автордың кітабын онлайн тегін оқу Memoir, Correspondence, And Miscellanies, From The Papers Of Thomas Jefferson, Volume 1
MEMOIR, CORRESPONDENCE, AND MISCELLANIES,
FROM THE PAPERS OF THOMAS JEFFERSON.
Edited by Thomas Jefferson Randolph.
1829
Volume One



EASTERN DISTRICT OF VIRGINIA, to wit:
Be it remembered, that on the seventeenth day of January, in
the fifty-third year of the Independence of the United
States of America, Thomas Jefferson Randolph, of the said
District, hath deposited in this office the title of a book,
the right whereof he claims as proprietor, in the words
following, to wit:
“Memoir, Correspondence, and Miscellanies, from the Papers
of Thomas Jefferson. Edited by Thomas Jefferson Randolph.”
In conformity to the act of the Congress of the United
States, entitled “An act for the encouragement of learning,
by securing the copies of maps, charts, and books, to the
authors and proprietors of such copies, during the times
therein mentioned.”
RD. JEFFRIES, Clerk of the Eastern District of Virginia.
CAMBRIDGE: E. W. Metcalf & Company.
CONTENTS
PREFACE.
MEMOIR.
APPENDIX TO THE MEMOIR.
[NOTE A.] Letter to John Saunderson, Esq.
[NOTE B.] Letter to Samuel A. Wells, Esq.
[NOTE C] August, 1774, Instructions to the first Delegation
[NOTE D.] August, 1774., Instructions for the Deputies
[NOTE E.] Monticello, November 1, 1778. [Re: Crimes and Punishment]
[NOTE F.] Coinage for the United States
[NOTE G.]
[NOTE H.]
CORRESPONDENCE
LETTER I. TO DR. WILLIAM SMALL, May 7, 1775
LETTER II. TO JOHN RANDOLPH, August 25,1775
LETTER III. TO JOHN RANDOLPH, November 29, 1775
LETTER IV. TO BENJAMIN FRANKLIN, August 13, 1777
LETTER V. TO PATRICK HENRY, March 27, 1779
LETTER VI. TO JOHN PAGE, January 22, 1779
LETTER VII. TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, June 23, 1779
LETTER VIII. TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, July 17, 1779
LETTER IX. TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, October 1, 1779
LETTER X. TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, October 2, 1779
LETTER XI. TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, Oct. 8, 1779
LETTER XII. TO COLONEL MATHEWS, October, 1779
LETTER XIII. TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, November 28, 1779
LETTER XIV. TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, December 10,1779
LETTER XV. TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, February 10, 1780
LETTER XVI. TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, June 11, 1780
LETTER XVII. TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, July 2, 1780
LETTER XVIII. TO GENERAL EDWARD STEVENS, August 4, 1780
LETTER XIX. TO MAJOR GENERAL GATES, August 15, 1780
LETTER XX. TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, September 8, 1780
LETTER XXI. TO GENERAL EDWARD STEVENS, September 12,1780
LETTER XXII. TO GENERAL EDWARD STEVENS, September 15, 1780
LETTER XXIII. TO MAJOR GENERAL GATES, September 23, 1780
LETTER XXIV. TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, September 23, 1780
LETTER XXV. TO HIS EXCELLENCY GENERAL WASHINGTON, September 26,1780
LETTER XXVI. TO MAJOR GENERAL GATES, October 4, 1780
LETTER XXVII. TO GENERAL GATES, October 15, 1780
LETTER XXVIII. TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, October 22, 1780
LETTER XXIX. TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, October 25,1780
LETTER XXX. TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, October 26, 1780
LETTER XXXI. TO GENERAL GATES, October 28, 1780
LETTER XXXII. TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, November 3,1780
LETTER XXXIII. TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, November 10, 1780
LETTER XXXIV. TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, November 26, 1780
LETTER XXXV. TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, December 15,1780
LETTER XXXVI. TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, January 10, 1781
LETTER XXXVII. TO THE PRESIDENT OF CONGRESS, Jan. 15, 1781
LETTER XXXVIII. TO THE PRESIDENT OF CONGRESS, Jan. 15, 1781
LETTER XXXIX. TO THE PRESIDENT OF CONGRESS, Jan. 17, 1781
LETTER XL. TO THE VIRGINIA DELEGATES IN CONGRESS, Jan. 18, 1781
LETTER XLI. TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, February 8, 1781
LETTER XLII. TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, February 12, 1781
LETTER XLIII. TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, February 17, 1781
LETTER XLIV. TO GENERAL GATES, February 17, 1781
LETTER XLV. TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, February 26,1781
LETTER XLVI. TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, March 8, 1781
LETTER XLVII. TO THE PRESIDENT OF CONGRESS, March 19,1781
LETTER XLVIII. TO THE PRESIDENT OF CONGRESS, March 21, 1781
LETTER XLIX. TO THE PRESIDENT OF CONGRESS, March 26,1781
LETTER L. TO THE PRESIDENT OF CONGRESS, March 28, 1781
LETTER LI. TO THE PRESIDENT OF CONGRESS, March 31, 1781
LETTER LII. TO THE PRESIDENT OF CONGRESS, April 7, 1781
LETTER LIII. TO THE PRESIDENT OF CONGRESS, April 18, 1781
LETTER LIV. TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, April 23,1781
LETTER LV. TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, May 9, 1781
LETTER LVI. TO THE VIRGINIA DELEGATES IN CONGRESS, May 10, 1781
LETTER LVII. TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, May 28,1781
LETTER, LVIII. TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, April 16, 1784
LETTER LIX. TO COLONEL URIAH FORREST, October 20, 1784
LETTER LX. TO JOHN JAY, May 11, 1785
LETTER LXI. TO GENERAL CHASTELLUX, June 7,1785
LETTER LXII. TO JOHN ADAMS, June 15, 1785
LETTER LXIII. TO THE GOVERNOR OF VIRGINIA, June 16, 1785
LETTER LXIV. TO COLONEL MONROE, June 17, 1785
LETTER LXV. TO CHARLES THOMSON, June 21, 1785
LETTER LXVI. TO WILLIAM CARMICHAEL, June 22, 1785
LETTER LXVII. TO JOHN ADAMS, June 23, 1785
LETTER LXVIII. TO COLONEL MONROE, July 5, 1785
LETTER LXIX. TO MRS. SPROWLE, July 5,1785
LETTER LXX. TO JOHN ADAMS, July 7, 1785
LETTER LXXI. TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, July 10, 1785
LETTER LXXII. TO THE GOVERNOR OF VIRGINIA, July 11, 1785
LETTER LXXIII. TO THE PRESIDENT OF CONGRESS, July 12, 1785
LETTER LXXIV. TO THE VIRGINIA DELEGATES IN CONGRESS, July 12,1785
LETTER LXXV. TO JOHN JAY, July 12,1785
LETTER LXXVI. TO MONSIEUR BRIET, July 13, 1785
LETTER LXXVII. TO MESSRS. FRENCH AND NEPHEW, July 13,1785
LETTER LXXVIII. TO DR. STILES, July 17,1785
LETTER LXXIX. TO JOHN ADAMS, July 28, 1785
LETTER LXXX. TO HOGENDORP, July 29, 1785
LETTER LXXXI. TO MESSRS. N. AND J. VAN STAPHORST, July 30, 1785
LETTER LXXXII. TO JOHN ADAMS, July 31, 1785
LETTER LXXXIII. TO M. DE CASTRIES, August 3,1785
LETTER LXXXIV. TO CAPTAIN JOHN PAUL JONES, August 3,1785
LETTER LXXXV. TO JOHN ADAMS, August 6, 1785
LETTER LXXXVI. TO DR. PRICE, August 7,1785
LETTER LXXXVII. TO JOHN ADAMS, August 10,1785
LETTER LXXXVIII. TO MRS. SPROWLE, August 10, 1785
LETTER LXXXIX. TO CAPTAIN JOHN PAUL JONES, August 13, 1785
LETTER XC. TO MESSRS. BUCHANAN AND HAY, August 13, 1785
LETTER XCI. TO JOHN JAY, August 14, 1785
LETTER XCII. TO THE COUNT DE VERGENNES, August 15, 1785
LETTER XCIII. TO CAPTAIN JOHN PAUL JONES, August 17, 1785
LETTER XCIV. TO WILLIAM CARMICHAEL, August 18, 1785
LETTER XCV. TO PETER CARR
LETTER XCVI. TO JOHN PAGE, August 20 1785
LETTER XCVII. TO JOHN JAY, August 23, 1785
LETTER XCVIII. TO COLONEL MONROE, August 28, 1735
LETTER XCIX. TO CAPTAIN JOHN PAUL JONES, August 29,1785
LETTER C. TO JOHN JAY, August 30,1785
LETTER CI. TO JAMES MADISON, September 1,1785
LETTER CII. TO MESSRS. DUMAS AND SHORT, September 1, 1785
LETTER CIII. TO JOHN ADAMS, September 4, 1785
LETTER CIV. TO DAVID HARTLEY, September 5, 1785
LETTER CV. TO BARON GEISMER, September 6, 1785
LETTER CVI. TO JOHN LANGDON, September 11, 1785
LETTER CVII. LISTER ASQUITH, September 14, 1785
LETTER CVIII. TO JOHN ADAMS, September 19, 1785
LETTER CIX. TO JAMES MADISON, September 20, 1785
LETTER CX. TO EDMUND RANDOLPH, September 20,1785
LETTER CXI. TO JOHN ADAMS, September 24, 1785
LETTER CXII. TO JOHN ADAMS, September 24,1785
LETTER CXIII. TO F. HOPKINSON, September 25, 1785
LETTER CXIV. TO LISTER ASQUITH, September 26,1785
LETTER CXV. TO R. IZARD, September 26,1783
LETTER CXVI. TO RICHARD O’BRYAN, September 29, 1785
LETTER CXVII. TO MR. BELLINI, September 30,1785
LETTER CXVIII. JAMES MADISON, October 2, 1785
LETTER CXIX. TO DR. FRANKLIN, October 5,1785
LETTER CXX. TO SAMUEL OSGOOD, October 5, 1785
LETTER CXXI. TO JOHN JAY, October 6, 1785
LETTER CXXII. TO ELBRIDGE GERRY, October 11, 1785
LETTER CXXIII. TO THE COUNT DE VERGENNES, October 11, 1785
LETTER CXXIV. TO JOHN JAY, October 11,1785
LETTER CXXV. TO MESSRS. VAN STAPHORST, October 12, 1785
LETTER CXXVI. TO MONSIEUR DESBORDES, October 12,1785
LETTER CXXVII. TO HOGENDORP, October 13,1785
LETTER CXXVIII. TO J. BANNISTER, JUNIOR, October 15,1785
LETTER CXXIX. TO MR. CARMICHAEL, October 18, 1785
LETTER CXXX. TO MESSRS. VAN STAPHORSTS, October 25,1785
LETTER CXXXI. TO WILLIAM CARMICHAEL, November 4, 1785
LETTER CXXXII. TO RICHARD O’BRYAN, November 4, 1785
LETTER CXXXIII. TO W. W. SEWARD, November 12,1785
LETTER CXXXIV. TO THE COUNT DE VERGENNES, November 14,1785
LETTER CXXXV. TO JOHN ADAMS, November 19, 1785
LETTER CXXXVI. TO THE COUNT DE VERGENNES, November 20, 1785
LETTER CXXXVII. TO LISTER ASQUITH, November 23, 1785
LETTER CXXXVIII. TO JOHN ADAMS, November 27, 1785
LETTER CXXXIX. TO COLONEL HUMPHREYS, December 4,1785
LETTER CXL. TO JOHN ADAMS, December 10, 1785
LETTER CXLI. TO JOHN ADAMS, December 11, 1785
LETTER CXLII. TO THE COUNT DE VERGENNES, December 21, 1785
LETTER CXLIII. TO THE GOVERNOR OF GEORGIA, December 22, 1785
LETTER CXLIV. TO THE GEORGIA DELEGATES IN CONGRESS, Dec. 22, 1785
LETTER CXLV. TO JOHN ADAMS, December 27, 1785
LETTER CXLVI. TO JOHN JAY, January 2,1786
LETTER CXLVII. TO T. HOPKINSON, January 3, 1786
LETTER CXLVIII. TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, January 4, 1786
LETTER CXLIX. TO A. CARY, January 7, 1786
LETTER CL. TO MAJOR GENERAL GREENE, January 12, 1786
LETTER CLI. TO LISTER ASQUITH, January 13, 1786
RE QUESTIONS FOR ECONOMIE POLITIQUE ET DIPLOMATIQUE
ARTICLE BY JEFFERSON: ‘Etats Unis,’ FOR THE Encyclopédie Méthodique
LETTER CLII. TO MR. RITTENHOUSE, January 25,1786
LETTER CLIII. TO A. STEWART, January 25, 1786
LETTER CLIV. TO THE COMMISSIONERS OF THE TREASURY, January 26, 1786
LETTER CLV. TO MESSRS. BUCHANAN AND HAY, January 26, 1786
LETTER CLVI. TO JOHN ADAMS, February 7, 1786
LETTER CLVII. TO JAMES MADISON, February 8, 1786
LETTER CLVIII. TO THE MARQUIS DE LA FAYETTE, February 9, 1786
LETTER CLIX. TO MONSIEUR HILLIARD d’AUBERTEUIL, Feb. 20, 1786
LETTER CLX. TO THE COUNT DE VERGENNES, February 28,1786
LETTER CLXI. TO MONSIEUR DE REYNEVAL, March 8, 1786
LETTER CLXII. TO JOHN JAY, March 12, 1786
LETTER CLXIII. TO COLONEL HUMPHREYS, March 14, 1786
APPENDIX.
[NOTE A.] TO THE GOVERNOR OF VIRGINIA.
IN COUNCIL, June 18, 1779
[NOTE B] IN COUNCIL, September 29, 1779.
[NOTE C] IN COUNCIL, October 8, 1779.
[NOTE D.] FEMALE CONTRIBUTIONS, IN AID OF THE WAR, probably in 1780
[NOTE E.] FROM LORD CORNWALLIS
[NOTE F.] TO LORD CORNWALLIS
List of Illustrations
Book Spines, 1829 Set of Jefferson Papers
Steel Engraving by Longacre from Painting of G. Stuart
Titlepage of Volume One (of Four)
Page One of Jefferson’s Memoir, Page001
Draft of Declaration Of Independence, Page016
Draft of Declaration Of Independence, Page017
Draft of Declaration Of Independence, Page018
Draft of Declaration Of Independence, Page019
Draft of Declaration Of Independence, Page020
Draft of Declaration Of Independence, Page021
Facsimile of Declaration in Jefferson’s Handwriting—p1
Facsimile of Declaration in Jefferson’s Handwriting—p2
Facsimile of Declaration in Jefferson’s Handwriting—p3
Facsimile of Declaration in Jefferson’s Handwriting—p4
Financial Projection, American Embassy Paris, Page068
Acts of King George and Parliament, Page107
Bill for Proportioning Crimes and Punishments, Page120
Bill for Proportioning Crimes and Punishments, Page121
Bill for Proportioning Crimes and Punishments, Page122
Bill for Proportioning Crimes and Punishments, Page123
Bill for Proportioning Crimes and Punishments, Page124
Bill for Proportioning Crimes and Punishments, Page125
Bill for Proportioning Crimes and Punishments, Page126
Bill for Proportioning Crimes and Punishments, Page127
Bill for Proportioning Crimes and Punishments, Page128
Bill for Proportioning Crimes and Punishments, Page129
Bill for Proportioning Crimes and Punishments, Page130
Bill for Proportioning Crimes and Punishments, Page131
Bill for Proportioning Crimes and Punishments, Page132
Bill for Proportioning Crimes and Punishments, Page133
Monetary Arithmetic
Sir Isaac Newton’s Assay, Page137
Projected Coin Weights, Page138
Suggested Packet Project, Page251
The Plexi-chronometer, Page391
Population Estimates—1775, Page422
Population Estimates—1785, Page424
PREFACE.
The opinion universally entertained of the extraordinary abilities of Thomas Jefferson, and the signal evidence given by his country, of a profound sense of his patriotic services, and of veneration for his memory, have induced the Editor, who is both his Executor and the Legatee of his Manuscript Papers, to believe that an extensive publication from them would be particularly acceptable to the American people.
The Memoir, contained in the first volume, commences with circumstantial notices of his earliest life; and is continued to his arrival in New York, in March, 1790, when he entered on the duties of the Department of State, of which he had been just appointed Secretary.
From the aspect of the Memoir, it may be presumed that parts of it, at least, had been written for his own and his family’s use only; and in a style without the finish of his revising pen. There is, however, no part of it, minute and personal as it may be, which the Reader would wish to have been passed over by the Editor; whilst not a few parts of that description will, by some, be regarded with a particular interest.
The contents of the Memoir, succeeding the biographical pages, may be designated as follows:
I. General facts and anecdotes relating to the origin and early stages of the contest with Great Britain.
II. Historical circumstances relating to the Confederation of the States.
III. Facts and anecdotes, local and general, preliminary to the Declaration of Independence.
IV. An exact account of the circumstances attending that memorable act, in its preparation and its progress through Congress; with a copy from the original draught, in the hand-writing of the Author; and a parallel column, in the same hand, showing the alterations made in the draught by Congress.
The Memoir will be considered not a little enriched by the Debates in Congress, on the great question of Independence, as they were taken down by Mr. Jefferson at the time, and which, though in a compressed form, present the substance of what passed on that memorable occasion. This portion of the work derives peculiar value from its perfect authenticity, being all in the hand-writing of that distinguished member of the body; from the certainty that this is the first disclosure to the world of those Debates; and from the probability, or rather certainty, that a like knowledge of them is not to be expected from any other source. The same remarks are applicable to the Debates in the same Congress, preserved in the same manner, on two of the original Articles of Confederation. The first is the Article fixing the rate of assessing the quotas of supply to the common Treasury: the second is the Article which declares, “that in determining questions, each Colony shall have one vote.” The Debates on both are not only interesting in themselves, but curious, also, in relation to like discussions of the same subjects on subsequent occasions.
V. Views of the connections and transactions of the United States with foreign nations, at different periods; particularly, a narrative, with many details, personal and political, of the causes and early course of the French Revolution, as exhibited to the observation of the Author, during his diplomatic residence at Paris. The narrative, with the intermingled reflections on the character and consequences of that Revolution, fills a considerable space in the Memoir, and forms a very important part of it.
VI. Within the body of the Memoir, or referred to as an appendix, are other papers which were thought well entitled to the place they occupy. Among them, are, 1. A paper drawn up in the year 1774, as “Instructions to our Delegates in Congress.” Though heretofore in print, it will be new to most readers; and will be regarded by all, as the most ample and precise enumeration of British violations that had then appeared, or, perhaps, that has since been presented in a form at once so compact and so complete. 2. A Penal Code, being part of a Revised Code of Laws, prepared by appointment of the Legislature of Virginia, in 1776, with reference to the Republican form of Government, and to the principles of humanity congenial therewith, and with the improving spirit of the age. Annexed to the several articles, are explanatory and other remarks of the Author, worthy of being preserved by the aid of the press. 3. A historical and critical review of the repeal of the laws establishing the Church in Virginia; which was followed by the “Act for establishing religious freedom.” This act, it is well known, was always held by Mr. Jefferson to be one of his best efforts in the cause of liberty, to which he was devoted: and it is certainly the strongest legal barrier that could be erected against a connection between Church and State, so fatal in its tendency to the purity of both. 4. An elaborate paper concerning a Money Unit, prepared in the year 1784, and which laid the foundation of the system adopted by Congress, for a coinage and money of account. For other particulars, not here noted, the Reader is referred to the volume itself.
The termination of the Memoir, at the date mentioned, by the Author, may be explained by the laborious tasks assumed or not declined by him, on his return to private life; which, with his great age, did not permit him to reduce his materials into a state proper to be embodied in such a work.
The other volumes contain, I. Letters from 1775, to his death, addressed to a very great variety of individuals; and comprising a range of information, and, in many instances, regular essays, on subjects of History, Politics, Science, Morals, and Religion. The letters to him are omitted, except in a very few instances, where it was supposed their publication would be generally acceptable, from the important character of the communication, or the general interest in the views of the writer; or where the whole or a part of a letter had been filed for the better understanding of the answer.
In these cases, such letters are inserted in the body of the work, or in an appendix, as their importance, and connection with the subject discussed by the author, rendered advisable. And where inferences from the tenor of the answer, might in any way affect the correspondent, his name does not appear in the copy filed. The historical parts of the letters, and the entire publication, have the rare value of coming from one of the chief actors himself, and of being written, not for the public eye, but in the freedom and confidence of private friendship.
II. Notes of conversations, whilst Secretary of State, with President Washington, and others high in office; and memoranda of Cabinet Councils, committed to paper on the spot, and filed; the whole, with the explanatory and miscellaneous additions, showing the views and tendencies of parties, from the year 1789 to 1800.
Appended to the publication, is a ‘Facsimile’ of the rough draught of the Declaration of Independence, in which will be seen the erasures, interlineations, and additions of Dr. Franklin and Mr. Adams, two of the appointed Committee, in the handwriting of each.
The Editor, though he cannot be insensible to the genius, the learning, the philosophic inspiration, the generous devotion to virtue, and the love of country, displayed in the writings now committed to the press, is restrained, not less by his incompetency, than by his relation to the Author, from dwelling on themes which belong to an eloquence that can do justice to the names of illustrious benefactors to their country and to their fellow men.
Albemarle, Va., January, 1829.

MEMOIR.
January 6, 1821. At the age of 77, I begin to make some memoranda, and state some recollections of dates and facts concerning myself, for my own more ready reference, and for the information of my family.
The tradition in my father’s family was, that their ancestor came to this country from Wales, and from near the mountain of Snowden, the highest in Great Britain. I noted once a case from Wales, in the law reports, where a person of our name was either plaintiff or defendant; and one of the same name was secretary to the Virginia Company. These are the only instances in which I have met with the name in that country. I have found it in our early records; but the first particular information I have of any ancestor was of my grandfather, who lived at the place in Chesterfield called Ozborne’s, and owned the lands afterwards the glebe of the parish. He had three sons; Thomas who died young, Field who settled on the waters of Roanoke and left numerous descendants, and Peter, my father, who settled on the lands I still own, called Shadwell, adjoining my present residence. He was born February 29, 1707-8, and intermarried 1739, with Jane Randolph, of the age of 19, daughter of Isham Randolph, one of the seven sons of that name and family settled at Dungeoness in Goochland. They trace their pedigree far back in England and Scotland, to which let every one ascribe the faith and merit he chooses.
My father’s education had been quite neglected; but being of a strong mind, sound judgment, and eager after information, he read much and improved himself, insomuch that he was chosen, with Joshua Fry, professor of Mathematics in William and Mary college, to continue the boundary line between Virginia and North Carolina, which had been begun by Colonel Byrd; and was afterwards employed with the same Mr. Fry, to make the first map of Virginia which had ever been made, that of Captain Smith being merely a conjectural sketch. They possessed excellent materials for so much of the country as is below the Blue Ridge; little being then known beyond that Ridge. He was the third or fourth settler, about the year 1737, of the part of the country in which I live. He died August 17th, 1757, leaving my mother a widow, who lived till 1776, with six daughters and two sons, myself the elder. To my younger brother he left his estate on James river, called Snowden, after the supposed birth-place of the family: to myself, the lands on which I was born and live. He placed me at the English school at five years of age; and at the Latin at nine, where I continued until his death. My teacher, Mr. Douglas, a clergyman from Scotland, with the rudiments of the Latin and Greek languages, taught me the French; and on the death of my father, I went to the Reverend Mr. Maury, a correct classical scholar, with whom I continued two years; and then, to wit, in the spring of 1760, went to William and Mary college, where I continued two years. It was my great good fortune, and what probably fixed the destinies of my life, that Dr. William Small of Scotland was then professor of Mathematics, a man profound in most of the useful branches of science, with a happy talent of communication, correct and gentlemanly manners, and an enlarged and liberal mind. He, most happily for me, became soon attached to me, and made me his daily companion when not engaged in the school; and from his conversation I got my first views of the expansion of science, and of the system of things in which we are placed. Fortunately, the philosophical chair became vacant soon after my arrival at college, and he was appointed to fill it per interim: and he was the first who ever gave, in that college, regular lectures in Ethics, Rhetoric, and Belles lettres. He returned to Europe in 1762, having previously filled up the measure of his goodness to me, by procuring for me, from his most intimate friend George Wythe, a reception as a student of Law, under his direction, and introduced me to the acquaintance and familiar table of Govenor Fauquier, the ablest man who had ever filled that office. With him, and at his table, Dr. Small and Mr. Wythe, his amici omnium horarum, and myself, formed a partie quarrée, and to the habitual conversations on these occasions I owed much instruction. Mr. Wythe continued to be my faithful and beloved Mentor in youth, and my most affectionate friend through life. In 1767, he led me into the practice of the law at the bar of the General Court, at which I continued until the Revolution shut up the courts of justice.*
* For a sketch of the life and character of Mr. Wythe, see
my letter of August 31, 1820, to Mr. John Saunderson. [See
Appendix, note A.]
In 1769, I became a member of the legislature by the choice of the county in which I live, and so continued until it was closed by the Revolution. I made one effort in that body for the permission of the emancipation of slaves, which was rejected: and indeed, during the regal government, nothing liberal could expect success. Our minds were circumscribed within narrow limits, by an habitual belief that it was our duty to be subordinate to the mother country in all matters of government, to direct all our labors in subservience to her interests, and even to observe a bigoted intolerance for all religions but hers. The difficulties with our representatives were of habit and despair, not of reflection and conviction. Experience soon proved that they could bring their minds to rights, on the first summons of their attention. But the King’s Council, which acted as another house of legislature, held their places at will, and were in most humble obedience to that will: the Governor too, who had a negative on our laws, held by the same tenure, and with still greater devotedness to it: and, last of all, the Royal negative closed the last door to every hope of melioration.
On the 1st of January, 1772, I was married to Martha Skelton, widow of Bathurst Skelton, and daughter of John Wayles, then twenty-three years old. Mr. Wayles was a lawyer of much practice, to which he was introduced more by his great industry, punctuality and practical readiness, than by eminence in the science of his profession. He was a most agreeable companion, full of pleasantry and good humor, and welcomed in every society. He acquired a handsome fortune, and died in May, 1773, leaving three daughters: the portion which came on that event to Mrs. Jefferson, after the debts should be paid, which were very considerable, was about equal to my own patrimony, and consequently doubled the ease of our circumstances.
When the famous Resolutions of 1765, against the Stamp-act, were proposed, I was yet a student of law in Williamsburg. I attended the debate, however, at the door of the lobby of the House of Burgesses, and heard the splendid display of Mr. Henry’s talents as a popular orator. They were great indeed; such as I have never heard from any other man. He appeared to me, to speak as Homer wrote. Mr. Johnson, a lawyer, and member from the Northern Neck, seconded the resolutions, and by him the learning and logic of the case were chiefly maintained. My recollections of these transactions may be seen page 60 of the “Life of Patrick Henry,” by Wirt, to whom I furnished them.
In May, 1769, a meeting of the General Assembly was called by the Governor, Lord Botetourt. I had then become a member; and to that meeting became known the joint resolutions and address of the Lords and Commons of 1768-9, on the proceedings in Massachusetts. Counter-resolutions, and an address to the King by the House of Burgesses, were agreed to with little opposition, and a spirit manifestly displayed itself of considering the cause of Massachusetts as a common one. The Governor dissolved us: but we met the next day in the Apollo* of the Raleigh tavern, formed ourselves into a voluntary convention, drew up articles of association against the use of any merchandise imported from Great Britain, signed and recommended them to the people, repaired to our several counties, and were re-elected without any other exception than of the very few who had declined assent to our proceedings.
* The name of a public room in the Raleigh.
Nothing of particular excitement occurring for a considerable time, our countrymen seemed to fall into a state of insensibility to our situation; the duty on tea, not yet repealed, and the declaratory act of a right in the British Parliament, to bind us by their laws in all cases whatsoever, still suspended over us. But a court of inquiry held in Rhode Island in 1762, with a power to send persons to England to be tried for offences committed here, was considered, at our session of the spring of 1773, as demanding attention. Not thinking our old and leading members up to the point of forwardness and zeal which the times required, Mr. Henry, Richard Henry Lee, Francis L. Lee, Mr. Carr, and myself agreed to meet in the evening, in a private room of the Raleigh, to consult on the state of things. There may have been a member or two more whom I do not recollect. We were all sensible that the most urgent of all measures was that of coming to an understanding with all the other colonies, to consider the British claims as a common cause to all, and to produce a unity of action: and for this purpose that a committee of correspondence in each colony would be the best instrument for intercommunication: and that their first measure would probably be, to propose a meeting of deputies from every colony, at some central place, who should be charged with the direction of the measures which should be taken by all. We therefore drew up the resolutions which may be seen in Wirt, page 87. The consulting members proposed to me to move them, but I urged that it should be done by Mr. Carr, my friend and brother-in-law, then a new member, to whom I wished an opportunity should be given of making known to the house his great worth and talents. It was so agreed; he moved them, they were agreed to nem. con. and a committee of correspondence appointed, of whom Peyton Randolph, the speaker, was chairman.
The Governor (then Lord Dunmore) dissolved us, but the committee met the next day, prepared a circular letter to the speakers, of the other colonies, inclosing to each a copy of the resolutions, and left it in charge with their chairman to forward them by expresses.
The origination of these committees of correspondence between the colonies, has been since claimed for Massachusetts, and Marshall * has given in to this error, although the very note of his appendix to which he refers, shows that their establishment was confined to their own towns. This matter will be seen clearly stated in a letter of Samuel Adams Wells to me of April 2nd, 1819, and my answer of May 12th. I was corrected by the letter of Mr. Wells in the information I had given Mr. Wirt, as stated in his note, page 87, that the messengers of Massachusetts and Virginia crossed each other on the way, bearing similar propositions; for Mr. Wells shows that Massachusetts did not adopt the measure, but on the receipt of our proposition, delivered at their next session. Their message, therefore, which passed ours, must have related to something else, for I well remember Peyton Randolph’s informing me of the crossing of our messengers. **
* Life of Washington, vol. ii. p. 151.
** See Appendix, note B.
The next event which excited our sympathies for Massachusetts, was the Boston port bill, by which that port was to be shut up on the 1st of June, 1774. This arrived while we were in session in the spring of that year. The lead in the House, on these subjects, being no longer left to the old members, Mr. Henry, R. H. Lee, Fr. L. Lee, three or four other members, whom I do not recollect, and myself, agreeing that we must boldly take an unequivocal stand in the line with Massachusetts, determined to meet and consult on the proper measures, in the council chamber, for the benefit of the library in that room. We were under conviction of the necessity of arousing our people from the lethargy into which they had fallen, as to passing events; and thought that the appointment of a day of general fasting and prayer, would be most likely to call up and alarm their attention. No example of such a solemnity had existed since the days of our distress in the war of ‘55, since which a new generation had grown up. With the help, therefore, of Rushworth, whom we rummaged over for the revolutionary precedents and forms of the Puritans of that day, preserved by him, we cooked up a resolution, somewhat modernizing their phrases, for appointing the 1st day of June, on which the port bill was to commence, for a day of fasting, humiliation, and prayer, to implore Heaven to avert from us the evils of civil war, to inspire us with firmness in support of our rights, and to turn the hearts of the King and Parliament to moderation and justice. To give greater emphasis to our proposition, we agreed to wait the next morning on Mr. Nicholas, whose grave and religious character was more in unison with the tone of our resolution, and to solicit him to move it. We accordingly went to him in the morning. He moved it the same day; the 1st of June was proposed; and it passed without opposition. The Governor dissolved us, as usual. We retired to the Apollo, as before, agreed to an association, and instructed the committee of correspondence to propose to the corresponding committees of the other colonies, to appoint deputies to meet in Congress at such place, annually, as should be convenient, to direct, from time to time, the measures required by the general interest: and we declared that an attack on any one colony should be considered as an attack on the whole. This was in May. We further recommended to the several counties to elect deputies to meet at Williamsburg, the 1st of August ensuing, to consider the state of the colony, and particularly to appoint delegates to a general Congress, should that measure be acceded to by the committees of correspondence generally. It was acceded to; Philadelphia was appointed for the place, and the 5th of September for the time of meeting. We returned home, and in our several counties invited the clergy to meet assemblies of the people on the 1st of June, to perform the ceremonies of the day, and to address to them discourses suited to the occasion. The people met generally, with anxiety and alarm in their countenances, and the effect of the day, through the whole colony, was like a shock of electricity, arousing every man and placing him erect and solidly on his centre. They chose, universally, delegates for the convention. Being elected one for my own county, I prepared a draught of instructions to be given to the delegates whom we should send to the Congress, which I meant to propose at our meeting. [See Appendix, note C.] In this I took the ground that, from the beginning, I had thought the only one orthodox or tenable, which was, that the relation between Great Britain and these colonies was exactly the same as that of England and Scotland, after the accession of James and until the union, and the same as her present relations with Hanover, having the same executive chief, but no other necessary political connection; and that our emigration from England to this country gave her no more rights over us, than the emigrations of the Danes and Saxons gave to the present authorities of the mother country, over England. In this doctrine, however, I had never been able to get any one to agree with me but Mr. Wythe. He concurred in it from the first dawn of the question, What was the political relation between us and England? Our other patriots, Randolph, the Lees, Nicholas, Pendleton, stopped at the half-way house of John Dickinson, who admitted that England had a right to regulate our commerce, and to lay duties on it for the purposes of regulation, but not of raising revenue. But for this ground there was no foundation in compact, in any acknowledged principles of colonization, nor in reason: expatriation being a natural right, and acted on as such, by all nations, in all ages. I set out for Williamsburg some days before that appointed for the meeting, but taken ill of a dysentery on the road, and was unable to proceed, I sent on, therefore, to Williamsburg two copies of my draught, the one under cover to Peyton Randolph, who I knew would be in the of the convention, the other to Patrick Henry. Whether Mr. Henry disapproved the ground taken, or was too lazy to read it (for he was the laziest man in reading I ever knew) I never learned: but he communicated it to nobody. Peyton Randolph informed the convention he had received such a paper from a member, prevented by sickness from offering it in his place, and he laid it on the table for perusal. It was read generally by the members, approved by many, though thought too bold for the present state of things; but they printed it in pamphlet form, under the title of ‘A Summary View of the Rights of British America.’ It found its way to England, was taken up by the opposition, interpolated a little by Mr. Burke so as to make it answer opposition purposes, and in that form ran rapidly through several editions. This information I had from Parson Hurt, who happened at the time to be in London, whither he had gone to receive clerical orders; and I was informed afterwards by Peyton Randolph, that it had procured me the honor of having my name inserted in a long list of proscriptions, enrolled in a bill of attainder commenced in one of the Houses of Parliament, but suppressed in embryo by the hasty step of events, which warned them to be a little cautious. Montague, agent of the House of Burgesses in England, made extracts from the bill, copied the names, and sent them to Peyton Randolph. The names I think were about twenty, which he repeated to me, but I recollect those only of Hancock, the two Adamses, Peyton Randolph himself, Patrick Henry, and myself.* The convention met on the 1st of August, renewed their association, appointed delegates to the Congress, gave them instructions very temperately and properly expressed, both as to style and matter; ** and they repaired to Philadelphia at the time appointed. The splendid proceedings of that Congress, at their first session, belong to general history, are known to every one, and need not therefore be noted here. They terminated their session on the 26th of October, to meet again on the 10th of May ensuing. The convention, at their ensuing session of March ‘75, approved of the proceedings of Congress, thanked their delegates, and reappointed the same persons to represent the colony at the meeting to be held in May: and foreseeing the probability that Peyton Randolph, their president, and speaker also of the House of Burgesses, might be called off, they added me, in that event, to the delegation.
* See Girardin’s History of Virginia, Appendix No. 12. note.
** See Appendix, note D.
Mr. Randolph was according to expectation obliged the chair of Congress, to attend the General Assembly summoned by Lord Dunmore, to meet on the 1st day of June,1775. Lord North’s conciliatory propositions, as they were called received by the Governor, and furnished the subject for which this assembly was convened. Mr. Randolph accordingly attended, and the tenor of these propositions being generally known, as having been addressed to all the governors, he was anxious that the answer of our Assembly, likely to be the first, should harmonise with what he knew to be the sentiments and wishes of the body he had recently left. He feared that Mr. Nicholas, whose mind was not yet up to the mark of the times, would undertake the answer, and therefore pressed me to prepare it. I did so, and, with his aid, carried it through the House, with long and doubtful scruples from Mr. Nicholas and James Mercer, and a dash of cold water on it here and there, enfeebling it somewhat, but finally with unanimity, or a vote approaching it. This being passed, I repaired immediately to Philadelphia, and conveyed to Congress the first notice they had of it. It was entirely approved there. I took my seat with them on the 21st of June. On the 24th, a committee which had been appointed to prepare a declaration of the causes of taking up arms, brought in their report (drawn, I believe, by J. Rutledge) which, not being liked, the House recommitted it, on the 26th, and added Mr. Dickinson and myself to the committee. On the rising of the House, the committee having not yet met, I happened to find myself near Governor W. Livingston, and proposed to him to draw the paper. He excused himself and proposed that I should draw it. On my pressing him with urgency, ‘We are as yet but new acquaintances, sir,’ said he, ‘why are you so earnest for my doing it?’ ‘Because,’ said I, ‘I have been informed that you drew the Address to the people of Great Britain, a production, certainly, of the finest pen in America.’ ‘On that,’ says he, ‘perhaps, sir, you may not have been correctly informed.’ I had received the information in Virginia from Colonel Harrison on his return from that Congress. Lee, Livingston, and Jay had been the committee for the draught. The first, prepared by Lee, had been disapproved and recommitted. The second was drawn by Jay, but being presented by Governor Livingston, had led Colonel Harrison into the error. The next morning, walking in the hall of Congress, many members being assembled, but the House formed, I observed Mr. Jay speaking to R. H. Lee, and leading him by the button of his coat to me. ‘I understand, sir,’ said he to me, ‘that this gentleman informed you, that Governor Livingston drew the Address to the people of Great Britain.’ I assured him at once that I had not received that information from Mr. Lee and that not a word had ever passed on the subject between Mr. Lee and myself; and after some explanations the subject was dropped. These gentlemen had had some sparrings in debate before, and continued ever very hostile to each other.
I prepared a draught of the declaration committed to us. It was too strong for Mr. Dickinson. He still retained the hope of reconciliation with the mother country, and was unwilling it should be lessened by offensive statements. He was so honest a man, and so able a one, that he was greatly indulged even by those who could not feel his scruples. We therefore requested him to take the paper, and put it into a form he could approve. He did so, preparing an entire new statement, and preserving of the former only the last four paragraphs and half of the preceding one. We approved and reported it to Congress, who accepted it. Congress gave a signal proof of their indulgence to Mr. Dickinson, and of their great desire not to go too fast for any respectable part of our body, in permitting him to draw their second petition to the King according to his own ideas, and passing it with scarcely any amendment. The disgust against its humility was general; and Mr. Dickinson’s delight at its passage was the only circumstance which reconciled them to it. The vote being passed, although further observation on it was out of order, he could not refrain from rising and expressing his satisfaction, and concluded by saying, ‘There is but one word, Mr. President, in the paper which I disapprove, and that is the word Congress;’ on which Ben Harrison rose and said, ‘There is but one word in the paper, Mr. President, of which I approve, and that is the word Congress?’
On the 22nd of July, Dr. Franklin, Mr. Adams, R. H. Lee, and myself were appointed a committee to consider and report on Lord North’s conciliatory resolution. The answer of the Virginia Assembly on that subject having been approved, I was requested by the committee to prepare this report, which will account for the similarity of feature in the two instruments.
On the 15th of May, 1776, the convention of Virginia instructed their delegates in Congress, to propose to that body to declare the colonies independent of Great Britain, and appointed a committee to prepare a declaration of rights and plan of government.
Here, in the original manuscript, commence the ‘two
preceding sheets’ referred to by Mr. Jefferson, page 21, as
containing ‘notes’ taken by him ‘whilst these things were
going on.’ They are easily distinguished from the body of
the MS. in which they were inserted by him, being of a paper
very different in size, quality, and color, from that on
which the latter is written:
In Congress, Friday, June 7, 1776. The delegates from Virginia moved, in obedience to instructions from their constituents, that the Congress should declare that these United Colonies and of right ought to be, free and independent states, that they are absolved from all allegiance to the British crown, and that all political connection between them and the state of Great Britain is and ought to be, totally dissolved; that measures should be immediately taken for procuring the assistance of foreign powers and a confederation be formed to bind the colonial more closely together.
The House being obliged to attend at that time to some other business, the proposition was referred to the next day, when the members were ordered to attend punctually at ten o’clock.
Saturday, June 8. They proceeded to take it into consideration, and referred it to a committee of the whole, into which they immediately resolved themselves, and passed that day and Monday the 10th in debating on the subject.
It was argued by Wilson, Robert R. Livingston, E. Rutledge, Dickinson, and others—
That, though they were friends to the measures themselves, and saw the impossibility that we should ever again be united with Great Britain, yet they were against adopting them at this time:
That the conduct we had formerly observed was wise and proper now, of deferring to take any capital step till the voice of the people drove us into it:
That they were our power, and without them our declarations could not be carried into effect:
That the people of the middle colonies (Maryland, Delaware, Pennsylvania, the Jerseys, and New York) were not yet ripe for bidding adieu to British connection, but that they were fast ripening, and, in a short time, would join in the general voice of America:
That the resolution, entered into by this House on the 15th of May, for suppressing the exercise of all powers derived from the crown, had shown, by the ferment into which it had thrown these middle colonies, that they had not yet accommodated their minds to a separation from the mother country:
That some of them had expressly forbidden their delegates to consent to such a declaration, and others had given no instructions, and consequently no powers to give such consent:
That if the delegates of any particular colony had no power to declare such colony independent, certain they were, the others could not declare it for them; the colonies being as yet perfectly independent of each other:
That the assembly of Pennsylvania was now sitting above stairs, their convention would sit within a few days, the convention of New York was now sitting, and those of the Jerseys and Delaware counties would meet on the Monday following, and it was probable these bodies would take up the question of Independence, and would declare to their delegates the voice of their state:
That if such a declaration should now be agreed to, these delegates must retire, and possibly their colonies might secede from the Union:
That such a secession would weaken us more than could be compensated by any foreign alliance:
That in the event of such a division, foreign powers would either refuse to join themselves to our fortunes, or, having us so much in their power as that desperate declaration would place us, they would insist on terms proportionably more hard and prejudicial:
That we had little reason to expect an alliance with those to whom alone, as yet, we had cast our eyes:
That France and Spain had reason to be jealous of that rising power, which would one day certainly strip them of all their American possessions:
That it was more likely they should form a connection with the British Court, who, if they should find themselves unable otherwise to extricate themselves from their difficulties, would agree to a partition of our territories, restoring Canada to France, and the Floridas to Spain, to accomplish for themselves a recovery of these colonies:
That it would not be long before we should receive certain information of the disposition of the French court, from the agent whom we had sent to Paris for that purpose:
That if this disposition should be favorable, by waiting the event of the present campaign, which we all hoped would be successful, we should have reason to expect an alliance on better terms:
That this would in fact work no delay of any effectual aid from such ally, as, from the advance of the season and distance of our situation, it was impossible we could receive any assistance during this campaign:
That it was prudent to fix among ourselves the terms on which we would form alliance, before we declared we would form one at all events:
And that if these were agreed on, and our Declaration of Independence ready by the time our Ambassador should be prepared to sail, it would be as well, as to go into that Declaration at this day.
On the other side, it was urged by J. Adams, Lee, Wythe and others, that no gentleman had argued against the policy or the right of separation from Britain, nor had supposed it possible we should ever renew our connection; that they had only opposed its being now declared:
That the question was not whether, by a Declaration of Independence, we should make ourselves what we are not; but whether we should declare a fact which already exists:
That, as to the people or parliament of England, we had always been independent of them, their restraints on our trade deriving efficacy from our acquiescence only, and not from any rights they possessed of imposing them, and that so far, our connection had been federal only, and was now dissolved by the commencement of hostilities:
That, as to the King, we had been bound to him by allegiance, but that this bond was now dissolved by his assent to the late act of parliament, by which he declares us out of his protection, and by his levying war on us, a fact which had long ago proved us out of his protection; it being a certain position in law, that allegiance and protection are reciprocal, the one ceasing when the other is withdrawn:
That James the II. never declared the people of England out of his protection, yet his actions proved it and the parliament declared it:
No delegates then can be denied, or ever want, a power of declaring an existent truth:
That the delegates from the Delaware counties having declared their constituents ready to join, there are only two colonies, Pennsylvania and Maryland, whose delegates are absolutely tied up, and that these had, by their instructions, only reserved a right of confirming or rejecting the measure:
That the instructions from Pennsylvania might be accounted for from the times in which they were drawn, near a twelvemonth ago, since which the face of affairs has totally changed:
That within that time, it had become apparent that Britain was determined to accept nothing less than a carte-blanche, and that the King’s answer to the Lord Mayor, Aldermen, and Common Council of London, which had come to hand four days ago, must have satisfied every one of this point:
That the people wait for us to lead the way:
That they are in favor of the measure, though the instructions given by some of their representatives are not:
That the voice of the representatives is not always consonant with the voice of the people, and that this is remarkably the case in these middle colonies:
That the effect of the resolution of the 15th of May has proved this, which, raising the murmurs of some in the colonies of Pennsylvania and Maryland, called forth the opposing voice of the freer part of the people, and proved them to be the majority even in these colonies:
That the backwardness of these two colonies might be ascribed, partly to the influence of proprietary power and connections, and partly, to their having not yet been attacked by the enemy:
That these causes were not likely to be soon removed, as there seemed no probability that the enemy would make either of these the seat of this summer’s war:
That it would be vain to wait either weeks or months for perfect unanimity, since it was impossible that all men should ever become of one sentiment on any question:
That the conduct of some colonies, from the beginning of this contest, had given reason to suspect it was their settled policy to keep in the rear of the confederacy, that their particular prospect might be better, even in the worst event:
That, therefore, it was necessary for those colonies who had thrown themselves forward and hazarded all from the beginning, to come forward now also, and put all again to their own hazard:
That the history of the Dutch revolution, of whom three states only confederated at first, proved that a secession of some colonies would not be so dangerous as some apprehended:
That a declaration of Independence alone could render it consistent with European delicacy, for European powers to treat with us, or even to receive an Ambassador from us:
That till this, they would not receive our vessels into their ports, nor acknowledge the adjudications of our courts of admiralty to be legitimate, in cases of capture of British vessels:
That though France and Spain may be jealous of our rising power, they must think it will be much more formidable with the addition of Great Britain; and will therefore see it their interest to prevent a coalition; but should they refuse, we shall be but where we are; whereas without trying, we shall never know whether they will aid us or not:
That the present campaign may be unsuccessful, and therefore we had better propose an alliance while our affairs wear a hopeful aspect:
That to wait the event of this campaign will certainly work delay, because, during this summer, France may assist us effectually, by cutting off those supplies of provisions from England and Ireland, on which the enemy’s armies here are to depend; or by setting in motion the great power they have collected in the West Indies, and calling our enemy to the defence of the possessions they have there:
That it would be idle to lose time in settling the terms of alliance, till we had first determined we would enter into alliance:
That it is necessary to lose no time in opening a trade for our people, who will want clothes, and will want money too, for the payment of taxes:
And that the only misfortune is, that we did not enter into alliance with France six months sooner, as, besides opening her ports for the vent of our last year’s produce, she might have marched an army into Germany, and prevented the petty princes there, from selling their unhappy subjects to subdue us.
