автордың кітабын онлайн тегін оқу Seven Pillars of Wisdom. Illustrated
T.E. Lawrence
Seven Pillars of Wisdom
Illustrated
Seven Pillars of Wisdom is the autobiographical account of the experiences of British Army Colonel T. E. Lawrence ("Lawrence of Arabia"), of serving as a military advisor to Bedouin forces during the Arab Revolt against the Ottoman Turks of 1916 to 1918.
Winston Churchill quoted in an advertisement for the 1935 edition said "It ranks with the greatest books ever written in the English language. As a narrative of war and adventure it is unsurpassable."
The book was adapted into the film Lawrence of Arabia.
To S.A.
I loved you, so I drew these tides of men into my hands
and wrote my will across the sky in stars
To earn you Freedom, the seven-pillared worthy house,
that your eyes might be shining for me
When we came.
Death seemed my servant on the road, till we were near
and saw you waiting:
When you smiled, and in sorrowful envy he outran me
and took you apart:
Into his quietness.
Love, the way-weary, groped to your body, our brief wage
ours for the moment
Before earth's soft hand explored your shape, and the blind
worms grew fat upon
Your substance.
Men prayed me that I set our work, the inviolate house,
as a memory of you.
But for fit monument I shattered it, unfinished: and now
The little things creep out to patch themselves hovels
in the marred shadow
Of your gift.
AUTHOR'S PREFACE
Mr Geoffrey Dawson persuaded All Souls College to give me leisure, in 1919-20, to write about the Arab Revolt. Sir Herbert Baker let me live and work in his Westminster houses.
The book so written passed in 1921 into proof: where it was fortunate in the friends who criticized it. Particularly it owes its thanks to Mr and Mrs Bernard Shaw for countless suggestions of great value and diversity: and for all the present semi-colons.
It does not pretend to be impartial. I was fighting for my hand, upon my own midden. Please take it as a personal narrative pieced out of memory. I could not make proper notes: indeed it would have been a breach of my duty to the Arabs if I had picked such flowers while they fought. My superior officers, Wilson, Joyce, Dawnay, Newcombe, and Davenport, could each tell a like tale. The same is true of Stirling, Young, Lloyd, and Maynard: of Buxton and Winterton: of Ross, Stent, and Siddons: of Peake, Hornby, Scott-Higgins, and Garland: of Wordie, Bennett, and MacIndoe: of Bassett, Scott, Goslett, Wood, and Gray: of Hinde, Spence, and Bright: of Brodie and Pascoe, Gilman and Grisenthwaite, Greenhill, Dowsett, and Wade: of Henderson, Leeson, Makins, and Nunan.
And there were many other leaders or lonely fighters to whom this self-regardant picture is not fair. It is still less fair, of course, like all war-stories, to the unnamed rank and file, who miss their share of credit, as they must do, until they can write the despatches.
T. E. S.
PREFACE BY A. W. LAWRENCE
THE seven pillars of wisdom are first mentioned in the Bible, in the Book of Proverbs (ix. 1).
‘Wisdom hath builded a house: she hath hewn out her seven pillars’.
The title was originally applied by the author to a book of his about seven cities. He decided not to publish this early book because he considered it immature, but he transferred the title as a memento.
A four-page leaflet entitled SOME NOTES ON THE WRITING OF THE SEVEN PILLARS OF WISDOM BY T. E. SHAW was issued by my brother to those who bought or were presented with copies of the 1926 edition. It contains the following information:
MANUSCRIPTS
Text I
I WROTE Books 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 and 10 in Paris between February and June of 1919. The Introduction was written between Paris and Egypt on my way out to Cairo by Handley-Page in July and August 1919. Afterwards in England I wrote Book 1: and then lost all but the Introduction and drafts of Books 9 and 10 at Reading Station, while changing trains. This was about Christmas, 1919.
Text I, if completed, would have been about 250,000 words, a little less than the privately printed Seven Pillars as subscribers received it. My war-time notes, on which it was largely constructed, were destroyed as each section was finished. Only three people read much of it, before I lost it.
