same type will either verify or discredit.
On the other hand, in his Descent of Man, Darwin, discussing the rôle of sexual selection in evolution of the species, makes this observation: "Naturalists are much divided with respect to the object of the singing of birds. Few more careful observers ever lived than Montagu, and he maintained that the 'males of songbirds and of many others do not in general search for the female, but, on the contrary, their business in spring is to perch on some conspicuous spot, breathing out their full and amorous notes, which, by instinct, the female knows and repairs to the spot to choose her mate.'"
This is a typical statement of a fact of natural history. It is not, however, the rather vague generality of the statement that makes it scientific. It is its representative character, the character which makes it possible of verification by further observation which makes it a scientific fact.
It is from facts of this kind, collected, compared, and classified, irrespective of time or place, that the more general conclusions are drawn, upon which Darwin based his theory of the "descent of man." This theory, as Darwin conceived it, was not an interpretation of the facts but an explanation.
The relation between history and sociology, as well as the manner in which the more abstract social sciences have risen out of the more concrete, may be illustrated by a comparison between history and geography. Geography as a science is concerned with the visible world, the earth, its location in space, the distribution of the land masses, and of the plants, animals, and peoples upon its surface. The order, at least the fundamental order, which it seeks and finds among the objects it investigates is spatial. As soon as the geographer begins to compare and classify the plants, the animals, and the peoples with which he comes in contact, geography passes over into the special sciences, i.e., botany, zoölogy, and anthropology.
History, on the other hand, is concerned with a world of events. Not everything that happened, to be sure, is history, but every event that ever was or ever will be significant is history.
Geography attempts to reproduce for us the visible world as it exists in space; history, on the contrary, seeks to re-create for us in the present the significance of the past. As soon as historians seek to take events out of their historical setting, that is to say, out of their time and space relations, in order to compare them and classify them; as soon as historians begin to emphasize the typical and representative rather than the unique character of events, history ceases to be history and becomes sociology.
The differences here indicated between history and sociology are based upon a more fundamental distinction between the historical and the natural sciences first clearly defined by Windelband, the historian of philosophy, in an address to the faculty of the University of Strassburg in 1894.
The distinction between natural science and history begins at the point where we seek to convert facts into knowledge. Here again we observe that the one (natural science) seeks to formulate laws, the other (history) to portray events. In the one case thought proceeds from the description of particulars to the general relations. In the other case it clings to a genial depiction of the individual object or event. For the natural scientist the object of investigation which cannot be repeated never has, as such, scientific value. It serves his purpose only so far as it may be regarded as a type or as a special instance of a class from which the type may be deduced. The natural scientist considers the single case only so far as he can see in it the features which serve to throw light upon a general law. For the historian the problem is to revive and call up into the present, in all its particularity, an event in the past. His aim is to do for an actual event precisely what the artist seeks to do for the object of his imagination. It is just here that we discern the kinship between history and art, between the historian and the writer of literature. It is for this reason that natural science emphasized the abstract; the historian, on the other hand, is interested mainly in the concrete.
The fact that natural science emphasizes the abstract and history the concrete will become clearer if we compare the results of the researches of the two sciences. However finespun the conceptions may be which the historical critic uses in working over his materials, the final goal of such study is always to create out of the mass of events a vivid portrait of the past. And what history offers us is pictures of men and of human life, with all the wealth of their individuality, reproduced in all their characteristic vivacity. Thus do the peoples and languages of the past, their forms and beliefs, their struggles for power and freedom, speak to us through the mouth of history.
How different it is with the world which the natural sciences have created for us! However concrete the materials with which they started, the goal of these sciences is theories, eventually mathematical formulations of laws of change. Treating the individual, sensuous, changing objects as mere unsubstantial appearances (phenomena), scientific investigation becomes a search for the universal laws which rule the timeless changes of events. Out of this colorful world of the senses, science creates a system of abstract concepts, in which the true nature of things is conceived to exist—a world of colorless and soundless atoms, despoiled of all their earthly sensuous qualities. Such is the triumph of thought over perception. Indifferent to change, science casts her anchor in the eternal and unchangeable. Not the change as such but the unchanging form of change is what she seeks.
This raises the question: What is the more valuable for the purposes of knowledge in general, a knowledge of law or a knowledge of events? As far as that is concerned, both scientific procedures may be equally justified. The knowledge of the universal laws has everywhere a practical value in so far as they make possible man's purposeful intervention in the natural processes. That is quite as true of the movements of the inner as of the outer world. In the latter case knowledge of nature's laws has made it possible to create those tools through which the control of mankind over external nature is steadily being extended.
Not less for the purposes of the common life are we dependent upon the results of historical knowledge. Man is, to change the ancient form of the expression, the animal who has a history. His cultural life rests on the transmission from generation to generation of a constantly increasing body of historical memories. Whoever proposes to take an active part in this cultural process must have an understanding of history. Wherever the thread is once broken—as history itself proves—it must be painfully gathered up and knitted again into the historical fabric.
It is, to be sure, true that it is an economy for human understanding to be able to reduce to a formula or a general concept the common characteristics of individuals. But the more man seeks to reduce facts to concepts and laws, the more he is obliged to sacrifice and neglect the individual. Men have, to be sure, sought, in characteristic modern fashion, "to make of history a natural science." This was the case with the so-called philosophy of history of positivism. What has been the net result of the laws of history which it has given us? A few trivial generalities which justify themselves only by the most careful consideration of their numerous exceptions.
On the other hand it is certain that all interest and values of life are concerned with what is unique in men and events. Consider how quickly our appreciation is deadened as some object is multiplied or is regarded as one case in a thousand. "She is not the first" is one of the cruel passages in Faust. It is in the individuality and the uniqueness of an object that all our sense of value has its roots. It is upon this fact that Spinoza's doctrine of the conquest of the passions by knowledge rests, since for him knowledge is the submergence of the individual in the universal, the "once for all" into the eternal.
The fact that all our livelier appreciations rest upon the unique character of the object is illustrated above all in our relations to persons. Is it not an unendurable thought, that a loved object, an adored person, should have existed at some other time in just the form in which it now exists for us? Is it not horrible and unthinkable that one of us, with just this same individuality should actually have existed in a second edition?
What is true of the individual man is quite as true of the whole historical process: it has value only when it is unique. This is the principle which the Christian doctrine successfully maintained, as over against Hellenism in the Patristic philosophy. The middle point of their conception of the world was the fall and the salvation of mankind as a unique event. That was the first and great perception of the inalienable metaphysical right of the historian to preserve for the memory of mankind, in all their uniqueness and individuality, the actual events of life.[12]
Like every other species of animal, man has a natural history. Anthropology is the science of man considered as one of the animal species, Homo sapiens. History and sociology, on the other hand, are concerned with man as a person, as a "political animal," participating with his fellows in a common fund of social traditions and cultural ideals. Freeman, the English historian, said that history was "past politics" and politics "present history." Freeman uses the word politics in the large and liberal sense in which it was first used by Aristotle. In that broad sense of the word, the political process, by which men are controlled and states governed, and the cultural process, by which man has been domesticated and human nature formed, are not, as we ordinarily assume, different, but identical, procedures.
All this suggests the intimate relations which exist between history, politics, and sociology. The important thing, however, is not the identities but the distinctions. For, however much the various disciplines may, in practice, overlap, it is necessary for the sake of clear thinking to have their limits defined. As far as sociology and history are concerned the differences may be summed up in a word. Both history and sociology are concerned with the life of man as man. History, however, seeks to reproduce and interpret concrete events as they actually occurred in time and space. Sociology, on the other hand, seeks to arrive at natural laws and generalizations in regard to human nature and society, irrespective of time and of place.
In other words, history seeks to find out what actually happened and how it all came about. Sociology, on the other hand, seeks to explain, on the basis of a study of other instances, the nature of the process involved.
By nature we mean just that aspect and character of things in regard to which it is possible to make general statements and formulate laws. If we say, in explanation of the peculiar behavior of some individual, that it is natural or that it is after all "simply human nature," we are simply saying that this behavior is what we have learned to expect of this individual or of human beings in general. It is, in other words, a law.
Natural law, as the term is used here, is any statement which describes the behavior of a class of objects or the character of a class of acts. For example, the classic illustration of the so-called "universal proposition" familiar to students of formal logic, "all men are mortal," is an assertion in regard to a class of objects we call men. This is, of course, simply a more formal way of saying that "men die." Such general statements and "laws" get meaning only when they are applied to particular cases, or, to speak again in the terms of formal logic, when they find a place in a syllogism, thus: "Men are mortal. This is a man." But such syllogisms may always be stated in the form of a hypothesis. If this is a man, he is mortal. If a is b, a is also c. This statement, "Human nature is a product of social contact," is a general assertion familiar to students of sociology. This law or, more correctly, hypothesis, applied to an individual case explains the so-called feral man. Wild men, in the proper sense of the word, are not the so-called savages, but the men who have never been domesticated, of which an individual example is now and then discovered.
To state a law in the form of a hypothesis serves to emphasize the fact that laws—what we have called natural laws at any rate—are subject to verification and restatement. Under the circumstances the exceptional instance, which compels a restatement of the hypothesis, is more important for the purposes of science than other instances which merely confirm it.
Any science which operates with hypotheses and seeks to state facts in such a way that they can be compared and verified by further observation and experiment is, so far as method is concerned, a natural science.
III. HUMAN NATURE AND LAW
One thing that makes the conception of natural history and natural law important to the student of sociology is that in the field of the social sciences the distinction between natural and moral law has from the first been confused. Comte and the social philosophers in France after the Revolution set out with the deliberate purpose of superseding legislative enactments by laws of human nature, laws which were to be positive and "scientific." As a matter of fact, sociology, in becoming positive, so far from effacing, has rather emphasized the distinctions that Comte sought to abolish. Natural law may be distinguished from all other forms of law by the fact that it aims at nothing more than a description of the behavior of certain types or classes of objects. A description of the way in which a class, i.e., men, plants, animals, or physical objects, may be expected under ordinary circumstances to behave, tells us what we may in a general way expect of any individual member of that class. If natural science seeks to predict, it is able to do so simply because it operates with concepts or class names instead, as is the case with history, with concrete facts and, to use a logical phrase, "existential propositions."
That the chief end of science is descriptive formulation has probably been clear to keen analytic minds since the time of Galileo, especially to the great discoverers in astronomy, mechanics, and dynamics. But as a definitely stated conception, corrective of misunderstandings, the view of science as essentially descriptive began to make itself felt about the beginning of the last quarter of the nineteenth century, and may be associated with the names of Kirchhoff and Mach. It was in 1876 that Kirchhoff defined the task of mechanics as that of "describing completely and in the simplest manner the motions which take place in nature." Widening this a little, we may say that the aim of science is to describe natural phenomena and occurrences as exactly as possible, as simply as possible, as completely as possible, as consistently as possible, and always in terms which are communicable and verifiable. This is a very different rôle from that of solving the riddles of the universe, and it is well expressed in what Newton said in regard to the law of gravitation: "So far I have accounted for the phenomena presented to us by the heavens and the sea by means of the force of gravity, but I have as yet assigned no cause to this gravity.... I have not been able to deduce from phenomena the raison d'être of the properties of gravity and I have not set up hypotheses." (Newton, Philosophiae naturalis principia Mathematica, 1687.)
"We must confess," said Prof. J. H. Poynting (1900, p. 616), "that physical laws have greatly fallen off in dignity. No long time ago they were quite commonly described as the Fixed Laws of Nature, and were supposed sufficient in themselves to govern the universe. Now we can only assign to them the humble rank of mere descriptions, often erroneous, of similarities which we believe we have observed.... A law of nature explains nothing, it has no governing power, it is but a descriptive formula which the careless have sometimes personified." It used to be said that "the laws of Nature are the thoughts of God"; now we say that they are the investigator's formulae summing up regularities of recurrence.[13]
If natural law aims at prediction it tells us what we can do. Moral laws, on the other hand, tell us, not what we can, but what we ought to do. The civil or municipal law, finally, tells us not what we can, nor what we ought, but what we must do. It is very evident that these three types of law may be very intimately related. We do not know what we ought to do until we know what we can do; and we certainly should consider what men can do before we pass laws prescribing what they must do. There is, moreover, no likelihood that these distinctions will ever be completely abolished. As long as the words "can," "ought," and "must" continue to have any meaning for us the distinctions that they represent will persist in science as well as in common sense.
The immense prestige which the methods of the natural sciences have gained, particularly in their application to the phenomena of the physical universe, has undoubtedly led scientific men to overestimate the importance of mere conceptual and abstract knowledge. It has led them to assume that history also must eventually become "scientific" in the sense of the natural sciences. In the meantime the vast collections of historical facts which the industry of historical students has accumulated are regarded, sometimes even by historians themselves, as a sort of raw material, the value of which can only be realized after it has been worked over into some sort of historical generalization which has the general character of scientific and ultimately, mathematical formula.
"History," says Karl Pearson, "can never become science, can never be anything but a catalogue of facts rehearsed in a more or less pleasing language until these facts are seen to fall into sequences which can be briefly resumed in scientific formulae."[14] And Henry Adams, in a letter to the American Historical Association already referred to, confesses that history has thus far been a fruitless quest for "the secret which would transform these odds and ends of philosophy into one self-evident, harmonious, and complete system."
You may be sure that four out of five serious students of history who are living today have, in the course of their work, felt that they stood on the brink of a great generalization that would reduce all history under a law as clear as the laws which govern the material world. As the great writers of our time have touched one by one the separate fragments of admitted law by which society betrays its character as a subject for science, not one of them can have failed to feel an instant's hope that he might find the secret which would transform these odds and ends of philosophy into one self-evident, harmonious, and complete system. He has seemed to have it, as the Spanish say, in his inkstand. Scores of times he must have dropped his pen to think how one short step, one sudden inspiration, would show all human knowledge; how, in these thickset forests of history, one corner turned, one faint trail struck, would bring him on the highroad of science. Every professor who has tried to teach the doubtful facts which we now call history must have felt that sooner or later he or another would put order in the chaos and bring light into darkness. Not so much genius or favor was needed as patience and good luck. The law was certainly there, and as certainly was in places actually visible, to be touched and handled, as though it were a law of chemistry or physics. No teacher with a spark of imagination or with an idea of scientific method can have helped dreaming of the immortality that would be achieved by the man who should successfully apply Darwin's method to the facts of human history.[15]
The truth is, however, that the concrete facts, in which history and geography have sought to preserve the visible, tangible, and, generally speaking, the experiential aspects of human life and the visible universe, have a value irrespective of any generalization or ideal constructions which may be inferred from or built up out of them. Just as none of the investigations or generalizations of individual psychology are ever likely to take the place of biography and autobiography, so none of the conceptions of an abstract sociology, no scientific descriptions of the social and cultural processes, and no laws of progress are likely, in the near future at any rate, to supersede the more concrete facts of history in which are preserved those records of those unique and never fully comprehended aspects of life which we call events.
It has been the dream of philosophers that theoretical and abstract science could and some day perhaps would succeed in putting into formulae and into general terms all that was significant in the concrete facts of life. It has been the tragic mistake of the so-called intellectuals, who have gained their knowledge from textbooks rather than from observation and research, to assume that science had already realized its dream. But there is no indication that science has begun to exhaust the sources or significance of concrete experience. The infinite variety of external nature and the inexhaustible wealth of personal experience have thus far defied, and no doubt will continue to defy, the industry of scientific classification, while, on the other hand, the discoveries of science are constantly making accessible to us new and larger areas of experience.
What has been said simply serves to emphasize the instrumental character of the abstract sciences. History and geography, all of the concrete sciences, can and do measurably enlarge our experience of life. Their very purpose is to arouse new interests and create new sympathies; to give mankind, in short, an environment so vast and varied as will call out and activate all his instincts and capacities.
The more abstract sciences, just to the extent that they are abstract and exact, like mathematics and logic, are merely methods and tools for converting experience into knowledge and applying the knowledge so gained to practical uses.
IV. HISTORY, NATURAL HISTORY, AND SOCIOLOGY
Although it is possible to draw clear distinctions in theory between the purpose and methods of history and sociology, in practice the two forms of knowledge pass over into one another by almost imperceptible gradations.
The sociological point of view makes its appearance in historical investigation as soon as the historian turns from the study of "periods" to the study of institutions. The history of institutions, that is to say, the family, the church, economic institutions, political institutions, etc., leads inevitably to comparison, classification, the formation of class names or concepts, and eventually to the formulation of law. In the process, history becomes natural history, and natural history passes over into natural science. In short, history becomes sociology.
Westermarck's History of Human Marriage is one of the earliest attempts to write the natural history of a social institution. It is based upon a comparison and classification of marriage customs of widely scattered peoples, living under varied physical and social conditions. What one gets from a survey of this kind is not so much history as a study of human behavior. The history of marriage, as of any other institution, is, in other words, not so much an account of what certain individuals or groups of individuals did at certain times and certain places, as it is a description of the responses of a few fundamental human instincts to a variety of social situations. Westermarck calls this kind of history sociology.[16]
It is in the firm conviction that the history of human civilization should be made an object of as scientific a treatment as the history of organic nature that I write this book. Like the phenomena of physical and psychical life those of social life should be classified into certain groups and each group investigated with regard to its origin and development. Only when treated in this way can history lay claim to the rank and honour of a science in the highest sense of the term, as forming an important part of Sociology, the youngest of the principal branches of learning.
Descriptive historiography has no higher object than that of offering materials to this science.[17]
Westermarck refers to the facts which he has collected in his history of marriage as phenomena. For the explanation of these phenomena, however, he looks to the more abstract sciences.
The causes on which social phenomena are dependent fall within the domain of different sciences—Biology, Psychology, or Sociology. The reader will find that I put particular stress upon the psychological causes, which have often been deplorably overlooked, or only imperfectly touched upon. And more especially do I believe that the mere instincts have played a very important part in the origin of social institutions and rules.[18]
Westermarck derived most of his materials for the study of marriage from ethnological materials. Ethnologists, students of folklore (German Völkerkunde), and archaeology are less certain than the historians of institutions whether their investigations are historical or sociological.
Jane Harrison, although she disclaims the title of sociologist, bases her conception of the origin of Greek religion on a sociological theory, the theory namely that "among primitive peoples religion reflects collective feeling and collective thinking." Dionysius, the god of the Greek mysteries, is according to her interpretation a product of the group consciousness.
The mystery-god arises out of those instincts, emotions, desires which attend and express life; but these emotions, desires, instincts, in so far as they are religious, are at the outset rather of a group than of individual consciousness.... It is a necessary and most important corollary to this doctrine, that the form taken by the divinity reflects the social structure of the group to which the divinity belongs. Dionysius is the Son of his Mother because he issues from a matrilinear group.[19]
This whole study is, in fact, merely an application of Durkheim's conception of "collective representations."
Robert H. Lowie, in his recent volume, Primitive Society, refers to "ethnologists and other historians," but at the same time asks: "What kind of an historian shall the ethnologist be?"
He answers the question by saying that, "If there are laws of social evolution, he [the ethnologist] must assuredly discover them," but at any rate, and first of all, "his duty is to ascertain the course civilization has actually followed.... To strive for the ideals of another branch of knowledge may be positively pernicious, for it can easily lead to that factitious simplification which means falsification."
In other words, ethnology, like history, seeks to tell what actually happened. It is bound to avoid abstraction, "over-simplification," and formulae, and these are the ideals of another kind of scientific procedure. As a matter of fact, however, ethnology, even when it has attempted nothing more than a description of the existing cultures of primitive peoples, their present distribution and the order of their succession, has not freed itself wholly from the influence of abstract considerations. Theoretical problems inevitably arise for the solution of which it is necessary to go to psychology and sociology. One of the questions that has arisen in the study, particularly the comparative study, of cultures is: how far any existing cultural trait is borrowed and how far it is to be regarded as of independent origin.
[2] From Robert E. Park, "Sociology and the Social Sciences," American Journal of Sociology, XXVI (1920-21), 401-24; XXVII (1921-22), 1-21; 169-83.
[3] Harriet Martineau, The Positive Philosophy of Auguste Comte, freely translated and condensed (London, 1893), II, 61.
[4] Harriet Martineau, op. cit., II, 59-61.
[5] Montesquieu, Baron M. de Secondat, The Spirit of Laws, translated by Thomas Nugent (Cincinnati, 1873), I, xxxi.
[6] David Hume, Inquiry Concerning Human Understanding, Part II, sec. 7.
[7] Condorcet, Esquisse d'un tableau historique des progrès de l'esprit humain (1795), 292. See Paul Barth, Die Philosophie der Geschichte als Sociologie (Leipzig, 1897), Part I, pp. 21-23.
[8] Œuvres de Saint-Simon et d'Enfantin (Paris, 1865-78), XVII, 228. Paul Barth, op. cit., Part I, p. 23.
[9] Henry Adams, The Degradation of the Democratic Dogma (New York, 1919), p. 126.
[10] James Harvey Robinson, The New History, Essays Illustrating the Modern Historical Outlook (New York, 1912), pp. 54-55.
[11] James Harvey Robinson, op. cit., p. 83.
[12] Wilhelm Windelband, Geschichte und Naturwissenschaft, Rede zum Antritt des Rectorats der Kaiser-Wilhelms Universität Strassburg (Strassburg, 1900). The logical principle outlined by Windelband has been further elaborated by Heinrich Rickert in Die Grenzen der naturwissenschaftlichen Begriffsbildung, eine logische Einleitung in die historischen Wissenschaften (Tübingen u. Leipzig, 1902). See also Georg Simmel, Die Probleme der Geschichtsphilosophie, eine erkenntnistheoretische Studie (2d ed., Leipzig, 1915).
[13] J. Arthur Thomson, The System of Animate Nature (New York, 1920), pp. 8-9. See also Karl Pearson, The Grammar of Science (2d ed.; London, 1900), chap. iii, "The Scientific Law."
[14] Karl Pearson, op. cit., p. 359.
[15] Henry Adams, op. cit., p. 127.
[16] Professor Robertson Smith (Nature, XLIV, 270), criticizing Westermarck's History of Human Marriage, complains that the author has confused history with natural history. "The history of an institution," he writes, "which is controlled by public opinion and regulated by law is not natural history. The true history of marriage begins where the natural history of pairing ends.... To treat these topics (polyandry, kinship through the female only, infanticide, exogamy) as essentially a part of the natural history of pairing involves a tacit assumption that the laws of society are at bottom mere formulated instincts, and this assumption really underlies all our author's theories. His fundamental position compels him, if he will be consistent with himself, to hold that every institution connected with marriage that has universal validity, or forms an integral part of the main line of development, is rooted in instinct, and that institutions which are not based on instinct are necessarily exceptional and unimportant for scientific history."
[17] Edward Westermarck, The History of Human Marriage (London, 1901), p. 1.
[18] Ibid., p. 5.
[19] Jane Ellen Harrison, Themis, A Study of the Social Origins of Greek Religion (Cambridge, 1912), p. ix.
In the historical reconstruction of culture the phenomena of distribution play, indeed, an extraordinary part. If a trait occurs everywhere, it might veritably be the product of some universally operative social law. If it is found in a restricted number of cases, it may still have evolved through some such instrumentality acting under specific conditions that would then remain to be determined by analysis of the cultures in which the feature is embedded.... Finally, the sharers of a cultural trait may be of distinct lineage but through contact and borrowing have come to hold in common a portion of their cultures....
Since, as a matter of fact, cultural resemblances abound between peoples of diverse stock, their interpretation commonly narrows to a choice between two alternatives. Either they are due to like causes, whether these can be determined or not; or they are the result of borrowing. A predilection for one or the other explanation has lain at the bottom of much ethnological discussion in the past; and at present influential schools both in England and in continental Europe clamorously insist that all cultural parallels are due to diffusion from a single center. It is inevitable to envisage this moot-problem at the start, since uncompromising championship of either alternative has far-reaching practical consequences. For if every parallel is due to borrowing, then sociological laws, which can be inferred only from independently developing likenesses, are barred. Then the history of religion or social life or technology consists exclusively in a statement of the place of origin of beliefs, customs and implements, and a recital of their travels to different parts of the globe. On the other hand, if borrowing covers only part of the observed parallels, an explanation from like causes becomes at least the ideal goal in an investigation of the remainder.[20]
An illustration will exhibit the manner in which problems originally historical become psychological and sociological. Tyler in his Early History of Mankind has pointed out that the bellows used by the negro blacksmiths of continental Africa are of a quite different type from those used by natives of Madagascar. The bellows used by the Madagascar blacksmiths, on the other hand, are exactly like those in use by the Malays of Sumatra and in other parts of the Malay Archipelago. This indication that the natives of Madagascar are of Malay origin is in accordance with other anthropological and ethnological data in regard to these peoples, which prove the fact, now well established, that they are not of African origin.
Similarly Boas' study of the Raven cycle of American Indian mythology indicated that these stories originated in the northern part of British Columbia and traveled southward along the coast. One of the evidences of the direction of this progress is the gradual diminution of complexity in the stories as they traveled into regions farther removed from the point of origin.
All this, in so far as it seeks to determine the point of origin, direction, speed, and character of changes that take place in cultural materials in the process of diffusion, is clearly history and ethnology.
Other questions, however, force themselves inevitably upon the attention of the inquiring student. Why is it that certain cultural materials are more widely and more rapidly diffused than others? Under what conditions does this diffusion take place and why does it take place at all? Finally, what is the ultimate source of customs, beliefs, languages, religious practices, and all the varied technical devices which compose the cultures of different peoples? What are the circumstances and what are the processes by which cultural traits are independently created? Under what conditions do cultural fusions take place and what is the nature of this process?
These are all fundamentally problems of human nature, and as human nature itself is now regarded as a product of social intercourse, they are problems of sociology.
The cultural processes by which languages, myth, and religion have come into existence among primitive peoples have given rise in Germany to a special science. Folk-psychology (Völkerpsychologie) had its origin in an attempt to answer in psychological terms the problems to which a comparative study of cultural materials has given rise.
From two different directions ideas of folk-psychology have found their way into modern science. First of all there was a demand from the different social sciences [Geisteswissenschaften] for a psychological explanation of the phenomena of social life and history, so far as they were products of social [geistiger] interaction. In the second place, psychology itself required, in order to escape the uncertainties and ambiguities of pure introspection, a body of objective materials.
Among the social sciences the need for psychological interpretation first manifested itself in the studies of language and mythology. Both of these had already found outside the circle of the philological studies independent fields of investigation. As soon as they assumed the character of comparative sciences it was inevitable that they should be driven to recognize that in addition to the historical conditions, which everywhere determines the concrete form of these phenomena, there had been certain fundamental psychical forces at work in the development of language and myth.[21]
The aim of folk-psychology has been, on the whole, to explain the genesis and development of certain cultural forms, i.e., language, myth, and religion. The whole matter may, however, be regarded from a quite different point of view. Gabriel Tarde, for example, has sought to explain, not the genesis, but the transmission and diffusion of these same cultural forms. For Tarde, communication (transmission of cultural forms and traits) is the one central and significant fact of social life. "Social" is just what can be transmitted by imitation. Social groups are merely the centers from which new ideas and inventions are transmitted. Imitation is the social process.
There is not a word that you say, which is not the reproduction, now unconscious, but formerly conscious and voluntary, of verbal articulations reaching back to the most distant past, with some special accent due to your immediate surroundings. There is not a religious rite that you fulfil, such as praying, kissing the icon, or making the sign of the cross, which does not reproduce certain traditional gestures and expressions, established through imitation of your ancestors. There is not a military or civil requirement that you obey, nor an act that you perform in your business, which has not been taught you, and which you have not copied from some living model. There is not a stroke of the brush that you make, if you are a painter, nor a verse that you write, if you are a poet, which does not conform to the customs or the prosody of your school, and even your very originality itself is made up of accumulated commonplaces, and aspires to become commonplace in its turn.
Thus, the unvarying characteristic of every social fact whatsoever is that it is imitative. And this characteristic belongs exclusively to social facts.[22]
Tarde's theory of transmission by imitation may be regarded, in some sense, as complementary, if not supplementary, to Wundt's theory of origins, since he puts the emphasis on the fact of transmission rather than upon genesis. In a paper, "Tendencies in Comparative Philology," read at the Congress of Arts and Sciences at the St. Louis Exposition in 1904, Professor Hanns Oertel, of Yale University, refers to Tarde's theory of imitation as an alternative explanation to that offered by Wundt for "the striking uniformity of sound changes" which students of language have discovered in the course of their investigation of phonetic changes in widely different forms of speech.
It seems hard to maintain that the change in a syntactical construction or in the meaning of a word owes its universality to a simultaneous and independent primary change in all the members of a speech-community. By adopting the theory of imitative spread, all linguistic changes may be viewed as one homogeneous whole. In the second place, the latter view seems to bring linguistic changes into line with the other social changes, such as modifications in institutions, beliefs, and customs. For is it not an essential characteristic of a social group that its members are not co-operative in the sense that each member actively participates in the production of every single element which goes to make up either language, or belief, or customs? Distinguishing thus between primary and secondary changes and between the origin of a change and its spread, it behooves us to examine carefully into the causes which make the members of a social unit, either consciously or unconsciously, willing to accept the innovation. What is it that determines acceptance or rejection of a particular change? What limits one change to a small area, while it extends the area of another? Before a final decision can be reached in favor of the second theory of imitative spread it will be necessary to follow out in minute detail the mechanism of this process in a number of concrete instances; in other words to fill out the picture of which Tarde (Les lois de l'imitation) sketched the bare outlines. If his assumptions prove true, then we should have here a uniformity resting upon other causes than the physical uniformity that appears in the objects with which the natural sciences deal. It would enable us to establish a second group of uniform phenomena which is psycho-physical in its character and rests upon the basis of social suggestion. The uniformities in speech, belief, and institutions would belong to this second group.[23]
What is true of the comparative study of languages is true in every other field in which a comparative study of cultural materials has been made. As soon as these materials are studied from the point of view of their similarities rather than from the point of view of their historical connections, problems arise which can only be explained by the more abstract sciences of psychology or sociology. Freeman begins his lectures on Comparative Politics with the statement that "the comparative method of study has been the greatest intellectual achievement of our time. It has carried light and order into whole branches of human knowledge which before were shrouded in darkness and confusion. It has brought a line of argument which reaches moral certainty into a region which before was given over to random guess-work. Into matters which are for the most part incapable of strictly external proof it has brought a form of strictly internal proof which is more convincing, more unerring."
Wherever the historian supplements external by internal proof, he is in a way to substitute a sociological explanation for historical interpretation. It is the very essence of the sociological method to be comparative. When, therefore, Freeman uses, in speaking of comparative politics, the following language he is speaking in sociological rather than historical terms:
For the purposes then of the study of Comparative Politics, a political constitution is a specimen to be studied, classified, and labelled, as a building or an animal is studied, classified, and labelled by those to whom buildings or animals are objects of study. We have to note the likenesses, striking and unexpected as those likenesses often are, between the political constitutions of remote times and places; and we have, as far as we can, to classify our specimens according to the probable causes of those likenesses.[24]
Historically sociology has had its origin in history. It owes its existence as a science to the attempt to apply exact methods to the explanation of historical facts. In the attempt to achieve this, however, it has become something quite different from history. It has become like psychology with which it is most intimately related, a natural and relatively abstract science, and auxiliary to the study of history, but not a substitute for it. The whole matter may be summed up in this general statement: history interprets, natural science explains. It is upon the interpretation of the facts of experience that we formulate our creeds and found our faiths. Our explanations of phenomena, on the other hand, are the basis for technique and practical devices for controlling nature and human nature, man and the physical world.
V. THE SOCIAL ORGANISM: HUMANITY OR LEVIATHAN?
After Comte the first great name in the history of sociology is Spencer. It is evident in comparing the writings of these two men that, in crossing the English Channel, sociology has suffered a sea change. In spite of certain similarities in their points of view there are profound and interesting differences. These differences exhibit themselves in the different ways in which they use the term "social organism."
Comte calls society a "collective organism" and insists, as Spencer does, upon the difference between an organism like a family, which is made up of independent individuals, and an organism like a plant or an animal, which is a physiological unit in which the different organs are neither free nor conscious. But Spencer, if he points out the differences between the social and the biological organisms, is interested in the analogy. Comte, on the other hand, while he recognizes the analogy, feels it important to emphasize the distinctions.
Society for Comte is not, as Lévy-Bruhl puts it, "a polyp." It has not even the characteristics of an animal colony in which the individuals are physically bound together, though physiologically independent. On the contrary, "this 'immense organism' is especially distinguished from other beings in that it is made up of separable elements of which each one can feel its own co-operation, can will it, or even withhold it, so long as it remains a direct one."[25]
On the other hand, Comte, although he characterized the social consensus and solidarity as "collective," nevertheless thought of the relations existing between human beings in society—in the family, for example, which he regards as the unit and model of all social relations—as closer and more intimate than those which exist between the organs of a plant or an animal. The individual, as Comte expressed it, is an abstraction. Man exists as man only by participation in the life of humanity, and "although the individual elements of society appear to be more separable than those of a living being, the social consensus is still closer than the vital."[26]
Thus the individual man was, in spite of his freedom and independence, in a very real sense "an organ of the Great Being" and the great being was humanity. Under the title of humanity Comte included not merely all living human beings, i.e., the human race, but he included all that body of tradition, knowledge, custom, cultural ideas and ideals, which make up the social inheritance of the race, an inheritance into which each of us is born, to which we contribute, and which we inevitably hand on through the processes of education and tradition to succeeding generations. This is what Comte meant by the social organism.
If Comte thought of the social organism, the great being, somewhat mystically as itself an individual and a person, Herbert Spencer, on the other hand, thought of it realistically as a great animal, a leviathan, as Hobbes called it, and a very low-order leviathan at that.[27]
Spencer's manner of looking at the social organism may be illustrated in what he says about growth in "social aggregates."
When we say that growth is common to social aggregates and organic aggregates, we do not thus entirely exclude community with inorganic aggregates. Some of these, as crystals, grow in a visible manner; and all of them on the hypothesis of evolution, have arisen by integration at some time or other. Nevertheless, compared with things we call inanimate, living bodies and societies so conspicuously exhibit augmentation of mass, that we may fairly regard this as characterizing them both. Many organisms grow throughout their lives; and the rest grow throughout considerable parts of their lives. Social growth usually continues either up to times when the societies divide, or up to times when they are overwhelmed.
Here, then, is the first trait by which societies ally themselves with the organic world and substantially distinguish themselves from the inorganic world.[28]
In this same way, comparing the characteristic general features of "social" and "living bodies," noting likeness and differences, particularly with reference to complexity of structure, differentiation of function, division of labor, etc., Spencer gives a perfectly naturalistic account of the characteristic identities and differences between societies and animals, between sociological and biological organizations. It is in respect to the division of labor that the analogy between societies and animals goes farthest and is most significant.
This division of labour, first dwelt upon by political economists as a social phenomenon, and thereupon recognized by biologists as a phenomenon of living bodies, which they called the "physiological division of labour," is that which in the society, as in the animal, makes it a living whole. Scarcely can I emphasize enough the truth that in respect of this fundamental trait, a social organism and an individual organism are entirely alike.[29]
The "social aggregate," although it is "discrete" instead of "concrete"—that is to say, composed of spatially separated units—is nevertheless, because of the mutual dependence of these units upon one another as exhibited in the division of labor, to be regarded as a living whole. It is "a living whole" in much the same way that the plant and animal communities, of which the ecologists are now writing so interestingly, are a living whole; not because of any intrinsic relations between the individuals who compose them, but because each individual member of the community, finds in the community as a whole, a suitable milieu, an environment adapted to his needs and one to which he is able to adapt himself.
Of such a society as this it may indeed be said, that it "exists for the benefit of its members, not its members for the benefit of society. It has ever to be remembered that great as may be the efforts made for the prosperity of the body politic, yet the claims of the body politic are nothing in themselves, and become something only in so far as they embody the claims of its component individuals."[30]
In other words, the social organism, as Spencer sees it, exists not for itself but for the benefit of the separate organs of which it is composed, whereas, in the case of biological organism the situation is reversed. There the parts manifestly exist for the whole and not the whole for the parts.
Spencer explains this paradoxical conclusion by the reflection that in social organisms sentience is not localized as it is in biological organisms. This is, in fact, the cardinal difference between the two. There is no social sensorium.
In the one (the individual), consciousness is concentrated in a small part of the aggregate. In the other (society), it is diffused throughout the aggregate: all the units possess the capacities for happiness and misery, if not in equal degrees, still in degrees that approximate. As then, there is no social sensorium, the welfare of the aggregate, considered apart from that of the units, is not an end to be sought. The society exists for the benefit of its members; not its members for the benefit of the society.[31]
The point is that society, as distinct from the individuals who compose it, has no apparatus for feeling pain or pleasure. There are no social sensations. Perceptions and mental imagery are individual and not social phenomena. Society lives, so to speak, only in its separate organs or members, and each of these organs has its own brain and organ of control which gives it, among other things, the power of independent locomotion. This is what is meant when society is described as a collectivity.
VI. SOCIAL CONTROL AND SCHOOLS OF THOUGHT
The fundamental problem which Spencer's paradox raises is that of social control. How does a mere collection of individuals succeed in acting in a corporate and consistent way? How in the case of specific types of social group, for example an animal herd, a boys' gang, or a political party, does the group control its individual members; the whole dominate the parts? What are the specific sociological differences between plant and animal communities and human society? What kind of differences are sociological differences, and what do we mean in general by the expression "sociological" anyway?
Since Spencer's essay on the social organism was published in 1860,[32] this problem and these questions, in one form or another, have largely absorbed the theoretical interest of students of society. The attempts to answer them may be said to have created the existing schools into which sociologists are divided.
A certain school of writers, among them Paul Lilienfeld, Auguste Schäffle, and René Worms, have sought to maintain, to extend, or modify the biological analogy first advanced by Spencer. In doing so they have succeeded sometimes in restating the problem but have not solved it. René Worms has been particularly ingenious in discovering identities and carrying out the parallelism between the social and the biological organizations. As a result he has reached the conclusion that, as between a social and a biological organism, there is no difference of kind but only one of degree. Spencer, who could not find a "social sensorium," said that society was conscious only in the individuals who composed it. Worms, on the other hand, declares that we must assume the existence of a social consciousness, even without a sensorium, because we see everywhere the evidence of its existence.
Force manifests itself by its effects. If there are certain phenomena that we can only make intelligible, provided we regard them as the products of collective social consciousness, then we are bound to assume the existence of such a consciousness. There are many illustrations ... the attitude for example, of a crowd in the presence of a crime. Here the sentiment of indignation is unanimous. A murderer, if taken in the act, will get summary justice from the ordinary crowd. That method of rendering justice, "lynch law," is deplorable, but it illustrates the intensity of the sentiment which, at the moment, takes possession of the social consciousness.
Thus, always in the presence of great and common danger the collective consciousness of society is awakened; for example France of the Valois after the Treaty of Troyes, or modern France before the invasion of 1791 and before the German invasion in 1870; or Germany, herself, after the victories of Napoleon I. This sentiment of national unity, born of resistance to the stranger, goes so far that a large proportion of the members of society do not hesitate to give their lives for the safety and glory of the state, at such a moment the individual comprehends that he is only a small part of a large whole and that he belongs to the collectivity of which he is a member. The proof that he is entirely penetrated by the social consciousness is the fact that in order to maintain its existence he is willing to sacrifice his own.[33]
There is no question that the facts of crowd excitement, of class, caste, race, and national consciousness, do show the way in which the individual members of a group are, or seem to be, dominated, at certain moments and under certain circumstances, by the group as a whole. Worms gives to this fact, and the phenomena which accompany it, the title "collective consciousness." This gives the problem a name, to be sure, but not a solution. What the purpose of sociology requires is a description and an explanation. Under what conditions, precisely, does this phenomenon of collective consciousness arise? What are the mechanisms—physical, physiological, and social—by which the group imposes its control, or what seems to be control, upon the individual members of the group?
This question had arisen and been answered by political philosophers, in terms of political philosophy, long before sociology attempted to give an objective account of the matter. Two classic phrases, Aristotle's "Man is a political animal" and Hobbes's "War of each against all," omnes bellum omnium, measure the range and divergence of the schools upon this topic.
According to Hobbes, the existing moral and political order—that is to say the organization of control—is in any community a mere artefact, a control resting on consent, supported by a prudent calculation of consequences, and enforced by an external power. Aristotle, on the other hand, taught that man was made for life in society just as the bee is made for life in the hive. The relations between the sexes, as well as those between mother and child, are manifestly predetermined in the physiological organization of the individual man and woman. Furthermore, man is, by his instincts and his inherited dispositions, predestined to a social existence beyond the intimate family circle. Society must be conceived, therefore, as a part of nature, like a beaver's dam or the nests of birds.
As a matter of fact, man and society present themselves in a double aspect. They are at the same time products of nature and of human artifice. Just as a stone hammer in the hand of a savage may be regarded as an artificial extension of the natural man, so tools, machinery, technical and administrative devices, including the formal organization of government and the informal "political machine," may be regarded as more or less artificial extensions of the natural social group.
So far as this is true, the conflict between Hobbes and Aristotle is not absolute. Society is a product both of nature and of design, of instinct and of reason. If, in its formal aspect, society is therefore an artefact, it is one which connects up with and has its roots in nature and in human nature.
This does not explain social control but simplifies the problem of corporate action. It makes clear, at any rate, that as members of society, men act as they do elsewhere from motives they do not fully comprehend, in order to fulfil aims of which they are but dimly or not at all conscious. Men are activated, in short, not merely by interests, in which they are conscious of the end they seek, but also by instincts and sentiments, the source and meaning of which they do not clearly comprehend. Men work for wages, but they will die to preserve their status in society, or commit murder to resent an insult. When men act thus instinctively, or under the influence of the mores, they are usually quite unconscious of the sources of the impulses that animate them or of the ends which are realized through their acts. Under the influence of the mores men act typically, and so representatively, not as individuals but as members of a group.
The simplest type of social group in which we may observe "social control" is in a herd or a flock. The behavior of a herd of cattle is, to be sure, not so uniform nor so simple a matter as it seems to the casual observer, but it may be very properly taken as an illustration of the sort of follow-the-leader uniformity that is more or less characteristic of all social groups. We call the disposition to live in the herd and to move in masses, gregariousness, and this gregariousness is ordinarily regarded as an instinct and undoubtedly is pretty largely determined in the original nature of gregarious animals.
There is a school of thought which seeks in the so-called gregarious instincts an explanation of all that is characteristically social in the behavior of human beings.
The cardinal quality of the herd is homogeneity. It is clear that the great advantage of the social habit is to enable large numbers to act as one, whereby in the case of the hunting gregarious animal strength in pursuit and attack is at once increased to beyond that of the creatures preyed upon, and in protective socialism the sensitiveness of the new unit to alarms is greatly in excess of that of the individual member of the flock.
To secure these advantages of homogeneity, it is evident that the members of the herd must possess sensitiveness to the behaviour of their fellows. The individual isolated will be of no meaning, the individual as a part of the herd will be capable of transmitting the most potent impulses. Each member of the flock tending to follow its neighbour and in turn to be followed, each is in some sense capable of leadership; but no lead will be followed that departs widely from normal behaviour. A lead will be followed only from its resemblance to the normal. If the leader go so far ahead as definitely to cease to be in the herd, he will necessarily be ignored.
The original in conduct, that is to say, resistiveness to the voice of the herd, will be suppressed by natural selection; the wolf which does not follow the impulses of the herd will be starved; the sheep which does not respond to the flock will be eaten.
Again, not only will the individual be responsive to impulses coming from the herd, but he will treat the herd as his normal environment. The impulse to be in and always to remain with the herd will have the strongest instinctive weight. Anything which tends to separate him from his fellows, as soon as it becomes perceptible as such, will be strongly resisted.[34]
According to sociologists of this school, public opinion, conscience, and authority in the state rest upon the natural disposition of the animal in the herd to conform to "the decrees of the herd."
Conscience, then, and the feelings of guilt and of duty are the peculiar possessions of the gregarious animal. A dog and a cat caught in the commission of an offence will both recognize that punishment is coming; but the dog, moreover, knows that he has done wrong, and he will come to be punished, unwillingly it is true, and as if dragged along by some power outside him, while the cat's sole impulse is to escape. The rational recognition of the sequence of act and punishment is equally clear to the gregarious and to the solitary animal, but it is the former only who understands that he has committed a crime, who has, in fact, the sense of sin.[35]
The concepts upon which this explanation of society rests is homogeneity. If animals or human beings act under all circumstances in the same way, they will act or seem to act, as if they had a common purpose. If everybody follows the crowd, if everyone wears the same clothes, utters the same trite remarks, rallies to the same battles cries and is everywhere dominated, even in his most characteristically individual behavior, by an instinctive and passionate desire to conform to an external model and to the wishes of the herd, then we have an explanation of everything characteristic of society—except the variants, the nonconformists, the idealists, and the rebels. The herd instinct may be an explanation of conformity but it does not explain variation. Variation is an important fact in society as it is in nature generally.
Homogeneity and like-mindedness are, as explanations of the social behavior of men and animals, very closely related concepts. In "like response to like stimulus," we may discern the beginning of "concerted action" and this, it is urged, is the fundamental social fact. This is the "like-mindedness" theory of society which has been given wide popularity in the United States through the writings of Professor Franklin Henry Giddings. He describes it as a "developed form of the instinct theory, dating back to Aristotle's aphorism that man is a political animal."
Any given stimulus may happen to be felt by more than one organism, at the same or at different times. Two or more organisms may respond to the same given stimulus simultaneously or at different times. They may respond to the same given stimulus in like or in unlike ways; in the same or in different degrees; with like or with unlike promptitude; with equal or with unequal persistence. I have attempted to show that in like response to the same given stimulus we have the beginning, the absolute origin, of all concerted activity—the inception of every conceivable form of co-operation; while in unlike response, and in unequal response, we have the beginning of all those processes of individuation, of differentiation, of competition, which in their endlessly varied relations to combination, to co-operation, bring about the infinite complexity of organized social life.[36]
Closely related, logically if not historically, to Giddings' conception of "like-mindedness" is Gabriel Tarde's conception of "imitation." If for Giddings "like response to like stimulus" is the fundamental social fact, for Tarde "imitation" is the process through which alone society exists. Society, said Tarde, exists in imitation. As a matter of fact, Tarde's doctrine may be regarded as a corollary to Giddings'. Imitation is the process by which that like-mindedness, by which Giddings explains corporate action, is effected. Men are not born like-minded, they are made so by imitation.
