автордың кітабын онлайн тегін оқу Глоссариум по искусственному интеллекту: 2500 терминов. Том 2
Александр Юрьевич Чесалов
Александр Николаевич Власкин
Матвей Олегович Баканач
Глоссариум по искусственному интеллекту: 2500 терминов
Том 2
Шрифты предоставлены компанией «ПараТайп»
Редактор Хаджимурад Ахмедович Магомедов
Корректор Александр Хафизович Юлдашев
Иллюстратор Александр Юрьевич Чесалов
Дизайнер обложки Александр Юрьевич Чесалов
© Александр Юрьевич Чесалов, 2024
© Александр Николаевич Власкин, 2024
© Матвей Олегович Баканач, 2024
© Александр Юрьевич Чесалов, иллюстрации, 2024
© Александр Юрьевич Чесалов, дизайн обложки, 2024
Дорогой читатель!
Вашему вниманию предлагается уникальная книга!
Современный глоссарий из более чем 2500 популярных терминов и определений по машинному обучению и искусственному интеллекту.
Эта книга написана экспертами-практиками, которые вместе работали над Программой Центра искусственного интеллекта, а также программами «Искусственный интеллект» и «Глубокая аналитика» проекта «Приоритет 2030» в МГТУ им. Н. Э. Баумана в 2021—2022 годах.
ISBN 978-5-0060-9410-9 (т. 2)
ISBN 978-5-0060-9411-6
Создано в интеллектуальной издательской системе Ridero
Оглавление
От авторов-составителей
Александр Юрьевич Чесалов,
Власкин Александр Николаевич,
Баканач Матвей Олегович
Эксперты по информационным технологиям и искусственному интеллекту, разработчики программы Центра искусственного интеллекта МГТУ им. Н. Э. Баумана, программы «Искусственный интеллект» и «Глубокая аналитика» проекта «Приоритет 2030» МГТУ им. Н. Э. Баумана в 2021—2022 годах.
Дорогие Друзья и Коллеги!
Авторы составители этой книги посвятили подготовке и созданию данного глоссария (краткого словаря специализированных терминов) два года.
«Пилотная» версия книги была подготовлена всего за восемь месяцев и представлена на на 35-ой Московской международной книжной ярмарке в 2022 году.
В какой-то момент времени книга выросла до восьми ста шестидесяти страниц и нам пришлось подготовить двухтомное издание.
Сейчас мы рады представить Вам второй том книги, который содержит более тысячи двух сот пятидесяти терминов и определений по искусственному интеллекту на английском языке.
Изображение обложки к книге нарисовано в системе генеративного искусственного интеллекта Easy Diffusion.

Почему книга называется «Глоссариум»?
«Glossarium» на латинском языке означает словарь узкоспециализированных терминов.
Идея составления «глоссариев» принадлежит одному из соавторов книги — Александру Чесалову. Первый его опыт в этой области был в составлении глоссария по искусственному интеллекту и информационным технологиям, который он опубликовал в декабре 2021 года.[1] В нем первоначально было всего 400 терминов. Затем, уже в 2022 году, Александр его существенно расширил до более чем 1000 актуальных терминов и определений. Впоследствии он опубликовал целую серию книг, раскрывающих темы четвертой промышленной революции, цифровой экономики, цифрового здравоохранения и многих других.
Идея создания большого глоссария по искусственному интеллекту родилась в начале 2022 года. Авторы пришли к единодушному решению объединить свои усилия и свой опыт последних лет в области искусственного интеллекта, который был подкреплен несколькими знаменательными и судьбоносными событиями.