Text II
A month or so later I began, in London, to scribble out what I remembered of the first text. The original Introduction was of course still available. The other ten Books I completed in less than three months, by doing many thousand words at a time, in long sittings. Thus Book VI was written entire between sunrise and sunrise. Naturally the style was careless: and so Text II (though it introduced few new episodes) came to over 400,000 words. I corrected it at intervals throughout 1920, checking it with the files of the Arab Bulletin, and with two diaries and some of my surviving field-notes. Though hopelessly bad as a text, it became substantially complete and accurate. All but one page of this text was burned by me in 1922.
Text III
With Text II available on the table, Text III was begun in London, and worked on there, in Jeddah, and in Amman during 1921, and again in London till February 1922. It was composed with great care. This manuscript still exists. It is nearly 330,000 words long.
PRIVATELY PRINTED TEXTS
Oxford 1922
THOUGH the story, as completed in Text III, appeared to me still diffuse and unsatisfactory, yet for security's sake it was set up and printed textually, in sheets, at Oxford in the first quarter of 1922, by care of the Oxford Times staff. Since eight copies were required, and the book was very large, printing was preferred to typewriting. Five copies (bound in book form, for the convenience of those former members of the Hejaz Expeditionary Force who undertook to read it critically for me) have not yet (April 1927) been destroyed.
Subscribers' Text 1. xii. 26
This text, as issued to subscribers in December 1926 and January 1927, was a recension of the Oxford sheets of 1922. They were condensed (the single canon of change being literary) during 1923 and 1924 (Royal Tank Corps) and 1925 and 1926 (Royal Air Force) in my spare evenings. Beginners in literature are inclined to fumble with a handful of adjectives round the outline of what they want to describe: but by 1924 I had learnt my first lessons in writing, and was often able to combine two or three of my 1921 phrases into one.
There were four exceptions to the rule of condensation:
i) An incident, of less than a page, was cut out because two seniors of our party thought it unpleasantly unnecessary.
ii) Two characters of Englishmen were modified: one into nothing, because the worm no longer seemed worth treading on: the other into plain praise, because what I had innocently written as complaint was read ambiguously by an authority well able to judge.
iii) One chapter of the Introduction was omitted. My best critic told me it was much inferior to the rest.
iv) Book VIII, intended as a ‘flat’, to interpose between the comparative excitements of Book VII and the final advance on Damascus, was shortened of an abortive reconnaissance, some 10,000 words long. Several of those who read the Oxford text complained of the inordinate boredom of the ‘flat’, and upon reflection I agreed with them that it was perhaps too successful.
By thus excising 3 per cent and condensing the rest of the Oxford text a total reduction of 15 per cent was achieved, and the length of the subscribers' text brought down to some 280,000 words. It is swifter and more pungent than the Oxford text; and it would have been improved yet more if, I had had leisure to carry the process of revision further.
The Seven Pillars was so printed and assembled that nobody but myself knew how many copies were produced. I propose to keep this knowledge to myself. Newspaper statements of 107 copies can be easily disproved, for there were more than 107 subscribers: and in addition I gave away, not perhaps as many copies as I owed, but as many as my bankers could afford, to those who had shared with me in the Arab effort, or in the actual production of the volume.
POSTSCRIPT
THE subscribers' edition of Seven Pillars of Wisdom contained no chapter eleven, for the original first chapter had been omitted in the course of proof-correction, and renumbering proceeded only as far as the next ten. For the first published edition (1935) the chapters were renumbered throughout, so as to remove this anomaly. In this edition the suppressed chapter again appears in its rightful place, but, in order to avoid further renumbering, it has been entitled Introductory Chapter. In 1939, it was included in Oriental Assembly among other uncollected writings of T. E. Lawrence, together with a short explanatory note of my own.
INTRODUCTORY CHAPTER
THE story which follows was first written out in Paris during the Peace Conference, from notes jotted daily on the march, strengthened by some reports sent to my chiefs in Cairo. Afterwards, in the autumn of 1919, this first draft and some of the notes were lost. It seemed to me historically needful to reproduce the tale, as perhaps no one but myself in Feisal's army had thought of writing down at the time what we felt, what we hoped, what we tried. So it was built again with heavy repugnance in London in the winter of 1919-20 from memory and my surviving notes. The record of events was not dulled in me and perhaps few actual mistakes crept in – except in details of dates or numbers – but the outlines and significance of things had lost edge in the haze of new interests.