This minute inter-agreement of minds and wills, which forms the basis of the social life, even in troublous times—this presence of so many common ideas, ends, and means, in the minds and wills of all members of the same society at any given moment—is not due, I maintain, to organic heredity, which insures the birth of men quite similar to one another, nor to mere identity of geographical environment, which offers very similar resources to talents that are nearly equal; it is rather the effect of that suggestion-imitation process which, starting from one primitive creature possessed of a single idea or act, passed this copy on to one of its neighbors, then to another, and so on. Organic needs and spiritual tendencies exist in us only as potentialities which are realizable under the most diverse forms, in spite of their primitive similarity; and, among all these possible realizations, the indications furnished by some first initiator who is imitated determine which one is actually chosen.[37]
In contrast with these schools, which interpret action in terms of the herd and the flock—i.e., men act together because they act alike—is the theory of Émile Durkheim who insists that the social group has real corporate existence and that, in human societies at least, men act together not because they have like purposes but a common purpose. This common purpose imposes itself upon the individual members of a society at the same time as an ideal, a wish and an obligation. Conscience, the sense of obligation which members of a group feel only when there is conflict between the wishes of the individual and the will of the group, is a manifestation, in the individual consciousness, of the collective mind and the group will. The mere fact that in a panic or a stampede, human beings will sometimes, like the Gadarene swine, rush down a steep place into the sea, is a very positive indication of like-mindedness but not an evidence of a common purpose. The difference between an animal herd and a human crowd is that the crowd, what Le Bon calls the "organized crowd," the crowd "in being" to use a nautical term, is dominated by an impulse to achieve a purpose that is common to every member of the group. Men in a state of panic, on the other hand, although equally under the influence of the mass excitement, act not corporately but individually, each individual wildly seeking to save his own skin. Men in a state of panic have like purposes but no common purpose. If the "organized crowd," "the psychological crowd," is a society "in being," the panic and the stampede is a society "in dissolution."
Durkheim does not use these illustrations nor does he express himself in these terms. The conception of the "organized" or "psychological" crowd is not his, but Le Bon's. The fact is that Durkheim does not think of a society as a mere sum of particulars. Neither does he think of the sentiments nor the opinions which dominate the social group as private and subjective. When individuals come together under certain circumstances, the opinions and sentiments which they held as individuals are modified and changed under the influence of the new contacts. Out of the fermentation which association breeds, a new something (autre chose) is produced, an opinion and sentiment, in other words, that is not the sum of, and not like, the sentiments and opinions of the individuals from which it is derived. This new sentiment and opinion is public, and social, and the evidence of this is the fact that it imposes itself upon the individuals concerned as something more or less external to them. They feel it either as an inspiration, a sense of personal release and expansion, or as an obligation, a pressure and an inhibition. The characteristic social phenomenon is just this control by the group as a whole of the individuals that compose it. This fact of control, then, is the fundamental social fact.
Now society also gives the sensation of a perpetual dependence. Since it has a nature which is peculiar to itself and different from our individual nature, it pursues ends which are likewise special to it; but, as it cannot attain them except through our intermediacy; it imperiously demands our aid. It requires that, forgetful of our own interests, we make ourselves its servitors, and it submits us to every sort of inconvenience, privation, and sacrifice, without which social life would be impossible. It is because of this that at every instant we are obliged to submit ourselves to rules of conduct and of thought which we have neither made nor desired, and which are sometimes even contrary to our most fundamental inclinations and instincts.
Even if society were unable to maintain these concessions and sacrifices from us except by a material constraint, it might awaken in us only the idea of a physical force to which we must give way of necessity, instead of that of a moral power such as religions adore. But as a matter of fact, the empire which it holds over consciences is due much less to the physical supremacy of which it has the privilege than to the moral authority with which it is invested. If we yield to its orders, it is not merely because it is strong enough to triumph over our resistance; it is primarily because it is the object of a venerable respect.
Now the ways of action to which society is strongly enough attached to impose them upon its members, are, by that very fact, marked with a distinctive sign provocative of respect. Since they are elaborated in common, the vigour with which they have been thought of by each particular mind is retained in all the other minds, and reciprocally. The representations which express them within each of us have an intensity which no purely private states of consciousness could ever attain; for they have the strength of the innumerable individual representations which have served to form each of them. It is society who speaks through the mouths of those who affirm them in our presence; it is society whom we hear in hearing them; and the voice of all has an accent which that of one alone could never have. The very violence with which society reacts, by way of blame or material suppression, against every attempted dissidence, contributes to strengthening its empire by manifesting the common conviction through this burst of ardour. In a word, when something is the object of such a state of opinion, the representation which each individual has of it gains a power of action from its origins and the conditions in which it was born, which even those feel who do not submit themselves to it. It tends to repel the representations which contradict it, and it keeps them at a distance; on the other hand it commands those acts which will realize it, and it does so, not by a material coercion or by the perspective of something of this sort, but by the simple radiation of the mental energy which it contains.[38]
But the same social forces, which are found organized in public opinion, in religious symbols, in social convention, in fashion, and in science—for "if a people did not have faith in science all the scientific demonstrations in the world would be without any influence whatsoever over their minds"—are constantly re-creating the old order, making new heroes, overthrowing old gods, creating new myths, and imposing new ideals. And this is the nature of the cultural process of which sociology is a description and an explanation.
VII. SOCIAL CONTROL AND THE COLLECTIVE MIND
Durkheim is sometimes referred to, in comparison with other contemporary sociologists, as a realist. This is a reference to the controversy of the medieval philosophers in regard to the nature of concepts. Those who thought a concept a mere class-name applied to a group of objects because of some common characteristics were called nominalists. Those who thought the concept was real, and not the name of a mere collection of individuals, were realists. In this sense Tarde and Giddings and all those writers who think of society as a collection of actually or potentially like-minded persons would be nominalists, while other writers like Simmel, Ratzenhofer, and Small, who think of society in terms of interaction and social process may be called realists. They are realist, at any rate, in so far as they think of the members of a society as bound together in a system of mutual influences which has sufficient character to be described as a process.
Naturally this process cannot be conceived of in terms of space or physical proximity alone. Social contacts and social forces are of a subtler sort but not less real than physical. We know, for example, that vocations are largely determined by personal competition; that the solidarity of what Sumner calls the "in" or "we" group is largely determined by its conflict with the "out" or "other" groups. We know, also, that the status and social position of any individual inside any social group is determined by his relation to all other members of that group and eventually of all other groups. These are illustrations of what is meant concretely by social interaction and social process and it is considerations of this kind which seem to justify certain writers in thinking of individual persons as "parts" and of society as a "whole" in some other sense than that in which a dust heap is a whole of which the individual particles are parts.
[20] Robert H. Lowie, Primitive Society (New York, 1920), pp. 7-8.
[21] Wilhelm Wundt, Völkerpsychologie, eine Untersuchung der Entwicklungsgesetze von Sprache, Mythus und Sitte. Erster Band, Die Sprache, Erster Theil (Leipzig, 1900), p. 13. The name folk-psychology was first used by Lazarus and Steinthal, Zeitschrift für Völkerpsychologie und Sprachwissenschaft, I, 1860. Wundt's folk-psychology is a continuation of the tradition of these earlier writers.
[22] G. Tarde, Social Laws, An Outline of Sociology, translated from the French by Howard C. Warren (New York, 1899), pp. 40-41.
[23] Hanns Oertel, "Some Present Problems and Tendencies in Comparative Philology," Congress of Arts and Science, Universal Exposition, St. Louis, 1904 (Boston, 1906), III, 59.
[24] Edward A. Freeman, Comparative Politics (London, 1873), p. 23.
[25] L. Lévy-Bruhl, The Philosophy of Auguste Comte, authorized translation; an Introduction by Frederic Harrison (New York, 1903), p. 337.
[26] Ibid., p. 234.
[27] Hobbes's statement is as follows: "For by art is created that great Leviathan called a Commonwealth, or State, in Latin Civitas, which is but an artificial man; though of greater stature and strength than the natural, for whose protection and defence it was intended; and in which the sovereignty is an artificial soul, as giving life and motion to the whole body; the magistrates, and other officers of judicature, artificial joints; reward and punishment, by which fastened to the seat of the sovereignty every joint and member is moved to perform his duty, are the nerves, that do the same in the body natural." Spencer criticizes this conception of Hobbes as representing society as a "factitious" and artificial rather than a "natural" product. Herbert Spencer, The Principles of Sociology (London, 1893), I, 437, 579-80. See also chap. iii, "Social Growth," pp. 453-58.
[28] Herbert Spencer, op. cit., I, 437.
[29] Ibid., p. 440.
[30] Ibid., p. 450.
[31] Ibid., pp. 449-50.
[32] Westminster Review, January, 1860.
[33] René Worms, Organisme et Société, "Bibliothèque Sociologique Internationale" (Paris, 1896), pp. 210-13.
[34] W. Trotter, Instincts of the Herd in Peace and War (New York, 1916), pp. 29-30.
[35] Ibid., pp. 40-41.
[36] Franklin Henry Giddings, The Concepts and Methods of Sociology, Congress of Arts and Science, Universal Exposition (St. Louis, 1904), pp. 789-90.
[37] G. Tarde, op. cit., pp. 38-39.
[38] Émile Durkheim, Elementary Forms of Religious Life (New York, 1915), pp. 206-8.
Society not only continues to exist by transmission, by communication, but it may fairly be said to exist in transmission, in communication. There is more than a verbal tie between the words common, community, and communication.[39]
Communication, if not identical with, is at least a form of, what has been referred to here as social interaction. But communication as Dewey has defined the term, is something more and different than what Tarde calls "inter-stimulation." Communication is a process by which we "transmit" an experience from an individual to another but it is also a process by which these same individuals get a common experience.
Try the experiment of communicating, with fullness and accuracy, some experience to another, especially if it be somewhat complicated, and you will find your own attitude toward your experience changing; otherwise you resort to expletives and ejaculations. Except in dealing with commonplaces and catch phrases one has to assimilate, imaginatively, something of another's experience in order to tell him intelligently of one's own experience. All communication is like art.[40]
Not only does communication involve the creation, out of experiences that are individual and private, of an experience that is common and public but such a common experience becomes the basis for a common and public existence in which every individual, to greater or less extent, participates and is himself a part. Furthermore, as a part of this common life, there grows up a body of custom, convention, tradition, ceremonial, language, social ritual, public opinion, in short all that Sumner includes under the term "mores" and all that ethnologists include under the term "culture."
The thing that characterizes Durkheim and his followers is their insistence upon the fact that all cultural materials, and expressions, including language, science, religion, public opinion, and law, since they are the products of social intercourse and social interaction, are bound to have an objective, public, and social character such as no product of an individual mind either has or can have. Durkheim speaks of these mental products, individual and social, as representations. The characteristic product of the individual mind is the percept, or, as Durkheim describes it, the "individual representation." The percept is, and remains, a private and an individual matter. No one can reproduce, or communicate to another, subjective impressions or the mental imagery in the concrete form in which they come to the individual himself. My neighbor may be able to read my "thoughts" and understand the motives that impel me to action better than I understand myself, but he cannot reproduce the images, with just the fringes of sense and feeling with which they come to my mind.
The characteristic product of a group of individuals, in their efforts to communicate is, on the other hand, something objective and understood, that is, a gesture, a sign, a symbol, a word, or a concept in which an experience or purpose that was private becomes public. This gesture, sign, symbol, concept, or representation in which a common object is not merely indicated, but in a sense created, Durkheim calls a "collective representation."
Dewey's description of what takes place in communication may be taken as a description of the process by which these collective representations come into existence. "To formulate an experience," as Dewey says, "requires getting outside of it, seeing it as another would see it, considering what points of contact it has with the life of another so that it may be gotten into such form that he can appreciate its meaning." The result of such a conscious effort to communicate an experience is to transform it. The experience, after it has been communicated, is not the same for either party to the communication. To publish or to give publicity to an event is to make of that event something other than it was before publication. Furthermore, the event as published is still something different from the event as reflected in the minds of the individuals to whom the publication is addressed.
It will be evident upon reflection that public opinion is not the opinion of all, nor even of a majority of the persons who compose a public. As a matter of fact, what we ordinarily mean by public opinion is never the opinion of anyone in particular. It is composite opinion, representing a general tendency of the public as a whole. On the other hand, we recognize that public opinion exists, even when we do not know of any individual person, among those who compose the public, whose private and personal opinion exactly coincides with that of the public of which he or she is a part.
Nevertheless, the private and personal opinion of an individual who participates in making public opinion is influenced by the opinions of those around him, and by public opinion. In this sense every opinion is public opinion.
Public opinion, in respect to the manner in which it is formed and the manner in which it exists—that is to say relatively independent of the individuals who co-operate to form it—has the characteristics of collective representation in general. Collective representations are objective, in just the sense that public opinion is objective, and they impose themselves upon the individual as public opinion does, as relatively but not wholly external forces—stabilizing, standardizing, conventionalizing, as well as stimulating, extending, and generalizing individual representations, percepts.
The collective representations are exterior to the individual consciousness because they are not derived from the individuals taken in isolation but from their convergence and union (concours).... Doubtless, in the elaboration of the common result, each (individual) bears his due share; but the private sentiments do not become social except by combining under the action of the forces sui generis which association develops. As a result of these combinations, and of the mutual alterations which result therefrom, they (the private sentiments) become something else (autre chose). A chemical synthesis results, which concentrates, unifies, the elements synthetized, and by that very process transforms them.... The resultant derived therefrom extends then beyond (deborde) the individual mind as the whole is greater than the part. To know really what it is, one must take the aggregate in its totality. It is this that thinks, that feels, that wills, although it may not be able to will, feel, or act save by the intermediation of individual consciousnesses.[41]
This, then, after nearly a century of criticism, is what remains of Comte's conception of the social organism. If society is, as the realists insist, anything more than a collection of like-minded individuals, it is so because of the existence (1) of a social process and (2) of a body of tradition and opinion—the products of this process—which has a relatively objective character and imposes itself upon the individual as a form of control, social control. This process and its product are the social consciousness. The social consciousness, in its double aspect as process and product, is the social organism. The controversy between the realists and the nominalists reduces itself apparently to this question of the objectivity of social tradition and of public opinion. For the present we may let it rest there.
Meanwhile the conceptions of the social consciousness and the social mind have been adopted by writers on social topics who are not at all concerned with their philosophical implications or legitimacy. We are just now seeing the first manifestations of two new types of sociology which call themselves, the one rural and the other urban sociology. Writers belonging to these two schools are making studies of what they call the "rural" and the "urban" minds. In using these terms they are not always quite certain whether the mind of which they are thinking is a collective mind, in Durkheim's realistic sense of the word, or whether it is the mind of the typical inhabitant of a rural or an urban community, an instance of "like-mindedness," in the sense of Giddings and the nominalists.
A similar usage of the word "mind," "the American mind," for example, is common in describing characteristic differences in the attitudes of different nations and their "nationals."
The origin of the phrase, "the American mind," was political. Shortly after the middle of the eighteenth century, there began to be a distinctly American way of regarding the debatable question of British Imperial control. During the period of the Stamp Act agitation our colonial-bred politicians and statesmen made the discovery that there was a mode of thinking and feeling which was native—or had by that time become a second nature—to all the colonists. Jefferson, for example, employs those resonant and useful words "the American mind" to indicate that throughout the American colonies an essential unity of opinion had been developed as regards the chief political question of the day.[42]
Here again, it is not quite clear, whether the American mind is a name for a characteristic uniformity in the minds of individual Americans; whether the phrase refers rather to an "essential unity of opinion," or whether, finally, it is intended to cover both the uniformity and the unity characteristic of American opinion.
Students of labor problems and of the so-called class struggle, on the other hand, use the term "psychology" in much the same way that the students of rural and urban sociology use the term "mind." They speak of the "psychology" of the laboring class, the "psychology" of the capitalistic class, in cases where psychology seems to refer indifferently either to the social attitudes of the members of a class, or to attitude and morale of the class as a whole.
The terms "class-conscious" and "class-consciousness," "national" and "racial" consciousness are now familiar terms to students although they seem to have been used, first of all, by the so-called "intelligentsia", who have been the leaders in the various types of mass movement to which these terms apply. "Consciousness," in the sense in which it is here used, has a similar, though somewhat different, connotation than the word "mind" when applied to a group. It is a name not merely for the attitudes characteristic of certain races or classes, but for these attitudes when they are in the focus of attention of the group, in the "fore-consciousness" to use a Freudian term. In this sense "conscious" suggests not merely the submergence of the individual and the consequent solidarity of the group, but it signifies a mental mobilization and preparedness of the individual and of the group for collective or corporate action. To be class-conscious is to be prepared to act in the sense of that class.
There is implicit in this rather ambiguous popular usage of the terms "social mind" and "social consciousness" a recognition of the dual aspect of society and of social groups. Society may be regarded at the same time from an individualistic and a collectivistic point of view. Looking at it from the point of view of the individual, we regard as social just that character of the individual which has been imparted to, and impressed upon, him as a result of his participation in the life of the group. Social psychology, from Baldwin's first studies of the development of personality in the child to Ellwood's studies of the society in its "psychological aspects" has been mainly concerned with the investigation of the effects upon the individual of his contacts with other individuals.[43]
On the other hand, we have had, in the description of the crowd and the public by Le Bon, Tarde, Sighele, and their successors, the beginnings of a study of collective behavior and "corporate action." In these two points of view we seem to have again the contrast and the opposition, already referred to, between the nominalistic and realistic conceptions of society. Nominalism represented by social psychology emphasizes, or seems to emphasize, the independence of the individual. Realism, represented by collective psychology, emphasizes the control of the group over the individual, of the whole over the part.
While it is true that society has this double aspect, the individual and the collective, it is the assumption of this volume that the touchstone of society, the thing that distinguishes a mere collection of individuals from a society is not like-mindedness, but corporate action. We may apply the term social to any group of individuals which is capable of consistent action, that is to say, action, consciously or unconsciously, directed to a common end. This existence of a common end is perhaps all that can be legitimately included in the conception "organic" as applied to society.
From this point of view social control is the central fact and the central problem of society. Just as psychology may be regarded as an account of the manner in which the individual organism, as a whole, exercises control over its parts or rather of the manner in which the parts co-operate together to carry on the corporate existence of the whole, so sociology, speaking strictly, is a point of view and a method for investigating the processes by which individuals are inducted into and induced to co-operate in some sort of permanent corporate existence which we call society.
To put this emphasis on corporate action is not to overlook the fact that through this corporate action the individual member of society is largely formed, not to say created. It recognized, however, that if corporate action tends to make of the individual an instrument, as well as an organic part, of the social group, it does not do this by making him "like" merely; it may do so by making him "different." The division of labor, in making possible an ever larger and wider co-operation among men, has indirectly multiplied individual diversities. What like-mindedness must eventually mean, if it is to mean anything, is the existence of so much of a consensus among the individuals of a group as will permit the group to act. This, then, is what is meant here by society, the social organism and the social group.
Sociology, so far as it can be regarded as a fundamental science and not mere congeries of social-welfare programs and practices, may be described as the science of collective behavior. With this definition it is possible to indicate in a general and schematic way its relation to the other social sciences.
Historically, sociology has had its origin in history. History has been and is the great mother science of all the social sciences. Of history it may be said nothing human is foreign to it. Anthropology, ethnology, folklore, and archaeology have grown up largely, if not wholly, to complete the task which history began and answer the questions which historical investigation first raised. In history and the sciences associated with it, i.e., ethnology, folklore, and archaeology, we have the concrete records of that human nature and experience which sociology has sought to explain. In the same sense that history is the concrete, sociology is the abstract, science of human experience and human nature.
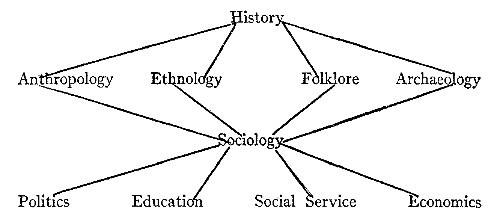
Fig. 1
On the other hand, the technical (applied) social sciences, that is, politics, education, social service, and economics—so far as economics may be regarded as the science of business—are related to sociology in a different way. They are, to a greater or lesser extent, applications of principles which it is the business of sociology and of psychology to deal with explicitly. In so far as this is true, sociology may be regarded as fundamental to the other social sciences.
VIII. SOCIOLOGY AND SOCIAL RESEARCH
Among the schools which, since Comte and Spencer, have divided sociological thinking between them the realists have, on the whole, maintained the tradition of Comte; the nominalists, on the other hand, have preserved the style and manner, if not the substance, of Spencer's thought. Later writers, however, realist as well as nominalist, have directed their attention less to society than to societies, i.e., social groups; they have been less interested in social progress than in social process; more concerned with social problems than with social philosophy.
This change marks the transformation of sociology from a philosophy of history to a science of society. The steps in this transition are periods in the history of the science, that is:
1. The period of Comte and Spencer; sociology, conceived in the grand style, is a philosophy of history, a "science" of progress (evolution).
2. The period of the "schools"; sociological thought, dispersed among the various schools, is absorbed in an effort to define its point of view and to describe the kinds of facts that sociology must look for to answer the questions that sociology asks.
3. The period of investigation and research, the period into which sociology is just now entering.
Sociological research is at present (1921) in about the situation in which psychology was before the introduction of laboratory methods, in which medicine was before Pasteur and the germ theory of disease. A great deal of social information has been collected merely for the purpose of determining what to do in a given case. Facts have not been collected to check social theories. Social problems have been defined in terms of common sense, and facts have been collected, for the most part, to support this or that doctrine, not to test it. In very few instances have investigations been made, disinterestedly, to determine the validity of a hypothesis.
Charles Booth's studies of poverty in London, which extended over eighteen years and were finally embodied in seventeen volumes, is an example of such a disinterested investigation. It is an attempt to put to the test of fact the popular conception of the relation between wages and welfare. He says:
My object has been to attempt to show the numerical relation which poverty, misery, and depravity bear to regular earnings and comparative comfort, and to describe the general conditions under which each class lives.
If the facts thus stated are of use in helping social reformers to find remedies for the evils which exist, or do anything to prevent the adoption of false remedies, my purpose is answered. It was not my intention to bring forward any suggestions of my own, and if I have ventured here and there, and especially in the concluding chapters, to go beyond my programme, it has been with much hesitation.
With regard to the disadvantages under which the poor labour, and the evils of poverty, there is a great sense of helplessness: the wage earners are helpless to regulate their work and cannot obtain a fair equivalent for the labour they are willing to give; the manufacturer or dealer can only work within the limits of competition; the rich are helpless to relieve want without stimulating its sources. To relieve this helplessness a better stating of the problems involved is the first step.... In this direction must be sought the utility of my attempt to analyze the population of a part of London.[44]
This vast study did, indeed, throw great light, not only upon poverty in London, but upon human nature in general. On the other hand, it raised more questions than it settled and, if it demonstrated anything, it was the necessity, as Booth suggests, for a restatement of the problem.
Sociology seems now, however, in a way to become, in some fashion or other, an experimental science. It will become so as soon as it can state existing problems in such a way that the results in one case will demonstrate what can and should be done in another. Experiments are going on in every field of social life, in industry, in politics, and in religion. In all these fields men are guided by some implicit or explicit theory of the situation, but this theory is not often stated in the form of a hypothesis and subjected to a test of the negative instances. We have, if it is permitted to make a distinction between them, investigation rather than research.
What, then, in the sense in which the expression is here used, is social research? A classification of problems will be a sort of first aid in the search for an answer.
1. Classification of social problems.—Every society and every social group, capable of consistent action, may be regarded as an organization of the wishes of its members. This means that society rests on, and embodies, the appetites and natural desires of the individual man; but it implies, also, that wishes, in becoming organized, are necessarily disciplined and controlled in the interest of the group as a whole.
Every such society or social group, even the most ephemeral, will ordinarily have (a) some relatively formal method of defining its aim and formulating its policies, making them explicit, and (b) some machinery, functionary, or other arrangement for realizing its aim and carrying its policies into effect. Even in the family there is government, and this involves something that corresponds to legislation, adjudication, and administration.
Social groups, however, maintain their organizations, agencies, and all formal methods of behavior on a basis and in a setting of instinct, of habit, and of tradition which we call human nature. Every social group has, or tends to have, its own culture, what Sumner calls "folkways," and this culture, imposing its patterns upon the natural man, gives him that particular individuality which characterizes the members of groups. Not races merely but nationalities and classes have marks, manners, and patterns of life by which we infallibly recognize and classify them.
Social problems may be conveniently classified with reference to these three aspects of group life, that is to say, problems of (a) organization and administration, (b) policy and polity (legislation), and (c) human nature (culture).
a) Administrative problems are mainly practical and technical. Most problems of government, of business and social welfare, are technical. The investigations, i.e., social surveys, made in different parts of the country by the Bureau of Municipal Research of New York City, are studies of local administration made primarily for the purpose of improving the efficiency of an existing administrative machine and its personnel rather than of changing the policy or purpose of the administration itself.
b) Problems of policy, in the sense in which that term is used here, are political and legislative. Most social investigations in recent years have been made in the interest of some legislative program or for the purpose of creating a more intelligent public opinion in regard to certain local problems. The social surveys conducted by the Sage Foundation, as distinguished from those carried out by the New York Bureau of Municipal Research, have been concerned with problems of policy, i.e., with changing the character and policy of social institutions rather than improving their efficiency. This distinction between administration and policy is not always clear, but it is always important. Attempts at reform usually begin with an effort to correct administrative abuses, but eventually it turns out that reforms must go deeper and change the character of the institutions themselves.
c) Problems of human nature are naturally fundamental to all other social problems. Human nature, as we have begun to conceive it in recent years, is largely a product of social intercourse; it is, therefore, quite as much as society itself, a subject for sociological investigation. Until recent years, what we are now calling the human factor has been notoriously neglected in most social experiments. We have been seeking to reform human nature while at the same time we refused to reckon with it. It has been assumed that we could bring about social changes by merely formulating our wishes, that is, by "arousing" public opinion and formulating legislation. This is the "democratic" method of effecting reforms. The older "autocratic" method merely decreed social changes upon the authority of the monarch or the ruling class. What reconciled men to it was that, like Christian Science, it frequently worked.
The oldest but most persistent form of social technique is that of "ordering-and-forbidding"—that is, meeting a crisis by an arbitrary act of will decreeing the disappearance of the undesirable or the appearance of the desirable phenomena, and the using arbitrary physical action to enforce the decree. This method corresponds exactly to the magical phase of natural technique. In both, the essential means of bringing a determined effect is more or less consciously thought to reside in the act of will itself by which the effect is decreed as desirable and of which the action is merely an indispensable vehicle or instrument; in both, the process by which the cause (act of will and physical action) is supposed to bring its effect to realization remains out of reach of investigation; in both, finally, if the result is not attained, some new act of will with new material accessories is introduced, instead of trying to find and remove the perturbing causes. A good instance of this in the social field is the typical legislative procedure of today.[45]
2. Types of social group.—The varied interests, fields of investigation, and practical programs which find at present a place within the limits of the sociological discipline are united in having one common object of reference, namely, the concept of the social group. All social problems turn out finally to be problems of group life, although each group and each type of group has its own distinctive problems. Illustrations may be gathered from the most widely separated fields to emphasize the truth of this assertion.[46]
Religious conversion may be interpreted from one point of view as a change from one social group to another. To use the language of religious sentiment, the convert "comes out of a life of sin and enters into a life of grace." To be sure, this change involves profound disturbances of the personality, but permanence of the change in the individual is assured by the breaking up of the old and the establishment of new associations. So the process by which the immigrant makes the transition from the old country to the new involves profound changes in thought and habit. In his case the change is likely to take place slowly, but it is not less radical on that account.
The following paragraph from a recent social survey illustrates, from a quite different point of view, the manner in which the group is involved in changes in community life.
In short, the greatest problem for the next few years in Stillwater is the development of a community consciousness. We must stop thinking in terms of city of Stillwater, and country outside of Stillwater, and think in terms of Stillwater Community. We must stop thinking in terms of small groups and think in terms of the entire community, no matter whether it is industry, health, education, recreation or religion. Anything which is good will benefit the entire community. Any weakness will be harmful to all. Community co-operation in all lines indicated in this report will make this, indeed, the Queen of the St. Croix.[47]
In this case the solution of the community problem was the creation of "community consciousness." In the case of the professional criminal the character of the problem is determined, if we accept the description of a writer in the Atlantic Monthly, by the existence among professional criminals of a primary group consciousness:
The professional criminal is peculiar in the sense that he lives a very intense emotional life. He is isolated in the community. He is in it, but not of it. His social life—for all men are social—is narrow; but just because it is narrow, it is extremely tense. He lives a life of warfare and has the psychology of the warrior. He is at war with the whole community. Except his very few friends in crime he trusts no one and fears everyone. Suspicion, fear, hatred, danger, desperation and passion are present in a more tense form in his life than in that of the average individual. He is restless, ill-humored, easily roused and suspicious. He lives on the brink of a deep precipice. This helps to explain his passionate hatred, his brutality, his fear, and gives poignant significance to the adage that dead men tell no tales. He holds on to his few friends with a strength and passion rare among people who live a more normal existence. His friends stand between him and discovery. They are his hold upon life, his basis of security.
Loyalty to one's group is the basic law in the underworld. Disloyalty is treason and punishable by death; for disloyalty may mean the destruction of one's friends; it may mean the hurling of the criminal over the precipice on which his whole life is built.
To the community the criminal is aggressive. To the criminal his life is one of defense primarily. The greater part of his energy, of his hopes, and of his successes, centres around escapes, around successful flight, around proper covering-up of his tracks, and around having good, loyal, and trustworthy friends to participate in his activities, who will tell no tales and keep the rest of the community outside. The criminal is thus, from his own point of view—and I am speaking of professional criminals—living a life of defensive warfare with the community; and the odds are heavy against him. He therefore builds up a defensive psychology against it—a psychology of boldness, bravado, and self-justification. The good criminal—which means the successful one, he who has most successfully carried through a series of depradations against the enemy, the common enemy, the public—is a hero. He is recognized as such, toasted and feasted, trusted and obeyed. But always by a little group. They live in a world of their own, a life of their own, with ideals, habits, outlook, beliefs, and associations which are peculiarly fitted to maintain the morale of the group. Loyalty, fearlessness, generosity, willingness to sacrifice one's self, perseverance in the face of prosecution, hatred of the common enemy—these are the elements that maintain the morale, but all of them are pointed against the community as a whole.[48]
The manner in which the principle of the primary group was applied at Sing Sing in dealing with the criminal within the prison walls is a still more interesting illustration of the fact that social problems are group problems.[49]
Assuming, then, that every social group may be presumed to have its own (a) administrative, (b) legislative, and (c) human-nature problems, these problems may be still further classified with reference to the type of social group. Most social groups fall naturally into one or the other of the following classes:
a) The family.
b) Language (racial) groups.
c) Local and territorial communities: (i) neighborhoods, (ii) rural communities, (iii) urban communities.
d) Conflict groups: (i) nationalities, (ii) parties, (iii) sects, (iv) labor organizations, (v) gangs, etc.
e) Accommodation groups: (i) classes, (ii) castes, (iii) vocational, (iv) denominational groups.
The foregoing classification is not quite adequate nor wholly logical. The first three classes are more closely related to one another than they are to the last two, i.e., the so-called "accommodation" and "conflict" groups. The distinction is far-reaching, but its general character is indicated by the fact that the family, language, and local groups are, or were originally, what are known as primary groups, that is, groups organized on intimate, face-to-face relations. The conflict and accommodation groups represent divisions which may, to be sure, have arisen within the primary group, but which have usually arisen historically by the imposition of one primary group upon another.
Every state in history was or is a state of classes, a polity of superior and inferior social groups, based upon distinctions either of rank or of property. This phenomenon must, then, be called the "State."[50]
It is the existence at any rate of conflict and accommodation within the limits of a larger group which distinguishes it from groups based on primary relations, and gives it eventually the character described as "secondary."
When a language group becomes militant and self-conscious, it assumes the character of a nationality. It is perhaps true, also, that the family which is large enough and independent enough to be self-conscious, by that fact assumes the character of a clan. Important in this connection is the fact that a group in becoming group-conscious changes its character. External conflict has invariably reacted powerfully upon the internal organization of social groups.
Group self-consciousness seems to be a common characteristic of conflict and accommodation groups and distinguishes them from the more elementary forms of society represented by the family and the local community.
3. Organization and structure of social groups.—Having a general scheme for the classification of social groups, it is in order to discover methods of analysis that are applicable to the study of all types of groups, from the family to the sect. Such a scheme of analysis should reveal not only the organization and structure of typical groups, but it should indicate the relation of this organization and structure to those social problems that are actual and generally recognized. The sort of facts which are now generally recognized as important in the study, not merely of society, but the problems of society are:
a) Statistics: numbers, local distribution, mobility, incidence of births, deaths, disease, and crime.
b) Institutions: local distribution, classification (i.e., (i) industrial, (ii) religious, (iii) political, (iv) educational, (v) welfare and mutual aid), communal organization.
c) Heritages: the customs and traditions transmitted by the group, particularly in relation to religion, recreation and leisure time, and social control (politics).
d) Organization of public opinion: parties, sects, cliques, and the press.
4. Social process and social progress.—Social process is the name for all changes which can be regarded as changes in the life of the group. A group may be said to have a life when it has a history. Among social processes we may distinguish (a) the historical, (b) the cultural, (c) the political, and (d) the economic.
a) We describe as historical the processes by which the fund of social tradition, which is the heritage of every permanent social group, is accumulated and transmitted from one generation to another.
History plays the rôle in the group of memory in the individual. Without history social groups would, no doubt, rise and decline, but they would neither grow old nor make progress.
Immigrants, crossing the ocean, leave behind them much of their local traditions. The result is that they lose, particularly in the second generation, that control which the family and group tradition formerly exercised over them; but they are, for that very reason, all the more open to the influence of the traditions and customs of their adopted country.
b) If it is the function of the historical process to accumulate and conserve the common fund of social experience, it is the function of the cultural process to shape and define the social forms and the social patterns which each preceding generation imposes upon its successors.
The individual living in society has to fit into a pre-existing social world, to take part in the hedonistic, economic, political, religious, moral, aesthetic, intellectual activities of the group. For these activities the group has objective systems, more or less complex sets of schemes, organized either by traditional association or with a conscious regard to the greatest possible efficiency of the result, but with only a secondary, or even with no interest in the particular desires, abilities and experiences of the individuals who have to perform these activities.
There is no pre-existing harmony whatever between the individual and the social factors of personal evolution, and the fundamental tendencies of the individual are always in some disaccordance with the fundamental tendencies of social control. Personal evolution is always a struggle between the individual and society—a struggle for self-expression on the part of the individual, for his subjection on the part of society—and it is in the total course of this struggle that the personality—not as a static "essence" but as a dynamic, continually evolving set of activities—manifests and constructs itself.[51]
c) In general, standards of behavior that are in the mores are not the subject of discussion, except so far as discussion is necessary to determine whether this or that act falls under one or the other of the accepted social sanctions. The political as distinguished from the cultural process is concerned with just those matters in regard to which there is division and difference. Politics is concerned with issues.
The Negro, particularly in the southern states, is a constant theme of popular discussion. Every time a Negro finds himself in a new situation, or one in which the white population is unaccustomed to see him, the thing provokes comment in both races. On the other hand, when a southerner asks the question: "Would you want your daughter to marry a Negro?" it is time for discussion to cease. Any questions of relations between the races can always be immediately disposed of as soon as it is seen to come, directly or indirectly, under the intolerable formula. Political questions are matters of compromise and expediency. Miscegenation, on the other hand, is contrary to the mores. As such the rule against it is absolute.
The political process, by which a society or social group formulates its wishes and enforces them, goes on within the limits of the mores and is carried on by public discussion, legislation, and the adjudication of the courts.
d) The economic process, so far as it can be distinguished from the production and distribution of goods, is the process by which prices are made and an exchange of values is effected. Most values, i.e., my present social status, my hopes of the future, and memory of the past, are personal and not values that can be exchanged. The economic process is concerned with values that can be treated as commodities.
All these processes may, and do, arise within most but not every society or social group. Commerce presupposes the freedom of the individual to pursue his own profit, and commerce can take place only to the extent and degree that this freedom is permitted. Freedom of commerce is, however, limited on the one hand by the mores and on the other by formal law, so that the economic process takes place ordinarily within limitations that are defined by the cultural and the political processes. It is only where there is neither a cultural nor a political order that commerce is absolutely free.
The areas of (1) the cultural, (2) the political, (3) the economic processes and their relations to one another may be represented by concentric circles.
In this representation the area of widest cultural influences is coterminous with the area of commerce, because commerce in its widest extension is invariably carried on under some restraints of custom and customary law. Otherwise it is not commerce at all, but something predacious outside the law. But if the area of the economic process is almost invariably coterminous with the widest areas of cultural influence, it does not extend to the smaller social groups. As a rule trade does not invade the family. Family interests are always personal even when they are carried on under the forms of commerce. Primitive society, within the limits of the village, is usually communistic. All values are personal, and the relations of individuals to one another, economic or otherwise, are preordained by custom and law.
The impersonal values, values for exchange, seem to be in any given society or social group in inverse relation to the personal values.
The attempt to describe in this large way the historical, cultural, political, and economic processes, is justified in so far as it enables us to recognize that the aspects of social life, which are the subject-matter of the special social sciences, i.e., history, political science, and economics, are involved in specific forms of change that can be viewed abstractly, formulated, compared, and related. The attempt to view them in their interrelations is at the same time an effort to distinguish and to see them as parts of one whole.
Fig. 2 a = area of most extended cultural influences and of commerce; b = area of formal political control; c = area of purely personal relationships, communism.
In contrast with the types of social change referred to there are other changes which are unilateral and progressive; changes which are described popularly as "movements," mass movements. These are changes which eventuate in new social organizations and institutions.
All more marked forms of social change are associated with certain social manifestations that we call social unrest. Social unrest issues, under ordinary conditions, as an incident of new social contacts, and is an indication of a more lively tempo in the process of communication and interaction.
All social changes are preceded by a certain degree of social and individual disorganization. This will be followed ordinarily under normal conditions by a movement of reorganization. All progress implies a certain amount of disorganization. In studying social changes, therefore, that, if not progressive, are at least unilateral, we are interested in:
(1) Disorganization: accelerated mobility, unrest, disease, and crime as manifestations and measures of social disorganization.
(2) Social movements (reorganization) include: (a) crowd movements (i.e., mobs, strikes, etc.); (b) cultural revivals, religious and linguistic; (c) fashion (changes in dress, convention, and social ritual); (d) reform (changes in social policy and administration); (e) revolutions (changes in institutions and the mores).
5. The individual and the person.—The person is an individual who has status. We come into the world as individuals. We acquire status, and become persons. Status means position in society. The individual inevitably has some status in every social group of which he is a member. In a given group the status of every member is determined by his relation to every other member of that group. Every smaller group, likewise, has a status in some larger group of which it is a part and this is determined by its relation to all the other members of the larger group.
The individual's self-consciousness—his conception of his rôle in society, his "self," in short—while not identical with his personality is an essential element in it. The individual's conception of himself, however, is based on his status in the social group or groups of which he is a member. The individual whose conception of himself does not conform to his status is an isolated individual. The completely isolated individual, whose conception of himself is in no sense an adequate reflection of his status, is probably insane.
It follows from what is said that an individual may have many "selves" according to the groups to which he belongs and the extent to which each of these groups is isolated from the others. It is true, also, that the individual is influenced in differing degrees and in a specific manner, by the different types of group of which he is a member. This indicates the manner in which the personality of the individual may be studied sociologically.
Every individual comes into the world in possession of certain characteristic and relatively fixed behavior patterns which we call instincts. This is his racial inheritance which he shares with all members of the species. He comes into the world, also, endowed with certain undefined capacities for learning other forms of behavior, capacities which vary greatly in different individuals. These individual differences and the instincts are what is called original nature.[52]
Sociology is interested in "original nature" in so far as it supplies the raw materials out of which individual personalities and the social order are created. Both society and the persons who compose society are the products of social processes working in and through the materials which each new generation of men contributes to it.
Charles Cooley, who was the first to make the important distinction between primary and secondary groups, has pointed out that the intimate, face-to-face associations of primary groups, i.e., the family, the neighborhood, and the village community, are fundamental in forming the social nature and ideals of the individual.[53]
There is, however, an area of life in which the associations are more intimate than those of the primary group as that group is ordinarily conceived. Such are the relations between mother and child, particularly in the period of infancy, and the relations between men and women under the influence of the sexual instinct. These are the associations in which the most lasting affections and the most violent antipathies are formed. We may describe it as the area of touch relationships.
Finally, there is the area of secondary contacts, in which relationships are relatively impersonal, formal, and conventional. It is in this region of social life that the individual gains, at the same time, a personal freedom and an opportunity for distinction that is denied him in the primary group.
As a matter of fact, many, if not most, of our present social problems have their source and origin in the transition of great masses of the population—the immigrants, for example—out of a society based on primary group relationships into the looser, freer, and less controlled existence of life in great cities.
[39] John Dewey, Democracy and Education (New York, 1916), p. 5.
[40] Ibid., pp. 6-7.
[41] Émile Durkheim, "Représentations individuelles et représentations collectives," Revue métaphysique, VI (1898), 295. Quoted and translated by Charles Elmer Gehlke, "Émile Durkheim's Contributions to Sociological Theory," Studies in History, Economics, and Public Law, LXIII, 29-30.
[42] Bliss Perry, The American Mind (Boston, 1912), p. 47.
[43] James Mark Baldwin, Mental Development in the Child and the Race (New York and London, 1895); Charles A. Ellwood, Sociology in Its Psychological Aspects (New York and London, 1912).
[44] Labour and Life of the People (London, 1889), I, pp. 6-7.
[45] Thomas and Znaniecki, The Polish Peasant in Europe and America (Boston, 1918), I, 3.
[46] Walter B. Bodenhafer, "The Comparative Rôle of the Group Concept in Ward's Dynamic Sociology and Contemporary American Sociology," American Journal of Sociology, XXVI (1920-21), 273-314; 425-74; 588-600; 716-43.
[47] Stillwater, the Queen of the St. Croix, a report of a social survey, published by The Community Service of Stillwater, Minnesota, 1920, p. 71.
[48] Frank Tannenbaum, "Prison Democracy," Atlantic Monthly, October, 1920, pp. 438-39. (Psychology of the criminal group.)
[49] Ibid., pp. 443-46.
[50] Franz Oppenheimer, The State (Indianapolis, 1914), p. 5.
[51] Thomas and Znaniecki, op. cit., III, 34-36.
[52] Original nature in its relation to social welfare and human progress has been made the subject-matter of a special science, eugenics. For a criticism of the claims of eugenics as a social science see Leonard T. Hobhouse, Social Evolution and Political Theory (Columbia University Press, 1917).
[53] Charles H. Cooley, Social Organization, p. 28.
The "moral unrest" so deeply penetrating all western societies, the growing vagueness and indecision of personalities, the almost complete disappearance of the "strong and steady character" of old times, in short, the rapid and general increase of Bohemianism and Bolshevism in all societies, is an effect of the fact that not only the early primary group controlling all interests of its members on the general social basis, not only the occupational group of the mediaeval type controlling most of the interests of its members on a professional basis, but even the special modern group dividing with many others the task of organizing permanently the attitudes of each of its members, is more and more losing ground. The pace of social evolution has become so rapid that special groups are ceasing to be permanent and stable enough to organize and maintain organized complexes of attitudes of their members which correspond to their common pursuits. In other words, society is gradually losing all its old machinery for the determination and stabilization of individual characters.[54]
Every social group tends to create, from the individuals that compose it, its own type of character, and the characters thus formed become component parts of the social structure in which they are incorporated. All the problems of social life are thus problems of the individual; and all problems of the individual are at the same time problems of the group. This point of view is already recognized in preventive medicine, and to some extent in psychiatry. It is not yet adequately recognized in the technique of social case work.
Further advance in the application of social principles to social practice awaits a more thoroughgoing study of the problems, systematic social research, and an experimental social science.
REPRESENTATIVE WORKS IN SYSTEMATIC SOCIOLOGY AND METHODS OF SOCIOLOGICAL RESEARCH
I. THE SCIENCE OF PROGRESS
(1) Comte, Auguste. Cours de philosophie positive, 5th ed. 6 vols. Paris, 1892.
(2) ——. Positive Philosophy. Translated by Harriet Martineau, 3d ed. London, 1893.
(3) Spencer, Herbert. Principles of Sociology. 3d ed. 3 vols. New York, 1906.
(4) Schaeffle, Albert. Bau und Leben des socialen Körpers. 2d ed., 2 vols. Tuebingen, 1896.
(5) Lilienfeld, Paul von. Gedanken über die Socialwissenschaft der Zukunft. 5 vols. Mitau, 1873-81.
(6) Ward, Lester F. Dynamic Sociology. 2 vols. New York, 1883.
(7) De Greef, Guillaume. Introduction à la sociologie. 3 vols. Paris, 1886.
(8) Worms, René. Organisme et société. Paris, 1896.
II. THE SCHOOLS
A. Realists
(1) Ratzenhofer, Gustav. Die sociologische Erkenntnis. Leipzig, 1898.
(2) Small, Albion W. General Sociology. Chicago, 1905.
(3) Durkheim, Émile. De la Division du travail social. Paris, 1893.
(4) Simmel, Georg. Soziologie. Untersuchungen über die Formen der Vergesellschaftung. Leipzig, 1908.
(5) Cooley, Charles Horton. Social Organization. A study of the larger mind. New York, 1909.
(6) Ellwood, Charles A. Sociology and Its Psychological Aspects. New York and London, 1912.
B. Nominalists
(1) Tarde, Gabriel. Les Lois de l'imitation. Paris, 1895.
(2) Giddings, Franklin H. The Principles of Sociology. New York, 1896.
(3) Ross, Edward Alsworth. The Principles of Sociology. New York, 1920.
C. Collective Behavior
(1) Le Bon, Gustave. The Crowd. A study of the popular mind. New York, 1903.
(2) Sighele, Scipio. Psychologie des sectes. Paris, 1898.
(3) Tarde, Gabriel. L'Opinion et la foule. Paris, 1901.
(4) McDougall, William. The Group Mind. Cambridge, 1920.
(5) Vincent, George E. The Social Mind and Education. New York, 1897.
III. METHODS OF SOCIOLOGICAL INVESTIGATION
A. Critical Observation on Methods of Research
(1) Small, Albion W. The Meaning of Social Science. Chicago, 1910.
(2) Durkheim, Émile. Les Règles de la méthode sociologique. Paris, 1904.
(3) Thomas, W. I., and Znaniecki, F. The Polish Peasant in Europe and America. "Methodological Note," I, 1-86. 5 vols. Boston, 1918-20.
B. Studies of Communities
(1) Booth, Charles. Labour and Life of the People: London. 2 vols. London, 1891.
(2) ——. Life and Labour of the People in London. 9 vols. London, 1892-97. 8 additional vols. London, 1902.
(3) The Pittsburgh Survey. Edited by Paul U. Kellogg. 6 vols. Russell Sage Foundation. New York, 1909-14.
(4) The Springfield Survey. Edited by Shelby M. Harrison. 3 vols. Russell Sage Foundation. New York, 1918-20.
(5) Americanization Studies of the Carnegie Corporation of New York. Edited by Allen T. Burns. 10 vols. New York, 1920-21.
(6) Chapin, F. Stuart. Field Work and Social Research. New York, 1920.
C. Studies of the Individual
(1) Healy, William. The Individual Delinquent. Boston, 1915.