It appearing in the course of these debates, that the colonies of New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Delaware, Maryland, and South Carolina were not yet matured for falling from the parent stem, but that they were fast advancing to that state, it was thought most prudent to wait awhile for them, and to postpone the final decision to July 1st: but, that this might occasion as little delay as possible, a committee was appointed to prepare a Declaration of Independence. The committee were John Adams, Dr. Franklin, Roger Sherman, Robert R. Livingston, and myself. Committees were also appointed, at the same time, to prepare a plan of confederation for the colonies, and to state the terms proper to be proposed for foreign alliance. The committee for drawing the Declaration of Independence, desired me to do it. It was accordingly done, and being approved by them, I reported it to the House on Friday, the 28th of June, when it was read and ordered to lie on the table. On Monday, the 1st of July, the House resolved itself into a committee of the whole, and resumed the consideration of the original motion made by the delegates of Virginia, which, being again debated through the day, was carried in the affirmative by the votes of New Hampshire, Connecticut, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, New Jersey, Maryland, Virginia, North Carolina, and Georgia. South Carolina and Pennsylvania voted against it. Delaware had but two members present, and they were divided. The delegates from New York declared they were for it themselves, and were assured their constituents were for it; but that their instructions having been drawn near a twelvemonth before, when reconciliation was still the general object, they were enjoined by them to do nothing which should impede that object. They therefore thought themselves not justifiable in voting on either side, and asked leave to withdraw from the question; which was given them. The committee rose and reported their resolution to the House. Mr. Edward Rutledge, of South Carolina, then requested the determination might be put off to the next day, as he believed his colleagues, though they disapproved of the resolution, would then join in it for the sake of unanimity. The ultimate question, whether the House would agree to the resolution of the committee, was accordingly postponed to the next day, when it was again moved, and South Carolina concurred in voting for it. In the mean time, a third member had come post from the Delaware counties, and turned the vote of that colony in favor of the resolution. Members of a different sentiment attending that morning from Pennsylvania also, her vote was changed, so that the whole twelve colonies, who were authorized to vote at all, gave their voices for it; and, within a few days, [July 9.] the convention of New York approved of it, and thus supplied the void occasioned by the withdrawing of her delegates from the vote.
Congress proceeded the same day to consider the Declaration of Independence, which had been reported and laid on the table the Friday preceding, and on Monday referred to a committee of the whole. The pusillanimous idea that we had friends in England worth keeping terms with, still haunted the minds of many. For this reason, those passages which conveyed censures on the people of England were struck out, lest they should give them offence. The clause too, reprobating the enslaving the inhabitants of Africa, was struck out in complaisance to South Carolina and Georgia, who had never attempted to restrain the importation of slaves, and who, on the contrary, still wished to continue it. Our northern brethren also, I believe, felt a little tender under those censures; for though their people had very few slaves themselves, yet they had been pretty considerable carriers of them to others. The debates having taken up the greater parts of the 2nd, 3rd, and 4th days of July, were, on the evening of the last, closed; the Declaration was reported by the committee, agreed to by the House, and signed by every member present, except Mr. Dickinson. As the sentiments of men are known, not only by what they receive, but what they reject also, I will state the form of the Declaration as originally reported. The parts struck out by Congress shall be distinguished by a black line drawn under them; * and those inserted by them shall be placed in the margin, or in a concurrent column.






* In this publication, the parts struck out are printed in
Italics and inclosed in brackets—and those inserted are
inclosed in parenthesis.
A DECLARATION BY THE REPRESENTATIVES OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA, IN GENERAL CONGRESS ASSEMBLED.
When, in the course of human events, it becomes necessary for one people to dissolve the political bands which have connected them with another, and to assume among the powers of the earth the separate and equal station to which the laws of nature and of nature’s God entitle them, a decent respect to the opinions of mankind requires that they should declare the causes which impel them to the separation.
We hold these truths to be self evident: that all men are created equal; that they are endowed by their creator with [inherent and] (certain) inalienable rights; that among these are life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness; that to secure these rights, governments are instituted among men, deriving their just powers from the consent of the governed; that whenever any form of government becomes destructive of these ends, it is the right of the people to alter or abolish it, and to institute new government, laying its foundation on such principles, and organizing its powers in such form, as to them shall seem most likely to effect their safety and happiness. Prudence, indeed, will dictate that governments long established should not be changed for light and transient causes; and accordingly all experience hath shown that mankind are more disposed to suffer while evils are sufferable, than to right themselves by abolishing the forms to which they are accustomed. But when a long train of abuses and usurpations [begun at a distinguished period and] pursuing invariably the same object, evinces a design to reduce them under absolute despotism, it is their right, it is their duty to throw off such government, and to provide new guards for their future security. Such has been the patient sufferance of these colonies; and such is now the necessity which constrains them to [expunge] (alter) their former systems of government. The history of the present king of Great Britain is a history of [unremitting] (repeated) injuries and usurpations, [among which appears no solitary act to contradict the uniform tenor of the rest, but all have] (all having) in direct object the establishment of an absolute tyranny over these states. To prove this, let facts be submitted to a candid world [for the truth of which we pledge a faith yet unsullied by falsehood.]
He has refused his assent to laws the most wholesome and necessary for the public good.
He has forbidden his governors to pass laws of immediate and pressing importance, unless suspended in their operation till his assent should be obtained; and, when so suspended, he has utterly neglected to attend to them.
He has refused to pass other laws for the accommodation of large districts of people, unless those people would relinquish the right of representation in the legislature, a right inestimable to them, and formidable to tyrants only.
He has called together legislative bodies at places unusual, uncomfortable, and distant from the depository of their public records, for the sole purpose of fatiguing them into compliance with his measures.
He has dissolved representative houses repeatedly [and continually] for opposing with manly firmness his invasions on the rights of the people.
He has refused for a long time after such dissolutions to cause others to be elected, whereby the legislative powers, incapable of annihilation, have returned to the people at large for their exercise, the state remaining, in the mean time, exposed to all the dangers of invasion from without and convulsions within.
He has endeavored to prevent the population of these states; for that purpose obstructing the laws for naturalization of foreigners, refusing to pass others to encourage their migrations hither, and raising the conditions of new appropriations of lands.
He has [suffered] (obstructed) the administration of justice [totally to cease in some of these states] (by) refusing his assent to laws for establishing judiciary powers.
He has made [our] judges dependant on his will alone for the tenure of their offices, and the amount and payment of their salaries.
He has erected a multitude of new offices, [by a self-assumed power] and sent hither swarms of new officers to harass our people and eat out their substance.
He has kept among us in times of peace standing armies [and ships of war] without the consent of our legislatures.
He has affected to render the military independent of, and superior to, the civil power.
He has combined with others to subject us to a jurisdiction foreign to our constitutions and unacknowledged by our laws, giving his assent to their acts of pretended legislation for quartering large bodies of armed troops among us; for protecting them by a mock trial from punishment for any murders which they should commit on the inhabitants of these states; for cutting off our trade with all parts of the world; for imposing taxes on us without our consent; for depriving us [ ] in many cases of the benefits of trial by jury; for transporting us beyond seas to be tried for pretended offences; for abolishing the free system of English laws in a neighboring province, establishing therein an arbitrary government, and enlarging its boundaries, so as to render it at once an example and fit instrument for introducing the same absolute rule into these [states] (colonies); for taking away our charters, abolishing our most valuable laws, and altering fundamentally the forms of our governments; for suspending our own legislatures, and declaring themselves invested with power to legislate for us in all cases whatsoever.
He has abdicated government here [withdrawing his governors, and declaring us out of his allegiance and protection.] (by declaring us out of his protection and waging war against us.)
He has plundered our seas, ravaged our coasts, burnt our towns, and destroyed the lives of our people.
He is at this time transporting large armies of foreign mercenaries to complete the works of death, desolation, and tyranny already begun with circumstances of cruelty and perfidy [ ] (scarcely paralleled in the most barbarous ages and totally) unworthy the head of a civilized nation.
He has constrained our fellow citizens taken captive on the high seas to bear arms against their country, to become the executioners of their friends and brethren, or to fall themselves by their hands.
He has [ ] (excited domestic insurrections amoungst us and has) endeavored to bring on the inhabitants of our frontiers the merciless Indian savages, whose known rule of warfare is an undistinguished destruction of all ages, sexes, and conditions [of existence.]
[He has incited treasonable insurrections of our fellow citizens, with the allurements of forfeiture and confiscation of our property.
He has waged cruel war against human nature itself, violating its most sacred rights of life and, liberty in the persons of a distant people who never offended him, captivating and carrying them into slavery in another hemisphere, or to incur miserable death in their transportation thither. This piratical warfare, the opprobrium of INFIDEL powers, is the warfare of the CHRISTIAN king of Great Britain. Determined to keep open a market where men should be bought and sold, he has prostituted his negative for suppressing every legislative attempt to prohibit or to restrain this execrable commerce. And that this assemblage of horrors might want no fact of distinguished die, he is now exciting those very people to rise in arms among us, and to purchase that liberty of which he has deprived them, by murdering the people on whom he also obtruded them: thus paying off former crimes committed against the liberties of one people with crimes which he urges them to commit against the lives of another.]
In every stage of these oppressions we have petitioned for redress in the most humble terms: our repeated petitions have been answered only by repeated injuries.
A prince whose character is thus marked by every act which may define a tyrant is unfit to be the ruler of a [ ] (free) people [who mean to be free. Future ages will scarcely believe that the hardiness of one man adventured, within the short compass of twelve years only, to lay a foundation so broad and so undisguised for tyranny over a people fostered and fixed in principles of freedom.]
Nor have we been wanting in attentions to our British brethren. We have warned them from time to time of attempts by their legislature to extend [a] (an unwarrantable) jurisdiction over [these our states] (us). We have reminded them of the circumstances of our emigration and settlement here, [no one of which could warrant so strange a pretension: that these were effected at the expense of our own blood and treasure, unassisted by the wealth or the strength of Great Britain: that in constituting indeed our several forms of government, we had adopted one common king, thereby laying a foundation for perpetual league and amity with them: but that submission to their parliament was no part of our constitution, nor ever in idea, if history may be credited: and,] we [ ] (have) appealed to their native justice and magnanimity [as well as to] (and we have conjured them by) the ties of our common kindred to disavow these usurpations which [were likely to] (would inevitably) interrupt our connection and correspondence. They too have been deaf to the voice of justice and of consanguinity, [and when occasions have been given them, by the regular course of their laws, of removing from their councils the disturbers of our harmony, they have, by their free election, re-established, them in power. At this very time too, they are permitting their chief magistrate to send over not only soldiers of our common blood, but Scotch and foreign mercenaries to invade and destroy us. These facts have given the last stab to agonizing affection, and manly spirit bids us to renounce for ever these unfeeling brethren. We must endeavor to forget our former love for them, and hold them as we hold the rest of mankind, enemies in war, in peace friends. We might have been a free and a great people together; but a communication of grandeur and of freedom, it seems, is below their dignity. Be it so, since they will have it. The road to happiness and to glory is open to us too. We will tread it apart from them, and] (We must therefore) acquiesce in the necessity which denounces our [eternal] separation [ ]! (and hold them as we hold the rest of mankind, enemies in war, in peace friends.)
[We therefore the representatives of the United States of America in General Congress assembled, do in the name, and by the authority of the good people of these states reject and renounce all allegiance and subjection to the kings of Great Britain and all others who may hereafter claim by, through, or under them; we utterly dissolve all political connection which may heretofore have subsisted between us and, the people or parliament of Great Britain: and finally we do assert and declare these colonies to be free and independent states, and that as free and independent states, they have full power to levy war, conclude peace, contract alliances, establish commerce, and to do all other acts and things which independent states may of right do.
And for the support of this declaration, we mutually pledge to each other our lives, our fortunes, and our sacred honor.]
(We therefore the representatives of the United States of America in General Congress assembled, appealing to the supreme judge of the world for the rectitude of our intentions, do in the name, and by the authority of the good people of these colonies, solemnly publish and declare, that these united colonies are, and of right ought to be, free and independent states; that they are absolved from all allegiance to the British crown, and that all political connection between them and the state of Great Britain is, and ought to be, totally dissolved; and that as free and independent states, they have full power to levy war, conclude peace, contract alliances, establish commerce, and to do all other acts and things which independent states may of right do.
And for the support of this declaration, with a firm reliance on the protection of divine providence, we mutually pledge to each other our lives, our fortunes, and our sacred honor.)
The declaration thus signed on the 4th, on paper, was engrossed on parchment, and signed again on the 2nd of August.
[* Some erroneous statements of the proceedings on the Declaration of Independence having got before the public in latter times, Mr. Samuel A. Wells asked explanations of me, which are given in my letter to him of May 12, ‘19, before and now again referred to. (See Appendix, note B.) I took notes in my place while these things were going on, and at their close wrote them out in form and with correctness, and from 1 to 7 of the two preceding sheets, are the originals then written; as the two following are of the earlier debates on the Confederation, which I took in like manner.]
* The above note of the author is on a slip of paper, pasted
in at the end of the Declaration. Here is also sewed into
the MS. a slip of newspaper containing, under the head
‘Declaration of Independence,’ a letter from Thomas Mc’Kean
to Messrs. William M’Corkle & Son, dated ‘Philadelphia,
June 16 1817.’ This letter is to be found in the Port Folio,
Sept. 1817, p. 249.
[The following four images are from engravings taken from the Jefferson’s draft of the Declaration of Independence in his handwriting with some ammendations and changes in the handrwriting of Benjamin Franklin and John Adams--Click on any of these to enlarge the image to full-size.]
ENLARGE

ENLARGE

ENLARGE

ENLARGE

On Friday, July 12, the committee appointed to draw the articles of Confederation reported them, and on the 22nd, the House resolved themselves into a committee to take them into consideration. On the 30th and 31st of that month, and 1st of the ensuing, those articles were debated which determined the proportion, or quota, of money which each state should furnish to the common treasury, and the manner of voting in Congress. The first of these articles was expressed in the original draught in these words. ‘Art. XI. All charges of war and all other expenses that shall be incurred for the common defence, or general welfare, and allowed by the United States assembled, shall be defrayed out of a common treasury, which shall be supplied by the several colonies in proportion to the number of inhabitants of every age, sex, and quality, except Indians not paying taxes, in each colony, a true account-of which, distinguishing the white inhabitants, shall be triennially taken and transmitted to the Assembly of the United States.’
Mr. Chase moved that the quotas should be fixed, not by the number of inhabitants of every condition, but by that of the ‘white inhabitants.’ He admitted that taxation should be always in proportion to property; that this was, in theory, the true rule; but that, from a variety of difficulties, it was a rule which could never be adopted in practice. The value of the property in every state, could never be estimated justly and equally. Some other measures for the wealth of the state must therefore be devised, some standard referred to, which would be more simple. He considered the number of inhabitants as a tolerably good criterion of property, and that this might always be obtained. He therefore thought it the best mode which we could adopt, with one exception only: he observed that negroes are property, and as such, cannot be distinguished from the lands or personalities held in those states where there are few slaves; that the surplus of profit which a Northern farmer is able to lay by, he invests in cattle, horses, &c. whereas a Southern farmer lays out the same surplus in slaves. There is no more reason therefore for taxing the Southern states on the farmer’s head, and on his slave’s head, than the Northern ones on their farmers’ heads and the heads of their cattle: that the method proposed would, therefore, tax the Southern states according to their numbers and their wealth conjunctly, while the Northern would be taxed on numbers only; that negroes, in fact, should not be considered as members of the state, more than cattle, and that they have no more interest in it.
Mr. John Adams observed, that the numbers of people were taken by this article, as an index of the wealth of the state, and not as subjects of taxation; that, as to this matter, it was of no consequence by what name you called your people, whether by that of freemen or of slaves; that in some countries the laboring poor were called freemen, in others they were called slaves; but that the difference as to the state was imaginary only. What matters it whether a landlord employing ten laborers on his farm, give them annually as much money as will buy them the necessaries of life, or gives them those necessaries at short hand? The ten laborers add as much wealth annually to the state, increase its exports as much, in the one case as the other. Certainly five hundred freemen produce no more profits, no greater surplus for the payment of taxes, than five hundred slaves. Therefore the state in which are the laborers called freemen, should be taxed no more than that in which are those called slaves. Suppose, by an extraordinary operation of nature or of law, one half the laborers of a state could in the course of one night be transformed into slaves; would the state be made the poorer or the less able to pay taxes? That the condition of the laboring poor in most countries, that of the fishermen particularly of the Northern states, is as abject as that of slaves. It is the number of laborers which produces the surplus for taxation, and numbers, therefore, indiscriminately, are the fair index of wealth; that it is the use of the word ‘property’ here, and its application to some of the people of the state, which produces the fallacy. How does the Southern farmer procure slaves? Either by importation or by purchase from his neighbor. If he imports a slave, he adds one to the number of laborers in his country, and proportionably to its profits and abilities to pay-taxes; if he buys from his neighbor, it is only a transfer of a laborer from one farm to another, which does not change the annual produce of the state, and therefore should not change its tax: that if a Northern farmer works ten laborers on his farm, he can, it is true, invest the surplus of ten men’s labor in cattle; but so may the Southern farmer, working ten slaves; that a state of one hundred thousand freemen can maintain no more cattle, than one of one hundred thousand slaves. Therefore, they have no more of that kind of property; that a slave may, indeed, from the custom of speech, be more properly called the wealth of his master, than the free laborer might be called the wealth of his employer: but as to the state, both were equally its wealth, and should therefore equally add to the quota of its tax.
Mr. Harrison proposed, as a compromise, that two slaves should be counted as one freeman. He affirmed that slaves did not do as much work as freemen, and doubted if two effected more than one; that this was proved by the price of labor; the hire of a laborer in the Southern colonies being from £8 to £12, while in the Northern it was generally £24.
Mr. Wilson said, that if this amendment should take place, the Southern colonies would have all the benefit of slaves, whilst the Northern ones would bear the burthen: that slaves increase the profits of a state, which the Southern states mean to take to themselves; that they also increase the burthen of defence, which would of course fall so much the heavier on the Northern: that slaves occupy the places of freemen and eat their food. Dismiss your slaves, and freemen will take their places. It is our duty to lay every discouragement on the importation of slaves; but this amendment would give the jus trium liberorum to him who would import slaves: that other kinds of property were pretty equally distributed through all the colonies: there were as many cattle, horses, and sheep, in the North as the South, and South as the North; but not so as to slaves: that experience has shown that those colonies have, been always able to pay most, which have the most inhabitants, whether they be black or white: and the practice of the Southern colonies has always been to make every farmer pay poll taxes upon all his laborers, whether they be black or white. He acknowledges indeed, that freemen work the most; but they consume the most also. They do not produce a greater surplus for taxation. The slave is neither fed nor clothed so expensively as a freeman. Again, white women are exempted from labor generally, but negro women are not. In this then the Southern states have an advantage as the article now stands. It has sometimes been said that slavery is necessary, because the commodities they raise would be too dear for market if cultivated by freemen: but now it is said that the labor of the slave is the dearest.
Mr. Payne urged the original resolution of Congress, to proportion the quotas of the states to the number of souls.
Dr. Witherspoon was of opinion, that the value of lands and houses was the best estimate of the wealth of a nation, and that it was practicable to obtain such a valuation. This is the true barometer of wealth. The one now proposed is imperfect in itself, and unequal between the states. It has been objected that negroes eat the food of freemen, and therefore should be taxed; horses also eat the food of freemen; therefore they also should be taxed. It has been said too, that in carrying slaves into the estimate of the taxes the state is to pay, we do no more than those states themselves do, who always take slaves into the estimate of the taxes the individual is to pay. But the cases are not parallel. In the Southern colonies slaves pervade the whole colony; but they do not pervade the whole continent. That as to the original resolution of Congress, to proportion the quotas according to the souls, it was temporary only, and related to the monies heretofore emitted; whereas we are now entering into a new compact, and therefore stand on original ground.
August 1. The question being put, the amendment proposed was rejected by the votes of New Hampshire, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, Connecticut, New York, New Jersey, and Pennsylvania, against those of Delaware, Maryland, Virginia, North and South Carolina. Georgia was divided.
The other article was in these words. ‘Art. XVII. In determining questions, each colony shall have one vote.’
July 30, 31, August 1. Present forty-one members. Mr. Chase observed that this article was the most likely to divide us, of any one proposed in the draught then under consideration: that the larger colonies had threatened they would not confederate at all, if their weight in Congress should not be equal to the numbers of people they added to the confederacy; while the smaller ones declared against a union, if they did not retain an equal vote for the protection of their rights. That it was of the utmost consequence to bring the parties together, as, should we sever from each other, either no foreign power will ally with us at all, or the different states will form different alliances, and thus increase the horrors of those scenes of civil war and bloodshed, which in such a state of separation and independence, would render us a miserable people. That our importance, our interests, our peace required that we should confederate, and that mutual sacrifices should be made to effect a compromise of this difficult question. He was of opinion, the smaller colonies would lose their rights, if they were not in some instances allowed an equal vote; and, therefore, that a discrimination should take place among the questions which would come before Congress. That the smaller states should be secured in all questions concerning life or liberty, and the greater ones, in all respecting property. He therefore proposed, that in votes relating to money, the voice of each colony should be proportioned to the number of its inhabitants.
Dr. Franklin thought, that the votes should be so proportioned in all cases. He took notice that the Delaware counties had bound up their delegates to disagree to this article. He thought it a very extraordinary language to be held by any state, that they would not confederate with us, unless we would let them dispose of our money. Certainly, if we vote equally, we ought to pay equally; but the smaller states will hardly purchase the privilege at this price. That had he lived in a state where the representation, originally equal, had become unequal by time and accident, he might have submitted rather than disturb government: but that we should be very wrong to set out in this practice, when it is in our power to establish what is right. That at the time of the Union between England and Scotland, the latter had made the objection which the smaller states now do; but experience had proved that no unfairness had ever been shown them: that their advocates had prognosticated that it would again happen, as in times of old, that the whale would swallow Jonas, but he thought the prediction reversed in event, and that Jonas had swallowed the whale; for the Scotch had in fact got possession of the government, and gave laws to the English. He reprobated the original agreement of Congress to vote by colonies, and, therefore, was for their voting, in all cases, according to the number of taxables.
Dr. Witherspoon opposed every alteration of the article. All men admit that a confederacy is necessary. Should the idea get abroad that there is likely to be no union among us, it will damp the minds of the people, diminish the glory of our struggle, and lessen its importance; because it will open to our view future prospects of war and dissension among ourselves. If an equal vote be refused, the smaller states will become vassals to the larger; and all experience has shown that the vassals and subjects of free states are the most enslaved. He instanced the Helots of Sparta, and the provinces of Rome. He observed that foreign powers, discovering this blemish, would make it a handle for disengaging the smaller states from so unequal a confederacy. That the colonies should in fact be considered as individuals; and that, as such, in all disputes, they should have an equal vote; that they are now collected as individuals making a bargain with each other, and, of course, had a right to vote as individuals. That in the East India Company they voted by persons, and not by their proportion of stock. That the Belgic confederacy voted by provinces. That in questions of war the smaller states were as much interested as the larger, and therefore, should vote equally; and indeed, that the larger states were more likely to bring war on the confederacy, in proportion as their frontier was more extensive. He admitted that equality of representation was an excellent principle, but then it must be of things which are co-ordinate; that is of things similar, and of the same nature: that nothing relating to individuals could ever come before Congress; nothing but what would respect colonies. He distinguished between an incorporating and a federal union. The union of England was an incorporating one; yet Scotland had suffered by that union; for that its inhabitants were drawn from it by the hopes of places and employments; nor was it an instance of equality of representation; because, while Scotland was allowed nearly a thirteenth of representation, they were to pay only one fortieth of the land tax. He expressed his hopes, that in the present enlightened state of men’s minds, we might expect a lasting confederacy, if it was founded on fair principles.
John Adams advocated the voting in proportion to numbers. He said, that we stand here as the representatives of the people; that in some states the people are many, in others they are few; that therefore their vote here should be proportioned to the numbers from whom it comes. Reason, justice, and equity never had weight enough on the face of the earth, to govern the councils of men. It is interest alone which does it, and it is interest alone which can be trusted; that therefore the interests, within doors, should be the mathematical representatives of the interests without doors; that the individuality of the colonies is a mere sound. Does the individuality of a colony increase its wealth or numbers? If it does, pay equally. If it does not add weight in the scale of the confederacy, it cannot add to their rights, nor weigh in argument. A. has £50, B. £500, C. £1000, in partnership. Is it just they should equally dispose of the monies of the partnership? It has been said, we are independent individuals, making a bargain together. The question is not, what we are now, but what we ought to be, when our bargain shall be made. The confederacy is to make us one individual only; it is to form us, like separate parcels of metal, into one common mass. We shall no longer retain our separate individuality, but become a single individual as to all questions submitted to the confederacy. Therefore all those reasons, which prove the justice and expediency of equal representation in other assemblies, hold good here. It has been objected, that a proportional vote will endanger the smaller states. We answer, that an equal vote will endanger the larger. Virginia, Pennsylvania, and Massachusetts, are the three greater colonies. Consider their distance, their difference of produce, of interests, and of manners, and it is apparent they can never have an interest or inclination to combine for the oppression of the smaller; that the smaller will naturally divide on all questions with the larger. Rhode Island, from its relation, similarity, and intercourse, will generally pursue the same objects with Massachusetts; Jersey, Delaware, and Maryland, with Pennsylvania.
Dr. Rush took notice, that the decay of the liberties of the Dutch republic proceeded from three causes. 1. The perfect unanimity requisite on all occasions. 2. Their obligation to consult their constituents. 3. Their voting by provinces. This last destroyed the equality of representation, and the liberties of Great Britain also are sinking from the same defect. That a part of our rights is deposited in the hands of our legislatures. There, it was admitted, there should be an equality of representation. Another part of our rights is deposited in the hands of Congress; why is it not equally necessary, there should be an equal representation there? Were it possible to collect the whole body of the people together, they would determine the questions submitted to them by their majority. Why should not the same majority decide, when voting here, by their representatives? The larger colonies are so providentially divided in situation, as to render every fear of their combining visionary. Their interests are different, and their circumstances dissimilar. It is more probable they will become rivals, and leave it in the power of the smaller states to give preponderance to any scale they please. The voting by the number of free inhabitants, will have one excellent effect, that of inducing the colonies to discourage slavery, and to encourage the increase of their free inhabitants.
Mr. Hopkins observed, there were four larger, four smaller, and four middle-sized colonies. That the four largest would contain more than half the inhabitants of the confederating states, and therefore would govern the others as they should please. That history affords no instance of such a thing as equal representation. The Germanic body votes by states. The Helvetic body does the same; and so does the Belgic confederacy. That too little is known of the ancient confederations, to say what was their practice.
Mr. Wilson thought, that taxation should be in proportion to wealth, but that representation should accord with the number of freemen. That government is a collection or result of the wills of all: that if any government could speak the will of all, it would be perfect; and that, so far as it departs from this, it becomes imperfect. It has been said, that Congress is a representation of states, not of individuals. I say, that the objects of its care are all the individuals of the states. It is strange, that annexing the name of ‘State’ to ten thousand men, should give them an equal right with forty thousand. This must be the effect of magic, not of reason. As to those matters which are referred to Congress, we are not so many states; we are one large state. We lay aside our individuality, whenever we come here. The Germanic body is a burlesque on government: and their practice on any point, is a sufficient authority and proof that it is wrong. The greatest imperfection in the constitution of the Belgic confederacy is their voting by provinces. The interest of the whole is constantly sacrificed to that of the small, states. The history of the war in the reign of Queen Anne, sufficiently proves this. It is asked, shall nine colonies put it into the power of four, to govern them as they please? I invert the question, and ask, shall two millions of people put it into the power of one million, to govern them as they please? It is pretended, too, that the smaller colonies will be in danger from the greater. Speak in honest language and say, the minority will be in danger from the majority. And is there an assembly on earth, where this danger may not be equally pretended? The truth is, that our proceedings will then be consentaneous with the interests of the majority, and so they ought to be. The probability is much greater, that the larger states will disagree, than that they will combine. I defy the wit of man to invent a possible case, or to suggest any one thing on earth, which shall be for the interests of Virginia, Pennsylvania, and Massachusetts, and which will not also be for the interest of the other states.*
* Here terminate the author’s notes of the ‘earlier debates
on the confederation,’ and recommences the MS. begun by him
in 1821.
These articles, reported July 12, ‘76, were debated from day to day, and time to time, for two years, were ratified July 9, ‘78, by ten states, by New-Jersey on the 26th of November of the same year, and by Delaware on the 23rd of February following. Maryland alone held off two years more, acceding to them March 1, ‘81, and thus closing the obligation.
Our delegation had been renewed for the ensuing year, commencing August 11; but the new government was now organized, a meeting of the legislature was to be held in October, and I had been elected a member by my county. I knew that our legislation, under the regal government, had many very vicious points which urgently required reformation, and I thought I could be of more use in forwarding that work. I therefore retired from my seat in Congress on the 2nd of September, resigned it, and took my place in the legislature of my state, on the 7th of October.
On the 11th, I moved for leave to bring in a bill for the establishment of courts of justice, the organization of which was of importance. I drew the bill; it was approved by the committee, reported and passed, after going through its due course.
On the 12th, I obtained leave to bring in a bill declaring tenants in tail to hold their lands in fee simple. In the earlier times of the colony, when lands were to be obtained for little or nothing, some provident individuals procured large grants; and, desirous of founding great families for themselves, settled them on their descendants in fee tail. The transmission of this property from generation to generation, in the same name, raised up a distinct set of families, who, being privileged by law in the perpetuation of their wealth, were thus formed into a Patrician order, distinguished by the splendor and luxury of their establishments. From this order, too, the king habitually selected his Counsellors of state; the hope of which distinction devoted the whole corps to the interests and will of the crown. To annul this privilege, and instead of an aristocracy of wealth, of more harm and danger, than benefit, to society, to make an opening for the aristocracy of virtue and talent, which nature has wisely provided for the direction of the interests of society, and scattered with equal hand through all its conditions, was deemed essential to a well ordered republic. To effect it, no violence was necessary, no deprivation of natural right, but rather an enlargement of it by a repeal of the law. For this would authorize the present holder to divide the property among his children equally, as his affections were divided; and would place them, by natural generation, on the level of their fellow citizens. But this repeal was strongly opposed by Mr. Pendleton, who was zealously attached to ancient establishments; and who, taken all in all, was the ablest man in debate I have ever met with. He had not indeed the poetical fancy of Mr. Henry, his sublime imagination, his lofty and overwhelming diction; but he was cool, smooth, and persuasive; his language flowing, chaste, and embellished; his conceptions quick, acute, and full of resource; never vanquished; for if he lost the main battle, he returned upon you, and regained so much of it as to make it a drawn one, by dexterous manoeuvres, skirmishes in detail, and the recovery of small advantages which, little singly, were important all together. You never knew when you were clear of him, but were harassed by his perseverance, until the patience was worn down of all who had less of it than himself. Add to this, that he was one of the most virtuous and benevolent of men, the kindest friend, the most amiable and pleasant of companions, which ensured a favorable reception to whatever came from him. Finding that the general principle of entails could not be maintained, he took his stand on an amendment which he proposed, instead of an absolute abolition, to permit the tenant in tail to convey in fee simple, if he chose it: and he was within a few votes of saving so much of the old law. But the bill passed finally for entire abolition.
In that one of the bills for organizing our judiciary system, which proposed a court of Chancery, I had provided for a trial by jury of all matters of fact, in that as well as in the courts of law. He defeated it by the introduction of four words only, ‘if either party choose?’ The consequence has been, that as no suitor will say to his judge, ‘Sir, I distrust you, give me a jury,’ juries are rarely, I might say perhaps never, seen in that court, but when called for by the Chancellor of his own accord.
The first establishment in Virginia, which became permanent, was made in 1607. I have found no mention of negroes in the colony until about 1650. The first brought here as slaves were by a Dutch ship; after which the English commenced the trade, and continued it until the revolutionary war. That suspended, ipso facto, their further importation for the present, and the business of the war pressing constantly on the legislature, this subject was not acted on finally until the year ‘78, when I brought in a bill to prevent their further importation. This passed without opposition, and stopped the increase of the evil by importation, leaving to future efforts its final eradication.
The first settlers of this colony were Englishmen, loyal subjects to their king and church; and the grant to Sir Walter Raleigh contained an express proviso, that their laws should not be against the true Christian faith, now professed in the church of England.’ As soon as the state of the colony admitted, it was divided into parishes, in each of which was established a minister of the Anglican church, endowed with a fixed salary, in tobacco, a glebe house and land, with the other necessary appendages. To meet these expenses, all the inhabitants of the parishes were assessed, whether they were or not members of the established church. Towards Quakers, who came here, they were most cruelly intolerant, driving them from the colony by the severest penalties. In process of time, however, other sectarisms were introduced, chiefly of the Presbyterian family; and the established clergy, secure for life in their glebes and salaries, adding to these, generally, the emoluments of a classical school, found employment enough in their farms and school-rooms, for the rest of the week, and devoted Sunday only to the edification of their flock, by service, and a sermon at their parish church. Their other pastoral functions were little attended to. Against this inactivity, the zeal and industry of sectarian preachers had an open and undisputed field; and by the time of the revolution, a majority of the inhabitants had become dissenters from the established church, but were still obliged to pay contributions to support the pastors of the minority. This unrighteous compulsion, to maintain teachers of what they deemed religious errors, was grievously felt during the regal government, and without a hope of relief. But the first republican legislature, which met in ‘76, was crowded with petitions to abolish, this spiritual tyranny. These brought on the severest contests in which I have ever been engaged. Our great opponents were Mr. Pendleton and Robert Carter Nicholas; honest men, but zealous churchmen. The petitions were referred to the committee of the whole House on the state of the country; and, after desperate contests in that committee, almost daily, from the 11th of October to the 5th of December, we prevailed so far only, as to repeal the laws, which rendered criminal the maintenance of any religious opinions, the forbearance of repairing to church, or the exercise of any mode of worship: and further, to exempt dissenters from contributions to the support of the established church; and to suspend, only until the next session, levies on the members of the church for the salaries of their own incumbents. For although the majority of our citizens were dissenters, as has been observed, a majority of the legislature were churchmen. Among these, however, were some reasonable and liberal men, who enabled us, on some points, to obtain feeble majorities. But our opponents carried, in the general resolutions of the committee of November 19, a declaration, that religious assemblies ought to be regulated, and that provision ought to be made for continuing the succession of the clergy, and superintending their conduct. And in the bill now passed, was inserted an express reservation of the question, Whether a general assessment should not be established by law, on every one, to the support of the pastor of his choice; or whether all should be left to voluntary contributions: and on this question, debated at every session from ‘76 to ‘79 (some of our dissenting allies, having now secured their particular object, going over to the advocates of a general assessment), we could only obtain a suspension from session to session until ‘79, when the question against a general assessment was finally carried, and the establishment of the Anglican church entirely put down. In justice to the two honest but zealous opponents, who have been named, I must add, that although, from their natural temperaments, they were more disposed generally to acquiesce in things as they are, than to risk innovations; yet, whenever the public will had once decided, none were more faithful or exact in their obedience to it.
The seat of our government had been originally fixed in the peninsula of Jamestown, the first settlement of the colonists; and had been afterwards removed a few miles inland to Williamsburg. But this was at a time when our settlements had not extended beyond the tide waters. Now they had crossed the Allegany; and the centre of population was very far removed from what it had been. Yet Williamsburg was still the depository of our archives, the habitual residence of the Governor, and many other of the public functionaries, the established place for the sessions of the legislature, and the magazine of our military stores: and its situation was so exposed, that it might be taken at any time in war, and, at this time particularly, an enemy might in the night run up either of the rivers, between which it lies, land a force above, and take possession of the place, without the possibility of saving either persons or things. I had proposed its removal so early as October, ‘76; but it did not prevail until the session of May, ‘79.
Early in the session of May, ‘79, I prepared, and obtained leave to bring in a bill, declaring who should be deemed citizens, asserting the natural right of expatriation, and prescribing the mode of exercising it. This, when I withdrew from the house on the 1st of June following, I left in the hands of George Mason, and it was passed on the 26th of that month.
In giving this account of the laws, of which I was myself the mover and draughtsman, I by no means mean to claim to myself the merit of obtaining their passage. I had many occasional and strenuous coadjutors in debate, and one, most steadfast, able, and zealous; who was himself a host. This was George Mason, a man of the first order of wisdom among those who acted on the theatre of the revolution, of expansive mind, profound judgment, cogent in argument, learned in the lore of our former constitution, and earnest for the republican change, on democratic principles. His elocution was neither flowing nor smooth; but his language was strong, his manner most impressive, and strengthened by a dash of biting cynicism, when provocation made it seasonable.
Mr. Wythe, while speaker in the two sessions of 1777, between his return from Congress and his appointment to the Chancery, was an able and constant associate in whatever was before a committee of the whole. His pure integrity, judgment, and reasoning powers gave him great weight. Of him, see more in some notes inclosed in my letter of August 31, 1821, to Mr. John Saunderson. [See Appendix, note A.]
Mr. Madison came into the House in 1776, a new member, and young; which circumstances, concurring with his extreme modesty, prevented his venturing himself in debate before his removal to the Council of State, in November, ‘77. From thence he went to Congress, then consisting of few members. Trained in these successive schools, he acquired a habit of self-possession, which placed at ready command the rich resources of his luminous and discriminating mind, and of his extensive information, and rendered him the first of every assembly afterwards, of which he became a member. Never wandering from his subject into vain declamation, but pursuing it closely, in language pure, classical, and copious, soothing always the feelings of his adversaries by civilities and softness of expression, he rose to the eminent station which he held in the great National Convention of 1787; and in that of Virginia, which followed, he sustained the new constitution in all its parts, bearing off the palm against the logic of George Mason, and the fervid declamation of Mr. Henry. With these consummate powers, was united a pure and spotless virtue, which no calumny has ever attempted to sully. Of the powers and polish of his pen, and of the wisdom of his administration in the highest office of the nation, I need say nothing. They have spoken, and will for ever speak for themselves.
So far we were proceeding in the details of reformation only; selecting points of legislation, prominent in character and principle, urgent, and indicative of the strength of the general pulse of reformation. When I left Congress in ‘76, it was in the persuasion, that our whole code must be reviewed, adapted to our republican form of government, and, now that we had no negatives of Councils, Governors, and Kings to restrain us from doing right, that it should be corrected, in all its parts, with a single eye to reason, and the good of those for whose government it was framed. Early, therefore, in the session of ‘76, to which I returned, I moved and presented a bill for the revision of the laws; which was passed on the 24th of October, and on the 5th of November, Mr. Pendleton, Mr. Wythe, George Mason, Thomas L. Lee, and myself, were appointed a committee to execute the work. We agreed to meet at Fredericksburg to settle the plan of operation, and to distribute the work. We met there accordingly, on the 13th of January, 1777. The first question was, whether we should propose to abolish the whole existing system of laws, and prepare a new and complete Institute, or preserve the general system, and only modify it to the present state of things. Mr. Pendleton, contrary to his usual disposition in favor of ancient things, was for the former proposition, in which he was joined by Mr. Lee. To this it was objected, that to abrogate our whole system would be a bold measure, and probably far beyond the views of the legislature; that they had been in the practice of revising, from time to time, the laws of the colony, omitting the expired, the repealed, and the obsolete, amending only those retained, and probably meant we should now do the same, only including the British statutes as well as our own: that to compose a new Institute, like those of Justinian and Bracton, or that of Blackstone, which was the model proposed by Mr. Pendleton, would be an arduous undertaking, of vast research, of great consideration and judgment; and when reduced to a text, every word of that text, from the imperfection of human language, and its incompetence to express distinctly every shade of idea, would become a subject of question and chicanery, until settled by repeated adjudications; that this would involve us for ages in litigation, and render property uncertain, until, like the statutes of old, every word had been tried and settled by numerous decisions, and by new volumes of reports and commentaries; and that no one of us, probably, would undertake such a work, which, to be systematical, must be the work of one hand. This last was the opinion of Mr. Wythe, Mr. Mason, and myself. When we proceeded to the distribution of the work, Mr. Mason excused himself, as, being no lawyer, he felt himself unqualified for the work, and he resigned soon after. Mr. Lee excused himself on the same ground, and died indeed in a short time. The other two gentlemen, therefore, and myself, divided the work among us. The common law and statutes to the 4 James I. (when our separate legislature was established) were assigned to me; the British statutes, from that period to the present day, to Mr. Wythe; and the Virginia laws to Mr. Pendleton. As the law of Descents, and the Criminal law, fell of course within my portion, I wished the committee to settle the leading principles of these, as a guide for me in framing them; and, with respect to the first, I proposed to abolish the law of primogeniture, and to make real estate descendible in parcenery to the next of kin, as personal property is, by the statute of distribution. Mr. Pendleton wished to preserve the right of primogeniture; but seeing at once that that could not prevail, he proposed we should adopt the Hebrew principle, and give a double portion to the elder son. I observed, that if the elder son could eat twice as much, or do double work, it might be a natural evidence of his right to a double portion; but being on a par, in his powers and wants, with his brothers and sisters, he should be on a par also in the partition of the patrimony; and such was the decision of the other members.
On the subject of the Criminal law, all were agreed, that the punishment of death should be abolished, except for treason and murder; and that, for other felonies, should be substituted hard labor in the public works, and, in some cases, the Lex talionis. How this last revolting principle came to obtain our approbation, I do not remember. There remained, indeed, in our laws, a vestige of it in a single case of a slave; it was the English law, in the time of the Anglo-Saxons, copied probably from the Hebrew law of an ‘eye for an eye, a tooth for a tooth,’ and it was the law of several ancient people; but the modern mind had left it far in the rear of its advances. These points, however, being settled, we repaired to our respective homes for the preparation of the work.
In the execution of my part, I thought it material not to vary the diction of the ancient statutes by modernizing it, nor to give rise to new questions by new expressions. The text of these statutes had been so fully explained and defined, by numerous adjudications, as scarcely ever now to produce a question in our courts. I thought it would be useful, also, in all new draughts, to reform the style of the later British statutes, and of our own acts of Assembly; which, from their verbosity, their endless tautologies, their involutions of case within case, and parenthesis within parenthesis, and their multiplied efforts at certainty, by saids and afore-saids, by ors and by ands, to make them more plain, are really rendered more perplexed and incomprehensible, not only to common readers, but to the lawyers themselves. We were employed in this work from that time to February, 1779, when we met at Williamsburg; that is to say, Mr. Pendleton, Mr. Wythe, and myself; and meeting day by day, we examined critically our several parts, sentence by sentence, scrutinizing and amending, until we had agreed on the whole. We then returned home, had fair copies made of our several parts, which were reported to the General Assembly, June 18, 1779, by Mr. Wythe and myself, Mr. Pendleton’s residence being distant, and he having authorized us by letter to declare his approbation. We had, in this work, brought so much of the Common law as it was thought necessary to alter, all the British statutes from Magna Charta to the present day, and all the laws of Virginia, from the establishment of our legislature in the 4th Jac. I. to the present time, which we thought should be retained, within the compass of one hundred and twenty-six bills, making a printed folio of ninety pages only. Some bills were taken out, occasionally, from time to time, and passed; but the main body of the work was not entered on by the legislature, until after the general peace, in 1785, when, by the unwearied exertions of Mr. Madison, in opposition to the endless quibbles, chicaneries, perversions, vexations, and delays of lawyers and demi-lawyers, most of the bills were passed by the legislature, with little alteration.
The bill for establishing religious freedom, the principles of which had, to a certain degree, been enacted before, I had drawn in all the latitude of reason and right. It still met with opposition; but, with some mutilations in the preamble, it was finally passed; and a singular proposition proved, that its protection of opinion was meant to be universal. Where the preamble declares that coercion is a departure from the plan of the holy author of our religion, an amendment was proposed, by inserting the words ‘Jesus Christ,’ so that it should read, ‘a departure from the plan of Jesus Christ, the holy author of our religion;’ the insertion was rejected by a great majority, in proof that they meant to comprehend, within the mantle of its protection, the Jew and the Gentile, the Christian and Mahometan, the Hindoo, and Infidel of every denomination.
Beccaria, and other writers on crimes and punishments, had satisfied the reasonable world of the unrightfulness and inefficacy of the punishment of crimes by death; and hard labor on roads, canals, and other public works, had been suggested as a proper substitute. The Revisors had adopted these opinions; but the general idea of our country had not yet advanced to that point. The bill, therefore, for proportioning crimes and punishments, was lost in the House of Delegates by a majority of a single vote. I learned afterwards, that the substitute of hard labor in public, was tried (I believe it was in Pennsylvania) without success. Exhibited as a public spectacle, with shaved heads, and mean clothing, working on the high roads, produced in the criminals such a prostration of character, such an abandonment of self-respect, as, instead of reforming, plunged them into the most desperate and hardened depravity of morals and character. To pursue the subject of this law.—I was written to in 1785 (being then in Paris) by Directors appointed to superintend the building of a Capitol in Richmond, to advise them as to a plan, and to add to it one of a Prison. Thinking it a favorable opportunity of introducing into the state an example of architecture, in the classic style of antiquity, and the Maison Quarrée of Nismes, an ancient Roman temple, being considered as the most perfect model existing of what may be called Cubic architecture, I applied to M. Clerissault, who had published drawings of the antiquities of Nismes, to have me a model of the building made in stucco, only changing the order from Corinthian to Ionic, on account of the difficulty of the Corinthian capitals. I yielded, with reluctance, to the taste of Clerissault, in his preference of the modern capital of Scamozzi to the more noble capital of antiquity. This was executed by the artist whom Choiseul Gouffier had carried with him to Constantinople, and employed, while Ambassador there, in making those beautiful models of the remains of Grecian architecture, which are to be seen at Paris. To adapt the exterior to our use, I drew a plan for the interior, with the apartments necessary for legislative, executive, and judiciary purposes; and accommodated in their size and distribution to the form and dimensions of the building. These were forwarded to the Directors, in 1786, and were carried into execution, with some variations, not for the better, the most important of which, however, admit of future correction. With respect to the plan of a Prison, requested at the same time, I had heard of a benevolent society, in England, which had been indulged by the government, in an experiment of the effect of labor, in solitary confinement, on some of their criminals; which experiment had succeeded beyond expectation. The same idea had been suggested in France, and an Architect of Lyons had proposed a plan of a well contrived edifice, on the principle of solitary confinement. I procured a copy, and as it was too large for our purposes, I drew one on a scale less extensive, but susceptible of additions as they should be wanting. This I sent to the Directors, instead of a plan of a common prison, in the hope that it would suggest the idea of labor in solitary confinement, instead of that on the public works, which we had adopted in our Revised Code. Its principle, accordingly, but not its exact form, was adopted by Latrobe in carrying the plan into execution, by the erection of what is now called the Penitentiary, built under his direction. In the mean while, the public opinion was ripening, by time, by reflection, and by the example of Pennsylvania, where labor on the highways had been tried, without approbation, from 1786 to ‘89, and had been followed by their Penitentiary system on the principle of confinement and labor, which was proceeding auspiciously. In 1796, our legislature resumed the subject, and passed the law for amending the Penal laws of the commonwealth. They adopted solitary, instead of public, labor, established a gradation in the duration of the confinement, approximated the style of the law more to the modern usage, and, instead of the settled distinctions of murder and manslaughter, preserved in my bill, they introduced the new terms of murder in the first and second degree. Whether these have produced more or fewer questions of definition, I am not sufficiently informed of our judiciary transactions, to say. I will here, however, insert the text of my bill, with the notes I made in the course of my researches into the subject. [See Appendix, Note E.]
The acts of Assembly concerning the College of William and Mary, were properly within Mr. Pendleton’s portion of the work; but these related chiefly to its revenue, while its constitution, organization, and scope of science, were derived from its charter. We thought that on this subject, a systematical plan of general education should be proposed, and I was requested to undertake it. I accordingly prepared three bills for the Revisal, proposing three distinct grades of education, reaching all classes. 1st. Elementary schools, for all children generally, rich and poor. 2nd. Colleges, for a middle degree of instruction, calculated for the common purposes of life, and such as would be desirable for all who were in easy circumstances. And, 3rd., an ultimate grade for teaching the sciences generally, and in their highest degree. The first bill proposed to lay off every county into Hundreds, or Wards, of a proper size and population for a school, in which reading, writing, and common arithmetic should be taught; and that the whole state should be divided into twenty-four districts, in each of which should be a school for classical learning, grammar, geography, and the higher branches of numerical arithmetic. The second bill proposed to amend the constitution of William and Mary college, to enlarge its sphere of science, and to make it in fact a University. The third was for the establishment of a library. These bills were not acted on until the same year, ‘96, and then only so much of the first as provided for elementary schools. The College of William and Mary was an establishment purely of the Church of England; the Visitors were required to be all of that Church; the Professors to subscribe its Thirty-nine Articles; its Students to learn its Catechism; and one of its fundamental objects was declared to be, to raise up Ministers for that Church. The religious jealousies, therefore, of all the dissenters, took alarm lest this might give an ascendancy to the Anglican sect, and refused acting on that bill. Its local eccentricity, too, and unhealthy autumnal climate, lessened the general inclination towards it. And in the Elementary bill, they inserted a provision which completely defeated it; for they left it to the court of each county to determine for itself, when this act should be carried into execution, within their county. One provision of the bill was, that the expenses of these schools should be borne by the inhabitants of the county, every one in proportion to his general tax rate. This would throw on wealth the education of the poor; and the justices, being generally of the more wealthy class, were unwilling to incur that burthen, and I believe it was not suffered to commence in a single county. I shall recur again to this subject, towards the close of my story, if I should have life and resolution enough to reach that term; for I am already tired of talking about myself.