Dates and places are correct, so far as my notes preserved them: but the personal names are not. Since the adventure some of those who worked with me have buried themselves in the shallow grave of public duty. Free use has been made of their names. Others still possess themselves, and here keep their secrecy. Sometimes one man carried various names. This may hide individuality and make the book a scatter of featureless puppets, rather than a group of living people: but once good is told of a man, and again evil, and some would not thank me for either blame or praise.
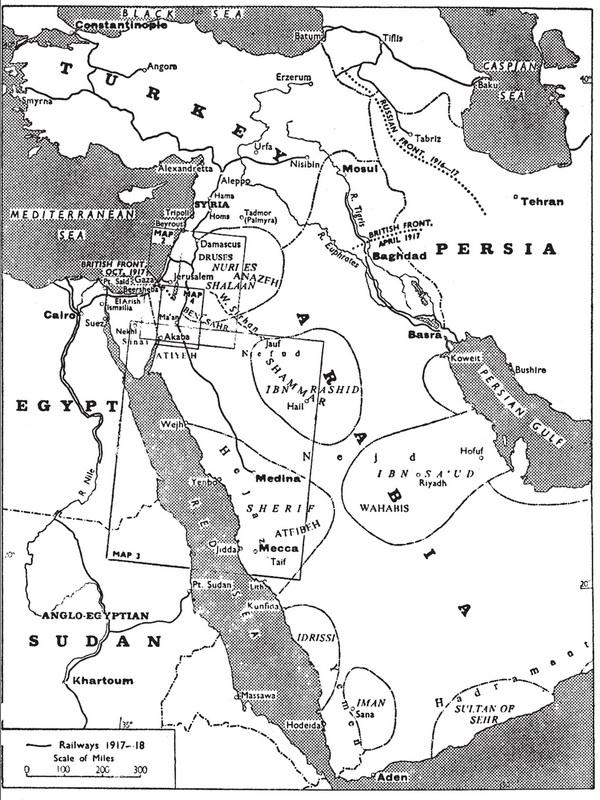
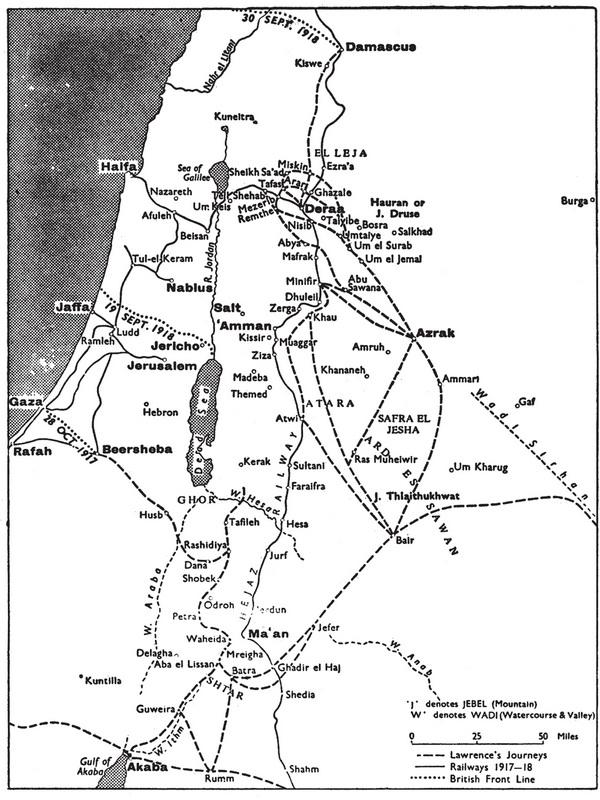
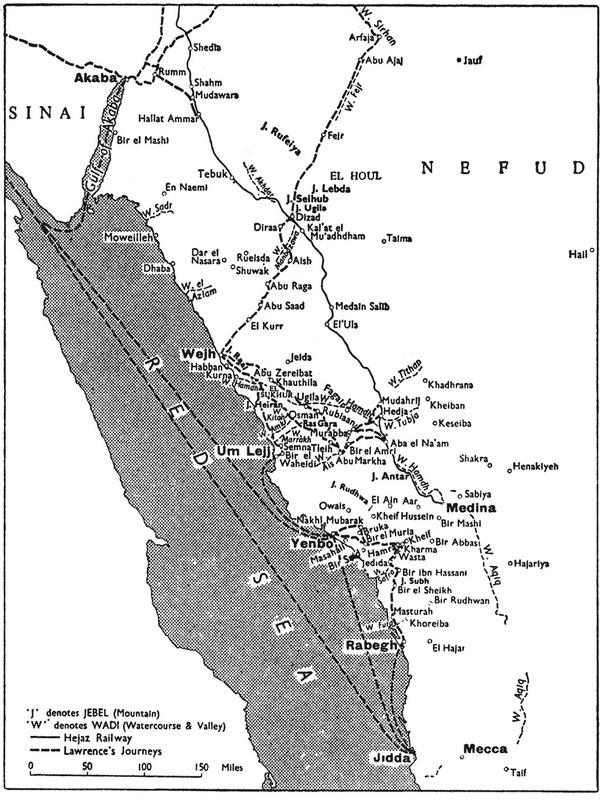
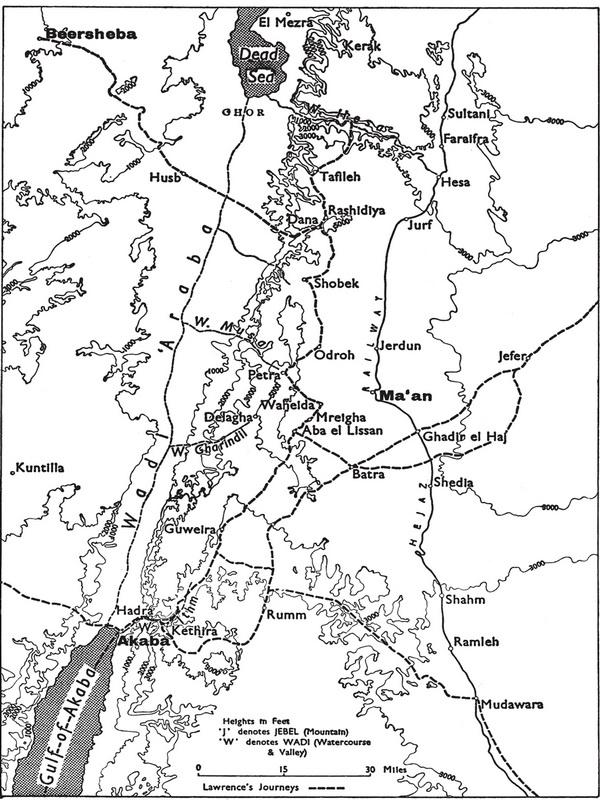
This isolated picture throwing the main light upon myself is unfair to my British colleagues. Especially I am most sorry that I have not told what the non-commissioned of us did. They were inarticulate, but wonderful, especially when it is taken into account that they had not the motive, the imaginative vision of the end, which sustained the officers. Unfortunately my concern was limited to this end, and the book is just a designed procession of Arab freedom from Mecca to Damascus. It is intended to rationalize the campaign, that everyone may see how natural the success was and how inevitable, how little dependent on direction or brain, how much less on the outside assistance of the few British. It was an Arab war waged and led by Arabs for an Arab aim in Arabia.
My proper share was a minor one, but because of a fluent pen, a free speech, and a certain adroitness of brain, I took upon myself, as I describe it, a mock primacy. In reality I never had any office among the Arabs: was never in charge of the British mission with them. Wilson, Joyce, Newcombe, Dawnay and Davenport were all over my head. I flattered myself that I was too young, not that they had more heart or mind in the work. I did my best. Wilson, Newcombe, Joyce, Dawnay, Davenport, Buxton, Marshall, Stirling, Young, Maynard, Ross, Scott, Winterton, Lloyd, Wordie, Siddons, Goslett, Stent, Henderson, Spence, Gilman, Garland, Brodie, Makins, Nunan, Leeson, Hornby, Peake, Scott-Higgins, Ramsay, Wood, Hinde, Bright, MacIndoe, Greenhill, Grisenthwaite, Dowsett, Bennett, Wade, Gray, Pascoe and the others also did their best.