(2) Thomas, W. I., and Znaniecki, F. The Polish Peasant in Europe and America. "Life Record of an Immigrant," Vol. III. Boston, 1919.
(3) Richmond, Mary. Social Diagnosis. Russell Sage Foundation. New York, 1917.
IV. PERIODICALS
(1) American Journal of Sociology. Chicago, University of Chicago Press, 1896-.
(2) American Sociological Society, Papers and Proceedings. Chicago, University of Chicago Press, 1907-.
(3) Annales de l'institut international de sociologie. Paris, M. Giard et Cie., 1895.
(4) L'Année sociologique. Paris, F. Alcan, 1898-1912.
(5) The Indian Journal of Sociology. Baroda, India, The College, 1920-.
(6) Kölner Vierteljahrshefte für Sozialwissenschaften. Leipzig and München, Duncker und Humblot, 1921-.
(7) Rivista italiana di sociologia. Roma, Fratelli Bocca, 1897-.
(8) Revue del'institut de sociologie. Bruxelles, l'Institut de Sociologie, 1920-. [Successor to Bulletin del'institut de sociologie Solvay. Bruxelles, 1910-14.]
(9) Revue internationale de sociologie. Paris, M. Giard et Cie., 1893-.
(10) The Sociological Review. Manchester, Sherratt and Hughes, 1908-. [Preceded by Sociological Papers, Sociological Society, London, 1905-7.]
(11) Schmollers Jahrbuch für Gesetzgebung, Verwaltung und Volkswirtschaft im deutschen Reiche. Leipzig, Duncker und Humblot, 1877-.
(12) Zeitschrift für Sozialwissenschaft. Berlin, G. Reimer, 1898-.
TOPICS FOR WRITTEN THEMES
1. Comte's Conception of Humanity
2. Herbert Spencer on the Social Organism
3. The Social Process as Defined by Small
4. Imitation and Like-mindedness as Fundamental Social Facts
5. Social Control as a Sociological Problem
6. Group Consciousness and the Group Mind
7. Investigation and Research as Illustrated by the Pittsburgh Survey and the Carnegie Americanization Studies
8. The Concept of the Group in Sociology
9. The Person, Personality, and Status
10. Sociology in Its Relation to Economics and to Politics
QUESTIONS FOR DISCUSSION
1. What do you understand was Comte's purpose in demanding for sociology a place among the sciences?
2. Are social phenomena susceptible to scientific prevision? Compare with physical phenomena.
3. What is Comte's order of the sciences? What is your explanation for the late appearance of sociology in the series?
4. What do you understand by the term "positive" when applied to the social sciences?
5. Can sociology become positive without becoming experimental?
6. "Natural science emphasizes the abstract, the historian is interested in the concrete." Discuss.
7. How do you distinguish between the historical method and the method of natural science in dealing with the following phenomena: (a) electricity, (b) plants, (c) cattle, (d) cities?
8. Distinguish between history, natural history, and natural science.
9. Is Westermarck's Origin and Development of the Moral Ideas history, natural history, or sociology? Why?
10. "History is past politics, politics is present history." Do you agree? Elaborate your position.
11. What is the value of history to the person?
12. Classify the following formulas of behavior under either (a) natural law (social law in the scientific sense), and (b) moral law (customary sanction, ethical principles), (c) civil law: "birds of a feather flock together"; "thou shalt not kill"; an ordinance against speeding; "honesty is the best policy"; monogamy; imitation tends to spread in geometric ratio; "women first"; the Golden Rule; "walk in the trodden paths"; the federal child-labor statute.
13. Give an illustration of a sociological hypothesis.
14. Of the following statements of fact, which are historical and which sociological?
Auguste Comte suffered from myopia.
"Man is born free, and everywhere he is in chains."
"Science works not at all for nationality or its spirit. It makes entirely for cosmopolitanism."
15. How would you verify each of the foregoing statements? Distinguish between the sociological and historical methods of verification.
16. Is the use of the comparative method that of history or that of natural science?
17. "The social organism: humanity or Leviathan?" What is your reaction to this alternative? Why?
18. What was the difference in the conception of the social organism held by Comte and that held by Spencer?
19. "How does a mere collection of individuals succeed in acting in a corporate and consistent way?" What was the answer to this question given by Hobbes, Aristotle, Worms?
20. "Man and society are at the same time products of nature and of human artifice." Explain.
21. What are the values and limitations of the following explanations of the control of the group over the behavior of its members: (a) homogeneity, (b) like-mindedness, (c) imitation, (d) common purpose?
22. What bearing have the facts of a panic or a stampede upon the theories of like-mindedness, imitation, and common purpose as explanations of group behavior?
23. "The characteristic social phenomenon is just this control by the group as a whole of the individuals which compose it. This fact of control is the fundamental social fact." Give an illustration of the control of the group over its members.
24. What is the difference between group mind and group consciousness as indicated in current usage in the phrases "urban mind," "rural mind," "public mind," "race consciousness," "national consciousness," "class consciousness"?
25. What do you understand by "a group in being"? Compare with the nautical expression "a fleet in being." Is "a fleet in being" a social organism? Has it a "social mind" and "social consciousness" in the sense that we speak of "race consciousness", for example, or "group consciousness"?
26. In what sense is public opinion objective? Analyze a selected case where the opinion of the group as a whole is different from the opinion of its members as individuals.
27. For what reason was the fact of "social control" interpreted in terms of "the collective mind"?
28. Which is the social reality (a) that society is a collection of like-minded persons, or (b) that society is a process and a product of interaction? What is the bearing upon this point of the quotation from Dewey: "Society may fairly be said to exist in transmission"?
29. What three steps were taken in the transformation of sociology from a philosophy of history to a science of society?
30. What value do you perceive in a classification of social problems?
31. Classify the following studies under (a) administrative problems or (b) problems of policy or (c) problems of human nature: a survey to determine the feasibility of health insurance to meet the problem of sickness; an investigation of the police force; a study of attitudes toward war; a survey of the contacts of racial groups; an investigation for the purpose of improving the technique of workers in a social agency; a study of the experiments in self-government among prisoners in penal institutions.
32. Is the description of great cities as "social laboratories" metaphor or fact?
33. What do you understand by the statement: Sociology will become an experimental science as soon as it can state its problems in such a way that the results in one instance show what can be done in another?
34. What would be the effect upon political life if sociology were able to predict with some precision the effects of political action, for example, the effect of prohibition?
35. Would you favor turning over the government to control of experts as soon as sociology became a positive science? Explain.
36. How far may the politician who makes a profession of controlling elections be regarded as a practicing sociologist?
37. What is the distinction between sociology as an art and as a science?
38. Distinguish between research and investigation as the terms are used in the text.
39. What illustrations in American society occur to you of the (a) autocratic and (b) democratic methods of social change?
40. "All social problems turn out finally to be problems of group life." Are there any exceptions?
41. Select twelve groups at random and enter under the heads in the classification of social groups. What groups are difficult to classify?
42. Study the organization and structure of one of the foregoing groups in terms of (a) statistical facts about it; (b) its institutional aspect; (c) its heritages; and (d) its collective opinion.
43. "All progress implies a certain amount of disorganization." Explain.
44. What do you understand to be the differences between the various social processes: (a) historical, (b) cultural, (c) economic, (d) political?
45. What is the significance of the relative diameters of the areas of the cultural, political, and economic processes?
46. "The person is an individual who has status." Does an animal have status?
47. "In a given group the status of every member is determined by his relation to every other member of that group." Give an illustration.
48. Why are the problems of the person, problems of the group as well?
49. What does the organization of the bibliography and the sequence of the volumes referred to suggest in regard to the development of sociological science?
50. How far does it seem to you that the emphasis upon process rather than progress accounts for the changes which have taken place in the sociological theory and point of view?
FOOTNOTES:
[2] From Robert E. Park, "Sociology and the Social Sciences," American Journal of Sociology, XXVI (1920-21), 401-24; XXVII (1921-22), 1-21; 169-83.
[3] Harriet Martineau, The Positive Philosophy of Auguste Comte, freely translated and condensed (London, 1893), II, 61.
[4] Harriet Martineau, op. cit., II, 59-61.
[5] Montesquieu, Baron M. de Secondat, The Spirit of Laws, translated by Thomas Nugent (Cincinnati, 1873), I, xxxi.
[6] David Hume, Inquiry Concerning Human Understanding, Part II, sec. 7.
[7] Condorcet, Esquisse d'un tableau historique des progrès de l'esprit humain (1795), 292. See Paul Barth, Die Philosophie der Geschichte als Sociologie (Leipzig, 1897), Part I, pp. 21-23.
[8] Œuvres de Saint-Simon et d'Enfantin (Paris, 1865-78), XVII, 228. Paul Barth, op. cit., Part I, p. 23.
[9] Henry Adams, The Degradation of the Democratic Dogma (New York, 1919), p. 126.
[10] James Harvey Robinson, The New History, Essays Illustrating the Modern Historical Outlook (New York, 1912), pp. 54-55.
[11] James Harvey Robinson, op. cit., p. 83.
[12] Wilhelm Windelband, Geschichte und Naturwissenschaft, Rede zum Antritt des Rectorats der Kaiser-Wilhelms Universität Strassburg (Strassburg, 1900). The logical principle outlined by Windelband has been further elaborated by Heinrich Rickert in Die Grenzen der naturwissenschaftlichen Begriffsbildung, eine logische Einleitung in die historischen Wissenschaften (Tübingen u. Leipzig, 1902). See also Georg Simmel, Die Probleme der Geschichtsphilosophie, eine erkenntnistheoretische Studie (2d ed., Leipzig, 1915).
[13] J. Arthur Thomson, The System of Animate Nature (New York, 1920), pp. 8-9. See also Karl Pearson, The Grammar of Science (2d ed.; London, 1900), chap. iii, "The Scientific Law."
[14] Karl Pearson, op. cit., p. 359.
[15] Henry Adams, op. cit., p. 127.
[16] Professor Robertson Smith (Nature, XLIV, 270), criticizing Westermarck's History of Human Marriage, complains that the author has confused history with natural history. "The history of an institution," he writes, "which is controlled by public opinion and regulated by law is not natural history. The true history of marriage begins where the natural history of pairing ends.... To treat these topics (polyandry, kinship through the female only, infanticide, exogamy) as essentially a part of the natural history of pairing involves a tacit assumption that the laws of society are at bottom mere formulated instincts, and this assumption really underlies all our author's theories. His fundamental position compels him, if he will be consistent with himself, to hold that every institution connected with marriage that has universal validity, or forms an integral part of the main line of development, is rooted in instinct, and that institutions which are not based on instinct are necessarily exceptional and unimportant for scientific history."
[17] Edward Westermarck, The History of Human Marriage (London, 1901), p. 1.
[18] Ibid., p. 5.
[19] Jane Ellen Harrison, Themis, A Study of the Social Origins of Greek Religion (Cambridge, 1912), p. ix.
[20] Robert H. Lowie, Primitive Society (New York, 1920), pp. 7-8.
[21] Wilhelm Wundt, Völkerpsychologie, eine Untersuchung der Entwicklungsgesetze von Sprache, Mythus und Sitte. Erster Band, Die Sprache, Erster Theil (Leipzig, 1900), p. 13. The name folk-psychology was first used by Lazarus and Steinthal, Zeitschrift für Völkerpsychologie und Sprachwissenschaft, I, 1860. Wundt's folk-psychology is a continuation of the tradition of these earlier writers.
[22] G. Tarde, Social Laws, An Outline of Sociology, translated from the French by Howard C. Warren (New York, 1899), pp. 40-41.
[23] Hanns Oertel, "Some Present Problems and Tendencies in Comparative Philology," Congress of Arts and Science, Universal Exposition, St. Louis, 1904 (Boston, 1906), III, 59.
[24] Edward A. Freeman, Comparative Politics (London, 1873), p. 23.
[25] L. Lévy-Bruhl, The Philosophy of Auguste Comte, authorized translation; an Introduction by Frederic Harrison (New York, 1903), p. 337.
[26] Ibid., p. 234.
[27] Hobbes's statement is as follows: "For by art is created that great Leviathan called a Commonwealth, or State, in Latin Civitas, which is but an artificial man; though of greater stature and strength than the natural, for whose protection and defence it was intended; and in which the sovereignty is an artificial soul, as giving life and motion to the whole body; the magistrates, and other officers of judicature, artificial joints; reward and punishment, by which fastened to the seat of the sovereignty every joint and member is moved to perform his duty, are the nerves, that do the same in the body natural." Spencer criticizes this conception of Hobbes as representing society as a "factitious" and artificial rather than a "natural" product. Herbert Spencer, The Principles of Sociology (London, 1893), I, 437, 579-80. See also chap. iii, "Social Growth," pp. 453-58.
[28] Herbert Spencer, op. cit., I, 437.
[29] Ibid., p. 440.
[30] Ibid., p. 450.
[31] Ibid., pp. 449-50.
[32] Westminster Review, January, 1860.
[33] René Worms, Organisme et Société, "Bibliothèque Sociologique Internationale" (Paris, 1896), pp. 210-13.
[34] W. Trotter, Instincts of the Herd in Peace and War (New York, 1916), pp. 29-30.
[35] Ibid., pp. 40-41.
[36] Franklin Henry Giddings, The Concepts and Methods of Sociology, Congress of Arts and Science, Universal Exposition (St. Louis, 1904), pp. 789-90.
[37] G. Tarde, op. cit., pp. 38-39.
[38] Émile Durkheim, Elementary Forms of Religious Life (New York, 1915), pp. 206-8.
[39] John Dewey, Democracy and Education (New York, 1916), p. 5.
[40] Ibid., pp. 6-7.
[41] Émile Durkheim, "Représentations individuelles et représentations collectives," Revue métaphysique, VI (1898), 295. Quoted and translated by Charles Elmer Gehlke, "Émile Durkheim's Contributions to Sociological Theory," Studies in History, Economics, and Public Law, LXIII, 29-30.
[42] Bliss Perry, The American Mind (Boston, 1912), p. 47.
[43] James Mark Baldwin, Mental Development in the Child and the Race (New York and London, 1895); Charles A. Ellwood, Sociology in Its Psychological Aspects (New York and London, 1912).
[44] Labour and Life of the People (London, 1889), I, pp. 6-7.
[45] Thomas and Znaniecki, The Polish Peasant in Europe and America (Boston, 1918), I, 3.
[46] Walter B. Bodenhafer, "The Comparative Rôle of the Group Concept in Ward's Dynamic Sociology and Contemporary American Sociology," American Journal of Sociology, XXVI (1920-21), 273-314; 425-74; 588-600; 716-43.
[47] Stillwater, the Queen of the St. Croix, a report of a social survey, published by The Community Service of Stillwater, Minnesota, 1920, p. 71.
[48] Frank Tannenbaum, "Prison Democracy," Atlantic Monthly, October, 1920, pp. 438-39. (Psychology of the criminal group.)
[49] Ibid., pp. 443-46.
[50] Franz Oppenheimer, The State (Indianapolis, 1914), p. 5.
[51] Thomas and Znaniecki, op. cit., III, 34-36.
[52] Original nature in its relation to social welfare and human progress has been made the subject-matter of a special science, eugenics. For a criticism of the claims of eugenics as a social science see Leonard T. Hobhouse, Social Evolution and Political Theory (Columbia University Press, 1917).
[53] Charles H. Cooley, Social Organization, p. 28.
[54] Thomas and Znaniecki, op. cit., III, 63-64.
CHAPTER II
HUMAN NATURE
I. INTRODUCTION
1. Human Interest in Human Nature
The human interest in human nature is proverbial. It is an original tendency of man to be attentive to the behavior of other human beings. Experience heightens this interest because of the dependence of the individual upon other persons, not only for physical existence, but for social life.
The literature of every people is to a large extent but the crystallization of this persistent interest. Old saws and proverbs of every people transmit from generation to generation shrewd generalizations upon human behavior. In joke and in epigram, in caricature and in burlesque, in farce and in comedy, men of all races and times have enjoyed with keen relish the humor of the contrast between the conventional and the natural motives in behavior. In Greek mythology, individual traits of human nature are abstracted, idealized, and personified into gods. The heroes of Norse sagas and Teutonic legends are the gigantic symbols of primary emotions and sentiments. Historical characters live in the social memory not alone because they are identified with political, religious, or national movements but also because they have come to typify human relationships. The loyalty of Damon and Pythias, the grief of Rachel weeping for her children, the cynical cruelty of the egocentric Nero, the perfidy of Benedict Arnold, the comprehending sympathy of Abraham Lincoln, are proverbial, and as such have become part of the common language of all the peoples who participate in our occidental culture.
Poetry, drama, and the plastic arts are interesting and significant only so far as they reveal in new and ever changing circumstances the unchanging characteristics of a fundamental human nature. Illustrations of this naïve and unreflecting interest in the study of mankind are familiar enough in the experience and observation of any of us. Intellectual interest in, and the scientific observation of, human traits and human behavior have their origin in this natural interest and unreflective observation by man of his fellows. History, ethnology, folklore, all the comparative studies of single cultural traits, i.e., of language, of religion, and of law, are but the more systematic pursuit of this universal interest of mankind in man.
2. Definition of Human Nature
The natural history of the expression "human nature" is interesting. Usage has given it various shades of meaning. In defining the term more precisely there is a tendency either unwarrantedly to narrow or unduly to extend and overemphasize some one or another of the different senses of the term. A survey of these varied uses reveals the common and fundamental meaning of the phrase.
The use which common sense makes of the term human nature is significant. It is used in varied contexts with the most divergent implications but always by way of explanation of behavior that is characteristically human. The phrase is sometimes employed with cynical deprecation as, "Oh, that's human nature." Or as often, perhaps, as an expression of approbation, "He's so human."
The weight of evidence as expressed in popular sayings is distinctly in depreciation of man's nature.
It's human natur', p'raps,—if so, Oh, isn't human natur' low,
are two lines from Gilbert's musical comedy "Babette's Love." "To err is human, to forgive divine" reminds us of a familiar contrast. "Human nature is like a bad clock; it might go right now and then, or be made to strike the hour, but its inward frame is to go wrong," is a simile that emphasizes the popular notion that man's behavior tends to the perverse. An English divine settles the question with the statement, "Human nature is a rogue and a scoundrel, or why would it perpetually stand in need of laws and religion?"
Even those who see good in the natural man admit his native tendency to err. Sir Thomas Browne asserts that "human nature knows naturally what is good but naturally pursues what is evil." The Earl of Clarendon gives the equivocal explanation that "if we did not take great pains to corrupt our nature, our nature would never corrupt us." Addison, from the detached position of an observer and critic of manners and men, concludes that "as man is a creature made up of different extremes, he has something in him very great and very mean."
The most commonly recognized distinction between man and the lower animals lies in his possession of reason. Yet familiar sayings tend to exclude the intellectual from the human attributes. Lord Bacon shrewdly remarks that "there is in human nature, generally, more of the fool than of the wise." The phrase "he is a child of nature" means that behavior in social relations is impulsive, simple, and direct rather than reflective, sophisticated, or consistent. Wordsworth depicts this human type in his poem "She Was a Phantom of Delight":
A creature not too bright or good For human nature's daily food; For transient sorrows, simple wiles, Praise, blame, love, kisses, tears and smiles.
The inconsistency between the rational professions and the impulsive behavior of men is a matter of common observation. "That's not the logic, reason, or philosophy of it, but it's the human nature of it." It is now generally recognized that the older English conception of the "economic man" and the "rational man," motivated by enlightened self-interest, was far removed from the "natural man" impelled by impulse, prejudice, and sentiment, in short, by human nature. Popular criticism has been frequently directed against the reformer in politics, the efficiency expert in industry, the formalist in religion and morals on the ground that they overlook or neglect the so-called "human factor" in the situation. Sir Arthur Helps says:
No doubt hard work is a great police-agent; if everybody were worked from morning till night, and then carefully locked up, the register of crimes might be greatly diminished. But what would become of human nature? Where would be the room for growth in such a system of things? It is through sorrow and mirth, plenty and need, a variety of passions, circumstances, and temptations, even through sin and misery, that men's natures are developed.
Certain sayings already quoted imply that the nature of man is a fact to be reckoned with in controlling his behavior. "There are limits to human nature" which cannot lightly be overstepped. "Human nature," according to Periander, "is hard to overcome." Yet we also recognize with Swift that "it is the talent of human nature to run from one extreme to another." Finally, nothing is more trite and familiar than the statement that "human nature is the same all over the world." This fundamental likeness of human nature, despite artificial and superficial cultural differences, has found a classic expression in Kipling's line: "The Colonel's Lady an' Judy O'Grady are sisters under their skins!"
Human nature, then, as distinct from the formal wishes of the individual and the conventional order of society, is an aspect of human life that must be reckoned with. Common sense has long recognized this, but until recently no systematic attempt has been made to isolate, describe, and explain the distinctively human factors in the life either of the individual or of society.
Of all that has been written on this subject the most adequate statement is that of Cooley. He has worked out with unusual penetration and peculiar insight an interpretation of human nature as a product of group life.
[54] Thomas and Znaniecki, op. cit., III, 63-64.
SOCIOLOGY AND THE SOCIAL SCIENCES[2]
We have to contemplate social phenomena as susceptible of prevision, like all other classes, within the limits of exactness compatible with their higher complexity. Comprehending the three characteristics of political science which we have been examining, prevision of social phenomena supposes, first, that we have abandoned the region of metaphysical idealities, to assume the ground of observed realities by a systematic subordination of imagination to observation; secondly, that political conceptions have ceased to be absolute, and have become relative to the variable state of civilization, so that theories, following the natural course of facts, may admit of our foreseeing them; and, thirdly, that permanent political action is limited by determinate laws, since, if social events were always exposed to disturbance by the accidental intervention of the legislator, human or divine, no scientific prevision of them would be possible. Thus, we may concentrate the conditions of the spirit of positive social philosophy on this one great attribute of scientific prevision.[3]
Men were long in learning that Man's power of modifying phenomena can result only from his knowledge of their natural laws; and in the infancy of each science, they believed themselves able to exert an unbounded influence over the phenomena of that science.... Social phenomena are, of course, from their extreme complexity, the last to be freed from this pretension: but it is therefore only the more necessary to remember that the pretension existed with regard to all the rest, in their earliest stage, and to anticipate therefore that social science will, in its turn, be emancipated from the delusion.... It [the existing social science] represents the social action of Man to be indefinite and arbitrary, as was once thought in regard to biological, chemical, physical, and even astronomical phenomena, in the earlier stages of their respective sciences.... The human race finds itself delivered over, without logical protection, to the ill-regulated experimentation of the various political schools, each one of which strives to set up, for all future time, its own immutable type of government. We have seen what are the chaotic results of such a strife; and we shall find that there is no chance of order and agreement but in subjecting social phenomena, like all others, to invariable natural laws, which shall, as a whole, prescribe for each period, with entire certainty, the limits and character of political action: in other words, introducing into the study of social phenomena the same positive spirit which has regenerated every other branch of human speculation.[4]
I have first of all considered mankind; and the result of my thoughts has been, that amidst such an infinite diversity of laws and manners, they are not solely conducted by the caprice of fancy.[5]
Hume, likewise, put politics among the natural sciences.[6] Condorcet wanted to make history positive.[7] But there were, in the period between 1815 and 1840 in France, conditions which made the need of a new science of politics peculiarly urgent. The Revolution had failed and the political philosophy, which had directed and justified it, was bankrupt. France, between 1789 and 1815, had adopted, tried, and rejected no less than ten different constitutions. But during this period, as Saint-Simon noted, society, and the human beings who compose society, had not changed. It was evident that government was not, in any such sense as the philosophers had assumed, a mere artefact and legislative construction. Civilization, as Saint-Simon conceived it, was a part of nature. Social change was part of the whole cosmic process. He proposed, therefore, to make politics a science as positive as physics. The subject-matter of political science, as he conceived it, was not so much political forms as social conditions. History had been literature. It was destined to become a science.[8]
Hume, likewise, put politics among the natural sciences.[6] Condorcet wanted to make history positive.[7] But there were, in the period between 1815 and 1840 in France, conditions which made the need of a new science of politics peculiarly urgent. The Revolution had failed and the political philosophy, which had directed and justified it, was bankrupt. France, between 1789 and 1815, had adopted, tried, and rejected no less than ten different constitutions. But during this period, as Saint-Simon noted, society, and the human beings who compose society, had not changed. It was evident that government was not, in any such sense as the philosophers had assumed, a mere artefact and legislative construction. Civilization, as Saint-Simon conceived it, was a part of nature. Social change was part of the whole cosmic process. He proposed, therefore, to make politics a science as positive as physics. The subject-matter of political science, as he conceived it, was not so much political forms as social conditions. History had been literature. It was destined to become a science.[8]
Hume, likewise, put politics among the natural sciences.[6] Condorcet wanted to make history positive.[7] But there were, in the period between 1815 and 1840 in France, conditions which made the need of a new science of politics peculiarly urgent. The Revolution had failed and the political philosophy, which had directed and justified it, was bankrupt. France, between 1789 and 1815, had adopted, tried, and rejected no less than ten different constitutions. But during this period, as Saint-Simon noted, society, and the human beings who compose society, had not changed. It was evident that government was not, in any such sense as the philosophers had assumed, a mere artefact and legislative construction. Civilization, as Saint-Simon conceived it, was a part of nature. Social change was part of the whole cosmic process. He proposed, therefore, to make politics a science as positive as physics. The subject-matter of political science, as he conceived it, was not so much political forms as social conditions. History had been literature. It was destined to become a science.[8]
No one who has watched the course of history during the last generation can have felt doubt of its tendency. Those of us who read Buckle's first volume when it appeared in 1857, and almost immediately afterwards, in 1859, read the Origin of Species and felt the violent impulse which Darwin gave to the study of natural laws, never doubted that historians would follow until they had exhausted every possible hypothesis to create a science of history. Year after year passed, and little progress has been made. Perhaps the mass of students are more skeptical now than they were thirty years ago of the possibility that such a science can be created. Yet almost every successful historian has been busy with it, adding here a new analysis, a new generalization there; a clear and definite connection where before the rupture of idea was absolute; and, above all, extending the field of study until it shall include all races, all countries, and all times. Like other branches of science, history is now encumbered and hampered by its own mass, but its tendency is always the same, and cannot be other than what it is. That the effort to make history a science may fail is possible, and perhaps probable; but that it should cease, unless for reasons that would cause all science to cease, is not within the range of experience. Historians will not, and even if they would they can not, abandon the attempt. Science itself would admit its own failure if it admitted that man, the most important of all its subjects, could not be brought within its range.[9]
Fifty years have elapsed since Buckle's book appeared, and I know of no historian who would venture to maintain that we had made any considerable advance toward the goal he set for himself. A systematic prosecution of the various branches of social science, especially political economy, sociology, anthropology, and psychology, is succeeding in explaining many things; but history must always remain, from the standpoint of the astronomer, physicist, or chemist, a highly inexact and fragmentary body of knowledge.... History can no doubt be pursued in a strictly scientific spirit, but the data we possess in regard to the past of mankind are not of a nature to lend themselves to organization into an exact science, although, as we shall see, they may yield truths of vital importance.[10]
Sociology, as Comte conceived it, was not, as it has been characterized, "a highly important point of view," but a fundamental science, i.e., a method of investigation and "a body of discoveries about mankind."[11] In the hierarchy of the sciences, sociology, the last in time, was first in importance. The order was as follows: mathematics, astronomy, physics, chemistry, biology including psychology, sociology. This order represented a progression from the more elementary to the more complex. It was because history and politics were concerned with the most complex of natural phenomena that they were the last to achieve what Comte called the positive character. They did this in sociology.
What is true of the individual man is quite as true of the whole historical process: it has value only when it is unique. This is the principle which the Christian doctrine successfully maintained, as over against Hellenism in the Patristic philosophy. The middle point of their conception of the world was the fall and the salvation of mankind as a unique event. That was the first and great perception of the inalienable metaphysical right of the historian to preserve for the memory of mankind, in all their uniqueness and individuality, the actual events of life.[12]
"We must confess," said Prof. J. H. Poynting (1900, p. 616), "that physical laws have greatly fallen off in dignity. No long time ago they were quite commonly described as the Fixed Laws of Nature, and were supposed sufficient in themselves to govern the universe. Now we can only assign to them the humble rank of mere descriptions, often erroneous, of similarities which we believe we have observed.... A law of nature explains nothing, it has no governing power, it is but a descriptive formula which the careless have sometimes personified." It used to be said that "the laws of Nature are the thoughts of God"; now we say that they are the investigator's formulae summing up regularities of recurrence.[13]
"History," says Karl Pearson, "can never become science, can never be anything but a catalogue of facts rehearsed in a more or less pleasing language until these facts are seen to fall into sequences which can be briefly resumed in scientific formulae."[14] And Henry Adams, in a letter to the American Historical Association already referred to, confesses that history has thus far been a fruitless quest for "the secret which would transform these odds and ends of philosophy into one self-evident, harmonious, and complete system."
You may be sure that four out of five serious students of history who are living today have, in the course of their work, felt that they stood on the brink of a great generalization that would reduce all history under a law as clear as the laws which govern the material world. As the great writers of our time have touched one by one the separate fragments of admitted law by which society betrays its character as a subject for science, not one of them can have failed to feel an instant's hope that he might find the secret which would transform these odds and ends of philosophy into one self-evident, harmonious, and complete system. He has seemed to have it, as the Spanish say, in his inkstand. Scores of times he must have dropped his pen to think how one short step, one sudden inspiration, would show all human knowledge; how, in these thickset forests of history, one corner turned, one faint trail struck, would bring him on the highroad of science. Every professor who has tried to teach the doubtful facts which we now call history must have felt that sooner or later he or another would put order in the chaos and bring light into darkness. Not so much genius or favor was needed as patience and good luck. The law was certainly there, and as certainly was in places actually visible, to be touched and handled, as though it were a law of chemistry or physics. No teacher with a spark of imagination or with an idea of scientific method can have helped dreaming of the immortality that would be achieved by the man who should successfully apply Darwin's method to the facts of human history.[15]
Westermarck's History of Human Marriage is one of the earliest attempts to write the natural history of a social institution. It is based upon a comparison and classification of marriage customs of widely scattered peoples, living under varied physical and social conditions. What one gets from a survey of this kind is not so much history as a study of human behavior. The history of marriage, as of any other institution, is, in other words, not so much an account of what certain individuals or groups of individuals did at certain times and certain places, as it is a description of the responses of a few fundamental human instincts to a variety of social situations. Westermarck calls this kind of history sociology.[16]
Descriptive historiography has no higher object than that of offering materials to this science.[17]
The causes on which social phenomena are dependent fall within the domain of different sciences—Biology, Psychology, or Sociology. The reader will find that I put particular stress upon the psychological causes, which have often been deplorably overlooked, or only imperfectly touched upon. And more especially do I believe that the mere instincts have played a very important part in the origin of social institutions and rules.[18]
The mystery-god arises out of those instincts, emotions, desires which attend and express life; but these emotions, desires, instincts, in so far as they are religious, are at the outset rather of a group than of individual consciousness.... It is a necessary and most important corollary to this doctrine, that the form taken by the divinity reflects the social structure of the group to which the divinity belongs. Dionysius is the Son of his Mother because he issues from a matrilinear group.[19]
Since, as a matter of fact, cultural resemblances abound between peoples of diverse stock, their interpretation commonly narrows to a choice between two alternatives. Either they are due to like causes, whether these can be determined or not; or they are the result of borrowing. A predilection for one or the other explanation has lain at the bottom of much ethnological discussion in the past; and at present influential schools both in England and in continental Europe clamorously insist that all cultural parallels are due to diffusion from a single center. It is inevitable to envisage this moot-problem at the start, since uncompromising championship of either alternative has far-reaching practical consequences. For if every parallel is due to borrowing, then sociological laws, which can be inferred only from independently developing likenesses, are barred. Then the history of religion or social life or technology consists exclusively in a statement of the place of origin of beliefs, customs and implements, and a recital of their travels to different parts of the globe. On the other hand, if borrowing covers only part of the observed parallels, an explanation from like causes becomes at least the ideal goal in an investigation of the remainder.[20]
Among the social sciences the need for psychological interpretation first manifested itself in the studies of language and mythology. Both of these had already found outside the circle of the philological studies independent fields of investigation. As soon as they assumed the character of comparative sciences it was inevitable that they should be driven to recognize that in addition to the historical conditions, which everywhere determines the concrete form of these phenomena, there had been certain fundamental psychical forces at work in the development of language and myth.[21]
Thus, the unvarying characteristic of every social fact whatsoever is that it is imitative. And this characteristic belongs exclusively to social facts.[22]
It seems hard to maintain that the change in a syntactical construction or in the meaning of a word owes its universality to a simultaneous and independent primary change in all the members of a speech-community. By adopting the theory of imitative spread, all linguistic changes may be viewed as one homogeneous whole. In the second place, the latter view seems to bring linguistic changes into line with the other social changes, such as modifications in institutions, beliefs, and customs. For is it not an essential characteristic of a social group that its members are not co-operative in the sense that each member actively participates in the production of every single element which goes to make up either language, or belief, or customs? Distinguishing thus between primary and secondary changes and between the origin of a change and its spread, it behooves us to examine carefully into the causes which make the members of a social unit, either consciously or unconsciously, willing to accept the innovation. What is it that determines acceptance or rejection of a particular change? What limits one change to a small area, while it extends the area of another? Before a final decision can be reached in favor of the second theory of imitative spread it will be necessary to follow out in minute detail the mechanism of this process in a number of concrete instances; in other words to fill out the picture of which Tarde (Les lois de l'imitation) sketched the bare outlines. If his assumptions prove true, then we should have here a uniformity resting upon other causes than the physical uniformity that appears in the objects with which the natural sciences deal. It would enable us to establish a second group of uniform phenomena which is psycho-physical in its character and rests upon the basis of social suggestion. The uniformities in speech, belief, and institutions would belong to this second group.[23]
For the purposes then of the study of Comparative Politics, a political constitution is a specimen to be studied, classified, and labelled, as a building or an animal is studied, classified, and labelled by those to whom buildings or animals are objects of study. We have to note the likenesses, striking and unexpected as those likenesses often are, between the political constitutions of remote times and places; and we have, as far as we can, to classify our specimens according to the probable causes of those likenesses.[24]
Society for Comte is not, as Lévy-Bruhl puts it, "a polyp." It has not even the characteristics of an animal colony in which the individuals are physically bound together, though physiologically independent. On the contrary, "this 'immense organism' is especially distinguished from other beings in that it is made up of separable elements of which each one can feel its own co-operation, can will it, or even withhold it, so long as it remains a direct one."[25]
On the other hand, Comte, although he characterized the social consensus and solidarity as "collective," nevertheless thought of the relations existing between human beings in society—in the family, for example, which he regards as the unit and model of all social relations—as closer and more intimate than those which exist between the organs of a plant or an animal. The individual, as Comte expressed it, is an abstraction. Man exists as man only by participation in the life of humanity, and "although the individual elements of society appear to be more separable than those of a living being, the social consensus is still closer than the vital."[26]
If Comte thought of the social organism, the great being, somewhat mystically as itself an individual and a person, Herbert Spencer, on the other hand, thought of it realistically as a great animal, a leviathan, as Hobbes called it, and a very low-order leviathan at that.[27]
Here, then, is the first trait by which societies ally themselves with the organic world and substantially distinguish themselves from the inorganic world.[28]
This division of labour, first dwelt upon by political economists as a social phenomenon, and thereupon recognized by biologists as a phenomenon of living bodies, which they called the "physiological division of labour," is that which in the society, as in the animal, makes it a living whole. Scarcely can I emphasize enough the truth that in respect of this fundamental trait, a social organism and an individual organism are entirely alike.[29]
Of such a society as this it may indeed be said, that it "exists for the benefit of its members, not its members for the benefit of society. It has ever to be remembered that great as may be the efforts made for the prosperity of the body politic, yet the claims of the body politic are nothing in themselves, and become something only in so far as they embody the claims of its component individuals."[30]
In the one (the individual), consciousness is concentrated in a small part of the aggregate. In the other (society), it is diffused throughout the aggregate: all the units possess the capacities for happiness and misery, if not in equal degrees, still in degrees that approximate. As then, there is no social sensorium, the welfare of the aggregate, considered apart from that of the units, is not an end to be sought. The society exists for the benefit of its members; not its members for the benefit of the society.[31]
Since Spencer's essay on the social organism was published in 1860,[32] this problem and these questions, in one form or another, have largely absorbed the theoretical interest of students of society. The attempts to answer them may be said to have created the existing schools into which sociologists are divided.
Thus, always in the presence of great and common danger the collective consciousness of society is awakened; for example France of the Valois after the Treaty of Troyes, or modern France before the invasion of 1791 and before the German invasion in 1870; or Germany, herself, after the victories of Napoleon I. This sentiment of national unity, born of resistance to the stranger, goes so far that a large proportion of the members of society do not hesitate to give their lives for the safety and glory of the state, at such a moment the individual comprehends that he is only a small part of a large whole and that he belongs to the collectivity of which he is a member. The proof that he is entirely penetrated by the social consciousness is the fact that in order to maintain its existence he is willing to sacrifice his own.[33]
Again, not only will the individual be responsive to impulses coming from the herd, but he will treat the herd as his normal environment. The impulse to be in and always to remain with the herd will have the strongest instinctive weight. Anything which tends to separate him from his fellows, as soon as it becomes perceptible as such, will be strongly resisted.[34]
Conscience, then, and the feelings of guilt and of duty are the peculiar possessions of the gregarious animal. A dog and a cat caught in the commission of an offence will both recognize that punishment is coming; but the dog, moreover, knows that he has done wrong, and he will come to be punished, unwillingly it is true, and as if dragged along by some power outside him, while the cat's sole impulse is to escape. The rational recognition of the sequence of act and punishment is equally clear to the gregarious and to the solitary animal, but it is the former only who understands that he has committed a crime, who has, in fact, the sense of sin.[35]
Any given stimulus may happen to be felt by more than one organism, at the same or at different times. Two or more organisms may respond to the same given stimulus simultaneously or at different times. They may respond to the same given stimulus in like or in unlike ways; in the same or in different degrees; with like or with unlike promptitude; with equal or with unequal persistence. I have attempted to show that in like response to the same given stimulus we have the beginning, the absolute origin, of all concerted activity—the inception of every conceivable form of co-operation; while in unlike response, and in unequal response, we have the beginning of all those processes of individuation, of differentiation, of competition, which in their endlessly varied relations to combination, to co-operation, bring about the infinite complexity of organized social life.[36]
This minute inter-agreement of minds and wills, which forms the basis of the social life, even in troublous times—this presence of so many common ideas, ends, and means, in the minds and wills of all members of the same society at any given moment—is not due, I maintain, to organic heredity, which insures the birth of men quite similar to one another, nor to mere identity of geographical environment, which offers very similar resources to talents that are nearly equal; it is rather the effect of that suggestion-imitation process which, starting from one primitive creature possessed of a single idea or act, passed this copy on to one of its neighbors, then to another, and so on. Organic needs and spiritual tendencies exist in us only as potentialities which are realizable under the most diverse forms, in spite of their primitive similarity; and, among all these possible realizations, the indications furnished by some first initiator who is imitated determine which one is actually chosen.[37]
Now the ways of action to which society is strongly enough attached to impose them upon its members, are, by that very fact, marked with a distinctive sign provocative of respect. Since they are elaborated in common, the vigour with which they have been thought of by each particular mind is retained in all the other minds, and reciprocally. The representations which express them within each of us have an intensity which no purely private states of consciousness could ever attain; for they have the strength of the innumerable individual representations which have served to form each of them. It is society who speaks through the mouths of those who affirm them in our presence; it is society whom we hear in hearing them; and the voice of all has an accent which that of one alone could never have. The very violence with which society reacts, by way of blame or material suppression, against every attempted dissidence, contributes to strengthening its empire by manifesting the common conviction through this burst of ardour. In a word, when something is the object of such a state of opinion, the representation which each individual has of it gains a power of action from its origins and the conditions in which it was born, which even those feel who do not submit themselves to it. It tends to repel the representations which contradict it, and it keeps them at a distance; on the other hand it commands those acts which will realize it, and it does so, not by a material coercion or by the perspective of something of this sort, but by the simple radiation of the mental energy which it contains.[38]
Society not only continues to exist by transmission, by communication, but it may fairly be said to exist in transmission, in communication. There is more than a verbal tie between the words common, community, and communication.[39]
Try the experiment of communicating, with fullness and accuracy, some experience to another, especially if it be somewhat complicated, and you will find your own attitude toward your experience changing; otherwise you resort to expletives and ejaculations. Except in dealing with commonplaces and catch phrases one has to assimilate, imaginatively, something of another's experience in order to tell him intelligently of one's own experience. All communication is like art.[40]
The collective representations are exterior to the individual consciousness because they are not derived from the individuals taken in isolation but from their convergence and union (concours).... Doubtless, in the elaboration of the common result, each (individual) bears his due share; but the private sentiments do not become social except by combining under the action of the forces sui generis which association develops. As a result of these combinations, and of the mutual alterations which result therefrom, they (the private sentiments) become something else (autre chose). A chemical synthesis results, which concentrates, unifies, the elements synthetized, and by that very process transforms them.... The resultant derived therefrom extends then beyond (deborde) the individual mind as the whole is greater than the part. To know really what it is, one must take the aggregate in its totality. It is this that thinks, that feels, that wills, although it may not be able to will, feel, or act save by the intermediation of individual consciousnesses.[41]
The origin of the phrase, "the American mind," was political. Shortly after the middle of the eighteenth century, there began to be a distinctly American way of regarding the debatable question of British Imperial control. During the period of the Stamp Act agitation our colonial-bred politicians and statesmen made the discovery that there was a mode of thinking and feeling which was native—or had by that time become a second nature—to all the colonists. Jefferson, for example, employs those resonant and useful words "the American mind" to indicate that throughout the American colonies an essential unity of opinion had been developed as regards the chief political question of the day.[42]
There is implicit in this rather ambiguous popular usage of the terms "social mind" and "social consciousness" a recognition of the dual aspect of society and of social groups. Society may be regarded at the same time from an individualistic and a collectivistic point of view. Looking at it from the point of view of the individual, we regard as social just that character of the individual which has been imparted to, and impressed upon, him as a result of his participation in the life of the group. Social psychology, from Baldwin's first studies of the development of personality in the child to Ellwood's studies of the society in its "psychological aspects" has been mainly concerned with the investigation of the effects upon the individual of his contacts with other individuals.[43]
With regard to the disadvantages under which the poor labour, and the evils of poverty, there is a great sense of helplessness: the wage earners are helpless to regulate their work and cannot obtain a fair equivalent for the labour they are willing to give; the manufacturer or dealer can only work within the limits of competition; the rich are helpless to relieve want without stimulating its sources. To relieve this helplessness a better stating of the problems involved is the first step.... In this direction must be sought the utility of my attempt to analyze the population of a part of London.[44]
The oldest but most persistent form of social technique is that of "ordering-and-forbidding"—that is, meeting a crisis by an arbitrary act of will decreeing the disappearance of the undesirable or the appearance of the desirable phenomena, and the using arbitrary physical action to enforce the decree. This method corresponds exactly to the magical phase of natural technique. In both, the essential means of bringing a determined effect is more or less consciously thought to reside in the act of will itself by which the effect is decreed as desirable and of which the action is merely an indispensable vehicle or instrument; in both, the process by which the cause (act of will and physical action) is supposed to bring its effect to realization remains out of reach of investigation; in both, finally, if the result is not attained, some new act of will with new material accessories is introduced, instead of trying to find and remove the perturbing causes. A good instance of this in the social field is the typical legislative procedure of today.[45]
2. Types of social group.—The varied interests, fields of investigation, and practical programs which find at present a place within the limits of the sociological discipline are united in having one common object of reference, namely, the concept of the social group. All social problems turn out finally to be problems of group life, although each group and each type of group has its own distinctive problems. Illustrations may be gathered from the most widely separated fields to emphasize the truth of this assertion.[46]
In short, the greatest problem for the next few years in Stillwater is the development of a community consciousness. We must stop thinking in terms of city of Stillwater, and country outside of Stillwater, and think in terms of Stillwater Community. We must stop thinking in terms of small groups and think in terms of the entire community, no matter whether it is industry, health, education, recreation or religion. Anything which is good will benefit the entire community. Any weakness will be harmful to all. Community co-operation in all lines indicated in this report will make this, indeed, the Queen of the St. Croix.[47]
To the community the criminal is aggressive. To the criminal his life is one of defense primarily. The greater part of his energy, of his hopes, and of his successes, centres around escapes, around successful flight, around proper covering-up of his tracks, and around having good, loyal, and trustworthy friends to participate in his activities, who will tell no tales and keep the rest of the community outside. The criminal is thus, from his own point of view—and I am speaking of professional criminals—living a life of defensive warfare with the community; and the odds are heavy against him. He therefore builds up a defensive psychology against it—a psychology of boldness, bravado, and self-justification. The good criminal—which means the successful one, he who has most successfully carried through a series of depradations against the enemy, the common enemy, the public—is a hero. He is recognized as such, toasted and feasted, trusted and obeyed. But always by a little group. They live in a world of their own, a life of their own, with ideals, habits, outlook, beliefs, and associations which are peculiarly fitted to maintain the morale of the group. Loyalty, fearlessness, generosity, willingness to sacrifice one's self, perseverance in the face of prosecution, hatred of the common enemy—these are the elements that maintain the morale, but all of them are pointed against the community as a whole.[48]
The manner in which the principle of the primary group was applied at Sing Sing in dealing with the criminal within the prison walls is a still more interesting illustration of the fact that social problems are group problems.[49]
Every state in history was or is a state of classes, a polity of superior and inferior social groups, based upon distinctions either of rank or of property. This phenomenon must, then, be called the "State."[50]
There is no pre-existing harmony whatever between the individual and the social factors of personal evolution, and the fundamental tendencies of the individual are always in some disaccordance with the fundamental tendencies of social control. Personal evolution is always a struggle between the individual and society—a struggle for self-expression on the part of the individual, for his subjection on the part of society—and it is in the total course of this struggle that the personality—not as a static "essence" but as a dynamic, continually evolving set of activities—manifests and constructs itself.[51]
Every individual comes into the world in possession of certain characteristic and relatively fixed behavior patterns which we call instincts. This is his racial inheritance which he shares with all members of the species. He comes into the world, also, endowed with certain undefined capacities for learning other forms of behavior, capacities which vary greatly in different individuals. These individual differences and the instincts are what is called original nature.[52]
Charles Cooley, who was the first to make the important distinction between primary and secondary groups, has pointed out that the intimate, face-to-face associations of primary groups, i.e., the family, the neighborhood, and the village community, are fundamental in forming the social nature and ideals of the individual.[53]
The "moral unrest" so deeply penetrating all western societies, the growing vagueness and indecision of personalities, the almost complete disappearance of the "strong and steady character" of old times, in short, the rapid and general increase of Bohemianism and Bolshevism in all societies, is an effect of the fact that not only the early primary group controlling all interests of its members on the general social basis, not only the occupational group of the mediaeval type controlling most of the interests of its members on a professional basis, but even the special modern group dividing with many others the task of organizing permanently the attitudes of each of its members, is more and more losing ground. The pace of social evolution has become so rapid that special groups are ceasing to be permanent and stable enough to organize and maintain organized complexes of attitudes of their members which correspond to their common pursuits. In other words, society is gradually losing all its old machinery for the determination and stabilization of individual characters.[54]
By human nature we may understand those sentiments and impulses that are human in being superior to those of lower animals, and also in the sense that they belong to mankind at large, and not to any particular race or time. It means, particularly, sympathy and the innumerable sentiments into which sympathy enters, such as love, resentment, ambition, vanity, hero-worship, and the feeling of social right and wrong.