The bill on the subject of slaves, was a mere digest of the existing laws respecting them, without any intimation of a plan for a future and general emancipation. It was thought better that this should be kept back, and attempted only by way of amendment, whenever the bill should be brought on. The principles of the amendment, however, were agreed on, that is to say, the freedom of all born after a certain day, and deportation at a proper age. But it was found that the public mind would not yet bear the proposition, nor will it bear it even at this day. Yet the day is not distant when it must bear and adopt it, or worse will follow. Nothing is more certainly written in the book of fate, than that these people are to be free; nor is it less certain that the two races, equally free, cannot live in the same government. Nature, habit, opinion, have drawn indelible lines of distinction between them. It is still in our power to direct the process of emancipation and deportation, peaceably, and in such slow degree, as that the evil will wear off insensibly, and their place be, pari passu, filled up by free white laborers. If, on the contrary, it is left to force itself on, human nature must shudder at the prospect held up. We should in vain look for an example in the Spanish deportation or deletion of the Moors. This precedent would fall far short of our case.
I considered four of these bills, passed or reported, as forming a system by which every fibre would be eradicated of ancient or future aristocracy; and a foundation laid for a government truly republican. The repeal of the laws of entail would prevent the accumulation and perpetuation of wealth, in select families, and preserve the soil of the country from being daily more and more absorbed in mortmain. The abolition of primogeniture, and equal partition of inheritances, removed the feudal and unnatural distinctions which made one member of every family rich, and all the rest poor, substituting equal partition, the best of all Agrarian laws. The restoration of the rights of conscience relieved the people from taxation for the support of a religion not theirs; for the establishment was truly of the religion of the rich, the dissenting sects being entirely composed of the less wealthy people; and these, by the bill for a general education, would be qualified to understand their rights, to maintain them, and to exercise with intelligence their parts in self-government: and all this would be effected, without the violation of a single natural right of any one individual citizen. To these, too, might be added, as a further security, the introduction of the trial by jury into the Chancery courts, which have already ingulphed, and continue to ingulph, so great a proportion of the jurisdiction over our property.
On the 1st of June, 1779, I was appointed Governor of the Commonwealth, and retired from the legislature. Being elected, also, one of the Visitors of William and Mary college, a self-electing body, I effected, during my residence in Williamsburg that year, a change in the organization of that institution, by abolishing the Grammar school, and the two professorships of Divinity and Oriental languages, and substituting a professorship of Law and Police, one of Anatomy, Medicine, and Chemistry, and one of Modern Languages; and the charter confining us to six professorships, We added the Law of Nature and Nations, and the Fine Arts, to the duties of the Moral professor, and Natural History to those of the professor of Mathematics and Natural Philosophy.
Being now, as it were, identified with the Commonwealth itself, to write my own history, during the two years of my administration, would be to write the public history of that portion of the revolution within this state. This has been done by others, and particularly by Mr. Girardin, who wrote his Continuation of Burke’s History of Virginia, while at Milton in this neighborhood, had free access to all my papers while composing it, and has given as faithful an account as I could myself. For this portion, therefore, of my own life, I refer altogether to his history. From a belief that, under the pressure of the invasion under which we were then laboring, the public would have more confidence in a military chief, and that the military commander, being invested with the civil power also, both might be wielded with more energy, promptitude, and effect for the defence of the state, I resigned the administration at the end of my second year, and General Nelson was appointed to succeed me.
Soon after my leaving Congress, in September, ‘76, to wit, on the last day of that month, I had been appointed, with Dr. Franklin, to go to France, as a Commissioner to negotiate treaties of alliance and commerce with that government. Silas Deane, then in France, acting as agent for procuring military stores,* was joined with us in commission. But such was the state of my family that I could not leave it, nor could I expose it to the dangers of the sea, and of capture by the British ships, then covering the ocean. I saw, too, that the laboring oar was really at home, where much was to be done, of the most permanent interest, in new-modelling our governments, and much to defend our fanes and fire-sides from the desolations of an invading enemy, pressing on our country in every point. I declined, therefore, and Dr. Lee was appointed in my place. On the 15th of June, 1781, I had been appointed, with Mr. Adams, Dr. Franklin, Mr. Jay, and Mr. Laurens, a Minister Plenipotentiary for negotiating peace, then expected to be effected through the mediation of the Empress of Russia. The same reasons obliged me still to decline; and the negotiation was in fact never entered on. But, in the autumn of the next year, 1782, Congress receiving assurances that a general peace would be concluded in the winter and spring, they renewed my appointment on the 13th of November of that year. I had, two months before that, lost the cherished companion of my life, in whose affections, unabated on both sides, I had lived the last ten years in unchequered happiness. With the public interests, the state of my mind concurred in recommending the change of scene proposed; and I accepted the appointment, and left Monticello on the 19th of December, 1782, for Philadelphia, where I arrived on the 27th. The Minister of France, Luzerne, offered me a passage in the Romulus frigate, which I accepted; but she was then lying a few miles below Baltimore, blocked up in the ice. I remained, therefore, a month in Philadelphia, looking over the papers in the office of State, in order to possess myself of the general state of our foreign relations, and then went to Baltimore, to await the liberation of the frigate from the ice. After waiting there nearly a month, we received information that a Provisional treaty of peace had been signed by our Commissioners on the 3rd of September, 1782, to become absolute, on the conclusion of peace between France and Great Britain. Considering my proceeding to Europe as now of no utility to the public, I returned immediately to Philadelphia, to take the orders of Congress, and was excused by them from further proceeding. I therefore returned home, where I arrived on the 15th of May, 1783.
* His ostensible character was to be that of a merchant, his
real one that of agent for military supplies, and also for
sounding the dispositions of the government of France, and
seeing how far they would favor us, either secretly or
openly. His appointment had been by the Committee of Foreign
Correspondence, March, 1776.
On the 6th of the following month, I was appointed by the legislature a delegate to Congress, the appointment to take place on the 1st of November ensuing, when that of the existing delegation would expire. I accordingly left home on the 16th of October, arrived at Trenton, where Congress was sitting, on the 3rd of November, and took my seat on the 4th, on which day Congress adjourned, to meet at Annapolis on the 26th.
Congress had now become a very small body, and the members very remiss in their attendance on its duties, insomuch that a majority of the states, necessary by the Confederation to constitute a House, even for minor business, did not assemble until the 13th of December.
They, as early as January 7, 1782, had turned their attention to the monies current in the several states, and had directed the Financier, Robert Morris, to report to them a table of rates, at which the foreign coins should be received at the treasury. That officer, or rather his assistant, Gouverneur Morris, answered them on the 15th, in an able and elaborate statement of the denominations of money current in the several states, and of the comparative value of the foreign coins chiefly in circulation with us, He went into the consideration of the necessity of establishing a standard of value with us, and of the adoption of a money unit. He proposed for that unit, such a fraction of pure silver as would be a common measure of the penny of every state, without leaving a fraction. This common divisor he found to be 1/1440 of a dollar, or 1/1600 the crown sterling. The value of a dollar was, therefore, to be expressed by 1440 units, and of a crown by 1600; each unit containing a quarter of a grain of fine silver. Congress turning again their attention to this subject the following year, the Financier, by a letter of April 30,1783, further explained and urged the unit he had proposed: but nothing more was done on it until the ensuing year, when it was again taken up, and referred to a committee, of which I was a member. The general views of the Financier were sound, and the principle was ingenious, on which he proposed to found his unit; but it was too minute for ordinary use, too laborious for computation, either by the head or in figures. The price of a loaf of bread, 1/20 of a dollar, would be 72 units. A pound of butter, 1/5 of a dollar, 288 units. A horse, or bullock, of eighty dollars’ value, would require a notation of six figures, to wit, 115,200, and the public debt, suppose of eighty millions, would require twelve figures, to wit, 115,200,000,000 units. Such a system of money-arithmetic would be entirely unmanageable for the common purposes of society. I proposed, therefore, instead of this, to adopt the Dollar as our unit of account and payment, and that its divisions and subdivisions should be in the decimal ratio. I wrote some Notes on the subject, which I submitted to the consideration of the Financier. I received his answer and adherence to his general system, only agreeing to take for his unit one hundred of those he first proposed, so that a Dollar should be 14 40/100 and a crown 16 units. I replied to this, and printed my Notes and Reply on a flying sheet, which I put into the hands of the members of Congress for consideration, and the Committee agreed to report on my principle. This was adopted the ensuing year, and is the system which now prevails. I insert, here, the Notes and Reply, as showing the different views on which the adoption of our money system hung. [See Appendix, note F.]The divisions into dismes, cents, and mills is now so well understood, that it would be easy of introduction into the kindred branches of weights and measures. I use, when I travel, an Odometer of Clarke’s invention, which divides the mile into cents, and I find every one comprehends a distance readily, when stated to him in miles and cents; so he would in feet and cents, pounds and cents, &c.
The remissness of Congress, and their permanent session began to be a subject of uneasiness; and even some of the legislatures had recommended to them intermissions, and periodical sessions. As the Confederation had made no provision for a visible head of the government, during vacations of Congress, and such a one was necessary to superintend the executive business, to receive and communicate with foreign ministers and nations, and to assemble Congress on sudden and extraordinary emergencies, I proposed, early in April, the appointment of a committee, to be called the ‘Committee of the States,’ to consist of a member from each state, who should remain in session during the recess of Congress: that the functions of Congress should be divided into executive and legislative, the latter to be reserved, and the former, by a general resolution, to be delegated to that Committee. This proposition was afterwards agreed to; a Committee appointed who entered on duty on the subsequent adjournment of Congress, quarrelled very soon, split into two parties, abandoned their post, and left the government without any visible head, until the next meeting of Congress. We have since seen the same thing take place, in the Directory of France; and I believe it will for ever take place in any Executive consisting of a plurality. Our plan, best, I believe, combines wisdom and practicability, by providing a plurality of Counsellors, but a single Arbiter for ultimate decision. I was in France when we heard of this schism and separation of our Committee, and, speaking with Dr. Franklin of this singular disposition of men to quarrel, and divide into parties, he gave his sentiments, as usual, by way of Apologue. He mentioned the Eddystone light-house, in the British channel, as being built on a rock, in the mid-channel, totally inaccessible in winter, from the boisterous character of that sea, in that season; that, therefore, for the two keepers employed to keep up the lights, all provisions for the winter were necessarily carried to them in autumn, as they could never be visited again till the return of the milder season; that, on the first practicable day in the spring, a boat put off to them with fresh supplies. The boatmen met at the door one of the keepers, and accosted him with a ‘How goes it, friend?’ ‘Very well.’ ‘How is your companion?’ ‘I do not know.’ ‘Don’t know? Is not he here?’ ‘I can’t tell.’ ‘Have not you seen him to-day?’ ‘No.’ ‘When did you see him?’ ‘Not since last fall.’ ‘You have killed him?’ ‘Not I, indeed.’ They were about to lay hold of him, as having certainly murdered his companion; but he desired them to go up stairs and examine for themselves. They went up, and there found the other keeper. They had quarrelled, it seems, soon after being left there, had divided into two parties, assigned the cares below to one, and those above to the other, and had never spoken to, or seen, one another since.
But to return to our Congress at Annapolis. The definitive treaty of peace which had been signed at Paris on the 3rd of September, 1783, and received here, could not be ratified without a House of nine states. On the 23rd of December, therefore, we addressed letters to the several Governors, stating the receipt of the definitive treaty; that seven states only were in attendance, while nine were necessary to its ratification; and urging them to press on their delegates the necessity of their immediate attendance. And on the 26th, to save time, I moved that the Agent of Marine (Robert Morris) should be instructed to have ready a vessel at this place, at New York, and at some Eastern port, to carry over the ratification of the treaty when agreed to. It met the general sense of the House, but was opposed by Dr. Lee, on the ground of expense, which it would authorize the Agent to incur for us; and, he said, it would be better to ratify at once, and send on the ratification. Some members had before suggested, that seven states were competent to the ratification. My motion was therefore postponed, and another brought forward by Mr. Read, of South Carolina, for an immediate ratification. This was debated the 26th and 27th. Read, Lee, Williamson, and Jeremiah Chase urged that ratification was a mere matter of form; that the treaty was conclusive from the moment it was signed by the ministers; that, although the Confederation requires the assent of nine states to enter into a treaty, yet, that its conclusion could not be called the entrance into it; that supposing nine states requisite, it would be in the power of five states to keep us always at war; that nine states had virtually authorized the ratification, having ratified the provisional treaty, and instructed their ministers to agree to a definitive one in the same terms, and the present one was, in fact, substantially, and almost verbatim, the same; that there now remain but sixty-seven days for the ratification, for its passage across the Atlantic, and its exchange; that there was no hope of our soon having nine states present in fact, that this was the ultimate point of time to which we could venture to wait; that if the ratification was not in Paris by the time stipulated, the treaty would become void; that if ratified by seven states, it would go under our seal, without its being known to Great Britain that only seven had concurred; that it was a question of which they had no right to take cognizance, and we were only answerable for it to our constituents; that it was like the ratification which Great Britain had received from the Dutch, by the negotiations of Sir William Temple.
On the contrary, it was argued by Monroe, Gerry, Howel, Ellery, and myself, that by the modern usage of Europe, the ratification was considered as the act which gave validity to a treaty, until which, it was not obligatory.* That the commission to the ministers, reserved the ratification to Congress; that the treaty itself stipulated, that it should be ratified; that it became a second question, who were competent to the ratification? That the Confederation expressly required nine states to enter into any treaty; that, by this, that instrument must have intended, that the assent of nine states should be necessary, as well to the completion as to the commencement of the treaty, its object having been to guard the rights of the Union in all those important cases, where nine states are called for; that by the contrary construction, seven states, containing less than one third of our whole citizens, might rivet on us a treaty, commenced indeed under commission and instructions from nine states, but formed by the minister in express contradiction to such instructions, and in direct sacrifice of the interests of so great a majority; that the definitive treaty was admitted not to be a verbal copy of the provisional one, and whether the departures from it were of substance, or not, was a question on which nine states alone were competent to decide; that the circumstances of the ratification of the provisional articles by nine states, the instructions to our ministers to form a definitive one by them, and their actual agreement in substance, do not render us competent to ratify in the present instance; if these circumstances are in themselves a ratification, nothing further is requisite than to give attested copies of them, in exchange for the British ratification; if they are not, we remain where we were, without a ratification by nine states, and incompetent ourselves to ratify; that it was but four days since the seven states, now present, unanimously concurred in a resolution to be forwarded to the Governors of the absent states, in which they stated, as a cause for urging on their delegates, that nine states were necessary to ratify the treaty; that in the case of the Dutch ratification, Great Britain had courted it, and therefore was glad to accept it as it was; that they knew our Constitution, and would object to a ratification by seven; that, if that circumstance was kept back, it would be known hereafter, and would give them ground to deny the validity of a ratification, into which they should have been surprised and cheated, and it would be a dishonorable prostitution of our seal; that there is a hope of nine states; that if the treaty would become null, if not ratified in time, it would not be saved by an imperfect ratification; but that, in fact, it would not be null, and would be placed on better ground, going in unexceptionable form, though a few days too late, and rested on the small importance of this circumstance, and the physical impossibilities which had prevented a punctual compliance in point of time; that this would be approved by all nations, and by Great Britain herself, if not determined to renew the war, and if so determined, she would never want excuses, were this out of the way. Mr. Read gave notice, he should call for the yeas and nays; whereon those in opposition, prepared a resolution, expressing pointedly the reasons of their dissent from his motion. It appearing, however, that his proposition could not be carried, it was thought better to make no entry at all. Massachusetts alone would have been for it; Rhode Island, Pennsylvania, and Virginia against it, Delaware, Maryland, and North Carolina, would have been divided.
Our body was little numerous, but very contentious. Day after day was wasted on the most unimportant questions. A member, one of those afflicted with the morbid rage of debate, of an ardent mind, prompt imagination, and copious flow of words, who heard with impatience any logic which was not his own, sitting near me on some occasion of a trifling but wordy debate, asked me how I could sit in silence, hearing so much false reasoning, which a word should refute? I observed to him, that to refute indeed was easy, but to silence impossible; that in measures brought forward by myself, I took the laboring oar, as was incumbent on me; but that in general, I was willing to listen; that if every sound argument or objection was used by some one or other of the numerous debaters, it was enough; if not, I thought it sufficient to suggest the omission, without going into a repetition of what had been already said by others: that this was a waste and abuse of the time and patience of the House, which could not be justified. And I believe, that if the members of deliberate bodies were to observe this course generally, they would do in a day, what takes them a week; and it is really more questionable, than may at first be thought, whether Bonaparte’s dumb legislature, which said nothing, and did much, may not be preferable to one which talks much, and does nothing. I served with General Washington in the legislature of Virginia, before the revolution, and, during it, with Dr. Franklin in Congress. I never heard either of them speak ten minutes at a time, nor to any but the main point, which was to decide the question. They laid their shoulders to the great points, knowing that the little ones would follow of themselves. If the present Congress errs in too much talking, how can it be otherwise, in a body to which the people send one hundred and fifty lawyers, whose trade it is, to question every thing, yield nothing, and talk by the hour? That one hundred and fifty lawyers should do business together, ought not to be expected. But to return again to our subject.
Those, who thought seven states competent to the ratification, being very restless under the loss of their motion, I proposed, on the third of January, to meet them on middle ground, and therefore moved a resolution, which premised, that there were but seven states present, who were unanimous for the ratification, but that they differed in opinion on the question of competency; that those however in the negative, were unwilling, that any powers which it might be supposed they possessed, should remain unexercised for the restoration of peace, provided it could be done, saving their good faith, and without importing any opinion of Congress, that seven states were competent, and resolving that the treaty be ratified so far as they had power; that it should be transmitted to our ministers, with instructions to keep it uncommunicated; to endeavor to obtain three months longer for exchange of ratifications; that they should be informed, that so soon as nine states shall be present, a ratification by nine shall be sent them: if this should get to them before the ultimate point of time for exchange, they were to use it, and not the other; if not, they were to offer the act of the seven states in exchange, informing them the treaty had come to hand while Congress was not in session, that but seven states were as yet assembled, and these had unanimously concurred in the ratification. This was debated on the third and fourth; and on the fifth, a vessel being to sail for England, from this port, (Annapolis), the House directed the President to write to our ministers accordingly.
January 14. Delegates from Connecticut having attended yesterday, and another from South Carolina coming in this day, the treaty was ratified without a dissenting voice; and three instruments of ratification were ordered to be made out, one of which was sent by Colonel Harmer, another by Colonel Franks, and the third transmitted to the Agent of Marine, to be forwarded by any good opportunity.
Congress soon took up the consideration of their foreign relations. They deemed it necessary to get their commerce placed, with every nation, on a footing as favorable as that of other nations; and for this purpose, to propose to each a distinct treaty of commerce. This act too would amount to an acknowledgment, by each, of our independence, and of our reception into the fraternity of nations; which, although as possessing our station of right, and, in fact, we would not condescend to ask, we were not unwilling to furnish opportunities for receiving their friendly salutations and welcome. With France, the United Netherlands, and Sweden, we had already treaties of commerce; but commissions were given for those countries also, should any amendments be thought necessary. The other states to which treaties were to be proposed, were England, Hamburg, Saxony, Prussia, Denmark, Russia, Austria, Venice, Rome, Naples, Tuscany, Sardinia, Genoa, Spain, Portugal, the Porte, Algiers, Tripoli, Tunis, and Morocco.
On the 7th of May, Congress resolved that a Minister Plenipotentiary should be appointed, in addition to Mr. Adams and Dr. Franklin, for negotiating treaties of commerce with foreign nations, and I was elected to that duty. I accordingly left Annapolis on the 11th, took with me my eldest daughter; then at Philadelphia (the two others being too young for the voyage), and proceeded to Boston, in quest of a passage. While passing through the different states, I made a point of informing myself of the state of the commerce of each, went on to New Hampshire with the same view, and returned to Boston. Thence I sailed on the 5th of July, in the Ceres, a merchant ship of Mr. Nathaniel Tracy, bound to Cowes. He was himself a passenger, and, after a pleasant voyage of nineteen days, from land to land, we arrived at Cowes on the 26th. I was detained there a few days by the indisposition of my daughter. On the 30th we embarked for Havre, arrived there on the 31st, left it on the 3rd of August, and arrived at Paris on the 6th. I called immediately on Dr. Franklin, at Passy, communicated to him our charge, and we wrote to Mr. Adams, then at the Hague, to join us at Paris.
Before I had left America, that is to say, in the year 1781, 1 had received a letter from M. de Marbois, of the French legation in Philadelphia, informing me, he had been instructed by his government to obtain such statistical accounts of the different states of our Union, as might be useful for their information; and addressing to me a number of queries relative to the state of Virginia. I had always made it a practice, whenever an opportunity occurred of obtaining any information of our country, which might be of use to me in any station, public or private, to commit it to writing. These memoranda were on loose papers, bundled up without order, and difficult of recurrence, when I had occasion for a particular one. I thought this a good occasion to embody their substance, which I did in the order of Mr. Marbois’ queries, so as to answer his wish, and to arrange them for my own use. Some friends, to whom they were occasionally communicated, wished for copies; but their volume rendering this too laborious by hand, I proposed to get a few printed for their gratification. I was asked such a price however, as exceeded the importance of the object. On my arrival at Paris, I found it could be done for a fourth of what I had been asked here. I therefore corrected and enlarged them, and had two hundred copies printed, under the title of ‘Notes on Virginia.’ I gave a very few copies to some particular friends in Europe, and sent the rest to my friends in America. An European copy, by the death of the owner, got into the hands of a bookseller, who engaged its translation, and when ready for the press, communicated his intentions and manuscript to me, suggesting that I should correct it, without asking any other permission for the publication. I never had seen so wretched an attempt at translation. Interverted, abridged, mutilated, and often reversing the sense of the original, I found it a blotch of errors from beginning to end. I corrected some of the most material, and, in that form, it was printed in French. A London bookseller, on seeing the translation, requested me to permit him to print the English original. I thought it best to do so, to let the world see that it was not really so bad as the French translation had made it appear. And this is the true history of that publication.
Mr. Adams soon joined us at Paris, and our first employment was to prepare a general form, to be proposed to such nations as were disposed to treat with us. During the negotiations for peace with the British Commissioner, David Hartley, our Commissioners had proposed, on the suggestion of Dr. Franklin, to insert an article, exempting from capture by the public or private armed ships, of either belligerent, when at war, all merchant vessels and their cargoes, employed merely in carrying on the commerce between nations. It was refused by England, and unwisely, in my opinion. For, in the case of a war with us, their superior commerce places infinitely more at hazard on the ocean, than ours; and, as hawks abound in proportion to game, so our privateers would swarm, in proportion to the wealth exposed to their prize, while theirs would be few, for want of subjects of capture. We inserted this article in our form, with a provision against the molestation of fishermen, husbandmen, citizens unarmed, and following their occupations in unfortified places, for the humane treatment of prisoners of war, the abolition of contraband of war, which exposes merchant vessels to such vexatious and ruinous detentions and abuses; and for the principle of free bottoms, free goods.
In a conference with the Count de Vergennes, it was thought better to leave to legislative regulation, on both sides, such modifications of our commercial intercourse, as would voluntarily flow from amicable dispositions. Without urging, we sounded the ministers of the several European nations, at the court of Versailles, on their dispositions towards mutual commerce, and the expediency of encouraging it by the protection of a treaty. Old Frederic, of Prussia, met us cordially, and without hesitation, and appointing the Baron de Thulemeyer, his minister at the Hague, to negotiate with us, we communicated to him our Projet, which, with little alteration by the King, was soon concluded. Denmark and Tuscany entered also into negotiations with us. Other powers appearing indifferent, we did not think it proper to press them. They seemed, in fact, to know little about us, but as rebels, who had been successful in throwing off the yoke of the mother country. They were ignorant of our commerce, which had been always monopolized by England, and of the exchange of articles it might offer advantageously to both parties. They were inclined, therefore, to stand aloof, until they could see better what relations might be usefully instituted with us. The negotiations, therefore, begun with Denmark and Tuscany, we protracted designedly, until our powers had expired; and abstained from making new propositions to others having no colonies; because our commerce being an exchange of raw for wrought materials, is a competent price for admission into the colonies of those possessing them; but were we to give it, without price, to others, all would claim it, without price, on the ordinary ground of gentis amicissimæ.
Mr. Adams, being appointed Minister Plenipotentiary of the United States to London, left us in June, and in July, 1785, Dr. Franklin returned to America, and I was appointed his successor at Paris. In February, 1786, Mr. Adams wrote to me, pressingly, to join him in London immediately, as he thought he discovered there some symptoms of better disposition towards us. Colonel Smith, his secretary of legation, was the bearer of his urgencies for my immediate attendance. I, accordingly, left Paris on the 1st of March, and, on my arrival in London, we agreed on a very summary form of treaty, proposing an exchange of citizenship for our citizens, our ships, and our productions generally, except as to office. On my presentation, as usual, to the King and Queen, at their levees, it was impossible for any thing to be more ungracious, than their notice of Mr. Adams and myself. I saw, at once, that the ulcerations of mind in that quarter left nothing to be expected on the subject of my attendance; and, on the first conference with the Marquis of Caermarthen, the Minister for foreign affairs, the distance and disinclination which he betrayed in his conversation, the vagueness and evasions of his answers to us, confirmed me in the belief of their aversion to have any thing to do with us. We delivered him, however, our Projet, Mr. Adams not despairing as much as I did of its effect. We afterwards, by one or more, notes, requested his appointment of an interview and conference, which, without directly declining, he evaded, by pretence of other pressing occupations for the moment. After staying there seven weeks, till within a few days of the expiration of our commission, I informed the minister, by note, that my duties at Paris required my return to that place, and that I should, with pleasure, be the bearer of any commands to his Ambassador there. He answered, that he had none, and, wishing me a pleasant journey, I left London the 26th, and arrived at Paris the 30th of April.
While in London, we entered into negotiations with the Chevalier Pinto, Ambassador of Portugal, at that place. The only article of difficulty between us was, a stipulation that our bread-stuff should be received in Portugal, in the form of flour as well as of grain. He approved of it himself, but observed that several nobles, of great influence at their court, were the owners of windmills in the neighborhood of Lisbon, which depended much for their profits on manufacturing our wheat, and that this stipulation would endanger the whole treaty. He signed it, however, and its fate was what he had candidly portended.
My duties, at Paris, were confined to a few objects; the receipt of our whale-oils, salted fish, and salted meats, on favorable terms; the admission of our rice on equal terms with that of Piedmont, Egypt, and the Levant; a mitigation of the monopolies of our tobacco by the farmers-general, and a free admission of our productions into their islands, were the principal commercial objects which required attention; and on these occasions, I was powerfully aided by all the influence and the energies of the Marquis de la Fayette, who proved himself equally zealous for the friendship and welfare of both nations; and, in justice, I must also say, that I found the government entirely disposed to befriend us on all occasions, and to yield us every indulgence, not absolutely injurious to themselves. The Count de Vergennes had the reputation with the diplomatic corps, of being wary and slippery in his diplomatic intercourse; and so he might be, with those whom he knew to be slippery, and double-faced themselves. As he saw that I had no indirect views, practised no subtleties, meddled in no intrigues, pursued no concealed object, I found him as frank, as honorable, as easy of access to reason, as any man with whom I had ever done business; and I must say the same for his successor, Montmorin, one of the most honest and worthy of human beings.
Our commerce, in the Mediterranean, was placed under early alarm, by the capture of two of our vessels and crews by the Barbary cruisers. I was very unwilling that we should acquiesce in the European humiliation, of paying a tribute to those lawless pirates, and endeavored to form an association of the powers subject to habitual depredations from them. I accordingly prepared, and proposed to their Ministers at Paris, for consultation with their governments, articles of a special confederation, in the following form.
‘Proposals for concerted operation among the powers at war with the piratical States of Barbary.
‘1. It is proposed, that the several powers at war with the piratical States of Barbary, or any two or more of them who shall be willing, shall enter into a convention to carry on their operations against those States, in concert, beginning with the Algerines.
‘2. This convention shall remain open to any other power, who shall, at any future time, wish to accede to it; the parties reserving the right to prescribe the conditions of such accession, according to the circumstances existing at the time it shall be proposed.
‘3. The object of the convention shall be to compel the piratical States to perpetual peace, without price, and to guaranty that peace to each other.
‘4. The operations for obtaining this peace shall be constant cruises on their coast, with a naval force now to be agreed on. It is not proposed, that this force shall be so considerable, as to be inconvenient to any party. It is believed, that half a dozen frigates, with as many tenders or xebecs, one half of which shall be in cruise, while the other half is at rest, will suffice.
‘5. The force agreed to be necessary, shall be furnished by the parties, in certain quotas, now to be fixed; it being expected, that each will be willing to contribute, in such proportion as circumstances may render reasonable.
‘6. As miscarriages often proceed from the want of harmony among officers of different nations, the parties shall now consider and decide, whether it will not be better to contribute their quotas in money, to be employed in fitting out and keeping on duty a single fleet of the force agreed on.
‘7. The difficulties and delays, too, which will attend the management of these operations, if conducted by the parties themselves separately, distant as their courts may be from one another, and incapable of meeting in consultation, suggest a question, whether it will not be better for them to give full powers, for that purpose, to their Ambassadors, or other Ministers resident at some one court of Europe, who shall form a Committee, or Council, for carrying this convention into effect; wherein, the vote of each member shall be computed in proportion to the quota of his sovereign, and the majority so computed, shall prevail in all questions within the view of this convention. The court of Versailles is proposed, on account of its neighborhood to the Mediterranean, and because all those powers are represented there, who are likely to become parties to this convention.
‘8. To save to that Council the embarrassment of personal solicitations for office, and to assure the parties, that their contributions will be applied solely to the object for which they are destined, there shall be no establishment of officers for the said Council, such as Commissioners, Secretaries, or any other kind, with either salaries or perquisites, nor any other lucrative appointments, but such whose functions are to be exercised on board the said vessels.
‘9. Should war arise between any two of the parties to this convention, it shall not extend to this enterprise, nor interrupt it; but as to this, they shall be reputed at peace.
‘10. When Algiers shall be reduced to peace, the other piratical States, if they refuse to discontinue their piracies, shall become the objects of this convention, either successively or together, as shall seem best.
‘11. Where this convention would interfere with treaties actually existing between any of the parties and the said States of Barbary, the treaty shall prevail, and such party shall be allowed to withdraw from the operations against that state.’
Spain had just concluded a treaty with Algiers, at the expense of three millions of dollars, and did not like to relinquish the benefit of that, until the other party should fail in their observance of it. Portugal, Naples, the Two Sicilies, Venice, Malta, Denmark, and Sweden were favorably disposed to such an association; but their representatives at Paris expressed apprehensions that France would interfere, and, either openly or secretly, support the Barbary powers; and they required, that I should ascertain the dispositions of the Count de Vergennes on the subject. I had before taken occasion to inform him of what we were proposing, and, therefore, did not think it proper to insinuate any doubt of the fair conduct of his government; but stating our propositions, I mentioned the apprehensions entertained by us that England would interfere in behalf of those piratical governments. ‘She dares not do it,’ said he. I pressed it no further. The other Agents were satisfied with this indication of his sentiments, and nothing was now wanting to bring it into direct and formal consideration, but the assent of our government, and their authority to make the formal proposition. I communicated to them the favorable prospect of protecting our commerce from the Barbary depredations, and for such a continuance of time, as, by an exclusion of them from the sea, to change their habits and characters, from a predatory to an agricultural people: towards which, however, it was expected they would contribute a frigate, and its expenses, to be in constant cruise. But they were in no condition to make any such engagement. Their recommendatory powers for obtaining contributions, were so openly neglected by the several states, that they declined an engagement, which they were conscious they could not fulfil with punctuality; and so it fell through.
[In the original MS., the paragraph ending with ‘fell
through,’ terminates page 81; between this page and the
next, there is stitched in a leaf of old writing,
constituting a memorandum, whereof note G, in the Appendix,
is a copy.]
In 1786, while at Paris, I became acquainted with John Ledyard, of Connecticut, a man of genius, of some science, and of fearless courage and enterprise. He had accompanied Captain Cook in his voyage to the Pacific, had distinguished himself on several occasions by an unrivalled intrepidity, and published an account of that voyage, with details unfavorable to Cook’s deportment towards the savages, and lessening our regrets at his fate; Ledyard had come to Paris, in the hope of forming a company to engage in the fur-trade of the Western coast of America. He was disappointed in this, and being out of business, and of a roaming, restless character, I suggested to him the enterprise of exploring the Western part of our continent, by passing through St. Petersburg to Kamtschatka, and procuring a passage thence in some of the Russian vessels to Nootka sound, whence he might make his way across the continent to the United States; and I undertook to have the permission of the Empress of Russia solicited. He eagerly embraced the proposition, and M. de Semoulin, the Russian Ambassador, and more particularly Baron Grimm, the special correspondent of the Empress, solicited her permission for him to pass through her dominions, to the Western coast of America. And here I must correct a material error, which I have committed in another place, to the prejudice of the Empress. In writing some notes of the life of Captain Lewis, prefixed to his ‘Expedition to the Pacific,’ I stated, that the Empress gave the permission asked, and afterwards retracted it. This idea, after a lapse of twenty-six years, had so insinuated itself into my mind, that I committed it to paper, without the least suspicion of error. Yet I find, on returning to my letters of that date, that the Empress refused permission at once, considering the enterprise as entirely chimerical. But Ledyard would not relinquish it, persuading himself, that, by proceeding to St. Petersburg, he could satisfy the Empress of its practicability, and obtain her permission. He went accordingly, but she was absent on a visit to some distant part of her dominions, and he pursued his course to within two hundred miles of Kamtschatka, where he was overtaken by an arrest from the Empress, brought back to Poland, and there dismissed. I must, therefore, in justice, acquit the Empress of ever having for a moment countenanced, even by the indulgence of an innocent passage through her territories, this interesting enterprise.
The pecuniary distresses of France produced this year a measure, of which there had been no example for near two centuries; and the consequences of which, good and evil, are not yet calculable. For its remote causes, we must go a little back.
Celebrated writers of France and England had already sketched good principles on the subject of government: yet the American Revolution seems first to have awakened the thinking part of the French nation in general from the sleep of despotism in which they were sunk. The officers, too, who had been to America, were mostly young men, less shackled by habit and prejudice, and more ready to assent to the suggestions of common sense, and feeling of common rights, than others. They came back with new ideas and impressions. The press, notwithstanding its shackles, began to disseminate them; conversation assumed new freedoms; politics became the theme of all societies, male and female, and a very extensive and zealous party was formed, which acquired the appellation of the Patriotic party, who, sensible of the abusive government under which they lived, sighed for occasions for reforming it. This party comprehended all the honesty of the kingdom, sufficiently at leisure to think, the men of letters, the easy Bourgeois, the young nobility, partly from reflection, partly from mode; for these sentiments became matter of mode, and, as such, united most of the young women to the party. Happily for the nation, it happened, at the same moment, that the dissipations of the queen and court, the abuses of the pension-list, and dilapidations in the administration of every branch of the finances, had exhausted the treasures and credit of the nation, insomuch, that its most necessary functions were paralyzed. To reform these abuses would have overset the Minister; to impose new taxes by the authority of the king, was known to be impossible, from the determined opposition of the Parliament to their enregistry. No resource remained, then, but to appeal to the nation. He advised, therefore, the call of an Assembly of the most distinguished characters of the nation, in the hope, that, by promises of various and valuable improvements in the organization and regimen of the government, they would be induced to authorize new taxes, to control the opposition of the Parliament, and to raise the annual revenue to the level of expenditures. An Assembly of Notables, therefore, about one hundred and fifty in number, named by the King, convened on the 22nd of February. The Minister (Calonne) stated to them, that the annual excess of expenses beyond the revenue, when Louis XVI. came to the throne, was thirty-seven millions of livres; that four hundred and forty millions had been borrowed to re-establish the navy; that the American war had cost them fourteen hundred and forty millions (two hundred and fifty-six millions of dollars), and that the interest of these sums, with other increased expenses, had added forty millions more to the annual deficit. (But a subsequent and more candid estimate made it fifty-six millions.) He proffered them an universal redress of grievances, laid open those grievances fully, pointed out sound remedies, and, covering his canvass with objects of this magnitude, the deficit dwindled to a little accessory, scarcely attracting attention. The persons chosen, were the most able and independent characters in the kingdom, and their support, if it could be obtained, would be enough for him. They improved the occasion for redressing their grievances, and agreed that the public wants should be relieved; but went into an examination of the causes of them. It was supposed that Calonne was conscious that his accounts could not bear examination; and it was said, and believed, that he asked of the King, to send four members to the Bastile, of whom the Marquis de la Fayette was one, to banish twenty others, and two of his Ministers. The King found it shorter to banish him. His successor went on in full concert with the Assembly. The result was an augmentation of the revenue, a promise of economies in its expenditure, of an annual settlement of the public accounts before a council, which the Comptroller, having been heretofore obliged to settle only with the King in person, of course never settled at all; an acknowledgment that the King could not lay a new tax, a reformation of the Criminal laws, abolition of torture, suppression of corvees, reformation of the gabelles, removal of the interior custom-houses, free commerce of grain, internal and external, and the establishment of Provincial Assemblies; which, altogether, constituted a great mass of improvement in the condition of the nation. The establishment of the Provincial Assemblies was, in itself, a fundamental improvement. They would be, of the choice of the people, one third renewed every year, in those provinces where there are no states, that is to say, over about three fourths of the kingdom. They would be partly an Executive themselves, and partly an Executive Council to the Intendant, to whom the executive power, in his province, had been heretofore entirely delegated. Chosen by the people, they would soften the execution of hard laws, and, having a right of representation to the King, they would censure bad laws, suggest good ones, expose abuses, and their representations, when united, would command respect. To the other advantages, might be added the precedent itself of calling the Assemblée des Notables, which would perhaps grow into habit. The hope was, that the improvements thus promised would be carried into effect; that they would be maintained during the present reign, and that that would be long enough for them to take some root in the constitution, so that they might come to be considered as a part of that, and be protected by time, and the attachment of the nation.
The Count de Vergennes had died a few days before the meeting of the Assembly, and the Count de Montmorin had been named Minister of foreign affairs, in his place. Villedeuil succeeded Calonne, as Comptroller General, and Lomenie de Brienne, Archbishop of Toulouse, afterwards of Sens, and ultimately Cardinal Lomenie, was named Minister principal, with whom the other Ministers were to transact the business of their departments, heretofore done with the King in person; and the Duke de Nivernois, and M. de Malesherbes, were called to the Council. On the nomination of the Minister principal, the Marshals de Segur and de Castries retired from the departments of War and Marine, unwilling to act subordinately, or to share the blame of proceedings taken out of their direction. They were succeeded by the Count de Brienne, brother of the Prime Minister, and the Marquis de la Luzerne, brother to him who had been Minister in the United States.
A dislocated wrist, unsuccessfully set, occasioned advice from my surgeon, to try the mineral waters of Aix, in Provence, as a corroborant. I left Paris for that place therefore, on the 28th of February, and proceeded up the Seine, through Champagne and Burgundy, and down the Rhone through the Beaujolais by Lyons, Avignon, Nismes, to Aix; where, finding on trial no benefit from the waters, I concluded to visit the rice country of Piedmont, to see if any thing might be learned there, to benefit the rivalship of our Carolina rice with that, and thence to make a tour of the seaport towns of France, along its Southern and Western coast, to inform myself, if any thing could be done to favor our commerce with them. From Aix, therefore, I took my route by Marseilles, Toulon, Hieres, Nice, across the Col de Tende, by Coni, Turin, Vercelli, Novara, Milan, Pavia, Novi, Genoa. Thence, returning along the coast by Savona. Noli, Albenga, Oneglia, Monaco, Nice, Antibes, Frejus, Aix, Marseilles, Avignon, Nismes, Montpellier, Frontignan, Sette, Agde, and along the canal of Languedoc, by Beziers, Narbonne, Carcassonne, Castelnaudari, through the Souterrain of St. Feriol, and back by Castelnaudari, to Toulouse; thence to Montauban, and down the Garonne by Langon to Bordeaux. Thence to Rochefort, la Rochelle, Nantes, L’Orient; then back by Rennes to Nantes, and up the Loire by Angers, Tours, Amboise, Blois, to Orleans, thence direct to Paris, where I arrived on the 10th of June. Soon after my return from this journey, to wit, about the latter part of July, I received my younger daughter, Maria, from Virginia, by the way of London, the youngest having died some time before.
The treasonable perfidy of the Prince of Orange, Stadtholder and Captain General of the United Netherlands, in the war which England waged against them, for entering into a treaty of commerce with the United States, is known to all. As their Executive officer, charged with the conduct of the war, he contrived to baffle all the measures of the States General, to dislocate all their military plans, and played false into the hands of England against his own country, on every possible occasion, confident in her protection, and in that of the King of Prussia, brother to his Princess. The States General, indignant at this patricidal conduct, applied to France for aid, according to the stipulations of the treaty, concluded with her in ‘85. It was assured to them readily, and in cordial terms, in a letter from the Count de Vergennes, to the Marquis de Verac, Ambassador of France at the Hague, of which the following is an extract.
‘Extrait de la dépêche de Monsieur le Comte de Vergennes à Monsieur le Marquis de Verac, Ambassadeurde France à la Haye, du ler Mars, 1786.
‘Le Roi concourrera, autant qu’il sera en son pouvoir, au succès de la chose, et vous inviterez, de sa part, les Patriotes de lui communiquer leurs vues, leurs plans, et leurs envies. Vous les assurerez, que le roi prend un interêt véritable à leurs personnes cornme à leur cause, et qu’ils peuvent compter sur sa protection. Us doivent y compter d’autant plus, Monsieur, que nous ne dissimulons pas, que si Monsieur le Stadtholder reprend son ancienne influence, le système Anglois ne tardera pas de prévaloir, et que notre alliance deviendroit un être de raison. Les Patriotes sentiront facilement, que cette position seroit incompatible avec la dignité, comme avec la considération de sa Majesté. Mais dans le cas, Monsieur, ou les chefs des Patriotes auroient à craindre une scission, ils auroient le temps suffisant peur ramener ceux de leurs amis, que les Anglomanes ont égarés, et préparer les choses, de maniere que la question de nouveau mise en délibération, soit decidée selon leurs desirs. Dans cette hypothèse, le roi vous autorise à agir de concert avec eux, de suivre la direction qu’ils jugeront devoir vous donner, et d’employer tous les moyens pour augmenter le nombre des partisans de la bonne cause. Il me reste, Monsieur, de vous parler de la sureté personelle des Patriotes. Vous les assurerez, que dans tout état de cause, le roi les prend sous sa protection immédiate, et vous ferez connoître, partout où vous le jugerez nécessaire, que sa Majesté regarderoit comme une offense personelle, tout ce qu’on entreprenderoit contre leur liberté. Il est á presumer que ce langage, tenu avec énergie, en imposera á l’audace des Anglomanes, et que Monsieur le Prince de Nassau croira courir quelque risque en provoquant le ressentiment de sa Majesté.’ *
[*Extract from the despatch of the Count de Vergennes, to
the Marquis de Verac, Ambassador from France, at the Hague,
dated March 1, 1788.
‘The King will give his aid, as far as may be in his power,
towards the success of the affair, and you will, on his
part, invite the Patriots to communicate to him their views,
their plans, and their discontents. You may assure them,
that the King takes a real interest in themselves, as well
as their cause, and that they may rely upon his protection.
On this they may place the greater dependence, as we do not
conceal, that if the Stadtholder resumes his former
influence, the English system will soon prevail, and our
alliance become a mere affair of the imagination. The
Patriots will readily feel, that this position would be
incompatible both with the dignity and consideration of his
Majesty. But in case the chief of the Patriots should have
to fear a division, they would have time sufficient to
reclaim those whom the Anglomaniacs had misled, and to
prepare matters in such a manner, that the question when
again agitated, might be decided according to their wishes.
In such a hypothetical case, the King authorizes you to act
in concert with them, to pursue the direction which they may
think proper to give you, and to employ every means to
augment the number of the partisans of the good cause. It
remains for me to speak of the personal security of the
Patriots. You may assure them, that under every
circumstance, the King will take them under his immediate
protection, and you will make known wherever you may judge
necessary, that his Majesty will regard, as a personal
offence, every undertaking against their libeity. It is to
be presumed that this language, energetically maintained,
may have some effect on the audacity of the Anglomaniacs,
and that the Prince de Nassau will feel that he runs some
risk in provoking the resentment of his Majesty.‘]
This letter was communicated by the Patriots to me, when at Amsterdam, in 1788, and a copy sent by me to Mr. Jay, in my letter to him of March 16, 1788.
The object of the Patriots was, to establish a representative and republican government. The majority of the States General were with them, but the majority of the populace of the towns was with the Prince of Orange; and that populace was played off with great effect by the triumvirate of * * * Harris, the English Ambassador, afterwards Lord Malmesbury, the Prince of Orange, a stupid man, and the Princess, as much a man as either of her colleagues, in audaciousness, in enterprise, and in the thirst of domination. By these, the mobs of the Hague were excited against the members of the States General; their persons were insulted, and endangered in the streets; the sanctuary of their houses was violated; and the Prince, whose function and duty it was to repress and punish these violations of order, took no steps for that purpose. The States General, for their own protection, were therefore obliged to place their militia under the command of a Committee. The Prince filled the courts of London and Berlin with complaints at this usurpation of his prerogatives, and, forgetting that he was but the first servant of a Republic, marched his regular troops against the city of Utrecht, where the States were in session. They were repulsed by the militia. His interests now became marshaled with those of the public enemy, and against his own country. The States, therefore, exercising their rights of sovereignty, deprived him of all his powers. The great Frederic had died in August, ‘86. He had never intended to break with France in support of the Prince of Orange. During the illness of which he died, he had, through the Duke of Brunswick, declared to the Marquis de la Fayette, who was then at Berlin, that he meant not to support the English interest in Holland: that he might assure the government of France, his only wish was, that some honorable place in the Constitution should be reserved for the Stadtholder and his children, and that he would take no part in the quarrel, unless an entire abolition of the Stadtholderate should be attempted. But his place was now occupied by Frederic William, his great nephew, a man of little understanding, much caprice, and very inconsiderate: and the Princess, his sister, although her husband was in arms against the legitimate authorities of the country, attempting to go to Amsterdam, for the purpose of exciting the mobs of that place, and being refused permission to pass a military post on the way, he put the Duke of Brunswick at the head of twenty thousand men, and made demonstrations of marching on Holland. The King of France hereupon declared, by his Chargé des Affaires in Holland, that if the Prussian troops continued to menace Holland with an invasion, his Majesty, in quality of Ally, was determined to succor that province. In answer to this, Eden gave official information to Count Montmorin, that England must consider as at an end, its convention with France relative to giving notice of its naval armaments, and that she was arming generally. War being now imminent, Eden, since Lord Aukland, questioned me on the effect of our treaty with France, in the case of a war, and what might be our dispositions. I told him frankly, and without hesitation, that our dispositions would be neutral, and that I thought it would be the interest of both these powers that we should be so; because, it would relieve both from all anxiety as to feeding their West India islands; that, England, too, by suffering us to remain so, would avoid a heavy land war on our Continent, which might very much cripple her proceedings elsewhere; that our treaty, indeed, obliged us to receive into our ports the armed vessels of France, with their prizes, and to refuse admission to the prizes made on her by her enemies: that there was a clause, also, by which we guaranteed to France her American possessions, which might perhaps force us into the war, if these were attacked. ‘Then it will be war,’ said he, ‘for they will assuredly be attacked.’ Liston, at Madrid, about the same time, made the same enquiries of Carmichael. The government of France then declared a determination to form a camp of observation at Givet, commenced arming her marine, and named the Bailli de Suffrein their Generalissimo on the Ocean. She secretly engaged, also, in negotiations with Russia, Austria, and Spain, to form a quadruple alliance. The Duke of Brunswick having advanced to the confines of Holland, sent some of his officers to Givet, to reconnoitre the state of things there, and report them to him. He said afterwards, that ‘if there, had been only a few tents at that place, he should not have advanced further, for that the king would not, merely for the interest of his sister, engage in a war with France.’ But, finding that there was not a single company there, he boldly entered the country, took their towns as fast as he presented himself before them, and advanced on Utrecht. The States had appointed the Rhingrave of Salm their Commander in chief; a Prince without talents, without courage, and without principle. He might have held out in Utrecht, for a considerable time, but he surrendered the place without firing a gun, literally ran away and hid himself, so that for months it was not known what was become of him. Amsterdam was then attacked, and capitulated. In the mean time, the negotiations for the quadruple alliance were proceeding favorably; but the secrecy with which they were attempted to be conducted, was penetrated by Fraser, Chargé des Affaires of England at St. Petersburg, who instantly notified his court, and gave the alarm to Prussia. The King saw at once what would be his situation, between the jaws of France, Austria, and Russia. In great dismay, he besought the court of London not to abandon him, sent Alvensleben to Paris to explain and soothe; and England, through the Duke of Dorset and Eden, renewed her conferences for accommodation. The Archbishop, who shuddered at the idea of war, and preferred a peaceful surrender of right, to an armed vindication of it, received them with open arms, entered into cordial conferences, and a declaration, and counter-declaration, were cooked up at Versailles, and sent to London for approbation. They were approved there, reached Paris at one o’clock of the 27th, and were signed that night at Versailles. It was said and believed at Paris, that M. de Montrnorin, literally ‘pleuroit cotnrae un enfant,’ when obliged to sign this counter-declaration; so distressed was he by the dishonor of sacrificing the Patriots, after assurances so solemn of protection, and absolute encouragement to proceed. The Prince of Orange was reinstated in all his powers, now become regal. A great emigration of the Patriots took place; all were deprived of office, many exiled, and their property confiscated. They were received in France, and subsisted, for some time, on her bounty. Thus fell Holland, by the treachery of her Chief, from her honorable independence, to become a province of England; and so, also, her Stadtholder, from the high station of the first citizen of a free Republic, to be the servile Viceroy of a foreign Sovereign. And this was effected by a mere scene of bullying and demonstration; not one of the parties, France, England, or Prussia, having ever really meant to encounter actual war for the interest of the Prince of Orange. But it had all the effect of a real and decisive war.