It would be impertinent in me to praise them. When I wish to say ill of one outside our number, I do it: though there is less of this than was in my diary, since the passage of time seems to have bleached out men's stains. When I wish to praise outsiders, I do it: but our family affairs are our own. We did what we set out to do, and have the satisfaction of that knowledge. The others have liberty some day to put on record their story, one parallel to mine but not mentioning more of me than I of them, for each of us did his job by himself and as he pleased, hardly seeing his friends.
In these pages the history is not of the Arab movement, but of me in it. It is a narrative of daily life, mean happenings, little people. Here are no lessons for the world, no disclosures to shock peoples. It is filled with trivial things, partly that no one mistake for history the bones from which some day a man may make history, and partly for the pleasure it gave me to recall the fellowship of the revolt. We were fond together, because of the sweep of the open places, the taste of wide winds, the sunlight, and the hopes in which we worked. The morning freshness of the world-to-be intoxicated us. We were wrought up with ideas inexpressible and vaporous, but to be fought for. We lived many lives in those whirling campaigns, never sparing ourselves: yet when we achieved and the new world dawned, the old men came out again and took our victory to re-make in the likeness of the former world they knew. Youth could win, but had not learned to keep: and was pitiably weak against age. We stammered that we had worked for a new heaven and a new earth, and they thanked us kindly and made their peace.
All men dream: but not equally. Those who dream by night in the dusty recesses of their minds wake in the day to find that it was vanity: but the dreamers of the day are dangerous men, for they may act their dream with open eyes, to make it possible. This I did. I meant to make a new nation, to restore a lost influence, to give twenty millions of Semites the foundations on which to build an inspired dream-palace of their national thoughts. So high an aim called out the inherent nobility of their minds, and made them play a generous part in events: but when we won, it was charged against me that the British petrol royalties in Mesopotamia were become dubious, and French Colonial policy ruined in the Levant.
I am afraid that I hope so. We pay for these things too much in honour and in innocent lives. I went up the Tigris with one hundred Devon Territorials, young, clean, delightful fellows, full of the power of happiness and of making women and children glad. By them one saw vividly how great it was to be their kin, and English. And we were casting them by thousands into the fire to the worst of deaths, not to win the war but that the corn and rice and oil of Mesopotamia might be ours. The only need was to defeat our enemies (Turkey among them), and this was at last done in the wisdom of Allenby with less than four hundred killed, by turning to our uses the hands of the oppressed in Turkey. I am proudest of my thirty fights in that I did not have any of our own blood shed. All our subject provinces to me were not worth one dead Englishman.
We were three years over this effort and I have had to hold back many things which may not yet be said. Even so, parts of this book will be new to nearly all who see it, and many will look for familiar things and not find them. Once I reported fully to my chiefs, but learnt that they were rewarding me on my own evidence. This was not as it should be. Honours may be necessary in a professional army, as so many emphatic mentions in despatches, and by enlisting we had put ourselves, willingly or not, in the position of regular soldiers.
For my work on the Arab front I had determined to accept nothing. The Cabinet raised the Arabs to fight for us by definite promises of self-government afterwards. Arabs believe in persons, not in institutions. They saw in me a free agent of the British Government, and demanded from me an endorsement of its written promises. So I had to join the conspiracy, and, for what my word was worth, assured the men of their reward. In our two years’ partnership under fire they grew accustomed to believing me and to think my Government, like myself, sincere. In this hope they performed some fine things, but, of course, instead of being proud of what we did together, I was continually and bitterly ashamed.