Human nature in this sense is justly regarded as a comparatively permanent element in society. Always and everywhere men seek honor and dread ridicule, defer to public opinion, cherish their goods and their children, and admire courage, generosity, and success. It is always safe to assume that people are and have been human.
Human nature is not something existing separately in the individual, but a group nature or primary phase of society, a relatively simple and general condition of the social mind. It is something more, on the one hand, than the mere instinct that is born in us—though that enters into it—and something less, on the other, than the more elaborate development of ideas and sentiments that makes up institutions. It is the nature which is developed and expressed in those simple, face-to-face groups that are somewhat alike in all societies; groups of the family, the playground, and the neighborhood. In the essential similarity of these is to be found the basis, in experience, for similar ideas and sentiments in the human mind. In these, everywhere, human nature comes into existence. Man does not have it at birth; he cannot acquire it except through fellowship, and it decays in isolation.[55]
3. Classification of the Materials
With the tacit acceptance by biologists, psychologists, and sociologists of human behavior as a natural phenomenon, materials upon human nature have rapidly accumulated. The wealth and variety of these materials are all the greater because of the diversity of the points of view from which workers in this field have attacked the problem. The value of the results of these investigations is enhanced when they are brought together, classified, and compared.
The materials fall naturally into two divisions: (a) "The Original Nature of Man" and (b) "Human Nature and Social Life." This division is based upon a distinction between traits that are inborn and characters socially acquired; a distinction found necessary by students in this field. Selections under the third heading, "Personality and the Social Self" indicate the manner in which the individual develops under the social influences, from the raw material of "instinct" into the social product "the person." Materials in the fourth division, "Biological and Social Inheritance," contrast the method of the transmission of original tendencies through the germ plasm with the communication of the social heritage through education.
a) The original nature of man.—No one has stated more clearly than Thorndike that human nature is a product of two factors, (a) tendencies to response rooted in original nature and (b) the accumulated effects of the stimuli of the external and social environment. At birth man is a bundle of random tendencies to respond. Through experience, and by means of the mechanisms of habit and character, control is secured over instinctive reactions. In other words, the original nature of man is, as Comte said, an abstraction. It exists only in the psychic vacuum of antenatal life, or perhaps only in the potentiality of the germ plasm. The fact of observation is that the structure of the response is irrevocably changed in the process of reaction to the stimulus. The Biography of a Baby gives a concrete picture of the development of the plastic infant in the environment of the social group.
The three papers on differences between sexes, races, and individuals serve as an introduction into the problem of differentiating the aspects of behavior which are in original nature from those that are acquired through social experience. Are the apparent differences between men and women, white and colored, John and James, those which arise from differences in the germ plasm or from differences in education and in cultural contacts? The selections must not be taken as giving the final word upon the subject. At best they represent merely the conclusions reached by three investigators. Attempts to arrive at positive differences in favor either of original nature or of education are frequently made in the interest of preconceived opinion. The problem, as far as science is concerned, is to discover what limitations original nature places upon response to social copies, and the ways in which the inborn potentialities find expression or repression in differing types of social environment.
b) Human nature and social life.—Original nature is represented in human responses in so far as they are determined by the innate structure of the individual organism. The materials assembled under this head treat of inborn reactions as influenced, modified, and reconstructed by the structure of the social organization.
The actual reorganization of human nature takes place in response to the folkways and mores, the traditions and conventions, of the group. So potentially fitted for social life is the natural man, however, so manifold are the expressions that the plastic original tendencies may take, that instinct is replaced by habit, precedent, personal taboo, and good form. This remade structure of human nature, this objective mind, as Hegel called it, is fixed and transmitted in the folkways and mores, social ritual, i.e., Sittlichkeit, to use the German word, and convention.
c) Personality and the social self.—The selections upon "Personality and the Social Self" bring together and compare the different definitions of the term. These definitions fall under three heads:
(1) The organism as personality: This is a biological statement, satisfactory as a definition only as preparatory to further analysis.
(2) Personality as a complex: Personality defined in terms of the unity of mental life is a conception that has grown up in the recent "individual psychology," so called. Personality includes, in this case, not only the memories of the individual and his stream of consciousness, but also the characteristic organization of mental complexes and trends which may be thought of as a supercomplex. The phenomena of double and multiple personalities occur when this unity becomes disorganized. Disorganization in releasing groups of complexes from control may even permit the formation of independent organizations. Morton Prince's book The Dissociation of a Personality is a classic case study of multiple personality. The selections upon "The Natural Person versus the Social and Conventional Person" and "The Divided Self and the Moral Consciousness" indicate the more usual and less extreme conflicts of opposing sentiments and interests within the organization of personality.
(3) Personality as the rôle of the individual in the group: The word personality is derived from the Latin persona, a mask used by actors. The etymology of the term suggests that its meaning is to be found in the rôle of the individual in the social group. By usage, personality carries the implication of the social expression of behavior. Personality may then be defined as the sum and organization of those traits which determine the rôle of the individual in the group. The following is a classification of the characteristics of the person which affect his social status and efficiency:
(a) physical traits, as physique, physiognomy, etc.; (b) temperament; (c) character; (d) social expression, as by facial expression, gesture, manner, speech, writing, etc.; (e) prestige, as by birth, past success, status, etc.; (f) the individual's conception of his rôle.
The significance of these traits consists in the way in which they enter into the rôle of the individual in his social milieu. Chief among these may be considered the individual's conception of the part which he plays among his fellows. Cooley's discriminating description of "the looking-glass self" offers a picture of the process by which the person conceives himself in terms of the attitudes of others toward him.
The reflected or looking-glass self seems to have three principal elements: the imagination of our appearance to the other person; the imagination of his judgment of that appearance; and some sort of self-feeling, such as pride or mortification. The comparison with a looking-glass self hardly suggests the second element, the imagined judgment, which is quite essential. The thing that moves us to pride or shame is not the mere mechanical reflection of ourselves, but an imputed sentiment, the imagined effect of this reflection upon another's mind. This is evident from the fact that the character and weight of that other, in whose mind we see ourselves, makes all the difference with our feeling.[56]
Veblen has made a subtle analysis of the way in which conduct is controlled by the individual's conception of his social rôle in his analysis of "invidious comparison" and "conspicuous expenditure."[57]
d) Biological and social inheritance.—The distinction between biological and social inheritance is sharply made by the noted biologist, J. Arthur Thomson, in the selection entitled "Nature and Nurture." The so-called "acquired characters" or modifications of original nature through experience, he points out, are transmitted not through the germ plasm but through communication.
Thorndike's "Inventory of Original Tendencies" offers a detailed classification of the traits transmitted biologically. Since there exists no corresponding specific analysis of acquired traits, the following brief inventory of types of social heritages is offered.
TYPES OF SOCIAL HERITAGES
(a) means of communication, as language, gesture, etc.; (b) social attitudes, habits, wishes, etc.; (c) character; (d) social patterns, as folkways, mores, conventions, ideals, etc.; (e) technique; (f) culture (as distinguished from technique, formal organization, and machinery); (g) social organization (primary group life, institutions, sects, secondary groups, etc.).
On the basis of the work of Mendel, biologists have made marked progress in determining the inheritance of specific traits of original nature. The selection from a foremost American student of heredity and eugenics, C. B. Davenport, entitled "Inheritance of Original Nature" indicates the precision and accuracy with which the prediction of the inheritance of individual innate traits is made.
The mechanism of the transmission of social heritages, while more open to observation than biological inheritance, has not been subjected to as intensive study. The transmission of the social heritage takes place by communication, as Keller points out, through the medium of the various senses. The various types of the social heritages are transmitted in two ways: (a) by tradition, as from generation to generation, and (b) by acculturation, as from group to group.
In the communication of the social heritages, either by tradition or by acculturation, two aspects of the process may be distinguished: (a) Because of temperament, interest, and run of attention of the members of the group, the heritage, whether a word, an act of skill, or a social attitude, may be selected, appropriated, and incorporated into its culture. This is communication by imitation. (b) On the other hand, the heritage may be imposed upon the members of the group through authority and routine, by tabu and repression. This is communication by inculcation. In any concrete situation the transmission of a social heritage may combine varying elements of both processes. Education, as the etymology of the term suggests, denotes culture of original tendencies; yet the routine of a school system is frequently organized about formal discipline rather than around interest, aptitude, and attention.
Historically, the scientific interest in the question of biological and social inheritance has concerned itself with the rather sterile problem of the weight to be attached on the one hand to physical heredity and on the other to social heritage. The selection, "Temperament, Tradition, and Nationality" suggests that a more important inquiry is to determine how the behavior patterns and the culture of a racial group or a social class are determined by the interaction of original nature and the social tradition. According to this conception, racial temperament is an active selective agency, determining interest and the direction of attention. The group heritages on the other hand represent a detached external social environment, a complex of stimuli, effective only in so far as they call forth responses. The culture of a group is the sum total and organization of the social heritages which have acquired a social meaning because of racial temperament and of the historical life of the group.
II. MATERIALS
A. THE ORIGINAL NATURE OF MAN
1. Original Nature Defined[58]
A man's nature and the changes that take place in it may be described in terms of the responses—of thought, feeling, action, and attitude—which he makes, and of the bonds by which these are connected with the situations which life offers. Any fact of intellect, character, or skill means a tendency to respond in a certain way to a certain situation—involves a situation or state of affairs influencing the man, a response or state of affairs in the man, and a connection or bond whereby the latter is the result of the former.
Any man possesses at the very start of his life—that is, at the moment when the ovum and spermatozoön which are to produce him have united—numerous well-defined tendencies to future behavior. Between the situations which he will meet and the responses which he will make to them, pre-formed bonds exist. It is already determined by the constitution of these two germs that under certain circumstances he will see and hear and feel and act in certain ways. His intellect and morals, as well as his bodily organs and movements, are in part the consequence of the nature of the embryo in the first moment of its life. What a man is and does throughout life is a result of whatever constitution he has at the start and of the forces that act upon it before and after birth. I shall use the term "original nature" for the former and "environment" for the latter. His original nature is thus a name for the nature of the combined germ-cells from which he springs, and his environment is a name for the rest of the universe, so far as it may, directly or indirectly, influence him.
Three terms, reflexes, instincts, and inborn capacities, divide the work of naming these unlearned tendencies. When the tendency concerns a very definite and uniform response to a very simple sensory situation, and when the connection between the situation and the response is very hard to modify and is also very strong so that it is almost inevitable, the connection or response to which it leads is called a reflex. Thus the knee-jerk is a very definite and uniform response to the simple sense-stimulus of sudden hard pressure against a certain spot.
When the response is more indefinite, the situation more complex, and the connection more modifiable, instinct becomes the customary term. Thus one's misery at being scorned is too indefinite a response to too complex a situation and is too easily modifiable to be called a reflex. When the tendency is to an extremely indefinite response or set of responses to a very complex situation, as when the connection's final degree of strength is commonly due to very large contributions from training, it has seemed more appropriate to replace reflex and instinct by some term like capacity, or tendency, or potentiality. Thus an original tendency to respond to the circumstances of school education by achievement in learning the arts and sciences is called the capacity for scholarship.
There is, of course, no gap between reflexes and instincts, or between instincts and the still less easily describable original tendencies. The fact is that original tendencies range with respect to the nature of the responses from such as are single, simple, definite, uniform within the individual and only slightly variable amongst individuals, to responses that are highly compound, complex, vague, and variable within one individual's life and amongst individuals.
A typical reflex, or instinct, or capacity, as a whole, includes the ability to be sensitive to a certain situation, the ability to make a certain response, and the existence of a bond or connection whereby that response is made to that situation. For instance, the young chick is sensitive to the absence of other members of his species, is able to peep, and is so organized that the absence of other members of the species makes him peep. But the tendency to be sensitive to a certain situation may exist without the existence of a connection therewith of any further exclusive response, and the tendency to make a certain response may exist without the existence of a connection limiting that response exclusively to any single situation. The three-year-old child is by inborn nature markedly sensitive to the presence and acts of other human beings, but the exact nature of his response varies. The original tendency to cry is very strong, but there is no one situation to which it is exclusively bound. Original nature seems to decide that the individual will respond somehow to certain situations more often than it decides just what he will do, and to decide that he will make certain responses more often than it decides just when he will make them. So, for convenience in thinking about man's unlearned equipment, this appearance of multiple response to one same situation and multiple causation of one same response may be taken roughly as the fact.
2. Inventory of Original Tendencies[59]
I. Sensory capacities
II. Original attentiveness
III. Gross bodily control
IV. Food getting and habitation
A. Food getting
1. Eating. 2. Reaching, grasping, putting into the mouth.
3. Acquisition and possession. 4. Hunting (a) a small
escaping object, (b) a small or moderate-sized object not of
offensive mien, moving away from or past him. 5. Possible
specialized tendencies. 6. Collecting and hoarding.
7. Avoidance and repulsion. 8. Rivalry and co-operation
B. Habitation
1. Responses to confinement. 2. Migration and domesticity
V. Fear, fighting, and anger
A. Fear
1. Unpleasant expectation and dread. 2. Anxiety and
worry. 3. Dislike and avoidance. 4. Shock. 5. Flight,
paralysis, etc.
B. Fighting
1. Escape from restraint. 2. Overcoming a moving obstacle.
3. Counter-attack. 4. Irrational response to pain.
5. Combat in rivalry. 6. Resentment of presence of other
males in courtship. 7. Angry behavior at persistent
thwarting.
C. Anger
VI. Responses to the behavior of other human beings
A. Motherly behavior
B. Filial behavior
C. Responses to presence, approval, and scorn of men
1. Gregariousness. 2. Attention to human beings. 3. Attention-getting.
4. Responses to approval and scorn.
5. Responses by approval and scorn
D. Mastering and submissive behavior
1. Display. 2. Shyness. 3. Self-conscious behavior
E. Other social instincts
1. Sex behavior. 2. Secretiveness. 3. Rivalry. 4. Co-operation.
5. Suggestibility and opposition. 6. Envious
and jealous behavior. 7. Greed. 8. Ownership. 9. Kindliness.
10. Teasing, tormenting, and bullying
F. Imitation
1. General imitativeness. 2. Imitation of particular forms
of behavior
VII. Original satisfiers and annoyers
VIII. Minor bodily movements and cerebral connections
A. Vocalization
B. Visual exploration
C. Manipulation
D. Other possible specializations
1. Constructiveness. 2. Cleanliness. 3. Adornment and art
E. Curiosity and mental control
1. Curiosity. 2. The instinct of multiform mental activity.
3. The instinct of multiform physical activity.
4. The instinct of workmanship and the desire for excellence
F. Play
IX. The emotions and their expression
X. Consciousness, learning, and remembering
3. Man Not Born Human[60]
Man is not born human. It is only slowly and laboriously, in fruitful contact, co-operation, and conflict with his fellows, that he attains the distinctive qualities of human nature. In the course of his prenatal life he has already passed roughly through, or, as the biologists say, "recapitulated," the whole history of his animal ancestors. He brings with him at birth a multitude of instincts and tendencies, many of which persist during life and many of which are only what G. Stanley Hall calls "vestigial traces" of his brute ancestry, as is shown by the fact that they are no longer useful and soon disappear.
These non-volitional movements of earliest infancy and of later childhood (such as licking things, clicking with the tongue, grinding the teeth, biting the nails, shrugging corrugations, pulling buttons, or twisting garments, strings, etc., twirling pencils, etc.) are relics of past forms of utilities now essentially obsolete. Ancient modes of locomotion, prehension, balancing, defense, attack, sensuality, etc., are all rehearsed, some quite fully and some only by the faintest mimetic suggestion, flitting spasmodic tensions, gestures, or facial expressions.
Human nature may therefore be regarded on the whole as a superstructure founded on instincts, dispositions, and tendencies, inherited from a long line of human and animal ancestors. It consists mainly in a higher organization of forces, a more subtle distillation of potencies latent in what Thorndike calls "the original nature of man."
The original nature of man is roughly what is common to all men minus all adaptations to tools, houses, clothes, furniture, words, beliefs, religions, laws, science, the arts, and to whatever in other men's behavior is due to adaptations to them. From human nature as we find it, take away, first, all that is in the European but not in the Chinaman, all that is in the Fiji Islander but not in the Esquimaux, all that is local or temporary. Then take away also the effects of all products of human art. What is left of human intellect and character is largely original—not wholly, for all those elements of knowledge which we call ideas and judgments must be subtracted from his responses. Man originally possesses only capacities which, after a given amount of education, will produce ideas and judgments.
Such, in general, is the nature of human beings before that nature has been modified by experience and formed by the education and the discipline of contact and intercourse with their fellows.
Several writers, among them William James, have attempted to make a rough inventory of the special instinctive tendencies with which human beings are equipped at birth. First of all there are the simpler reflexes such as "crying, sneezing, snoring, coughing, sighing, sobbing, gagging, vomiting, hiccuping, starting, moving the limb in response to its being tickled, touched or blown upon, spreading the toes in response to its being touched, tickled, or stroked on the sole of the foot, extending and raising the arms at any sudden sensory stimulus, or the quick pulsation of the eyelid."
Then there are the more complex original tendencies such as sucking, chewing, sitting up, and gurgling. Among the more general unlearned responses of children are fear, anger, pugnacity, envy, jealousy, curiosity, constructiveness, love of festivities, ceremonies and ordeals, sociability and shyness, secretiveness, etc. Thorndike, who quotes this list at length, has sought to give definiteness to its descriptions by clearly defining and distinguishing the character of the situation to which the behavior cited is a response. For example, to the situation, "strange man or animal, to solitude, black things, dark places, holes and corners, a human corpse," the native and unlearned response is fear. The original response of man to being alone is an experience of discomfort, to perceiving a crowd, "a tendency to join them and do what they are doing and an unwillingness to leave off and go home." It is part of man's original nature when he is in love to conceal his love affairs, and so forth.
It is evident from this list that what is meant by original nature is not confined to the behavior which manifests itself at birth, but includes man's spontaneous and unlearned responses to situations as they arise in the experience of the individual.
The widespread interest in the study of children has inspired in recent years a considerable literature bearing upon the original and inherited tendencies of human nature. The difficulty of distinguishing between what is original and what is acquired among the forms of behavior reported upon, and the further difficulty of obtaining accurate descriptions of the situations to which the behavior described was a response, has made much of this literature of doubtful value for scientific purposes. These studies have, nevertheless, contributed to a radical change in our conceptions of human nature. They have shown that the distinction between the mind of man and that of the lower animals is not so wide nor so profound as was once supposed. They have emphasized the fact that human nature rests on animal nature, and the transition from one to the other, in spite of the contrast in their separate achievements, has been made by imperceptible gradations. In the same way they have revealed, beneath differences in culture and individual achievement, the outlines of a pervasive and relatively unchanging human nature in which all races and individuals have a common share.
The study of human nature begins with description, but it goes on from that point to explanation. If the descriptions which we have thus far had of human nature are imperfect and lacking in precision, it is equally true that the explanations thus far invented have, on the whole, been inadequate. One reason for this has been the difficulty of the task. The mechanisms which control human behavior are, as might be expected, tremendously complicated, and the problem of analyzing them into their elementary forms and reducing their varied manifestations to precise and lucid formulas is both intricate and perplexing.
The foundation for the explanation of human nature has been laid, however, by the studies of behavior in animals and the comparative study of the physiology of the nervous system. Progress has been made, on the one hand, by seeking for the precise psycho-chemical process involved in the nervous reactions, and on the other, by reducing all higher mental processes to elementary forms represented by the tropisms and reflex actions.
In this, science has made a considerable advance upon common sense in its interpretations of human behavior, but has introduced no new principle; it has simply made its statements more detailed and exact. For example, common sense has observed that "the burnt child shuns the fire," that "the moth seeks the flame." These are both statements of truths of undoubted generality. In order to give them the validity of scientific truth, however, we need to know what there is in the nature of the processes involved that makes it inevitable that the child should shun the fire and the moth should seek the flame. It is not sufficient to say that the action in one case is instinctive and in the other intelligent, unless we are able to give precise and definite meanings to those terms; unless, in short, we are able to point out the precise mechanisms through which these reactions are carried out. The following illustration from Loeb's volume on the comparative physiology of the brain will illustrate the distinction between the common sense and the more precise scientific explanation of the behavior in man and the lower animals.
It is a well-known fact that if an ant be removed from a nest and afterward put back it will not be attacked, while almost invariably an ant belonging to another nest will be attacked. It has been customary to use the words memory, enmity, friendship, in describing this fact. Now Bethe made the following experiment: an ant was placed in the liquids (blood and lymph) squeezed out from the bodies of nest companions and was then put back into its nest; it was not attacked. It was then put in the juice taken from the inmates of a "hostile" nest and was at once attacked and killed. Bethe was able to prove by special experiments that these reactions of ants are not learned by experience, but are inherited. The "knowing" of "friend and foe" among ants is thus reduced to different reactions, depending upon the nature of the chemical stimulus and in no way depending upon memory.
Here, again, there is no essential difference between the common sense and the scientific explanation of the behavior of the ant except so far as the scientific explanation is more accurate, defining the precise mechanisms by which the recognition of "friend and foe" is effected, and the limitations to which it is subject.
Another result of the study of the comparative behavior of man and the lower animals has been to convince students that there is no fundamental difference between what was formerly called intelligent and instinctive behavior; that they may rather be reduced, as has been said, to the elementary form of reaction represented by the simple reflex in animals and the tropism in plants. Thus Loeb says:
A prominent psychologist has maintained that reflexes are to be considered as the mechanical effects of acts of volition of past generations. The ganglion-cell seems the only place where such mechanical effects could be stored up. It has therefore been considered the most essential element of the reflex mechanism, the nerve-fibers being regarded, and probably correctly, merely as conductors.
Both the authors who emphasize the purposefulness of the reflex act, and those who see in it only a physical process, have invariably looked upon the ganglion-cell as the principal bearer of the structures for the complex co-ordinated movements in reflex action.
I should have been as little inclined as any other physiologist to doubt the correctness of this conception had not the establishment of the identity of the reactions of animals and plants to light proved the untenability of this view and at the same time offered a different conception of reflexes. The flight of the moth into the flame is a typical reflex process. The light stimulates the peripheral sense organs, the stimulus passes to the central nervous system, and from there to the muscles of the wings, and the moth is caused to fly into the flame. This reflex process agrees in every point with the heliotropic effects of light on plant organs. Since plants possess no nerves, this identity of animal with plant heliotropism can offer but one inference—these heliotropic effects must depend upon conditions which are common to both animals and plants.
On the other hand, Watson, in his Introduction to Comparative Psychology, defines the reflex as "a unit of analysis of instinct," and this means that instinctive actions in man and in animals may be regarded as combinations of simple reflex actions, that is to say of "fairly definite and generally predictable but unlearned responses of lower and higher organisms to stimuli." Many of these reflex responses are not fixed, as they were formerly supposed to be, but "highly unstable and indefinite." This fact makes possible the formation of habits, by combination and fixation of these inherited responses.
These views in the radical form in which they are expressed by Loeb and Watson have naturally enough been the subject of considerable controversy, both on scientific and sentimental grounds. They seem to reduce human behavior to a system of chemical and physical reactions, and rob life of all its spiritual values. On the other hand, it must be remembered that human beings, like other forms of nature, have this mechanical aspect and it is precisely the business of natural science to discover and lay them bare. It is only thus that we are able to gain control over ourselves and of others. It is a matter of common experience that we do form habits and that education and social control are largely dependent upon our ability to establish habits in ourselves and in others. Habit is, in fact, a characteristic example of just what is meant by "mechanism," in the sense in which it is here used. It is through the fixation of habit that we gain that control over our "original nature," which lifts us above the brutes and gives human nature its distinctive character as human. Character is nothing more than the sum and co-ordination of those mechanisms which we call habit and which are formed on the basis of the inherited and instinctive tendencies and dispositions which we share in so large a measure with the lower animals.
4. The Natural Man[61]
"Its first act is a cry, not of wrath, as Kant said, nor a shout of joy, as Schwartz thought, but a snuffling, and then a long, thin, tearless á-á, with the timbre of a Scotch bagpipe, purely automatic, but of discomfort. With this monotonous and dismal cry, with its red, shriveled, parboiled skin (for the child commonly loses weight the first few days), squinting, cross-eyed, pot-bellied, and bow-legged, it is not strange that, if the mother has not followed Froebel's exhortations and come to love her child before birth, there is a brief interval occasionally dangerous to the child before the maternal instinct is fully aroused."
The most curious of all the monkey traits shown by the new-born baby is the one investigated by Dr. Louis Robinson. It was suggested by The Luck of Roaring Camp. The question was raised in conversation whether a limp and molluscous baby, unable so much as to hold up its head on its helpless little neck, could do anything so positive as to "rastle with" Kentuck's finger; and the more knowing persons present insisted that a young baby does, as a matter of fact, have a good firm hand-clasp. It occurred to Dr. Robinson that if this was true it was a beautiful Darwinian point, for clinging and swinging by the arms would naturally have been a specialty with our ancestors if they ever lived a monkey-like life in the trees. The baby that could cling best to its mother as she used hands, feet, and tail to flee in the best time over the trees, or to get at the more inaccessible fruits and eggs in time of scarcity, would be the baby that lived to bequeath his traits to his descendants; so that to this day our housed and cradled human babies would keep in their clinging powers a reminiscence of our wild treetop days.
There is another class of movements, often confused with the reflex—that is, instinctive movements. Real grasping (as distinguished from reflex grasping), biting, standing, walking, are examples of this class. They are race movements, the habits of the species to which the animal belongs, and every normal member of the species is bound to come to them; yet they are not so fixed in the bodily mechanism as the reflex movements.
The one instinct the human baby always brings into the world already developed is half a mere reflex act—that of sucking. It is started as a reflex would be, by the touch of some object—pencil, finger, or nipple, it may be—between the lips; but it does not act like a reflex after that. It continues and ceases without reference to this external stimulus, and a little later often begins without it, or fails to begin when the stimulus is given. If it has originally a reflex character, that character fades out and leaves it a pure instinct.
My little niece evidently felt a difference between light and darkness from the first hour, for she stopped crying when her face was exposed to gentle light. Two or three report also a turning of the head toward the light within the first week. The nurse, who was intelligent and exact, thought she saw this in the case of my niece. I did not, but I saw instead a constant turning of the eyes toward a person coming near her—that is, toward a large dark mass that interrupted the light. No other sign of vision appeared in the little one during the first fortnight. The eyes were directed to nothing, fixed on nothing. They did not wink if one made a pass at them. There was no change of focus for near or distant seeing.
The baby showed no sign of hearing anything until the third day, when she started violently at the sound of tearing paper, some eight feet from her. After that, occasional harsh or sudden sounds—oftener the rustling of paper than anything else—could make her start or cry. It is well established by the careful tests of several physiologists that babies are deaf for a period lasting from several hours to several days after birth.
Taste and smell were senses that the baby gave no sign of owning till much later. The satisfaction of hunger was quite enough to account for the contentment she showed in nursing; and when she was not hungry she would suck the most tasteless object as cheerfully as any other.
Our baby showed from the first that she was aware when she was touched. She stopped crying when she was cuddled or patted. She showed comfort in the bath, which may have been in part due to freedom from the contact of clothes, and to liking for the soft touches of the water. She responded with sucking motions to the first touch of the nipple on her lips.
Our baby showed temperament—luckily of the easy-going and cheerful kind—from her first day, though we could hardly see this except by looking backward. On the twenty-fifth day, toward evening, when the baby was lying on her grandmother's knee by the fire, in a condition of high well-being and content, gazing at her grandmother's face with an expression of attention, I came and sat down close by, leaning over the baby, so that my face must have come within the indirect range of her vision. At that she turned her eyes to my face and gazed at it with the same appearance of attention, and even of some effort, shown by the slight tension of brows and lips, then turned her eyes back to her grandmother's face, and again to mine, and so several times. The last time she seemed to catch sight of my shoulder, on which a high light struck from the lamp, and not only moved her eyes but threw her head far back to see it better, and gazed for some time with a new expression on her face—"a sort of dim and rudimentary eagerness," says my note. She no longer stared, but really looked.
The baby's increased interest in seeing centered especially on the faces about her, at which she gazed with rapt interest. Even during the period of mere staring, faces had oftenest held her eyes, probably because they were oftener brought within the range of her clearest seeing than other light surfaces. The large, light, moving patch of the human face (as Preyer has pointed out) coming and going in the field of vision, and oftener chancing to hover at the point of clearest seeing than any other object, embellished with a play of high lights on cheeks, teeth, and eyes, is calculated to excite the highest degree of attention a baby is capable of at a month old. So from the very first—before the baby has yet really seen his mother—her face and that of his other nearest friends become the most active agents in his development and the most interesting things in his experience.
Our baby was at this time in a way aware of the difference between companionship and solitude. In the latter days of the first month she would lie contentedly in the room with people near by, but would fret if left alone. But by the end of the month she was apt to fret when she was laid down on a chair or lounge, and to become content only when taken into the lap. This was not yet distinct memory and desire, but it showed that associations of pleasure had been formed with the lap, and that she felt a vague discomfort in the absence of these.
Nature has provided an educational appliance almost ideally adapted to the child's sense condition, in the mother's face, hovering close above him, smiling, laughing, nodding, with all manner of delightful changes in the high lights; in the thousand little meaningless caressing sounds, the singing, talking, calling, that proceed from it; the patting, cuddling, lifting, and all the ministrations that the baby feels while gazing at it, and associates with it, till finally they group together and round out into the idea of his mother as a whole.
Our baby's mother rather resented the idea of being to her baby only a collection of detached phenomena, instead of a mamma; but the more you think of it, the more flattering it is to be thus, as it were, dissolved into your elements and incorporated item by item into the very foundations of your baby's mental life. Herein is hinted much of the philosophy of personality; and Professor Baldwin has written a solid book, mainly to show from the development of babies and little children that all other people are part of each of us, and each of us is part of all other people, and so there is really no separate personality, but we are all one spirit, if we did but know it.
5. Sex Differences[62]
As children become physically differentiated in respect of sex, so also does a mental differentiation ensue. Differences are observed in the matter of occupation, of games, of movements, and numerous other details. Since man is to play the active part in life, boys rejoice especially in rough outdoor games. Girls, on the other hand, prefer such games as correspond to their future occupations. Hence their inclination to mother smaller children, and to play with dolls. Watch how a little girl takes care of her doll, washes it, dresses and undresses it. When only six or seven years of age she is often an excellent nurse. Her need to occupy herself in such activities is often so great that she pretends that her doll is ill.
In all kinds of ways, we see the little girl occupying herself in the activities and inclinations of her future existence. She practices house work; she has a little kitchen, in which she cooks for herself and her doll. She is fond of needlework. The care of her own person, and more especially its adornment, is not forgotten. I remember seeing a girl of three who kept on interrupting her elders' conversation by crying out, "New clothes!" and would not keep quiet until these latter had been duly admired. The love of self-adornment is almost peculiar to female children; boys, on the other hand, prefer rough outdoor games, in which their muscles are actively employed, robber-games, soldier-games, and the like. And whereas, in early childhood, both sexes are fond of very noisy games, the fondness for these disappears earlier in girls than in boys.
Differences between the sexes have been established also by means of experimental psychology, based upon the examination of a very large number of instances. Berthold Hartmann has studied the childish circle of thought, by means of a series of experiments. Schoolboys to the number of 660 and schoolgirls to the number of 652, at ages between five and three-fourths and six and three-fourths years, were subjected to examination. It was very remarkable to see how, in respect to certain ideas, such as those of the triangle, cube, and circle, the girls greatly excelled the boys; whereas in respect of animals, minerals, and social ideas, the boys were better informed than the girls. Characteristic of the differences between the sexes, according to Meumann, from whom I take these details and some of those that follow, is the fact that the idea of "marriage" was known to only 70 boys as compared to 227 girls; whilst the idea of "infant baptism" was known to 180 boys as compared to 220 girls. The idea of "pleasure" was also much better understood by girls than by boys. Examination of the memory has also established the existence of differences between the sexes in childhood. In boys the memory for objects appears to be at first the best developed; to this succeeds the memory for words with a visual content; in the case of girls, the reverse of this was observed. In respect of numerous details, however, the authorities conflict. Very striking is the fact, one upon which a very large number of investigators are agreed, that girls have a superior knowledge of colors.
There are additional psychological data relating to the differences between the sexes in childhood. I may recall Stern's investigations concerning the psychology of evidence, which showed that girls were much more inaccurate than boys.
It has been widely assumed that these psychical differences between the sexes result from education, and are not inborn. Others, however, assume that the psychical characteristics by which the sexes are differentiated result solely from individual differences in education. Stern believes that in the case of one differential character, at least, he can prove that for many centuries there has been no difference between the sexes in the matter of education; this character is the capacity for drawing. Kerschensteiner has studied the development of this gift, and considers that his results have established beyond dispute that girls are greatly inferior in this respect to boys of like age. Stern points out that there can be no question here of cultivation leading to a sexual differentiation of faculty, since there is no attempt at a general and systematic teaching of draughtsmanship to the members of one sex to the exclusion of members of the other.
I believe that we are justified in asserting that at the present time the sexual differentiation manifested in respect of quite a number of psychical qualities is the result of direct inheritance. It would be quite wrong to assume that all these differences arise in each individual in consequence of education. It does, indeed, appear to me to be true that inherited tendencies may be increased or diminished by individual education; and further, that when the inherited tendency is not a very powerful one, it may in this way even be suppressed.
We must not forget the frequent intimate association between structure and function. Rough outdoor games and wrestling thus correspond to the physical constitution of the boy. So, also, it is by no means improbable that the little girl, whose pelvis and hips have already begun to indicate by their development their adaption for the supreme functions of the sexually mature woman, should experience obscurely a certain impulsion toward her predestined maternal occupation, and that her inclinations and amusements should in this way be determined. Many, indeed, and above all the extreme advocates of women's rights, prefer to maintain that such sexually differentiated inclinations result solely from differences in individual education: if the boy has no enduring taste for dolls and cooking, this is because his mother and others have told him, perhaps with mockery, that such amusements are unsuited to a boy; whilst in a similar way the girl is dissuaded from the rough sports of boyhood. Such an assumption is the expression of that general psychological and educational tendency, which ascribes to the activity of the will an overwhelmingly powerful influence upon the development of the organs subserving the intellect, and secondarily also upon that of the other organs of the body. We cannot dispute the fact that in such a way the activity of the will may, within certain limits, be effective, especially in cases in which the inherited tendency thus counteracted is comparatively weak; but only within certain limits. Thus we can understand how it is that in some cases, by means of education, a child is impressed with characteristics normally foreign to its sex; qualities and tendencies are thus developed which ordinarily appear only in a child of the opposite sex. But even though we must admit that the activity of the individual may operate in this way, none the less we are compelled to assume that certain tendencies are inborn. The failure of innumerable attempts to counteract such inborn tendencies by means of education throws a strong light upon the limitations of the activity of the individual will; and the same must be said of a large number of other experiences.
Criminological experiences appear also to confirm the notion of an inherited sexual differentiation, in children as well as in adults. According to various statistics, embracing not only the period of childhood, but including as well the period of youth, we learn that girls constitute one-fifth only of the total number of youthful criminals. A number of different explanations have been offered to account for this disproportion. Thus, for instance, attention has been drawn to the fact that a girl's physical weakness renders her incapable of attempting violent assaults upon the person, and this would suffice to explain why it is that girls so rarely commit such crimes. In the case of offenses for which bodily strength is less requisite, such as fraud, theft, etc., the number of youthful female offenders is proportionately larger, although here also they are less numerous than males of corresponding age charged with the like offenses. It has been asserted that in the law courts girls find more sympathy than boys, and that for this reason the former receive milder sentences than the latter; hence it results that in appearance merely the criminality of girls is less than that of boys. Others, again, refer the differences in respect of criminality between the youthful members of the two sexes to the influences of education and general environment. Morrison, however, maintains that all these influences combined are yet insufficient to account for the great disproportion between the sexes, and insists that there exists in youth as well as in adult life a specific sexual differentiation, based, for the most part, upon biological differences of a mental and physical character.
Such a marked differentiation as there is between the adult man and the adult woman certainly does not exist in childhood. Similarly in respect of many other qualities, alike bodily and mental, in respect of many inclinations and numerous activities, we find that in childhood sexual differentiation is less marked than it is in adult life. None the less, a number of sexual differences can be shown to exist even in childhood; and as regards many other differences, though they are not yet apparent, we are nevertheless compelled to assume that they already exist potentially in the organs of the child.
6. Racial Differences[63]
The results of the Cambridge expedition to the Torres Straits have shown that in acuteness of vision, hearing, smell, etc., these peoples are not noticeably different from our own. We conclude that the remarkable tales adduced to the contrary by various travelers are to be explained, not by the acuteness of sensation, but by the acuteness of interpretation of primitive peoples. Take the savage into the streets of a busy city and see what a number of sights and sounds he will neglect because of their meaninglessness to him. Take the sailor whose powers of discerning a ship on the horizon appear to the landsman so extraordinary, and set him to detect micro-organisms in the field of a microscope. Is it then surprising that primitive man should be able to draw inferences which to the stranger appear marvelous, from the merest specks in the far distance or from the faintest sounds, odors, or tracks in the jungle? Such behavior serves only to attest the extraordinary powers of observation in primitive man with respect to things which are of use and hence of interest to him. The same powers are shown in the vast number of words he will coin to denote the same object, say a certain tree at different stages of its growth.
We concluded, then, that no fundamental difference in powers of sensory acuity, nor, indeed, in sensory discrimination, exists between primitive and civilized communities. Further, there is no proof of any difference in memory between them, save, perhaps, in a greater tendency for primitive folk to use and to excel in mere mechanical learning, in preference to rational learning. But this surely is also the characteristic of the European peasant. He will never commit things to memory by thinking of their meaning, if he can learn them by rote.
In temperament we meet with just the same variations in primitive as in civilized communities. In every primitive society is to be found the flighty, the staid, the energetic, the indolent, the cheerful, the morose, the even-, the hot-tempered, the unthinking, the philosophical individual. At the same time, the average differences between different primitive peoples are as striking as those between the average German and the average Italian.
It is a common but manifest error to suppose that primitive man is distinguished from the civilized peasant in that he is freer and that his conduct is less under control. On the contrary, the savage is probably far more hidebound than we are by social regulations. His life is one round of adherence to the demands of custom. For instance, he may be compelled even to hand over his own children at their birth to others; he may be prohibited from speaking to certain of his relatives; his choice of a wife may be very strictly limited by traditional laws; at every turn there are ceremonies to be performed and presents to be made by him so that misfortune may be safely averted. As to the control which primitive folk exercise over their conduct, this varies enormously among different peoples; but if desired, I could bring many instances of self-control before you which would put to shame the members even of our most civilized communities.
Now since in all these various mental characters no appreciable difference exists between primitive and advanced communities, the question arises, what is the most important difference between them? I shall be told, in the capacity for logical and abstract thought. But by how much logical and abstract thought is the European peasant superior to his primitive brother? Study our country folklore, study the actual practices in regard to healing and religion which prevail in every European peasant community today, and what essential differences are discoverable? Of course, it will be urged that these practices are continued unthinkingly, that they are merely vestiges of a period when once they were believed and were full of meaning. But this, I am convinced, is far from being generally true, and it also certainly applies to many of the ceremonies and customs of primitive peoples.
It will be said that although the European peasant may not in the main think more logically and abstractly, he has, nevertheless, the potentiality for such thought, should only the conditions for its manifestations—education and the like—ever be given. From such as he have been produced the geniuses of Europe—the long line of artists and inventors who have risen from the lowest ranks.
I will consider this objection later. At present it is sufficient for my purpose to have secured the admission that the peasants of Europe do not as a whole use their mental powers in a much more logical or abstract manner than do primitive people. I maintain that such superiority as they have is due to differences (1) of environment and (2) of variability.
We must remember that the European peasant grows up in a (more or less) civilized environment; he learns a (more or less) well-developed and written language, which serves as an easier instrument and a stronger inducement for abstract thought; he is born into a (more or less) advanced religion. All these advantages and the advantage of a more complex education the European peasant owes to his superiors in ability and civilization. Rob the peasant of these opportunities, plunge him into the social environment of present primitive man, and what difference in thinking power will be left between them?
The answer to this question brings me to the second point of difference which I have mentioned—the difference in variability. I have already alluded to the divergencies in temperament to be found among the members of every primitive community. But well marked as are these and other individual differences, I suspect that they are less prominent among primitive than among more advanced peoples. This difference in variability, if really existent, is probably the outcome of more frequent racial admixture and more complex social environment in civilized communities. In another sense, the variability of the savage is indicated by the comparative data afforded by certain psychological investigations. A civilized community may not differ much from a primitive one in the mean or average of a given character, but the extreme deviations which it shows from that mean will be more numerous and more pronounced. This kind of variability has probably another source. The members of a primitive community behave toward the applied test in the simplest manner, by the use of a mental process which we will call A, whereas those of a more advanced civilization employ other mental processes, in addition to A, say B, C, D, or E, each individual using them in different degrees for the performance of one and the same test. Finally, there is in all likelihood a third kind of variability, whose origin is ultimately environmental, which is manifested by extremes of nervous instability. Probably the exceptionally defective and the exceptional genius are more common among civilized than among primitive peoples.
Similar features undoubtedly meet us in the study of sexual differences. The average results of various tests of mental ability applied to men and women are not, on the whole, very different for the two sexes, but the men always show considerably greater individual variation than the women. And here, at all events, the relation between the frequency of mental deficiency and genius in the two sexes is unquestionable. Our asylums contain a considerably greater number of males than of females, as a compensation for which genius is decidedly less frequent in females than in males.
7. Individual Differences[64]
The life of a man is a double series—a series of effects produced in him by the rest of the world, and a series of effects produced in that world by him. A man's make-up or nature equals his tendencies to be influenced in certain ways by the world and to react in certain ways to it.
If we could thus adequately describe each of a million human beings—if, for each one, we could prophesy just what the response would be to every possible situation of life—the million men would be found to differ widely. Probably no two out of the million would be so alike in mental nature as to be indistinguishable by one who knew their entire natures. Each has an individuality which marks him off from other men. We may study a human being in respect to his common humanity, or in respect to his individuality. In other words, we may study the features of intellect and character which are common to all men, to man as a species; or we may study the differences in intellect and character which distinguish individual men.
Individuals are commonly considered as differing in respect to such traits either quantitatively or qualitatively, either in degree or in kind. A quantitative difference exists when the individuals have different amounts of the same trait. Thus, "John is more attentive to his teacher than James is"; "Mary loves dolls less than Lucy does"; "A had greater devotion to his country than B had"; are reports of quantitative differences, of differences in the amount of what is assumed to be the same kind of thing. A qualitative difference exists when some quality or trait possessed by one individual is lacking in the other. Thus, "Tom knows German, Dick does not"; "A is artistic, B is scientific"; "C is a man of thought, D is a man of action"; are reports of the fact that Tom has some positive amount or degree of the trait "knowledge of German" while Dick has none of it; that A has some positive amount of ability and interest in art while B has zero; whereas B has a positive amount of ability in science, of which A has none; and so on.
A qualitative difference in intellect or character is thus really a quantitative difference wherein one term is zero, or a compound of two or more quantitative differences. All intelligible differences are ultimately quantitative. The difference between any two individuals, if describable at all, is described by comparing the amounts which A possesses of various traits with the amounts which B possesses of the same traits. In intellect and character, differences of kind between one individual and another turn out to be definable, if defined at all, as compound differences of degree.
If we could list all the traits, each representing some one characteristic of human nature, and measure the amount of each of them possessed by a man, we could represent his nature—read his character—in a great equation. John Smith would equal so many units of this, plus so many units of that, and so on. Such a mental inventory would express his individuality conceivably in its entirety and with great exactitude. No such list has been made for any man, much less have the exact amounts of each trait possessed by him been measured. But in certain of the traits, many individuals have been measured; and certain individuals have been measured, each in a large number of traits.
It is useless to recount the traits in which men have been found to differ. For there is no trait in which they do not differ. Of course, if the scale by which individuals are measured is very coarsely divided, their differences may be hidden. If, for example, ability to learn is measured on a scale with only two divisions, (1) "ability to learn less than the average kitten can" and (2) "ability to learn more than the average kitten can," all men may be put in class two, just as if their heights were measured on a scale of one yard, two yards, or three yards, nearly all men would alike be called two yards high. But whenever the scale of measurement is made fine enough, differences at once appear. Their existence is indubitable to any impartial observer. The early psychologists neglected or failed to see them precisely because the early psychology was partial. It believed in a typical or pattern mind, after the manner of which all minds were created, and from whom they differed only by rare accidents. It studied "the mind," and neglected individual minds. It studied "the will" of "man," neglecting the interests, impulses, and habits of actual men.
The differences exist at birth and commonly increase with progress toward maturity. Individuality is already clearly manifest in children of school age. The same situation evokes widely differing responses; the same task is done at differing speeds and with different degrees of success; the same treatment produces differing results. There can be little doubt that of a thousand ten-year-olds taken at random, some will be four times as energetic, industrious, quick, courageous, or honest as others, or will possess four times as much refinement, knowledge of arithmetic, power of self-control, sympathy, or the like. It has been found that among children of the same age and, in essential respects, of the same home training and school advantages, some do in the same time six times as much, or do the same amount with only one-tenth as many errors.
B. HUMAN NATURE AND SOCIAL LIFE
1. Human Nature and Its Remaking[65]
Human beings as we find them are artificial products; and for better or for worse they must always be such. Nature has made us: social action and our own efforts must continually remake us. Any attempt to reject art for "nature" can only result in an artificial naturalness which is far less genuine and less pleasing than the natural work of art.
Further, as self-consciousness varies, the amount or degree of this remaking activity will vary. Among the extremely few respects in which human history shows unquestionable growth we must include the degree and range of self-consciousness. The gradual development of psychology as a science and the persistent advance of the subjective or introspective element in literature and in all fine art are tokens of this change. And as a further indication and result, the art of human reshaping has taken definite character, has left its incidental beginnings far behind, has become an institution, a group of institutions.