Our first essay, in America, to establish a federative government had fallen, on trial, very short of its object. During the war of Independence, while the pressure of an external enemy hooped us together, and their enterprises kept us necessarily on the alert, the spirit of the people, excited by danger, was a supplement to the Confederation, and urged them to zealous exertions, whether claimed by that instrument or not; but, when peace and safety were restored, and every man became engaged in useful and profitable occupation, less attention was paid to the calls of Congress. The fundamental defect of the Confederation was, that Congress was not authorized to act immediately on the people, and by its own officers. Their power was only requisitory, and these requisitions were addressed to the several Legislatures, to be by them carried into execution, without other coercion than the moral principle of duty. This allowed, in fact, a negative to every legislature, on every measure proposed by Congress; a negative so frequently exercised in practice, as to benumb the action of the Federal government, and to render it inefficient in its general objects, and more especially in pecuniary and foreign concerns. The want, too, of a separation of the Legislative, Executive, and Judiciary functions, worked disadvantageously in practice. Yet this state of things afforded a happy augury of the future march of our Confederacy, when it was seen that the good sense and good dispositions of the people, as soon as they perceived the incompetence of their first compact, instead of leaving its correction to insurrection and civil war, agreed, with one voice, to elect deputies to a general Convention, who should peaceably meet and agree on such a Constitution as ‘would ensure peace, justice, liberty, the common defence, and general welfare.’
This Convention met at Philadelphia on the 25th of May, ‘87. It sat with closed doors, and kept all its proceedings secret, until its dissolution on the 17th of September, when the results of its labors were published all together. I received a copy, early in November, and read and contemplated its provisions with great satisfaction. As not a member of the Convention, however, nor probably a single citizen of the Union, had approved it in all its parts, so I, too, found articles which I thought objectionable. The absence of express declarations ensuring freedom of religion, freedom of the press, freedom of the person under the uninterrupted protection of the habeas corpus and trial by jury in civil, as well as in criminal cases, excited my jealousy; and the re-eligibility of the President for life, I quite disapproved. I expressed freely, in letters to my friends, and most particularly to Mr. Madison and General Washington, my approbations and objections. How the good should be secured, and the ill brought to rights, was the difficulty. To refer it back to a new Convention, might endanger the loss of the whole. My first idea was, that the nine states first acting, should accept it unconditionally, and thus secure what in it was good, and that the four last should accept on the previous condition, that certain amendments should be agreed to; but a better course was devised, of accepting the whole, and trusting that the good sense and honest intentions of our citizens would make the alterations which should be deemed necessary. Accordingly, all accepted, six without objection, and seven with recommendations of specified amendments. Those respecting the press, religion, and juries, with several others, of great value, were accordingly made; but the habeas corpus was left to the discretion of Congress, and the amendment against the re-eligibility of the President was not proposed. My fears of that feature were founded on the importance of the office, on the fierce contentions it might excite among ourselves, if continuable for life, and the dangers of interference, either with money or arms, by foreign nations, to whom the choice of an American President might become interesting. Examples of this abounded in history; in the case of the Roman Emperors, for instance; of the Popes, while of any significance; of the German Emperors; the Kings of Poland, and the Deys of Barbary. I had observed, too, in the feudal history, and in the recent instance, particularly, of the Stadtholder of Holland, how easily offices, or tenures for life, slide into inheritances. My wish, therefore, was that the President should be elected for seven years, and be ineligible afterwards. This term I thought sufficient to enable him, with the concurrence of the Legislature, to carry though and establish any system of improvement he should propose for the general good. But the practice adopted, I think, is better, allowing his continuance for eight years, with a liability to be dropped at half way of the term, making that a period of probation. That his continuance should be restrained to seven years, was the opinion of the Convention at an earlier stage of its session, when it voted that term, by a majority of eight against two, and by a simple majority, that he should be ineligible a second time. This opinion was confirmed by the House so late as July 26, referred to the Committee of detail, reported favorably by them, and changed to the present form by final vote, on the last day, but one only, of their session. Of this change, three states expressed their disapprobation; New York, by recommending an amendment, that the President should not be eligible a third time, and Virginia and North Carolina, that he should not be capable of serving more than eight, in any term of sixteen years; and although this amendment has not been made in form, yet practice seems to have established it. The example of four Presidents, voluntarily retiring at the end of their eighth year, and the progress of public opinion, that the principle is salutary, have given it in practice the force of precedent and usage; insomuch, that should a President consent to be a candidate for a third election, I trust he would be rejected, on this demonstration of ambitious views.
But there was another amendment, of which none of us thought at the time, and in the omission of which, lurks the germ that is to destroy this happy combination of National powers, in the general government, for matters of National concern, and independent powers in the States, for what concerns the States severally. In England, it was a great point gained at the Revolution, that the commissions of the Judges, which had hitherto been during pleasure, should thenceforth be made during good behavior. A Judiciary, dependant on the will of the King, had proved itself the most oppressive of all tools in the hands of that magistrate. Nothing, then, could be more salutary, than a change there, to the tenure of good behavior; and the question of good behavior, left to the vote of a simple majority in the two Houses of Parliament. Before the Revolution, we were all good English Whigs, cordial in their free principles, and in their jealousies of their Executive magistrate. These jealousies are very apparent, in all our state Constitutions; and, in the General government in this instance, we have gone even beyond the English caution, by requiring a vote of two thirds, in one of the Houses, for removing a Judge; a vote so impossible, where * any defence is made, before men of ordinary prejudices and passions, that our Judges are effectually independent of the nation. But this ought not to be. I would not, indeed, make them dependant on the Executive authority, as they formerly were in England; but I deem it indispensable to the continuance of this government, that they should be submitted to some practical and impartial control; and that this, to be impartial, must be compounded of a mixture of State and Federal authorities. It is not enough, that honest men are appointed Judges. All know the influence of interest on the mind of man, and how unconsciously his judgment is warped by that influence. To this bias add that of the esprit de corps, of their peculiar maxim and creed, that ‘it is the office of a good Judge to enlarge his jurisdiction,’ and the absence of responsibility; and how can we expect impartial decision between the General government, of which they are themselves so eminent a part, and an individual state, from which they have nothing to hope or fear? We have seen, too, that, contrary to all correct example, they are in the habit of going out of the question before them, to throw an anchor ahead, and grapple further hold for future advances of power. They are then, in fact, the corps of sappers and miners, steadily working to undermine the independent rights of the states, and to consolidate all power in the hands of that government, in which they have so important a freehold estate. But it is not by the consolidation, or concentration of powers, but by their distribution, that good government is effected. Were not this great country already divided into states, that division must be made, that each might do for itself what concerns itself directly, and what it can so much better do than a distant authority. Every state again is divided into counties, each to take care of what lies within its local bounds; each county again into townships or wards, to manage minuter details; and every ward into farms, to be governed each by its individual proprietor. Were we directed from Washington when to sow, and when to reap, we should soon want bread. It is by this partition of cares, descending in gradation from general to particular, that the mass of human affairs may be best managed, for the good and prosperity of all. I repeat, that I do not charge the judges with wilful and ill-intentioned error; but honest error must be arrested, where its toleration leads to public ruin. As, for the safety of society, we commit honest maniacs to Bedlam, so judges should be withdrawn from their bench, whose erroneous biases are leading us to dissolution. It may, indeed, injure them in fame or in fortune; but it saves the Republic, which is the first and supreme law.
* In the impeachment of Judge Pickering, of New Hampshire, a
habitual and maniac drunkard, no defence was made. Had there
been, the party vote of more than one third of the Senate
would have acquitted him.
Among the debilities of the government of the Confederation, no one was more distinguished or more distressing, than the utter impossibility of obtaining, from the States, the monies necessary for the payment of debts, or even for the ordinary expenses of the government. Some contributed a little, some less, and some nothing; and the last, furnished at length an excuse for the first, to do nothing also. Mr. Adams, while residing at the Hague, had a general authority to borrow what sums might be requisite, for ordinary and necessary expenses. Interest on the public debt, and the maintenance of the diplomatic establishment in Europe, had been habitually provided in this way. He was now elected Vice-President of the United States, was soon to return to America, and had referred our bankers to me for future counsel, on our affairs in their hands. But I had no powers, no instructions, no means, and no familiarity with the subject. It had always been exclusively under his management, except as to occasional and partial deposites in the hands of Mr. Grand, banker in Paris, for special and local purposes. These last had been exhausted for some time, and I had fervently pressed the Treasury board to replenish this particular deposite, as Mr. Grand now refused to make further advances. They answered candidly, that no funds could be obtained until the new government should get into action, and have time to make its arrangements. Mr. Adams had received his appointment to the court of London, while engaged at Paris, with Dr. Franklin and myself, in the negotiations under our joint commissions. He had repaired thence to London, without returning to the Hague, to take leave of that government. He thought it necessary, however, to do so now, before he should leave Europe, and accordingly went there. I learned his departure from London, by a letter from Mrs. Adams, received on the very day on which he would arrive at the Hague. A consultation with him, and some provision for the future, was indispensable, while we could yet avail ourselves of his powers; for when they would be gone, we should be without resource. I was daily dunned by a Company who had formerly made a small loan to the United States, the principal of which was now become due; and our bankers in Amsterdam had notified me, that the interest on our general debt would be expected in June; that if we failed to pay it, it would be deemed an act of bankruptcy, and would effectually destroy the credit of the Upited States, and all future prospects of obtaining money there; that the loan they had been authorized to open, of which a third only was filled, had now ceased to get forward, and rendered desperate that hope of resource. I saw that there was not a moment to lose, and set out for the Hague on the 2nd morning after receiving the information of Mr. Adams’s journey. I went the direct road by Louvres, Senlis, Roye, Pont St. Maxence, Bois le Due, Gournay, Peronne, Cambray, Bouchain, Valenciennes, Mons, Bruxelles, Malines, Antwerp, Mordick, and Rotterdam, to the Hague, where I happily found Mr. Adams. He concurred with me at once in opinion, that something must be done, and that we ought to risk ourselves on doing it without instructions, to save the credit of the United States. We foresaw, that before the new government could be adopted, assembled, establish its financial system, get the money into the Treasury, and place it in Europe, considerable time would elapse; that, therefore, we had better provide at once for the years ‘88, ‘89, and ‘90, in order to place our government at its ease, and our credit in security, during that trying interval. We set out, therefore, by the way of Leyden, for Amsterdam, where we arrived on the 10th, I had prepared an estimate, showing, that

Florins.
There would be necessary for the year ‘88—531,937-10 ‘89—538,540 ‘90—473,540 —————————— Total, 1,544,017-10
Florins.
To meet this, the bankers had in hand, 79,268-2-8 and the unsold bonds would yield, 542,800
622,068-2-8
Leaving a deficit of 921,949-7-4
We proposed then to borrow a million, yielding 920,000
Which would leave a small deficiency of 1,949-7-4
Mr. Adams accordingly executed 1000 bonds, for 1000 florins each, and deposited them in the hands of our bankers, with instructions, however, not to issue them until Congress should ratify the measure. This done, he returned to London, and I set out for Paris; and, as nothing urgent forbade it, I determined to return along the banks of the Rhine, to Strasburg, and thence strike off to Paris. I accordingly left Amsterdam on the 30th of March, and proceeded by Utrecht, Nimegnen, Cleves, Duysberg, Dusseldorf, Cologne, Bonne, Coblentz, Nassau, Hocheim, Frankfort, and made an excursion to Hanau, then to Mayence, and another excursion to Rudesheim, and Johansberg; then by Oppenheim, Worms, and Manheim, making an excursion to Heidelberg, then by Spire, Carlsruhe, Rastadt, and Kelh, to Sfrasburg, where I arrived April the 16th, and proceeded again on the 18th, by Phalsbourg, Fenestrange, Dieuze, Moyenvie, Nancy, Toul, Ligny, Barleduc, St. Diziers, Vitry, Chalons sur Marne, Epernay, Chateau Thierri, Meaux, to Paris, where I arrived on the 23d of April: and I had the satisfaction to reflect, that by this journey, our credit was secured, the new government was placed at ease for two years to come, and that, as well as myself, relieved from the torment of incessant duns, whose just complaints could not be silenced by any means within our power.
A Consular Convention had been agreed on in ‘84, between Dr. Franklin and the French government, containing several articles, so entirely inconsistent with the laws of the several states, and the general spirit of our citizens, that Congress withheld their ratification, and sent it back to me, with instructions to get those articles expunged, or modified, so as to render them compatible with our laws. The Minister unwillingly released us from these concessions, which, indeed, authorized the exercise of powers very offensive in a free state. After much discussion, the Convention was reformed in a considerable degree, and was signed by the Count Montmorin and myself, on the 14th of November, ‘88; not indeed, such as I would have wished; but such as could be obtained with good humor and friendship.
On my return from Holland, I found Paris as I had left it, still in high fermentation. Had the Archbishop, on the close of the Assembly of Notables, immediately carried into operation the measures contemplated, it was believed they would all have been registered by the Parliament; but he was slow, presented his edicts, one after another, and at considerable intervals, which gave time for the feelings excited by the proceedings of the Notables to cool off, new claims to be advanced, and a pressure to arise for a fixed constitution, not subject to changes at the will of the King. Nor should we wonder at this pressure, when we consider the monstrous abuses of power under which this people were ground to powder; when we pass in review the weight of their taxes, and the inequality of their distribution; the oppressions of the tythes, the failles, the corvees, the gabelles, the farms and the barriers; the shackles on commerce by monopolies; on industry by guilds and corporations; on the freedom of conscience, of thought, and of speech; on the freedom of the press by the censure; and of the person by lettres de cachet; the cruelty of the criminal code generally; the atrocities of the rack; the venality of Judges, and their partialities to the rich; the monopoly of military honors by the noblesse; the enormous expenses of the Queen, the Princes, and the Court; the prodigalities of pensions; and the riches, luxury, indolence, and immorality of the Clergy. Surely under such a mass of misrule and oppression, a people might justly press for thorough reformation, and might even dismount their roughshod riders, and leave them to walk, on their own legs. The edicts, relative to the corvees and free circulation of grain, were first presented to the Parliament and registered; but those for the impot territorial, and stamp tax, offered some time after, were refused by the Parliament, which proposed a call of the States General, as alone competent to their authorization. Their refusal produced a bed of justice, and their exile to Troyes. The Advocates, however, refusing to attend them, a suspension in the administration of justice took place. The Parliament held out for awhile, but the ennui of their exile and absence from Paris, began at length to be felt, and some dispositions for compromise to appear. On their consent, therefore, to prolong some of the former taxes, they were recalled from exile. The King met them in session, November 19, ‘87, promised to call the States General in the year ‘92, and a majority expressed their assent to register an edict for successive and annual loans from 1788 to ‘92; but a protest being entered by the Duke of Orleans, and this encouraging others in a disposition to retract, the King ordered peremptorily the registry of the edict, and left the assembly abruptly. The Parliament immediately protested, that the votes for the enregistry had not been legally taken, and that they gave no sanction to the loans proposed. This was enough to discredit and defeat them. Hereupon issued another edict, for the establishment of a cour plenière and the suspension of all the Parliaments in the kingdom. This being opposed, as might be expected, by reclamations from all the Parliaments and Provinces, the King gave way, and by an edict of July 5th, ‘88, renounced his cour plenière, and promised the States General for the first of May, of the ensuing year: and the Archbishop, finding the times beyond his faculties, accepted the promise of a Cardinal’s hat, was removed (September ‘88) from the Ministry, and Mr. Necker was called to the department of finance. The innocent rejoicings of the people of Paris on this change, provoked the interference of an officer of the city guards, whose order for their dispersion not being obeyed, he charged them with fixed bayonets, killed two or three, and wounded many. This dispersed them for the moment, but they collected the next day in great numbers, burnt ten or twelve guardhouses, killed two or three of the guards, and lost six or eight more of their own number. The city was hereupon put under martial law, and after a while the tumult subsided. The effect of this change of ministers, and the promise of the States General at an early day tranquillized the nation. But two great questions now occurred. 1st. What proportion shall the number of deputies of the Tiers Etat bear to those of the Nobles and Clergy? And, 2nd. Shall they sit in the same or in distinct apartments? Mr. Necker, desirous of avoiding himself these knotty questions, proposed a second call of the same Notables, and that their advice should be asked on the subject. They met, November 9, ‘88, and, by five bureaux against one, they recommended the forms of the States General of 1614; wherein the Houses were separate, and voted by orders, not by persons. But the whole nation declaring at once against this, and that the Tiers Etat should be, in numbers, equal to both the other orders, and the Parliament deciding for the same proportion, it was determined so to be, by a declaration of December 27th, ‘88. A Report of Mr. Necker, to the King, of about the same date, contained other very important concessions. 1. That the King could neither lay a new tax, nor prolong an old one. 2. It expressed a readiness to agree on the periodical meeting of the States. 3. To consult on the necessary restriction on lettres de cachet; and 4. How far the press might be made free. 5. It admits that the States are to appropriate the public money; and 6. That Ministers shall be responsible for public expenditures. And these concessions came from the very heart of the King. He had not a wish but for the good of the nation; and for that object, no personal sacrifice would ever have cost him a moment’s regret; but his mind was weakness itself, his constitution timid, his judgment null, and without sufficient firmness even to stand by the faith of his word. His Queen, too, haughty and bearing no contradiction, had an absolute ascendancy over him; and around her were rallied the King’s brother D’Artois, the court generally, and the aristocratic part of his Ministers, particularly Breteuil, Broglio, Vauguyon, Foulon, Luzerne, men whose principles of government were those of the age of Louis XIV. Against this host, the good counsels of Necker, Montmorin, St. Priest, although in unison with the wishes of the King himself, were of little avail. The resolutions of the morning, formed under their advice, would be reversed in the evening, by the influence of the Queen and court. But the hand of Heaven weighed heavily indeed on the machinations of this junto; producing collateral incidents, not arising out of the case, yet powerfully co-exciting the nation to force a regeneration of its government, and overwhelming, with accumulated difficulties, this liberticide resistance. For, while laboring under the want of money for even ordinary purposes, in a government which required a million of livres a day, and driven to the last ditch by the universal call for liberty, there came on a winter of such severe cold, as was without example in the memory of man, or in the written records of history. The Mercury was at times 50° below the freezing point of Farenheit, and 22° below that of Reaumur. All out-door labor was suspended, and the poor, without the wages of labor, were, of course, without either bread or fuel. The government found its necessities aggravated by that of procuring immense quantities of firewood, and of keeping great fires at all the cross streets, around which the people gathered in crowds, to avoid perishing with cold. Bread, too, was to be bought, and distributed daily, gratis, until a relaxation of the season should enable the people to work: and the slender stock of bread-stuff had for some time threatened famine, and had raised that article to an enormous price. So great, indeed, was the scarcity of bread, that, from the highest to the lowest citizen, the bakers were permitted to deal but a scanty allowance per head, even to those who paid for it; and, in cards of invitation to dine in the richest houses, the guest was notified to bring his own bread. To eke out the existence of the people, every person who had the means, was called on for a weekly subscription, which the Cures collected, and employed in providing messes for the nourishment of the poor, and vied with each other in devising such economical compositions of food, as would subsist the greatest number with the smallest means. This want of bread had been foreseen for some time past, and M. de Montmorin had desired me to notify it in America, and that, in addition to the market price, a premium should be given on what should be brought from the United States. Notice was accordingly given, and produced considerable supplies. Subsequent information made the importations from America, during the months of March, April, and May, into the Atlantic ports of France, amount to about twenty-one thousand barrels of flour, besides what went to other ports, and in other months; while our supplies to their West Indian islands relieved them also from that drain. This distress for bread continued till July.
Hitherto no acts of popular violence had been produced by the struggle for political reformation. Little riots, on ordinary incidents, had taken place at other times, in different parts of the kingdom, in which some lives, perhaps a dozen or twenty, had been lost; but in the month of April, a more serious one occurred in Paris, unconnected, indeed, with the Revolutionary principle, but making part of the history of the day. The Fauxbourg St. Antoine, is a quarter of the city inhabited entirely by the class of day-laborers and journeymen in every line. A rumor was spread among them, that a great paper-manufacturer, of the name of Reveillon, had proposed, on some occasion, that their wages should be lowered to fifteen sous a day. Inflamed at once into rage, and without inquiring into its truth, they flew to his house in vast numbers, destroyed every thing in it, and in his magazines and work-shops, without secreting, however, a pin’s worth to themselves, and were continuing this work of devastation, when the regular troops were called in. Admonitions being disregarded, they were of necessity fired on, and a regular action ensued, in which about one hundred of them were killed, before the rest would disperse. There had rarely passed a year without such a riot, in some part or other of the kingdom; and this is distinguished only as cotemporary with the Revolution, although not produced by it.
The States General were opened on the 5th of May, ‘89, by speeches from the King, the Garde des Sceaux, Lamoignon, and Mr. Necker. The last was thought to trip too lightly over the constitutional reformations which were expected. His notices of them in this speech, were not as full as in his previous Rapport au Roi. This was observed, to his disadvantage: but much allowance should have been made for the situation in which he was placed, between his own counsels and those of the ministers and party of the court. Overruled in his own opinions, compelled to deliver, and to gloss over those of his opponents, and even to keep their secrets, he could not come forward in his own attitude.
The composition of the Assembly, although equivalent, on the whole, to what had been expected, was something different in its elements. It had been supposed, that a superior education would carry into the scale of the Commons, a respectable portion of the Noblesse. It did so as to those of Paris, of its vicinity, and of the other considerable cities, whose greater intercourse with enlightened society had liberalized their minds, and prepared them to advance up to the measure of the times. But the Noblesse of the country, which constituted two thirds of that body, were far in their rear. Residing constantly on their patrimonial feuds, and familiarized, by daily habit, with Seigneurial powers and practices, they had not yet learned to suspect their inconsistence with reason and right. They were willing to submit to equality of taxation, but not to descend from their rank and prerogatives to be incorporated in session with the Tiers Etat. Among the Clergy, on the other hand, it had been apprehended that the higher orders of the Hierarchy, by their wealth and connections, would have carried the elections generally; but it turned out, that in most cases, the lower clergy had obtained the popular majorities. These consisted of the Cureés sons of the peasantry, who had been employed to do all the drudgery of parochial services for ten, twenty, or thirty louis a year; while their superiors were consuming their princely revenues in palaces of luxury and indolence. The objects for which this body was convened, being of the first order of importance, I felt it very interesting to understand the views of the parties of which it was composed, and especially the ideas prevalent, as to the organization contemplated for their government. I went, therefore, daily from Paris to Versailles, and attended their debates, generally till the hour of adjournment. Those of the Noblesse were impassioned and tempestuous. They had some able men on both sides, actuated by equal zeal. The debates of the Commons were temperate, rational, and inflexibly firm. As preliminary to all other business, the awful questions came on: Shall the States sit in one, or in distinct apartments? And shall they vote by heads or houses? The opposition was soon found to consist of the Episcopal order among the clergy, and two thirds of the Noblesse; while the Tiers Etat were, to a man, united and determined. After various propositions of compromise had failed, the Commons undertook to cut the Gordian knot. The Abbe Sieyes, the most logical head of the nation, (author of the pamphlet ‘Qu’est ce que le Tiers Etat?’ which had electrified that country, as Paine’s ‘Common Sense’ did us,) after an impressive speech on the 10th of June, moved that a last invitation should be sent to the Nobles and Clergy, to attend in the hall of the States, collectively or individually, for the verification of powers, to which the Commons would proceed immediately, either in their presence or absence. This verification being finished, a motion was made, on the 15th, that they should constitute themselves a National Assembly; which was decided on the 17th, by a majority of four fifths. During the debates on this question, about twenty of the Curés had joined them, and a proposition was made, in the chamber of the Clergy, that their whole body should join. This was rejected, at first, by a small majority only; but, being afterwards somewhat modified, it was decided affirmatively, by a majority of eleven. While this was under debate, and unknown to the court, to wit, on the 19th, a council was held in the afternoon, at Marly, wherein it was proposed that the King should interpose, by a declaration of his sentiments, in a séance royale. A form of declaration was proposed by Necker, which, while it censured, in general, the preceedings, both of the Nobles and Commons, announced the King’s views, such as substantially to coincide with the Commons. It was agreed to in Council, the séance was fixed for the 22nd, the meetings of the States were till then to be suspended, and every thing, in the mean time, kept secret. The members, the next morning (the 20th) repairing to their house, as usual, found the doors shut and guarded, a proclamation posted up for a séance, royale on the 22nd, and a suspension of their meetings in the mean, time. Concluding that their dissolution was now to take place, they repaired to a building called the Jeu de paume (or Tennis court), and there bound themselves by oath to each other, never to separate, of their own accord, till they had settled a constitution for the nation, on a solid basis, and, if separated by force, that they would reassemble in some other place. The next day they met in the church of St. Louis, and were joined by a majority of the clergy. The heads of the aristocracy saw that all was lost without some bold exertion. The King was still at Marly. Nobody was permitted to approach him but their friends. He was assailed by falsehoods in all shapes. He was made to believe that the Commons were about to absolve the army from their oath of fidelity to him, and to raise their pay. The court party were now all rage and desperation. They procured a committee to be held, consisting of the King and his Ministers, to which Monsieur and the Count d’Artois should be admitted. At this committee, the latter attacked Mr. Necker personally, arraigned his declaration, and proposed one which some of his prompters had put into his hands. Mr. Necker was browbeaten and intimidated, and the King shaken. He determined that the two plans should be deliberated on the next day, and the séance royale put off a day longer. This encouraged a fiercer attack on Mr. Necker the next day. His draught of a declaration was entirely broken up, and that of the Count d’Artois inserted into it. Himself and Montmorin offered their resignation, which was refused; the Count d’Artois saying to Mr. Necker, ‘No, sir, you must be kept as the hostage; we hold you responsible for all the ill which shall happen.’ This change of plan was immediately whispered without doors. The Noblesse were in triumph; the people in consternation. I was quite alarmed at this state of things. The soldiery had not yet indicated which side they should take, and that which they should support would be sure to prevail. I considered a successful reformation of government in France as insuring a general reformation through Europe, and the resurrection to a new life of their people, now ground to dust by the abuses of the governing powers. I was much acquainted with the leading patriots of the Assembly. Being from a country which had successfully passed through a similar reformation, they were disposed to my acquaintance, and had some confidence in me. I urged, most strenuously, an immediate compromise; to secure what the government was now ready to yield, and trust to future occasions for what might still be wanting. It was well understood that the King would grant, at this time, 1. Freedom of the person by habeas corpus. 2. Freedom of conscience: 3. Freedom of the press: 4. Trial by jury: 5. A representative legislature: 6. Annual meetings: 7. The origination of laws: 8. The exclusive right of taxation and appropriation: and 9. The responsibility of ministers: and with the exercise of these powers they could obtain, in future, whatever might be further necessary to improve and preserve their constitution. They thought otherwise, however, and events have proved their lamentable error. For, after thirty years of war, foreign and domestic, the loss of millions of lives, the prostration of private happiness, and the foreign subjugation of their own country for a time, they have obtained no more, nor even that securely. They were unconscious of (for who could foresee?) the melancholy sequel of their well-meant perseverance; that their physical force would be usurped by a first tyrant to trample on the independence, and even the existence, of other nations: that this would afford a fatal example for the atrocious conspiracy of kings against their people; would generate their unholy and homicide alliance to make common cause among themselves, and to crush, by the power of the whole, the efforts of any part, to moderate their abuses and oppressions. When the King passed, the next day, through the lane formed from the Chateau to the Hotel des Etats, there was a dead silence. He was about an hour in the House, delivering his speech and declaration. On his coming out, a feeble cry of Vive le Roy was raised by some children, but the people remained silent and sullen. In the close of his speech, he had ordered that the members should follow him, and resume their deliberations the next day. The Noblesse followed him, and so did the clergy, except about thirty, who, with the Tiers, remained in the room, and entered into deliberation. They protested against what the King had done, adhered to all their former proceedings, and resolved the inviolability of their own persons. An officer came to order them out of the room in the King’s name. ‘Tell those who sent you,’ said Mirabeau, ‘that we shall not move hence but at our own will, or the point of the bayonet.’ In the afternoon, the people, uneasy, began to assemble in great numbers in the courts and vicinities of the palace. This produced alarm. The Queen sent for Mr. Necker. He was conducted, amidst the shouts and acclamations of the multitude, who filled all the apartments of the palace. He was a few minutes only with the Queen, and what passed between them did not transpire. The King went out to ride. He passed through the crowd to his carriage, and into it, without being in the least noticed. As Mr. Necker followed him, universal acclamations were raised of ‘Vive Monsieur Necker, vive le sauveur de la France opprimée.’ He was conducted back to his house, with the same demonstrations of affection and anxiety. About two hundred deputies of the Tiers, catching the enthusiasm of the moment, went to his house, and extorted from him a promise that he would not resign. On the 25th, forty-eight of the Nobles joined the Tiers, and among them the Duke of Orleans. There were then with them one hundred and sixty-four members of the clergy, although the minority of that body still sat apart, and called themselves the Chamber of the Clergy. On the 26th, the Archbishop of Paris joined the Tiers, as did some others of the clergy and of the Noblesse.
These proceedings had thrown the people into violent ferment. It gained the soldiery, first of the French guards, extended to those of every other denomination, except the Swiss, and even to the body guards of the King. They began to quit their barracks, to assemble in squads, to declare they would defend the life of the King, but would not be the murderers of their fellow-citizens. They called themselves the soldiers of the nation, and left now no doubt on which side they would be, in case of a rupture. Similar accounts came in from the troops in other parts of the kingdom, giving good reason to believe they would side with their fathers and brothers, rather than with their officers. The operation of this medicine at Versailles, was as sudden as it was powerful. The alarm there was so complete, that in the afternoon of the 27th, the King wrote with his own hand letters to the Presidents of the Clergy and Nobles, engaging them immediately to join the Tiers. These two bodies were debating, and hesitating, when notes from the Count d’Artois decided their compliance. They went in a body, and took their seats with the Tiers, and thus rendered the union of the orders in one chamber complete.
The Assembly now entered on the business of their mission, and first proceeded to arrange the order in which they would take up the heads of their constitution, as follows:
First, and as preliminary to the whole, a general declaration of the rights of man. Then, specifically, the principles of the monarchy; rights of the nation; rights of the king; rights of the citizens; organization and rights of the National Assembly; forms necessary for the enactment of laws; organization and functions of the Provincial and Municipal Assemblies; duties and limits of the Judiciary power; functions and duties of the Military power.
A declaration of the rights of man, as the preliminary of their work, was accordingly prepared and proposed by the Marquis de la Fayette.
But the quiet of their march was soon disturbed by information that troops, and particularly the foreign troops, were advancing on Paris from various quarters. The King had probably been advised to this on the pretext of preserving peace in Paris. But his advisers were believed to have other things in contemplation. The Marshal de Broglio was appointed to their command, a highflying aristocrat, cool and capable of every thing. Some of the French guards were soon arrested, under other pretexts, but really on account of their dispositions in favor of the national cause. The people of Paris forced their prison, liberated them, and sent a deputation to the Assembly to solicit a pardon. The Assembly recommended peace and order to the people of Paris, the prisoners to the King, and asked from him the removal of the troops. His answer was negative and dry, saying they might remove themselves, if they pleased, to Noyon or Soissons. In the mean time, these troops, to the number of twenty or thirty thousand, had arrived, and were posted in and between Paris and Versailles. The bridges and passes were guarded. At three o’clock in the afternoon of the 11th of July, the Count de la Luzerne was sent to notify Mr. Necker of his dismission, and to enjoin him to retire instantly, without saying a word of it to any body. He went home, dined, and proposed to his wife a visit to a friend, but went in fact to his country-house at St. Ouen, and at midnight set out for Brussels. This was not known till the next day (the 12th), when the whole ministry was changed, except Villedeuil, of the domestic department, and Barenton, Garde des Sceaux. The changes were as follows.
The Baron de Breteuil, President of the Council of Finance; de la Galasiere, Comptroller General, in the room of Mr. Necker; the Marshal de Broglio, Minister of War, and Foulon under him, in the room of Puy-Segur; the Duke de la Vauguyon, Minister of Foreign Affairs, instead of the Count de Montmorin; de la Porte, Minister of Marine, in place of the Count de la Luzerne; St. Priest was also removed from the Council. Lucerne and Puy Segur had been strongly of the aristocratic party in the Council but they were not considered as equal to the work now to be done. The King was now completely in the hands of men, the principal among whom had been noted through their lives for the Turkish despotism of their characters, and who were associated around the King as proper instruments for what was to be executed. The news of this change began to be known at Paris about one or two o’clock. In the afternoon, a body of about one hundred German cavalry were advanced, and drawn up in the Place Louis XV., and about two hundred Swiss posted at a little distance in their rear. This drew people to the spot, who thus accidentally found themselves in front of the troops, merely at first as spectators; but, as their numbers increased, their indignation rose. They retired a few steps, and posted themselves on and behind large piles of stones, large and small, collected in that place for a bridge, which was to be built adjacent to it. In this position, happening to be in my carriage on a visit, I passed through the lane they had formed, without interruption. But the moment after I had passed, the people attacked the cavalry with stones. They charged, but the advantageous position of the people, and the showers of stones, obliged the horse to retire, and quit the field altogether, leaving one of their number on the ground, and the Swiss in their rear, not moving to their aid. This was the signal for universal insurrection, and this body of cavalry, to avoid being massacred, retired towards Versailles. The people now armed themselves with such weapons as they could find in armorers’ shops, and private houses, and with bludgeons; and were roaming all night, through all parts of the city, without any decided object. The next day (the 13th), the Assembly pressed on the king to send away the troops, to permit the Bourgeoisie of Paris, to arm for the preservation of order in the city, and offered to send a deputation from their body to tranquillize them: but their propositions were refused. A committee of magistrates and electors of the city were appointed by those bodies, to take upon them its government. The people, now openly joined by the French guards, forced the prison of St. Lazare, released all the prisoners, and took a great store of corn, which they carried to the corn market. Here they got some arms, and the French guards began to form and train; them. The city-committee determined to raise forty-eight thousand Bourgeois, or rather to restrain their numbers to forty-eight thousand. On the 14th, they sent one of their members (Monsieur de Corny) to the Hotel des Invalides, to ask arms for their Garde Bourgeoise. He was followed by, and he found there, a great collection of people. The Governor of the Invalids came out, and represented the impossibility of his delivering arms, without the orders of those from whom he received them. De Corny advised the people then to retire, and retired himself; but the people took possession of the arms, it was remarkable, that not only the Invalids themselves made no opposition, but that a body of five thousand foreign troops, within four hundred yards, never stirred. M. de Corny, and five others, were then sent to ask arms of M. de Launay, Governor of the Bastile. They found a great collection of people already before the place, and they immediately planted a flag of truce, which was answered by a like flag hoisted on the parapet. The deputation prevailed on the people to fall back a little, advanced themselves to make their demand of the Governor, and in that instant, a discharge from the Bastile killed four persons, of those nearest to the deputies. The deputies retired. I happened to be at the house of M. de Corny, when he returned to it, and received from him a narrative of these transactions. On the retirement of the deputies, the people rushed forward, and almost in an instant, were in possession of a fortification, of infinite strength, defended by one hundred men, which in other times, had stood several regular sieges, and had never been taken. How they forced their entrance has never been explained. They took all the arms, discharged the prisoners, and such of the garrison as were not killed in the first moment of fury; carried the Governor and Lieutenant Governor to the Place de Greve (the place of public execution), cut off their heads, and sent them through the city, in triumph, to the Palais Royal. About the same instant, a treacherous correspondence having been discovered in M. de Flesselles, Prévôt des Marchands, they seized him in the Hotel de Ville, where he was in the execution of his office, and cut off his head. These events, carried imperfectly to Versailles, were the subject of two successive deputations from the Assembly to the King, to both of which he gave dry and hard answers; for nobody had as yet been permitted to inform him, truly and fully, of what had passed at Paris. But at night, the Duke de Liancourt forced his way into the King’s bed-chamber, and obliged him to hear a full and animated detail of the disasters of the day in Paris. He went to bed fearfully impressed. The decapitation of De Launay worked powerfully, through the night, on the whole Aristocratical party; insomuch, that in the morning, those of the greatest influence on the Count d’Artois, represented to him the absolute necessity, that the King should give up every thing to the Assembly. This according with the dispositions of the King, he went about eleven o’clock, accompanied only by his brothers, to the Assembly, and there read to them a speech, in which he asked their interposition to re-establish order. Although couched in terms of some caution, yet the manner in which it was delivered made it evident, that it was meant as a surrender at discretion. He returned to the Chateau afoot, accompanied by the Assembly. They sent off a deputation to quiet Paris, at the head of which was the Marquis de la Fayette, who had, the same morning, been named Commandant en Chef of the Milice Bourgeoise; and Monsieur Bailly, former President of the States General, was called for as Prévôt des Marchands. The demolition of the Bastile was now ordered and begun. A body of the Swiss guards, of the regiment of Ventimille, and the city horse-guards joined the people. The alarm at Versailles increased. The foreign troops were ordered off instantly. Every Minister resigned. The King confirmed Bailly as Prévôt des Marchands, wrote to Mr. Necker, to recall him, sent his letter open to the Assembly, to be forwarded by them, and invited them to go with him to Paris the next day, to satisfy the city of his dispositions; and that night, and the next morning, the Count d’Artois, and M. de Montesson, a deputy connected with him, Madame de Polignac, Madame de Guiche, and the Count de Vaudreuil, favorites of the Queen, the Abbe de Vermont her confessor, the Prince of Conde. and Duke of Bourbon fled. The King came to Paris, leaving the Queen in consternation for his return. Omitting the less important figures of the procession, the King’s carriage was in the centre; on each side of it, the Assembly, in two ranks afoot; at their head the Marquis de la Fayette, as commander-in-chief, on horse-back, and Bourgeois guards before and behind. About sixty thousand citizens, of all forms and conditions, armed with the conquests of the Bastile and Invalids, as far as they would go, the rest with pistols, swords, pikes, pruning hooks, scythes, &c. lined all the streets through which the procession passed, and with the crowds of people in the streets, doors, and windows, saluted them everywhere with the cries of ‘Vive la Nation,’ but not a single ‘Vive le Roi’ was heard. The King stopped at the Hotel de Ville. There M. Bailly presented, and put into his hat, the popular cockade, and addressed him. The King being unprepared, and unable to answer, Bailly went to him, gathered from him some scraps of sentences, and made out an answer, which he delivered to the audience, as from the King. On their return, the popular cries were ‘Vive le Roi et la Nation.’ He was conducted by a garde Bourgeoise, to his palace at Versailles, and thus concluded such an ‘amende honorable,’ as no sovereign ever made, and no people ever received.
And here, again, was lost another precious occasion of sparing to France the crimes and cruelties through which she has since passed, and to Europe, and finally America, the evils which flowed on them also from this mortal source. The King was now become a passive machine in the hands of the National Assembly, and had he been left to himself, he would have willingly acquiesced in whatever they should devise as best for the nation. A wise constitution would have been formed, hereditary in his line, himself placed at its head, with powers so large, as to enable him to do all the good of his station, and so limited, as to restrain him from its abuse. This he would have faithfully administered, and more than this, I do not believe, he ever wished. But he had a Queen of absolute sway over his weak mind and timid virtue, and of a character the reverse of his in all points. This angel, as gaudily painted in the rhapsodies of Burke, with some smartness of fancy, but no sound sense, was proud, disdainful of restraint, indignant at all obstacles to her will, eager in the pursuit of pleasure, and firm enough to hold to her desires, or perish in their wreck. Her inordinate gambling and dissipations, with those of the Count d’Artois, and others of her clique, had been a sensible item in the exhaustion of the treasury, which called into action the reforming hand of the nation; and her opposition to it, her inflexible perverseness, and dauntless spirit, led herself to the Guillotine, drew the King on with her, and plunged the world into crimes and calamities which will for ever stain the pages of modern history. I have ever believed, that had there been no Queen, there would have been no revolution. No force would have been provoked, nor exercised. The King would have gone hand in hand with the wisdom of his sounder counsellors, who, guided by the increased lights of the age, wished only, with the same pace, to advance the principles of their social constitution. The deed which closed the mortal course of these sovereigns, I shall neither approve nor condemn. I am not prepared to say, that the first magistrate of a nation cannot commit treason against his country, or is unamenable to its punishment: nor yet, that where there is no written law, no regulated tribunal, there is not a law in our hearts, and a power in our hands, given for righteous employment in maintaining right, and redressing wrong. Of those who judged the King, many thought him wilfully criminal; many, that his existence would keep the nation in perpetual conflict with the horde of Kings, who would war against a regeneration which might come home to themselves, and that it were better that one should die than all. I should not have voted with this portion of the legislature. I should have shut up the Queen in a convent, putting harm out of her power, and placed the King in his station, investing him with limited powers, which, I verily believe, he would have honestly exercised, according to the measure of his understanding. In this way, no void would have been created, courting the usurpation of a military adventurer, nor occasion given for those enormities which demoralized the nations of the world, and destroyed, and is yet to destroy, millions and millions of its inhabitants. There are three epochs in history, signalized by the total extinction of national morality. The first was of the successors of Alexander, not omitting himself: the next, the successors of the first Cæsar: the third, our own age. This was begun by the partition of Poland, followed by that of the treaty of Pilnitz; next the conflagration of Copenhagen; then the enormities of Bonaparte, partitioning the earth at his will, and devastating it with fire and sword; now the conspiracy of Kings, the successors of Bonaparte, blasphemously calling themselves ‘The Holy Alliance,’ and treading in the footsteps of their incarcerated leader; not yet, indeed, usurping the government of other nations, avowedly and in detail, but controlling by their armies the forms in which they will permit them to be governed; and reserving, in petto, the order and extent of the usurpations further meditated. But I will return from a digression, anticipated, too, in time, into which I have been led by reflection on the criminal passions which refused to the world a favorable occasion of saving it from the afflictions it has since suffered.
Mr. Necker had reached Basle before he was overtaken by the letter of the King, inviting him back to resume the office he had recently left. He returned immediately, and all the other ministers having resigned, a new administration was named, to wit: St. Priest and Montmorin were restored; the Archbishop of Bordeaux was appointed Garde des Sceaux; La Tour du Pin, Minister of War; La Luzerne, Minister of Marine. This last was believed to have been effected by the friendship of Montmorin; for although differing in politics, they continued firm in friendship, and Luzerne, although not an able man, was thought an honest one. And the Prince of Bauvau was taken into the Council.
Seven Princes of the blood royal, six ex-ministers, and many of the high Noblesse, having fled, and the present ministers, except Luzerne, being all of the popular party, all the functionaries of government moved, for the present, in perfect harmony.
In the evening of August the 4th, and on the motion of the Viscount de Noailles, brother-in-law of La Fayette, the Assembly abolished all titles of rank, all the abusive privileges of feudalism, the tythes and casuals of the clergy, all provincial privileges, and, in fine, the feudal regimen generally. To the suppression of tythes, the Abbe Sieyes was vehemently opposed; but his learned and logical arguments were unheeded, and his estimation lessened by a contrast of his egoism (for he was beneficed on them) with the generous abandonment of rights by the other members of the Assembly. Many days were employed in putting into the form of laws the numerous demolitions of ancient abuses; which done, they proceeded to the preliminary work of a declaration of rights. There being much concord of sentiment on the elements of this instrument, it was liberally framed, and passed with a very general approbation. They then appointed a committee for the ‘reduction of a projet’ of a constitution, at the head of which was the Archbishop of Bordeaux. I received from him, as chairman of the committee, a letter of July the 20th, requesting me to attend and assist at their deliberations; but I excused myself, on the obvious considerations, that my mission was to the King as Chief Magistrate of the nation, that my duties were limited to the concerns of my own country, and forbade me to intermeddle with the internal transactions of that in which I had been received under a specific character only. Their plan of a constitution was discussed in sections, and so reported from time to time, as agreed to by the committee. The first respected the general frame of the government; and that this should be formed into three departments, executive, legislative, and judiciary, was generally agreed. But when they proceeded to subordinate developments, many and various shades of opinion came into conflict, and schism, strongly marked, broke the Patriots into fragments of very discordant principles. The first question, Whether there should be a King? met with no open opposition; and it was readily agreed, that the government of France should be monarchical and hereditary. Shall the King have a negative on the laws? Shall that negative be absolute, or suspensive only? Shall there be two Chambers of Legislation, or one only? If two, shall one of them be hereditary? or for life? or for a fixed term? and named by the King? or elected by the people? These questions found strong differences of opinion, and produced repulsive combinations among the Patriots. The aristocracy was cemented by a common principle of preserving the ancient regime or whatever should be nearest to it. Making this their polar star, they moved in phalanx, gave preponderance on every question to the minorities of the Patriots, and always to those who advocated the least change. The features of the new constitution were thus assuming a fearful aspect, and great alarm was produced among the honest Patriots by these dissensions in their ranks. In this uneasy state of things, I received one day a note from the Marquis de la Fayette, informing me, that he should bring a party of six or eight friends, to ask a dinner of me the next day. I assured him of their welcome. When they arrived, they were La Fayette himself, Duport, Barnave, Alexander la Meth, Blacon, Mounier, Maubourg, and Dagout. These were leading Patriots, of honest but differing opinions, sensible of the necessity of effecting a coalition by mutual sacrifices, knowing each other, and not afraid, therefore, to unbosom themselves mutually. This last was a material principle in the selection. With this view, the Marquis had invited the conference, and had fixed the time and place inadvertently, as to the embarrassment under which it might place me. The cloth being removed, and wine set on the table, after the American manner, the Marquis introduced the objects of the conference, by summarily reminding them of the state of things in the Assembly, the course which the principles of the constitution were taking, and the inevitable result, unless checked by more concord among the Patriots themselves. He observed, that although he also had his opinion, he was ready to sacrifice it to that of his brethren of the same cause; but that a common opinion must now be formed, or the aristocracy would carry every thing, and that, whatever they should now agree on, he, at the head of the national force, would maintain. The discussions began at the hour of four, and were continued till ten o’clock in the evening; during which time I was a silent witness to a coolness and candor of argument unusual in the conflicts of political opinion; to a logical reasoning, and chaste eloquence, disfigured by no gaudy tinsel of rhetoric or declamation, and truly worthy of being placed in parallel with the finest dialogues of antiquity, as handed to us by Xenophon, by Plato, and Cicero. The result was, that the King should have a suspensive veto on the laws, that the legislature should be composed of a single body only, and that to be chosen by the people. This Concordat decided the fate of the constitution. The Patriots all rallied to the principles thus settled, carried every question agreeably to them, and reduced the aristocracy to insignificance and impotence. But duties of exculpation were now incumbent on me. I waited on Count Montmorin the next morning, and explained to him, with truth and candor, how it happened that my house had been made the scene of conferences of such a character. He told me he already knew every thing which had passed, that so far from taking umbrage at the use made of my house on that occasion, he earnestly wished I would habitually assist at such conferences, being sure I should be useful in moderating the warmer spirits, and promoting a wholesome and practicable reformation only. I told him I knew too well the duties I owed to the King, to the nation, and to my own country, to take any part in councils concerning their internal government, and that I should persevere, with care, in the character of a neutral and passive spectator, with wishes only, and very sincere ones, that those measures might prevail which would be for the greatest good of the nation. I have no doubt, indeed, that this conference was previously known and approved by this honest minister, who was in confidence and communication with the Patriots, and wished for a reasonable reform of the constitution.