It was evident from the beginning that if we won the war these promises would be dead paper, and had I been an honest adviser of the Arabs I would have advised them to go home and not risk their lives fighting for such stuff: but I salved myself with the hope that, by leading these Arabs madly in the final victory I would establish them, with arms in their hands, in a position so assured (if not dominant) that expediency would counsel to the Great Powers a fair settlement of their claims. In other words, I presumed (seeing no other leader with the will and power) that I would survive the campaigns, and be able to defeat not merely the Turks on the battlefield, but my own country and its allies in the council-chamber. It was an immodest presumption: it is not yet clear if I succeeded: but it is clear that I had no shadow of leave to engage the Arabs, unknowing, in such hazard. I risked the fraud, on my conviction that Arab help was necessary to our cheap and speedy victory in the East, and that better we win and break our word than lose.
The dismissal of Sir Henry McMahon confirmed my belief in our essential insincerity: but I could not so explain myself to General Wingate while the war lasted, since I was nominally under his orders, and he did not seem sensible of how false his own standing was. The only thing remaining was to refuse rewards for being a successful trickster and, to prevent this unpleasantness arising, I began in my reports to conceal the true stories of things, and to persuade the few Arabs who knew to an equal reticence. In this book also, for the last time, I mean to be my own judge of what to say.
INTRODUCTION
FOUNDATIONS OF REVOLT
Chapters I to VII
SOME Englishmen, of whom Kitchener was chief, believed that a rebellion of Arabs against Turks would enable England, while fighting Germany, simultaneously to defeat her ally Turkey.
Their knowledge of the nature and power and country of the Arabic-speaking peoples made them think that the issue of such a rebellion would be happy: and indicated its character and method.
So they allowed it to begin, having obtained for it formal assurances of help from the British Government. Yet none the less the rebellion of the Sherif of Mecca came to most as a surprise, and found the Allies unready. It aroused mixed feelings and made strong friends and strong enemies, amid whose clashing jealousies its affairs began to miscarry.
CHAPTER I
SOME of the evil of my tale may have been inherent in our circumstances. For years we lived anyhow with one another in the naked desert, under the indifferent heaven. By day the hot sun fermented us; and we were dizzied by the beating wind. At night we were stained by dew, and shamed into pettiness by the innumerable silences of stars. We were a self-centred army without parade or gesture, devoted to freedom, the second of man's creeds, a purpose so ravenous that it devoured all our strength, a hope so transcendent that our earlier ambitions faded in its glare.
As time went by our need to fight for the ideal increased to an unquestioning possession, riding with spur and rein over our doubts. Willy-nilly it became a faith. We had sold ourselves into its slavery, manacled ourselves together in its chain-gang, bowed ourselves to serve its holiness with all our good and ill content. The mentality of ordinary human slaves is terrible have lost the world – and we had surrendered, not body alone, but soul to the overmastering greed of victory. By our own act we were drained of morality, of volition, of responsibility, like dead leaves in the wind.
The everlasting battle stripped from us care of our own lives or of others’. We had ropes about our necks, and on our heads prices which showed that the enemy intended hideous tortures for us if we were caught. Each day some of us passed; and the living knew themselves just sentient puppets on God's stage: indeed, our taskmaster was merciless, merciless, so long as our bruised feet could stagger forward on the road. The weak envied those tired enough to die; for success looked so remote, and failure a near and certain, if sharp, release from toil. We lived always in the stretch or sag of nerves, either on the crest or in the trough of waves of feeling. This impotency was bitter to us, and made us live only for the seen horizon, reckless what spite we inflicted or endured, since physical sensation showed itself meanly transient. Gusts of cruelty, perversions, lusts ran lightly over the surface without troubling us; for the moral laws which had seemed to hedge about these silly accidents must be yet fainter words. We had learned that there were pangs too sharp, griefs too deep, ecstasies too high for our finite selves to register. When emotion reached this pitch the mind choked; and memory went white till the circumstances were humdrum once more.
Such exaltation of thought, while it let adrift the spirit, and gave it licence in strange airs, lost it the old patient rule over the body. The body was too coarse to feel the utmost of our sorrows and of our joys. Therefore, we abandoned it as rubbish: we left it below us to march forward, a breathing simulacrum, on its own unaided level, subject to influences from which in normal times our instincts would have shrunk. The men were young and sturdy; and hot flesh and blood unconsciously claimed a right in them and tormented their bellies with strange longings. Our privations and dangers fanned this virile heat, in a climate as racking as can be conceived. We had no shut places to be alone in, no thick clothes to hide our nature. Man in all things lived candidly with man.