Wherever a language exists, as a magazine of established meanings, there will be found a repertoire of epithets of praise and blame, at once results and implements of this social process. The simple existence of such a vocabulary acts as a persistent force; but the effect of current ideals is redoubled when a coherent agency, such as public religion, assumes protection of the most searching social maxims and lends to them the weight of all time, all space, all wonder, and all fear. For many centuries religion held within itself the ripening self-knowledge and self-discipline of the human mind. Now, beside this original agency we have its offshoots, politics, education, legislation, the penal art. And the philosophical sciences, including psychology and ethics, are the especial servants of these arts.
As to structure, human nature is undoubtedly the most plastic part of the living world, the most adaptable, the most educable. Of all animals, it is man in whom heredity counts for least, and conscious building forces for most. Consider that his infancy is longest, his instincts least fixed, his brain most unfinished at birth, his powers of habit-making and habit-changing most marked, his susceptibility to social impressions keenest; and it becomes clear that in every way nature, as a prescriptive power, has provided in him for her own displacement. His major instincts and passions first appear on the scene, not as controlling forces, but as elements of play, in a prolonged life of play. Other creatures nature could largely finish: the human creature must finish himself.
And as to history, it cannot be said that the results of man's attempts at self-modeling appear to belie the liberty thus promised in his constitution. If he has retired his natural integument in favor of a device called clothing, capable of expressing endless nuances, not alone of status and wealth, but of temper and taste as well—conservatism or venturesomeness, solemnity, gaiety, profusion, color, dignity, carelessness or whim, he has not failed to fashion his inner self into equally various modes of character and custom. That is a hazardous refutation of socialism which consists in pointing out that its success would require a change in human nature. Under the spell of particular ideas monastic communities have flourished, in comparison with whose demands upon human nature the change required by socialism—so far as it calls for purer altruism and not pure economic folly—is trivial. To any one who asserts as a dogma that "human nature never changes," it is fair to reply, "It is human nature to change itself."
When one reflects to what extent racial and national traits are manners of the mind, fixed by social rather than by physical heredity, while the bodily characters themselves may be due in no small measure to sexual choices at first experimental, then imitative, then habitual, one is not disposed to think lightly of the human capacity for self-modification. But it is still possible to be skeptical as to the depth and permanence of any changes which are genuinely voluntary. There are few maxims of conduct, and few laws so contrary to nature that they could not be put into momentary effect by individuals or by communities. Plato's Republic has never been fairly tried; but fragments of this and other Utopias have been common enough in history. No one presumes to limit what men can attempt; one only inquires what the silent forces are which determine what can last.
What, to be explicit, is the possible future of measures dealing with divorce, with war, with political corruption, with prostitution, with superstition? Enthusiastic idealism is too precious an energy to be wasted if we can spare it false efforts by recognizing those permanent ingredients of our being indicated by the words pugnacity, greed, sex, fear. Machiavelli was not inclined to make little of what an unhampered ruler could do with his subjects; yet he saw in such passions as these a fixed limit to the power of the Prince. "It makes him hated above all things to be rapacious, and to be violator of the property and women of his subjects, from both of which he must abstain." And if Machiavelli's despotism meets its master in the undercurrents of human instinct, governments of less determined stripe, whether of states or of persons, would hardly do well to treat these ultimate data with less respect.
2. Human Nature, Folkways, and the Mores[66]
[55] Charles H. Cooley, Social Organization, pp. 28-30.
[56] Charles H. Cooley, Human Nature and the Social Order, pp. 152-53.
[57] The Theory of the Leisure Class (New York, 1899).
[58] From Edward L. Thorndike, The Original Nature of Man, pp. 1-7. (Teachers College, Columbia University, 1913. Author's copyright.)
[59] Compiled from Edward L. Thorndike, The Original Nature of Man, pp. 43-194. (Teachers College, Columbia University, 1913. Author's copyright.)
[60] From Robert E. Park, Principles of Human Behavior, pp. 9-16. (The Zalaz Corporation, 1915.)
[61] Adapted from Milicent W. Shinn, The Biography of a Baby, pp. 20-77. (Houghton Mifflin Co., 1900. Author's copyright.)
[62] From Albert Moll, Sexual Life of the Child, pp. 38-49. Translated from the German by Dr. Eden Paul. (Published by The Macmillan Co., 1902. Reprinted by permission.)
[63] From C. S. Myers, "On the Permanence of Racial Differences," in Papers on Inter-racial Problems, edited by G. Spiller, pp. 74-76. (P. S. King & Son, 1911.)
[64] From Edward L. Thorndike, Individuality, pp. 1-8. (By permission of and special arrangement with Houghton Mifflin Co., 1911.)
[65] From W. E. Hocking, Human Nature and Its Remaking, pp. 2-12. (Yale University Press, 1918.)
[66] From William G. Sumner, Folkways, pp. 2-8. (Ginn & Co., 1906.)
It is generally taken for granted that men inherited some guiding instincts from their beast ancestry, and it may be true, although it has never been proved. If there were such inheritances, they controlled and aided the first efforts to satisfy needs. Analogy makes it easy to assume that the ways of beasts had produced channels of habit and predisposition along which dexterities and other psycho-physical activities would run easily. Experiments with new born animals show that in the absence of any experience of the relation of means to ends, efforts to satisfy needs are clumsy and blundering. The method is that of trial and failure, which produces repeated pain, loss, and disappointments. Nevertheless, it is the method of rude experiment and selection. The earliest efforts of men were of this kind. Need was the impelling force. Pleasure and pain, on the one side and the other, were the rude constraints which defined the line on which efforts must proceed. The ability to distinguish between pleasure and pain is the only psychical power which is to be assumed. Thus ways of doing things were selected which were expedient. They answered the purpose better than other ways, or with less toil and pain. Along the course on which efforts were compelled to go, habit, routine, and skill were developed. The struggle to maintain existence was carried on, not individually, but in groups. Each profited by the other's experience; hence there was concurrence toward that which proved to be most expedient.
All at last adopted the same way for the same purpose; hence the ways turned into customs and became mass phenomena. Instincts were developed in connection with them. In this way folkways arise. The young learn them by tradition, imitation, and authority. The folkways, at a time, provide for all the needs of life then and there. They are uniform, universal in the group, imperative, and invariable.
The operation by which folkways are produced consists in the frequent repetition of petty acts, often by great numbers acting in concert or, at least, acting in the same way when face to face with the same need. The immediate motive is interest. It produces habit in the individual and custom in the group. It is, therefore, in the highest degree original and primitive. Out of the unconscious experiment which every repetition of the ways includes, there issues pleasure or pain, and then, so far as the men are capable of reflection, convictions that the ways are conducive to social welfare. When this conviction as to the relation to welfare is added to the folkways, they are converted into mores, and, by virtue of the philosophical and ethical element added to them, they win utility and importance and become the source of the science and the art of living.
It is of the first importance to notice that, from the first acts by which men try to satisfy needs, each act stands by itself, and looks no further than immediate satisfaction. From recurrent needs arise habits for the individual and customs for the group, but these results are consequences which were never conscious and never foreseen or intended. They are not noticed until they have long existed, and it is still longer before they are appreciated. Another long time must pass, and a higher stage of mental development must be reached, before they can be used as a basis from which to deduce rules for meeting, in the future, problems whose pressure can be foreseen. The folkways, therefore, are not creations of human purpose and wit. They are like products of natural forces which men unconsciously set in operation, or they are like the instinctive ways of animals, which are developed out of experience, which reach a final form of maximum adaptation to an interest, which are handed down by tradition and admit of no exception or variation, yet change to meet new conditions, still within the same limited methods, and without rational reflection or purpose. From this it results that all the life of human beings, in all ages and stages of culture, is primarily controlled by a vast mass of folkways handed down from the earliest existence of the race, having the nature of the ways of other animals, only the topmost layers of which are subject to change and control, and have been somewhat modified by human philosophy, ethics, and religion, or by other acts of intelligent reflection. We are told of savages that "it is difficult to exhaust the customs and small ceremonial usages of a savage people. Custom regulates the whole of a man's actions—his bathing, washing, cutting his hair, eating, drinking, and fasting. From his cradle to his grave he is the slave of ancient usage. In his life there is nothing free, nothing original, nothing spontaneous, no progress toward a higher and better life, and no attempt to improve his condition, mentally, morally, or spiritually." All men act in this way, with only a little wider margin of voluntary variation.
The folkways are, therefore: (1) subject to a strain of improvement toward better adaptation of means to ends, as long as the adaptation is so imperfect that pain is produced. They are also (2) subject to a strain of consistency with each other, because they all answer their several purposes with less friction and antagonism when they co-operate and support each other. The forms of industry, the forms of the family, the notions of property, the constructions of rights, and the types of religion show the strain of consistency with each other through the whole history of civilization. The two great cultural divisions of the human race are the oriental and occidental. Each is consistent throughout; each has its own philosophy and spirit; they are separated from top to bottom by different mores, different standpoints, different ways, and different notions of what societal arrangements are advantageous. In their contrast they keep before our minds the possible range of divergence in the solution of the great problems of human life, and in the views of earthly existence by which life-policy may be controlled. If two planets were joined in one, their inhabitants could not differ more widely as to what things are best worth seeking, or what ways are most expedient for well-living.
Custom is the product of concurrent action through time. We find it existent and in control at the extreme reach of our investigations. Whence does it begin, and how does it come to be? How can it give guidance "at the outset"? All mass actions seem to begin because the mass wants to act together. The less they know what it is right and best to do, the more open they are to suggestion from an incident in nature, or from a chance act of one, or from the current doctrines of ghost fear. A concurrent drift begins which is subject to later correction. That being so, it is evident that instinctive action, under the guidance of traditional folkways, is an operation of the first importance in all societal matters. Since the custom never can be antecedent to all action, what we should desire most is to see it arise out of the first actions, but, inasmuch as that is impossible, the course of the action after it is started is our field of study. The origin of primitive customs is always lost in mystery, because when the action begins the men are never conscious of historical action or of the historical importance of what they are doing. When they become conscious of the historical importance of their acts, the origin is already far behind.
3. Habit and Custom, the Individual and the General Will[67]
The term Sitte (mores) is a synonym of habit and of usage, of convention and tradition, but also of fashion, propriety, practise, and the like. Those words which characterize the habitual are usually regarded as having essentially unequivocal meanings. The truth is that language, careless of the more fundamental distinctions, confuses widely different connotations. For example, I find that custom—to return to this most common expression—has a threefold significance, namely:
1. The meaning of a simple objective matter of fact.—In this sense we speak of the man with the habit of early rising, or of walking at a particular time, or of taking an afternoon nap. By this we mean merely that he is accustomed to do so, he does it regularly, it is a part of his manner of life. It is easily understood how this meaning passes over into the next:
2. The meaning of a rule, of a norm which the man sets up for himself.—For example, we say he has made this or that a custom, and in a like meaning, he has made it a rule, or even a law; and we mean that this habit works like a law or a precept. By it a person governs himself and regards habit as an imperative command, a structure of subjective kind, that, however, has objective form and recognition. The precept will be formulated, the original will be copied. A rule may be presented as enjoined, insisted upon, imposed as a command which brings up the third meaning of habit:
3. An expression for a thing willed, or a will.—This third meaning, which is generally given the least consideration, is the most significant. If, in truth, habit is the will of man, then this alone can be his real will. In this sense the proverb is significant that habit is called a second nature, and that man is a creature of habit. Habit is, in fact, a psychic disposition, which drives and urges to a specific act, and this is the will in its most outstanding form, as decision, or as "fixed" purpose.
Imperceptibly, the habitual passes over into the instinctive and the impulsive. What we are accustomed to do, that we do "automatically." Likewise we automatically make gestures, movements of welcome and aversion which we have never learned but which we do "naturally." They have their springs of action in the instinct of self-preservation and in the feelings connected with it. But what we are accustomed to do, we must first have learned and practiced. It is just that practice, the frequent repetition, that brings about the performance of the act "of itself," like a reflex, rapidly and easily. The rope dancer is able to walk the rope, because he is accustomed to it. Habit and practice are also the reasons not only why a man can perform something but also why he performs it with relatively less effort and attention. Habit is the basis not only for our knowing something but also for our actually doing it. Habit operates as a kind of stimulus, and, as may be said, as necessity. The "power of habit" has often been described and often condemned.
As a rule, opinions (mental attitudes) are dependent upon habit, by which they are conditioned and circumscribed. Yet, of course, opinions can also detach themselves from habit, and rise above it, and this is done successfully when they become general opinions, principles, convictions. As such they gain strength which may even break down and overcome habit. Faith, taken in the conventional religious sense of assurance of things hoped for, is a primitive form of will. While in general habit and opinion on the whole agree, there is nevertheless in their relations the seeds of conflict and struggle. Thought continually tends to become the dominating element of the mind, and man thereby becomes the more human.
The same meaning that the will, in the usual individual sense, has for individual man, the social will has for any community or society, whether there be a mere loose relationship, or a formal union and permanent association. And what is this meaning? I have pointed this out in my discussion of habit, and present here the more general statement: The social will is the general volition which serves for the government and regulation of individual wills. Every general volition can be conceived as corresponding to a "thou shalt," and in so far as an individual or an association of individuals directs this "thou shalt" to itself, we recognize the autonomy and freedom of this individual or of this association. The necessary consequence of this is that the individual against all opposing inclinations and opinions, the association against opposing individuals, wherever their opposition manifests itself, attempt, at least, to carry through their will so that they work as a constraint and exert pressure. And this is essentially independent of the means which are used to that end. These pressures extend, at least in the social sense, from measures of persuasion, which appeal to a sense of honor and of shame, to actual coercion and punishment which may take the form of physical compulsion. Sitte develops into the most unbending, overpowering force.
4. The Law, Conscience, and the General Will[68]
In the English language we have no name for it (Sittlichkeit), and this is unfortunate, for the lack of a distinctive name has occasioned confusion both of thought and of expression. Sittlichkeit is the system of habitual or customary conduct, ethical rather than legal, which embraces all those obligations of the citizen which it is "bad form" or "not the thing" to disregard. Indeed, regard for these obligations is frequently enjoined merely by the social penalty of being "cut" or looked on askance. And yet the system is so generally accepted and is held in so high regard, that no one can venture to disregard it without in some way suffering at the hands of his neighbors for so doing. If a man maltreats his wife and children, or habitually jostles his fellow-citizens in the street, or does things flagrantly selfish or in bad taste, he is pretty sure to find himself in a minority and the worse off in the end. But not only does it not pay to do these things, but the decent man does not wish to do them. A feeling analogous to what arises from the dictates of his more private and individual conscience restrains him. He finds himself so restrained in the ordinary affairs of daily life. But he is guided in his conduct by no mere inward feeling, as in the case of conscience. Conscience and, for that matter, law, overlap parts of the sphere of social obligation about which I am speaking. A rule of conduct may, indeed, appear in more than one sphere, and may consequently have a twofold sanction. But the guide to which the citizen mostly looks is just the standard recognized by the community, a community made up mainly of those fellow-citizens whose good opinion he respects and desires to have. He has everywhere round him an object-lesson in the conduct of decent people toward each other and toward the community to which they belong. Without such conduct and the restraints which it imposes there could be no tolerable social life, and real freedom from interference would not be enjoyed. It is the instinctive sense of what to do and what not to do in daily life and behavior that is the source of liberty and ease. And it is this instinctive sense of obligation that is the chief foundation of society. Its reality takes objective shape and displays itself in family life and in our other civic and social institutions. It is not limited to any one form, and it is capable of manifesting itself in new forms and of developing and changing old forms. Indeed, the civic community is more than a political fabric. It includes all the social institutions in and by which the individual life is influenced—such as are the family, the school, the church, the legislature, and the executive. None of these can subsist in isolation from the rest; together they and other institutions of the kind form a single organic whole, the whole which is known as the nation. The spirit and habit of life which this organic entirety inspires and compels are what, for my present purpose, I mean by Sittlichkeit.
Sitte is the German for custom, and Sittlichkeit implies custom and a habit of mind and action. It also implies a little more. Fichte defines it in words which are worth quoting, and which I will put into English:
What, to begin with, does Sitte signify, and in what sense do we use the word? It means for us, and means in every accurate reference we make of it, those principles of conduct which regulate people in their relations to each other, and which have become matter of habit and second nature at the stage of culture reached, and of which, therefore, we are not explicitly conscious. Principles, we call them, because we do not refer to the sort of conduct that is casual or is determined on casual grounds, but to the hidden and uniform ground of action which we assume to be present in the man whose action is not deflected and from which we can pretty certainly predict what he will do. Principles, we say, which have become a second nature and of which we are not explicitly conscious. We thus exclude all impulses and motives based on free individual choice, the inward aspect of Sittlichkeit, that is to say, morality, and also the outward side, or law, alike. For what a man has first to reflect over and then freely to resolve is not for him a habit in conduct; and in so far as habit in conduct is associated with a particular age, it is regarded as the unconscious instrument of the Time Spirit.
The system of ethical habit in a community is of a dominating character, for the decision and influence of the whole community is embodied in that social habit. Because such conduct is systematic and covers the whole of the field of society, the individual will is closely related by it to the will and the spirit of the community. And out of this relation arises the power of adequately controlling the conduct of the individual. If this power fails or becomes weak, the community degenerates and may fall to pieces. Different nations excel in their Sittlichkeit in different fashions. The spirit of the community and its ideals may vary greatly. There may be a low level of Sittlichkeit; and we have the spectacle of nations which have even degenerated in this respect. It may possibly conflict with law and morality, as in the case of the duel. But when its level is high in a nation we admire the system, for we see it not only guiding a people and binding them together for national effort, but affording the greatest freedom of thought and action for those who in daily life habitually act in harmony with the General Will.
Thus we have in the case of a community, be it the city or be it the state, an illustration of a sanction which is sufficient to compel observance of a rule without any question of the application of force. This kind of sanction may be of a highly compelling quality, and it often extends so far as to make the individual prefer the good of the community to his own. The development of many of our social institutions, of our hospitals, of our universities, and of other establishments of the kind, shows the extent to which it reaches and is powerful. But it has yet higher forms in which it approaches very nearly to the level of the obligation of conscience, although it is distinct from that form of obligation. I will try to make clear what I mean by illustrations. A man may be impelled to action of a high order by his sense of unity with the society to which he belongs, action of which, from the civic standpoint, all approve. What he does in such a case is natural to him, and is done without thought of reward or punishment; but it has reference to standards of conduct set up by society and accepted just because society has set them up. There is a poem by the late Sir Alfred Lyall which exemplifies the high level that may be reached in such conduct. The poem is called Theology in Extremis, and it describes the feelings of an Englishman who had been taken prisoner by Mahometan rebels in the Indian Mutiny. He is face to face with a cruel death. They offer him his life if he will repeat something from the Koran. If he complies, no one is likely ever to hear of it, and he will be free to return to England and to the woman he loves. Moreover, and here is the real point, he is not a believer in Christianity, so that it is no question of denying his Savior. What ought he to do? Deliverance is easy, and the relief and advantage would be unspeakably great. But he does not really hesitate, and every shadow of doubt disappears when he hears his fellow-prisoner, a half-caste, pattering eagerly the words demanded.
I will take another example, this time from the literature of ancient Greece. In one of the shortest but not least impressive of his Dialogues, the "Crito," Plato tells us of the character of Socrates, not as a philosopher, but as a good citizen. He has been unjustly condemned by the Athenians as an enemy to the good of the state. Crito comes to him in prison to persuade him to escape. He urges on him many arguments, his duty to his children included. But Socrates refuses. He chooses to follow, not what anyone in the crowd might do, but the example which the ideal citizen should set. It would be a breach of his duty to fly from the judgment duly passed in the Athens to which he belongs, even though he thinks the decree should have been different. For it is the decree of the established justice of his city state. He will not "play truant." He hears the words, "Listen, Socrates, to us who have brought you up"; and in reply he refuses to go away, in these final sentences: "This is the voice which I seem to hear murmuring in my ears, like the sound of the flute in the ears of the mystic; that voice, I say, is murmuring in my ears, and prevents me from hearing any other. And I know that anything more which you may say will be vain."
Why do men of this stamp act so, it may be when leading the battle line, it may be at critical moments of quite other kinds? It is, I think, because they are more than mere individuals. Individual they are, but completely real, even as individual, only in their relation to organic and social wholes in which they are members, such as the family, the city, the state. There is in every truly organized community a Common Will which is willed by those who compose that community, and who in so willing are more than isolated men and women. It is not, indeed, as unrelated atoms that they have lived. They have grown, from the receptive days of childhood up to maturity, in an atmosphere of example and general custom, and their lives have widened out from one little world to other and higher worlds, so that, through occupying successive stations in life, they more and more come to make their own the life of the social whole in which they move and have their being. They cannot mark off or define their own individualities without reference to the individualities of others. And so they unconsciously find themselves as in truth pulse-beats of the whole system, and themselves the whole system. It is real in them and they in it. They are real only because they are social. The notion that the individual is the highest form of reality, and that the relationship of individuals is one of mere contract, the notion of Hobbes and of Bentham and of Austin, turns out to be quite inadequate. Even of an everyday contract, that of marriage, it has been well said that it is a contract to pass out of the sphere of contract, and that it is possible only because the contracting parties are already beyond and above that sphere. As a modern writer, F. H. Bradley of Oxford, to whose investigations in these regions we owe much, has finely said: "The moral organism is not a mere animal organism. In the latter the member is not aware of itself as such, while in the former it knows itself, and therefore knows the whole in itself. The narrow external function of the man is not the whole man. He has a life which we cannot see with our eyes, and there is no duty so mean that it is not the realization of this, and knowable as such. What counts is not the visible outer work so much as the spirit in which it is done. The breadth of my life is not measured by the multitude of my pursuits, nor the space I take up amongst other men; but by the fulness of the whole life which I know as mine. It is true that less now depends on each of us as this or that man; it is not true that our individuality is therefore lessened; that therefore we have less in us."
There is, according to this view, a General Will with which the will of the good citizen is in accord. He feels that he would despise himself were his private will not in harmony with it. The notion of the reality of such a will is no new one. It is as old as the Greeks, for whom the moral order and the city state were closely related; and we find it in modern books in which we do not look for it. Jean Jacques Rousseau is probably best known to the world by the famous words in which he begins the first chapter of the Social Contract: "Man is born free, and everywhere he is in chains. Those who think themselves to be the masters of others cease not to be greater slaves than the people they govern." He goes on in the next paragraph to tell us that if he were only to consider force and the effects of it, he would say that if a nation was constrained to obey and did obey, it did well, but that whenever it could throw off its yoke and did throw it off, it acted better. His words, written in 1762, became a text for the pioneers of the French Revolution. But they would have done well to read further into the book. As Rousseau goes on, we find a different conception. He passes from considering the fiction of a social contract to a discussion of the power over the individual of the General Will, by virtue of which a people becomes a people. This General Will, the Volonté Générale, he distinguishes from the Volonté de Tous, which is a mere numerical sum of individual wills. These particular wills do not rise above themselves. The General Will, on the other hand, represents what is greater than the individual volition of those who compose the society of which it is the will. On occasions, this higher will is more apparent than at other times. But it may, if there is social slackness, be difficult to distinguish from a mere aggregate of voices, from the will of a mob. What is interesting is that Rousseau, so often associated with doctrine of quite another kind, should finally recognize the bond of a General Will as what really holds the community together. For him, as for those who have had a yet clearer grasp of the principle, in willing the General Will we not only realize our true selves but we may rise above our ordinary habit of mind. We may reach heights which we could not reach, or which at all events most of us could not reach, in isolation. There are few observers who have not been impressed with the wonderful unity and concentration of purpose which an entire nation may display—above all, in a period of crisis. We see it in time of war, when a nation is fighting for its life or for a great cause. We have marvelled at the illustrations with which history abounds of the General Will rising to heights of which but few of the individual citizens in whom it is embodied have ever before been conscious even in their dreams.
By leadership a common ideal can be made to penetrate the soul of a people and to take complete possession of it. The ideal may be very high, or it may be of so ordinary a kind that we are not conscious of it without the effort of reflection. But when it is there it influences and guides daily conduct. Such idealism passes beyond the sphere of law, which provides only what is necessary for mutual protection and liberty of just action. It falls short, on the other hand, in quality of the dictates of what Kant called the Categorical Imperative that rules the private and individual conscience, but that alone, an Imperative which therefore gives insufficient guidance for ordinary and daily social life. Yet the ideal of which I speak is not the less binding; and it is recognized as so binding that the conduct of all good men conforms to it.
C. PERSONALITY AND THE SOCIAL SELF
1. The Organism as Personality[69]
The organism and the brain, as its highest representation, constitute the real personality, containing in itself all that we have been, and the possibility of all that we shall be. The complete individual character is inscribed there with all its active and passive aptitudes, sympathies, and antipathies; its genius, talents, or stupidity; its virtues, vices, torpor, or activity. Of all these, what emerges and actually reaches consciousness is only a small item compared with what remains buried below, albeit still active. Conscious personality is always but a feeble portion of physical personality.
The unity of the ego, consequently, is not that of the one-entity of spiritualists which is dispersed into multiple phenomena, but the co-ordination of a certain number of incessantly renascent states, having for their support the vague sense of our bodies. This unity does not pass from above to below, but from below to above; the unity of the ego is not an initial, but a terminal point.
Does there really exist a perfect unity? Evidently not in the strict, mathematical sense. In a relative sense it is met with, rarely and incidentally. In a clever marksman in the act of taking aim, or in a skilled surgeon performing a difficult operation all is found to converge, both physically and mentally. Still, let us take note of the result: in these conditions the awareness of real personality disappears; the conscious individual is reduced to an idea; whence it would follow that perfect unity of consciousness and the awareness of personality exclude each other. By a different course we again reach the same conclusion; the ego is a co-ordination. It oscillates between two extreme points at which it ceases to exist: viz., perfect unity and absolute inco-ordination. All the intermediate degrees are met with, in fact, and without any line of demarcation between the healthy and the morbid; the one encroaches upon the other.
Even in the normal state the co-ordination is often sufficiently loose to allow several series to coexist separately. We can walk or perform manual work with a vague and intermittent consciousness of the movements, at the same time singing, musing; but if the activity of thought increases, the singing will cease. With many people it is a kind of substitute for intellectual activity, an intermediate state between thinking and not-thinking.
The unity of the ego, in a psychological sense, is, therefore, the cohesion, during a given time, of a certain number of clear states of consciousness, accompanied by others less clear, and by a multitude of physiological states which, without being accompanied by consciousness like the others, yet operate as much as, and even more than, the former. Unity, in fact, means co-ordination. The conclusion to be drawn from the above remarks is namely this, that the consensus of consciousness being subordinate to the consensus of the organism, the problem of the unity of the ego is, in its ultimate form, a biological problem. To biology pertains the task of explaining, if it can, the genesis of organisms and the solidarity of their component parts. Psychological interpretation can only follow in its wake.
2. Personality as a Complex[70]
Ideas, after being experienced in consciousness, become dormant (conserved as physiological dispositions) and may or may not afterward be reawakened in consciousness as memories. Many such ideas, under conditions with some of which we are all familiar, tend to form part of our voluntary or involuntary memories and many do not. But when such is the case, the memories do not ordinarily include the whole of a given mental experience, but only excerpts or abstracts of it. Hence one reason for the fallibility of human memory and consequent testimony.
Now under special conditions, the ideas making up an experience at any given moment tend to become organized into a system or complex, so that when we later think of the experience or recall any of the ideas belonging to it, the complex as a whole is revived. This is one of the principles underlying the mechanism of memory. Thus it happens that memory may, to a large extent, be made up of complexes. These complexes may be very loosely organized in that the elementary ideas are weakly bound together, in which case, when we try to recall the original experience, only a part of it is recalled. Or a complex may be very strongly organized, owing to the conditions under which it is formed, and then a large part of the experience can be recalled. In this case, any idea associated with some element in the complex may, by the law of association, revive the whole original complex. If, for instance, we have gone through a railroad accident involving exciting incidents, loss of life, etc., the words "railroad," "accident," "death," or a sudden crashing sound, or the sight of blood, or even riding in a railroad train may recall the experience from beginning to end, or at least the prominent features in it, i.e., so much as was organized. The memory of the greater part of this experience is well organized, while the earlier events and those succeeding the accident may have passed out of all possibility of voluntary recall.
To take an instance commonplace enough but which happens to have just come within my observation: A fireman was injured severely by being thrown from a hose wagon rushing to a fire against a telegraph pole with which the wagon collided. He narrowly escaped death. Although three years have passed he still cannot ride on a wagon to a fire without the memory of the whole accident rising in his mind. When he does so he again lives through the accident, including the thoughts just previous to the actual collision when, realizing his situation, he was overcome with terror, and he again manifests all the organic physical expressions of fear, viz.: perspiration, tremor, and muscular weakness. Here is a well-organized and fairly limited complex.
Among the loosely organized complexes in many individuals, and possibly in all of us, there are certain dispositions toward views of life which represent natural inclinations, desires, and modes of activity which, for one reason or another, we tend to suppress or are unable to give full play to. Many individuals, for example, are compelled by the exactions of their duties and responsibilities to lead serious lives, to devote themselves to pursuits which demand all their energies and thought and which, therefore, do not permit of indulgence in the lighter enjoyments of life, and yet there may be a natural inclination to partake of the pleasures which innately appeal to all mankind and which many pursue. The longing for these recurs from time to time. The mind dwells on them, the imagination is excited and weaves a fabric of pictures, thoughts, and emotions which thus become associated into a complex. There may be a rebellion and "kicking against the pricks" and thereby a liberation of the emotional force that impresses a stronger organization on the whole process. The recurrence of such a complex is one form of what we call a "mood," which has a distinctly emotional tone of its own. The revival of this feeling tone tends to revive the associated ideas and vice versa. Such a feeling-idea complex is often spoken of as "a side to one's character," to which a person may from time to time give play. Or the converse of this may hold, and a person who devotes his life to the lighter enjoyments may have aspirations and longings for more serious pursuits, and in this respect the imagination may similarly build up a complex which may express itself in a mood. Thus a person is often said to have "many sides to his character," and exhibits certain alternations of personality which may be regarded as normal prototypes of those which occur as abnormal states.
Most of what has been said about the formation of complexes is a statement of commonplace facts, and I would not repeat it here were it not that, in certain abnormal conditions, disposition, subject, and other complexes, though loosely organized, often play an important part. This is not the place to enter into an explanation of dissociated personality, but in such conditions we sometimes find that disposition complexes, for instance, come to the surface and displace or substitute themselves for the other complexes which make up a personality. A complex which is only a mood or a "side of the character" of a normal individual may, in conditions of dissociation, become the main, perhaps sole, complex and chief characteristic of the new personality. In Miss Beauchamp, for instance, the personality known as BI was made up almost entirely of the religious and ethical ideas which formed one side of the original self. In the personality known as Sally we had for the most part the complex which represented the enjoyment of youthful pleasures and sports, the freedom from conventionalities and artificial restraints generally imposed by duties and responsibilities. In BIV the complex represented the ambitions and activities of practical life. In Miss Beauchamp as a whole, normal, without disintegration, it was easy to recognize all three dispositions as "sides of her character," though each was kept ordinarily within proper bounds by the correcting influence of the others. It was only necessary to put her in an environment which encouraged one or the other side, to associate her with people who strongly suggested one or the other of her own characteristics, whether religious, social, pleasure loving, or intellectual, to see the characteristics of BI, Sally, or BIV stand out in relief as the predominant personality. Then we had the alternating play of these different sides of her character.
In fact, the total of our complexes, which, regarded as a whole and in view of their reaction to the environment, their behavior under the various conditions of social life, their aptitudes, feeling-tones, "habits," and faculties, we term character and personality, are in large part predetermined by the mental experiences of the past and the vestiges of memory which have been left as residual from these experiences. We are the offspring of our past.
The great mass of our ideas involve associations of the origin of which we are unaware because the memories of the original experience have become split and a large portion thus has become forgotten even if ever fully appreciated. We all have our prejudices, our likes and dislikes, our tastes and aversions; it would tax our ingenuity to give a sufficient psychological account of their origin. They were born long ago in educational, social, personal, and other experiences, the details of which we have this many a year forgotten. It is the residua of these experiences that have persisted and become associated into complexes which are retained as traits of our personality.
3. The Self as the Individual's Conception of His Rôle[71]
Suggestion may have its end and aim in the creation of a new personality. The experimenter then chooses the sort of personality he wishes to induce and obliges the subject to realize it. Experiments of this kind succeeding in a great many somnambulists, and usually producing very curious results, have long been known and have been repeated, one might say, almost to satiety within the last few years.
When we are awake and in full possession of all our faculties we can imagine sensations different from those which we ordinarily experience. For example, when I am sitting quietly at my table engaged in writing this book, I can conceive the sensations that a soldier, a woman, an artist, or an Englishman would experience in such and such a situation. But, however fantastic the conceptions may be that we form, we do not cease to be conscious withal of our own personal existence. Imagination has taken flight fairly in space, but the memory of ourselves always remains behind. Each of us knows that he is himself and not another, that he did this yesterday, that he has just written a letter, that he must write another such letter tomorrow, that he was out of Paris for a week, etc. It is this memory of passed facts—a memory always present to the mind—that constitutes the consciousness of our normal personality.
It is entirely different in the case of the two women, A—— and B——, that M. Richet studied.
Put to sleep and subjected to certain influences, A—— and B—— forget their identity; their age, their clothing, their sex, their social position, their nationality, the place and the time of their life—all this has entirely disappeared. Only a single idea remains—a single consciousness—it is the consciousness of the idea and of the new being that dawns upon their imagination.
They have lost the idea of their late existence. They live, talk, and think exactly like the type that is suggested to them. With what tremendous intensity of life these types are realized, only those who have been present at these experiments can know. Description can only give a weak and imperfect idea of it.
Instead of imagining a character simply, they realize it, objectify it. It is not like a hallucination, of which one witnesses the images unfolding before him, as a spectator would. He is rather like an actor who is seized with passion, imagines that the drama he plays is a reality, not a fiction, and that he has been transformed, body and soul, into the personality that he sets himself to play.
In order to have this transformation of personality work it is sufficient to pronounce a word with some authority. I say to A——, "You are an old woman," she considers herself changed into an old woman, and her countenance, her bearing, her feelings, become those of an old woman. I say to B——, "You are a little girl," and she immediately assumes the language, games, and tastes of a little girl.
Although the account of these scenes is quite dull and colorless compared with the sight of the astonishing and sudden transformations themselves, I shall attempt, nevertheless, to describe some of them. I quote some of M——'s objectivations:
As a peasant.—She rubs her eyes and stretches herself. "What time is it? Four o'clock in the morning!" She walks as if she were dragging sabots. "Now, then, I must get up. Let us go to the stable. Come up, red one! come up, get about!" She seems to be milking a cow. "Let me alone, Gros-Jean, let me alone, I tell you. When I am through my work. You know well enough that I have not finished my work. Oh! yes, yes, later."
As an actress.—Her face took a smiling aspect instead of the dull and listless manner which she had just had. "You see my skirt? Well, my manager makes me wear it so long. These managers are too tiresome. As for me, the shorter the skirt the better I like it. There is always too much of it. A simple fig leaf! Mon Dieu, that is enough! You agree with me, don't you, my dear, that it is not necessary to have more than a fig leaf? Look then at this great dowdy Lucie—where are her legs, eh?"
As a priest.—She imagines that she is the Archbishop of Paris. Her face becomes very grave. Her voice is mildly sweet and drawling, which forms a great contrast with the harsh, blunt tone she had as a general. (Aside.) "But I must accomplish my charge." She leans her head on her hand and reflects. (Aloud.) "Ah! it is you, Monsieur Grand Vicar; what is your business with me? I do not wish to be disturbed. Yes, today is the first of January, and I must go to the cathedral. This throng of people is very respectful, don't you think so, monsieur? There is a great deal of religion in the people, whatever one does. Ah! a child! let him come to me to be blessed. There, my child." She holds out to him her imaginary bishop's ring to kiss. During this whole scene she is making gestures of benediction with her right hand on all sides. "Now I have a duty to perform. I must go and pay my respects to the president of the Republic. Ah! Mr. President, I come to offer you my allegiance. It is the wish of the church that you may have many years of life. She knows that she has nothing to fear, notwithstanding cruel attacks, while such an honorable man is at the head of the Republic." She is silent and seems to listen attentively. (Aside.) "Yes, fair promises. Now let us pray!" She kneels down.
As a religious sister.—She immediately kneels down and begins to say her prayers, making a great many signs of the cross; then she arises. "Now to the hospital. There is a wounded man in this ward. Well, my friend, you are a little better this morning, aren't you? Now, then, let me take off your bandage." She gestures as if she were unrolling a bandage. "I shall do it very gently; doesn't that relieve you? There! my poor friend, be as courageous before pain as you were before the enemy."
I might cite other objectivations from A——'s case, in the character of old woman, little girl, young man, gay woman, etc. But the examples given seem sufficient to give some idea of the entire transformation of the personality into this or that imaginary type. It is not a simple dream, it is a living dream.
The complete transformation of feelings is not the least curious phenomenon of these objectivations. A—— is timid, but she becomes very daring when she thinks herself a bold person. B—— is silent, she becomes talkative when she represents a talkative person. The disposition is thus completely changed. Old tastes disappear and give place to the new tastes that the new character represented is supposed to have.
In a more recent paper, prepared with the co-operation of M. Ferrari and M. Hericourt, M. Richet has added a curious detail to the preceding experiments. He has shown that the subject on whom a change of personality is imposed not only adapts his speech, gestures, and attitudes to the new personality, but that even his handwriting is modified and brought into relation with the new ideas that absorb his consciousness. This modification of handwriting is an especially interesting discovery, since handwriting, according to current theories, is nothing more than a sort of imitation. I cite some examples borrowed from these authors.
It is suggested in succession to a young student that he is a sly and crafty peasant, then a miser, and finally a very old man. While the subject's features and behavior generally are modified and brought into harmony with the idea of the personality suggested, we may observe also that his handwriting undergoes similar modifications which are not less marked. It has a special character peculiar to each of the new states of personality. In short, the graphic movements change like the gestures generally.
In a note on the handwriting of hysterical patients, I have shown that under the influence of suggested emotions, or under the influence of sensorial stimulations, the handwriting of a hysterical patient may be modified. It gets larger, for example, in cases of dynamogenic excitation.
The characteristic of the suggestion that we have just studied is that it does not bear exclusively on perception or movement—that is to say, on a limited psychic element; but there are comprehensive suggestions. They impose a topic on the subject that he is obliged to develop with all the resources of his intellect and imagination, and if the observations be carefully examined, it will also be seen that in these suggestions the faculties of perception are affected and perverted by the same standard as that of ideation. Thus the subject, under the influence of his assumed personality, ceases to perceive the external world as it exists. He has hallucinations in connection with his new psychological personality. When a bishop, he thinks he is in Notre Dame, and sees a host of the faithful. When a general, he thinks he is surrounded by troops, etc. Things that harmonize with the suggestion are conjured up. This systematic development of states of consciousness belongs to all kinds of suggestions, but is perhaps nowhere else so marked as in these transformations of personality.
On the other hand, everything that is inconsistent with the suggestion gets inhibited and leaves the subject's consciousness. As has been said, alterations of personality imply phenomena of amnesia. In order that the subject may assume the fictitious personality he must begin by forgetting his true personality. The infinite number of memories that represent his past experience and constitute the basis of his normal ego are for the time being effaced, because these memories are inconsistent with the ideal of the suggestion.
4. The Natural Person versus the Social and Conventional Self[72]
Somewhat after the order of Dr. Jekyll and Mr. Hyde I seem to possess two distinct personalities, being both at the same time but presenting no such striking contrast as the Jekyll-Hyde combination. They are about equally virtuous. Their main difference seems to be one of age, one being a decade or so in advance of the other.
At times they work harmoniously together and again at cross-purposes. I do not seem to have developed equally. Part of me sits humbly at the feet of the other part of me and receives advice and instruction. Part of me feels constrained to confess to the other part of me when it has done wrong and meekly receives rebuke. Part of me tries to shock the other part of me and to force the more dignified part to misbehave and giggle and do things not considered correct in polite society.
My younger part delights to tease the older, to doubt her motives, to interrupt her meditations. It wants to play, while my older self is more seriously inclined. My younger self is only twelve years old. This is my real self. To my own mind I am still a little girl with short dresses and a bunch of curls. For some reason my idea of self has never advanced beyond this point. The long dress and the hair piled high will never seem natural. Sometimes I enjoy this duality and again I do not. Sometimes the two parts mingle delightfully together, again they wrangle atrociously, while I (there seems to be a third part of me) sit off and watch the outcome.
The older part gets tired before the younger. The younger, still fresh and in a good humor, undertakes to furnish amusement for the older. I have often thrown myself on the bed wearied and exhausted and been made to shake with laughter at the capers of the younger part of me. They are capers indeed. On these occasions she will carry on conversations with friends—real friends—fairly bristling with witticisms, and although taking both parts herself, the parry and thrust is delightful.
Sometimes, however, the younger part of me seems to get up all awry. She will carry on quarrels—heated quarrels—from morning to night, taking both sides herself, with persons whom I (the combination) dearly love, and against whom I have no grievance whatever. These are a great distress to my older self.
On other days she seems to take the greatest delight in torturing me with imaginary horrors. She cuts my throat, pulls my eyes out of their sockets, removes tumors, and amputates limbs until I wonder that there is anything left of me. She does it all without administering anæsthetics and seems to enjoy my horror and disgust.
Again, some little jingle or tune will take her fancy and she will repeat it to herself until I am almost driven to madness. Sometimes it is only a word, but it seems to have a fascination for her and she rolls it as a sweet morsel under her tongue until sleep puts an end to it.
Again, if I (the combination) fall ill, one part of me, I have never discovered which, invariably hints that I am not ill at all but merely pretending. So much so that it has become with me a recognized symptom of incipient illness.
Moreover, the younger and older are never on the same side of any question. One leans to wisdom, the other to fun. I am a house divided against itself. The younger longs to dance, to go to the theater and to play cards, all of which the older disapproves. The younger mocks the older, calls her a hypocrite and the like until the older well-nigh believes it herself and almost yields to her pleadings. The older listens sedately to the sermon, while the younger plans her Easter suit or makes fun of the preacher.
The older declares she will never marry, while the younger scouts the idea of being an old maid. But even if she could gain the consent of the older, it were but little better, they differ so as to their ideals.
In society the difference is more marked. I seem to be a combination chaperone and protégée. The older appears at ease, the younger shy and awkward—she has never made her début. If one addresses a remark to her she is thrown into utter confusion until the older rushes to the rescue. My sympathy is with the younger, however, for even to this day I, the combination, can scarce resist the temptation to say nothing when there is nothing to say.
There is something tragic to me in this Siamese-twins arrangement of two so uncongenial. I am at one and the same time pupil and teacher, offender and judge, performer and critic, chaperone and protégée, a prim, precise, old maid and a rollicking schoolgirl, a tomboy and a prude, a saint and sinner. What can result from such a combination? That we get on tolerably is a wonder. Some days, however, we get on admirably together, part of me paying compliments to the other part of me—whole days being given to this—until each of us has such a good opinion of herself and the other that we feel on equal terms and are at our happiest.
But how dreadful are the days when we turn against each other! There are not words enough to express the contempt which we feel for ourselves. We seem to set each other in the corner and the combination as a whole is utterly miserable.
I can but wonder and enjoy and wait to see what Myself and I will make of Me.
5. The Divided Self and Moral Consciousness[73]
Two ways of looking at life are characteristic respectively of what we call the healthy-minded, who need to be born only once, and of the sick souls, who must be twice-born in order to be happy. The result is two different conceptions of the universe of our experience. In the religion of the once-born the world is a sort of rectilineal or one-storied affair, whose accounts are kept in one denomination, whose parts have just the values which naturally they appear to have, and of which a simple algebraic sum of pluses and minuses will give the total worth. Happiness and religious peace consist in living on the plus side of the account. In the religion of the twice-born, on the other hand, the world is a double-storied mystery. Peace cannot be reached by the simple addition of pluses and elimination of minuses from life. Natural good is not simply insufficient in amount and transient; there lurks a falsity in its very being. Cancelled as it all is by death, if not by earlier enemies, it gives no final balance, and can never be the thing intended for our lasting worship. It keeps us from our real good, rather; and renunciation and despair of it are our first step in the direction of the truth. There are two lives, the natural and the spiritual, and we must lose the one before we can participate in the other.
In their extreme forms, of pure naturalism and pure salvationism, the two types are violently contrasted; though here, as in most other current classifications, the radical extremes are somewhat ideal abstractions, and the concrete human beings whom we oftenest meet are intermediate varieties and mixtures. Practically, however, you all recognize the difference: you understand, for example, the disdain of the Methodist convert for the mere sky-blue healthy-minded moralist; and you likewise enter into the aversion of the latter to what seems to him the diseased subjectivism of the Methodist, dying to live, as he calls it, and making of paradox and the inversion of natural appearances the essence of God's truth.
The psychological basis of the twice-born character seems to be a certain discordancy or heterogeneity in the native temperament of the subject, an incompletely unified moral and intellectual constitution.
"Homo duplex, homo duplex!" writes Alphonse Daudet. "The first time that I perceived that I was two was at the death of my brother Henri, when my father cried out so dramatically, 'He is dead, he is dead!' While my first self wept, my second self thought, 'How truly given was that cry, how fine it would be at the theater.' I was then fourteen years old. This horrible duality has often given me matter for reflection. Oh, this terrible second me, always seated whilst the other is on foot, acting, living, suffering, bestirring itself. This second me that I have never been able to intoxicate, to make shed tears, or put to sleep. And how it sees into things, and how it mocks!"
Some persons are born with an inner constitution which is harmonious and well balanced from the outset. Their impulses are consistent with one another, their will follows without trouble the guidance of their intellect, their passions are not excessive, and their lives are little haunted by regrets. Others are oppositely constituted; and are so in degrees which may vary from something so slight as to result in a merely odd or whimsical inconsistency, to a discordancy of which the consequences may be inconvenient in the extreme. Of the more innocent kinds of heterogeneity I find a good example in Mrs. Annie Besant's autobiography.
[67] Translated and adapted from Ferdinand Tönnies, Die Sitte, pp. 7-14. (Literarische Anstalt, Rütten und Loening, 1909.)
[68] From Viscount Haldane, "Higher Nationality," in International Conciliation, November, 1913, No. 72, pp. 4-12.
[69] From Th. Ribot, The Diseases of Personality, pp. 156-57. Translated from the French. (The Open Court Publishing Co., 1891.)
[70] From Morton Prince, "The Unconscious," in the Journal of Abnormal Psychology, III (1908-9), 277-96, 426.
[71] From Alfred Binet, Alterations of Personality, pp. 248-57. (D. Appleton & Co., 1896.)
[72] From L. G. Winston, "Myself and I," in the American Journal of Psychology, XIX (1908), 562-63.
[73] From William James, The Varieties of Religious Experience, pp. 166-73. (Longmans, Green & Co., 1902.)