Here I discontinue my relation of the French Revolution. The minuteness with which I have so far given its details, is disproportioned to the general scale of my narrative. But I have thought it justified by the interest which the whole world must take in this Revolution. As yet, we are but in the first chapter of its history. The appeal to the rights of man, which had been made in the United States, was taken up by France, first of the European nations. From her the spirit has spread over those of the South. The tyrants of the North have allied indeed against it; but it is irresistible. Their opposition will only multiply its millions of human victims; their own satellites will catch it, and the condition of man through the civilized world, will be finally and greatly meliorated. This is a wonderful instance of great events from small causes. So inscrutable is the arrangement of causes and consequences in this world, that a two-penny duty on tea, unjustly imposed in a sequestered part of it, changes the condition of all its inhabitants. I have been more minute in relating the early transactions of this regeneration, because I was in circumstances peculiarly favorable for a knowledge of the truth. Possessing the confidence and intimacy of the leading Patriots, and more than all, of the Marquis Fayette, their head and Atlas, who had no secrets from me, I learned with correctness the views and proceedings of that party; while my intercourse with the diplomatic missionaries of Europe at Paris, all of them with the court, and eager in prying into its councils and proceedings, gave me a knowledge of these also. My information was always, and immediately committed to writing, in letters to Mr. Jay, and often to my friends, and a recurrence to these letters now insures me against errors of memory. These opportunities of information ceased at this period, with my retirement from this interesting scene of action. I had been more than a year soliciting leave to go home, with a view to place my daughters in the society and care of their friends, and to return for a short time to my station at Paris. But the metamorphosis through which our government was then passing from its chrysalid to its organic form, suspended its action in a great degree; and it was not till the last of August that I received the permission I had asked. And here I cannot leave this great and good country, without expressing my sense of its pre-eminence of character among the nations of the earth. A more benevolent people I have never known, nor greater warmth and devotedness in their select friendships. Their kindness and accommodation to strangers is unparalleled, and the hospitality of Paris is beyond any thing I had conceived to be practicable in a large city. Their eminence, too, in science, the communicative dispositions of their scientific men, the politeness of the general manners, the ease and vivacity of their conversation, give a charm to their society, to be found nowhere else. In a comparison of this with other countries, we have the proof of primacy, which was given to Themistocles after the battle of Salamis. Every general voted to himself the first reward of valor, and the second to Themistocles. So, ask the traveled inhabitant of any nation, In what country on earth would you rather live?—Certainly, in my own, where are all my friends, my relations, and the earliest and sweetest affections and recollections of my life. Which would be your second choice? France.
On the 26th of September, I left Paris for Havre, where I was detained by contrary winds, until the 8th of October. On that day, and the 9th, I crossed over to Cowes, where I had engaged the Clermont, Capt. Colley, to touch for me. She did so; but here again we were detained by contrary winds, until the 22nd, when we embarked, and landed at Norfolk on the 23rd of November. On my way home, I passed some days at Eppington, in Chesterfield, the residence of my friend and connection, Mr. Eppes; and, while there, I received a letter from the President, General Washington, by express, covering an appointment to be Secretary of State. [See Appendix, note H.] I received it with real regret. My wish had been to return to Paris, where I had left my household establishment, as if there myself, and to see the end of the Revolution, which, I then thought, would be certainly and happily closed in less than a year. I then meant to return home, to withdraw from political life, into which I had been impressed by the circumstances of the times, to sink into the bosom of my family and friends, and devote myself to studies more congenial to my mind. In my answer of December 15th, I expressed these dispositions candidly to the President, and my preference of a return to Paris; but assured him, that if it was believed I could be more useful in the administration of the government, I would sacrifice my own inclinations without hesitation, and repair to that destination: this I left to his decision. I arrived at Monticello on the 23rd of December, where I received a second letter from the President, expressing his continued wish, that I should take my station there, but leaving me still at liberty to continue in my former office, if I could not reconcile myself to that now proposed. This silenced my reluctance, and I accepted the new appointment.
In the interval of my stay at home, my eldest daughter had been happily married to the eldest son of the Tuckahoe branch of Randolphs, a young gentleman of genius, science, and honorable mind, who afterwards filled a dignified station in the General Government, and the most dignified in his own State. I left Monticello on the 1st of March, 1790, for New York. At Philadelphia I called on the venerable and beloved Franklin. He was then on the bed of sickness from which he never rose. My recent return from a country in which he had left so many friends, and the perilous convulsions to which they had been exposed, revived all his anxieties to know what part they had taken, what had been their course, and what their fate. He went over all in succession, with a rapidity and animation, almost too much for his strength. When all his inquiries were satisfied, and a pause took place, I told him I had learned with much pleasure that, since his return to America, he had been occupied in preparing for the world, the history of his own life. ‘I cannot say much of that,’ said he; ‘but I will give you a sample of what I shall leave:’ and he directed his little grandson (William Bache) who was standing by the bedside, to hand him a paper from the table, to which he pointed. He did so; and the Doctor putting it into my hands, desired me to take it, and read it at my leisure. It was about a quire of folio paper, written in a large and running hand, very like his own. I looked into it slightly, then shut it, and said I would accept his permission to read it, and would carefully return it. He said, ‘No, keep it.’ Not certain of his meaning, I again looked into it, folded it for my pocket, and said again, I would certainly return it. ‘No,’ said he, ‘keep it.’ I put it into my pocket, and shortly after, took leave of him. He died on the 17th of the ensuing month of April; and as I understood that he had bequeathed all his papers to his grandson, William Temple Franklin, I immediately wrote to Mr. Franklin, to inform him I possessed this paper, which I should consider as his property, and would deliver to his order. He came on immediately to New York, called on me for it, and I delivered it to him. As he put it into his pocket, he said carelessly, he had either the original, or another copy of it, I do not recollect which. This last expression struck my attention forcibly, and for the first time suggested to me the thought, that Dr. Franklin had meant it as a confidential deposite in my hands, and that I had done wrong in parting from it. I have not yet seen the collection he published of Dr. Franklin’s works, and therefore know not if this is among them. I have been told it is not. It contained a narrative of the negotiations between Dr. Franklin and the British Ministry, when he was endeavoring to prevent the contest of arms which followed. The negotiation was brought about by the intervention of Lord Howe and his sister, who, I believe, was called Lady Howe, but I may misremember her title. Lord Howe seems to have been friendly to America, and exceedingly anxious to prevent a rupture. His intimacy with Dr. Franklin, and his position with the Ministry, induced him to undertake a mediation between them; in which his sister seemed to have been associated. They carried from one to the other, backwards and forwards, the several propositions and answers which passed, and seconded with their own intercessions, the importance of mutual sacrifices, to preserve the peace and connection of the two countries. I remember that Lord North’s answers were dry, unyielding, in the spirit of unconditional submission, and betrayed an absolute indifference to the occurrence of a rupture; and he said to the mediators distinctly, at last, that ‘a rebellion was not to be deprecated on the part of Great Britain; that the confiscations it would produce, would provide for many of their friends.’ This expression was reported by the mediators to Dr. Franklin, and indicated so cool and calculated a purpose in the Ministry, as to render compromise hopeless, and the negotiation was discontinued. If this is not among the papers published, we ask, what has become of it? I delivered it with my own hands, into those of Temple Franklin. It certainly established views so atrocious in the British government, that its suppression would, to them, be worth a great price. But could the grandson of Dr. Franklin be, in such degree, an accomplice in the parricide of the memory of his immortal grandfather? The suspension, for more than twenty years, of the general publication, bequeathed and confided to him, produced for a while hard suspicions against him: and if, at last, all are not published, a part of these suspicions may remain with some.
I arrived at New York on the 21st of March, where Congress was in session.
APPENDIX TO THE MEMOIR.
[NOTE A.] Letter to John Saunderson, Esq.
Sir,
Monticello, August 31, 1820.
Your letter of the 19th was received in due time, and I wish it were in my power to furnish you more fully, than in the enclosed paper, with materials for the biography of George Wythe; but I possess none in writing, am very distant from the place of his birth and early life, and know not a single person in that quarter from whom inquiry could be made, with the expectation of collecting any thing material. Add to this, that feeble health disables me, almost, from writing; and, entirely, from the labor of going into difficult research. I became acquainted with Mr. Wythe when he was about thirty-five years of age. He directed my studies in the law, led me into business, and continued, until death, my most affectionate friend. A close intimacy with him, during that period of forty odd years, the most important of his life, enables me to state its leading facts, which, being of my own knowledge, I vouch their truth. Of what precedes that period, I speak from hearsay only, in which there may be error, but of little account, as the character of the facts will themselves manifest. In the epoch of his birth I may err a little, stating that from the recollection of a particular incident, the date of which, within a year or two, I do not distinctly remember. These scanty outlines, you will be able, I hope, to fill up from other information, and they may serve you, sometimes, as landmarks to distinguish truth from error, in what you hear from others. The exalted virtue of the man will also be a polar star to guide you in all matters which may touch that element of his character. But on that you will receive imputation from no man; for, as far as I know, he never had an enemy. Little as I am able to contribute to the just reputation of this excellent man, it is the act of my life most gratifying to my heart: and leaves me only to regret that a waning memory can do no more.
Of Mr. Hancock I can say nothing, having known him only in the chair of Congress. Having myself been the youngest man but one in that body, the disparity of age prevented any particular intimacy. But of him there can be no difficulty in obtaining full information in the North.
I salute you, Sir, with sentiments of great respect.
Th: Jefferson.
Notes for the Biography of George Wythe.
George Wythe was born about the year 1727 or 1728, of a respectable family in the county of Elizabeth City, on the shores of the Chesapeake. He inherited, from his father, a fortune sufficient for independence and ease. He had not the benefit of a regular education in the schools, but acquired a good one of himself, and without assistance; insomuch, as to become the best Latin and Greek scholar in the state. It is said, that while reading the Greek Testament, his mother held an English one, to aid him in rendering the Greek text conformably with that. He also acquired, by his own reading, a good knowledge of Mathematics, and of Natural and Moral Philosophy. He engaged in the study of the law under the direction of a Mr. Lewis, of that profession, and went early to the bar of the General Court, then occupied by men of great ability, learning, and dignity in their profession. He soon became eminent among them, and, in process of time, the first at the bar, taking into consideration his superior learning, correct elocution, and logical style of reasoning; for in pleading he never indulged himself with an useless or declamatory thought or word; and became as distinguished by correctness and purity of conduct in his profession, as he was by his industry and fidelity to those who employed him. He was early elected to the House of Representatives, then called the House of Burgesses, and continued in it until the Revolution. On the first dawn of that, instead of higgling on half-way principles, as others did who feared to follow their reason, he took his stand on the solid ground, that the only link of political union between us and Great Britain, was the identity of our Executive; that that nation and its Parliament had no more authority over us, than we had over them, and that we were co-ordinate nations with Great Britain and Hanover.
In 1774, he was a member of a Committee of the House of Burgesses, appointed to prepare a Petition to the King, a Memorial to the House of Lords, and a Remonstrance to the House of Commons, on the subject of the proposed Stamp Act. He was made draughtsman of the last, and, following his own principles, he so far overwent the timid hesitations of his colleagues, that his draught was subjected by them to material modifications; and, when the famous Resolutions of Mr. Henry, in 1775, were proposed, it was not on any difference of principle that they were opposed by Wythe. Randolph, Pendleton, Nicholas, Bland, and other worthies, who had long been the habitual leaders of the House; but because those papers of the preceding session had already expressed the same sentiments and assertions of right, and that an answer to them was yet to be expected.
In August, 1775, he was appointed a member of Congress, and in 1776, signed the Declaration of Independence, of which he had, in debate, been an eminent supporter. And subsequently, in the same year, he was appointed by the Legislature of Virginia, one of a committee to revise the laws of the state, as well of British, as of Colonial enactment, and to prepare bills for re-enacting them, with such alterations as the change in the form and principles of the government, and other circumstances, required: and of this work, he executed the period commencing with the revolution in England, and ending with the establishment of the new government here; excepting the Acts for regulating descents, for religious freedom, and for proportioning crimes and punishments. In 1777, he was chosen speaker of the House of Delegates, being of distinguished learning in parliamentary law and proceedings; and towards the end of the same year, he was appointed one of the three Chancellors, to whom that department of the Judiciary was confided, on the first organization of the new government. On a subsequent change of the form of that court, he was appointed sole Chancellor, in which office he continued to act until his death, which happened in June, 1806, about the seventy-eighth or seventy-ninth year of his age.
Mr. Wythe had been twice married; first, I believe, to a daughter of Mr. Lewis, with whom he had studied law, and afterwards, to a Miss Taliaferro, of a wealthy and respectable family in the neighborhood of Williamsburg; by neither of whom did he leave issue.
No man ever left behind him a character more venerated than George Wythe. His virtue was of the purest tint; his integrity inflexible, and his justice exact; of warm patriotism, and, devoted as he was to liberty, and the natural and equal rights of man, he might truly be called the Cato of his country, without the avarice of the Roman; for a more disinterested person never lived. Temperance and regularity in all his habits, gave him general good health, and his unaffected modesty and suavity of manners endeared him to every one. He was of easy elocution, his language chaste, methodical in the arrangement of his matter, learned and logical in the use of it, and of great urbanity in debate; not quick of apprehension, but, with a little time, profound in penetration, and sound in conclusion. In his philosophy he was firm, and neither troubling, nor perhaps trusting, any one with his religious creed, he left the world to the conclusion, that that religion must be good which could produce a life of exemplary virtue.
His stature was of the middle size, well formed and proportioned, and the features of his face were manly, comely, and engaging. Such was George Wythe, the honor of his own, and the model of future times.
[NOTE B.]—Letter to Samuel A. Wells, Esq.
Sir,
Monticello, May 12, 1829.
An absence, of sometime, at an occasional and distant residence, must apologize for the delay in acknowledging the receipt of your favor of April 12th; and candor obliges me to add, that it has been somewhat extended by an aversion to writing, as well as to calls on my memory for facts so much obliterated from it by time, as to lessen my own confidence in the traces which seem to remain. One of the enquiries in your letter, however, may be answered without an appeal to the memory. It is that respecting the question, Whether committees of correspondence originated in Virginia, or Massachusetts? on which you suppose me to have claimed it for Virginia; but certainly I have never made such a claim. The idea, I suppose, has been taken up from what is said in Wirt’s history of Mr. Henry, page 87, and from an inexact attention to its precise terms. It is there said, ‘This House [of Burgesses, of Virginia] had the merit of originating that powerful engine of resistance, corresponding committees between the legislatures of the different colonies.’ That the fact, as here expressed, is true, your letter bears witness, when it says, that the resolutions of Virginia, for this purpose, were transmitted to the speakers of the different assemblies, and by that of Massachusetts was laid, at the next session, before that body, who appointed a committee for the specified object: adding, ‘Thus, in Massachusetts, there were two committees of correspondence, one chosen by the people, the other appointed by the House of Assembly; in the former, Massachusetts preceded Virginia; in the latter, Virginia preceded Massachusetts.’ To the origination of committees for the interior correspondence between the counties and towns of a state, I know of no claim on the part of Virginia; and certainly none was ever made by myself. I perceive, however, one error, into which memory had led me. Our committee for national correspondence was appointed in March, ‘73, and I well remember, that going to Williamsburg in the month of June following, Peyton Randolph, our chairman, told me that messengers bearing despatches between the two states had crossed each other by the way, that of Virginia carrying our propositions for a committee of national correspondence, and that of Massachusetts, bringing, as my memory suggested, a similar proposition. But here I must have misremembered; and the resolutions brought us from Massachusetts were probably those you mention of the town-meeting of Boston, on the motion of Mr. Samuel Adams, appointing a committee ‘to state the rights of the colonists, and of that province in particular, and the infringements of them; to communicate them to the several towns, as the sense of the town of Boston, and to request, of each town, a free, communication of its sentiments on this subject.’ I suppose, therefore, that these resolutions were not received, as you think, while the House of Burgesses was in session in March, 1773, but a few days after we rose, and were probably what was sent by the messenger, who crossed ours by the way. They may, however, have been still different. I must, therefore, have been mistaken in supposing, and stating to Mr. Wirt, that the proposition of a committee for national correspondence was nearly simultaneous in Virginia and Massachusetts.
A similar misapprehension of another passage in Mr. Wirt’s book, for which I am also quoted, has produced a similar reclamation on the part of Massachusetts, by some of her most distinguished and estimable citizens. I had been applied to by Mr. Wirt, for such facts respecting Mr. Henry, as my intimacy with him and participation in the transactions of the day, might have placed within my knowledge. I accordingly committed them to paper; and Virginia being the theatre of his action, was the only subject within my contemplation. While speaking of him, of the resolutions and measures here, in which he had the acknowledged lead, I used the expression that ‘Mr. Henry certainly gave the first impulse to the ball of revolution.’ [Wirt, page 41.] The expression is indeed general, and in all its extension would comprehend all the sister states; but indulgent construction would restrain it, as was really meant, to the subject matter under contemplation, which was Virginia alone; according to the rule of the lawyers, and a fair canon of general criticism, that every expression should be construed secundum subjectam materiam. Where the first attack was made, there must have been of course, the first act of resistance, and that was in Massachusetts. Our first overt act of war, was Mr. Henry’s embodying a force of militia from several counties, regularly armed and organized, marching them in military array, and making reprisal on the King’s treasury at the seat of government, for the public powder taken away by his Governor. This was on the last days of April, 1775. Your formal battle of Lexington was ten or twelve days before that, and greatly overshadowed in importance, as it preceded in time, our little affray, which merely amounted to a levying of arms against the King; and very possibly, you had had military affrays before the regular battle of Lexington.
These explanations will, I hope, assure you, Sir, that so far as either facts or opinions have been truly quoted from me, they have never been meant to intercept the just fame of Massachusetts, for the promptitude and perseverance of her early resistance. We willingly cede to her the laud of having been (although not exclusively) ‘the cradle of sound principles,’ and, if some of us believe she has deflected from them in her course, we retain full confidence in her ultimate return to them.
I will now proceed to your quotation from Mr. Galloway’s statement of what passed in Congress, on their Declaration of Independence; in which statement there is not one word of truth, and where bearing some resemblance to truth, it is an entire perversion of it. I do not charge this on Mr. Galloway himself; his desertion having taken place long before these measures, he doubtless received his information from some of the loyal friends whom he left behind him. But as yourself, as well as others, appear embarrassed by inconsistent accounts of the proceedings on that memorable occasion, and as those who have endeavored to restore the truth, have themselves committed some errors, I will give you some extracts from a written document on that subject; for the truth of which, I pledge myself to heaven and earth; having, while the question of Independence was under consideration before Congress, taken written notes, in my seat, of what was passing, and reduced them to form on the final conclusion. I have now before me that paper, from which the following are extracts. ‘Friday, June 7th, 1776. The delegates from Virginia moved, in obedience to instructions from their constituents, that the Congress should declare that these United Colonies are, and of right ought to be, free and independent states; that they are absolved from all allegiance to the British crown, and that all political connection between them and the state of Great Britain is, and ought to be, totally dissolved; that measures should be immediately taken for procuring the assistance of foreign powers, and a Confederation be formed to bind the colonies more closely together. The House being obliged to attend at that time to some other business, the proposition was referred to the next day, when the members were ordered to attend punctually at ten o’clock. Saturday, June 8th. They proceeded to take it into consideration, and referred it to a committee of the whole, into which they immediately resolved themselves, and passed that day and Monday, the 10th, in debating on the subject.
‘It appearing, in the course of these debates, that the colonies of New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Delware, Maryland, and South Carolina, were not yet matured for falling from the parent stem, but that they were fast advancing to that state, it was thought most prudent to wait a while for them, and to postpone the final decision to July 1st. But, that this might occasion as little delay as possible, a Committee was appointed to prepare a Declaration of Independence. The Committee were John Adams, Dr. Franklin, Roger Sherman, Robert R. Livingston, and myself. This was reported to the House on Friday the 28th of June, when it was read and ordered to lie on the table. On Monday, the 1st of July, the House resolved itself into a Committee of the whole, and resumed the consideration of the original motion made by the delegates of Virginia, which, being again debated through the day, was carried in the affirmative by the votes of New Hampshire, Connecticut, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, New Jersey, Maryland, Virginia, North Carolina, and Georgia. South Carolina and Pennsylvania voted against it. Delaware had but two members present, and they were divided. The delegates from New York declared they were for it themselves, and were assured their constituents were for it; but that their instructions having been drawn near a twelvemonth before, when reconciliation was still the general object, they were enjoined by them, to do nothing which should impede that object. They, therefore, thought themselves not justifiable in voting on either side, and asked leave to withdraw from the question, which was given them. The Committee rose, and reported their resolution to the House. Mr. Rutledge, of South Carolina, then requested the determination might be put off to the next day, as he believed his colleagues, though they disapproved of the resolution, would then join in it for the sake of unanimity. The ultimate question, whether the House would agree to the resolution of the Committee, was accordingly postponed to the next day, when it was again moved, and South Carolina concurred in voting for it. In the mean time, a third member had come post from the Delaware counties, and turned the vote of that colony in favor of the resolution. Members of a different sentiment attending that morning from Pennsylvania also, her vote was changed; so that the whole twelve colonies, who were authorized to vote at all, gave their votes for it; and within a few days [July 9th] the convention of New York approved of it, and thus supplied the void occasioned by the withdrawing of their delegates from the vote.’ [Be careful to observe, that this vacillation and vote were on the original motion of the 7th of June, by the Virginia delegates, that Congress should declare the colonies independent.] ‘Congress proceeded, the same day, to consider the Declaration of Independence, which had been reported and laid on the table the Friday preceding, and on Monday referred to a Committee of the whole. The pusillanimous idea, that we had friends in England worth keeping terms with, still haunted the minds of many. For this reason, those passages which conveyed censures on the people of England were struck out, lest they should give them offence. The debates having taken up the greater parts of the second, third, and fourth days of July, were, in the evening of the last, closed: the Declaration was reported by the Committee, agreed to by the House, and signed by every member present except Mr. Dickinson.’ So far my notes.
Governor M’Kean, in his letter to M’Corkle of July 16th, 1817, has thrown some lights on the transactions of that day: but, trusting to his memory chiefly, at an age when our memories are not to be trusted, he has confounded two questions, and ascribed proceedings to one which belonged to the other. These two questions were, 1st, the Virginia motion of June the 7th, to declare Independence; and 2nd, the actual Declaration, its matter and form. Thus he states the question on the Declaration itself, as decided on the 1st of July; but it was the Virginia motion which was voted on that day in committee of the whole; South Carolina, as well as Pennsylvania, then voting against it. But the ultimate decision in the House, on the report of the Committee, being, by request, postponed to the next morning, all the states voted for it, except New York, whose vote was delayed for the reason before stated. It was not till the 2nd of July, that the Declaration itself was taken up; nor till the 4th, that it was decided, and it was signed by every member present, except Mr. Dickinson.
The subsequent signatures of members who were not then present, and some of them not yet in office, is easily explained, if we observe who they were; to wit, that they were of New York and Pennsylvania. New York did not sign till the 15th, because it was not till the 9th, (five days after the general signature,) that their Convention authorized them to do so. The Convention of Pennsylvania, learning that it had been signed by a majority only of their delegates, named a new delegation on the 20th, leaving out Mr. Dickinson, who had refused to sign, Willing and Humphreys, who had withdrawn, reappointing the three members who had signed, Morris, who had not been present, and five new ones, to wit, Rush, Clymer, Smith, Taylor, and Ross: and Morris and the five new members were permitted to sign, because it manifested the assent of their full delegation, and the express will of their Convention, which might have been doubted on the former signature of a minority only. Why the signature of Thornton, of New Hampshire, was permitted so late as the 4th of November, I cannot now say; but undoubtedly for some particular reason, which we should find to have been good, had it been expressed. These were the only post-signers, and you see, sir, that there were solid reasons for receiving those of New York and Pennsylvania, and that this circumstance in no wise affects the faith of this Declaratory Charter of our rights, and of the rights of man.
With a view to correct errors of fact before they become inveterate by repetition, I have stated what I find essentially material in my papers, but with that brevity which the labor of writing constrains me to use.
On the four particular articles of inquiry in your letter, respecting your grandfather, the venerable Samuel Adams, neither memory nor memorandums enable me to give any information. I can say that he was truly a great man, wise in council, fertile in resources, immovable in his purposes, and had, I think, a greater share than any other member, in advising and directing our measures in the Northern war. As a speaker, he could not be compared with his living colleague and namesake, whose deep conceptions, nervous style, and undaunted firmness, made him truly our bulwark in debate. But Mr. Samuel Adams, although not of fluent elocution, was so rigorously logical, so clear in his views, abundant in good sense, and master always of his subject, that he commanded the most profound attention whenever he rose in an assembly, by which the froth of declamation was heard with the most sovereign contempt. I sincerely rejoice that the record of his worth is to be undertaken by one so much disposed as you will be, to hand him down fairly to that posterity, for whose liberty and happiness he was so zealous a laborer.
With sentiments of sincere veneration for his memory, accept yourself this tribute to it, with the assurances of my great respect.
Th: Jefferson.
P. S. August 6th, 1822. Since the date of this letter, to wit, this day, August 6, ‘22, I have received the new publication of the Secret Journals of Congress, wherein is stated a resolution of July 19th, 1776, that the Declaration passed on the 4th, be fairly engrossed on parchment, and when engrossed, be signed by every member; and another of August 2nd, that being engrossed and compared at the table, it was signed by the members; that is to say, the copy engrossed on parchment (for durability) was signed by the members, after being compared at the table with the original one signed on paper, as before stated. I add this P. S. to the copy of my letter to Mr. Wells, to prevent confounding the signature of the original with that of the copy engrossed on parchment.
[NOTE C]—August, 1774, Instructions to the first Delegation
On the Instructions given to the first Delegation of Virginia to Congress, in August, 1774.
The Legislature of Virginia happened to be in session in Williamsburg, when news was received of the passage, by the British Parliament, of the Boston Port Bill, which was to take effect on the first day of June then ensuing. The House of Burgesses, thereupon, passed a resolution, recommending to their fellow-citizens that that day should be set apart for fasting and prayer to the Supreme Being, imploring him to avert the calamities then threatening us, and to give us one heart and one mind to oppose every invasion of our liberties. The next day, May the 20th, 1774, the Governor dissolved us. We immediately repaired to a room in the Raleigh tavern, about one hundred paces distant from the Capitol, formed ourselves into a meeting, Peyton Randolph in the chair, and came to resolutions, declaring, that an attack on one colony to enforce arbitrary acts, ought to be considered as an attack on all, and to be opposed by the united wisdom of all. We, therefore, appointed a Committee of Correspondence, to address letters to the Speakers of the several Houses of Representatives of the colonies, proposing the appointment of deputies from each, to meet annually in a general Congress, to deliberate on their common interests, and on the measures to be pursued in common. The members then separated to their several homes, except those of the Committee, who met the next day, prepared letters according to instructions, and despatched them by messengers express, to their several destinations. It had been agreed, also by the meeting, that the Burgesses, who should be elected under the writs then issuing, should be requested to meet in Convention on a certain day in August, to learn the result of these letters, and to appoint delegates to a Congress, should that measure be approved by the other colonies. At the election, the people re-elected every man of the former Assembly, as a proof of their approbation of what they had done. Before I left home to attend the Convention, I prepared what I thought might be given, in instruction, to the Delegates who should be appointed to attend the General Congress proposed. They were drawn in haste, with a number of blanks, with some uncertainties and inaccuracies of historical facts, which I neglected at the moment, knowing they could be readily corrected at the meeting. I set out on my journey, but was taken sick on the road, and was unable to proceed. I therefore sent on, by express, two copies, one under cover to Patrick Henry, the other to Peyton Randolph, who I knew would be in the chair of the Convention. Of the former no more was ever heard or known. Mr. Henry probably thought it too bold, as a first measure, as the majority of the members did. On the other copy being laid on the table of the Convention, by Peyton Randolph, as the proposition of a member who was prevented from attendance by sickness on the road, tamer sentiments were preferred, and, I believe, wisely preferred; the leap I proposed being too long, as yet, for the mass of our citizens. The distance between these, and the instructions actually adopted, is of some curiosity, however, as it shows the inequality of pace with which we moved, and the prudence required to keep front and rear together. My creed had been formed on unsheathing the sword at Lexington. They printed the paper, however, and gave it the title of ‘A Summary View of the Rights of British America.’ In this form it got to London, where the opposition took it up, shaped it to opposition views, and, in that form, it ran rapidly through several editions.
Mr. Marshall, in his history of General Washington, chapter 3, speaking of this proposition for Committees of correspondence and for a General Congress, says, ‘this measure had already been proposed in town meeting in Boston,’ and some pages before he had said, that ‘at a session of the General Court of Massachusetts, in September, 1770, that Court, in pursuance of a favorite idea of uniting all the colonies in one system of measures, elected a Committee of correspondence, to communicate with such Committees as might be appointed by the other colonies.’ This is an error. The Committees of correspondence, elected by Massachusetts, were expressly for a correspondence among the several towns of that province only. Besides the text of their proceedings, his own note X, proves this. The first proposition for a general correspondence between the several states, and for a General Congress, was made by our meeting of May, 1774. Botta, copying Marshall, has repeated his error, and so it will be handed on from copyist to copyist, ad infinitum. Here follow my proposition, and the more prudent one which was adopted.
‘Resolved, That it be an instruction to the said deputies, when assembled in General Congress, with the deputies from the other states of British America, to propose to the said Congress that an humble and dutiful address be presented to his Majesty, begging leave to lay before him, as Chief Magistrate of the British empire, the united complaints of his Majesty’s subjects in America; complaints which are excited by many unwarrantable encroachments and usurpations, attempted to be made by the legislature of one part of the empire upon the rights which God and the laws have given equally and independently to all. To represent to his Majesty that, these, his States, have often individually made humble application to his imperial throne, to obtain, through its intervention, some redress of their injured rights; to none of which was ever even an answer condescended. Humbly to hope that this, their joint address, penned in the language of truth, and divested of those expressions of servility which would persuade his Majesty that we are asking favors, and not rights, shall obtain from his Majesty a more respectful acceptance; and this his Majesty will think we have reason to expect, when he reflects that he is no more than the chief officer of the people, appointed by the laws, and circumscribed with definite powers, to assist in working the great machine of government, erected for their use, and, consequently, subject to their superintendence; and in order that these, our rights, as well as the invasions of them, may be laid more fully before his Majesty, to take a view of them from the origin and first settlement of these countries.
‘To remind him that our ancestors, before their emigration to America, were the free inhabitants of the British dominions in Europe, and possessed a right, which nature has given to all men, of departing from the country in which chance, not choice, has placed them, of going in quest of new habitations, and of there establishing new societies, under such laws and regulations, as to them shall seem most likely to promote public happiness. That their Saxon ancestors had, under this universal law, in like manner left their native wilds and woods in the North of Europe, had possessed themselves of the island of Britain, then less charged with inhabitants, and had established there that system of laws which has so long been the glory and protection of that country. Nor was ever any claim of superiority or dependence asserted over them, by that mother country from which they had migrated: and were such a claim made, it is believed his Majesty’s subjects in Great Britain have too firm a feeling of the rights derived to them from their ancestors, to bow down the sovereignty of their state before such visionary pretensions. And it is thought that no circumstance has occurred to distinguish, materially, the British from the Saxon emigration. America was conquered, and her settlements made and firmly established, at the expense of individuals, and not of the British public. Their own blood was spilt in acquiring lands for their settlement, their own fortunes expended in making that settlement effectual. For themselves they fought, for themselves they conquered, and for themselves alone they have right to hold. No shilling was ever issued from the public treasures of his Majesty, or his ancestors, for their assistance, till of very late times, after the colonies had become established on a firm and permanent fooling. That then, indeed, having become valuable to Great Britain for her commercial purposes, his Parliament was pleased to lend them assistance, against an enemy who would fain have drawn to herself the benefits of their commerce, to the great aggrandizement of herself, and danger of Great Britain. Such assistance, and in such circumstances, they had often before given to Portugal and other allied states, with whom they carry on a commercial intercourse. Yet these states never supposed, that by calling in her aid, they thereby submitted themselves to her sovereignty. Had such terms been proposed, they would have rejected them with disdain, and trusted for better to the moderation of their enemies, or to a vigorous exertion of their own force. We do not, however, mean to underrate those aids, which, to us, were doubtless valuable, on whatever principles granted: but we would show that they cannot give a title to that authority which the British Parliament would arrogate over us; and that they may amply be repaid, by our giving to the inhabitants of Great Britain such exclusive privileges in trade as may be advantageous to them, and, at the same time, not too restrictive to ourselves. That settlement having been thus effected in the wilds of America, the emigrants thought proper to adopt that system of laws, under which they had hitherto lived in the mother country, and to continue their union with her, by submitting themselves to the same common sovereign, who was thereby made the central link, connecting the several parts of the empire thus newly multiplied.
‘But that not long were they permitted, however far they thought themselves removed from the hand of oppression, to hold undisturbed, the rights thus acquired at the hazard of their lives and loss of their fortunes. A family of Princes was then on the British throne, whose treasonable crimes against their people brought on them, afterwards, the exertion of those sacred and sovereign rights of punishment, reserved in the hands of the people for cases of extreme necessity, and judged by the constitution unsafe to be delegated to any other judicature. While every day brought forth some new and unjustifiable exertion of power over their subjects on that side the water, it, was not to be expected that those here, much less able at that time to oppose the designs of despotism, should be exempted from injury. Accordingly, this country, which had been acquired by the lives, the labors, and fortunes of individual adventurers, was by these Princes, at several times, parted out and distributed among the favorites and followers of their fortunes; and, by an assumed right of the crown alone, were erected into distinct and independent governments; a measure, which, it is believed, his Majesty’s prudence and understanding would prevent him from imitating at this day; as no exercise of such power, of dividing and dismembering a country, has ever occurred in his Majesty’s realm of England, though now of very ancient standing; nor could it be justified or acquiesced under there, or in any other part of his Majesty’s empire.
‘That the exercise of a free trade with all parts of the world, possessed by the American colonists, as of natural right, and which no law of their own had taken away or abridged, was next the object of unjust encroachment. Some of the colonies having thought proper to continue the administration of their government in the name and under the authority of his Majesty, King Charles the First, whom, notwithstanding his late deposition by the Commonwealth of England, they continued in the sovereignty of their State, the Parliament, for the Commonwealth, took the same in high offence, and assumed upon themselves the power of prohibiting their trade with all other parts of the world, except the Island of Great Britain. This arbitrary act, however, they soon recalled, and by solemn treaty entered into on the 12th day of March, 1651, between the said Commonwealth by their Commissioners, and the colony of Virginia by their House of Burgesses, it was expressly stipulated by the eighth article of the said treaty, that they should have “free trade as the people of England do enjoy to all places and with all nations, according to the laws of that Commonwealth.” But that, upon the restoration of his Majesty, King Charles the Second, their rights of free commerce fell once more a victim to arbitrary power: and by several acts of his reign, as well as of some of his successors, the trade of the colonies was laid under such restrictions, as show what hopes they might form from the justice of a British Parliament, were its uncontrolled power admitted over these States.*
*12. C.2. c. 18. 15. C.2. c.11. 25. C.2. c.7. 7. 8. W. M.
c.22. 11. W.34. Anne. 6. C.2. c.13.
History has informed us, that bodies of men, as well as individuals, are susceptible of the spirit of tyranny. A view of these acts of Parliament for regulation, as it has been affectedly called, of the American trade, if all other evidences were removed out of the case, would undeniably evince the truth of this observation. Besides the duties they impose on our articles of export and import, they prohibit our going to any markets northward of Cape Finisterra, in the kingdom of Spain, for the sale of commodities which Great Britian will not take from us, and for the purchase of others, with which she cannot supply us; and that, for no other than the arbitrary purpose of purchasing for themselves, by a sacrifice of our rights and interests, certain privileges in their commerce with an allied state, who, in confidence that their exclusive trade with America will be continued, while the principles and power of the British Parliament be the same, have indulged themselves in every exorbitance which their avarice could dictate, or our necessities extort; have raised their commodities called for in America, to the double and treble of what they sold for, before such exclusive privileges were given them, and of what better commodities of the same kind would cost us elsewhere; and, at the same time, give us much less for what we carry thither, than might be had at more convenient ports. That these acts prohibit us from carrying, in quest of other purchasers, the surplus of our tobaccos, remaining after the consumption of Great Britain is supplied: so that we must leave them with the British merchant, for whatever he will please to allow us, to be by him re-shipped to foreign markets, where he will reap the benefits of making sale of them for full value. That, to heighten still the idea of Parliamentary justice, and to show with what moderation they are like to exercise power, where themselves are to feel no part of its weight, we take leave to mention to his Majesty certain other acts of the British Parliament, by which they would prohibit us from manufacturing, for our own use, the articles we raise on our own lands, with our own labor. By an act passed in the fifth year of the reign of his late Majesty, King George the Second, an American subject is forbidden to make a hat for himself, of the fur which he has taken, perhaps on his own soil; an instance of despotism, to which no parallel can be produced in the most arbitrary ages of British history. By one other act, passed in the twenty-third year of the same reign, the iron which we make, we are forbidden to manufacture; and, heavy as that article is, and necessary in every branch of husbandry, besides commission and insurance, we are to pay freight for it to Great Britain, and freight for it back again, for the purpose of supporting, not men, but machines, in the island of Great Britain. In the same spirit of equal and impartial legislation, is to be viewed the act of Parliament, passed in the fifth year of the same reign, by which American lands are made subject to the demands of British creditors, while their own lands were still continued unanswerable for their debts; from which one of these conclusions must necessarily follow, either that justice is not the same thing in America as in Britain, or else that the British Parliament pay less regard to it here than there. But, that we do not point out to his Majesty the injustice of these acts, with intent to rest on that principle the cause of their nullity; but to show that experience confirms the propriety of those political principles, which exempt us from the jurisdiction of the British Parliament. The true ground on which we declare these acts void, is, that the British Parliament has no right to exercise authority over us.
‘That these exercises of usurped power have not been confined to instances alone, in which themselves were interested; but they have also intermeddled with the regulation of the internal affairs of the colonies. The act of the 9th of Anne for establishing a post-office in America seems to have had little connection with British convenience, except that of accommodating his Majesty’s ministers and favorites with the sale of a lucrative and easy office.
‘That thus have we hastened through the reigns which preceded his Majesty’s, during which the violations of our rights were less alarming, because repeated at more distant intervals, than that rapid and bold succession of injuries, which is likely to distinguish the present from all other periods of American story. Scarcely have our minds been able to emerge from the astonishment, into which one stroke of Parliamentary thunder has involved us, before another more heavy and more alarming is fallen on us. Single acts of tyranny may be ascribed to the accidental opinion of a day; but a series of oppressions, begun at a distinguished period, and pursued unalterably through every change of ministers, too plainly prove a deliberate, systematical plan of reducing us to slavery.

‘That the act passed in the fourth year of his Majesty’s reign, entitled “an act [ Act for granting certain duties.]
‘One other act passed in the fifth year of his reign, entitled “an act [Stamp Act.]
‘One other act passed in the sixth year of his reign, entitled “an act [Act declaring the right of Parliament over the colonies.]
‘And one other act passed in the seventh year of his reign, entitled an act [ Act for granting duties on paper, tea, &c.
‘Form that connected chain of parliamentary usurpation, which has already been the subject of frequent applications to his Majesty, and the Houses of Lords and Commons of Great Britain; and, no answers having yet been condescended to any of these, we shall not trouble his Majesty with a repetition of the matters they contained.
‘But that one other act passed in the same seventh year of his reign, having been a peculiar attempt, must ever require peculiar mention. It is entitled “an act [Act suspending Legislature of New York.]
‘One free and independent legislature hereby takes upon itself to suspend the powers of another, free and independent as itself. Thus exhibiting a phenomenon unknown in nature, the creator and creature of its own power. Not only the principles of common sense, but the common feelings of human nature must be surrendered up, before his Majesty’s subjects here can be persuaded to believe, that they hold their political existence at the will of a British Parliament. Shall these governments be dissolved, their property annihilated, and their people reduced to a state of nature, at the imperious breath of a body of men whom they never saw, in whom they never confided, and over whom they have no powers of punishment or removal, let their crimes against the American public be ever so great? Can any one reason be assigned, why one hundred and sixty thousand electors in the island of Great Britain should give law to four millions in the states of America, every individual of whom is equal to every individual of them in virtue, in understanding, and in bodily strength? Were this to be admitted, instead of being a free people, as we have hitherto supposed, and mean to continue ourselves, we should suddenly be found the slaves, not of one, but of one hundred and sixty thousand tyrants; distinguished, too, from all others, by this singular circumstance, that they are removed from the reach of fear, the only restraining motive which may hold the hand of a tyrant.
‘That, by “an act to discontinue in such manner, and for such time as are therein mentioned, the landing and discharging, lading or shipping of goods, wares, and merchandise, at the town and within the harbor of Boston, in the province of Massachusetts Bay, in North America,” [14 G.3.] which was passed at the last session of the British Parliament, a large and populous town, whose trade was their sole subsistence, was deprived of that trade, and involved in utter ruin. Let us for a while, suppose the question of right suspended, in order to examine this act on principles of justice. An act of Parliament had been passed, imposing duties on teas, to be paid in America, against which act the Americans had protested, as inauthoritative. The East India Company, who till that time had never sent a pound of tea to America on their own account, step forth on that occasion, the asserters of Parliamentary right, and send hither many ship-loads of that obnoxious commodity. The masters of their several vessels, however, on their arrival in America, wisely attended to admonition, and returned with their cargoes. In the province of New England alone, the remonstrances of the people were disregarded, and a compliance, after being many days waited for, was flatly refused. Whether in this, the master of the vessel was governed by his obstinacy, or his instructions, let those who know, say. There are extraordinary situations which require extraordinary interposition. An exasperated people, who feel that they possess power, are not easily restrained within limits strictly regular. A number of them assembled in the town of Boston, threw the tea into the ocean, and dispersed without doing any other act of violence. If in this they did wrong, they were known, and were amenable to the laws of the land; against which, it could not be objected that they had ever, in any instance, been obstructed or diverted from their regular course, in favor of popular offenders. They should, therefore, not have been distrusted on this occasion. But that ill-fated colony had formerly been bold in their enmities against the House of Stuart, and were now devoted to ruin, by that unseen hand which governs the momentous affairs of this great empire. On the partial representations of a few worthless ministerial dependants, whose constant office it has been to keep that government embroiled, and who, by their treacheries, hope to obtain the dignity of British knighthood, without calling for a party accused, without asking a proof, without attempting a distinction between the guilty and the innocent, the whole of that ancient and wealthy town, is in a moment reduced from opulence to beggary. Men who had spent their lives in extending the British commerce, who had invested in that place, the wealth their honest endeavors had merited, found themselves and their families, thrown at once on the world, for subsistence by its charities. Not the hundredth part of the inhabitants of that town had been concerned in the act complained of; many of them were in Great Britain, and in other parts beyond sea; yet all were involved in one indiscriminate ruin, by a new executive power, unheard of till then, that of a British Parliament. A property of the value of many millions of money was sacrificed to revenge, not to repay, the loss of a few thousands. This is administering justice with a heavy hand indeed! And when is this tempest to be arrested in its course? Two wharves are to be opened again when his Majesty shall think proper: the residue which lined the extensive shores of the bay of Boston, are for ever interdicted the exercise of commerce. This little exception seems to have been thrown in for no other purpose, than that of setting a precedent for investing his Majesty with legislative powers. If the pulse of his people shall beat calmly under this experiment, another and another will be tried, till the measure of despotism be filled up. It would be an insult on common sense, to pretend that this exception was made in order to restore its commerce to that great town. The trade which cannot be received at two wharves alone, must of necessity be transferred to some other place; to which it will soon be followed by that of the two wharves. Considered in this light, it would be an insolent and cruel mockery at the annihilation of the town of Boston. By the act for the suppression of riots and tumults in the town of Boston, [14 G.3.] passed also in the last session of Parliament, a murder committed there, is, if the Governor pleases, to be tried in the court of King’s Bench, in the island of Great Britain, by a jury of Middlesex. The witnesses, too, on receipt of such a sum as the Governor shall think it reasonable for them to expend, are to enter into recognisance to appear at the trial. This is, in other words, taxing them to the amount of their recognisance; and that amount may be whatever a Governor pleases. For who does his Majesty think can be prevailed on to cross the Atlantic, for the sole purpose of bearing evidence to a fact? His expenses are to be borne, indeed, as they shall be estimated by a Governor; but who are to feed the wife and children whom he leaves behind, and who have had no other subsistence but his daily labor? Those epidemical disorders, too, so terrible in a foreign climate, is the cure of them to be estimated among the articles of expense, and their danger to be warded off by the almighty power of a Parliament? And the wretched criminal, if he happen to have offended on the American side, stripped of his privilege of trial by peers of his vicinage, removed from the place where alone full evidence could be obtained, without money, without counsel, without friends, without exculpatory proof, is tried before Judges predetermined to condemn. The cowards who would suffer a countryman to be torn from the bowelss of their society, in order to be thus offered a sacrifice to Parliamentary tyranny, would merit that everlasting infamy now fixed on the authors of the act! A clause, for a similar purpose, had been introduced into an act passed in the twelfth year of his Majesty’s reign, entitled, “an act for the better securing and preserving his Majesty’s dock-yards, magazines, ships, ammunition, and stores;” against which, as meriting the same censures, the several colonies have already protested.
‘That these are the acts of power, assumed by a body of men foreign to our constitutions, and unacknowledged by our laws; against which we do, on behalf of the inhabitants of British America, enter this our solemn and determined protest. And we do earnestly entreat his Majesty, as yet the only mediatory power between the several states of the British empire, to recommend to his Parliament of Great Britain, the total revocation of these acts, which, however nugatory they be, may yet prove the cause of further discontents and jealousies among us.
‘That we next proceed to consider the conduct of his Majesty, as holding the Executive powers of the laws of these states, and mark out his deviations from the line of duty. By the constitution of Great Britain, as well as of the several American States, his Majesty possesses the power of refusing to pass into a law, any bill which has already passed the other two branches of the legislature. His Majesty, however, and his ancestors, conscious of the impropriety of opposing their single opinion to the united wisdom of two Houses of Parliament, while their proceedings were unbiased by interested principles, for several ages past, have modestly declined the exercise of this power, in that part of his empire called Great Britain. But, by change of circumstances, other principles than those of justice simply, have obtained an influence on their determinations. The addition of new states to the British empire, has produced an addition of new, and sometimes, opposite interests. It is now, therefore, the great office of his Majesty, to resume the exercise of his negative power, and to prevent the passage of laws by any one legislature of the empire, which might bear injuriously on the rights and interests of another. Yet this will not excuse the wanton exercise of this power, which we have seen his Majesty practise on the laws of the American legislatures. For the most trifling reasons, and sometimes for no conceivable reason at all, his Majesty has rejected laws of the most salutary tendency. The abolition of domestic slavery is the great object of desire in those colonies, where it was, unhappily, introduced in their infant state. But previous to the enfranchisement of the slaves we have, it is necessary to exclude all further importations from Africa. Yet our repeated attempts to effect this, by prohibitions, and by imposing duties which might amount to a prohibition, have been hitherto defeated by his Majesty’s negative: thus preferring the immediate advantages of a few British corsairs to the lasting interests of the American States, and to the rights of human nature, deeply wounded by this infamous practice. Nay, the single interposition of an interested individual against a law, was scarcely ever known to fail of success, though in the opposite scale were placed the interests of a whole country. That this is so shameful an abuse of a power, trusted with his Majesty for other purposes, as if, not reformed, would call for some legal restrictions.