The Arab was by nature continent; and the use of universal marriage had nearly abolished irregular courses in his tribes. The public women of the rare settlements we encountered in our months of wandering would have been nothing to our numbers, even had their raddled meat been palatable to a man of healthy parts. In horror of such sordid commerce our youths began indifferently to slake one another's few needs in their own clean bodies – a cold convenience that, by comparison, seemed sexless and even pure. Later, some began to justify this sterile process, and swore that friends quivering together in the yielding sand with intimate hot limbs in supreme embrace, found there hidden in the darkness a sensual co-efficient of the mental passion which was welding our souls and spirits in one flaming effort. Several, thirsting to punish appetites they could not wholly prevent, took a savage pride in degrading the body, and offered themselves fiercely in any habit which promised physical pain or filth.
I was sent to these Arabs as a stranger, unable to think their thoughts or subscribe their beliefs, but charged by duty to lead them forward and to develop to the highest any movement of theirs profitable to England in her war. If I could not assume their character, I could at least conceal my own, and pass among them without evident friction, neither a discord nor a critic but an unnoticed influence. Since I was their fellow, I will not be their apologist or advocate. Today in my old garments, I could play the bystander, obedient to the sensibilities of our theatre… but it is more honest to record that these ideas and actions then passed naturally. What now looks wanton or sadic seemed in the field inevitable, or just unimportant routine.
Blood was always on our hands: we were licensed to it. Wounding and killing seemed ephemeral pains, so very brief and sore was life with us. With the sorrow of living so great, the sorrow of punishment had to be pitiless. We lived for the day and died for it. When there was reason and desire to punish we wrote our lesson with gun or whip immediately in the sullen flesh of the sufferer, and the case was beyond appeal. The desert did not afford the refined slow penalties of courts and gaols.
Of course our rewards and pleasures were as suddenly sweeping as our troubles; but, to me in particular, they bulked less large. Bedouin ways were hard even for those brought up to them, and for strangers terrible: a death in life. When the march or labour ended I had no energy to record sensation, nor while it lasted any leisure to see the spiritual loveliness which sometimes came upon us by the way. In my notes, the cruel rather than the beautiful found place. We no doubt enjoyed more the rare moments of peace and forgetfulness; but I remember more the agony, the terrors, and the mistakes. Our life is not summed up in what I have written (there are things not to be repeated in cold blood for very shame); but what I have written was in and of our life. Pray God that men reading the story will not, for love of the glamour of strangeness, go out to prostitute themselves and their talents in serving another race.
A man who gives himself to be a possession of aliens leads a Yahoo life, having bartered his soul to a brute-master. He is not of them. He may stand against them, persuade himself of a mission, batter and twist them into something which they, of their own accord, would not have been. Then he is exploiting his old environment to press them out of theirs. Or, after my model, he may imitate them so well that they spuriously imitate him back again. Then he is giving away his own environment: pretending to theirs; and pretences are hollow, worthless things. In neither case does he do a thing of himself, nor a thing so clean as to be his own (without thought of conversion), letting them take what action or reaction they please from the silent example.
In my case, the efforts for these years to live in the dress of Arabs, and to imitate their mental foundation, quitted me of my English self, and let me look at the West and its conventions with new eyes: they destroyed it all for me. At the same time I could not sincerely take on the Arab skin: it was an affectation only. Easily was a man made an infidel, but hardly might he be converted to another faith. I had dropped one form and not taken on the other, and was become like Mohammed's coffin in our legend, with a resultant feeling of intense loneliness in life, and a contempt, not for other men, but for all they do. Such detachment came at times to a man exhausted by prolonged physical effort and isolation. His body plodded on mechanically, while his reasonable mind left him, and from without looked down critically on him, wondering what that futile lumber did and why. Sometimes these selves would converse in the void; and then madness was very near, as I believe it would be near the man who could see things through the veils at once of two customs, two educations, two environments.