I have ever been the queerest mixture of weakness and strength, and have paid heavily for the weakness. As a child I used to suffer tortures of shyness, and if my shoe-lace was untied would feel shamefacedly that every eye was fixed on the unlucky string; as a girl I would shrink away from strangers and think myself unwanted and unliked, so that I was full of eager gratitude to anyone who noticed me kindly; as the young mistress of a house I was afraid of my servants, and would let careless work pass rather than bear the pain of reproving the ill-doer; when I have been lecturing and debating with no lack of spirit on the platform, I have preferred to go without what I wanted at the hotel rather than to ring and make the waiter fetch it. Combative on the platform in defense of any cause I cared for, I shrink from quarrel or disapproval in the house, and am a coward at heart in private while a good fighter in public. How often have I passed unhappy quarters of an hour screwing up my courage to find fault with some subordinate whom my duty compelled me to reprove, and how often have I jeered at myself for a fraud as the doughty platform combatant, when shrinking from blaming some lad or lass for doing their work badly. An unkind look or word has availed to make me shrink myself as a snail into its shell, while, on the platform, opposition makes me speak my best.
This amount of inconsistency will only count as amiable weakness; but a stronger degree of heterogeneity may make havoc of the subject's life. There are persons whose existence is little more than a series of zigzags, as now one tendency and now another gets the upper hand. Their spirit wars with their flesh, they wish for incompatibles, wayward impulses interrupt their most deliberate plans, and their lives are one long drama of repentance and of effort to repair misdemeanors and mistakes.
Whatever the cause of heterogeneous personality may be, we find the extreme examples of it in the psychopathic temperament. All writers about that temperament make the inner heterogeneity prominent in their descriptions. Frequently, indeed, it is only this trait that leads us to ascribe that temperament to a man at all. A dégénéré supérieur is simply a man of sensibility in many directions, who finds more difficulty than is common in keeping his spiritual house in order and running his furrow straight, because his feelings and impulses are too keen and too discrepant mutually. In the haunting and insistent ideas, in the irrational impulses, the morbid scruples, dreads, and inhibitions which beset the psychopathic temperament when it is thoroughly pronounced, we have exquisite examples of heterogeneous personality. Bunyan had an obsession of the words, "Sell Christ for this, sell him for that, sell him, sell him!" which would run through his mind a hundred times together, until one day out of breath with retorting, "I will not, I will not," he impulsively said, "Let him go if he will," and this loss of the battle kept him in despair for over a year. The lives of the saints are full of such blasphemous obsessions, ascribed invariably to the direct agency of Satan.
St. Augustine's case is a classic example of discordant personality. You all remember his half-pagan, half-Christian bringing up at Carthage, his emigration to Rome and Milan, his adoption of Manicheism and subsequent skepticism, and his restless search for truth and purity of life; and finally how, distracted by the struggle between the two souls in his breast, and ashamed of his own weakness of will when so many others whom he knew and knew of had thrown off the shackles of sensuality and dedicated themselves to chastity and the higher life, he heard a voice in the garden say, "Sume, lege" (take and read), and opening the Bible at random, saw the text, "not in chambering and wantonness," etc., which seemed directly sent to his address, and laid the inner storm to rest forever. Augustine's psychological genius has given an account of the trouble of having a divided self which has never been surpassed.
The new will which I began to have was not yet strong enough to overcome that other will, strengthened by long indulgence. So these two wills, one old, one new, one carnal, the other spiritual, contended with each other and disturbed my soul. I understood by my own experience what I had read, "Flesh lusteth against spirit, and spirit against flesh." It was myself indeed in both the wills, yet more myself in that which I approved in myself than in that which I disapproved in myself. Yet it was through myself that habit had obtained so fierce a mastery over me, because I had willingly come whither I willed not. Still bound to earth, I refused, O God, to fight on thy side, as much afraid to be freed from all bonds as I ought to have feared being trammeled by them.
Thus the thoughts by which I meditated upon thee were like the efforts of one who would awake, but being overpowered with sleepiness is soon asleep again. Often does a man when heavy sleepiness is on his limbs defer to shake it off, and though not approving it, encourage it; even so I was sure it was better to surrender to thy love than to yield to my own lusts, yet, though the former course convinced me, the latter pleased and held me bound. There was naught in me to answer thy call, "Awake, thou sleeper," but only drawling, drowsy words, "Presently; yes, presently; wait a little while." But the "presently" had no "present," and the "little while" grew long. For I was afraid thou wouldst hear me too soon, and heal me at once of my disease of lust, which I wished to satiate rather than to see extinguished. With what lashes of words did I not scourge my own soul. Yet it shrank back; it refused, though it had no excuse to offer. I said within myself: "Come, let it be done now," and as I said it, I was on the point of the resolve. I all but did it, yet I did not do it. And I made another effort, and almost succeeded, yet I did not reach it, and did not grasp it, hesitating to die to death, and live to life; and the evil to which I was so wonted held me more than the better life I had not tried.
There could be no more perfect description of the divided will, when the higher wishes lack just that last acuteness, that touch of explosive intensity, of dynamogenic quality (to use the slang of the psychologists), that enables them to burst their shell, and make irruption efficaciously into life and quell the lower tendencies forever.
6. Personality of Individuals and of Peoples[74]
In my opinion personality is not merely a unifying and directing principle which controls thought and action, but one which, at the same time, defines the relation of individuals to their fellows. The concept of personality includes, in addition to inner unity and co-ordination of the impulses, a definite attitude directed toward the outer world which is determined by the manner in which the individual organizes his external stimulations.
In this definition the objective aspect of personality is emphasized as over against the subjective. We should not in psychological matters be satisfied with subjective definitions. The mental life is not only a sum of subjective experiences but manifests itself invariably also in a definite series of objective expressions. These objective expressions are the contributions which the personality makes to its external social environment. More than that, only these objective expressions of personality are accessible to external observation and they alone have objective value.
According to Ribot, the real personality is an organism which is represented at its highest in the brain. The brain embraces all our past and the possibilities of our future. The individual character with all its active and passive peculiarities, with all its antipathies, genius, talents, stupidities, virtues, and vices, its inertia and its energy is predetermined in the brain.
Personality, from the objective point of view, is the psychic individual with all his original characters, an individual in free association with his social milieu. Neither innate mental ability, nor creative energy, nor what we call will, in and of themselves, constitutes personality. Nothing less than the totality of psychical manifestations, all these including idiosyncrasies which distinguish one man from another and determine his positive individuality, may be said to characterize, from the objective point of view, the human personality.
The intellectual horizon of persons on different cultural levels varies, but no one, for that reason (because of intellectual inferiority), loses the right to recognition as a person, provided that he maintains, over against his environment, his integrity as an individual and remains a self-determining person. It is the loss of this self-determined individuality alone that renders man completely impersonal. When individual spontaneity is feebly manifested, we speak of an ill-defined or a "passive" personality. Personality is, in short, from the objective point of view, a self-determining individual with a unique nature and a definite status in the social world around him.
If now, on the basis of the preceding definition, we seek to define the significance of personality in social and public life, it appears that personality is the basis upon which all social institutions, movements, and conditions, in short all the phenomena of social life, rest. The people of our time are no more, as in the Golden Age, inarticulate masses. They are a totality of more or less active personalities connected by common interests, in part by racial origin, and by a certain similarity of fundamental psychic traits. A people is a kind of collective personality possessing particular ethnic and psychological characteristics, animated by common political aspirations and political traditions. The progress of peoples, their civilization, and their culture naturally are determined by the advancement of the personalities which compose them. Since the emancipation of mankind from a condition of subjection, the life of peoples and of societies has rested upon the active participation of each member of society in the common welfare which represents the aim of all. The personality, considered as a psychic self-determining individual, asserts itself the more energetically in the general march of historical events, the farther a people is removed from the condition of subjection in which the rights of personality are denied.
In every field of activity, the more advanced personality "blazes a new trail." The passive personality, born in subjection, is disposed merely to imitate and to repeat. The sheer existence of modern states depends less on the crude physical force and its personified agencies, than on the moral cohesion of the personalities who constitute the nation.
Since the beginning of time, it is only the moral values that have endured. Force can support the state only temporarily. When a nation disregards the moral forces and seeks its salvation in the rude clash of arms, it bears within itself the seeds of its own destruction. No army in the world is strong enough to maintain a state, the moral basis of which is shaken, for the strength of the army rests upon its morale.
The importance of personality in the historic life of peoples is manifest in periods when social conditions accelerate the movement of social life. Personality, like every other force, reaches its maximum when it encounters resistance, in conflict and in rivalry—when it fights—hence its great value in friendly rivalry of nations in industry and culture, and especially in periods of natural calamities or of enemies from without. Since the fruits of individual development contribute to the common fund of social values, it is clear that societies and peoples which, other things being equal, possess the most advanced and active personalities contribute most to the enrichment of civilization. It does not seem necessary to demonstrate that the pacific competition of nations and their success depends on the development of the personalities which compose them. A nation weak in the development of individualities, of social units which compose it, could not defend itself against the exploitation of nations composed of personalities with a superior development.
D. BIOLOGICAL AND SOCIAL HEREDITY
1. Nature and Nurture[75]
We have seen that the scientific position in regard to the transmissibility of modifications should be one of active scepticism, that there seems to be no convincing evidence in support of the affirmative position, and that there is strong presumption in favor of the negative.
A modification is a definite change in the individual body, due to some change in "nurture." There is no secure evidence that any such individual gain or loss can be transmitted as such, or in any representative degree. How does this affect our estimate of the value of "nurture"? How should the sceptical or negative answer, which we believe to be the scientific one, affect our practice in regard to education, physical culture, amelioration of function, improvement of environment, and so on? Let us give a practical point to what we have already said.
a) Every inheritance requires an appropriate nurture if it is to realize itself in development. Nurture supplies the liberating stimuli necessary for the full expression of the inheritance. A man's character as well as his physique is a function of "nature" and of "nurture." In the language of the old parable of the talents, what is given must be traded with. A boy may be truly enough a chip of the old block, but how far he shows himself such depends on "nurture." The conditions of nurture determine whether the expression of the inheritance is to be full or partial. It need hardly be said that the strength of an (inherited) individuality may be such that it expresses itself almost in the face of inappropriate nurture. History abounds in instances. As Goethe said, "Man is always achieving the impossible." Corot was the son of a successful milliner and prosperous tradesman, and he was thirty before he left the draper's shop to study nature.
b) Although modifications do not seem to be transmitted as such, or in any representative degree, there is no doubt that they or their secondary results may in some cases affect the offspring. This is especially the case in typical mammals, where there is before birth a prolonged (placental) connection between the mother and the unborn young. In such cases the offspring is for a time almost part of the maternal body, and liable to be affected by modifications thereof, e.g., by good or bad nutritive conditions. In other cases, also, it may be that deeply saturating parental modifications, such as the results of alcoholic and other poisoning, affect the germ cells, and thus the offspring. A disease may saturate the body with toxins and waste products, and these may provoke prejudicial germinal variations.
c) Though modifications due to changed "nurture" do not seem to be transmissible, they may be re-impressed on each generation. Thus "nurture" becomes not less, but more, important in our eyes.
"Is my grandfather's environment not my heredity?" asks an American author quaintly and pathetically. Well, if not, let us secure for ourselves and for our children those factors in the "grandfather's environment" that made for progressive evolution, and eschew those that tended elsewhere.
Are modifications due to changed nurture not, as such, entailed on offspring? Perhaps it is just as well, for we are novices at nurturing even yet! Moreover, the non-transmissibility cuts both ways: if individual modificational gains are not handed on, neither are the losses.
Is the "nature"—the germinal constitution, to wit—all that passes from generation to generation, the capital sum without the results of individual usury; then we are freed, at least, from undue pessimism at the thought of the many harmful functions and environments that disfigure our civilization. Many detrimental acquired characters are to be seen all around us, but if they are not transmissible, they need not last.
In the development of "character," much depends upon early nurture, education, and surrounding influences generally, but how the individual reacts to these must largely depend on his inheritance. Truly the individual himself makes his own character, but he does so by his habitual adjustment of his (hereditarily determined) constitution to surrounding influences. Nurture supplies the stimulus for the expression of the moral inheritance, and how far the inheritance can express itself is limited by the nurture-stimuli available just as surely as the result of nurture is conditioned by the hereditarily determined nature on which it operates. It may be urged that character, being a product of habitual modes of feeling, thinking, and acting, cannot be spoken of as inherited, but bodily character is also a product dependent upon vital experience. It seems to us as idle to deny that some children are "born good" or "born bad," as it is to deny that some children are born strong and others weak, some energetic and others "tired" or "old." It may be difficult to tell how far the apparently hereditary goodness or badness of disposition is due to the nutritive influences of the mother, both before and after birth, and we must leave it to the reader's experience and observation to decide whether we are right or wrong in our opinion that quite apart from maternal nutritive influence there is a genuine inheritance of kindly disposition, strong sympathy, good humor, and good will. The further difficulty that the really organic character may be half-concealed by nurture-effects, or inhibited by the external heritage of custom and tradition, seems less serious, for the selfishness of an acquired altruism is as familiar as honor among thieves.
It is entirely useless to boggle over the difficulty that we are unable to conceive how dispositions for good or ill lie implicit within the protoplasmic unit in which the individual life begins. The fact is undoubted that the initiatives of moral character are in some degree transmissible, though from the nature of the case the influences of education, example, environment, and the like are here more potent than in regard to structural features. We cannot make a silk purse out of a sow's ear, though the plasticity of character under nurture is a fact which gives us all hope. Explain it we cannot, but the transmission of the raw material of character is a fact, and we must still say with Sir Thomas Browne: "Bless not thyself that thou wert born in Athens; but, among thy multiplied acknowledgments, lift up one hand to heaven that thou wert born of honest parents, that modesty, humility, and veracity lay in the same egg, and came into the world with thee."
2. Inheritance of Original Nature[76]
The principles of heredity (may be recapitulated as follows):
First of all, we find useful the principle of the unit-character. According to this principle, characters are, for the most part, inherited independently of each other, and each trait is inherited as a unit or may be broken up into characters that are so inherited.
Next, it must be recognized that characters, as such, are not inherited. Strictly, my son has not my nose, because I still have it; what was transmitted was something that determined the shape of his nose, and that is called in brief a "determiner." So the second principle is that unit-characters are inherited through determiners in the germ cells.
And finally, it is recognized that there really is no inheritance from parent to child, but that parent and child resemble each other because they are derived from the same germ plasm, they are chips from the same old block; and the son is the half-brother to his father, by another mother.
These three principles are the three corner stones of heredity as we know it today, the principles of the independent unit-characters each derived from a determiner in the germ plasm.
How far are the known facts of heredity in man in accord with these principles? No doubt all human traits are inherited in accordance with these principles; but knowledge proceeds slowly in this field.
As a first illustration I may take the case of human eye color. The iris is made up of a trestle-work of fibers, in which are suspended particles that give the blue color. In addition, in many eyes much brown pigment is formed which may be small in amount and gathered around the pupil or so extensive as to suffuse the entire iris and make it all brown. It is seen, then, that the brown iris is formed by something additional to the blue. And brown iris may be spoken of as a positive character, depending on a determiner for brown pigment; and blue as a negative character, depending on the absence of the determiner for brown.
Now when both parents have brown eyes and come from an ancestry with brown eyes, it is probable that all of their germ cells contain the determiner for brown iris pigmentation. So when these germ cells, both carrying the determiner, unite, all of the progeny will receive the determiner from both sides of the house; consequently the determiners are double in their bodies and the resulting iris pigmentation may be said to be duplex. When a character is duplex in an individual, that means that when the germ cells ripen in the body of that individual each contains a determiner. So that individual is capable, so far as he is concerned, of transmitting his trait in undiminished intensity.
If a parent has pure blue eyes, that is evidence that in neither of the united germ cells from which he arose was there a determiner for iris pigmentation; consequently in respect to brown iris pigmentation such a person may be said to be nulliplex. If, now, such a person marry an individual duplex in eye color, in whom all of the germ cells contain the determiner, each child will receive the determiner for iris pigmentation from one side of the house only. This determiner will, of course, induce pigmentation, but the pigmentation is simplex, being induced by one determiner only. Consequently, the pigmentation is apt to be weak. When a person whose pigment determiners have come from one side of the house forms germ cells, half will have and half will lack the determiner. If such a person marry a consort all of whose germ cells contain the determiner for iris pigmentation, all of the children will, of course, receive the iris pigmentation, but in half it will be duplex and in the other half it will be simplex. If the two parents both be simplex, so that, in each, half of the germ cells possess and half lack the determiner in the union of germ cells, there are four events that are equally apt to occur: (1) an egg with the determiner unites with a sperm with the determiner; (2) an egg with the determiner unites with a sperm without the determiner; (3) an egg without the determiner unites with a sperm with the determiner; (4) an egg without the determiner unites with a sperm without the determiner. Thus the character is duplex in one case, simplex in two cases, and nulliplex in one case; that is, one in four will have no brown pigment, or will be blue eyed. If one parent be simplex, so that the germ cells are equally with and without the determiner, while the other be nulliplex, then half of the children will be simplex and half nulliplex in eye pigment. Finally, if both parents be nulliplex in eye pigmentation (that is, blue eyed), then none of their germ cells will have the determiner, and all children will be nulliplex, or blue eyed. The inheritance of eye color serves as a paradigm of the method of inheritance of any unit-character.
Let us now consider some of the physical traits of man that follow the same law as brown eye color, traits that are clearly positive, and due to a definite determiner in the germ plasm.
Hair color is due either to a golden-brown pigment that looks black in masses, or else to a red pigment. The lighter tints differ from the darker by the absence of some pigment granules. If neither parent has the capacity of producing a large quantity of pigment granules in the hair, the children cannot have that capacity, that is, two flaxen-haired parents have only flaxen-haired children. But a dark-haired parent may be either simplex or duplex; and so two such parents may produce children with light hair; but not more than one out of four. In general, the hair color of the children tends not to be darker than that of the darker parent. Skin pigment follows a similar rule. It is really one of the surprises of modern studies that skin pigment should be found to follow the ordinary law of heredity; it was commonly thought to blend. The inheritance of skin color is not dependent on race; two blonds never have brunette offspring, but brunettes may have blondes. The extreme case is that of albinos with no pigment in skin, hair, and iris. Two albinos have only albino children, but albinos may come from two pigmented parents.
Similarly, straight-haired parents lack curliness, and two such have only straight-haired children. Also two tall parents have only tall children. Shortness is the trait: tallness is a negative character. Also when both parents lack stoutness (are slender), all children tend to lack it.
We may now consider briefly the inheritance of certain pathological or abnormal states, to see in how far the foregoing principles hold for them also. Sometimes the abnormal condition is positive, due to a new trait; but sometimes, on the contrary, the normal condition is the positive one and the trait is due to a defect.
Deaf-mutism is due to a defect; but the nature of the defect is different in different cases. Deaf-mutism is so varied that frequently two unrelated deaf mutes may have hearing children. But if the deaf-mute parents are cousins, the chances that the deafness is due to the same unit defect are increased and all of the children will probably be deaf.
From the studies of Dr. Goddard and others, it appears that when both parents are feeble-minded all of the children will be so likewise; this conclusion has been tested again and again. But if one of the parents be normal and of normal ancestry, all of the children may be normal; whereas, if the normal person have defective germ cells, half of his progeny by a feeble-minded woman will be defective.
Many criminals, especially those who offend against the person, are feeble-minded, as is shown by the way they occur in fraternities with feeble-mindedness, or have feeble-minded parents. The test of the mental condition of relatives is one that may well be applied by judges in deciding upon the responsibility of an aggressor.
Not only the condition of imperfect mental development, but also that of inability to withstand stress upon the nervous system, may be inherited. From the studies of Dr. Rosanoff and his collaborators, it appears that if both parents be subject to manic depressive insanity or to dementia precox, all children will be neuropathic also; that if one parent be affected and come from a weak strain, half of the children are liable to go insane; and that nervous breakdowns of these types never occur if both parents be of sound stock.
Finally, a study of families with special abilities reveals a method of inheritance quite like that of nervous defect. If both parents be color artists or have a high grade of vocal ability or are littérateurs of high grade, then all of their children tend to be of high grade also. If one parent has high ability, while the other has low ability but has ancestry with high ability, part of the children will have high ability and part low. It seems like an extraordinary conclusion that high ability is inherited as though due to the absence of a determiner in the same way as feeble-mindedness and insanity are inherited. We are reminded of the poet: "Great wits to madness sure are near allied." Evidence for the relationship is given by pedigrees of men of genius that often show the combination of ability and insanity. May it not be that just that lack of control that permits "flights of the imagination" is related to the flightiness characteristic of those with mental weakness or defect?
These studies of inheritance of mental defect inevitably raise the question how to eliminate the mentally defective. This is a matter of great importance because, on the one hand, it is now coming to be recognized that mental defect is at the bottom of most of our social problems. Extreme alcoholism is usually a consequence of a mental make-up in which self-control of the appetite for liquor is lacking. Pauperism is a consequence of mental defects that make the pauper incapable of holding his own in the world's competition. Sex immorality in either sex is commonly due to a certain inability to appreciate consequences, to visualize the inevitableness of cause and effect, combined sometimes with a sex-hyperesthesia and lack of self-control. Criminality in its worst forms is similarly due to a lack of appreciation of or receptivity to moral ideas.
If we seek to know what is the origin of these defects, we must admit that it is very ancient. They are probably derived from our ape-like ancestors, in which they were normal traits. There occurs in man a strain that has not yet acquired those traits of inhibition that characterized the more highly developed civilized persons. The evidence for this is that, as far back as we go, we still trace back the black thread of defective heredity.
We have now to answer the question as to the eugenical application of the laws of inheritance of defects. First, it may be pointed out that traits due to the absence of a determiner are characterized by their usual sparseness in the pedigree, especially when the parents are normal; by the fact that they frequently appear where cousin marriages abound, because cousins tend to carry the same defects in their germ plasm, though normal themselves; by the fact that two affected parents have exclusively normal children, while two normal parents who belong to the same strain, or who both belong to strains containing the same defect, have some (about 25 per cent) defective children. But a defective married to a pure normal will have no defective offspring.
The clear eugenical rule is then this: Let abnormals marry normals without trace of the defect, and let their normal offspring marry in turn into strong strains; thus the defect may never appear again. Normals from the defective strain may marry normals of normal ancestry, but must particularly avoid consanguineous marriages.
The sociological conclusion is: Prevent the feeble-minded, drunkards, paupers, sex-offenders, and criminalistic from marrying their like or cousins or any person belonging to a neuropathic strain. Practically it might be well to segregate such persons during the reproductive period for one generation. Then the crop of defectives will be reduced to practically nothing.
3. Inheritance of Acquired Nature: Tradition[77]
The factor in societal evolution corresponding to heredity in organic evolution is tradition; and the agency of transmission is the nervous system by way of its various "senses" rather than the germ-plasm. The organs of transmission are the eye, ear, tongue, etc., and not those of sex. The term tradition, like variation and selection, is taken in the broad sense. Variation in nature causes the offspring to differ from the parents and from one another; variation in the folkways causes those of one period (or place) to differ from their predecessors and to some extent among themselves. It is the vital fact at the bottom of change. Heredity in nature causes the offspring to resemble or repeat the present type; tradition in societal evolution causes the mores of one period to repeat those of the preceding period. Each is a stringent conservator. Variation means diversity; heredity and tradition mean the preservation of type. If there were no force of heredity or tradition, there could be no system or classification of natural or of societal forms; the creation hypothesis would be the only tenable one, for there could be no basis for a theory of descent. If there were no variation, all of nature and all human institutions would show a monotony as of the desert sand. Heredity and tradition allow respectively of the accumulation of organic or societal variations through repeated selection, extending over generations, in this or that direction. In short, what one can say of the general effects of heredity in the organic realm he can say of tradition in the field of the folkways. That the transmission is in the one case by way of the sex organs and the germ-plasm, and in the other through the action of the vocal cords, the auditory nerves, etc., would seem to be of small moment in comparison with the essential identity in the functions discharged.
Tradition is, in a sense and if such a comparison were profitable, more conservative than heredity. There is in the content of tradition an invariability which could not exist if it were a dual composite, as is the constitution of the germ-plasm. Here we must recall certain essential qualities of the mores which we have hitherto viewed from another angle. Tradition always looks to the folkways as constituting the matter to be transmitted. But the folkways, after the concurrence in their practice has been established, come to include a judgment that they conduce to societal and, indeed, individual welfare. This is where they come to be properly called mores. They become the prosperity-policy of the group, and the young are reared up under their sway, looking to the older as the repositories of precedent and convention. But presently the older die, and in conformity with the ideas of the time, they become beings of a higher power toward whom the living owe duty, and whose will they do not wish to cross. The sanction of ghost-fear is thus extended to the mores, which, as the prosperity-policy of the group, have already taken on a stereotyped character. They thus become in an even higher degree "uniform, universal in a group, imperative, invariable. As time goes on, they become more and more arbitrary, positive, and imperative. If asked why they act in a certain way in certain cases, primitive people always answer that it is because they and their ancestors always have done so." Thus the transmission of the mores comes to be a process embodying the greatest conservatism and the least likelihood of change. This situation represents an adaption of society to life-conditions; it would seem that because of the rapidity of succession of variations there is need of an intensely conserving force (like ethnocentrism or religion) to preserve a certain balance and poise in the evolutionary movement.
Transmission of the mores takes place through the agency of imitation or of inculcation; through one or the other according as the initiative is taken by the receiving or the giving party respectively. Inculcation includes education in its broadest sense; but since that term implies in general usage a certain, let us say protective, attitude taken by the educator (as toward the young), the broader and more colorless designation is chosen. Acculturation is the process by which one group or people learns from another, whether the culture or civilization be gotten by imitation or by inculcation. As there must be contact, acculturation is sometimes ascribed to "contagion."
4. Temperament, Tradition, and Nationality[78]
The temperament of the Negro, as I conceive it, consists in a few elementary but distinctive characteristics, determined by physical organizations and transmitted biologically. These characteristics manifest themselves in a genial, sunny, and social disposition, in an interest and attachment to external, physical things rather than to subjective states and objects of introspection, in a disposition for expression rather than enterprise and action.
The changes which have taken place in the manifestations of this temperament have been actuated by an inherent and natural impulse, characteristic of all living beings, to persist and maintain itself in a changed environment. Such changes have occurred as are likely to take place in any organism in its struggle to live and to use its environment to further and complete its own existence.
The result has been that this racial temperament has selected out of the mass of cultural materials to which it had access, such technical, mechanical, and intellectual devices as met its needs at a particular period of its existence. It has clothed and enriched itself with such new customs, habits, and cultural forms as it was able, or permitted to use. It has put into these relatively external things, moreover, such concrete meanings as its changing experience and its unchanging racial individuality demanded. Everywhere and always it has been interested rather in expression than in action; interested in life itself rather than in its reconstruction or reformation. The Negro is, by natural disposition, neither an intellectual nor an idealist, like the Jew; nor a brooding introspective, like the East Indian; nor a pioneer and frontiersman, like the Anglo-Saxon. He is primarily an artist, loving life for its own sake. His metier is expression rather than action. He is, so to speak, the lady among the races.
In reviewing the fortunes of the Negro's temperament as it is manifested in the external events of the Negro's life in America, our analysis suggests that this racial character of the Negro has exhibited itself everywhere in something like the rôle of the wish in the Freudian analysis of dream-life. The external cultural forms which he found here, like the memories of the individual, have furnished the materials in which the racial wish, i.e., the Negro temperament, has clothed itself. The inner meaning, the sentiment, the emphasis, the emotional color, which these forms assumed as the result of their transference from the white man to the Negro, these have been the Negro's own. They have represented his temperament—his temperament modified, however, by his experience and the tradition which he has accumulated in this country. The temperament is African, but the tradition is American.
If it is true that the Jew just because of his intellectuality is a natural-born idealist, internationalist, doctrinaire, and revolutionist, while the Negro, because of his natural attachment to known familiar objects, places, and persons, is pre-adapted to conservatism and to local and personal loyalties—if these things are true, we shall eventually have to take account of them practically. It is certain that the Negro has uniformly shown a disposition to loyalty during slavery to his master and during freedom to the South and the country as a whole. He has maintained this attitude of loyalty, too, under very discouraging circumstances. I once heard Kelly Miller, the most philosophical of the leaders and teachers of his race, say in a public speech that one of the greatest hardships the Negro suffered in this country was due to the fact that he was not permitted to be patriotic.
Of course all these alleged racial characteristics have a positive as well as a negative significance. Every race, like every individual, has the vices of its virtues. The question remains still to what extent so-called racial characteristics are actually racial, i.e., biological, and to what extent they are the effect of environmental conditions. The thesis of this paper, to state it again, is: (1) that fundamental temperamental qualities, which are the basis of interest and attention, act as selective agencies and as such determine what elements in the cultural environment each race will select; in what region it will seek and find its vocation in the larger social organization; (2) that, on the other hand, technique, science, machinery, tools, habits, discipline, and all the intellectual and mechanical devices with which the civilized man lives and works remain relatively external to the inner core of significant attitudes and values which constitute what we may call the will of the group. This racial will is, to be sure, largely social, that is, modified by social experience, but it rests ultimately upon a complex of inherited characteristics, which are racial.
The individual man is the bearer of a double inheritance. As a member of a race, he transmits by interbreeding a biological inheritance. As a member of society or a social group, on the other hand, he transmits by communication a social inheritance. The particular complex of inheritable characters which characterizes the individuals of a racial group constitutes the racial temperament. The particular group of habits, accommodations, sentiments, attitudes, and ideals transmitted by communication and education constitutes a social tradition. Between this temperament and this tradition there is, as has been generally recognized, a very intimate relationship. My assumption is that temperament is the basis of the interests; that as such it determines in the long run the general run of attention, and this, eventually, determines the selection in the case of an individual of his vocation, in the case of the racial group of its culture. That is to say, temperament determines what things the individual and the group will be interested in; what elements of the general culture, to which they have access, they will assimilate; what, to state it pedagogically, they will learn.
It will be evident at once that where individuals of the same race and hence the same temperament are associated, the temperamental interests will tend to reinforce one another, and the attention of members of the group will be more completely focused upon the specific objects and values that correspond to the racial temperament. In this way racial qualities become the basis for nationalities, a nationalistic group being merely a cultural and, eventually, a political society founded on the basis of racial inheritances.
On the other hand, when racial segregation is broken up and members of a racial group are dispersed, the opposite effect will take place. This explains the phenomena which have frequently been the subject of comment and observation, that the racial characteristics manifest themselves in an extraordinary way in large homogeneous gatherings. The contrast between a mass meeting of one race and a similar meeting of another is particularly striking. Under such circumstances characteristic racial and temperamental differences appear that would otherwise pass entirely unnoticed.
When the physical unity of a group is perpetuated by the succession of parents and children, the racial temperament, including fundamental attitudes and values which rest in it, is preserved intact. When, however, society grows and is perpetuated by immigration and adaptation, there ensues, as a result of miscegenation, a breaking up of the complex of the biologically inherited qualities which constitute the temperament of the race. This again initiates changes in the mores, traditions, and eventually in the institutions of the community. The changes which proceed from modification in the racial temperament will, however, modify but slightly the external forms of the social traditions, but they will be likely to change profoundly their content and meaning. Of course other factors, individual competition, the formation of classes, and especially the increase of communication, all co-operate to complicate the whole situation and to modify the effects which would be produced by racial factors working in isolation.
III. INVESTIGATIONS AND PROBLEMS
1. Conceptions of Human Nature Implicit in Religious and Political Doctrines
Although the systematic study of it is recent, there has always been a certain amount of observation and a great deal of assumption in regard to human nature. The earliest systematic treatises in jurisprudence, history, theology, and politics necessarily proceeded from certain more or less naïve assumptions in regard to the nature of man. In the extension of Roman law over subject peoples the distinction was made between jus gentium and jus naturae, i.e., the laws peculiar to a particular nation as contrasted with customs and laws common to all nations and derived from the nature of mankind. Macauley writes of the "principles of human nature" from which it is possible to deduce a theory of government. Theologians, in devising a logical system of thought concerning the ways of God to man, proceeded on the basis of certain notions of human nature. The doctrines of original sin, the innate depravity of man, the war of the natural man and the spiritual man had a setting in the dogmas of the fall of man, redemption through faith, and the probationary character of life on earth. In striking contrast with the pessimistic attitude of theologians toward human nature, social revolutionists like Rousseau have condemned social institutions as inherently vicious and optimistically placed reliance upon human nature as innately good.
In all these treatises the assumptions about human nature are either preconceptions or rationalizations from experience incidental to the legal, moral, religious, or political system of thought. There is in these treatises consequently little or no analysis or detailed description of the traits attributed to men. Certainly, there is no evidence of an effort to arrive at an understanding of human behavior from an objective study of its nature.
Historic assumptions in regard to human nature, no matter how fantastic or unscientific, have exerted, nevertheless, a far-reaching influence upon group action. Periods of social revolution are ushered in by theorists who perceive only the evil in institutions and the good in human nature. On the other hand, the "guardians of society," distrustful of the impulses of human nature, place their reliance upon conventions and upon existing forms of social organization. Communistic societies have been organized upon certain ideas of human nature and have survived as long as these beliefs which inspired them controlled the behavior of members of the group.
Philosophers from the time of Socrates have invariably sought to justify their moral and political theories upon a conception, if not a definition, of the nature of man. Aristotle, in his Politics and Hobbes in his Leviathan, to refer to two classics, offer widely divergent interpretations of human nature. Aristotle emphasized man's altruistic traits, Hobbes stressed his egoistic disposition. These opposite conceptions of human behavior are explicit and in each case presented with a display of evidence. Yet students soon realize that neither philosopher, in fashioning his conception, is entirely without animus or ulterior motive. When these definitions are considered in the context in which they occur, they seem less an outgrowth of an analysis of human nature, than formulas devised in the interest of a political theory. Aristotle was describing the ideal state; Hobbes was interested in the security of an existing social order.
Still, the contribution made by social and political philosophers has been real. Their descriptions of human behavior, if inadequate and unscientific, at least recognized that an understanding of human nature was a precondition to social reorganization. The fact that philosophical conceptions and ideal constructions are themselves social forces and as such frequently represent vested interests, has been an obstacle to social as well as physical science.
Comte's notion that every scientific discipline must pass through a theological and metaphysical stage before it assumed the character of a positive science seems to be true as far as sociology is concerned. Machiavelli shocked the moral sense of his time, if not the moralists of all time, when he proposed to accept human nature as it is as a basis for political science. Herbert Spencer insisted upon the futility of expecting "golden conduct from leaden instincts." To the utopian social reformers of his day he pointed out a series of welfare measures in England in which the outcome was the direct opposite of the results desired.
This negative criticism of preconceived notions and speculations about human nature prepared the way for disinterested observation and comparison. Certain modern tendencies and movements gave an impetus to the detached study of human behavior. The ethnologists collected objective descriptions of the behavior of primitive people. In psychology interest developed in the study of the child and in the comparative study of human and animal behavior. The psychiatrist, in dealing with certain types of abnormal behavior like hysteria and multiple personality, was forced to study human behavior objectively. All this has prepared the way for a science of human nature and of society based upon objective and disinterested observation.
2. Literature and the Science of Human Nature
The poets were the first to recognize that "the proper study of mankind is man" as they were also the first to interpret it objectively. The description and appreciation of human nature and personality by the poet and artist preceded systematic and reflective analysis by the psychologist and the sociologist. In recent years, moreover, there has been a very conscious effort to make literature, as well as history, "scientific." Georg Brandes in his Main Currents in Nineteenth Century Literature set himself the task to "trace first and foremost the connection between literature and life." Taine's History of English Literature attempts to delineate British temperament and character as mirrored in literary masterpieces.
The novel which emphasizes "milieu" and "character," as contrasted with the novel which emphasizes "action" and "plot," is a literary device for the analysis of human nature and society. Émile Zola in an essay The Experimental Novel has presented with characteristic audacity the case for works of fiction as instruments for the scientific dissection and explanation of human behavior.
[74] Translated from V. M. Bekhterev (W. v. Bechterew), Die Persönlichkeit und die Bedingungen ihrer Entwicklung und Gesundheit, pp. 3-5. (J. F. Bergmann, 1906.)
[75] From J. Arthur Thomson, Heredity, pp. 244-49. (G. P. Putnam's Sons, 1908.)
[76] Adapted from C. B. Davenport, "The Method of Evolution," in Castle, Coulter, Davenport, East, and Tower, Heredity and Eugenics, pp. 269-87. (The University of Chicago Press, 1912.)
[77] From Albert G. Keller, Societal Evolution, pp. 212-15. (Published by The Macmillan Co., 1915. Reprinted by permission.)
[78] From Robert E. Park, "Education in Its Relation to the Conflict and Fusion of Cultures," in the Publications of the American Sociological Society, XIII (1918), 58-63.
The novelist is equally an observer and an experimentalist. The observer in him gives the facts as he has observed them, suggests the points of departure, displays the solid earth on which his characters are to tread and the phenomena develop. Then the experimentalist appears and introduces an experiment, that is to say, sets his characters going in a certain story so as to show that the succession of facts will be such as the requirements of the determinism of the phenomena under examination call for. The novelist starts out in search of a truth. I will take as an example the character of the "Baron Hulot," in Cousine Bette, by Balzac. The general fact observed by Balzac is the ravages that the amorous temperament of a man makes in his home, in his family, and in society. As soon as he has chosen his subject he starts from known facts, then he makes his experiment and exposes Hulot to a series of trials, placing him among certain surroundings in order to exhibit how the complicated machinery of his passions works. It is then evident that there is not only observation there, but that there is also experiment, as Balzac does not remain satisfied with photographing the facts collected by him, but interferes in a direct way to place his characters in certain conditions, and of these he remains the master. The problem is to know what such a passion, acting in such surroundings and under such circumstances, would produce from the point of view of an individual and of society; and an experimental novel, Cousine Bette, for example, is simply the report of the experiment that the novelist conducts before the eyes of the public. In fact, the whole operation consists of taking facts in nature, then in studying the mechanism of these facts, acting upon them, by the modification of circumstances and surroundings, without deviating from the laws of nature. Finally, you possess knowledge of the man, scientific knowledge of him, in both his individual and social relations.[79]
After all that may be said for the experimental novel, however, its primary aim, like that of history, is appreciation and understanding, not generalization and abstract formulas. Insight and sympathy, the mystical sense of human solidarity, expressed in the saying "to comprehend all is to forgive all," this fiction has to give. And these are materials which the sociologist cannot neglect. As yet there is no autobiography or biography of an egocentric personality so convincing as George Meredith's The Egoist. The miser is a social type; but there are no case studies as sympathetic and discerning as George Eliot's Silas Marner. Nowhere in social science has the technique of case study developed farther than in criminology; yet Dostoévsky's delineation of the self-analysis of the murderer in Crime and Punishment dwarfs all comparison outside of similar studies in fiction. The function of the so-called psychological or sociological novel stops, however, with its presentation of the individual incident or case; it is satisfied by the test of its appeal to the experience of the reader. The scientific study of human nature proceeds a step farther; it seeks generalizations. From the case studies of history and of literature it abstracts the laws and principles of human behavior.
3. Research in the Field of Original Nature
Valuable materials for the study of human nature have been accumulated in archaeology, ethnology, and folklore. William G. Sumner, in his book Folkways, worked through the ethnological data and made it available for sociological use. By classification and comparison of the customs of primitive peoples he showed that cultural differences were based on variations in folkways and mores in adaptation to the environment, rather than upon fundamental differences in human nature.
The interests of research have resulted in a division of labor between the fields of original and acquired nature in man. The examination of original tendencies has been quite properly connected with the study of inheritance. For the history of research in this field, the student is referred to treatises upon genetics and evolution and to the works of Lamarck, Darwin, DeVries, Weismann, and Mendel. Recent discoveries in regard to the mechanism of biological inheritance have led to the organization of a new applied science, "eugenics." The new science proposes a social program for the improvement of the racial traits based upon the investigations of breeding and physical inheritance. Research in eugenics has been fostered by the Galton Laboratory in England, and by the Eugenics Record Office at Cold Spring Harbor in the United States. Interest has centered in the study of the inheritance of feeble-mindedness. Studies of feeble-minded families and groups, as The Kallikak Family by Goddard, The Jukes by Dugdale, and The Tribe of Ishmael by M'Culloch, have shown how mental defect enters as a factor into industrial inefficiency, poverty, prostitution, and crime.
4. The Investigation of Human Personality
The trend of research in human nature has been toward the study of personality. Scientific inquiry into the problems of personality was stimulated by the observation of abnormal behavior such as hysteria, loss of memory, etc., where the cause was not organic and, therefore, presumably psychic. A school of French psychiatrists and psychologists represented by Charcot, Janet, and Ribot have made signal contributions to an understanding of the maladies of personality. Investigation in this field, invaluable for an understanding of the person, has been made in the study of dual and multiple personality. The work of Freud, Jung, Adler, and others in psychoanalysis has thrown light upon the rôle of mental conflict, repression, and the wishes in the growth of personality.
In sociology, personality is studied, not only from the subjective standpoint of its organization, but even more in its objective aspects and with reference to the rôle of the person in the group. One of the earliest classifications of "kinds of conduct" has been ascribed by tradition to a disciple of Aristotle, Theophrastus, who styled himself "a student of human nature." The Characters of Theophrastus is composed of sketches—humorous and acute, if superficial—of types such as "the flatterer," "the boor," "the coward," "the garrulous man." They are as true to modern life as to the age of Alexander. Chief among the modern imitators of Theophrastus is La Bruyère, who published in 1688 Les caractères, ou les mœurs de ce siècle, a series of essays on the manners of his time, illustrated by portraits of his contemporaries.
Autobiography and biography provide source material for the study both of the subjective life and of the social rôle of the person. Three great autobiographies which have inspired the writing of personal narratives are themselves representative of the different types: Caesar's Commentaries, with his detached impersonal description of his great exploits; the Confessions of St. Augustine, with his intimate self-analysis and intense self-reproach, and the less well-known De Vita Propria Liber by Cardan. This latter is a serious attempt at scientific self-examination. Recently, attention has been directed to the accumulation of autobiographical and biographical materials which are interpreted from the point of view of psychiatry and psychoanalysis. The study Der Fall Otto Weininger by Dr. Ferdinand Probst is a representative monograph of this type. The outstanding example of this method and its use for sociological interpretation is "Life Record of an Immigrant" contained in the third volume of Thomas and Znaniecki, The Polish Peasant. In connection with the Recreation Survey of the Cleveland Foundation and the Americanization Studies of the Carnegie Corporation, the life-history has been developed as part of the technique of investigation.
5. The Measurement of Individual Differences
With the growing sense of the importance of individual differences in human nature, attempts at their measurement have been essayed. Tests for physical and mental traits have now reached a stage of accuracy and precision. The study of temperamental and social characteristics is still in the preliminary stage.
The field of the measurement of physical traits is dignified by the name "anthropometry." In the nineteenth century high hopes were widely held of the significance of measurements of the cranium and of physiognomy for an understanding of the mental and moral nature of the person. The lead into phrenology sponsored by Gall and Spurzheim proved to be a blind trail. The so-called "scientific school of criminology" founded by Cesare Lombroso upon the identification of the criminal type by certain abnormalities of physiognomy and physique was undermined by the controlled study made by Charles Goring. At the present time the consensus of expert opinion is that only for a small group may gross abnormalities of physical development be associated with abnormal mental and emotional reactions.
In 1905-11 Binet and Simon devised a series of tests for determining the mental age of French school children. The purpose of the mental measurements was to gauge innate mental capacity. Therefore the tests excluded material which had to do with special social experience. With their introduction into the United States certain revisions and modifications, such as the Goddard Revision, the Terman Revision, the Yerkes-Bridges Point Scale, were made in the interests of standardization. The application of mental measurements to different races and social classes raised the question of the extent to which individual groups varied because of differences in social experience. While it is not possible absolutely to separate original tendencies from their expression in experience, it is practicable to devise tests which will take account of divergent social environments.
The study of volitional traits and of temperament is still in its infancy. Many recent attempts at classification of temperaments rest upon as impressionistic a basis as the popular fourfold division into sanguine, melancholic, choleric, and phlegmatic. Two of the efforts to define temperamental differences rest, however, upon first-hand study of cases. Dr. June E. Downey has devised a series of tests based upon handwriting material for measuring will traits. In her pamphlet The Will Profile she presents an analysis of twelve volitional traits: revision, perseverance, co-ordination of impulses, care for detail, motor inhibition, resistance, assurance, motor impulsion, speed of decision, flexibility, freedom from inertia, and speed of movement. From a study of several hundred cases she defined certain will patterns which apparently characterize types of individuals. In her experience she has found the rating of the subject by the will test to have a distinct value in supplementing the test for mentality.
Kraepelin, on the basis of his examination of abnormal mental states, offers a classification of types of psychopathic personalities. He distinguishes six groups: the excitable, the unstable, the psychopathic trend, the eccentric, the anti-social, and the contentious. In psychoanalysis a simpler twofold division is frequently made between the introverts, or the "introspective" and the extroverts, or the "objective" types of individual.
The study of social types is as yet an unworked field. Literature and life surround us with increasing specializations in personalities, but attempts at classification are still in the impressionistic stage. The division suggested by Thomas into the Philistine, Bohemian, and Creative types, while suggestive, is obviously too simple for an adequate description of the rich and complex variety of personalities.
This survey indicates the present status of attempts to define and measure differences in original and human nature. A knowledge of individual differences is important in every field of social control. It is significant that these tests have been devised to meet problems of policies and of administration in medicine, in industry, in education, and in penal and reformatory institutions. Job analysis, personnel administration, ungraded rooms, classes for exceptional children, vocational guidance, indicate fields made possible by the development of tests for measuring individual differences.
SELECTED BIBLIOGRAPHY
I. ORIGINAL NATURE
A. Racial Inheritance
(1) Thomson, J. Arthur. Heredity. London and New York, 1908.
(2) Washburn, Margaret F. The Animal Mind. New York, 1908.
(3) Morgan, C. Lloyd. Habit and Instinct. London and New York, 1896.
(4) ——. Instinct and Experience. New York, 1912.
(5) Loeb, Jacques. Comparative Physiology of the Brain and Comparative Psychology. New York, 1900.
(6) ——. Forced Movements. Philadelphia and London, 1918.
(7) Jennings, H. S. Behavior of the Lower Organisms. New York, 1906.
(8) Watson, John. Behavior: an Introduction to Comparative Psychology. New York, 1914.
(9) Thorndike, E. L. The Original Nature of Man. Vol. I of "Educational Psychology." New York, 1913.
(10) Paton, Stewart. Human Behavior. In relation to the study of educational, social, and ethical problems. New York, 1921.
(11) Faris, Ellsworth. "Are Instincts Data or Hypotheses?" American Journal of Sociology, XXVII (Sept., 1921.)
B. Heredity and Eugenics
1. Systematic Treatises:
(1) Castle, W. E., Coulter, J. M., Davenport, C. B., East, E. M., and Tower, W. L. Heredity and Eugenics. Chicago, 1912.
(2) Davenport, C. B. Heredity in Relation to Eugenics. New York, 1911.