‘With equal inattention to the necessities of his people here, has his Majesty permitted our laws to lie neglected in England for years, neither confirming them by his assent, nor annulling them by his negative: so that such of them as have no suspending clause, we hold on the most precarious of all tenures, his Majesty’s will; and such of them as suspend themselves till his Majesty’s assent be obtained, we have feared might be called into existence at some future and distant period, when time and change of circumstances shall have rendered them destructive to his people here. And, to render this grievance still more oppressive, his Majesty, by his instructions, has laid his Governors under such restrictions, that they can pass no law of any moment, unless it have such suspending clause: so that, however immediate may be the call for legislative interposition, the law cannot be executed till it has twice crossed the Atlantic, by which time the evil may have spent its whole force.
‘But in what terms reconcilable to Majesty, and,at the same time to truth, shall we speak of a late instruction to his Majesty’s Governor of the colony of Virginia, by which he is forbidden to assent to any law for the division of a county, unless the new county will consent to have no representative in Assembly? That colony has as yet affixed no boundary to the westward. Their Western counties, therefore, are of indefinite extent. Some of them are actually seated many hundred miles from their Eastern limits. Is it possible, then that his Majesty can have bestowed a single thought on the situation of those people, who, in order to obtain justice for injuries, however great or small, must, by the laws of that colony, attend their county court at such a distance, with all their witnesses, monthly, till their litigation be determined? Or does his Majesty seriously wish, and publish it to the world, that his subjects should give up the glorious right of representation, with all the benefits derived from that, and submit themselves to be absolute slaves of his sovereign will? Or is it rather meant to confine the legislative body to their present numbers, that they may be the cheaper bargain, whenever they shall become worth a purchase?
‘One of the articles of impeachment against Tresilian and the other Judges of Westminster Hall, in the reign of Richard the Second, for which they suffered death, as traitors to their country, was, that they had advised the King that he might dissolve his Parliament at any time: and succeeding Kings have adopted the opinion of these unjust Judges. Since the establishment, however, of the British constitution, at the glorious Revolution, on its free and ancient principles, neither his Majesty nor his ancestors have exercised such a power of dissolution in the island of Great Britain;* and, when his Majesty was petitioned by the united voice of his people there to dissolve the present Parliament, who had become obnoxious to them, his Ministers were heard to declare, in open Parliament, that his Majesty possessed no such power by the constitution. But how different their language, and his practice, here! To declare, as their duty required, the known rights of their country, to oppose the usurpation of every foreign judicature, to disregard the imperious mandates of a Minister or Governor, have been the avowed causes of dissolving Houses of Representatives in America. But if such powers be really vested in his Majesty, can he suppose they are there placed to awe the members from such purposes as these? When the representative body have lost the confidence of their constituents, when they have notoriously made sale of their most valuable rights, when they have assumed to themselves powers which the people never put into their hands, then, indeed, their continuing in office becomes dangerous to the state, and calls for an exercise of the power of dissolution. Such being the causes for which the representative body should, and should not, be dissolved, will it not appear strange, to an unbiassed observer, that that of Great Britain was not dissolved, while those of the colonies have repeatedly incurred that sentence?
* On further inquiry, I find two instances of dissolutions
before the Parliament would, of itself, have been at an end:
viz. the Parliament called to meet August 24, 1698, was
dissolved by King William, December 19, 1700, and a new one
called, to meet February 6, 1701, which was also dissolved
November 11, 1701, and a new one met December 30, 1701.
But your Majesty or your Governors have carried this power beyond every limit known or provided for by the laws. After dissolving one House of Representatives, they have refused to call another, so that, for a great length of time, the legislature provided by the laws has been out of existence. From the nature of things, every society must at all times possess within itself the sovereign powers of legislation. The feelings of human nature revolt against the supposition of a state so situated, as that it may not, in any emergency, provide against dangers which perhaps threaten immediate ruin. While those bodies are in existence to whom the people have delegated the powers of legislation, they alone possess, and may exercise, those powers. But when they are dissolved, by the lopping off one or more of their branches, the power reverts to the people, who may use it to unlimited extent, either assembling together in person, sending deputies, or in any other way they may think proper. We forbear to trace consequences further; the dangers are conspicuous with which this practice is replete.
‘That we shall, at this time also, take notice of an error in the nature of our land-holdings, which crept in at a very early period of our settlement. The introduction of the feudal tenures into the kingdom of England, though ancient, is well enough understood to set this matter in a proper light. In the earlier ages of the Saxon settlement, feudal holdings were certainly altogether unknown, and very few, if any, had been introduced at the time of the Norman conquest. Our Saxon ancestors held their lands, as they did their personal property, in absolute dominion, disencumbered with any superior, answering nearly to the nature of those possessions which the Feudalists term Allodial. William the Norman first introduced that system generally. The lands which had belonged to those who fell in the battle of Hastings, and in the subsequent insurrections of his reign, formed a considerable proportion of the lands of the whole kingdom. These he granted out, subject to feudal duties, as did he also those of a great number of his new subjects, who, by persuasions or threats, were induced to surrender them for that purpose. But still much was left in the hands of his Saxon subjects, held of no superior, and not subject to feudal conditions. These, therefore, by express laws, enacted to render uniform the system of military defence, were made liable to the same military duties as if they had been feuds: and the Norman lawyers soon found means to saddle them, also, with all the other feudal burthens. But still they had not been surrendered to the King, they were not derived from his grant, and therefore they were not holden of him. A general principle, indeed, was introduced, that “all lands in England were held either mediately or immediately of the Crown:” but this was borrowed from those holdings which were truly feudal, and only applied to others for the purposes of illustration. Feudal holdings were, therefore, but exceptions out of the Saxon laws of possession, under which all lands were held in absolute right. These, therefore, still form the basis or groundwork of the common law, to prevail wheresoever the exceptions have not taken place. America was not conquered by William the Norman, nor its lands surrendered to him or any of his successors. Possessions there are, undoubtedly, of the Allodial nature. Our ancestors, however, who migrated hither, were laborers, not lawyers. The fictitious principle, that all lands belong originally to the King, they were early persuaded to believe real, and accordingly took grants of their own lands from the Crown. And while the Crown continued to grant for small sums and on reasonable rents, there was no inducement to arrest the error, and lay it open to public view. But his Majesty has lately taken on him to advance the terms of purchase and of holding to the double of what they were; by which means the acquisition of lands being rendered difficult, the population of our country is likely to be checked. It is time, therefore, for us to lay this matter before his Majesty, and to declare that he has no right to grant lands of himself. From the nature and purpose of civil institutions, all the lands within the limits which any particular society has circumscribed around itself, are assumed by that society, and subject to their allotment; this may be done by themselves assembled collectively, or by their legislature, to whom they may have delegated sovereign authority: and, if they are allotted in neither of these ways, each individual of the society may appropriate to himself such lands as he finds vacant, and occupancy will give him title.
‘That, in order to enforce the arbitrary measures before complained of, his Majesty has, from time to time, sent among us large bodies of armed forces, not made up of the people here, nor raised by the authority of our laws. Did his Majesty possess such a right as this, it might swallow up all our other rights whenever he should think proper. But his Majesty has no right to land a single armed man on our shores; and those whom he sends here are liable to our laws for the suppression and punishment of riots, routs, and unlawful assemblies, or are hostile bodies invading us in defiance of law. When, in the course of the late war, it became expedient that a body of Hanoverian troops should be brought over for the defence of Great Britain, his Majesty’s grandfather, our late sovereign, did not pretend to introduce them under any authority he possessed. Such a measure would have given just alarm to his subjects of Great Britain, whose liberties would not be safe if armed men of another country, and of another spirit, might be brought into the realm at any time, without the consent, of their legislature. He, therefore, applied to Parliament, who passed an act for that purpose, limiting the number to be brought in, and the time they were to continue. In like manner is his Majesty restrained in every part of the empire. He possesses indeed the executive power of the laws in every state; but they are the laws of the particular state, which he is to administer within that state, and not those of any one within the limits of another. Every state must judge for itself, the number of armed men which they may safely trust among them, of whom they are to consist, and under what restrictions they are to be laid. To render these proceedings still more criminal against our laws, instead of subjecting the military to the civil power, his Majesty has expressly made the civil subordinate to the military. But can his Majesty thus put down all law under his feet? Can he erect a power superior to that which erected himself? He has done it indeed by force; but let him remember that force cannot give right.
‘That these are our grievances, which we have thus laid before his Majesty, with that freedom of language and sentiment which becomes a free people, claiming their rights as derived from the laws of nature, and not as the gift of their Chief Magistrate. Let those flatter, who fear: it is not an American art. To give praise where it is not due, might be well from the venal, but would ill beseem those who are asserting the rights of human nature. They know, and will, therefore, say, that Kings are the servants, not the proprietors of the people. Open your breast, Sire, to liberal and expanded thought. Let not the name of George the Third be a blot on the page of history. You are surrounded by British counsellors, but remember that they are parties. You have no ministers for American affairs, because you have none taken from among us, nor amenable to the laws on which they are to give you advice. It behoves you, therefore, to think and to act for yourself and your people. The great principles of right and wrong are legible to every reader: to pursue them, requires not the aid of many counsellors. The whole art of government consists in the art of being honest. Only aim to do your duty, and mankind will give you credit where you fail. No longer persevere in sacrificing the rights of one part of the empire, to the inordinate desires of another: but deal out to all, equal and impartial right. Let no act be passed by any one legislature, which may infringe on the rights and liberties of another. This is the important post in which fortune has placed you, holding the balance of a great, if a well poised empire. This, Sire, is the advice of your great American council, on the observance of which may, perhaps, depend your felicity and future fame, and the preservation of that harmony which alone can continue, both to Great Britain and America, the reciprocal advantages of their connection. It is neither our wish nor our interest to separate from her. We are willing, on our part, to sacrifice every thing which reason can ask, to the restoration of that tranquillity for which all must wish. On their part, let them be ready to establish union on a generous plan. Let them name their terms, but let them be just. Accept of every commercial preference it is in our power to give, for such things as we can raise for their use, or they make for ours. But let them not think to exclude us from going to other markets, to dispose of those commodities which they cannot use, nor to supply those wants which they cannot supply. Still less, let it be proposed, that our properties, within our own territories, shall be taxed or regulated by any power on earth, but our own. The God who gave us life, gave us liberty at the same time: the hand of force may destroy, but cannot disjoin them. This, Sire, is our last, our determined resolution. And that you will be pleased to interpose, with that efficacy which your earnest endeavors may insure, to procure redress of these our great grievances, to quiet the minds of your subjects in British America against any apprehensions of future encroachment, to establish fraternal love and harmony through the whole empire, and that that may continue to the latest ages of time, is the fervent prayer of all British America,’
[NOTE D.]—August, 1774., Instructions for the Deputies
Instructions for the Deputies appointed to meet in General Congress on the Part of this Colony.
The unhappy disputes between Great Britain and her American colonies, which began about the third year of the reign of his present Majesty, and since, continually increasing, have proceeded to lengths so dangerous and alarming, as to excite just apprehensions in the minds of his Majesty’s faithful subjects of this colony, that they are in danger of being deprived of their natural, ancient, constitutional, and chartered rights, have compelled them to take the same into their most serious consideration; and, being deprived of their usual and accustomed mode of making known their grievances, have appointed us their representatives, to consider what is proper to be done in this dangerous crisis of American affairs. It being our opinion that the united wisdom of North America should be collected in a general congress of all the colonies, we have appointed the Honorable Peyton Randolph, Richard Henry Lee, George Washington, Patrick Henry, Richard Bland, Benjamin Harrison, and Edmund Pendleton, Esquires, deputies to represent this colony in the said Congress, to be held at Philadelphia, on the first Monday in September next.
And that they may be the better informed of our sentiments, touching the conduct we wish them to observe on this important occasion, we desire that they will express, in the first place, our faith and true allegiance to his Majesty, King George the Third, our lawful and rightful sovereign; and that we are determined, with our lives and fortunes, to support him in the legal exercise of all his just rights and prerogatives. And, however misrepresented, we sincerely approve of a constitutional connection with Great Britain, and wish, most ardently, a return of that intercourse of affection and commercial connection, that formerly united both countries, which can only be effected by a removal of those causes of discontent, which have of late unhappily divided us.
It cannot admit of a doubt, but that British subjects in America are entitled to the same rights and privileges, as their fellow subjects possess in Britain; and therefore, that the power assumed by the British Parliament, to bind America by their statutes, in all cases whatsoever, is unconstitutional, and the source of these unhappy differences.
The end of government would be defeated by the British Parliament exercising a power over the lives, the property, and the liberty of American subjects; who are not, and, from their local circumstances, cannot be, there represented. Of this nature, we consider the several acts of Parliament, for raising a revenue in America, for extending the jurisdiction of the courts of Admiralty, for seizing American subjects, and transporting them to Britain, to be tried for crimes committed in America, and the several late oppressive acts respecting the town of Boston and Province of the Massachusetts Bay.
The original constitution of the American colonies possessing their assemblies with the sole right of directing their internal polity, it is absolutely destructive of the end of their institution, that their legislatures should be suspended, or prevented, by hasty dissolutions, from exercising their legislative powers.
Wanting the protection of Britain, we have long acquiesced in their acts of navigation, restrictive of our commerce, which we consider as an ample recompense for such protection; but as those acts derive their efficacy from that foundation alone, we have reason to expect they will be restrained, so as to produce the reasonable purposes of Britain, and not injurious to us.
To obtain redress of these grievances, without which the people of America can neither be safe, free, nor happy, they are willing to undergo the great inconvenience that will be derived to them, from stopping all imports whatsoever, from Great Britain, after the first day of November next, and also to cease exporting any commodity whatsoever, to the same place, after the tenth day of August, 1775. The earnest desire we have to make as quick and full payment as possible of our debts to Great Britain, and to avoid the heavy injury that would arise to this country from an earlier adoption of the non-exportation plan, after the people have already applied so much of their labor to the perfecting of the present crop, by which means they have been prevented from pursuing other methods of clothing and supporting their families, have rendered it necessary to restrain you in this article of non-exportation; but it is our desire, that you cordially co-operate with our sister colonies in General Congress, in such other just and proper methods as they, or the majority, shall deem necessary for the accomplishment of these valuable ends.
The proclamation issued by General Gage, in the government of the Province of the Massachusetts Bay, declaring it treason for the inhabitants of that province to assemble themselves to consider of their grievances, and form associations for their common conduct on the occasion, and requiring the civil magistrates and officers to apprehend all such persons, to be tried for their supposed offences, is the most alarming process that ever appeared in a British government; that the said General Gage hath, thereby, assumed, and taken upon himself, powers denied by the constitution to our legal sovereign; that he, not having condescended to disclose by what authority he exercises such extensive and unheard-of powers, we are at a loss to determine, whether he intends to justify himself as the representative of the King, or as the Commander in Chief of his Majesty’s forces in America. If he considers himself as acting in the character of his Majesty’s representative, we would remind him that the statute 25 Edward the Third has expressed and defined all treasonable offences, and that the legislature of Great Britain hath declared, that no offence shall be construed to be treason, but such as is pointed out by that statute, and that this was done to take out of the hands of tyrannical Kings, and of weak and wicked Ministers, that deadly weapon, which constructive treason had furnished them with, and which had drawn the blood of the best and honestest men in the kingdom; and that the King of Great Britain hath no right by his proclamation to subject his people to imprisonment, pains, and penalties.
That if the said General Gage conceives he is empowered to act in this manner, as the Commander in Chief of his Majesty’s forces in America, this odious and illegal proclamation must be considered as a plain and full declaration, that this despotic Viceroy will be bound by no law, nor regard the constitutional rights of his Majesty’s subjects, whenever they interfere with the plan he has formed for oppressing the good people of the Massachusetts Bay; and, therefore, that the executing, or attempting to execute, such proclamation, will justify resistance and reprisal.
[NOTE E.]—Monticello, November 1, 1778.—[Re: Crimes and Punishment]
Dear Sir,
I have got through the bill ‘for proportioning crimes and punishments in cases heretofore capital,’ and now enclose it to you with a request that you will be so good, as scrupulously to examine and correct it, that it may be presented to our committee, with as few defects as possible. In its style, I have aimed at accuracy, brevity, and simplicity, preserving, however, the very words of the established law, wherever their meaning had been sanctioned by judicial decisions, or rendered technical by usage. The same matter, if couched in the modern statutory language, with all its tautologies, redundancies, and circumlocutions, would have spread itself over many pages, and been unintelligible to those whom it most concerns. Indeed, I wished to exhibit a sample of reformation in the barbarous style, into which modern statutes have degenerated from their ancient simplicity. And I must pray you to be as watchful over what I have not said, as what is said; for the omissions of this bill have all their positive meaning. I have thought it better to drop, in silence, the laws we mean to discontinue, and let them be swept away by the general negative words of this, than to detail them in clauses of express repeal. By the side of the text I have written the note? I made, as I went along, for the benefit of my own memory. They may serve to draw your attention to questions, to which the expressions or the omissions of the text may give rise. The extracts from the Anglo-Saxon laws, the sources of the Common law, I wrote in their original, for my own satisfaction;* but I have added Latin, or liberal English translations. From the time of Canute to that of the Magna Charta, you know, the text of our statutes is preserved to us in Latin only, and some old French.
* In this publication, the original Saxon words are given,
but, owing to the want of Saxon letter, they are printed in
common type.
I have strictly observed the scale of punishments settled by the Committee, without being entirely satisfied with it. The Lex talionis, although a restitution of the Common law, to the simplicity of which we have generally found it so advantageous to return, will be revolting to the humanized feelings of modern times. An eye for an eye, and a hand for a hand, will exhibit spectacles in execution, whose moral effect would be questionable; and even the membrum pro membro of Bracton, or the punishment of the offending member, although long authorized by our law, for the same offence in a slave, has, you know, been not long since repealed, in conformity with public sentiment. This needs reconsideration.
I have heard little of the proceedings of the Assembly, and do not expect to be with you till about the close of the month. In the mean time, present me respectfully to Mrs. Wythe, and accept assurances of the affectionate esteem and respect of, Dear Sir, Your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
George Wythe, Esq.














Bill for proportioning Crimes and Punishments, in Cases heretofore Capital.
Whereas, it frequently happens that wicked and dissolute men, resigning themselves to the dominion of inordinate passions, commit violations on the lives, liberties, and property of others, and, the secure enjoyment of these having principally induced men to enter into society, government would be defective in its principal purpose, were it not to restrain such criminal acts, by inflicting due punishments on those who perpetrate them; but it appears, at the same time, equally deducible from the purposes of society, that a member thereof, committing an inferior injury, does not wholly forfeit the protection of his fellow-citizens, but, after suffering a punishment in proportion to his offence, is entitled to their protection from all greater pain, so that it becomes a duty in the legislature to arrange, in a proper scale, the crimes which it may be necessary for them to repress, and to adjust thereto a corresponding gradation of punishments.
And whereas, the reformation of offenders, though an object worthy the attention of the laws, is not effected at all by capital punishments, which exterminate, instead of reforming, and should be the last melancholy resource against those whose existence is become inconsistent with the safety of their fellow-citizens, which also weaken the State, by cutting off so many who, if reformed, might be restored sound members to society, who, even under a course of correction, might be rendered useful in various labors for the public, and would be living and long continued spectacles to deter others from committing the like offences.
And forasmuch as the experience of all ages and countries hath shown, that cruel and sanguinary laws defeat their own purpose, by engaging the benevolence of mankind to withhold prosecutions, to smother testimony, or to listen to it with bias, when, if the punishment were only proportioned to the injury, men would feel it their inclination, as well as their duty, to see the laws observed.
For rendering crimes and punishments, therefore, more proportionate to each other.
Be it enacted by the General Assembly, that no crime shall be henceforth punished by deprivation of life or limb,* except those hereinafter ordained to be so punished.
* This takes away the punishment of cutting off the hand of
a person striking another, or drawing his sword in one of
the superior courts of justice. Stamf. P. C. 38; 33 H. 8. c.
12. In an earlier stage of the Common law, it was death.
‘Gif hwa gefeohte on Cyninges huse sy he scyldig ealles his
yrfes, and sy on Cyninges dome hwsether he lif age de nage:
si quis in regis domo pugnet, perdat omnem suam
ha; reditatem, et in regis sit arbitrio, possideat vitarn an
non possideat.‘ LI. Inae. 6. &c.
*If a man do levy war** against the Commonwealth [in the same], or be adherent to the enemies of the Commonwealth [within the same],*** giving to them aid or comfort in the Commonwealth, or elsewhere, and thereof be convicted of open deed, by the evidence of two sufficient witnesses, or his own voluntary confession, the said cases, and no others,**** shall be adjudged treasons which extend to the Commonwealth, and the person so convicted shall suffer death by hanging,***** and shall forfeit his lands and goods to the Commonwealth.
* 25 E 3. st. 5. c. 2; 7 W. 3. c. 3, § 2.
** Though the crime of an accomplice in treason is not here
described yet Lord Coke says, the partaking and maintaining
a treason herein described makes him a principal in that
treason. It being a rule that in treason all are principals.
3 inst. 138; 2 Inst. 590; H. 6. c. 5.
*** These words in the English statute narrow its operation.
A man adhering to the enemies of the Commonwealth, in a
foreign country, would certainly not be guilty of treason
with us, if these words be retained. The convictions of
treason of that kind in England, have been under that branch
of the statute which makes the compassing the king’s death
treason. Foster, 196, 197. But as we omit that branch, we
must by other means reach this flagrant case.
**** The stat. 25 E. 3. directs all other cases of treason
to await the opinion of Parliament. This has the effect of
negative words, excluding all other treasons. As we drop
that part of the statute, we must, by negative words,
prevent an inundation of common law treasons. I strike out
the word ‘it,’ therefore, and insert ‘the said cases and no
others.’ Quaere, how far those negative words may affect the
case of accomplices above mentioned? Though if their case
was within the statute, so as that it needed not await the
opinion of Parliament, it should seem to be also within our
act, so as not to be ousted by the negative words.
If any person commit petty treason, or a husband murder his wife, a parent his child,* or a child his parent, he shall suffer death by hanging, and his body be delivered to anatomists to be dissected.
* By the stat. 21.Tac. 1. c. 27. and Act Ass. 1710, c. 12.
concealment by the mother of the death of a bastard child is
made murder. In justification of this, it is said, that
shame is a feeling which operates so strongly on the mind,
as frequently to induce the mother of such a child to murder
it, in order to conceal her disgrace. The act of
concealment, therefore, proves she was influenced by shame,
and that influence produces a presumption that she murdered
the child. The effect of this law, then, is, to make what,
in its nature, is only presumptive evidence of a murder,
conclusive of that fact. To this I answer, 1. So many
children die before, or soon after birth, that to presume
all those murdered who are found dead, is a presumption
which will lead us oftener wrong than right, and
consequently would shed more blood than it would save. 2. If
the child were born dead, the mother would naturally choose
rather to conceal it, in hopes of still keeping a good
character in the neighborhood. So that the act of
concealment is far from proving the guilt of murder on the
mother. 3. If shame be a powerful affection of the mind, is
not parental love also? Is it not the strongest affection
known? Is it not greater than even that of self-
preservation? While we draw presumptions from shame, one
affection of the mind, against the life of the prisoner,
should we not give some weight to presumptions from parental
love, an affection at least as strong in favor of life? If
concealment of the fact is a presumptive evidence of murder,
so strong as to overbalance all other evidence that may
possibly be produced to take away the presumption, why not
trust the force of this incontestable presumption to the
jury, who are, in a regular course, to hear presumptive, as
well as positive testimony? If the presumption, arising from
the act of concealment, may be destroyed by proof positive
or circumstantial to the contrary, why should the
legislature preclude that contrary proof? Objection. The
crime is difficult to prove, being usually committed in
secret. Answer. But circumstantial proof will do; for
example, marks of violence, the behavior, countenance, &c.
of the prisoner, &c. And if conclusive proof be difficult to
be obtained, shall we therefore fasten irremovably upon
equivocal proof? Can we change the nature of what is
contestable, and make it incontestable? Can we make that
conclusive which God and nature have made inconclusive?
Solon made no law against, parricide, supposing it
impossible any one could be guilty of it; and the Persians,
from the same opinion, adjudged all who killed their reputed
parents to be bastards: and although parental, be yet
stronger than filial affection, we admit saticide proved on
the most equivocal testimony, whilst they rejected all proof
of an act, certainly not more repugnant to nature, as of a
thing impossible, improvable. See Beccaria, § 31.
Whosoever committeth murder by poisoning, shall suffer death by poison.
Whosoever committeth murder by way of duel, shall suffer death by hanging; and if he were the challenger, his body, after death, shall be gibbeted.* He who removeth it from the gibbet, shall be guilty of a misdemeanor; and the officer shall see that it be replaced.
* 25 G. 2. c. 37.
Whosoever shall commit murder in any other way, shall suffer death by hanging.
And in all cases of petty treason and murder, one half of the lands and goods of the offender shall be forfeited to the next of kin to the person killed, and the other half descend and go to his own representatives. Save only, where one shall slay the challenger in a duel,* in which case, no part of his lands or goods shall be forfeited to the kindred of the party slain, but, instead thereof, a moiety shall go to the Commonwealth.
* Quære, if the estates of both parties in a duel should not
be forfeited? The deceased is equally guilty with a suicide.
The same evidence* shall suffice, and order and course** of trial be observed in cases of petty treason, as in those of other*** murders.
* Quære, if these words may not be omitted? By the Common
law, one witness in treason was sufficient. Foster, 233.
Plowd. 8. a. Mirror, c. 3. § 34. Waterhouse on Fortesc de
Laud. 252. Carth. 144 per Holt. But Lord Coke, contra, 3
Inst 26. The stat. 1 E. 6. c 12. &5E.6. c. 11. first
required two witnesses in treason. The clause against high
treason supra, does the same as to high treason; but it
seems if 1st and 5th E. 6. are dropped, petty treason will
be tried and proved, as at Common law, by one witness. But
quære, Lord Coke being contra, whose opinion it is ever
dangerous to neglect.
** These words are intended to take away the peremptory
challenge of thirty-five jurors. The same words being used 1
& 2 Ph. k. M. c. 10. are deemed to have restored the
peremptory challenge in high treason; and consequently are
sufficient to take it away. Foster, 237.
*** Petty treason is considered in law only as an aggravated
murder. Foster, 107,323. A pardon of all murders, pardons
petty treason. 1 Hale P. C. 378. See 2 H. P. C. 340, 342. It
is also included in the word ‘felony,’ so that a pardon of
all felonies, pardons petty treason.
Whosoever shall be guilty of manslaughter,* shall, for the first offence, be condemned to hard labor** for seven years, in the public works, shall forfeit one half of his lands and goods to the next of kin to the person slain; the other half to be sequestered during such term, in the hands and to the use of the Commonwealth, allowing a reasonable part of the profits for the support of his family. The second offence shall be deemed murder.
* Manslaughter is punishable at law, by burning in the hand,
and forfeiture of chattels.
** It is best, in this act, to lay down principles only, in
order that it may not for ever be undergoing change: and, to
carry into effect the minuter parts of it; frame a bill ‘for
the employment and government of felons, or male-factors,
condemned to labor for the Commonwealth,’ which may serve as
an Appendix to this, and in which all the particulars
requisite may be directed: and as experience will, from time
to time, be pointing out amendments, these may be made
without touching this fundamental act. See More’s Utopia pa.
50, for some good hints. Fugitives might, in such a bill, be
obliged to work two days for every one they absent
themselves.
And where persons, meaning to commit a trespass* only, or larceny, or other unlawful deed, and doing an act from which involuntary homicide hath ensued, have heretofore been adjudged guilty of manslaughter, or of murder, by transferring such their unlawful intention to an act much more penal than they could have in probable contemplation; no such case shall hereafter be deemed manslaughter, unless manslaughter was intended, nor murder, unless murder was intended.
* The shooting at a wild fowl, and killing a man, is
homicide by misadventure. Shooting at a pullet, without any
design to take it away, is manslaughter; and with a design
to take it away, is murder. 6 Sta. tr. 222. To shoot at the
poultry of another, and thereby set fire to his house, is
arson, in the opinion of some. Dalt. c. 116 1 Hale’s P. C.
569, contra.
In other cases of homicide, the law will not add to the miseries of the party, by punishments or forfeitures.*
* Beccaria, § 32. Suicide. Homicides are, 1. Justifiable. 2.
Excusable. 3. Felonious. For the last, punishments have been
already provided. The first are held to be totally without
guilt, or rather commendable. The second are, in some cases,
not quite unblamable. These should subject the party to
marks of contrition; viz. the killing of a man in defence of
property; so also in defence of one’s person, which is a
species of excusable homicide; because, although cases may
happen where these also are commendable, yet most frequently
they are done on too slight appearance of danger; as in
return for a blow, kick, fillip, &c; or on a person’s
getting into a house, not anirno furandi, but perhaps
veneris causa, &c. Bracton says, ‘Si quis furem noctupnum
occiderit, ita demum impune foret, si parcere ei sine
periculo suo non potuit; si autem potuit, aliter erit.’
‘Item erit si quis hamsokne qua; dicitur invasio domus
contra pacem domini regis in domo sua se defenderit, et
invasor occisus fuerit; impersecutus et inultus ramanebit,
si ille quem invasit aliter se defendere non potuit; dicitur
enim quod non est dignus habere pacem qui non vult observare
earn.’ L.3. c.23. § 3. ‘Qui latronetn Occident, non tenetur,
nocturnum vel diurnnm, si aliter periculum evadere non
possit; tenetur ta-men, si possit. Item non tenetur si per
inforlunium, et non anitno et voluntate occidendi, nee
dolus, nec culpa ejus inveniatur.’ L.3. c.36. § 1. The stat.
24 H. 8. c. 5 is therefore merely declaratory of the Common
law. See on the general subject, Puffend. 2. 5. § 10, 11,
12, 16, 17. Excusable homicides are by misadventure, or in
self-defence. It is the opinion of some lawyers, that the
Common law punished these with death, and that the statute
of Marlbridge, c. 26. and Gloucester, c. 9. first took away
this by giving them title to a pardon, as matter of right,
and a writ of restitution of their goods. See 2 Inst, 148.
315; 3 Inst. 55. Bracton, L. 3. c. 4. § 2. Fleta L, 1. c.
23. § 14, 15; 21 E. 3. 23. But it is believed never to have
been capital. 1 H. P. C. 425; 1 Hawk. 75; Foster, 282; 4 Bl.
188. It seems doubtful also, whether at Common law, the
party forfeited all his chattels in this case, or only paid
a weregild. Foster, ubi supra, doubts, and thinks it of no
consequence, as the statute of Gloucester entitles the party
to Royal grace, which goes as well to forfeiture as life. To
me, there seems no reason for calling these excusable
homicides, and the killing a man in defence of property, a
justifiable homicide. The latter is less guiltless than
misadventure or self defence.
Suicide is by law punishable by forfeiture of chattels. This
bill exempts it from forfeiture. The suicide injures the
state less than he who leaves it with his effects. If the
latter then be not punished, the former should not. As to
the example, we need not fear its influence. Men are too
much attached to life, to exhibit frequent instances of
depriving themselves of it. At any rate, the quasi-
punishment of confiscation will not prevent it. For if one
be found who can calmly determine to renounce life, who is
so weary of his existence here, as rather to make experiment
of what is beyond the grave, can we suppose him, in such a
state of mind, susceptible of influence from the losses to
his family by confiscation? That men in general, too,
disapprove of this severity, is apparent from the constant
practice of juries finding the suicide in a state of
insanity; because they have no other way of saving the
forfeiture. Let it then be done away.
Whenever sentence of death shall have been pronounced against any person for treason or murder, execution shall be done on the next day but one after such sentence, unless it be Sunday, and then on the Monday following.*
* Beccaria, § 19; 25 G. 2. c. 37.
Whosoever shall be guilty of Rape,* Polygamy,** or Sodomy,*** with man or woman, shall be punished, if a man, by castration,**** if a woman, by cutting through the cartilage of her nose, a hole of one half inch in diameter at the least.
* 13 E. 1. c. 34. Forcible abduction of a woman having
substance, is felony by 3 H. 7, c 2; 3. Inst. 61; 4 Bl. 208.
If goods be taken, it will be felony as to them, without
this statute: and as to the abduction of the woman, quære if
not better to leave that, and also kidnapping, 4 Bl. 219. to
the Common law remedies, viz. fine, imprisonment, and
pillory, Raym. 474; 2 Show. 221; Skin. 47; Comb. 10. the
writs of Homine replegiando, Capias in Withernam, Habeas
corpus, and the action of trespass? Rape was felony at the
Common law. 3 Inst. 60 but see 2 Inst. 181. Further—for its
definition see 2 Inst. 180. Bracton L.3. 28. § 1. says, the
punishment of rape is ‘amissio membrorum, ut sit membrumpro
membra, quia virgo, cum corrumpitur, membrum amittit, et
ideo corruptor puniatur in eo in quo deliquit; oculos igitur
amittat propter aspectum decoris quo virginem concupivit;
amittat et testiculos qui calorem stupri induxerunt. Olim
quidem corruptores virginitatis et castitatis suspendebantur
et eorum fautores, &c. Modernis tamen temporibus aliter
observatur,’ &.c. And Fleta, ‘Solet justiciarius pro
quolibet mahemio ad amissionem testiculorum vel oculorum
convictum coudemnare, sed non sine errore, eo quod id
judicium nisi in corruptione virginum lantum competebat; nam
pro virginitatis corruptione solebant abscidi et merito
judicari, ut sic pro membro quod abstulit, membrum per quod
deliquit amitteret, viz. lesticulos, qui calorem stupri
induxerunt,’ &c. Fleta. L. 1. c. 40. § 4. ‘Gif theow man
theowne to nydhffimed genyde, gabete mid his eowende: Si
servus servam ad sfuprum coegerit, compenset hoc virga sua
virili. Si quis pnellam,’ &c. Ll.Æliridi. 25. ‘Hi purgst
femme per forze forfait ad les membres.’ LI. Gul. Conq. 19.
** 1 Jac. 1. c. 11. Polygamy was not penal till the statute
of 1 Jac. The law contented itself with the nullity of the
act. 4 Bl. 163. 3 Inst. 88.
*** 25. H. 8. c. 6. Buggery is twofold. 1. With mankind, 2.
with beasts. Buggery is the genus, of which Sodomy and
Bestiality are the species. 12 Co. 37. says, In Dyer, 304. a
man was indicted, and found guilty of a rape on a girl of
seven years old. The court doubted of the rape of so tender
a girl; but if she had been nine years old, it would have
been otherwise.’ 14 Eliz. Therefore the statute 18 Eliz. c.
6, says, ‘For plain declaration of law, be it enacted, that
if any person shall unlawfully and carnally know and abuse
any woman child, under the age of ten years, &c. he shall
suffer as a felon, without allowance of clergy.’ Lord Hale,
however, 1 P. C. 630. thinks it rape independent of that
statute, to know carnally a girl under twelve, the age of
consent. Yet, 4 Bl. 212. seems to neglect this opinion; and
as it was founded on the words of 3 E. 1. c. 13. and this is
with us omitted, the offence of carnally knowing a girl
under twelve, or ten years of age, will not be distinguished
from that of any other. Co. 37. says ‘note that Sodomy is
with mankind.’ But Finch’s L. B. 3. c. 24. ‘Sodomitry is a
carnal copulation against nature, to wit, of man or woman in
the same sex, or of either of them with beasts.’ 12 Co 36.
says, ‘It appears by the ancient authorities of the law
that this was felony.’ Yet the 25 H. 8. declares it felony,
as if supposed not to be so. Britton, c, 9. says, that
Sodomites are to be burnt. F. N. B. 269. b. Fleta, L 1. c.
37. says, ‘Pecorantes et Sodomise in terra, vivi
confodiantur.’ The Mirror makes it treason. Bestiality can
never make any progress; it cannot therefore be injurious to
society in any great degree, which is the true measure of
criminality in foro cirili, and will ever be properly and
severely punished, by universal derision. It may, therefore,
be omitted. It was anciently punished with death, as it has
been latterly. LI Ælfrid. 31. and 25 H. 8. c. 6. see
Beccaria, § 31. Montesq.
****Bracton, Fleta, &c.
But no one shall be punished for Polygamy, who shall have married after probable information of the death of his or her husband or wife, or after his or her husband or wife hath absented him or herself, so that no notice of his or her being alive hath reached such person for seven years together, or hath suffered the punishments before prescribed for rape, polygamy, or sodomy.
Whosoever, on purpose, and of malice forethought, shall maim* another, or shall disfigure him by cutting out or disabling the tongue, slitting or cutting off a nose, lip, or ear, branding, or otherwise, shall be maimed, or disfigured in like** sort: or if that cannot be for want of the same part, then as nearly as may be, in some other part of at least equal value and estimation, in the opinion of a jury, and moreover, shall forfeit one half of his lands and goods to the sufferer.
* 22 &l 23 Car. 2, c. 1. Maiming was felony at the Common
law. Britton, c 95. Mehemiurn autem dici poterit, ubi
aliquis in aliqua. parte sui corporis la sionern acceperit,
per quam affectus sit inutilis ad pugnandum: ut sirnanus
ampuletur, vel pes, octilus privetur, vel scerda de osse
capitis lavetnr, vel si quis dentes praer. isores amiserit,
vel castratus fuerit, et talis pro mahemiato poterit
adjudicari.’ Flela, L. 1. c. 40. ‘Et volons que nul maheme
nesoit tenus forsque de membre toilet dount home est plus
feble a combatre, sicome, del oyl, on de la mayn, ou del
pie, on de la tete debruse, ou de les dentz devant.’
Britton, c. 25. For further definitions, see Braclon, L. 3.
c. 24 § 3. 4. Finch, L. B. 3. c. 12; Co. L. 126. a b 288. a;
3 Bl. 121; 4 Bl 205; Stamf. P C. L. 1. c. 41. I do not find
any of these definitions confine the offence to wilful and
malicious perpetrations of it. 22&23 Car. 2. c. 1, called
the Coventry act, has the words ‘on purpose and of malice
forethought.’ or does the Common law-prescribe the same
punishment for disfiguring, as for maiming.
** The punishment was by retaliation. ‘Et come ascun appele
serra de tele felonie atteint et attende jugement, si soit
le jugement tiel que il perde autriel membre come il avera
toilet al pleintyre. El sy la pleynte soit faite de femme
que avera toilet a home ses membres, en tiei cas perdra la
femmela une meyn par jugement, come le membre dount ele
avera trespasse.’ Britton, c 25. Flela, B 1. c. 40; LI.
Ælfr. 19. 40.
Whosoever shall counterfeit* any coin, current by law within this Commonwealth, or any paper bills issued in the nature of money, or of certificates of loan on the credit of this Commonwealth, or of all or any of the United States of America, or any Inspectors’ notes for tobacco, or shall pass any such counterfeited coin, paper, bills, or notes, knowing them to be counterfeit; or, for the sake of lucre shall diminish,** case, or wash any such coin, shall be condemned to hard labor six years in the public works, and shall forfeit all his lands and goods to the Commonwealth.
* 25E.3. st 5. c. 2; 5 El c. 11; 18 El. c. 1; 8 and 9 W. 3.
c. 26; 15. and 16 G 2. c. 28; 7 Ann. q. 25. By the laws of
Æthelstan and Canute, this was punished by cutting off the
hand. ‘Gifse mynetereful wurthe sleaman tha hand of, the he
that fil mid worthe and sette iippon tha rnynet smithlhan.’
In English characters and words ‘if the minler foul
[Criminal] wert, slay the hand off, that he the foul [crime]
with wrought, and set upon the mint-smithery.’ LI,iEthelst.
14. ‘And selhe ofer this false wyrce, tholige thaera handa
the he thaet false mid worhte.’ ‘Et si quis prater hanc,
falsam fecerit, perdat manum quacum falsam confecit.’ LI.
Cnuti, 8. It had been death by the LI. Æihelredi, sub fine.
By those of H. 1. ‘Si quis cum falso deuario inventus
fueril—fiat justitia mea, saltern de dextro pugno et de
testiculis.’ Anno 1108. ‘Opera prelium vero est audire quam
severus rex fuerit in pravos. Monetarios enim fere omnes
totius Angliee fecit ementulari, et manus dextras abscindi,
quia monetam furtive corruperant.’ Wilkins ib. et anno 1125.
When the Common law became settled, it appears to have been
punishable by death. ‘Est aliud genus crirninis quod sub
nomine falsi continetur, et tangit coronam domini regis, et
nlfimum indncit supplicium, sicut de illis qui falsam
fabricant monetasn, et qui de re non reproba, faciunt
reprobam; sicut sunt retonsores deriarinruno’ Bract. L. 3. c
3. § 2. Fleta, L. 1. c. 22 § 4 Lord Hale thinks it was
deemed petty treason at common law. 1 H. P. C. 220, 224. The
bringing in false money with intent to merchandise, and make
payment of it is treason, by 25 E. 3. But the best proof of
the intention, is the act of passing it, and why not leave
room for repentance here, as in other cases of felonies
intended? I H P. C. 229.
** Clipping, filing, rounding, impairing, scaling,
lightening, (the words in the statutes) are included in
‘diminishing;’ gilding, in the word ‘casing;’ coloring in
the word ‘washing;’ and falsifying or marking, is
counterfeiting.’
Whosoever committeth Arson,* shall be condemned to hard labor five years in the public works, and shall make good the loss of the sufferers threefold.**
*43 El. c. 13. confined to four counties. 22 ^ 23 Car. 2. c.
7; 9 G. 1. c. 22, 9 G. 3. c. 29.
** Arson was a felony at Common law—3 Inst. 66; punished by
a fine, Ll. Æthelst. 6. But LI. Cnuti, 61. make it a ‘scetus
inexpiable.’ ‘Hus brec and baernet and open thyfth and
asbereniorth and hlaford swice after woruld laga is
boileds.’ Word for word, ‘House break and burnt, and open
theft, and manifest murdher, and lord-treachery, after
world’s law is bootless.’ Bracton says, it was punished by
death. ‘Si quis turbida seditione iricendium fecerit
nequiter et in felonia, vel ob inimicitias, vel praedandi
causa, capital puniatur pcena vel sententia.’ Bract. L. 3.
c. 27. He defines it as commissible by burning ‘cedes alien
as.’ Ib. Britton, c. 9. ‘Ausi soitenquis de ceux que
felonise-ment en temps de pees eient a litre blees ou autre
messons ars, et ceux que ser-rount de ceo alteyniz, soient
ars issint que eux soient punys par mesme cele chose dount
ils pecherent.’ Fleia, L. I. c. 37. is a copy of Bracton.
The Mirror, c. 1. § 8. says, ‘Ardours sont que ardent cilie,
ville, maison home, maison beast, ou auters chatelx, de lour
felonie en temps de pace pour haine ou vengeance.’ Again, c.
2. § II., pointing oul the words of the appellor ‘jeo dise
que Sebright, &c. entiel meas. on ou hiens mist de feu.’
Coke, 3 Inst. 67. says, ‘The ancient authors extended this
felony further than houses, viz. to stacks of corn, waynes
or carts of coal, wood, or other goods.’ He defines it as
commissibie, not only on the inset houses, parcel of the
mansion-house, but the outset also, as barn, stable, cow-
house, sheep-house, dairy-house, mill-house, and the like,
parcel of the mansion house.’ But ‘burning of a barn, being
no parcel of a mansion-house, is no felony,’ unless there be
corn or hay within it. Ib. The 22 k. 23 Car. 2. and 9 G. 1.
are the principal statutes against arson. They extend the
offence beyond the Common law.
If any person shall, within this Commonwealth, or, being a citizen thereof, shall without the same, wilfully destroy,* or run** away with any sea-vessel, or goods laden on board thereof, or plunder or pilfer any wreck, he shall be condemned to hard labor five years in the public works, and shall make good the loss of the sufferers threefold.
* Ann. st. 2. c. 9. 12 Ann. c. 18. 4 G. 1. c. 12. 26 G. 2.
c. 19.
** 11 h 12 W.3. c.7.
Whosoever committeth Robbery,* shall be condemned to hard labor four years in the public works, and shall make double reparation to the persons injured.
* Robbery was a felony at Common law. 3 Inst. 68. ‘Scelus
inexpiable,’ by the LI. Cnuti. 61. [See before in Arson.] It
was punished with death. Briit c. 15, ‘De robbours et de
larouns et de semblables mesfesours, soitaussi
ententivernent enquis—et tauntost soient ceux robbours
juges a la morl.’ Fleta says, ‘Si quis conviclus fuerit de
bonis viri robbatis vel asportatis ad sectam regis judicium
capitale subibit.’ L. 1. c. 39. See also Bract. L. 3. c. 32
§ I.
Whatsoever act, if committed on any mansion-house, would be deemed Burglary,* shall be Burglary, if committed on any other house; and he who is guilty of Burglary, shall be condemned to hard labor four years in the public works, and shall make double reparation to the persons injured.
* Burglary was felony at the Common law. 3 Inst. 63 It was
not distinguished by ancient authors, except the Mirror,
from simple House-breaking, ib. 65. Burglary and House-
breaking were called ‘Hamsockne.’ ‘Diximus etiam de pacis
violatione et de immunitatibus domus, si quis hoc in
posterum fecetit ut perdat ornne quod habet, et sit in regis
arbitro utrum vitam habeat.’ ‘Eac we quasdon be mundbryce
and be ham socnum,sethe hit ofer this do tha:t he dolie
enlles thces the age, and sy on Cyninges Jome hwsether be
life age: and we quoth of mound-breach, and of home-seeking
he who it after this do, that he dole all that he owe
[owns], and is in kings doom whether he life owes [owns].’
LI. Eadmundi, c. 6 and see LI. Cnuti. 61. ‘bus btec,’ in
notesion Arson, ante. A Burglar was also called a Burgessor.
‘Et soit enquis de Burgessours et sunt tenus Burgessours
trestous ceux que felonisement en temps de pees debrusornt
esglises ou auter mesons, ou murs ou portes de nos cytes, ou
de nos Burghes.’ Britt. c. 10. ‘Burglaria est nocturna
diruptio habitaculi alicujus, vel ecclesise, etiam murorum,
portarurnve civitatis aut burgi, ad feloniam aliquam
perpetrandam. Noclanter dico, recentiores se-cutus; veteres
enim hoc non adjungunt.’ Spelm. Gloss, verb. Burglaria. It
was punished with death. Ib. citn. from the office of a
Coroner. It may be committed in the outset houses, as well
as inset, 3 Inst. 65. though not under the same roof or
contiguous, provided they be within the Curtilage or Home-
stall. 4 BI. 225. As by the Common law all felonies were
clergiable, the stat. 23 H. 8. c. 1; 5 E. 6. c. 9. and 18
El. c. 7. first distinguished tfiem, by taking the clerical
privilege of impunity from the principals, and 3 & 4 W. M.
c. 9. from accessories before the fact. No statute defines
what Burglary is. The 12 Ann. c. 7. decides the doubt
whether, where breaking is subsequent to entry, it is
Burglary. Bacon’s Elements had affirmed, and T. H. P. C.
554. had denied it. Our bill must distinguish them by
different degrees of punishment.
Whatsoever act, if committed in the night time, shall constitute the crime of Burglary, shall, if committed in the day, be deemed House-breaking;* and whosoever is guilty thereof, shall be condemned to hard labor three years in the public works, and shall make reparation to the persons injured.