(3) Goddard, Henry H. Feeble-mindedness. New York, 1914.
2. Inherited Inferiority of Families and Communities:
(1) Dugdale, Richard L. The Jukes. New York, 1877.
(2) M'Culloch, O. C. The Tribe of Ishmael. A study in social degradation. National Conference of Charities and Correction, 1888, 154-59; 1889, 265; 1890, 435-37.
(3) Goddard, Henry H. The Kallikak Family. New York, 1912.
(4) Winship, A. E. Jukes-Edwards. A study in education and heredity. Harrisburg, Pa., 1900.
(5) Estabrook, A. H., and Davenport, C. B. The Nam Family. A study in cacogenics. Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y., 1912.
(6) Danielson, F. H., and Davenport, C. B. The Hill Folk. Report on a rural community of hereditary defectives. Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y., 1912.
(7) Kite, Elizabeth S. "The Pineys," Survey, XXXI (October 4, 1913), 7-13. 38-40.
(8) Gesell, A. L. "The Village of a Thousand Souls," American Magazine, LXXVI (October, 1913), 11-13.
(9) Kostir, Mary S. The Family of Sam Sixty. Columbus, 1916.
(10) Finlayson, Anna W. The Dack Family. A study on hereditary lack of emotional control. Cold Spring Harbor, N. Y., 1916.
II. HUMAN NATURE
A. Human Traits
(1) Cooley, Charles H. Human Nature and the Social Order. New York, 1902.
(2) Shaler, N. S. The Individual. New York, 1900.
(3) Hocking, W. E. Human Nature and Its Remaking. New Haven, 1918.
(4) Edman, Irwin. Human Traits and Their Social Significance. Boston, 1919.
(5) Wallas, Graham. Human Nature in Politics. London, 1908.
(6) Lippmann, Walter. A Preface to Politics. [A criticism of present politics from the point of view of human-nature studies.] New York and London, 1913.
(7) James, William. The Varieties of Religious Experience. A study in human nature. London and New York, 1902.
(8) Ellis, Havelock. Studies in the Psychology of Sex. 6 vols. Philadelphia, 1900-1905.
(9) Thomas, W. I. Source Book for Social Origins. Chicago, 1909. [Contains extensive bibliographies.]
B. The Mores
1. Comparative Studies of Cultural Traits:
(1) Tylor, E. B. Primitive Culture. Researches into the development of mythology, philosophy, religion, language, art, and custom. 4th ed. 2 vols. London, 1903.
(2) Sumner, W. G. Folkways. A study of the sociological importance of usages, manners, customs, mores, and morals. Boston, 1906.
(3) Westermarck, E. A. The Origin and Development of the Moral Ideas. London and New York, 1908.
(4) Ratzel, F. History of Mankind. Translated by A. J. Butler. London and New York, 1898.
(5) Vierkandt, A. Naturvölker und Kulturvölker. Leipzig, 1896.
(6) Lippert, Julius. Kulturgeschichte der Menschheit in ihrem organischem Aufbau. Stuttgart, 1886-87.
(7) Frazer, J. G. The Golden Bough. A study in magic and religion. 3d ed., 12 vols. (Volume XII is a bibliography of the preceding volumes.) London and New York, 1907-15.
(8) Dewey, John, and Tufts, James H. Ethics. New York, 1908.
2. Studies of Traits of Individual Peoples:
(1) Fouillée, A. Psychologie du peuple français. Paris, 1898.
(2) Rhŷs, J., and Brynmor-Jones, D. The Welsh People. London, 1900.
(3) Fishberg, M. The Jews. A study of race and environment. London and New York, 1911.
(4) Strausz, A. Die Bulgaren. Ethnographische Studien. Leipzig, 1898.
(5) Stern, B. Geschichtete der öffentlichen Sittlichkeit in Russland. Kultur, Aberglaube, Sitten, und Gebraüche. Zwei Bände. Berlin, 1907-8.
(6) Krauss, F. S. Sitte und Brauch der Südslaven. Wien, 1885.
(7) Kidd, D. The Essential Kafir. London, 1904.
(8) Spencer, B., and Gillen, F. J. The Native Tribes of Central Australia. London and New York, 1899.
C. Human Nature and Industry
(1) Taylor, F. W. The Principles of Scientific Management. New York, 1911.
(2) Tead, O., and Metcalf, H. C. Personnel Administration; Its Principles and Practice. New York, 1920.
(3) Tead, O. Instincts in Industry. A study of working-class psychology. Boston, 1918.
(4) Parker, C. H. The Casual Laborer and Other Essays. New York, 1920.
(5) Marot, Helen. Creative Impulse in Industry; A Proposition for Educators. New York, 1918.
(6) Williams, Whiting. What's on the Worker's Mind. New York, 1920.
(7) Hollingworth, H. L. Vocational Psychology; Its Problems and Methods. New York, 1916.
III. PERSONALITY
A. The Genesis of Personality
(1) Baldwin, J. M. Mental Development in the Child and the Race: Methods and Processes. 3d rev. ed. New York and London, 1906.
(2) Baldwin, J. M. Social and Ethical Interpretations in Mental Developments. Chap ii, "The Social Person," pp. 66-98. 3d ed., rev. and enl. New York and London, 1902.
(3) Sully, J. Studies of Childhood. rev. ed. New York, 1903.
(4) King, I. The Psychology of Child Development. Chicago, 1903.
(5) Thorndike, E. L. Notes on Child Study. New York, 1903.
(6) Hall, G. S. Adolescence. Its psychology and its relations to physiology, anthropology, sociology, sex, crime, religion, and education. 2 vols.. New York, 1904.
(7) Shinn, Milicent W. Notes on the Development of a Child. University of California Studies. Nos. 1-4. 1893-99.
(8) Kirkpatrick, E. A. The Individual in the Making. Boston and New York, 1911.
B. Psychology and Sociology of the Person
(1) James, William. The Principles of Psychology. Chap, x, "Consciousness of Self," I, 291-401. New York, 1890.
(2) Bekhterev, V. M. (Bechterew, W. v.) Die Persönlichkeit und die Bedingungen ihrer Entwicklung und Gesundheit. "Grenzfragen des Nerven und Seelenlebens," No. 45. Wiesbaden, 1906.
(3) Binet, A. Alterations of Personality. Translated by H. G. Baldwin. New York, 1896.
(4) Ribot, T. A. Diseases of Personality. Authorized translation, 2d rev. ed. Chicago, 1895.
(5) Adler, A. The Neurotic Constitution. New York, 1917.
(6) Prince, M. The Dissociation of a Personality. A biographical study in abnormal psychology. 2d ed. New York, 1913.
(7) ——. The Unconscious. The fundamentals of human personality, normal and abnormal. New York, 1914.
(8) Coblenz, Felix. Ueber das betende Ich in den Psalmen. Ein Beitrag zur Erklaerung des Psalters. Frankfort, 1897.
(9) Royce, J. Studies of Good and Evil. A series of essays upon problems of philosophy and life. Chap, viii, "Some Observations on the Anomalies of Self-consciousness," pp. 169-97. A paper read before the Medico-Psychological Association of Boston, March 21, 1894. New York, 1898.
(10) Stern, B. Werden and Wesen der Persönlichkeit. Biologische und historische Untersuchungen über menschliche Individualität. Wien und Leipzig, 1913.
(11) Shand, A. F. The Foundations of Character. Being a study of the tendencies of the emotions and sentiments. London, 1914.
C. Materials for the Study of the Person
(1) Theophrastus. The Characters of Theophrastus. Translated from the Greek by R. C. Jebb. London, 1870.
(2) La Bruyère, Jean de. Les caractères, ou les mœurs de ce siècle. Paris, 1916. The "Characters" of Jean de La Bruyère. Translated from the French by Henri Van Laun. London, 1885.
(3) Augustinus, Aurelius. The Confessions of St. Augustine. Translated from the Latin by E. B. Pusly. London, 1907.
(4) Wesley, John. The Journal of the Rev. John Wesley. New York and London, 1907.
(5) Amiel, H. Journal intime. Translated by Mrs. Ward. London and New York, 1885.
(6) Cellini, Benvenuto. Memoirs of Benvenuto Cellini. Translated from the Italian by J. A. Symonds. New York, 1898.
(7) Woolman, John. Journal of the Life, Gospel Labors, and Christian Experiences of That Faithful Minister of Jesus Christ, John Woolman. Dublin, 1794.
(8) Tolstoy, Count Leon. My Confession. Translated from the Russian. Paris and New York, 1887. My Religion. Translated from the French. New York, 1885.
(9) Riley, I. W. The Founder of Mormonism. A psychological study of Joseph Smith, Jr. New York, 1902.
(10) Wilde, Oscar. De Profundis. New York and London, 1905.
(11) Keller, Helen. The Story of My Life. New York, 1903.
(12) Simmel, Georg. Goethe. Leipzig, 1913.
(13) Thomas, W. I., and Znaniecki, F. The Polish Peasant in Europe and America. "Life-Record of an Immigrant," III, 89-400. Boston, 1919.
(14) Probst, Ferdinand. Der Fall Otto Weininger. "Grenzfragen des Nerven- und Seelenlebens," No. 31. Wiesbaden, 1904.
(15) Anthony, Katherine. Margaret Fuller. A psychological biography. New York, 1920.
(16) Willard, Josiah Flynt. My Life. New York, 1908.
(17) ——. Tramping with Tramps. New York, 1899.
(18) Cummings, B. F. The Journal of a Disappointed Man, by Barbellion, W. N. P. [pseud.] Introduction by H. G. Wells. New York, 1919.
(19) Audoux, Marguerite. Marie Claire. Introduction by Octave Mirabeau. Translated from the French by J. N. Raphael. London and New York, 1911.
(20) Clemens, Samuel L. The Adventures of Tom Sawyer, by Mark Twain [pseud.]. New York, 1903.
(21) Hapgood, Hutchins. The Autobiography of a Thief. New York, 1903.
(22) Johnson, James W. The Autobiography of an ex-Colored Man. Published anonymously. Boston, 1912.
(23) Washington, Booker T. Up from Slavery. An autobiography. New York, 1901.
(24) Du Bois, W. E. B. The Souls of Black Folk. Chicago, 1903.
(25) Beers, C. W. A Mind That Found Itself. An autobiography. 4th rev. ed. New York, 1917.
IV. INDIVIDUAL DIFFERENCES
A. The Nature of Individual Differences
(1) Thorndike, E. L. Individuality. Boston, 1911.
(2) ——. "Individual Differences and Their Causes," Educational Psychology, III, 141-388. New York, 1913-14.
(3) Stern, W. Ueber Psychologie der individuellen Differenzen. Leipzig, 1900.
(4) Hollingworth, Leta S. The Psychology of Subnormal Children. Chap. i. "Individual Differences." New York, 1920.
B. Mental Differences
(1) Goddard, H. H. Feeble-mindedness. Its causes and consequences. New York, 1914.
(2) Tredgold, A. F. Mental Deficiency. 2d ed. New York, 1916.
(3) Bronner, Augusta F. The Psychology of Special Abilities and Disabilities. Boston, 1917.
(4) Healy, William. Case Studies of Mentally and Morally Abnormal Types. Cambridge, Mass., 1912.
C. Temperamental Differences
1. Systematic Treatises:
(1) Fouillée, A. Tempérament et caractère selon les individus, les sexes et les races. Paris, 1895.
(2) Hirt, Eduard. Die Temperamente, ihr Wesen, ihre Bedeutung, für das seelische Erleben und ihre besonderen Gestaltungen. "Grenzfragen des Nerven- und Seelenlebens," No. 40. Wiesbaden, 1905.
(3) Hoch, A., and Amsden, G. S. "A Guide to the Descriptive Study of Personality," Review of Neurology and Psychiatry, (1913), pp. 577-87.
(4) Kraepelin, E. Psychiatrie. Ein Lehrbuch für Studierende und Ärzte. Vol. IV, chap. xvi, pp. 1973-2116. 8th ed. 4 vols. Leipzig, 1909-15.
(5) Loewenfeld, L. Ueber die geniale Geistesthätigkeit mit besonderer Berücksichtigung des Genie's für bildende Kunst. "Grenzfragen des Nerven- und Seelenlebens," No. 21. Wiesbaden, 1903.
2. Temperamental Types:
(1) Lombroso, C. The Man of Genius. Translated from the Italian. London and New York, 1891.
(2) ——. L'uomo delinquente in rapporto all'antropologia, alla giurisprudenza ed alle discipline carcerarie. 3 vols. 5th ed. Torino, 1896-97.
(3) Goring, Charles. The English Convict. A statistical study. London, 1913.
(4) Wilmanns, Karl. Psychopathologie des Landstreichers. Leipzig, 1906.
(5) Downey, June E. "The Will Profile." A tentative scale for measurement of the volitional pattern. University of Wyoming Bulletin, Laramie, 1919.
(6) Pagnier, A. Le vagabond. Paris, 1910.
(7) Kowalewski, A. Studien zur Psychologie der Pessimismus. "Grenzfragen des Nerven- und Seelenlebens," No. 24. Wiesbaden, 1904.
D. Sex Differences
(1) Ellis, H. H. Man and Woman. A study of human secondary sexual characters. 5th rev. ed. London and New York, 1914.
(2) Geddes, P., and Thomson, J. A. The Evolution of Sex. London, 1889.
(3) Thompson, Helen B. The Mental Traits of Sex. An experimental investigation of the normal mind in men and women. Chicago, 1903.
(4) Montague, Helen, and Hollingworth, Leta S. "The Comparative Variability of the Sexes at Birth," American Journal of Sociology, XX (1914-15), 335-70.
(5) Thomas, W. I. Sex and Society. Chicago, 1907.
(6) Weidensall, C. J. The Mentality of the Criminal Woman. A comparative study of the criminal woman, the working girl, and the efficient working woman, in a series of mental and physical tests. Baltimore, 1916.
(7) Hollingworth, Leta S. "Variability as Related to Sex Differences in Achievement," American Journal of Sociology, XIX (1913-14), 510-30. [Bibliography.]
E. Racial Differences
(1) Boas, F. The Mind of Primitive Man. New York, 1911.
(2) Cambridge Anthropological Expedition to Torres Straits. 5 vols. Cambridge, 1901-08.
(3) Le Bon, G. The Psychology of Peoples. Its influence on their evolution. New York and London, 1898. [Translation.]
(4) Reuter, E. B. The Mulatto in the United States. Boston, 1918.
(5) Bruner, F. G. "Hearing of Primitive Peoples," Archives of Psychology, No. 11. New York, 1908.
(6) Woodworth, R. S. "Racial Differences in Mental Traits," Science, new series, XXI (1910), 171-86.
(7) Morse, Josiah. "A Comparison of White and Colored Children Measured by the Binet-Simon Scale of Intelligence," Popular Science Monthly, LXXXIVC (1914), 75-79.
(8) Ferguson, G. O., Jr. "The Psychology of the Negro, an Experimental Study," Archives of Psychology, No. 36. New York, 1916. [Bibliography.]
TOPICS FOR WRITTEN THEMES
1. Cooley's Conception of Human Nature
2. Human Nature and the Instincts
3. Human Nature and the Mores
4. Studies in the Evolution of the Mores; Prohibition, Birth Control, the Social Status of Children
5. Labor Management as a Problem in Human Nature
6. Human Nature in Politics
7. Personality and the Self
8. Personality as a Sociological Concept
9. Temperament, Milieu, and Social Types; the Politician, Labor Leader, Minister, Actor, Lawyer, Taxi Driver, Chorus Girl, etc.
10. Bohemian, Philistine, and Genius
11. The Beggar, Vagabond, and Hobo
12. Literature as Source Material for the Study of Character
13. Outstanding Personalities in a Selected Community
14. Autobiography as Source Material for the Study of Human Nature
15. Individual and Racial Differences Compared
16. The Man of Genius as a Biological and a Sociological Product
17. The Jukes and Kindred Studies of Inferior Groups
18. History of the Binet-Simon Tests
19. Mental Measurements and Vocational Guidance
20. Psychiatry and Juvenile Delinquency
21. Recent Studies of the Adolescent Girl
22. Mental Inferiority and Crime
QUESTIONS FOR DISCUSSION
1. Is human nature that which is fundamental and alike in all individuals or is it those qualities which we recognize and appreciate as human when we meet them in individuals?
2. What is the relation between original nature and the environment?
3. What is the basis for the distinction made by Thorndike between reflexes, instincts, and inborn capacities?
4. Read carefully Thorndike's Inventory of Original Tendencies. What illustrations of the different original traits occur to you?
5. What do you understand by Park's statement that man is not born human?
6. "Human nature is a superstructure." What value has this metaphor? What are its limitations? Suggest a metaphor which more adequately illustrates the relation of original nature to acquired nature.
7. In what sense can it be said that habit is a means of controlling original nature?
8. What, according to Park, is the relation of character to instinct and habit? Do you agree with him?
9. What do you understand by the statement that "original nature is blind?"
10. What relation has an ideal to (a) instinct and (b) group life?
11. In what sense may we speak of the infant as the "natural man"?
12. To what extent are racial differences (a) those of original nature, (b) those acquired from experience?
13. What evidence is there for the position that sex differences in mental traits are acquired rather than inborn?
14. How do you distinguish between mentality and temperament?
15. How do you account for the great differences in achievement between the sexes?
16. What evidence is there of temperamental differences between the sexes? between races?
17. In the future will women equal men in achievement?
18. What, in your judgment, is the range of individual differences? Is it less or greater than that of racial and sex differences?
19. What do you understand is the distinction between racial inheritance as represented by the instincts, and innate individual differences? Do you think that both should be regarded as part of original nature?
20. What is the effect of education and the division of labor (a) upon instincts and (b) upon individual differences?
21. Are individual differences or likenesses more important for society?
22. What do you understand to be the significance of individual differences (a) for social life; (b) for education; (c) for industry?
23. What do you understand by the remaking of human nature? What is the importance of this principle for politics, industry, and social progress?
24. Explain the proverbs: "Habit is ten times nature," "Habit is second nature."
25. What is Cooley's definition of human nature? Do you agree or disagree with him? Elaborate your position.
26. To what extent does human nature differ with race and geographic environment?
27. How would you reinterpret Aristotle's and Hobbes's conception of human nature in the light of this definition?
28. What illustrations of the difference between folkways and mores would you suggest?
29. Classify the following forms of behavior under (a) folkways or (b) mores: tipping the hat, saluting an officer, monogamy, attending church, Sabbath observance, prohibition, immersion as a form of baptism, the afternoon tea of the Englishman, the double standard of morals, the Ten Commandments, the Golden Rule, the Constitution of the United States.
30. What do you understand to be the relation of the mores to human nature?
31. In what way is (a) habit related to will? (b) custom related to the general will?
32. How do you distinguish the general will (a) from law, (b) from custom?
33. Does any one of the following terms embody your conception of what is expressed by Sittlichkeit: good form, decency, self-respect, propriety, good breeding, convention?
34. Describe and analyze several concrete social situations where Sittlichkeit rather than conscience or law controlled the behavior of the person or of the group.
35. What do you understand by convention? What is the relation of convention to instinct? Is convention a part of human nature to the same extent as loyalty, honor, etc.?
36. What is meant by the saying that mores, ritual, and convention are in the words of Hegel "objective mind"?
37. "The organism, and the brain as its highest representative, constitute the real personality." What characteristics of personality are stressed in this definition?
38. Is there any significance to the fact that personality is derived from the Latin word persona (mask worn by actors)?
39. Is the conventional self a product of habit, or of Sittlichkeit, or of law, or of conscience?
40. What is the importance of other people to the development of self-consciousness?
41. Under what conditions does self-consciousness arise?
42. What do you understand by personality as a complex? As a total of mental complexes?
43. What is the relation of memory to personality as illustrated in the case of dual personality and of moods?
44. What do you understand Cooley to mean by the looking-glass self?
45. What illustration would you suggest to indicate that an individual's sense of his personality depends upon his status in the group?
46. "All the world's a stage, and all the men and women merely players." Is personality adequately defined in terms of a person's conception of his rôle?
47. What is the sociological significance of the saying, "If you would have a virtue, feign it"?
48. What, according to Bechterew, is the relation of personality to the social milieu?
49. What do you understand by the personality of peoples? What is the relation of the personality of peoples and the personalities of individuals who constitute the peoples?
50. What do you understand by the difference between nature and nurture?
51. What are acquired characters? How are they transmitted?
52. What do you understand by the Mendelian principles of inheritance: (a) the hypothesis of unit characters; (b) the law of dominance; and (c) the law of segregation?
53. What illustrations of the differences between instinct and tradition would you suggest?
54. What is the difference between the blue eye as a defect in pigmentation, and of feeble-mindedness as a defective characteristic?
55. Should it be the policy of society to eliminate all members below a certain mental level either by segregation or by more drastic measures?
56. What principles of treatment of practical value to parents and teachers would you draw from the fact that feeble inhibition of temper is a trait transmitted by biological inheritance?
57. Why is an understanding of the principles of biological inheritance of importance to sociology?
58. In what two ways, according to Keller, are acquired characters transmitted by tradition?
59. Make a list of the different types of things derived by the person (a) from his biological inheritance, and (b) from his social heritage.
60. What traits, temperament, mentality, manner, or character, are distinctive of members of your family? Which of these have been inherited, which acquired?
61. What problems in society are due to defects in man's original nature?
62. What problems are the result of defects in folkways and mores?
63. In what way do racial temperament and tradition determine national characteristics? To what extent is the religious behavior of the negro determined (a) by temperament, (b) by imitation of white culture? How do you explain Scotch economy, Irish participation in politics, the intellectuality of the Jew, etc.?
FOOTNOTES:
[55] Charles H. Cooley, Social Organization, pp. 28-30.
[56] Charles H. Cooley, Human Nature and the Social Order, pp. 152-53.
[57] The Theory of the Leisure Class (New York, 1899).
[58] From Edward L. Thorndike, The Original Nature of Man, pp. 1-7. (Teachers College, Columbia University, 1913. Author's copyright.)
[59] Compiled from Edward L. Thorndike, The Original Nature of Man, pp. 43-194. (Teachers College, Columbia University, 1913. Author's copyright.)
[60] From Robert E. Park, Principles of Human Behavior, pp. 9-16. (The Zalaz Corporation, 1915.)
[61] Adapted from Milicent W. Shinn, The Biography of a Baby, pp. 20-77. (Houghton Mifflin Co., 1900. Author's copyright.)
[62] From Albert Moll, Sexual Life of the Child, pp. 38-49. Translated from the German by Dr. Eden Paul. (Published by The Macmillan Co., 1902. Reprinted by permission.)
[63] From C. S. Myers, "On the Permanence of Racial Differences," in Papers on Inter-racial Problems, edited by G. Spiller, pp. 74-76. (P. S. King & Son, 1911.)
[64] From Edward L. Thorndike, Individuality, pp. 1-8. (By permission of and special arrangement with Houghton Mifflin Co., 1911.)
[65] From W. E. Hocking, Human Nature and Its Remaking, pp. 2-12. (Yale University Press, 1918.)
[66] From William G. Sumner, Folkways, pp. 2-8. (Ginn & Co., 1906.)
[67] Translated and adapted from Ferdinand Tönnies, Die Sitte, pp. 7-14. (Literarische Anstalt, Rütten und Loening, 1909.)
[68] From Viscount Haldane, "Higher Nationality," in International Conciliation, November, 1913, No. 72, pp. 4-12.
[69] From Th. Ribot, The Diseases of Personality, pp. 156-57. Translated from the French. (The Open Court Publishing Co., 1891.)
[70] From Morton Prince, "The Unconscious," in the Journal of Abnormal Psychology, III (1908-9), 277-96, 426.
[71] From Alfred Binet, Alterations of Personality, pp. 248-57. (D. Appleton & Co., 1896.)
[72] From L. G. Winston, "Myself and I," in the American Journal of Psychology, XIX (1908), 562-63.
[73] From William James, The Varieties of Religious Experience, pp. 166-73. (Longmans, Green & Co., 1902.)
[74] Translated from V. M. Bekhterev (W. v. Bechterew), Die Persönlichkeit und die Bedingungen ihrer Entwicklung und Gesundheit, pp. 3-5. (J. F. Bergmann, 1906.)
[75] From J. Arthur Thomson, Heredity, pp. 244-49. (G. P. Putnam's Sons, 1908.)
[76] Adapted from C. B. Davenport, "The Method of Evolution," in Castle, Coulter, Davenport, East, and Tower, Heredity and Eugenics, pp. 269-87. (The University of Chicago Press, 1912.)
[77] From Albert G. Keller, Societal Evolution, pp. 212-15. (Published by The Macmillan Co., 1915. Reprinted by permission.)
[78] From Robert E. Park, "Education in Its Relation to the Conflict and Fusion of Cultures," in the Publications of the American Sociological Society, XIII (1918), 58-63.
[79] Émile Zola, The Experimental Novel (New York, 1893), pp. 8-9. Translated from the French by Belle M. Sherman.
CHAPTER III
SOCIETY AND THE GROUP
I. INTRODUCTION
1. Society, the Community, and the Group
Human nature and the person are products of society. This is the sum and substance of the readings in the preceding chapter. But what, then, is society—this web in which the lives of individuals are so inextricably interwoven, and which seems at the same time so external and in a sense alien to them? From the point of view of common sense, "society" is sometimes conceived as the sum total of social institutions. The family, the church, industry, the state, all taken together, constitute society. In this use of the word, society is identified with social structure, something more or less external to individuals.
In accordance with another customary use of the term, "society" denotes a collection of persons. This is a vaguer notion but it at least identifies society with individuals instead of setting it apart from them. But this definition is manifestly superficial. Society is not a collection of persons in the sense that a brick pile is a collection of bricks. However we may conceive the relation of the parts of society to the whole, society is not a mere physical aggregation and not a mere mathematical or statistical unit.
Various explanations that strike deeper than surface observation have been proposed as solutions for this cardinal problem of the social one and the social many; of the relation of society to the individual. Society has been described as a tool, an instrument, as it were, an extension of the individual organism. The argument runs something like this: The human hand, though indeed a part of the physical organism, may be regarded as an instrument of the body as a whole. If, as by accident it be lost, it is conceivable that a mechanical hand might be substituted for it, which, though not a part of the body, would function for all practical purposes as a hand of flesh and blood. A hoe may be regarded as a highly specialized hand, so also logically, if less figuratively, a plow. So the hand of another person if it does your bidding may be regarded as your instrument, your hand. Language is witness to the fact that employers speak of "the hands" which they "work." Social institutions may likewise be thought of as tools of individuals for accomplishing their purposes. Logically, therefore, society, either as a sum of institutions or as a collection of persons, may be conceived of as a sum total of instrumentalities, extensions of the functions of the human organism which enable individuals to carry on life-activities. From this standpoint society is an immense co-operative concern of mutual services.
This latter is an aspect of society which economists have sought to isolate and study. From this point of view the relations of individuals are conceived as purely external to one another, like that of the plants in a plant community. Co-operation, so far as it exists, is competitive and "free."
In contrast with the view of society which regards social institutions and the community itself as the mere instruments and tools of the individuals who compose it, is that which conceives society as resting upon biological adaptations, that is to say upon instincts, gregariousness, for example, imitation, or like-mindedness. The classic examples of societies based on instinct are the social insects, the well-known bee and the celebrated ant. In human society the family, with its characteristic differences and interdependences of the sexes and the age groups, husband and wife, children and parents, most nearly realizes this description of society. In so far as the organization of society is predetermined by inherited or constitutional differences, as is the case pre-eminently in the so-called animal societies, competition ceases and the relations of its component individuals become, so to speak, internal, and a permanent part of the structure of the group.
The social organization of human beings, on the other hand, the various types of social groups, and the changes which take place in them at different times under varying circumstances, are determined not merely by instincts and by competition but by custom, tradition, public opinion, and contract. In animal societies as herds, flocks, and packs, collective behavior seems obviously to be explained in terms of instinct and emotion. In the case of man, however, instincts are changed into habits; emotions, into sentiments. Furthermore, all these forms of behavior tend to become conventionalized and thus become relatively independent of individuals and of instincts. The behavior of the person is thus eventually controlled by the formal standards which, implicit in the mores, are explicit in the laws. Society now may be defined as the social heritage of habit and sentiment, folkways and mores, technique and culture, all of which are incident or necessary to collective human behavior.
Human society, then, unlike animal society is mainly a social heritage, created in and transmitted by communication. The continuity and life of a society depend upon its success in transmitting from one generation to the next its folkways, mores, technique, and ideals. From the standpoint of collective behavior these cultural traits may all be reduced to the one term "consensus." Society viewed abstractly is an organization of individuals; considered concretely it is a complex of organized habits, sentiments, and social attitudes—in short, consensus.
The terms society, community, and social group are now used by students with a certain difference of emphasis but with very little difference in meaning. Society is the more abstract and inclusive term, and society is made up of social groups, each possessing its own specific type of organization but having at the same time all the general characteristics of society in the abstract. Community is the term which is applied to societies and social groups where they are considered from the point of view of the geographical distribution of the individuals and institutions of which they are composed. It follows that every community is a society, but not every society is a community. An individual may belong to many social groups but he will not ordinarily belong to more than one community, except in so far as a smaller community of which he is a member is included in a larger of which he is also a member. However, an individual is not, at least from a sociological point of view, a member of a community because he lives in it but rather because, and to the extent that, he participates in the common life of the community.
The term social group has come into use with the attempts of students to classify societies. Societies may be classified with reference to the rôle which they play in the organization and life of larger social groups or societies. The internal organization of any given social group will be determined by its external relation to other groups in the society of which it is a part as well as by the relations of individuals within the group to one another. A boys' gang, a girls' clique, a college class, or a neighborhood conforms to this definition quite as much as a labor union, a business enterprise, a political party, or a nation. One advantage of the term "group" lies in the fact that it may be applied to the smallest as well as to the largest forms of human association.
2. Classification of the Materials
Society, in the most inclusive sense of that term, the Great Society, as Graham Wallas described it, turns out upon analysis to be a constellation of other smaller societies, that is to say races, peoples, parties, factions, cliques, clubs, etc. The community, the world-community, on the other hand, which is merely the Great Society viewed from the standpoint of the territorial distribution of its members, presents a different series of social groupings and the Great Society in this aspect exhibits a totally different pattern. From the point of view of the territorial distribution of the individuals that constitute it, the world-community is composed of nations, colonies, spheres of influence, cities, towns, local communities, neighborhoods, and families.
These represent in a rough way the subject-matter of sociological science. Their organization, interrelation, constituent elements, and the characteristic changes (social processes) which take place in them are the phenomena of sociological science.
Human beings as we meet them are mobile entities, variously distributed through geographical space. What is the nature of the connection between individuals which permits them at the same time to preserve their distances and act corporately and consentiently—with a common purpose, in short? These distances which separate individuals are not merely spatial, they are psychical. Society exists where these distances have been relatively overcome. Society exists, in short, not merely where there are people but where there is communication.
The materials in this chapter are intended to show (1) the fundamental character of the relations which have been established between individuals through communication; (2) the gradual evolution of these relations in animal and human societies. On the basis of the principle thus established it is possible to work out a rational classification of social groups.
Espinas defines society in terms of corporate action. Wherever separate individuals act together as a unit, where they co-operate as though they were parts of the same organism, there he finds society. Society from this standpoint is not confined to members of one species, but may be composed of different members of species where there is permanent joint activity. In the study of symbiosis among animals, it is significant to note the presence of structural adaptations in one or both species. In the taming and domestication of animals by man the effects of symbiosis are manifest. Domestication, by the selection in breeding of traits desired by man, changes the original nature of the animal. Taming is achieved by control of habits in transferring to man the filial and gregarious responses of the young naturally given to its parents and members of its kind. Man may be thought of as domesticated through natural social selection. Eugenics is a conscious program of further domestication by the elimination of defective physical and mental racial traits and by the improvement of the racial stock through the social selection of superior traits. Taming has always been a function of human society, but it is dignified by such denominations as "education," "social control," "punishment," and "reformation."
The plant community offers the simplest and least qualified example of the community. Plant life, in fact, offers an illustration of a community which is not a society. It is not a society because it is an organization of individuals whose relations, if not wholly external, are, at any rate, "unsocial" in so far as there is no consensus. The plant community is interesting, moreover, because it exhibits in the barest abstraction, the character of competitive co-operation, the aspect of social life which constitutes part of the special subject-matter of economic science.
This struggle for existence, in some form or other, is in fact essential to the existence of society. Competition, segregation, and accommodation serve to maintain the social distances, to fix the status, and preserve the independence of the individual in the social relation. A society in which all distances, physical as well as psychical, had been abolished, in which there was neither taboo, prejudice, nor reserve of any sort; a society in which the intimacies were absolute, would be a society in which there were neither persons nor freedom. The processes of competition, segregation, and accommodation brought out in the description of the plant community are quite comparable with the same processes in animal and human communities. A village, town, city, or nation may be studied from the standpoint of the adaptation, struggle for existence, and survival of its individual members in the environment created by the community as a whole.
Society, as Dewey points out, if based on instinct is an effect of communication. Consensus even more than co-operation or corporate action is the distinctive mark of human society. Dewey, however, seems to restrict the use of consensus to group decisions in which all the members consciously and rationally participate. Tradition and sentiment are, however, forms of consensus quite as much as constitutions, rules, and elections.
Le Bon's classification of social groups into heterogeneous and homogeneous crowds, while interesting and suggestive, is clearly inadequate. Many groups familiar to all of us, as the family, the play-group, the neighborhood, the public, find no place in his system.[80]
Concrete descriptions of group behavior indicate three elements in the consensus of the members of the group. The first is the characteristic state of group feeling called esprit de corps. The enthusiasm of the two sides in a football contest, the ecstasy of religious ceremonial, the fellowship of members of a fraternity, the brotherhood of a monastic band are all different manifestations of group spirit.
The second element in consensus has become familiar through the term "morale." Morale may be defined as the collective will. Like the will of the individual it represents an organization of behavior tendencies. The discipline of the individual, his subordination to the group, lies in his participation and reglementation in social activities.
The third element of consensus which makes for unified behavior of the members of the group has been analyzed by Durkheim under the term "collective representations." Collective representations are the concepts which embody the objectives of group activity.
The totem of primitive man, the flag of a nation, a religious creed, the number system, and Darwin's theory of the descent of man—all these are collective representations. Every society and every social group has, or tends to have, its own symbols and its own language. The language and other symbolic devices by which a society carries on its collective existence are collective representations. Animals do not possess them.
II. MATERIALS
A. SOCIETY AND SYMBIOSIS
1. Definition of Society[81]
The idea of society is that of a permanent co-operation in which separate living beings undertake to accomplish an identical act. These beings may find themselves brought by their conditions to a point where their co-operation forces them to group themselves in space in some definite form, but it is by no means necessary that they should be in juxtaposition for them to act together and thus to form a society. A customary reciprocation of services among more or less independent individualities is the characteristic feature of the social life, a feature that contact or remoteness does not essentially modify, nor the apparent disorder nor the regular disposition of the parties in space.
Two beings may then form what is to the eyes a single mass, and may live, not only in contact with each other, but even in a state of mutual penetration without constituting a society. It is enough in such a case that one looks at them as entirely distinct, that their activities tend to opposite or merely different ends. If their functions, instead of co-operating, diverge; if the good of one is the evil of the other, whatever the intimacy of their contact may be, no social bond unites them.
But the nature of the functions and the form of the organs are inseparable. If two beings are endowed with functions that necessarily combine, they are also endowed with organs, if not similar, at least corresponding. And these beings with like or corresponding organs are either of the same species or of very nearly the same species.
However, circumstances may be met where two beings with quite different organs and belonging even to widely remote species may be accidentally and at a single point useful to each other. A habitual relation may be established between their activities, but only on this one point, and in the time limits in which the usefulness exists. Such a case gives the occasion, if not for a society, at least for an association; that is to say, a union less necessary, less strict, less durable, may find its origin in such a meeting. In other words, beside the normal societies formed of elements specifically alike, which cannot exist without each other, there will be room for more accidental groupings, formed of elements more or less specifically unlike, which convenience unites and not necessity. We will commence with a study of the latter.
To society the most alien relations of two living beings which can be produced are those of the predator and his prey. In general, the predator is bulkier than his prey, since he overcomes him and devours him. Yet smaller ones sometimes attack larger creatures, consuming them, however, by instalments, and letting them live that they themselves may live on them as long as possible. In such a case they are forced to remain for a longer or a shorter time attached to the body of their victim, carried about by it wherever the vicissitudes of its life lead them. Such animals have received the name of parasites. Parasitism forms the line inside of which our subject begins; for if one can imagine that the parasite, instead of feeding on the animal from whom he draws his subsistence, is content to live on the remains of the other's meals, one will find himself in the presence, not yet of an actual society, but of half the conditions of a society; that is to say, a relation between two beings such that, all antagonism ceasing, one of the two is useful to the other. Such is commensalism. However, this association does not yet offer the essential element of all society, co-operation. There is co-operation when the commensal is not less useful to his host than the latter is to the commensal himself, when the two are concerned in living in a reciprocal relation and in developing their double activity in corresponding ways toward a single and an identical goal. One has given to this mode of activity the name of mutualism. Domestication is only one form of it. Parasitism, commensalism, mutualism, exist with animals among the different species.
2. Symbiosis (literally "living together")[82]
[79] Émile Zola, The Experimental Novel (New York, 1893), pp. 8-9. Translated from the French by Belle M. Sherman.
Human nature is not something existing separately in the individual, but a group nature or primary phase of society, a relatively simple and general condition of the social mind. It is something more, on the one hand, than the mere instinct that is born in us—though that enters into it—and something less, on the other, than the more elaborate development of ideas and sentiments that makes up institutions. It is the nature which is developed and expressed in those simple, face-to-face groups that are somewhat alike in all societies; groups of the family, the playground, and the neighborhood. In the essential similarity of these is to be found the basis, in experience, for similar ideas and sentiments in the human mind. In these, everywhere, human nature comes into existence. Man does not have it at birth; he cannot acquire it except through fellowship, and it decays in isolation.[55]
The reflected or looking-glass self seems to have three principal elements: the imagination of our appearance to the other person; the imagination of his judgment of that appearance; and some sort of self-feeling, such as pride or mortification. The comparison with a looking-glass self hardly suggests the second element, the imagined judgment, which is quite essential. The thing that moves us to pride or shame is not the mere mechanical reflection of ourselves, but an imputed sentiment, the imagined effect of this reflection upon another's mind. This is evident from the fact that the character and weight of that other, in whose mind we see ourselves, makes all the difference with our feeling.[56]
Veblen has made a subtle analysis of the way in which conduct is controlled by the individual's conception of his social rôle in his analysis of "invidious comparison" and "conspicuous expenditure."[57]
1. Original Nature Defined[58]
2. Inventory of Original Tendencies[59]
3. Man Not Born Human[60]
4. The Natural Man[61]
5. Sex Differences[62]
6. Racial Differences[63]
7. Individual Differences[64]
1. Human Nature and Its Remaking[65]
2. Human Nature, Folkways, and the Mores[66]
3. Habit and Custom, the Individual and the General Will[67]
4. The Law, Conscience, and the General Will[68]
1. The Organism as Personality[69]
2. Personality as a Complex[70]
3. The Self as the Individual's Conception of His Rôle[71]
4. The Natural Person versus the Social and Conventional Self[72]
5. The Divided Self and Moral Consciousness[73]
6. Personality of Individuals and of Peoples[74]
1. Nature and Nurture[75]
2. Inheritance of Original Nature[76]
3. Inheritance of Acquired Nature: Tradition[77]
4. Temperament, Tradition, and Nationality[78]
The novelist is equally an observer and an experimentalist. The observer in him gives the facts as he has observed them, suggests the points of departure, displays the solid earth on which his characters are to tread and the phenomena develop. Then the experimentalist appears and introduces an experiment, that is to say, sets his characters going in a certain story so as to show that the succession of facts will be such as the requirements of the determinism of the phenomena under examination call for. The novelist starts out in search of a truth. I will take as an example the character of the "Baron Hulot," in Cousine Bette, by Balzac. The general fact observed by Balzac is the ravages that the amorous temperament of a man makes in his home, in his family, and in society. As soon as he has chosen his subject he starts from known facts, then he makes his experiment and exposes Hulot to a series of trials, placing him among certain surroundings in order to exhibit how the complicated machinery of his passions works. It is then evident that there is not only observation there, but that there is also experiment, as Balzac does not remain satisfied with photographing the facts collected by him, but interferes in a direct way to place his characters in certain conditions, and of these he remains the master. The problem is to know what such a passion, acting in such surroundings and under such circumstances, would produce from the point of view of an individual and of society; and an experimental novel, Cousine Bette, for example, is simply the report of the experiment that the novelist conducts before the eyes of the public. In fact, the whole operation consists of taking facts in nature, then in studying the mechanism of these facts, acting upon them, by the modification of circumstances and surroundings, without deviating from the laws of nature. Finally, you possess knowledge of the man, scientific knowledge of him, in both his individual and social relations.[79]
[80] See supra, chap. i, pp. 50-51.
[81] Translated from Alfred Espinas, Des sociétés animales (1878), pp. 157-60.
[82] Adapted from William M. Wheeler, Ants, Their Structure, Development, Behavior, pp. 339-424. (Columbia University Press, 1910.)
In gaining their wide and intimate acquaintance with the vegetable world the ants have also become acquainted with a large number of insects that obtain their nutriment directly from plants, either by sucking up their juices or by feeding on their foliage. To the former group belong the phytophthorous Homoptera, the plant lice, scale insects, or mealy bugs, tree-hoppers, lantern flies, and jumping plant lice; to the latter belong the caterpillars of the lycaenid butterflies, the "blues," or "azures," as they are popularly called. All of these creatures excrete liquids which are eagerly sought by the ants and constitute the whole, or, at any rate, an important part of the food of certain species. In return the Homoptera and caterpillars receive certain services from the ants, so that the relations thus established between these widely different insects may be regarded as a kind of symbiosis. These relations are most apparent in the case of the aphids, and these insects have been more often and more closely studied in Europe and America.
The consociation of the ants with the aphids is greatly facilitated by the gregarious and rather sedentary habits of the latter, especially in their younger, wingless stages, for the ants are thus enabled to obtain a large amount of food without losing time and energy in ranging far afield from their nests. Then, too, the ants may establish their nests in the immediate vicinity of the aphid droves or actually keep them in their nests or in "sheds" carefully constructed for the purpose.
Some ants obtain the honey-dew merely by licking the surface of the leaves and stems on which it has fallen, but many species have learned to stroke the aphids and induce them to void the liquid gradually so that it can be imbibed directly. A drove of plant lice, especially when it is stationed on young and succulent leaves or twigs, may produce enough honey-dew to feed a whole colony of ants for a considerable period.
As the relations between ants and the various Homoptera have been regarded as mutualistic, it may be well to marshal the facts which seem to warrant this interpretation. The term "mutualism" as applied to these cases means, of course, that the aphids, coccids, and membracids are of service to the ants and in turn profit by the companionship of these more active and aggressive insects. Among the modifications in structure and behavior which may be regarded as indicating on the part of aphids unmistakable evidence of adaptation to living with ants, the following may be cited:
1. The aphids do not attempt to escape from the ants or to defend themselves with their siphons, but accept the presence of these attendants as a matter of course.
2. The aphids respond to the solicitations of the ants by extruding the droplets of honey-dew gradually and not by throwing them off to a distance with a sudden jerk, as they do in the absence of ants.
3. Many species of Aphididae that live habitually with ants have developed a perianal circlet of stiff hairs which support the drop of honey-dew till it can be imbibed by the ants. This circlet is lacking in aphids that are rarely or never visited by ants.
4. Certain observations go to show that aphids, when visited by ants, extract more of the plant juices than when unattended.
The adaptations on the part of the ants are, with a single doubtful exception, all modifications in behavior and not in structure.
1. Ants do not seize and kill aphids as they do when they encounter other sedentary defenseless insects.
2. The ants stroke the aphids in a particular manner in order to make them excrete the honey-dew, and know exactly where to expect the evacuated liquid.
3. The ants protect the aphids. Several observers have seen the ants driving away predatory insects.
4. Many aphidicolous ants, when disturbed, at once seize and carry their charges in their mandibles to a place of safety, showing very plainly their sense of ownership and interest in these helpless creatures.
5. This is also exhibited by all ants that harbor root-aphids and root-coccids in their nests. Not only are these insects kept in confinement by the ants, but they are placed by them on the roots. In order to do this the ants remove the earth from the surfaces of the roots and construct galleries and chambers around them so that the Homoptera may have easy access to their food and even move about at will.
6. Many ants construct, often at some distance from their nests, little closed pavilions or sheds of earth, carton, or silk, as a protection for their cattle and for themselves. The singular habit may be merely a more recent development from the older and more general habit of excavating tunnels and chambers about roots and subterranean stems.
7. The solicitude of the ants not only envelops the adult aphids and coccids, but extends also to their eggs and young. Numerous observers have observed ants in the autumn collecting and storing aphid eggs in the chambers of their nests, caring for them through the winter and in the spring placing the recently hatched plant lice on the stems and roots of the plants.
In the foregoing I have discussed the ethological relations of ants to a variety of other organisms. This, however, did not include an account of some of the most interesting symbiotic relations, namely, those of the ants to other species of their own taxonomic group and to termites. This living together of colonies of different species may be properly designated as social symbiosis, to distinguish it from the simple symbiosis that obtains between individual organisms of different species and the intermediate form of symbiosis exhibited by individual organisms that live in ant or termite colonies.
The researches of the past forty years have brought to light a remarkable array of instances of social symbiosis, varying so much in intimacy and complexity that it is possible to construct a series ranging from mere simultaneous occupancy of a very narrow ethological station, or mere contiguity of domicile, to an actual fusion, involving the vital dependence or parasitism of a colony of one species on that of another. Such a series is, of course, purely conceptual and does not represent the actual course of development in nature, where, as in the animal and vegetable kingdoms in general, development has not followed a simple linear course, but has branched out repeatedly and terminated in the varied types at the present time.
It is convenient to follow the European writers, von Hagens, Forel, Wasmann, and others, in grouping all the cases of social symbiosis under two heads, the compound nests and the mixed colonies. Different species of ants or of ants and termites are said to form compound nests when their galleries are merely contiguous or actually interpenetrate and open into one another, although the colonies which inhabit them bring up their respective offspring in different apartments. In mixed colonies, on the other hand, which, in a state of nature, can be formed only by species of ants of close taxonomic affinities, the insects live together in a single nest and bring up their young in common. Although each of these categories comprises a number of dissimilar types of social symbiosis, and although it is possible, under certain circumstances, as will be shown in the sequel, to convert a compound nest into a mixed colony, the distinction is nevertheless fundamental. It must be admitted, however, that both types depend in last analysis on the dependent, adoption-seeking instincts of the queen ant and on the remarkable plasticity which enables allied species and genera to live in very close proximity to one another. By a strange paradox these peculiarities have been produced in the struggle for existence, although this struggle is severer among different species of ants than between ants and other organisms. As Forel says: "The greatest enemies of ants are other ants, just as the greatest enemies of men are other men."
3. The Taming and the Domestication of Animals[83]
Primitive man was a hunter almost before he had the intelligence to use weapons, and from the earliest times he must have learned something about the habits of the wild animals he pursued for food or for pleasure, or from which he had to escape. It was probably as a hunter that he first came to adopt young animals which he found in the woods or the plains, and made the surprising discovery that these were willing to remain under his protection and were pleasing and useful. He passed gradually from being a hunter to becoming a keeper of flocks and herds. From these early days to the present time, the human race has taken an interest in the lower animals, and yet extremely few have been really domesticated. The living world would seem to offer an almost unlimited range of creatures which might be turned to our profit and as domesticated animals minister to our comfort or convenience. And yet it seems as if there were some obstacle rooted in the nature of animals or in the powers of man, for the date of the adoption by man of the few domesticated species lies in remote, prehistoric antiquity. The surface of the earth has been explored, the physiology of breeding and feeding has been studied, our knowledge of the animal kingdom has been vastly increased, and yet there is hardly a beast bred in the farm-yard today with which the men who made stone weapons were not acquainted and which they had not tamed. Most of the domestic animals of Europe, America, and Asia came originally from Central Asia, and have spread thence in charge of their masters, the primitive hunters who captured them.
No monkeys have been domesticated. Of the carnivores only the cat and the dog are truly domesticated. Of the ungulates there are horses and asses, pigs, cattle, sheep, goats, and reindeer. Among rodents there are rabbits and guinea-pigs, and possibly some of the fancy breeds of rats and mice should be included. Among birds there are pigeons, fowls, peacocks, and guinea-fowl, and aquatic birds such as swans, geese, and ducks, whilst the only really domesticated passerine bird is the canary. Goldfish are domesticated, and the invertebrate bees and silk-moths must not be forgotten. It is not very easy to draw a line between domesticated animals and animals that are often bred in partial or complete captivity. Such antelopes as elands, fallow-deer, roe-deer, and the ostriches of ostrich farms are on the border-line of being domesticated.
It is also difficult to be quite certain as to what is meant by a tame animal. Cockroaches usually scuttle away when they are disturbed and seem to have learnt that human beings have a just grievance against them. But many people have no horror of them. A pretty girl, clean and dainty in her ways, and devoted to all kinds of animals, used to like sitting in a kitchen that was infested with these repulsive creatures, and told me that when she was alone they would run over her dress and were not in the least startled when she took them up. I have heard of a butterfly which used to come and sip sugar from the hand of a lady; and those who have kept spiders and ants declare that these intelligent creatures learn to distinguish their friends. So also fish, like the great carp in the garden of the palace of Fontainebleau, and many fishes in aquaria and private ponds, learn to come to be fed. I do not think, however, that these ought to be called tame animals. Most of the wild animals in menageries very quickly learn to distinguish one person from another, to obey the call of their keeper and to come to be fed, although certainly they would be dangerous even to the keeper if he were to enter their cages. To my mind, tameness is something more than merely coming to be fed, and, in fact, many tame animals are least tame when they are feeding. Young carnivores, for instance, which can be handled freely and are affectionate, very seldom can be touched whilst they are feeding. The real quality of tameness is that the tame animal is not merely tolerant of the presence of man, not merely has learned to associate him with food, but takes some kind of pleasure in human company and shows some kind of affection.
On the other hand, we must not take our idea of tameness merely from the domesticated animals. These have been bred for many generations, and those that were most wild and that showed any resistance to man were killed or allowed to escape. Dogs are always taken as the supreme example of tameness, and sentimentalists have almost exhausted the resources of language in praising them. Like most people, I am very fond of dogs, but it is an affection without respect. Dogs breed freely in captivity, and in the enormous period of time that has elapsed since the first hunters adopted wild puppies there has been a constant selection by man, and every dog that showed any independence of spirit has been killed off. Man has tried to produce a purely subservient creature, and has succeeded in his task. No doubt a dog is faithful and affectionate, but he would be shot or drowned or ordered to be destroyed by the local magistrate if he were otherwise. A small vestige of the original spirit has been left in him, merely from the ambition of his owners to possess an animal that will not bite them, but will bite anyone else. And even this watch-dog trait is mechanical, for the guardian of the house will worry the harmless, necessary postman, and welcome the bold burglar with fawning delight. The dog is a slave, and the crowning evidence of his docility, that he will fawn on the person who has beaten him, is the result of his character having been bred out of him. The dog is an engaging companion, an animated toy more diverting than the cleverest piece of clockwork, but it is only our colossal vanity that makes us take credit for the affection and faithfulness of our own particular animal. The poor beast cannot help it; all else has been bred out of him generations ago.
When wild animals become tame, they are really extending or transferring to human beings the confidence and affection they naturally give their mothers, and this view will be found to explain more facts about tameness than any other. Every creature that would naturally enjoy maternal, or it would be better to say parental, care, as the father sometimes shares in or takes upon himself the duty of guarding the young, is ready to transfer its devotion to other animals or to human beings, if the way be made easy for it, and if it be treated without too great violation of its natural instincts. The capacity to be tamed is greatest in those animals that remain longest with their parents and that are most intimately associated with them. The capacity to learn new habits is greatest in those animals which naturally learn most from their parents, and in which the period of youth is not merely a period of growing, a period of the awakening of instincts, but a time in which a real education takes place. These capacities of being tamed and of learning new habits are greater in the higher mammals than in the lower mammals, in mammals than in birds, and in birds than in reptiles. They are very much greater in very young animals, where dependence on the parents is greatest, than in older animals, and they gradually fade away as the animal grows up, and are least of all in fully grown and independent creatures of high intelligence.
Young animals born in captivity are no more easy to tame than those which have been taken from the mother in her native haunts. If they remain with the mother, they very often grow up even shyer and more intolerant of man than the mothers themselves. There is no inherited docility or tameness, and a general survey of the facts fully bears out my belief that the process of taming is almost entirely a transference to human beings of the confidence and affection that a young animal would naturally give its mother. The process of domestication is different, and requires breeding a race of animals in captivity for many generations and gradually weeding out those in which youthful tameness is replaced by the wild instinct of adult life, and so creating a strain with new and abnormal instincts.
B. PLANT COMMUNITIES AND ANIMAL SOCIETIES
1. Plant Communities[84]
Certain species group themselves into natural associations, that is to say, into communities which we meet with more or less frequently and which exhibit the same combination of growth-forms and the same facies. As examples in northern Europe may be cited a meadow with its grasses and perennial herbs, or a beech forest with its beech trees and all the species usually accompanying these. Species that form a community must either practice the same economy, making approximately the same demands on its environment (as regards nourishment, light, moisture, and so forth), or one species present must be dependent for its existence upon another species, sometimes to such an extent that the latter provides it with what is necessary or even best suited to it (Oxalis Acetosella and saprophytes which profit from the shade of the beech and from its humus soil); a kind of symbiosis seems to prevail between such species. In fact, one often finds, as in beech forests, that the plants growing under the shade and protection of other species, and belonging to the most diverse families, assume growth-forms that are very similar to one another, but essentially different from those of the forest trees, which, in their turn, often agree with one another.
The ecological analysis of a plant-community leads to the recognition of the growth-forms composing it as its ultimate units. From what has just been said in regard to growth-forms it follows that species of very diverse physiognomy can very easily occur together in the same natural community. But beyond this, as already indicated, species differing widely, not only in physiognomy but also in their whole economy, may be associated. We may therefore expect to find both great variety of form and complexity of interrelations among the species composing a natural community; as an example we may cite the richest of all types of communities—the tropical rain-forest. It may also be noted that the physiognomy of a community is not necessarily the same at all times of the year, the distinction sometimes being caused by a rotation of species.
The different communities, it need hardly be stated, are scarcely ever sharply marked off from one another. Just as soil, moisture, and other external conditions are connected by the most gradual transitions, so likewise are the plant-communities, especially in cultivated lands. In addition, the same species often occur in several widely different communities; for example, Linnaea borealis grows not only in coniferous forests, but also in birch woods, and even high above the tree limit on the mountains of Norway and on the fell-fields of Greenland. It appears that different combinations of external factors can replace one another and bring into existence approximately the same community, or at least can satisfy equally well one and the same species, and that, for instance, a moist climate often completely replaces the forest shade of dry climates.
The term "community" implies a diversity but at the same time a certain organized uniformity in the units. The units are the many individual plants that occur in every community, whether this be a beech forest, a meadow, or a heath. Uniformity is established when certain atmospheric, terrestrial, and other factors are co-operative, and appears either because a certain defined economy makes its impress on the community as a whole, or because a number of different growth-forms are combined to form a single aggregate which has a definite and constant guise.
The analysis of a plant-community usually reveals one or more of the kinds of symbiosis as illustrated by parasites, saprophytes, epiphytes, and the like. There is scarce a forest or a bushland where examples of these forms of symbiosis are lacking; if, for instance, we investigate the tropical rain-forest we are certain to find in it all conceivable kinds of symbiosis. But the majority of individuals of a plant-community are linked by bonds other than those mentioned—bonds that are best described as commensal. The term commensalism is due to Van Beneden, who wrote, "Le commensal est simplement un compagnon de table"; but we employ it in a somewhat different sense to denote the relationship subsisting between species which share with one another the supply of food-material contained in soil and air, and thus feed at the same table.
More detailed analysis of the plant-community reveals very considerable distinctions among commensals. Some relationships are considered in the succeeding paragraphs.
Like commensals.—When a plant-community consists solely of individuals belonging to one species—for example, solely of beech, ling, or Aira flexuosa—then we have the purest example of like commensals. These all make the same demands as regards nutriment, soil, light, and other like conditions; as each species requires a certain amount of space and as there is scarcely ever sufficient nutriment for all the offspring, a struggle for food arises among the plants so soon as the space is occupied by the definite numbers of individuals which, according to the species, can develop thereon. The individuals lodged in unfavorable places and the weaklings are vanquished and exterminated. This competitive struggle takes place in all plant-communities, with perhaps the sole exceptions of sub-glacial communities and in deserts. In these open communities the soil is very often or always so open and so irregularly clothed that there is space for many more individuals than are actually present; the cause for this is obviously to be sought in the climatically unfavorable conditions of life, which either prevent plants from producing seed and other propagative bodies in sufficient numbers to clothe the ground or prevent the development of seedlings. On such soil one can scarcely speak of a competitive struggle for existence; in this case a struggle takes place between the plant and inanimate nature, but to little or no extent between plant and plant.
That a congregation of individuals belonging to one species into one community may be profitable to the species is evident; it may obviously in several ways aid in maintaining the existence of the species, for instance, by facilitating abundant and certain fertilization (especially in anemophilous plants) and maturation of seeds; in addition, the social mode of existence may confer other less-known advantages. But, on the other hand, it brings with it greater danger of serious damage and devastation wrought by parasites.
The bonds that hold like individuals to a like habitat are, as already indicated, identical demands as regards existence, and these demands are satisfied in their precise habitat to such an extent that the species can maintain itself here against rivals. Natural unmixed associations of forest trees are the result of struggles with other species. But there are differences as regards the ease with which a community can arise and establish itself. Some species are more social than others, that is to say, better fitted to form communities. The causes for this are biological, in that some species, like Phragmites, Scirpus lacustris, Psamma (Ammophila) arenaria, Tussilago, Farfara, and Asperula odorata, multiply very readily by means of stolons; or others, such as Cirsium arvense, and Sonchus arvensis, produce buds from their roots; or yet others produce numerous seeds which are easily dispersed and may remain for a long time capable of germinating, as is the case with Calluna, Picea excelsa, and Pinus; or still other species, such as beech and spruce, have the power of enduring shade or even suppressing other species by the shade they cast. A number of species, such as Pteris aquilina, Acorus Calamus, Lemna minor, and Hypnum Schreberi, which are social, and likewise very widely distributed, multiply nearly exclusively by vegetative means, rarely or never producing fruit. On the contrary, certain species, for example, many orchids and Umbelliferae, nearly always grow singly.
In the case of many species certain geological conditions have favored their grouping together into pure communities. The forests of northern Europe are composed of few species, and are not mixed in the same sense as are those in the tropics, or even those in Austria and other southern parts of Europe: the cause for this may be that the soil is geologically very recent, inasmuch as the time that has elapsed since the glacial epoch swept it clear has been too short to permit the immigration of many competitive species.
Unlike commensals.—The case of a community consisting of individuals belonging to one species is, strictly speaking, scarcely ever met with; but the dominant individuals of a community may belong to a single species, as in the case of a beech forest, spruce forest, or ling heath—and only thus far does the case proceed. In general, many species grow side by side, and many different growth-forms and types of symbiosis, in the extended sense, are found collected in a community. For even when one species occupies an area as completely as the nature of the soil will permit, other species can find room and can grow between its individuals; in fact, if the soil is to be completely covered the vegetation must necessarily always be heterogeneous. The greatest aggregate of existence arises where the greatest diversity prevails. The kind of communal life resulting will depend upon the nature of the demands made by the species in regard to conditions of life. As in human communities, so in this case, the struggle between the like is the most severe, that is, between the species making more or less the same demands and wanting the same dishes from the common table. In a tropical mixed forest there are hundreds of species of trees growing together in such profuse variety that the eye can scarce see at one time two individuals of the same species, yet all of them undoubtedly represent tolerable uniformity in the demands they make as regards conditions of life, and in so far they are alike. And among them a severe competition for food must be taking place. In those cases in which certain species readily grow in each other's company—and cases of this kind are familiar to florists—when, for instance, Isoetes, Lobelia Dortmanna, and Litorella lacustris occur together—the common demands made as regards external conditions obviously form the bond that unites them. Between such species a competitive struggle must take place. Which of the species shall be represented by the greatest number of individuals certainly often depends upon casual conditions, a slight change in one direction or the other doubtless often playing a decisive rôle; but apart from this it appears that morphological and biological features, for example, development at a different season, may change the nature of the competition.
Yet there are in every plant-community numerous species which differ widely in the demands they make for light, heat, nutriment, and so on. Between such species there is less competition, the greater the disparity in their wants; the case is quite conceivable in which the one species should require exactly what the other would avoid; the two species would then be complementary to one another in their occupation and utilization of the same soil.
There are also obvious cases in which different species are of service to each other. The carpet of moss in a pine forest, for example, protects the soil from desiccation and is thus useful to the pine; yet, on the other hand, it profits from the shade cast by the latter.
As a rule, limited numbers of definite species are the most potent, and, like absolute monarchs, can hold sway over the whole area; while other species, though possibly present in far greater numbers than these, are subordinate or even dependent on them. This is the case where subordinate species only flourish in the shade or among the fallen fragments of dominant species. Such is obviously the relationship between trees and many plants growing on the ground of high forest, such as mosses, fungi, and other saprophytes, ferns, Oxalis Acetosella, and their associates. In this case, then, there is a commensalism in which individuals feed at the same table but on different fare. An additional factor steps in when species do not absorb their nutriment at the same season of the year. Many spring plants—for instance, Galanthus nivalis, Corydalis solida, and C. cava—have withered before the summer plants commence properly to develop. Certain species of animals are likewise confined to certain plant-communities. But one and the same tall plant may, in different places or soils, have different species of lowly plants as companions; the companion plants of high beech forests depend, for instance, upon climate and upon the nature of the forest soil; Pinus nigra, according to von Beck, can maintain under it in the different parts of Europe a Pontic, a central European, or a Baltic vegetation.
There are certain points of resemblance between communities of plants and those of human beings or animals; one of these is the competition for food which takes place between similar individuals and causes the weaker to be more or less suppressed. But far greater are the distinctions. The plant-community is the lowest form; it is merely a congregation of units, among which there is no co-operation for the common weal, but rather a ceaseless struggle of all against all. Only in a loose sense can we speak of certain individuals protecting others, as for example, when the outermost and most exposed individuals of scrub serve to shelter from the wind others, which consequently become taller and finer; for they do not afford protection from any special motive, such as is met with in some animal communities, nor are they in any way specially adapted to act as guardians against a common foe. In the plant-community egoism reigns supreme. The plant-community has no higher units or personages in the sense employed in connection with human communities, which have their own organizations and their members co-operating, as prescribed by law, for the common good. In plant-communities there is, it is true, often (or always) a certain natural dependence or reciprocal influence of many species upon one another; they give rise to definite organized units of a higher order; but there is no thorough or organized division of labor such as is met with in human and animal communities, where certain individuals or groups of individuals work as organs, in the wide sense of the term, for the benefit of the whole community.
Woodhead has suggested the term complementary association to denote a community of species that live together in harmony, because their rhizomes occupy different depths in the soil; for example, he described an "association" in which Holcus mollis is the "surface plant," Pteris aquilina has deeper-seated rhizomes, and Scilla festalis buries its bulbs at the greatest depth. The photophilous parts of these plants are "seasonably complementary." The opposite extreme is provided by competitive associations, composed of species that are battling with each other.
2. Ant Society[85]
There is certainly a striking parallelism between the development of human and ant societies. Some anthropologists, like Topinard, distinguish in the development of human societies six different types or stages, designated as the hunting, pastoral, agricultural, commercial, industrial, and intellectual. The ants show stages corresponding to the first three of these, as Lubbock has remarked.
Some species, such as Formica fusca, live principally on the produce of the chase; for though they feed partially on the honey-dew of aphids, they have not domesticated these insects. These ants probably retain the habits once common to all ants. They resemble the lower races of men, who subsist mainly by hunting. Like them they frequent woods and wilds, live in comparatively small communities, as the instincts of collective action are but little developed among them. They hunt singly, and their battles are single combats, like those of Homeric heroes. Such species as Lasius flavus represent a distinctly higher type of social life; they show more skill in architecture, may literally be said to have domesticated certain species of aphids, and may be compared to the pastoral stage of human progress—to the races which live on the products of their flocks and herds. Their communities are more numerous; they act much more in concert; their battles are not mere single combats, but they know how to act in combination. I am disposed to hazard the conjecture that they will gradually exterminate the mere hunting species, just as savages disappear before more advanced races. Lastly, the agricultural nations may be compared with the harvesting ants.
Granting the resemblances above mentioned between ant and human societies, there are nevertheless three far-reaching differences between insect and human organization and development to be constantly borne in mind:
a) Ant societies are societies of females. The males really take no part in the colonial activities, and in most species are present in the nest only for the brief period requisite to secure the impregnation of the young queens. The males take no part in building, provisioning, or guarding the nest or in feeding the workers or the brood. They are in every sense the sexus sequior. Hence the ants resemble certain mythical human societies like the Amazons, but unlike these, all their activities center in the multiplication and care of the coming generations.
b) In human society, apart from the functions depending on sexual dimorphism, and barring individual differences and deficiencies which can be partially or wholly suppressed, equalized, or augmented by an elaborate system of education, all individuals have the same natural endowment. Each normal individual retains its various physiological and psychological needs and powers intact, not necessarily sacrificing any of them for the good of the community. In ants, however, the female individuals, of which the society properly consists, are not all alike but often very different, both in their structure (polymorphism) and in their activities (physiological division of labor). Each member is visibly predestined to certain social activities to the exclusion of others, not as a man through the education of some endowment common to all the members of the society, but through the exigencies of structure, fixed at the time of hatching, i.e., the moment the individual enters on its life as an active member of the community.
c) Owing to this pre-established structure and the specialized functions which it implies, ants are able to live in a condition of anarchistic socialism, each individual instinctively fulfilling the demands of social life without "guide, overseer, or ruler," as Solomon correctly observed, but not without the imitation and suggestion involved in an appreciation of the activities of its fellows.
An ant society, therefore, may be regarded as little more than an expanded family, the members of which co-operate for the purpose of still further expanding the family and detaching portions of itself to found other families of the same kind. There is thus a striking analogy, which has not escaped the philosophical biologist, between the ant colony and the cell colony which constitutes the body of a Metazoan animal; and many of the laws that control the cellular origin, development, growth, reproduction, and decay of the individual Metazoan, are seen to hold good also of the ant society regarded as an individual of a higher order. As in the case of the individual animal, no further purpose of the colony can be detected than that of maintaining itself in the face of a constantly changing environment till it is able to reproduce other colonies of a like constitution. The queen-mother of the ant colony displays the generalized potentialities of all the individuals, just as the Metazoan egg contains in potentia all the other cells of the body. And, continuing the analogy, we may say that since the different castes of the ant colony are morphologically specialized for the performance of different functions, they are truly comparable with the differentiated tissues of the Metazoan body.
C. HUMAN SOCIETY
1. Social Life[86]
The most notable distinction between living and inanimate beings is that the former maintain themselves by renewal. A stone when struck resists. If its resistance is greater than the force of the blow struck, it remains outwardly unchanged. Otherwise, it is shattered into smaller bits. Never does the stone attempt to react in such a way that it may maintain itself against the blow, much less so as to render the blow a contributing factor to its own continued action. While the living thing may easily be crushed by superior force, it none the less tries to turn the energies which act upon it into means of its own further existence. If it cannot do so, it does not just split into smaller pieces (at least in the higher forms of life), but loses its identity as a living thing.
As long as it endures, it struggles to use surrounding energies in its own behalf. It uses light, air, moisture, and the material of soil. To say that it uses them is to say that it turns them into means of its own conservation. As long as it is growing, the energy it expends in thus turning the environment to account is more than compensated for by the return it gets: it grows. Understanding the word "control" in this sense, it may be said that a living being is one that subjugates and controls for its own continued activity the energies that would otherwise use it up. Life is a self-renewing process through action upon the environment. Continuity of life means continual readaptation of the environment to the needs of living organisms.
We have been speaking of life in its lowest terms—as a physical thing. But we use the word "life" to denote the whole range of experience, individual and racial. When we see a book called the Life of Lincoln we do not expect to find within its covers a treatise on physiology. We look for an account of social antecedents; a description of early surroundings, of the conditions and occupation of the family; of the chief episodes in the development of character; of signal struggles and achievements; of the individual's hopes, tastes, joys, and sufferings. In precisely similar fashion we speak of the life of a savage tribe, of the Athenian people, of the American nation. "Life" covers customs, institutions, beliefs, victories and defeats, recreations and occupations.
We employ the word "experience" in the same pregnant sense. And to it, as well as to life in the bare physiological sense, the principle of continuity through renewal applies. With the renewal of physical existence goes, in the case of human beings, the re-creation of beliefs, ideals, hopes, happiness, misery, and practices. The continuity of any experience, through renewing of the social group, is a literal fact. Education, in its broadest sense, is the means of this social continuity of life. Every one of the constituent elements of a social group, in a modern city as in a savage tribe, is born immature, helpless, without language, beliefs, ideas, or social standards. Each individual, each unit who is the carrier of the life-experience of his group, in time passes away. Yet the life of the group goes on.
Society exists through a process of transmission, quite as much as biological life. This transmission occurs by means of communication of habits of doing, thinking, and feeling from the older to the younger. Without this communication of ideals, hopes, expectations, standards, opinions from those members of society who are passing out of the group life to those who are coming into it, social life could not survive.
Society not only continues to exist by transmission, by communication, but it may fairly be said to exist in transmission, in communication. There is more than a verbal tie between the words common, community, and communication. Men live in a community in virtue of the things which they have in common; and communication is the way in which they come to possess things in common. What they must have in common in order to form a community or society are aims, beliefs, aspirations, knowledge—a common understanding—like-mindedness, as the sociologists say. Such things cannot be passed physically from one to another, like bricks; they cannot be shared as persons would share a pie by dividing it into physical pieces. The communication which insures participation in a common understanding is one which secures similar emotional and intellectual dispositions—like ways of responding to expectations and requirements.
Persons do not become a society by living in physical proximity any more than a man ceases to be socially influenced by being so many feet or miles removed from others. A book or a letter may institute a more intimate association between human beings separated thousands of miles from each other than exists between dwellers under the same roof. Individuals do not even compose a social group because they all work for a common end. The parts of a machine work with a maximum of co-operativeness for a common result, but they do not form a community. If, however, they were all cognizant of the common end and all interested in it so that they regulated their specific activity in view of it, then they would form a community. But this would involve communication. Each would have to know what the other was about and would have to have some way of keeping the other informed as to his own purpose and progress. Consensus demands communications.
We are thus compelled to recognize that within even the most social group there are many relations which are not as yet social. A large number of human relationships in any social group are still upon the machine-like plane. Individuals use one another so as to get desired results, without reference to the emotional and intellectual disposition and consent of those used. Such uses express physical superiority, or superiority of position, skill, technical ability, and command of tools, mechanical or fiscal. So far as the relations of parent and child, teacher and pupil, employer and employee, governor and governed, remain upon this level, they form no true social group, no matter how closely their respective activities touch one another. Giving and taking of orders modifies action and results, but does not of itself effect a sharing of purposes, a communication of interests.
Not only is social life identical with communication, but all communication (and hence all genuine social life) is educative. To be a recipient of a communication is to have an enlarged and changed experience. One shares in what another has thought and felt, and in so far, meagerly or amply, has his own attitude modified. Nor is the one who communicates left unaffected. Try the experiment of communicating, with fulness and accuracy, some experience to another, especially if it be somewhat complicated, and you will find your own attitude toward your experience changing; otherwise you resort to expletives and ejaculations. The experience has to be formulated in order to be communicated. To formulate requires getting outside of it, seeing it as another would see it, considering what points of contact it has with the life of another so that it may be got into such form that he can appreciate its meaning. Except in dealing with commonplaces and catch phrases one has to assimilate, imaginatively, something of another's experience in order to tell him intelligently of one's own experience. All communication is like art. It may fairly be said, therefore, that any social arrangement that remains vitally social, or vitally shared, is educative to those who participate in it. Only when it becomes cast in a mold and runs in a routine way does it lose its educative power.
In final account, then, not only does social life demand teaching and learning for its own permanence, but the very process of living together educates. It enlarges and enlightens experience; it stimulates and enriches imagination; it creates responsibility for accuracy and vividness of statement and thought. A man really living alone (alone mentally as well as physically) would have little or no occasion to reflect upon his past experience to extract its net meaning. The inequality of achievement between the mature and the immature not only necessitates teaching the young, but the necessity of this teaching gives an immense stimulus to reducing experience to that order and form which will render it most easily communicable and hence most usable.
2. Behavior and Conduct[87]
The word "behavior" is commonly used in an interesting variety of ways. We speak of the behavior of ships at sea, of soldiers in battle, and of little boys in Sunday school.
"The geologist," as Lloyd Morgan remarks, "tells us that a glacier behaves in many respects like a river, and discusses how the crust of the earth behaves under the stresses to which it is subjected. Weatherwise people comment on the behavior of the mercury in the barometer as a storm approaches. When Mary, the nurse maid, returns with the little Miss Smiths from Master Brown's birthday party, she is narrowly questioned as to their behavior."
In short, the word is familiar both to science and to common sense, and is applied with equal propriety to the actions of physical objects and to the manners of men. The abstract sciences, quite as much as the concrete and descriptive, are equally concerned with behavior. "The chemist and the physicist often speak of the behavior of the atoms and the molecules, or of that of gas under changing conditions of temperature and pressure." The fact is that every science is everywhere seeking to describe and explain the movements, changes, and reactions, that is to say the behavior, of some portion of the world about us. Indeed, wherever we consciously set ourselves to observe and reflect upon the changes going on about us, it is always behavior that we are interested in. Science is simply a little more persistent in its curiosity and a little nicer and more exact in its observation than common sense. And this disposition to observe, to take a disinterested view of things, is, by the way, one of the characteristics of human nature which distinguishes it from the nature of all other animals.
Since every science has to do with some form of behavior, the first question that arises is this: What do we mean by behavior in human beings as distinguished from that in other animals? What is there distinctive about the actions of human beings that marks them off and distinguishes them from the actions of animals and plants with which human beings have so much in common?
The problem is the more difficult because, in some one or other of its aspects, human behavior involves processes which are characteristic of almost every form of nature. We sometimes speak, for example, of the human machine. Indeed, from one point of view human beings may be regarded as psycho-physical mechanisms for carrying on the vital processes of nutrition, reproduction, and movement. The human body is, in fact, an immensely complicated machine, whose operations involve an enormous number of chemical and physical reactions, all of which may be regarded as forms of human behavior.
Human beings are, however, not wholly or merely machines; they are living organisms and as such share with the plants and the lower animals certain forms of behavior which it has not thus far, at any rate, been possible to reduce to the exact and lucid formulas of either chemistry or physics.
Human beings are, however, not merely organisms: they are the home and the habitat of minuter organisms. The human body is, in a certain sense, an organization—a sort of social organization—of the minute and simple organisms of which it is composed, namely, the cells, each of which has its own characteristic mode of behavior. In fact, the life of human beings, just as the life of all other creatures above the simple unicellular organisms, may be said to consist of the corporate life of the smaller organisms of which it is composed. In human beings, as in some great city, the division of labor among the minuter organisms has been carried further, the interdependence of the individual parts is more complete, and the corporate life of the whole more complex.
It is not strange, therefore, that Lloyd Morgan begins his studies of animal behavior by a description of the behavior of the cells and Thorndike in his volume, The Original Nature of Man, is led to the conclusion that the original tendencies of man have their basis in the neurones, or nerve cells, and in the changes which these cells and their ancestors have undergone, as a result of the necessity of carrying on common and corporate existences as integral parts of the human organism. All acquired characteristics of men, everything that they learn, is due to mutual stimulations and associations of the neurones, just as sociologists are now disposed to explain civilization and progress as phenomena due to the interaction and association of human beings, rather than to any fundamental changes in human nature itself. In other words, the difference between a savage and a civilized man is not due to any fundamental differences in their brain cells but to the connections and mutual stimulations which are established by experience and education between those cells. In the savage those possibilities are not absent but latent. In the same way the difference between the civilization of Central Africa and that of Western Europe is due, not to the difference in native abilities of the individuals and the peoples who have created them, but rather to the form which the association and interaction between those individuals and groups of individuals has taken. We sometimes attribute the difference in culture which we meet among races to the climate and physical conditions generally, but, in the long run, the difference is determined by the way in which climate and physical condition determine the contacts and communications of individuals.
So, too, in the corporate life of the individual man it is the association of the nerve cells, their lines of connection and communication, that is responsible for the most of the differences between the ignorant and the educated, the savage and civilized man. The neurone, however, is a little unicellular animal, like the amoeba or the paramecium. Its life consists of: (1) eating, (2) excreting waste products, (3) growing, (4) being sensitive, and (5) movement, and, as Thorndike expresses it: "The safest provisional hypothesis about the action of the neurones singly is that they retain the modes of behavior common to unicellular animals, so far as consistent with the special conditions of their life as an element of man's nervous system."
In the widest sense of the term, behavior may be said to include all the chemical and physical changes that go on inside the organism, as well as every response to stimulus either from within or from without the organism. In recent studies of animal behavior, however, the word has acquired a special and technical meaning in which it is applied exclusively to those actions that have been, or may be, modified by conscious experience. What the animal does in its efforts to find food is behavior, but the processes of digestion are relegated to another field of observation, namely, physiology.
In all the forms of behavior thus far referred to, human and animal nature are not fundamentally distinguished. There are, however, ways of acting that are peculiar to human nature, forms of behavior that man does not share with the lower animals. One thing which seems to distinguish man from the brute is self-consciousness. One of the consequences of intercourse, as it exists among human beings, is that they are led to reflect upon their own impulses and motives for action, to set up standards by which they seek to govern themselves. The clock is such a standard. We all know from experience that time moves more slowly on dull days, when there is nothing doing, than in moments of excitement. On the other hand, when life is active and stirring, time flies. The clock standardizes our subjective tempos and we control ourselves by the clock. An animal never looks at the clock and this is typical of the different ways in which human beings and animals behave.
Human beings, so far as we have yet been able to learn, are the only creatures who habitually pass judgment upon their own actions, or who think of them as right or wrong. When these thoughts about our actions or the actions of others get themselves formulated and expressed they react back upon and control us. That is one reason we hang mottoes on the wall. That is why one sees on the desk of a busy man the legend "Do it now!" The brutes do not know these devices. They do not need them perhaps. They have no aim in life. They do not work.
What distinguishes the action of men from animals may best be expressed in the word "conduct." Conduct as it is ordinarily used is applied to actions which may be regarded as right or wrong, moral or immoral. As such it is hardly a descriptive term since there does not seem to be any distinctive mark about the actions which men have at different times and places called moral or immoral. I have used it here to distinguish the sort of behavior which may be regarded as distinctively and exclusively human, namely, that which is self-conscious and personal. In this sense blushing may be regarded as a form of conduct, quite as much as the manufacture of tools, trade and barter, conversation or prayer.
No doubt all these activities have their beginnings in, and are founded upon, forms of behavior of which we may find the rudiments in the lower animals. But there is in all distinctively human activities a conventional, one might almost say a contractual, element which is absent in action of other animals. Human actions are more often than not controlled by a sense or understanding of what they look like or appear to be to others. This sense and understanding gets itself embodied in some custom or ceremonial observance. In this form it is transmitted from generation to generation, becomes an object of sentimental respect, gets itself embodied in definite formulas, is an object not only of respect and reverence but of reflection and speculation as well. As such it constitutes the mores, or moral customs, of a group and is no longer to be regarded as an individual possession.
3. Instinct and Character[88]
In no part of the world, and at no period of time, do we find the behavior of men left to unchartered freedom. Everywhere human life is in a measure organized and directed by customs, laws, beliefs, ideals, which shape its ends and guide its activities. As this guidance of life by rule is universal in human society, so upon the whole it is peculiar to humanity. There is no reason to think that any animal except man can enunciate or apply general rules of conduct. Nevertheless, there is not wanting something that we can call an organization of life in the animal world. How much of intelligence underlies the social life of the higher animals is indeed extremely hard to determine. In the aid which they often render to one another, in their combined hunting, in their play, in the use of warning cries, and the employment of "sentinels," which is so frequent among birds and mammals, it would appear at first sight that a considerable measure of mutual understanding is implied, that we find at least an analogue to human custom, to the assignment of functions, the division of labor, which mutual reliance renders possible. How far the analogy may be pressed, and whether terms like "custom" and "mutual understanding," drawn from human experience, are rightly applicable to animal societies, are questions on which we shall touch presently. Let us observe first that as we descend the animal scale the sphere of intelligent activity is gradually narrowed down, and yet behavior is still regulated. The lowest organisms have their definite methods of action under given conditions. The amoeba shrinks into itself at a touch, withdraws the pseudopodium that is roughly handled, or makes its way round the small object which will serve it as food. Given the conditions, it acts in the way best suited to avoid danger or to secure nourishment. We are a long way from the intelligent regulation of conduct by a general principle, but we still find action adapted to the requirements of organic life.
When we come to human society we find the basis for a social organization of life already laid in the animal nature of man. Like others of the higher animals, man is a gregarious beast. His interests lie in his relations to his fellows, in his love for wife and children, in his companionship, possibly in his rivalry and striving with his fellow-men. His loves and hates, his joys and sorrows, his pride, his wrath, his gentleness, his boldness, his timidity—all these permanent qualities, which run through humanity and vary only in degree, belong to his inherited structure. Broadly speaking, they are of the nature of instincts, but instincts which have become highly plastic in their mode of operation and which need the stimulus of experience to call them forth and give them definite shape.
The mechanical methods of reaction which are so prominent low down in the animal scale fill quite a minor place in human life. The ordinary operations of the body, indeed, go upon their way mechanically enough. In walking or in running, in saving ourselves from a fall, in coughing, sneezing, or swallowing, we react as mechanically as do the lower animals; but in the distinctly human modes of behavior, the place taken by the inherited structure is very different. Hunger and thirst no doubt are of the nature of instincts, but the methods of satisfying hunger and thirst are acquired by experience or by teaching. Love and the whole family life have an instinctive basis, that is to say, they rest upon tendencies inherited with the brain and nerve structure; but everything that has to do with the satisfaction of these impulses is determined by the experience of the individual, the laws and customs of the society in which he lives, the woman whom he meets, the accidents of their intercourse, and so forth. Instinct, already plastic and modifiable in the higher animals, becomes in man a basis of character which determines how he will take his experience, but without experience is a mere blank form upon which nothing is yet written.
For example, it is an ingrained tendency of average human nature to be moved by the opinion of our neighbors. This is a powerful motive in conduct, but the kind of conduct to which it will incite clearly depends on the kind of thing that our neighbors approve. In some parts of the world ambition for renown will prompt a man to lie in wait for a woman or child in order to add a fresh skull to his collection. In other parts he may be urged by similar motives to pursue a science or paint a picture. In all these cases the same hereditary or instinctive element is at work, that quality of character which makes a man respond sensitively to the feelings which others manifest toward him. But the kind of conduct which this sensitiveness may dictate depends wholly on the social environment in which the man finds himself. Similarly it is, as the ordinary phrase quite justly puts it, "in human nature" to stand up for one's rights. A man will strive, that is, to secure that which he has counted on as his due. But as to what he counts upon, as to the actual treatment which he expects under given circumstances, his views are determined by the "custom of the country," by what he sees others insisting on and obtaining, by what has been promised him, and so forth. Even such an emotion as sexual jealousy, which seems deeply rooted in the animal nature, is largely limited in its exercise and determined in the form it takes by custom. A hospitable savage, who will lend his wife to a guest, would kill her for acting in the same way on her own motion. In the one case he exercises his rights of proprietorship; in the other, she transgresses them. It is the maintenance of a claim which jealousy concerns itself with, and the standard determining the claim is the custom of the country.
In human society, then, the conditions regulating conduct are from the first greatly modified. Instinct, becoming vague and more general, has evolved into "character," while the intelligence finds itself confronted with customs to which it has to accommodate conduct. But how does custom arise? Let us first consider what custom is. It is not merely a habit of action; but it implies also a judgment upon action, and a judgment stated in general and impersonal terms. It would seem to imply a bystander or third party. If A hits B, B probably hits back. It is his "habit" so to do. But if C, looking on, pronounces that it was or was not a fair blow, he will probably appeal to the "custom" of the country—the traditional rules of fighting, for instance—as the ground of his judgment. That is, he will lay down a rule which is general in the sense that it would apply to other individuals under similar conditions, and by it he will, as an impartial third person, appraise the conduct of the contending parties. The formation of such rules, resting as it does on the power of framing and applying general conceptions, is the prime differentia of human morality from animal behavior. The fact that they arise and are handed on from generation to generation makes social tradition at once the dominating factor in the regulation of human conduct. Without such rules we can scarcely conceive society to exist, since it is only through the general conformity to custom that men can understand each other, that each can know how the other will act under given circumstances, and without this amount of understanding the reciprocity, which is the vital principle of society, disappears.
4. Collective Representation and Intellectual Life[89]
Logical thought is made up of concepts. Seeking how society can have played a rôle in the genesis of logical thought thus reduces itself to seeking how it can have taken a part in the formation of concepts.
The concept is opposed to sensual representations of every order—sensations, perceptions, or images—by the following properties.
Sensual representations are in a perpetual flux; they come after each other like the waves of a river, and even during the time that they last they do not remain the same thing. Each of them is an integral part of the precise instant when it takes place. We are never sure of again finding a perception such as we experienced it the first time; for if the thing perceived has not changed, it is we who are no longer the same. On the contrary, the concept is, as it were, outside of time and change; it is in the depths below all this agitation; it might be said that it is in a different portion of the mind, which is serener and calmer. It does not move of itself, by an internal and spontaneous evolution, but, on the contrary, it resists change. It is a manner of thinking that, at every moment of time, is fixed and crystallized. In so far as it is what it ought to be, it is immutable. If it changes, it is not because it is its nature to do so, but because we have discovered some imperfection in it; it is because it had to be rectified. The system of concepts with which we think in everyday life is that expressed by the vocabulary of our mother-tongue; for every word translates a concept. Now language is something fixed; it changes but very slowly, and consequently it is the same with the conceptual system which it expresses. The scholar finds himself in the same situation in regard to the special terminology employed by the science to which he has consecrated himself, and hence in regard to the special scheme of concepts to which this terminology corresponds. It is true that he can make innovations, but these are always a sort of violence done to the established ways of thinking.
And at the same time that it is relatively immutable, the concept is universal, or at least capable of becoming so. A concept is not my concept; I hold it in common with other men, or, in any case, can communicate it to them. It is impossible for me to make a sensation pass from my consciousness into that of another; it holds closely to my organism and personality and cannot be detached from them. All that I can do is to invite others to place themselves before the same object as myself and to leave themselves to its action. On the other hand, conversation and all intellectual communication between men is an exchange of concepts. The concept is an essentially impersonal representation; it is through it that human intelligences communicate.
The nature of the concept, thus defined, bespeaks its origin. If it is common to all, it is the work of the community. Since it bears the mark of no particular mind, it is clear that it was elaborated by a unique intelligence, where all others meet each other, and after a fashion, come to nourish themselves. If it has more stability than sensations or images, it is because the collective representations are more stable than the individual ones; for while an individual is conscious even of the slight changes which take place in his environment, only events of a greater gravity can succeed in affecting the mental status of a society. Every time that we are in the presence of a type of thought or action which is imposed uniformly upon particular wills or intelligences, this pressure exercised over the individual betrays the intervention of the group. Also, as we have already said, the concepts with which we ordinarily think are those of our vocabulary. Now it is unquestionable that language, and consequently the system of concepts which it translates, is the product of collective elaboration. What it expresses is the manner in which society as a whole represents the facts of experience. The ideas which correspond to the diverse elements of language are thus collective representations.
Even their contents bear witness to the same fact. In fact, there are scarcely any words among those which we usually employ whose meaning does not pass, to a greater or less extent, the limits of our personal experience. Very frequently a term expresses things which we have never perceived or experiences which we have never had or of which we have never been the witnesses. Even when we know some of the objects which it concerns, it is only as particular examples that they serve to illustrate the idea which they would never have been able to form by themselves. Thus there is a great deal of knowledge condensed in the word which I never collected, and which is not individual; it even surpasses me to such an extent that I cannot even completely appropriate all its results. Which of us knows all the words of the language he speaks and the entire signification of each?
This remark enables us to determine the sense in which we mean to say that concepts are collective representations. If they belong to a whole social group, it is not because they represent the average of the corresponding individual representations; for in that case they would be poorer than the latter in intellectual content, while, as a matter of fact, they contain much that surpasses the knowledge of the average individual. They are not abstractions which have a reality only in particular consciousnesses, but they are as concrete representations as an individual could form of his own personal environment; they correspond to the way in which this very special being, society, considers the things of its own proper experience. If, as a matter of fact, the concepts are nearly always general ideas, and if they express categories and classes rather than particular objects, it is because the unique and variable characteristics of things interest society but rarely; because of its very extent, it can scarcely be affected by more than their general and permanent qualities. Therefore it is to this aspect of affairs that it gives its attention: it is a part of its nature to see things in large and under the aspect which they ordinarily have. But this generality is not necessary for them, and, in any case, even when these representations have the generic character which they ordinarily have, they are the work of society and are enriched by its experience.
The collective consciousness is the highest form of the psychic life, since it is the consciousness of the consciousnesses. Being placed outside of and above individual and local contingencies, it sees things only in their permanent and essential aspects, which it crystallizes into communicable ideas. At the same time that it sees from above, it sees farther; at every moment of time, it embraces all known reality; that is why it alone can furnish the mind with the molds which are applicable to the totality of things and which make it possible to think of them. It does not create these molds artificially; it finds them within itself; it does nothing but become conscious of them. They translate the ways of being which are found in all the stages of reality but which appear in their full clarity only at the summit, because the extreme complexity of the psychic life which passes there necessitates a greater development of consciousness. Collective representations also contain subjective elements, and these must be progressively rooted out if we are to approach reality more closely. But howsoever crude these may have been at the beginning, the fact remains that with them the germ of a new mentality was given, to which the individual could never have raised himself by his own efforts; by them the way was opened to a stable, impersonal and organized thought which then had nothing to do except to develop its nature.
D. THE SOCIAL GROUP
1. Definition of the Group[90]
The term "group" serves as a convenient sociological designation for any number of people, larger or smaller, between whom such relations are discovered that they must be thought of together. The "group" is the most general and colorless term used in sociology for combinations of persons. A family, a mob, a picnic party, a trade union, a city precinct, a corporation, a state, a nation, the civilized or the uncivilized population of the world, may be treated as a group. Thus a "group" for sociology is a number of persons whose relations to each other are sufficiently impressive to demand attention. The term is merely a commonplace tool. It contains no mystery. It is only a handle with which to grasp the innumerable varieties of arrangements into which people are drawn by their variations of interest. The universal condition of association may be expressed in the same commonplace way: people always live in groups, and the same persons are likely to be members of many groups.
Individuals nowhere live in utter isolation. There is no such thing as a social vacuum. The few Robinson Crusoes are not exceptions to the rule. If they are, they are like the Irishman's horse. The moment they begin to get adjusted to the exceptional condition, they die. Actual persons always live and move and have their being in groups. These groups are more or less complex, more or less continuous, more or less rigid in character. The destinies of human beings are always bound up with the fate of the groups of which they are members. While the individuals are the real existences, and the groups are only relationships of individuals, yet to all intents and purposes the groups which people form are just as distinct and efficient molders of the lives of individuals as though they were entities that had existence entirely independent of the individuals.
The college fraternity or the college class, for instance, would be only a name, and presently not even that, if each of its members should withdraw. It is the members themselves, and not something outside of themselves. Yet to A, B, or C the fraternity or the class might as well be a river or a mountain by the side of which he stands, and which he is helpless to remove. He may modify it somewhat. He is surely modified by it somewhat; and the same is true of all the other groups in which A, B, or C belong. To a very considerable extent the question, Why does A, B, or C do so and so? is equivalent to the question, What are the peculiarities of the group to which A, B, or C belongs? It would never occur to A, B, or C to skulk from shadow to shadow of a night, with paint-pot and brush in hand, and to smear Arabic numerals of bill-poster size on sidewalk or buildings, if "class spirit" did not add stimulus to individual bent. Neither A, B, nor C would go out of his way to flatter and cajole a Freshman, if membership in a fraternity did not make a student something different from an individual. These are merely familiar cases which follow a universal law.
[83] Adapted from P. Chalmers Mitchell, The Childhood of Animals, pp. 204-21. (Frederick A. Stokes & Co., 1912.)
[84] Adapted from Eugenius Warming, Oecology of Plants, pp. 12-13, 91-95. (Oxford University Press, 1909.)
[85] Adapted from William E. Wheeler, Ants, Their Structure, Development, and Behavior, pp. 5-7. (Columbia University Press, 1910.)
[86] From John Dewey, Democracy and Education, pp. 1-7. (Published by The Macmillan Co., 1916. Reprinted by permission.)
[87] From Robert E. Park, Principles of Human Behavior, pp. 1-9. (The Zalaz Corporation, 1915.)
[88] Adapted from L. T. Hobhouse, Morals in Evolution, pp. 1-2, 10-12. (Henry Holt & Co., 1915.)
[89] Adapted from Émile Durkheim, Elementary Forms of Religious Life, pp. 432-37. (Allen & Unwin, 1915.)
[90] From Albion W. Small, General Sociology, pp. 495-97. (The University of Chicago Press, 1905.)