* At the Common law, the offence of House-breaking was not
distinguished from Burglary, and neither of them from any
other larceny. The statutes at first took away clergy from
Burglary, which made a leading distinction between the two
offences. Later statutes, however, have taken clergy from so
many cases of House-breaking, as nearly to bring the
offences together again. These are 23 H. 8. c. 1; 1 E. 6. c.
12; 5 k 6 E. 6. c. 9; 3 & 4 W. M. c. 9; 39 El. c. 15; 10&11
W. 3. c.23; 12 Ann. c. 7. See Burr. 428; 4 Bl. 240. The
circumstances, which in these statutes characterize the
offence, seem to have been occasional and unsystematical.
The houses on which Burglary may be committed, and the
circumstances which constitute that crime, being
ascertained, it will be better to define House-breoking by
the same subjects and circumstances, and let the crimes be
distinguished only by the hour at which they are committed,
and the degree of punishment.
Whosoever shall be guilty of Horse-stealing,* shall be condemned to hard labor three years in the public works, and shall make reparation to the person injured.
* The offence of Horse-stealing seems properly
distinguishable from other larcenies, here, where these
animals generally run at large, the temptation being so
great and frequent, and the facility of commission so
remarkable. See 1 E. 6. c. 12; 23 E. 6. c. 33; 31 El. c. 12.
Grand Larceny* shall be where the goods stolen are of the value of five dollars; and whosoever shall be guilty thereof, shall be forthwith put in the pillory for one half hour, shall be condemned to hard labor** two years in the public works, and shall make reparation to the person injured.
* The distinction between grand and petty larceny is very
ancient. At first 8d. was the sum which constituted grand
larceny. LI. Ælhelst. c. 1. ‘Ne parcatur ulli furi, qui
furtum manutenens captus sit, supra 12 annos nafo, et supra
8 denarios.’ Afterwards, in the same king’s reign, it was
raised to 12d. ‘Non parcaturalicui furi ultra 12 denarios,
et ultra 12 annos nato—ut occide-mus ilium et capiamus omne
quod possidet, et inprimis sumamus rei furto ablatse pretium
ab hserede, ac dividatur postea reliquum in duas partes, una
pars uxori, si munda, et facinoris conscia non sit; et
residuum in duo, dimi-dium capiat rex, dimidium societas.’
LI. Æthelst. Wilkins, p. 65. VOL. I. 17
** LI. Inse, c. 7. ‘Si quis furetur ita ut uxor ejus et
infans ipsius nesciani, solvat 60. solidos pcenae loco. Si
autem furetur testantibus omuibus haere-dibus suis, abeant
omnes in servilutem.’ Ina was King of the West Saxons, and
began to reign A. C. 688. After the union of the Heptarchy,
i. e. temp. Æthelst. inter 924 and 940, we find it
punishable with death as above. So it was inter 1017 and
1035, i. e. temp. Cnuti. LI. Cnuti 61. cited in notes on
Arson. In the time of William the Conqueror, it seems lo
have been made punishable by fine only. LI. Gul. Cohq. apud
Wilk. p. 218. 220. This commutation, however, was taken away
by LI. H. 1. anno 1108. ‘Si quis in furto vel latro-cinio
deprehensus fuisset, suspenderetur: sublata wirgildorum, id
est, pecu-niarse redemptions lege.’ Larceny is the felonious
taking and carrying away of the personal goods of another.
1. As to the taking, the 3 & 4 VV. M. c. 9. § 5, is not
additional to the Common law, but declaratory of it; because
where only the care or use, and not the possession, of
things is delivered, to take them was larceny at the Common
law. The 33 H. 6. c. 1 and 21 11. 8. c. 7., indeed., have
added to the Common law by making it larceny in a servant to
convert things of his master’s. But quære, if they should be
imitated more than as to other breaches of trust in general.
2. As to the subject of larceny, 4 G. 2. c.32; 6 G. 3. c. 36
48; 43 El. c. 7; 15 Car. 2. c. 2; 23 G. 2 c. 26; 31 G. 2. c.
35; 9 G. 3. c. 41; 25 G. 2. c. 10. have extended larceny to
things of various sorts, either real, or fixed to the
realty. But the enumeration is unsystematical, and in this
country, where the produce of the earth is so spontaneous as
to have rendered things of this kind scarcely a breach of
civility or good manners in the eyes of the people, quære,
if it would not too much enlarge the field of Criminal law?
The same may be questioned of 9 G. J. c. 22; 13 Car. 2. c.
10; 10 G. 2. c. 32; 5 G. 3. c. 14; 22 h 23 Car. 2. c. 25; 37
E. 3. c. 19. making it felony to steal animals ferte
natures.
Petty Larceny shall be, where the goods stolen are of less value than five dollars; and whosoever shall be guilty thereof, shall be forthwith put in the pillory for a quarter of an hour, shall be condemned to hard labor one year in the public works, and shall make reparation to the person injured.
Robbery* or larceny of bonds, bills obligatory, bills of exchange, or
promissory notes for the payment of money or tobacco, lottery tickets,
paper bills issued in the nature of money, or of certificates of loan on
the credit of this Commonwealth, or of all or any of the United States
of America, or Inspectors’ notes for tobacco, shall be punished in the
same manner as robbery,or larceny of the money or tobacco due on or
represented by such papers.* 2 G. 2. c. 25 §3; 7 G 3. c. 50.
Buyers* and receivers of goods taken by way of robbery or larceny, knowing them to have been so taken, shall be deemed accessaries to such robbery or larceny after the fact.
* 3 &. 4 W. & M. c. 9. § 4; 5 Ann. c. 31. § 5; 4 G. 1. c.
11. § 1.
Prison breakers,* also, shall be deemed accessaries after the fact, to traitors or felons whom they enlarge from prison.**
* 1 E. 2.
** Breach of prison at the Common law was capital, without
regard to the crime for which the party was committed. ‘Cum
pro criminis qualitate in carcerem recepti fuerint,
conspiraverint (ut ruptis vinculis aut fracto carcere)
evadant, atnplius (quam causa pro qua recepti sunt exposuit)
puniendi sunt, videlicet ultimo supplicio, quamvis ex eo
crimine innocentes inveniantur, propter quod inducti sunt in
carcerem et imparcati.’ Bracton L. 3, c. 9. § 4. Britt. c.
11. Fleta, L. 1. c. 26. § 4. Yet in the Y. B. Hill. 1 H. 7.
2. Hussey says, that, by the opinion of Billing and Choke,
and all the Justices, it was a felony in strangers only, but
not in the prisoner himself. S. C. Fitz. Abr. Co-ron. 48.
They are principal felons, not accessaries, ib. Whether it
was felony in the prisoner at Common law, is doubted. Stam.
P. C. 30. b. The Mirror c. 5. § 1. says, ‘Abusion est a
tener escape de prisoner, ou de bruserie del gaole pur peche
mortal 1, car eel usage nest garrant per nul ley, ne in nul
part est use forsque in cest realme, et en France, ems
[mais] est leu garrantie de ceo faire per la ley de nature’
2 Inst. 589. The stat. 1 E. 2, ‘de fragentibus priso-nam,’
‘restrained the judgment of life and limb for prison-
breaking, to cases where the offence of the prisoner
required such judgment.’
It is not only vain but wicked, in a legislator to frame
laws in opposition to the laws of nature, and to arm them
with the terrors of death. This is truly creating crimes in
order to punish them. The law of nature impels every one to
escape from confinement; it should not, therefore, be
subjected to punishment. Let the legislator restrain his
criminal by walls, not by parchment. As to strangers
breaking prison to enlarge an offender, they should, and may
be fairly considered as accessaries after the fact. This
bill saying nothing of the prisoner releasing himself by
breach of jail, he will have the benefit of the first
section of the bill, which repeals the judgment of life and
death at the Common law.
All attempts to delude the people, or to abuse their understanding by exercise of the pretended arts of witchcraft, conjuration, enchantment, or sorcery, or by pretended prophecies, shall be punished by ducking and whipping, at the discretion of a jury, not, exceeding fifteen stripes.*
* ‘Gifwiecan owwe wigleras mansworan, owwe morthwyrhtan owwe
fule afylede eebere horcwenan ahwhar on lande wurthan
agytene, thonne fyrsie man of earde, and claensie lha.
theode, owwe on earde forfare hi mid ealle, buton hi
geswican and the deoper gebetan:’ ‘if witches, or weirds,
man-swearers, or murther-wroughters, or foul, defiled, open
whore-queens, ay—where in the land were gotten, then force
them off earth, and cleanse the nation, or in earth forth-
fare them withal, buton they beseech, and deeply better.’
LI. Ed. et Guthr. c. 11. ‘Saga; mulieres barbara
factitantes sacrificia, aut pestiferi, si cui mortem
intulerint, neque id inficiari poterint, capitis pcena
esto.’ LI. Aethelst. c. 6. apud Lambard. LI. Aelfr. 30. LI.
Cnuti. c. 4. ‘Mesmo eel jugement (d’etrears) eyent
sorcers, et sorceresses,’ &c. ut supra. Fleta tit et ubi
supra. 3 Inst. 44. Trial of witches before Hale, in 1664.
The statutes 33 H. 8. c. 8. 5. El. c. 16 and 1. Jac. 1. c.
12. seem to be only in confirmation of the Common law. 9 G.
2. c. 25. punishes them with pillory and a year’s
imprisonment 3 E. 6 c 15. 5 El. c. 15. punish fond,
fantastical, and false prophecies, by fine and imprisonment.
If the principal offenders be fled,* or secreted from justice, in any case not touching life or member, the accessaries may, notwithstanding, be prosecuted as if their principal were convicted.**
* 1 Ann. c. 9. § 2.
**As every treason includes within it a misprision of
treason, so every felony includes a misprision, or
misdemeanor. 1 Hale P. C. 652. 75S. ‘Licet fuerit felonia,
tamen in eo continetur misprisio.’ 2 R. 3.10. Both principal
and accessary, therefore, may be proceeded against in any
case, either for felony, or misprision, at the Common law.
Capital cases not being mentioned here, accessaries to them
will of course be triable for misprisions, if the offender
flies.
If any offender stand mute of obstinacy,* or challenge preremp-torily more of the jurors than by law he may, being first warned of the consequence thereof, the court shall proceed as if he had confessed the charge,**
* 3E. I.e. 12.
** Whether the judgment of penance lay at Common law. See 2
Inst. 178.2. H. P. C. 321. 4 Bl. 322. It was given on
standing mute: but on challenging more than the legal
number, whether that sentence, or sentence of death is to be
given, seems doubtful. 2 H. P. C. 316. Quære, whether it
would not be better to consider the supernumerary challenge
as merely void, and to proceed in the trial. Quære too, in
case of silence.
Pardon and privilege of clergy shall henceforth be abolished, that none may be induced to injure through hope of impunity. But if the verdict be against the defendant, and the court, before whom the offence is heard and determined, shall doubt that it may be untrue for defect of testimony, or other cause, they may direct a new trial to be had.*
* ‘Cum Clericus sic de crimine convictus degradetur, non
sequitur aliapoe-na pro uno delicto, vel pluribus ante
degradationem perpetratis. Satis enim sufficit ei pro pcena
degradatio, quse est magna capitis diminutio, nisi forte
convictus fuerit de apostatia, quia hinc primo degradetur,
et postea per manum laicalem comburetur, secundum quod
accidit in concilio Oxoni celebrato a bonas memoriae S.
Cantuaren. Archiepiscopo de quodam diacono, qui seapos-
tatavit pro quadam Judaea; qui cum esset per episcopum
degradatus, statim fuit igni traditus per manum laicalem.’
Bract. L. 3. c. 9. § 2. ‘Et mesme eel jugement (i. e. qui
ils soient ars) eye n’t sorcers et sorceresses, et sodomites
et mescreauntz apertement atteyntz.’ Britt. c. 9.
‘Christiani autem Apostatae, sortilegii, et hujusmodi
detractari debent et comburi.’ Fleta, L. 1. c. 37. § 2. see
3 Inst. 39; 12 Rep. 92; 1 H. P. C. 393. The extent of the
clerical privilege at the Common law, 1. As to the crimes,
seems very obscure and uncertain. It extended to no case
where the judgment was not of life or limb. Note in 2. H. P.
C. 326. This, therefore, excluded it in trespass, petty
larceny, or killing se defendendo. In high treason against
the person of the King, it seems not to have been allowed.
Note 1 H. P. C. 185. Treasons, therefore, not against the
King’s person immediately, petty treasons and felonies, seem
to have been the cases where it was allowed; and even of
those, not for insidiatio viarum, depopulatio agrorum, or
combustio domorum. The statute de Clero, 25 E. 3. st. 3. c.
4. settled the law on this head. 2. As to the persons, it
extended to all clerks, always, and toties quoiies. 2 H. P.
C. 374. To nuns also. Fitz. Abr. Coron. 461. 22 E. 3. The
clerical habit and tonsure were considered as evidence of
the person being clerical. 26 Assiz. 19 & 20 E. 2. Fitz.
Coron. 233. By the 9 E. 4. 28. b. 34 H. 6. 49. a. b. simple
reading became the evidence. This extended impunity to a
great number of laymen, and toties quoties. The stat. 4 H.
7. c. 13. directed that real clerks should upon a second
arraignment, produce their orders, and all others to be
burnt in the hand with M. or T. on the first allowance of
clergy, and not to be admitted to it a second time. A
heretic, Jew, or Turk, (as being incapable of orders) could
not have clergy. H Co. Rep. 29. b. But a Greek, or other
alien, reading in a book of his own country, might. Bro.
Clergie. 20. So a blind man, if he could speak Latin. Ib.
21. qu, 11. Rep. 29. b. The orders entitling the party were
bishops, priests, deacons, and sub-deacons, the inferior
being reckoned Clerici in minoribus. 2 H. P. C. 373. Quære,
however, if this distinction is not founded on the stat. 23.
H. 8. c. 1; 25. H. 8. c. 32. By merely dropping all the
statutes, it should seem that none but clerks would be
entitled to this privilege, and that they would, toties
quoties.
No attainder shall work corruption of blood in any case.
In all cases of forfeiture, the widow’s dower shall be saved to her, during her title thereto; after which it shall be disposed of as if no such saving had been.
The aid of Counsel,* and examination of their witnesses on oath, shall be allowed to defendants in criminal prosecutions.
* 1 Ann. c. 9.
Slaves guilty of any offence* punishable in others by labor in the public works, shall be transported to such parts in the West Indies, South America, or Africa, as the Governor shall direct, there to be continued in slavery.
* Manslaghter, counterfeiting, arson, asportation of
vessels, robbery, burglary, house-breaking, horse-stealing,
larceny.
[NOTE F.]—Coinage for the United States
On the Establishment of a Money Unit, and of a Coinage for the United States.
In fixing the Unit of Money, these circumstances are of principal importance.
I. That it be of convenient size to be applied as a measure to the common money transactions of life.
II. That its parts and multiplies be in an easy proportion to each other, so as to facilitate the money arithmetic;
III. That the Unit and its parts, or divisions, be so nearly of the value of some of the known coins, as that they may be of easy adoption for the people.
The Spanish Dollar seems to fulfil all these conditions.
I. Taking into our view all money transactions, great and small, I question if a common measure of more convenient size than the Dollar could be proposed. The value of 100, 1000, 10,000 dollars is well estimated by the mind; so is that of the tenth or the hundredth of a dollar. Few transactions are above or below these limits. The expediency of attending to the size of the Money Unit will be evident to any one who will consider how inconvenient it would be to a manufacturer or merchant, if instead of the yard for measuring cloth, either the inch or the mile had been made the Unit of Measure.
II. The most easy ratio of multiplication and division is that by ten. Every one knows the facility of Decimal Arithmetic. Every one remembers, that, when learning Money-Arithmetic, he used to be puzzled with adding the farthings, taking out the fours and carrying them on; adding the pence, taking out the twelves and carrying them on; adding the shillings, taking out the twenties and carrying them on; but when he came to the pounds, where he had only tens to carry forward, it was easy and free from error. The bulk of mankind are school-boys through life. These little perplexities are always great to them. And even mathematical heads feel the relief of an easier, substituted for a more difficult process. Foreigners, too, who trade or travel among us, will find a great facility in understanding our coins and accounts from this ratio of subdivision. Those who have had occasion to convert the Livres, sols, and deniers of the French; the Gilders, stivers, and frenings of the Dutch; the Pounds, shillings, pence, and farthings of these several States, into each other, can judge how much they would have been aided, had their several subdivisions been in a decimal ratio. Certainly, in all cases, where we are free to choose between easy and difficult modes of operation, it is most rational to choose the easy. The Financier, therefore, in his report, well proposes that our Coins should be in decimal proportions to one another. If we adopt the Dollar for our Unit, we should strike four coins, one of gold, two of silver, and one of copper, viz.
1. A golden piece, equal in value to ten dollars:
2. The Unit or Dollar itself, of silver:
3. The tenth of a Dollar, of silver also:
4. The hundreth of a Dollar, of copper.
Compare the arithmetical operations, on the same sum of money expressed in this form, and expressed in the pound sterling and its divisions.
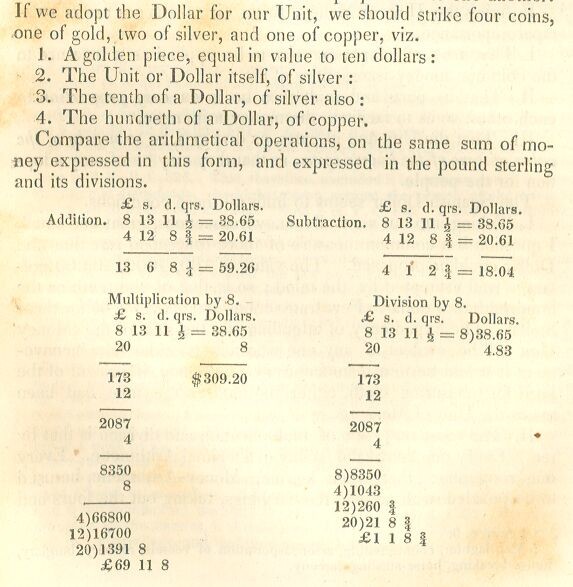
A bare inspection of the above operations, will evince the labor which is occasioned by subdividing the Unit into 20ths, 240ths, and 960ths, as the English do, and as we have done; and the ease of subdivision in a decimal ratio. The same difference arises in making payment. An Englishman, to pay £8 13s. 11d. 1/2qrs. must find, by calculation, what combination of the coins of his country will pay this sum; but an American, having the same sum to pay, thus expressed $38.65, will know, by inspection only, that three golden pieces, eight units or dollars, six tenths, and five coppers, pay it precisely.
III. The third condition required is, that the Unit, its multiples, and subdivisions, coincide in value with some of the known coins so nearly, that the people may, by a quick reference in the mind, estimate their value. If this be not attended to, they will be very long in adopting the innovation, if ever they adopt it. Let us examine, in this point of view, each of the four coins proposed.
1. The golden piece will be 1/5 more than a half joe and 1/15 more than a double guinea. It will be readily estimated, then, by reference to either of them; but more readily and accurately as equal to ten dollars.
2. The Unit, or Dollar, is a known coin, and the most familiar of all to the minds of the people. It is already adopted from South to North; has identified our currency, and therefore happily offers itself as a Unit already introduced. Our public debt, our requisitions, and their apportionments, have given it actual and long possession of the place of Unit. The course of our commerce, too, will bring us more of this than of any other foreign coin, and therefore renders it more worthy of attention. I know of no Unit which can be proposed in competition with the Dollar, but the Pound. But what is the Pound? 1547 grains of fine silver in Georgia; 1289 grains in Virginia, Connecticut, Rhode Island, Massachusetts, and New Hampshire; 1031 grains in Maryland, Delaware, Pennsylvania, and New Jersey; 966 grains in North Carolina and New York. Which of these shall we adopt? To which State give that pre-eminence of which all are so jealous? And on which impose the difficulties of a new estimate of their corn, their cattle, and other commodities? Or shall we hang the pound sterling, as a common badge, about all their necks? This contains 1718 grains of pure silver. It is difficult to familiarize a new coin to the people; it is more difficult to familiarize them to a new coin with an old name. Happily, the Dollar is familiar to them all, and is already as much referred to for a measure of value, as their respective provincial pounds.
3. The tenth will be precisely the Spanish bit, or half pistereen. This is a coin perfectly familiar to us all. When we shall make a new coin, then, equal in value to this, it will be of ready estimate with the people.
4. The hundredth, or copper, will differ little from the copper of the four Eastern States, which is 1/108 of a dollar; still less from the penny of New York and North Carolina, which is 1/96 of a dollar; and somewhat more from the penny or copper of Jersey, Pennsylvania, Delaware, and Maryland, which is 1/90 of a dollar. It will be about the medium between the old and the new coppers of these States, and will therefore soon be substituted for them both. In Virginia, coppers have never been in use. It will be as easy, therefore, to introduce them there of one value as of another. The copper coin proposed, will be nearly equal to three fourths of their penny, which is the same with the penny lawful of the Eastern States.
A great deal of small change is useful in a State, and tends to reduce the price of small articles. Perhaps it would not be amiss to coin three, more pieces of silver, one of the value of five tenths, or half a dollar, one of the value of two tenths, which would be equal to the Spanish pistereen, and one of the value of five coppers, which would be equal to the Spanish half-bit. We should then have five silver coins, viz.
1. The Unit or Dollar:
2. The half dollar or five tenths:
3. The double tenth, equal to 2/10, or one fifth of a dollar, or to the pistereen:
4. The tenth, equal to a Spanish bit:
5. The five copper piece, equal to 5/100 or one twentieth of a dollar, or the half-bit.
The plan reported by the Financier is worthy of his sound judgment. It admits, however, of objection, in the size of the Unit. He proposes that this shall be the 1440th part of a dollar; so that it will require 1440 of his units to make the one before proposed. He was led to adopt this by a mathematical attention to our old currencies, all of which this Unit will measure without leaving a fraction. But as our object is to get rid of those currencies, the advantage derived from this coincidence will soon be past, whereas the inconveniences of this Unit will for ever remain, if they do not altogether prevent its introduction. It is defective in two of the three requisites of a Money Unit. 1. It is inconvenient in its application to the ordinary money transactions. 10,000 dollars will require eight figures to express them, to wit, 14,400,000 units. A horse or bullock of eighty dollars’ value, will require a notation of six figures, to wit, 115,200 units. As a money of account, this will be laborious, even when facilitated by the aid of decimal arithmetic: as a common measure of the value of property, it will be too minute to be comprehended by the people. The French are subjected to very laborious calculations, the Livre being their ordinary money of account, and this but between 1/5 and 1/6 of a dollar; but what will be our labors, should our money of account be 1/1440 of a dollar only? 2. It is neither equal, nor near to any of the known coins in value.
If we determine that a Dollar shall be our Unit, we must then say with precision what a Dollar is. This coin, struck at different times, of different weights and fineness, is of different values. Sir Isaac Newton’s assay and representation to the Lords of the Treasury, in 1717, of those which he examined, make their values as follows:

The Seville piece of eight . . . . 387 grains of pure silver
The Mexico piece of eight . . . . 385 1/2 ”
The Pillar piece of eight . . . . 385 3/4 ”
The new Seville piece of eight . . 308 7/10 ”
The Financier states the old Dollar as containing 376 grains of fine silver, and the new 365 grains. If the Dollars circulating among us be of every date equally, we should examine the quantity of pure metal in each, and from them form an average for our Unit. This is a work proper to be committed to mathematicians as well as merchants, and which should be decided on actual and accurate experiment.
The quantum of alloy is also to be decided. Some is necessary, to prevent the coin from wearing too fast; too much, fills our pockets with copper, instead of silver. The silver coin assayed by Sir Isaac Newton, varied from 1 1/2 to 76 pennyweights alloy, in the pound troy of mixed metal. The British standard has 18 dwt.; the Spanish coins assayed by Sir Isaac Newton, have from 18 to 19 1/2 dwt.; the new French crown has in fact 19 1/2, though by edict it should have 20 dwt., that is 1/12.
The taste of our countrymen will require, that their furniture plate should be as good as the British standard. Taste cannot be controlled by law. Let it then give the law, in a point which is indifferent to a certain degree. Let the Legislatures fix the alloy of furniture plate at 18 dwt., the British standard, and Congress that of their coin at one ounce in the pound, the French standard. This proportion has been found convenient for the alloy of gold coin, and it will simplify the system of our mint to alloy both metals in the same degree. The coin too, being the least pure, will be the less easily melted into plate. These reasons are light, indeed, and, of course, will only weigh, if no heavier ones can be opposed to them.
The proportion between the values of gold and silver is a mercantile problem altogether. It would be inaccurate to fix it by the popular exchanges of a half Joe for eight dollars, a Louis for four French crowns, or five Louis for twenty-three dollars. The first of these, would be to adopt the Spanish proportion between gold and silver; the second, the French; the third, a mere popular barter, wherein convenience is consulted more than accuracy. The legal proportion in Spain is 16 for 1; in England, 15 1/2 for 1; in France, 15 for 1. The Spaniards and English are found, in experience, to retain an over proportion of gold coins, and to lose their silver. The French have a greater proportion of silver. The difference at market has been on the decrease. The Financier states it at present, as at 141/2 for one. Just principles will lead us to disregard legal proportions altogether; to inquire into the market price of gold, in the several countries with which we shall principally be connected in commerce, and to take an average from them. Perhaps we might, with safety, lean to a proportion somewhat above par for gold, considering our neighborhood and commerce with the sources of the coins, and the tendency which the high price of gold in Spain has, to draw thither all that of their mines, leaving silver principally for our and other markets. It is not impossible that 15 for 1, may be found an eligible proportion. I state it, however, as a conjecture only.
As to the alloy for gold coin, the British is an ounce in the pound; the French, Spanish, and Portuguese differ from that, only from a quarter of a grain, to a grain and a half. I should, therefore, prefer the British, merely because its fraction stands in a more simple form, and facilitates the calculations into which it enters.
Should the Unit be fixed at 365 grains of pure silver, gold at 15 for 1, and the alloy of both be one twelfth, the weights of the coins will be as follows:

The quantity of fine silver which shall constitute the Unit, being-settled, and the proportion of the value of gold, to that of silver; a table should be formed from the assay before suggested, classing the several foreign coins according to their fineness, declaring the worth of a pennyweight or grain in each class, and that they shall be lawful tenders at those rates, if not clipped or otherwise diminished; and where diminished, offering their value for them at the mint, deducting the expense of re-coinage. Here the Legislatures should co-operate with Congress, in providing that no money be received or paid at their treasuries, or by any of their officers, or any bank, but on actual weight; in making it criminal, in a high degree, to diminish their own coins, and, in some smaller degree, to offer them in payment when diminished.
That this subject may be properly prepared and in readiness for Congress to take up at their meeting in November, something must now be done. The present session drawing to a close, they probably would not choose to enter far into this undertaking themselves. The Committee of the States, however, during the recess, will have time to digest it thoroughly, if Congress will fix some general principles for their government. Suppose they be instructed,—
To appoint proper persons to assay and examine, with the utmost accuracy practicable, the Spanish milled dollars of different dates in circulation with us.
To assay and examine, in like manner, the fineness of all the other coins which may be found in circulation within these states.
To report to the Committee the result of these assays, by them to be laid before Congress.
To appoint, also, proper persons to inquire what are the proportions between the values of fine gold and fine silver, at the markets of the several countries with which we are, or probably may be, connected in commerce; and what would be a proper proportion here, having regard to the average of their values at those markets, and to other circumstances, and to report the same to the Committee, by them to be laid before Congress.
To prepare an Ordinance for establishing the Unit of Money within these States; for subdividing it; and for striking coins of gold, silver, and copper, on the following principles.
That the Money Unit of these States shall be equal in value to a Spanish milled dollar containing so much fine silver as the assay, before directed, shall show to be contained, on an average, in dollars of the several dates in circulation with us.
That this Unit shall be divided into tenths and hundredths; that there shall be a coin of silver of the value of a Unit; one other of the same metal, of the value of one tenth of a Unit; one other of copper, of the value of the hundredth of a Unit.
That there shall be a coin of gold of the value of ten units, according to the report before directed, and the judgment of the Committee thereon.
That the alloy of the said coins of gold and silver shall be equal in weight to one eleventh part of the fine metal.
That there be proper devices for these coins.
That measures be proposed for preventing their diminution, and also their currency, and that of any others, when diminished.
That the several foreign coins be described and classed in the said Ordinance, the fineness of each class stated, and its value by weight estimated in Units and decimal parts of Units.
And that the said draught of an Ordinance be reported to Congress at their next meeting, for their consideration and determination.
Supplementary Explanations.
The preceding notes having been submitted to the consideration of the Financier, he favored me with his opinion and observations on them, which render necessary the following supplementary explanations.
I observed in the preceding notes, that the true proportion of value between gold and silver was a mercantile problem altogether, and that, perhaps, fifteen for one, might be found an eligible proportion. The Financier is so good as to inform me, that this would be higher than the market would justify. Confident of his better information on this subject, I recede from that idea.*
* In a Newspaper, which frequently gives good details in political economy, I find, under the Hamburg head, that the present market price of Gold and Silver is, in England, 15.5 for 1: in Russia, 15: in Holland, 14.75: in Savoy, 14.96: in Fiance, 14.42: in Spain, 14.3: in Germany, 14.155: the average of which is 14.615 or 14 1/2. I would still incline to give a little more than the market price for gold, because of its superior convenience in transportation.
He also informs me, that the several coins in circulation among us, have already been assayed with accuracy, and the result published in a work on that subject. The assay of Sir Isaac Newton had superseded, in my mind, the necessity of this operation as to the older coins, which were the subject of his examination. This later work, with equal reason, may be considered as saving the same trouble as to the latter coins.
So far, then, I accede to the opinions of the Financier. On the other hand, he seems to concur with me, in thinking his smallest fractional division too minute for a Unit, and, therefore, proposes to transfer that denomination to his largest silver coin, containing 1000 of the units first proposed, and worth about 4s. 2d. lawful, or 25/36 of a dollar. The only question then remaining between us is, whether the Dollar, or this coin, be best for the Unit. We both agree that the ease of adoption with the people, is the thing to be aimed at.
1. As to the Dollar, events have overtaken and superseded the question. It is no longer a doubt whether the people can adopt it with ease; they have adopted it, and will have to be turned out of that, into another track of calculation, if another Unit be assumed. They have now two Units, which they use with equal facility, viz. the Pound of their respective state, and the Dollar. The first of these is peculiar to each state; the second, happily, common to all. In each state, the people have an easy rule for converting the pound of their state into dollars, or dollars into pounds; and this is enough for them, without knowing how this may be done in every state of the Union. Such of them as live near enough the borders of their state to have dealings with their neighbors, learn also the rule of their neighbors: Thus, in Virginia and the Eastern States, where the dollar is 6s. or 3/10 of a pound, to turn pounds into dollars, they multiply by 10, and divide by 3. To turn dollars into pounds, they multiply by 3, and divide by 10. Those in Virginia who live near to Carolina, where the dollar is 8s. or 4/10 of a pound, learn the operation of that state, which is a multiplication by 4, and division by 10, et e converso. Those who live near Maryland, where the dollar is 7s. 6d. or 3/8 of a pound, multiply by 3, and divide by 8, et e converso. All these operations are easy, and have been found by experience, not too much for the arithmetic of the people, when they have occasion to convert their old Unit into dollars, or the reverse.
2. As to the Unit of the Financier; in the States where the dollar is 3/10 of a pound, this Unit will be 5/24. Its conversion into the pound then, will be by a multiplication by 5, and a division by 24. In the States where the dollar is 3/8 of a pound, this Unit will be 25/96 of a pound, and the operation must be to multiply by 25, and divide by 96, et e converso. Where the dollar is 4/10 of a pound, this Unit will be 5/18. The simplicity of the fraction, and of course the facility of conversion and reconversion, is therefore against this Unit, and in favor of the dollar, in every instance. The only advantage it has over the dollar, is, that it will in every case express our farthing without a remainder; whereas, though the dollar and its decimals will do this in many cases, it will not in all. But, even in these, by extending your notation one figure farther, to wit, to thousands, you approximate a perfect accuracy within less than the two thousandth part of a dollar; an atom in money which every one would neglect. Against this single inconvenience, the other advantages of the dollar are more than sufficient to preponderate. This Unit will present to the people a new coin, and whether they endeavor to estimate its value by comparing it with a Pound, or with a Dollar, the Units they now possess, they will find the fraction very compound, and of course less accommodated to their comprehension and habits than the dollar. Indeed the probability is, that they could never be led to compute in it generally.
The Financier supposes that the 1/100 of a dollar is not sufficiently small, where the poor are purchasers or vendors. If it is not, make a smaller coin. But I suspect that it is small enough. Let us examine facts, in countries where we are acquainted with them. In Virginia, where our towns are few, small, and of course their demand for necessaries very limited, we have never yet been able to introduce a copper coin at all. The smallest coin which any body will receive there, is the half-bit, or 1/20 of a dollar. In those states where the towns are larger and more populous, a more habitual barter for small wants, has called for a copper coin of 1/90 or 1/96 or 1/108 of a dollar. In England, where the towns are many and pouplous, and where ages of experience have matured the conveniences of intercourse, they have found that some wants may be supplied for a farthing, or 1/208 of a dollar, and they have accommodated a coin to this want. This business is evidently progressive. In Virginia we are far behind. In some other states, they are farther advanced, to wit, to the appreciation of 1/90, 1/96 or 1/108 of a dollar. To this most advanced state, then, I accommodated my smartest coin in the decimal arrangement, as a money of payment, corresponding with the money of account. I have no doubt the time will come when a smaller coin will be called for. When that comes, let it be made. It will probably be the half of the copper I propose, that is to say 5/1000 or.005 of a dollar, this being very nearly the farthing of England. But it will be time enough to make it, when the people shall be ready to receive it.
My proposition then, is, that our notation of money shall be decimal, descending ad libitum of the person noting; that the Unit of this notation shall be a Dollar; that coins shall be accommodated to it from ten dollars to the hundredth of a dollar; and that, to set this on foot, the resolutions be adopted which were proposed in the notes, only substituting an inquiry into the fineness of the coins in lieu of an assay of them.
[NOTE G.]
I have sometimes asked myself, whether my country is the better for my having lived at all. I do not know that it is. I have been the instrument of doing the following things; but they would have been done by others; some of them, perhaps, a little better.
The Rivanna had never been used for navigation; scarcely an empty canoe had ever passed down it. Soon after I came of age I examined its obstructions, set on foot a subscription for removing them, got an act of Assembly passed, and the thing effected, so as to be used completely and fully for carrying down all our produce.
The Declaration of Independence.
I proposed the demolition of the Church establishment, and the freedom of religion. It could only be done by degrees; to wit, the act of 1776, c. 2. exempted dissenters from contributions to the Church, and left the Church clergy to be supported by voluntary contributions of their own sect; was continued from year to year, and made perpetual 1779, c. 36. I prepared the act for religious freedom in 1777, as part of the revisal, which was not reported to the Assembly till 1779, and that particular law not passed till 1785, and then by the efforts of Mr. Madison.
The act putting an end to entails.
The act prohibiting the importation of slaves.
The act concerning citizens, and establishing the natural right of man to expatriate himself at will.
The act changing the course of descents, and giving the inheritance to all the children, &c. equally, I drew as part of the revisal.
The act for apportioning crimes and punishments, part of the same work, I drew. When proposed to the Legislature by Mr. Madison, in 1785, it failed by a single vote. G. K. Taylor afterwards, in 1796, proposed the same subject; avoiding the adoption of any part of the diction of mine, the text of which had been studiously drawn in the technical terms of the law, so as to give no occasion for new questions by new expressions. When I drew mine, public labor was thought the best punishment to be substituted for death. But, while I was in France, I heard of a society in England who had successfully introduced solitary confinement, and saw the drawing of a prison at Lyons, in France, formed on the idea of solitary confinement. And, being applied to by the Governor of Virginia for the plan of a Capitol and Prison, I sent him the Lyons plan, accompanying it with a drawing on a smaller scale, better adapted to our use. This was in June, 1786. Mr. Taylor very judiciously adopted this idea, (which had now been acted on in Philadelphia, probably from the English model,) and substituted labor in confinement, to the public labor proposed by the Committee of revisal; which themselves would have done, had they been to act on the subject again. The public mind was ripe for this in 1796, when Mr. Taylor proposed it, and ripened chiefly by the experiment in Philadelphia; whereas, in 1785, when it had been proposed to our Assembly, they were not quite ripe for it.
In 1789 and 1790, I had a great number of olive plants, of the best kind, sent from Marseilles to Charleston, for South Carolina and Georgia. They were planted, and are flourishing; and, though not yet multiplied, they will be the germ of that cultivation in those States.
In 1790, I got a cask of heavy upland rice, from the river Denbigh, in Africa, about lat. 9° 30’ North, which I sent to Charleston, in hopes it might supersede the culture of the wet rice, which renders South Carolina and Georgia so pestilential through the summer. It was divided, and a part sent to Georgia. I know not whether it has been attended to in South Carolina; but it has spread in the upper parts of Georgia, so as to have become almost general, and is highly prized. Perhaps it may answer in Tennessee and Kentucky. The greatest service which can be rendered any country is, to add an useful plant to its culture; especially a bread grain; next in value to bread is oil.
Whether the Act for the more general diffusion of knowledge will ever be carried into complete effect, I know not. It was received, by the legislature, with great enthusiasm at first; and a small effort was made in 1796, by the act to establish public schools, to carry a part of it into effect, viz. that for the establishment of free English schools; but the option given to the courts has defeated the intention of the Act.*
* It appears, from a blank space at the bottom of this
paper, that a continuation had been intended. Indeed, from
the loose manner in which the above notes are written, it
may be inferred that they were originally intended as
memoranda only, to be used in some more permanent form.
[NOTE H.]
Sir,
New York, October 13, 1789.
In the selection of characters to fill the important offices of Government in the United States, I was naturally led to contemplate the talents and dispositions which I knew you to possess and entertain for the service of your country; and without being able to consult your inclination, or to derive any knowledge of your intentions from your letters, either to myself or to any other of your friends, I was determined, as well by motives of private regard, as a conviction of public propriety, to nominate you for the Department of State, which, under its present organization, involves many of the most interesting objects of the Executive authority.
But grateful as your acceptance of this commission would be to me, I am, at the same time, desirous to accommodate your wishes, and I have, therefore, forborne to nominate your successor at the court of Versailles until I should be informed of your determination.
Being on the eve of a journey through the Eastern States, with a view to observe the situation of the country, and in a hope of perfectly re-establishing my health, which a series of indispositions has much impaired, I have deemed it proper to make this communication of your appointment, in order that you might lose no time, should it be your wish to visit Virginia during the recess of Congress, which will probably be the most convenient season, both as it may respect your private concerns, and the public service.
Unwilling, as I am, to interfere in the direction of your choice of assistants, I shall only take the liberty of observing to you, that, from warm recommendations which I have received in behalf of Roger Alden, Esq., Assistant Secretary to the late Congress, I have placed all the papers thereunto belonging under his care. Those papers which more properly appertain to the office of Foreign Affairs, are under the superintendence of Mr. Jay, who has been so obliging as to continue his good offices, and they are in the immediate charge of Mr. Remsen.
With sentiments of very great esteem and regard, I have the honor to be, Sir,
Your most obedient servant,
George Washington.
The Honorable Thomas Jefferson.
I take the occasion to acknowledge the receipt of your several favors of the 4th and 5th of December of the last, and 10th of May of the present year, and to thank you for the communications therein. G. W.
New York, November 30, 1789.
Dear Sir,
You will perceive by the inclosed letter (which was left for you at the office of Foreign Affairs when I made a journey to the Eastern States), the motives, on which I acted with regard to yourself, and the occasion of my explaining them at that early period.
Having now reason to hope, from Mr. Trumbull’s report, that you will be arrived at Norfolk before this time (on which event I would most cordially congratulate you), and having a safe conveyance by Mr. Griffin, I forward your commission to Virginia; with a request to be made acquainted with your sentiments as soon as you shall find it convenient to communicate them to me. With sentiments of very great esteem and regard,
I am, dear Sir,
Your most obedient, humble servant,
George Washington.
The Honorable Thomas Jefferson.
CORRESPONDENCE
LETTER I.—TO DR. WILLIAM SMALL, May 7, 1775
TO DR. WILLIAM SMALL.
May 7, 1775.
Dear Sir,
Within this week we have received the unhappy news of an action of considerable magnitude, between the King’s troops and our brethren of Boston, in which, it is said, five hundred of the former, with the Earl of Percy, are slain. That such an action has occurred, is undoubted, though perhaps the circumstances may not have reached us with truth. This accident has cut off our last hope of reconciliation, and a phrenzy of revenge seems to have seized all ranks of people. It is a lamentable circumstance, that the only mediatory power, acknowledged by both parties, instead of leading to a reconciliation his divided people, should pursue the incendiary purpose of still blowing up the flames, as we find him constantly doing, in every speech and public declaration. This may, perhaps, be intended to intimidate into acquiescence, but the effect has been most unfortunately otherwise. A little knowledge of human nature, and attention to its ordinary workings, might have foreseen that the spirits of the people here were in a state, in which they were more likely to be provoked, than frightened, by haughty deportment. And to fill up the measure of irritation, a proscription of individuals has been substituted in the room of just trial. Can it be believed, that a grateful people will suffer those to be consigned to execution, whose sole crime has been the developing and asserting their rights? Had the Parliament possessed the power of reflection, they would have avoided a measure as impotent, as it was inflammatory. When I saw Lord Chatham’s bill, I entertained high hope that a reconciliation could have been brought about. The difference between his terms, and those offered by our Congress, might have been accommodated, if entered on, by both parties, with a disposition to accommodate. But the dignity of Parliament, it seems, can brook no opposition to its power. Strange, that a set of men, who have made sale of their virtue to the minister, should yet talk of retaining dignity. But I am getting into politics, though I sat down only to ask your acceptance of the wine: and express my constant wishes for your happiness.
Th: Jefferson.
LETTER II.—TO JOHN RANDOLPH, August 25,1775
TO JOHN RANDOLPH, ESQ.,
Monticello,
August 25,1775.
Dear Sir,
I am sorry the situation of our country should render it not eligible to you to remain longer in it. I hope the returning wisdom of Great Britain will, ere long, put an end to this unnatural contest. There may be people to whose tempers and dispositions contention is pleasing, and who, therefore, wish a continuance of confusion; but to me it is of all states but one, the most horrid: My first wish is a restoration of our just rights; my second, a return of the happy period, when, consistently with duty, I may withdraw myself totally from the public stage, and pass the rest of my days in domestic ease and tranquillity, banishing every desire of ever hearing what passes in the world. Perhaps, (for the latter adds considerably to the warmth of the former wish,) looking with fondness towards a reconciliation with Great Britain, I cannot help hoping you may be able to contribute towards expediting this good work. I think it must be evident to yourself, that the Ministry have been deceived by their officers on this side of the water, who (for what purpose, I cannot tell) have constantly represented the American opposition as that of a small faction, in which the body of the people took little part. This, you can inform them, of your own knowledge, is untrue. They have taken it into their heads, too, that we are cowards, and shall surrender at discretion to an armed force. The past and future operations of the war must confirm or undeceive them on that head. I wish they were thoroughly and minutely acquainted with every circumstance relative to America, as it exists in truth. I am persuaded, this would go far towards disposing them to reconciliation. Even those in Parliament who are called friends to America, seem to know nothing of our real determinations. I observe, they pronounced in the last Parliament, that the Congress of 1774 did not mean to insist rigorously on the terms they held out, but kept something in reserve, to give up: and, in fact, that they would give up every thing but the article of taxation. Now, the truth is far from this, as I can affirm, and put my honor to the assertion. Their continuance in this error may perhaps produce very ill consequences. The Congress stated the lowest terms they thought possible to be accepted, in order to convince the world they were not unreasonable. They gave up the monopoly and regulation of trade, and all acts of Parliament prior to 1764, leaving to British generosity to render these, at some future time, as easy to America as the interest of Britain would admit. But this was before blood was spilt. I cannot affirm, but have reason to think, these terms would not now be accepted. I wish no false sense of honor, no ignorance of our real intentions, no vain hope that partial concessions of right will be accepted, may induce the Ministry to trifle with accommodation, till it shall be out of their power ever to accommodate. If, indeed, Great Britain, disjoined from her colonies, be a match for the most potent nations of Europe, with the colonies thrown into their scale, they may go on securely. But if they are not assured of this, it would be certainly unwise, by trying the event of another campaign, to risk our accepting a foreign aid, which perhaps may not be obtainable but on condition of everlasting avulsion from Great Britain. This would be thought a hard condition to those who still wish for reunion with their parent country. I am sincerely one of those, and would rather be in dependence on Great Britain, properly limited, than on any nation upon earth, or than on no nation. But I am one of those, too, who, rather than submit to the rights of legislating for us, assumed by the British Parliament, and which late experience has shown they will so cruelly exercise, would lend my hand to sink the whole island in the ocean.
If undeceiving the Minister, as to matters of fact, may change his disposition, it will perhaps be in your power, by assisting to do this, to render service to the whole empire at the most critical time, certainly, that it has ever seen. Whether Britain shall continue the head of the greatest empire on earth, or shall return to her original station in the political scale of Europe, depends perhaps on the resolutions of the succeeding winter. God send they may be wise and salutary for us all. I shall be glad to hear from you as often as you may be disposed to think of things here. You may be at liberty, I expect; to communicate some things, consistently with your honor and the duties you will owe to a protecting nation. Such a communication among individuals may be mutually beneficial to the contending parties. On this or any future occasion, if I affirm to you any facts, your knowledge of me will enable you to decide on their credibility; if I hazard opinions on the dispositions of men or other speculative points, you can only know they are my opinions. My best wishes for your felicity attend you wherever you go; and believe me to be, assuredly,
Your friend and servant,
Th: Jefferson.
LETTER III.—TO JOHN RANDOLPH, November 29, 1775
TO JOHN RANDOLPH, ESQ..
Philadelphia,
November 29, 1775.
Dear Sir,
I am to give you the melancholy intelligence of the death of our most worthy Speaker, which happened here on the 22nd of the last month. He was struck with an apoplexy, and expired within five hours.
I have it in my power to acquaint you that the success of our arms has corresponded with the justness of our cause. Chambly and St. Johns were taken some weeks ago, and in them the whole regular army in Canada, except about forty or fifty men. This day certain intelligence has reached us that our General, Montgomery, is received into Montreal: and we expect every hour to be informed that Quebec has opened its arms to Colonel Arnold, who, with eleven hundred men, was sent from Boston up the Kennebec, and down the Chaudiere river to that place. He expected to be there early this month. Montreal acceded to us on the 13th, and Carleton set out, with the shattered remains of his little army, for Quebec, where we hope he will be taken up by Arnold. In a short time, we have reason to hope, the delegates of Canada will join us in Congress, and complete the American union as far as we wish to have it completed. We hear that one of the British transports has arrived at Boston; the rest are beating off the coast, in very bad weather. You will have heard, before this reaches you, that Lord Dunmore has commenced hostilities in Virginia. That people bore with every thing, till he attempted to burn the town of Hampton. They opposed and repelled him, with considerable loss on his side, and none on ours. It has raised our countrymen into a perfect phrenzy. It is an immense misfortune to the whole empire to have a King of such a disposition at such a time. We are told, and every thing proves it true, that he is the bitterest enemy we have. His Minister is able, and that satisfies me that ignorance, or wickedness, somewhere, controls him. In an earlier part of this contest, our petitions told him, that from our King there was but one appeal. The admonition was despised, and that appeal forced on us. To undo his empire, he has but one truth more to learn; that, after colonies have drawn the sword, there is but one step more they can take. That step is now pressed upon us by the measures adopted, as if they were afraid we would not take it. Believe me, dear Sir, there is not in the British empire a man who more cordially loves a union with Great Britain than I do. But, by the God that made me, I will cease to exist before I yield to a connection on such terms as the British Parliament propose; and in this, I think I speak the sentiments of America. We want neither inducement nor power to declare and assert a separation. It is will alone which is wanting, and that is growing apace under the fostering hand of our King. One bloody campaign will probably decide everlastingly our future course; I am sorry to find a bloody campaign is decided on. If our winds and waters should not combine to rescue their shores from slavery, and General Howe’s reinforcement should arrive in safety, we have hopes he will be inspirited to come out of Boston and take another drubbing: and we must drub him soundly before the sceptred tyrant will know we are not mere brutes, to crouch under his hand, and kiss the rod with which he deigns to scourge us.
Yours, &c.
Th: Jefferson.
LETTER IV.—TO BENJAMIN FRANKLIN, August 13, 1777
TO DR. BENJAMIN FRANKLIN, PARIS.
Virginia,
August 13, 1777.
Honorable Sir,
I forbear to write you news, as the time of Mr. Shore’s departure being uncertain, it might be old before you receive it, and he can, in person, possess you of all we have. With respect to the State of Virginia in particular, the people seem to have laid aside the monarchical, and taken up the republican government, with as much ease as would have attended their throwing off an old and putting on a new suit of clothes. Not a single throe has attended this important transformation. A half dozen aristocratical gentlemen, agonizing under the loss of pre-eminence, have sometimes ventured their sarcasms on our political metamorphosis. They have been thought fitter objects of pity than of punishment. We are at present in the complete and quiet exercise of well organized government, save only that our courts of justice do not open till the fall. I think nothing can bring the security of our continent and its cause into danger, if we can support the credit of our paper. To do that, I apprehend one of two steps must be taken. Either to procure free trade by alliance with some naval power able to protect it; or, if we find there is no prospect of that, to shut our ports totally to all the world, and turn our colonies into manufactories. The former would be most eligible, because most conformable to the habits and wishes of our people. Were the British Court to return to their senses in time to seize the little advantage which still remains within their reach from this quarter, I judge that, on acknowledging our absolute independence and sovereignty, a commercial treaty beneficial to them, and perhaps even a league of mutual offence and defence, might, not seeing the expense or consequences of such a measure, be approved by our people, if nothing in the mean time, done on your part, should prevent it. But they will continue to grasp at their desperate sovereignty, till every benefit short of that is for ever out of their reach. I wish my domestic situation had rendered it possible for me to join you in the very honorable charge confided to you. Residence in a polite Court, society of literati of the first order, a just cause and an approving God, will add length to a life for which all men pray, and none more than
Your most obedient
and humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
LETTER V.—TO PATRICK HENRY, March 27, 1779
TO HIS EXCELLENCY PATRICK HENRY.
Albemarle,
March 27, 1779.
Sir,
A report prevailing here, that in consequence of some powers from Congress, the Governor and Council have it in contemplation to remove the Convention troops, [The troops under Burgoyne, captured at Saratoga.] either wholly or in part, from their present situation, I take the liberty of troubling you with some observations on that subject. The reputation and interest of our country, in general, may be affected by such a measure; it would, therefore, hardly be deemed an indecent liberty, in the most private citizen, to offer his thoughts to the consideration of the Executive. The locality of my situation, particularly, in the neighborhood of the present barracks, and the public relation in which I stand to the people among whom they are situated, together with a confidence, which a personal knowledge of the members of the Executive gives me, that they Will be glad of information from any quarter, on a subject interesting to the public, induce me to hope that they will acquit me of impropriety in the present representation.
By an article in the Convention of Saratoga, it is stipulated, on the part of the United States, that the officers shall not be separated from their men. I suppose the term officers, includes general as well as regimental officers. As there are general officers who command all the troops, no part of them can be separated from these officers without a violation of the article: they cannot, of course, be separated from one another, unless the same general officer could be in different places at the same time. It is true, the article adds the words, ‘as far as circumstances will admit.’ This was a necessary qualification; because, in no place in America, I suppose, could there have been found quarters for both officers and men together; those for the officers to be according to their rank. So far, then, as the circumstances of the place where they should be quartered, should render a separation necessary, in order to procure quarters for the officers, according to their rank, the article admits that separation. And these are the circumstances which must have been under the contemplation of the parties; both of whom, and all the world beside (who are ultimate judges in the case), would still understand that they were to be as near in the environs of the camp, as convenient quarters could be procured; and not that the qualification of the article destroyed the article itself and laid it wholly at our discretion. Congress, indeed, have admitted of this separation; but are they so far lords of right and wrong as that our consciences may be quiet with their dispensation? Or is the case amended by saying they leave it optional in the Governor and Council to separate the troops or not? At the same time that it exculpates not them, it is drawing the Governor and Council into a participation in the breach of faith. If indeed it is only proposed, that a separation of the troops shall be referred to the consent of their officers; that is a very different matter. Having carefully avoided conversation with them on public subjects, I cannot say, of my own knowledge, how they would relish such a proposition. I have heard from others, that they will choose to undergo any thing together, rather than to be separated, and that they will remonstrate against it in the strongest terms. The Executive, therefore, if voluntary agents in this measure, must be drawn into a paper war with them, the more disagreeable, as it seems that faith and reason will be on the other side. As an American, I cannot help feeling a thorough mortification, that our Congress should have permitted an infraction of our public honor; as a citizen of Virginia, I cannot help hoping and confiding, that our supreme Executive, whose acts will be considered as the acts of the Commonwealth, estimate that honor too highly to make its infraction their own act. I may be permitted to hope, then, that if any removal takes place, it will be a general one: and, as it is said to be left to the Governor and Council to determine on this, I am satisfied, that, suppressing every other consideration, and weighing the matter dispassionately, they will determine upon this sole question, Is it for the benefit of those for whom they act, that, the Convention troops should be removed from among them? Under the head of interest, these circumstances, viz. the expense of building barracks, said to have been £25,000, and of removing the troops backwards and forwards, amounting to I know not how much, are not to be pre-termitted, merely because they are Continental expenses; for we are a part of the Continent; we must pay a shilling of every dollar wasted. But the sums of money, which, by these troops, or on their account, are brought into, and expended in this State, are a great and local advantage. This can require no proof. If, at the conclusion of the war, for instance, our share of the Continental debt should be twenty millions of dollars, or say that we are called on to furnish an annual quota of two millions four hundred thousand dollars, to Congress, to be raised by tax, it is obvious that we should raise these given sums with greater or less ease, in proportion to the greater or less quantity of money found in circulation among us. I expect that our circulating money is, by the presence of these troops, at the rate of $30,000 a week, at the least. I have heard, indeed, that an objection arises to their being kept within this state, from the information of the commissary that they cannot be subsisted here. In attending to the information of that officer, it should be borne in mind that the county of King William and its vicinities are one thing, the territory of Virginia another. If the troops could be fed upon long letters, I believe the gentleman at the head of that department in this country would be the best commissary upon earth. But till I see him determined to act, not to write; to sacrifice his domestic ease to the duties of his appointment, and apply to the resources of this country, wheresoever they are to be had, I must entertain a different opinion of him. I am mistaken, if, for the animal sub-sistence of the troops hitherto, we are not principally indebted to the genius and exertions of Hawkins, during the very short time he lived after his appointment to that department, by your board. His eye immediately pervaded the whole state; it was reduced at once to a regular machine, to a system, and the whole put into movement and animation by the fiat of a comprehensive mind. If the Commonwealth of Virginia cannot furnish these troops with bread, I would ask of the commissariat, which of the thirteen is now become the grain colony? If we are in danger of famine from the addition of four thousand mouths, what is become of that surplus of bread, the exportation of which used to feed the West Indies and Eastern States, and fill the colony with hard money? When I urge the sufficiency of this State, however, to subsist these troops, I beg to be understood, as having in contemplation the quantity of provisions necessary for their real use, and not as calculating what is to be lost by the wanton waste, mismanagement, and carelessness of those employed about it. If magazines of beef and pork are suffered to rot by slovenly butchering, or for want of timely provision and sale; if quantities of flour are exposed by the commissaries entrusted with the keeping it, to pillage and destruction; and if, when laid up in the Continental stores, it is still to be embezzled and sold, the land of Egypt itself would be insufficient for their supply, and their removal would be necessary, not to a more plentiful country, but to more able and honest commissaries. Perhaps, the magnitude of this question, and its relation to the whole state, may render it worth while to await, the opinion of the National Council, which is now to meet within a few weeks. There is no danger of distress in the mean time, as the commissaries affirm they have a great sufficiency of provisions for some time to come. Should the measure of removing them into another State be adopted, and carried into execution, before the meeting of Assembly, no disapprobation of theirs will bring them back, because they will then be in the power of others, who will hardly give them up.
Want of information as to what may be the precise measure proposed by the Governor and Council, obliges me to shift my ground, and take up the subject in every possible form. Perhaps they have not thought to remove the troops out of this State altogether, but to some other part of it. Here, the objections arising from the expenses of removal, and of building new barracks, recur. As to animal food, it may be driven to one part of the country as easily as to another: that circumstance, therefore, may be thrown out of the question. As to bread, I suppose they will require about forty or forty-five thousand bushels of grain a year. The place to which it is to be brought to them, is about the centre of the State. Besides that the country round about is fertile, all the grain made in the counties adjacent to any kind of navigation, may be brought by water to within twelve miles of the spot. For these twelve miles, wagons must be employed; I suppose half a dozen will be a plenty. Perhaps this part of the expense might have been saved, had the barracks been built on the water; but it is not sufficient to justify their being abandoned now they are built. Wagonage, indeed, seems to the commissariat, an article not worth economizing. The most wanton and studied circuity of transportation has been practised: to mention only one act, they have bought quantities of flour for these troops in Cumberland, have ordered it to be wagoned down to Manchester, and wagoned thence up to the barracks. This fact happened to fall within my own knowledge. I doubt not there are many more such, in order either to produce their total removal, or to run up the expenses of the present situation, and satisfy Congress that the nearer they are brought to the commissary’s own bed, the cheaper they will be subsisted. The grain made in the Western counties may be brought partly in wagons, as conveniently to this as to any other place; perhaps more so, on account of its vicinity to one of the best passes through the Blue Ridge; and partly by water, as it is near to James river, to the navigation of which, ten counties are adjacent above the falls. When I said that the grain might be brought hither from all the counties of the State, adjacent to navigation, I did not mean to say it would be proper to bring it from all. On the contrary, I think the commissary should be instructed, after the next harvest, not to send one bushel of grain to the barracks from below the falls of the rivers, or from the northern counties. The counties on tide water are accessible to the calls for our own army. Their supplies ought, therefore, to be husbanded for them. The counties in the northwestern parts of the State are not only within reach for our own grand army, but peculiarly necessary for the support of Macintosh’s army; or for the support of any other northwestern expedition, which the uncertain conduct of the Indians should render necessary; insomuch that if the supplies of that quarter should be misapplied to any other purpose, it would destroy in embryo every exertion, either for particular or general safety there. The counties above tide water, in the middle and southern and western parts of the country, are not accessible to calls for either of those purposes, but at such an expense of transportation as the article would not bear. Here, then, is a great field, whose supplies of bread cannot be carried to our army, or, rather, which will raise no supplies of bread, because there is no body to eat them. Was it not, then, wise in Congress to remove to that field four thousand idle mouths, who must otherwise have interfered with the pasture of our own troops? And, if they are removed to any other part of the country, will it not defeat this wise purpose? The mills on the waters of James river, above the falls, open to canoe navigation, are very many. Some of them are of great note, as manufacturers. The barracks are surrounded by mills. There are five or six round about Charlottesville. Any two or three of the whole might, in the course of the winter, manufacture flour sufficient for the year. To say the worst, then, of this situation, it is but twelve miles wrong. The safe custody of these troops is another circumstance worthy consideration. Equally removed from the access of an eastern or western enemy; central to the whole State, so that, should they attempt an irruption in any direction, they must pass through a great extent of hostile country; in a neighborhood thickly inhabited by a robust and hardy people, zealous in the American cause, acquainted with the use of arms, and the defiles and passes by which they must issue: it would seem, that in this point of view, no place could have been better chosen.
Their health is also of importance. I would not endeavor to show that their lives are valuable to us, because it would suppose a possibility, that humanity was kicked out of doors in America, and interest only attended to. The barracks occupy the top and brow of a very high hill, (you have been untruly told they were in a bottom.) They are free from fog, have four springs which seem to be plentiful, one within twenty yards of the piquet, two within fifty yards, and another within two hundred and fifty, and they propose to sink wells within the piquet. Of four thousand people, it should be expected, according to the ordinary calculations, that one should die every day. Yet, in the space of near three months, there have been but four deaths among them; two infants under three weeks old, and two others by apoplexy. The officers tell me, the troops were never before so healthy since they were embodied.
But is an enemy so execrable, that, though in captivity, his wishes and comforts are to be disregarded and even crossed? I think not. It is for the benefit of mankind to mitigate the horrors of war as much as possible. The practice, therefore, of modern nations, of treating captive enemies with politeness and generosity, is not only delightful in contemplation, but really interesting to all the world, friends, foes, and neutrals. Let us apply this: the officers, after considerable hardships, have all procured quarters comfortable and satisfactory to them. In order to do this, they were obliged, in many instances, to hire houses for a year certain, and at such exorbitant rents, as were sufficient to tempt independent owners to go out of them, and shift as they could. These houses, in most cases, were much out of repair. They have repaired them at a considerable expense. One of the general officers has taken a place for two years, advanced the rent for the whole time, and been obliged, moreover, to erect additional buildings for the accommodation of part of his family, for which there was not room in the house rented. Independent of the brick work, for the carpentry of these additional buildings, I know he is to pay fifteen hundred dollars. The same gentleman, to my knowledge, has-paid to one person, three thousand six hundred, and seventy dollars, for different articles to fix himself commodiously. They have generally laid in their stocks of grain and other provisions, for it is well known that officers do not live on their rations. They have purchased cows, sheep, &c, set in to farming, prepared their gardens, and have a prospect of comfort and quiet before them. To turn to the soldiers: the environs of the barracks are delightful, the ground cleared, laid off in hundreds of gardens, each enclosed in its separate paling; these well prepared, and exhibiting, a fine appearance. General Riedesel, alone, laid out upwards of two hundred pounds in garden seeds, for the German troops only. Judge what an extent of ground these seeds would cover. There is little doubt that their own gardens will furnish them a great abundance of vegetables through the year. Their poultry, pigeons, and other preparations of that kind, present to the mind the idea of a company of farmers, rather than a camp of soldiers. In addition to the barracks built for them by the public, and now very comfortable, they have built great numbers for themselves, in such messes as fancied each other: and the whole corps, both officers and men, seem now, happy and satisfied with their situation. Having thus found the art of rendering captivity itself comfortable, and carried it into execution, at their own great expense and labor, their spirit sustained by the prospect of gratifications rising before their eyes, does not every sentiment of humanity revolt against the proposition of stripping them of all this, and removing them into new situations, where from the advanced season of the year, no preparations can be made for carrying themselves comfortably through the heats of summer; and when it is known that the necessary advances for the conveniences already provided, have exhausted their funds and left them unable to make the like exertions anew. Again; review this matter as it may regard appearances. A body of troops, after staying a twelvemonth at Boston, are ordered to take a march of seven hundred miles to Virginia, where, it is said, they may be plentifully subsisted. As soon as they are there, they are ordered on some other march, because, in Virginia, it is said, they cannot be subsisted. Indifferent nations will charge this either to ignorance, or to whim and caprice; the parties interested, to cruelty. They now view the proposition in that light, and it is said, there is a general and firm persuasion among them, that they were marched from Boston with no other purpose than to harass and destroy them with eternal marches. Perseverance in object, though not by the most direct way, is often more laudable than perpetual changes, as often as the object shifts light. A character of steadiness in our councils is worth more than the subsistence of four thousand people.
There could not have been a more unlucky concurrence of circumstances than when these troops first came. The barracks were unfinished for want of laborers, the spell of weather the worst ever known within the memory of man, no stores of bread laid in, the roads, by the weather and number of wagons, soon rendered impassable: not only the troops themselves were greatly disappointed, but the people in the neighborhood were alarmed at the consequences which a total failure of provisions might produce. In this worst state of things, their situation was seen by many and disseminated through the country, so as to occasion a general dissatisfaction, which even seized the minds of reasonable men, who, if not infected with the contagion, must have foreseen that the prospect must brighten, and that great advantages to the people must necessarily arise. It has, accordingly, so happened. The planters, being more generally sellers than buyers, have felt the benefit of their presence in the most vital part about them, their purses, and are now sensible of its source. I have too good an opinion of their love of order, to believe that a removal of these troops would produce any irregular proofs of their disapprobation, but I am well assured it would be extremely odious to them.
To conclude. The separation of these troops would be a breach of public faith; therefore suppose it impossible. If they are removed to another State, it is the fault of the commissaries; if they are removed to any other part of the State, it is the fault of the commissaries; and in both cases, the public interest and public security suffer, the comfortable and plentiful subsistence of our own army is lessened, the health of the troops neglected, their wishes crossed, and their comforts torn from them, the character of whim and caprice, or, what is worse, of cruelty, fixed on us as a nation, and, to crown the whole, our own people disgusted with such a proceeding.
I have thus taken the liberty of representing to you the facts and the reasons, which seem to militate against the separation or removal of these troops. I am sensible, however, that the same subject may appear to different persons in very different lights. What I have urged as reasons, may, to sounder minds, be apparent fallacies. I hope they will appear, at least, so plausible, as to excuse the interposition of
your Excellency’s
most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
LETTER VI.—TO JOHN PAGE, January 22, 1779
TO JOHN PAGE.
Williamsburg,
January 22, 1779.
Dear Page,
I received your letter by Mr. Jamieson. It had given me much pain, that the zeal of our respective friends should ever have placed you and me in the situation of competitors. I was comforted, however, with the reflection, that it was their competition, not ours, and that the difference of the numbers which decided between us, was too insignificant to give you a pain, or me a pleasure, had our dispositions towards each other been such as to admit those sensations. I know you too well to need an apology for any thing you do, and hope you will for ever be assured of this; and as to the constructions of the world, they would only have added one to the many sins for which they are to go to the devil. As this is the first, I hope it will be the last, instance of ceremony between us. A desire to see my family, which is in Charles City, carries me thither to-morrow, and I shall not return till Monday. Be pleased to present my compliments to Mrs. Page, and add this to the assurances I have ever given you, that I am, dear Page,
your affectionate friend,
Th: Jefferson.
LETTER VII.—TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, June 23, 1779
TO HIS EXCELLENCY GENERAL WASHINGTON.
Williamsburg,
June 23, 1779.
Sir,
I have the pleasure to enclose you the particulars of Colonel Clarke’s success against St. Vincennes, as stated in his letter but lately received; the messenger, with his first letter, having been killed. I fear it will be impossible for Colonel Clarke to be so strengthened, as to enable him to do what he desires. Indeed, the express who brought this letter, gives us reason to fear, St. Vincennes is in danger from a large body of Indians, collected to attack it, and said, when he came from Kaskaskias, to be within thirty leagues of the place. I also enclose you a letter from Colonel Shelby, stating the effect of his success against the seceding Cherokees and Chuccamogga. The damage done them, was killing half a dozen, burning eleven towns, twenty thousand bushels of corn, collected probably to forward the expeditions which were to have been planned at the council which was to meet Governor Hamilton at the mouth of Tennessee, and taking as many goods as sold for twenty-five thousand pounds. I hope these two blows coming together, and the depriving them of their head, will, in some measure, effect the quiet of our frontiers this summer. We have intelligence, also, that Colonel Bowman, from Kentucky, is in the midst of the Shawnee country, with three hundred men, and hope to hear a good account of him. The enclosed order being in its nature important, and generally interesting, I think it proper to transmit it to you, with the reasons supporting it.* It will add much to our satisfaction, to know it meets your approbation.
I have the honor to be, with every sentiment of private respect and public gratitude,
Sir, your most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
P. S. The distance of our northern and western counties from the scene of southern service, and the necessity of strengthening our western quarter, have induced the Council to direct the new levies from the counties of Yohogania, Ohio, Monongalia, Frederick, Hampshire, Berkeley, Rockingham, and Greenbrier, amounting to somewhat less than three hundred men, to enter into the ninth regiment at Pittsburg. The aid they may give there, will be so immediate and important, and what they could do to the southward, would be so late, as, I hope, will apologize for their interference. T. J.
* For the letter of Colonel Clarke, and the order referred
to, see Appendix A.
LETTER VIII.—TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, July 17, 1779
TO HIS EXCELLENCY GENERAL WASHINGTON
Williamsburg,
July 17, 1779.
Sir,
I some time ago enclosed to you a printed copy of an order of Council, by which Governor Hamilton was to be confined in irons, in close jail, which has occasioned a letter from General Phillips, of which the enclosed is a copy. The General seems to think that a prisoner on capitulation cannot be put in close confinement, though his capitulation should not have provided against it. My idea was, that all persons taken in war, were to be deemed prisoners of war. That those who surrender on capitulation (or convention) are prisoners of war also, subject to the same treatment with those who surrender at discretion, except only so far as the terms of their capitulation or convention shall have guarded them. In the capitulation of Governor Hamilton (a copy of which I enclose), no stipulation is made as to the treatment of himself, or those taken with him. The Governor, indeed, when he signs, adds a flourish of reasons inducing him to capitulate, one of which is the generosity of his enemy. Generosity, on a large and comprehensive scale, seems to dictate the making a signal example of this gentleman; but waving that, these are only the private motives inducing him to surrender, and do not enter into the contract of Colonel Clarke. I have the highest idea of those contracts which take place between nation and nation, at war, and would be the last on earth to do any thing in violation of them. I can find nothing in those books usually recurred to as testimonials of the laws and usages of nature and nations, which convicts the opinions I have above expressed of error. Yet there may be such an usage as General Phillips seems to suppose, though not taken notice of by these writers. I am obliged to trouble your Excellency on this occasion, by asking of you information on this point. There is no other person, whose decision will so authoritatively decide this doubt in the public mind, and none with which I am disposed so implicitly to comply. If you shall be of opinion that the bare existence of a capitulation, in the case of Governor Hamilton, privileges him from confinement, though there be no article to that effect in the capitulation, justice shall most assuredly be done him. The importance of this point, in a public view, and my own anxiety under a charge of violation of national faith by the Executive of this Commonwealth, will, I hope, apologize for my adding this to the many troubles with which I know you to be burdened. I have the honor to be, with the most profound respect, your Excellency’s most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
P. S. I have just received a letter from Colonel Bland, containing information of numerous desertions from the Convention troops, not less than four hundred in the last fortnight. He thinks he has reason to believe it is with the connivance of some of their officers. Some of these have been retaken, all of them going northwardly. They had provided themselves with forged passports, and with certificates of having taken the oath of fidelity to the State; some of them forged, others really given by weak magistrates. I give this information to your Excellency, as perhaps it may be in your power to have such of them intercepted as shall be passing through Pennsylvania and Jersey.
Your letter enclosing the opinion of the board of war in the case of Allison and Lee, has come safe to hand, after a long passage. It shall be answered by next post. T. J.
LETTER IX.—TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, October 1, 1779
TO HIS EXCELLENCY GENERAL WASHINGTON.
Williamsburg,
October 1, 1779.
Sir,
On receipt of your letter of August 6th, during my absence, the Council had the irons taken off the prisoners of war. When your advice was asked, we meant it should decide with us; and upon my return to Williamsburg, the matter was taken up and the enclosed advice given. [See Appendix, note B.] A parole was formed, of which the enclosed is a copy, and tendered to the prisoners. They objected to that part of it which restrained them from saying any thing to the prejudice of the United States, and insisted on ‘freedom of speech.’ They were, in consequence, remanded to their confinement in the jail, which must be considered as a voluntary one, until they can determine with themselves to be inoffensive in word as well as deed. A flag sails hence to-morrow to New York, to negotiate the exchange of some prisoners. By her I have written to General Phillips on this subject, and enclosed to him copies of the within; intending it as an answer to a letter I received from him on the subject of Governor Hamilton.
I have the honor to be, Sir,
your most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
LETTER X.—TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, October 2, 1779
TO HIS EXCELLENCY GENERAL WASHINGTON.
Williamsburg,
October 2, 1779.
Sir,
Just as the letter accompanying this was going off, Colonel Mathews arrived on parole from New York, by the way of headquarters, bringing your Excellency’s letter on this subject, with that of the British commissary of prisoners. The subject is of great importance, and I must, therefore, reserve myself to answer after further consideration. Were I to speak from present impressions, I should say it was happy for Governor Hamilton that a final determination of his fate was formed before this new information. As the enemy have released Captain Willing from his irons, the Executive of this State will be induced perhaps not to alter their former opinion. But it is impossible they can be serious in attempting to bully us in this manner. We have too many of their subjects in our power, and too much iron to clothe them with, and, I will add, too much resolution to avail ourselves of both, to fear their pretended retaliation. However, I will do myself the honor of forwarding to your Excellency the ultimate result of Council on this subject.
In consequence of the information in the letter from the British commissary of prisoners, that no officers of the Virginia line should be exchanged till Governor Hamilton’s affair should be settled, we have stopped our flag, which was just hoisting anchor with a load of privates for New York. I must, therefore, ask the favor of your Excellency to forward the enclosed by flag, when an opportunity offers, as I suppose General Phillips will be in New York before it reaches you.
I have the honor to be, Sir, with the greatest esteem,
your most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
LETTER XI.—TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, Oct. 8, 1779
TO HIS EXCELLENCY GENERAL WASHINGTON.
In Council, Oct. 8, 1779.
Sir,
In mine of the second of the present month, written in the instant of Colonel Mathews’ delivery of your letter, I informed you what had been done on the subject of Governor Hamilton and his companions previous to that moment. I now enclose you an advice of Council, [See Appendix, note C.] in consequence of the letter you were pleased to enclose me, from the British commissary of prisoners, with one from Lord Rawdon; also a copy of my letter to Colonel Mathews, enclosing, also, the papers therein named. The advice of Council to allow the enlargement of prisoners, on their giving a proper parole, has not been recalled, nor will be, I suppose, unless something on the part of the enemy should render it necessary. I rather expect, however, that they will see it their interest to discontinue this kind of conduct. I am afraid I shall hereafter, perhaps be obliged to give your Excellency some trouble in aiding me to obtain information of the future usage of our prisoners. I shall give immediate orders for having in readiness every engine which the enemy have contrived for the destruction of our unhappy citizens, captivated by them. The presentiment of these operations is shocking beyond expression. I pray Heaven to avert them: but nothing in this world will do it, but a proper conduct in the enemy. In every event, I shall resign myself to the hard necessity under which I shall act.
I have the honor to be, with great regard and esteem,
your Excellency’s
most obedient and
most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
LETTER XII.—TO COLONEL MATHEWS, October, 1779
TO COLONEL MATHEWS.
In Council, October, 1779.
Sir,
The proceedings respecting Governor Hamilton and his companions, previous to your arrival here, you are acquainted with. For your more precise information, I enclose you the advice of Council, of June the 16th, of that of August the 28th, another of September the 19th, on the parole tendered them the 1st instant, and Governor Hamilton’s letter of the same day, stating his objections, in which he persevered: from that time his confinement has become a voluntary one. You delivered us your letters the next day, when, the post being just setting out, much business prevented the Council from taking them into consideration. They have this day attended to them, and found their resolution expressed in the enclosed advice bearing date this day. It gives us great pain that any of our countrymen should be cut off from the society of their friends and tenderest connections, while it seems as if it was in our power, to administer relief. But we trust to their good sense for discerning, and their spirit for bearing up against the fallacy of this appearance. Governor Hamilton and his companions were imprisoned and ironed, 1st. In retaliation for cruel treatment of our captive citizens by the enemy in general. 2nd. For the barbarous species of warfare which himself and his savage allies carried on in our western frontier. 3d. For particular acts of barbarity, of which he himself was personally guilty, to some of our citizens in his power. Any one of these charges was sufficient to justify the measures we took. Of the truth of the first, yourselves are witnesses. Your situation, indeed, seems to have been better since you were sent to New York; but reflect on what you suffered before that, and knew others of our countrymen to suffer, and what you know is now suffered by that more unhappy part of them, who are still confined on board the prison-ships of the enemy. Proofs of the second charge, we have under Hamilton’s own hand: and of the third, as sacred assurances as human testimony is capable of giving. Humane conduct on our part, was found to produce no effect; the contrary, therefore, was to be tried. If it produces a proper lenity to our citizens in captivity, it will have the effect we meant; if it does not, we shall return a severity as terrible as universal. If the causes of our rigor against Hamilton were founded in truth, that rigor was just, and would not give right to the enemy to commence any new hostilities on their part: and all such new severities are to be considered, not as retaliation, but as original and unprovoked. If those causes were, not founded in truth, they should have denied them. If, declining the tribunal of truth and reason, they choose to pervert this into a contest of cruelty and destruction, we will contend with them in that line, and measure out misery to those in our power, in that multiplied proportion which the advantage of superior numbers enables us to do. We shall think it our particular duty, after the information we gather from the papers which have been laid before us, to pay very constant attention to your situation, and that of your fellow prisoners. We hope that the prudence of the enemy will be your protection from injury; and we are assured that your regard for the honor of your country would not permit you to wish we should suffer ourselves to be bullied into an acquiescence, under every insult and cruelty they may choose to practise, and a fear to retaliate, lest you should be made to experience additional sufferings. Their officers and soldiers in our hands are pledges for your safety: we are determined to use them as such. Iron will be retaliated by iron, but a great multiplication on distinguished objects; prison-ships by prison-ships, and like for like in general. I do not mean by this to cover any officer who has acted, or shall act, improperly. They say Captain Willing was guilty of great cruelties at the Natchez; if so, they do right in punishing him. I would use any powers I have, for the punishment of any officer of our own, who should be guilty of excesses unjustifiable under the usages of civilized nations. However, I do not find myself obliged to believe the charge against Captain Willing to be true, on the affirmation of the British commissary, because, in the next breath, he affirms no cruelties have as yet been inflicted on him. Captain Willing has been in irons.
I beg you to be assured, there is nothing consistent with the honor of your country, which we shall not, at all times, be ready to do for the relief of yourself and companions in captivity. We know, that ardent spirit and hatred for tyranny, which brought you into your present situation, will enable you to bear up against it with the firmness, which has distinguished you as a soldier, and to look forward with pleasure to the day, when events shall take place, against which the wounded spirits of your enemies will find no comfort, even from reflections on the most refined of the cruelties with which they have glutted themselves.
I am, with great respect,
your most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
LETTER XIII.—TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, November 28, 1779
TO HIS EXCELLENCY GENERAL WASHINGTON.
Willlamsburg, November 28, 1779.
Sir,
Your Excellency’s letter on the discriminations which have been heretofore made, between the troops raised within this state, and considered as part of our quota, and those not so considered, was delivered me four days ago. I immediately laid it before the Assembly, who thereupon came to the resolution I now do myself the honor of enclosing you. The resolution of Congress, of March 15th, 1779, which you were so kind as to enclose, was never known in this state till a few weeks ago, when we received printed copies of the Journals of Congress. It would be a great satisfaction to us, to receive an exact return of all the men we have in Continental service, who come within the description of the resolution, together with our state troops in Continental service. Colonel Cabell was so kind as to send me a return of the Continental regiments, commanded by Lord Sterling, of the first and second Virginia State regiments, and of Colonel Gist’s regiment. Besides these are the following, viz. Colonel Harrison’s regiment of artillery, Colonel Bayler’s horse, Colonel Eland’s horse, General Scott’s new levies, part of which are gone to Carolina, and part are here, Colonel Gibson’s regiment stationed on the Ohio, Heath and Ohara’s independent companies at the same stations. Colonel Taylor’s regiment of guards to the Convention troops: of these, we have a return. There may, possibly, be others not occurring to me. A return of all these would enable us to see what proportion of the Continental army is contributed by us. We have, at present, very pressing calls to send additional numbers of men to the southward. No inclination is wanting in either the Legislature or Executive, to aid them or strengthen you: but we find it very difficult to procure men. I herewith transmit to your Excellency some recruiting commissions, to be put into such hands as you may think proper, for re-enlisting such of our soldiery as are not already engaged for the war. The Act of Assembly authorizing these instructions, requires that the men enlisted should be reviewed and received by an officer to be appointed for that purpose; a caution, less necessary in the case of men now actually in Service, therefore, doubtless able-bodied, than in the raising new recruits. The direction, however, goes to all cases, and, therefore, we must trouble your Excellency with the appointment of one or more officers of review. Mr. Moss, our agent, receives orders, which accompany this, to pay the bounty money and recruiting money, and to deliver the clothing. We have, however, certain reason to fear he has not any great sum of money on hand; and it is absolutely out of our power, at this time, to supply him, or to say, with certainty, when we shall be able to do it. He is instructed to note his acceptances under the draughts, and to assure payment as soon as we shall have it in our power to furnish him, as the only substitute for money. Your Excellency’s directions to the officer of review, will probably procure us the satisfaction of being informed, from time to time, how many men shall be re-enlisted.
By Colonel Mathews I informed your Excellency fully of the situation of Governor Hamilton and his companions. Lamothe and Dejean have given their paroles, and are at Hanover Court-House: Hamilton, Hay, and others, are still obstinate; therefore, still in close confinement, though their irons have never been on, since your second letter on the subject. I wrote full information of this matter to General Phillips also, from whom I had received letters on the subject. I cannot, in reason, believe that the enemy, on receiving this information either from yourself or General Phillips, will venture to impose any new cruelties on our officers in captivity with them. Yet their conduct, hitherto, has been most successfully prognosticated by reversing the conclusions of right reason. It is, therefore, my duty, as well as it was my promise to the Virginia captives, to take measures for discovering any change which may be made in their situation. For this purpose, I must apply for your Excellency’s interposition. I doubt not but you have an established mode of knowing, at all times, through your commissary of prisoners, the precise state of those in the power of the enemy. I must, therefore, pray you to put into motion any such means you have, for obtaining knowledge of the situation of Virginia officers in captivity. If you should think proper, as I could wish, to take upon yourself to retaliate any new sufferings which may be imposed on them, it will be more likely to have-due weight, and to restore the unhappy on both sides, to that benevolent treatment for which all should wish.
I have the honor to be, &c. &c.
Th: Jefferson.
LETTER XIV.—TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, December 10,1779
TO HIS EXCELLENCY GENERAL WASHINGTON.
Williamsburg, December 10,1779.
Sir,
I take the liberty of putting under cover to your Excellency some letters to Generals Phillips and Reidesel, uninformed whether they are gone into New York or not, and knowing that you can best forward them in either case.
I also trouble you with a letter from the master of the flag in this State, to the British commissary of prisoners in New York, trusting it will thus be more certainly conveyed than if sent to Mr. Adams. It is my wish the British commissary should return his answer through your Excellency, or your commissary of prisoners, and that they should not propose, under this pretext, to send another flag, as the mission of the present flag is not unattended with circumstances of suspicion; and a certain information of the situation of ourselves and our allies here, might influence the measures of the enemy.
Perhaps your commissary of prisoners can effect the former method of answer.
I enclose to you part of an Act of Assembly ascertaining the quantity of land, which shall be allowed to the officers and soldiers at the close of the war, and providing means of keeping that country vacant which has been allotted for them.
I am advised to ask your Excellency’s attention to the case of Colonel Bland, late commander of the barracks in Albemarle. When that gentleman was appointed to that command, he attended the Executive here and informed them he must either decline it, or be supported in such a way as would keep up that respect which was essential to his command; without, at the same time, ruining his private fortune.
The Executive were sensible he would be exposed to great and unavoidable expense: they observed, his command would be in a department separate from any other, and that he actually relieved a Major General from the same service. They did not think themselves authorized to say what should be done in this case, but undertook to represent the matter to Congress, and, in the mean time, gave it as their opinion that he ought to be allowed a decent table. On this, he undertook the office, and in the course of it incurred expenses which seemed to have been unavoidable, unless he would have lived in such a way as is hardly reconcileable to the spirit of an officer, or the reputation of those in whose service he is. Governor Henry wrote on the subject to Congress; Colonel Bland did the same; but we learn they have concluded the allowance to be unprecedented, and inadmissible in the case of an officer of his rank. The commissaries, on this, have called on Colonel Bland for reimbursement. A sale of his estate was about to take place, when we undertook to recommend to them to suspend their demand, till we could ask the favor of you to advocate this matter so far with Congress, as you may think it right; otherwise the ruin of a very worthy officer must inevitably follow. I have the honor to be, with the greatest respect and esteem,
your Excellency’s
most obedient servant,
Th: Jefferson.
LETTER XV.—TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, February 10, 1780
TO HIS EXCELLENCY GENERAL WASHINGTON.
Williamsburg, February 10, 1780.
Sir,
It is possible you may have heard, that in the course of last summer an expedition was meditated, by our Colonel Clarke, against Detroit: that he had proceeded so far as to rendezvous a considerable body of Indians, I believe four or five thousand, at St. Vincennes; but, being disappointed in the number of whites he expected, and not choosing to rely principally on the Indians, he was obliged to decline it. We have a tolerable prospect of reinforcing him this spring, to the number which he thinks sufficient for the enterprise. We have informed him of this, and left him to decide between this object, and that of giving vigorous chastisement to those tribes of Indians, whose eternal hostilities have proved them incapable of living on friendly terms with us. It is our opinion, his inclination will lead him to determine on the former. The reason of my laying before your Excellency this matter, is, that it has been intimated to me that Colonel Broadhead is meditating a similar expedition. I wished, therefore, to make you acquainted with what we had in contemplation. The enterprising and energetic genius of Clarke is not altogether unknown to you. You also know (what I am a stranger to) the abilities of Broadhead, and the particular force with which you will be able to arm him for such an expedition. We wish the most hopeful means should be used for removing so uneasy a thorn from our side. As yourself, alone, are acquainted with all the circumstances necessary for well informed decision, I am to ask the favor of your Excellency, if you should think Broadhead’s undertaking it most likely to produce success, that you will be so kind as to intimate to us to divert Clarke to the other object, which is also important to this State. It will, of course, have weight with you in forming your determination, that our prospect of strengthening Clarke’s hands, sufficiently, is not absolutely certain. It may be necessary, perhaps, to inform you, that these two officers cannot act together, which excludes the hopes of ensuring success by a joint expedition.
I have the honor to be, with the most sincere esteem,
your Excellency’s most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
LETTER XVI.—TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, June 11, 1780
TO HIS EXCELLENCY GENERAL WASHINGTON.
Richmond, June 11, 1780.
Sir,
Major Galvan, as recommended by your Excellency, was despatched to his station without delay, and has been furnished with every thing he desired, as far as we were able. The line of expresses formed between us is such, as will communicate intelligence from one to the other in twenty-three hours. I have forwarded to him information of our disasters in the South, as they have come to me.
Our intelligence from the southward is most lamentably defective. Though Charleston has been in the hands of the enemy a month, we hear nothing of their movements which can be relied on. Rumors are, that they are penetrating northward. To remedy this defect, I shall immediately establish a line of expresses from hence to the neighborhood of their army, and send thither a sensible, judicious person, to give us information of their movements. This intelligence will, I hope, be conveyed to us at the rate of one hundred and twenty miles in the twenty-four hours. They set out to their stations to-morrow. I wish it were possible, that a like speedy line of communication could be formed from hence to your Excellency’s head-quarters. Perfect and speedy information of what is passing in the South, might put it in your power, perhaps, to frame your measures by theirs. There is really nothing to oppose the progress of the enemy northward, but the cautious principles of the military art. North Carolina is without arms. We do not abound. Those we have, are freely imparted to them; but such is the state of their resources, that they have not been able to move a single musket from this State to theirs. All the wagons we can collect, have been furnished to the Marquis de Kalb, and are assembled for the march of twenty-five hundred men, under General Stevens, of Culpeper, who will move on the 19th instant. I have written to Congress to hasten supplies of arms and military stores for the southern states, and particularly to aid us with cartridge paper and boxes, the want of which articles, small as they are, renders our stores useless. The want of money cramps every effort. This will be supplied by the most unpalatable of all substitutes, force. Your Excellency will readily conceive, that after the loss of one arm, our eyes are turned towards the other, and that we comfort ourselves, if any aids can be furnished by you, without defeating the operations more beneficial to the general union, they will be furnished. At the same time, I am happy to find that the wishes of the people go no further, as far as I have an opportunity of learning their sentiments. Could arms be furnished, I think this State and North Carolina would embody from ten to fifteen thousand militia immediately, and more if necessary.
I hope, ere long, to be able to give you a more certain statement of the enemy’s as well as our situation, which I shall not fail to do. I enclose you a letter from Major Galvan, being the second I have forwarded to you.
With sentiments of the most perfect esteem and respect,
I have the honor to be
your Excellency’s
most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
LETTER XVII.—TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, July 2, 1780
TO HIS EXCELLENCY GENERAL WASHINGTON.
Richmond, July 2, 1780.
Sir,
I have received from the Committee of Congress, at headquarters, three letters calling for aids of men and provisions. I beg leave to refer you to my letter to them, of this date, on those subjects. I thought it necessary, however, to suggest to you the preparing an arrangement of officers for the men; for, though they are to supply our battalions, yet, as our whole line officers, almost, are in captivity, I suppose some temporary provision must be made. We cheerfully transfer to you every power which the Executive might exercise on this occasion. As it is possible you may cast your eye on the unemployed officers now within the State, I write to General Muhlenburg, to send you a return of them. I think the men will be rendezvoused within the present month. The bill, indeed, for raising them is not actually passed, but it is in its last stage, and no opposition to any essential parts of it. I will take care to notify you of its passage.
I have, with great pain, perceived your situation; and, the more so, as being situated between two fires, a division of sentiment has arisen, both in Congress and here, as to which the resources of this country should be sent. The removal of General Clinton to the northward, must, of course, have great influence on the determination of this question; and I have no doubt but considerable aids may be drawn hence for your army, unless a larger one should be embodied in the South, than the force of the enemy there seems to call for. I have the honor to be, with every sentiment of respect and esteem,
your Excellency’s
most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
[See Appendix, Note D.]
LETTER XVIII.—TO GENERAL EDWARD STEVENS, August 4, 1780
TO GENERAL EDWARD STEVENS.
Richmond, August 4, 1780.
Sir,
Your several favors of July the 16th, 21st, and 22nd, are now before me. Our smiths are engaged in making five hundred axes and some tomahawks for General Gates. About one hundred of these will go by the wagons now taking in their loads. As these are for the army in general, no doubt but you will participate of them. A chest of medicine was made up for you in Williamsburg, and by a strange kind of forgetfulness, the vessel ordered to bring that, left it and brought the rest of the shop. It is sent for again, and I am not without hopes will be here in time to go by the present wagons. They will carry some ammunition and the axes, and will make up their load with spirits. Tents, I fear, cannot be got in this country; we have, however, sent out powers to all the trading towns here, to take it wherever they can find it. I write to General Gates, to try whether the duck in North Carolina cannot be procured by the Executive of that State on Continental account; for, surely, the whole army, as well our militia as the rest, is Continental. The arms you have to spare may be delivered to General Gates’s order, taking and furnishing us with proper vouchers. We shall endeavor to send our drafts armed. I cannot conceive how the arms before sent could have got into so very bad order; they certainly went from hence in good condition. You wish to know how far the property of this State in your hands is meant to be subject to the orders of the commander in chief. Arms and military stores we mean to be perfectly subject to him. The provisions going from this country will be for the whole army. If we can get any tents, they must be appropriated to the use of our own troops. Medicine, sick stores, spirits, and such things, we expect shall be on the same footing as with the northern army. There, you know, each State furnishes its own troops with these articles, and, of course, has an exclusive right to what is furnished. The money put into your hands, was meant as a particular resource for any extra wants of our own troops, yet in case of great distress, you would probably not see the others suffer without communicating part of it for their use. We debit Congress with this whole sum. There can be nothing but what is right in your paying Major Mazaret’s troops out of it. I wish the plan you have adopted for securing a return of the arms from the militia, may answer. I apprehend any man, who has a good gun on his shoulder, would agree to keep it, and have the worth of it deducted out of his pay, more especially when the receipt of the pay is at some distance. What would you think of notifying to them, further, that a proper certificate that they are discharged, and have returned their arms, will be required before any pay is issued to them. A roll, kept and forwarded, of those so discharged, and who have delivered up their arms, would supply accidental losses of their certificates. We are endeavoring to get bayonet belts made. The State quarter-master affirms the cartouch boxes sent from this place, (nine hundred and fifty-nine in number,) were all in good condition. I therefore suppose the three hundred you received in such very bad order, must have gone from the continental quarter-master at Petersburg, or, perhaps, have been pillaged, on the road, of their flaps, to mend shoes, &c. I must still press the return of as many wagons as possible. All you will send, shall be loaded with spirits or something else for the army. By their next return, we shall have a good deal of bacon collected. The enclosed is a copy of what was reported to me, as heretofore sent by the wagons.
I am. Sir, with the greatest esteem,
your most obedient, humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
LETTER XIX.—TO MAJOR GENERAL GATES, August 15, 1780
TO MAJOR GENERAL GATES.
Richmond, August 15, 1780.
Sir,
Your favor of August 3rd is just now put into my hand. Those formerly received have been duly answered, and my replies will, no doubt, have reached you before this date. My last letter to you was by Colonel Drayton.
I spoke fully with you on the difficulty of procuring wagons here, when I had the pleasure of seeing you, and for that reason pressed the sending back as many as possible. One brigade of twelve has since returned, and is again on its way with medicine, military stores, and spirit. Any others which come, and as fast as they come, shall be returned to you with spirit and bacon. I have ever been informed, that the very plentiful harvests of North Carolina would render the transportation of flour from this State, as unnecessary as it would be tedious, and that, in this point of view, the wagons should carry hence only the articles before mentioned, which are equally wanting with you. Finding that no great number of wagons is likely to return to us, we will immediately order as many more to be bought and sent on, as we possibly can. But to prevent too great expectations, I must again repeat, that I fear no great number can be got. I do assure you, however, that neither attention nor expense shall be spared, to forward to you every support for which we can obtain means of transportation. You have, probably, received our order on Colonel Lewis to deliver you any of the beeves he may have purchased.
Tents, I fear, it is in vain to expect, because there is not in this country stuff to make them. We have agents and commissioners in constant pursuit of stuff, but hitherto researches have been fruitless. Your order to Colonel Carrington shall be immediately communicated. A hundred copies of the proclamation shall also be immediately printed and forwarded to you. General Muhlenburg is come to this place, which he will now make his headquarters. I think he will be able to set into motion, within a very few days, five hundred regulars, who are now equipped for their march, except some blankets still wanting, but I hope nearly procured and ready to be delivered.
I sincerely congratulate you on your successful advances on the enemy, and wish to do every thing to second your enterprises, which the situation of this country, and the means and powers put into my hands, enable me to do.
I am, Sir, with sincere respect and esteem,
your most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
LETTER XX.—TO GENERAL WASHINGTON, September 8, 1780
TO HIS EXCELLENCY GENERAL WASHINGTON.
Richmond, September 8, 1780.
Sir,
As I know the anxieties you must have felt, since the late misfortune to the South, and our latter accounts have not been quite so unfavorable as the first, I take the liberty of enclosing you a statement of this unlucky affair, taken from letters from General Gates, General Stevens, and Governor Nash, and, as to some circumstances, from an officer who was in the action.* Another army is collecting; this amounted, on the 23rd ultimo, to between four and five thousand men, consisting of about five hundred Maryland regulars, a few of Hamilton’s artillery, and Porterfield’s corps, Armand’s legion, such of the Virginia militia as had been reclaimed, and about three thousand North Carolina militia, newly embodied. We are told they will increase these to eight thousand. Our new recruits will rendezvous in this State between the 10th and 25th instant. We are calling out two thousand militia, who, I think, however, will not be got to Hillsborough till the 25th of October. About three hundred and fifty regulars marched from Chesterfield a week ago. Fifty march to-morrow, and there will be one hundred or one hundred and fifty more from that post, when they can be cleared of the hospital. This is as good a view as I can give you of the force we are endeavoring to collect; but they are unarmed. Almost the whole small arms seem to have been lost in the late rout. There are here, on their way southwardly, three thousand stand of arms, sent by Congress, and we have still a few in our magazine. I have written pressingly, as the subject well deserves, to Congress, to send immediate supplies, and to think of forming a magazine here, that in case of another disaster, we may not be left without all means of opposition.
[* The circumstances of the defeat of General Gates’s army,
near Camden in August, 1780, being of historical notoriety,
this statement is omitted.]
I enclosed to your Excellency, some time ago, a resolution of the Assembly, instructing us to send a quantity of tobacco to New York for the relief of our officers there, and asking the favor of you to obtain permission. Having received no answer, I fear my letter or your answer has miscarried. I therefore take the liberty of repeating my application to you.
I have the honor to be, with the most profound respect,
your Excellency’s most obedient
and most humble servant,
Th: Jefferson.