Несомненно, самое существенное событие, которое произошло несколько ранее в 2021 году — это участие авторов (как экспертов) в Конкурсе, проводимом Аналитическим Центром при Правительстве России по отбору получателей поддержки исследовательских центров в сфере искусственного интеллекта, в том числе в области «сильного» искусственного интеллекта, систем доверенного искусственного интеллекта и этических аспектов применения искусственного интеллекта. Перед нами стояла неординарная и еще на тот момент времени никем не решенная задача создания Центра разработки и внедрения сильного и прикладного искусственного интеллекта МГТУ им. Н. Э. Баумана. Все авторы этой книги приняли самое непосредственное участие в разработке и написании программы и плана мероприятий нового Центра. Подробнее об этой истории можно узнать из книги Александра Чесалова «Как создать центр искусственного интеллекта за 100 дней».
Далее мы приняли участие в Первом международном форуме «Этика искусственного интеллекта: начало доверия», который состоялся 26 октября 2021 года и в рамках которого была организована церемония торжественного подписания Национального кодекса этики искусственного интеллекта, устанавливающего общие этические принципы и стандарты поведения, которыми следует руководствоваться участникам отношений в сфере искусственного интеллекта в своей деятельности. По сути, форум стал первой в России специализированной площадкой, где собралось около полутора тысяч разработчиков и пользователей технологий искусственного интеллекта.
В дополнение ко всему мы не прошли мимо и Международной конференции по искусственному интеллекту и анализу данных AI Journey, в рамках которой 10 ноября 2021 года к подписанию Национального Кодекса этики искусственного интеллекта присоединились лидеры ИТ-рынка. Число спикеров конференции поражало воображение — их было более двухсот, а число онлайн-посещений сайта более сорока миллионов.
Уже в 2022 году мы приняли самое активное участие в Международном военно-техническом форуме «Армия-2022» с докладом «Разработка программно-аппаратных комплексов для решения широкого круга прикладных задач с использованием технологий машинного обучения и доверенного искусственного интеллекта в Оборонно-промышленном комплексе РФ».
Резюмируя всю нашу активную работу за последние пару лет, мы пришли к необходимости систематизировать накопленные знания и изложить их в новой книге, которую вы держите в своих руках.
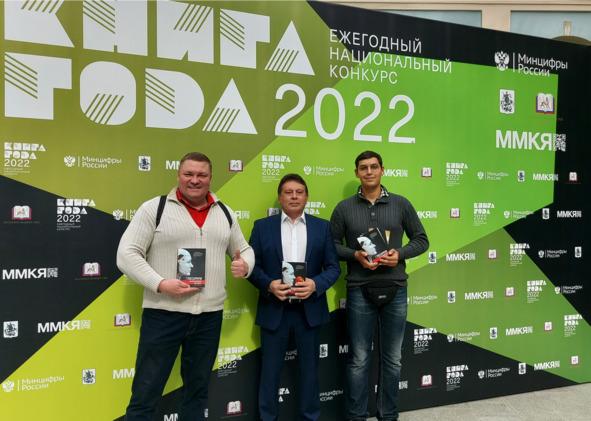
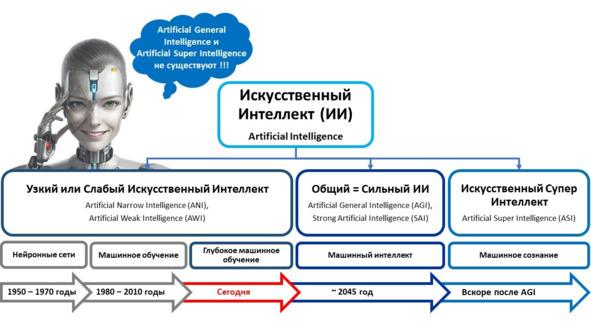
Мы часто с вами слышим «искусственный интеллект».
Но понимаем ли мы что это такое?
Например, в этой книге мы зафиксировали, что Искусственный интеллект — это компьютерная система, основанная на комплексе научных и инженерных знаний, а также технологий создания интеллектуальных машин, программ, сервисов и приложений, имитирующая мыслительные процессы человека или живых существ, способная с определенной степенью автономности воспринимать информацию, обучаться и принимать решения на основе анализа больших массивов данных, целью создания которой является помощь людям в решении их повседневных рутинных задач.
Или, еще один пример.
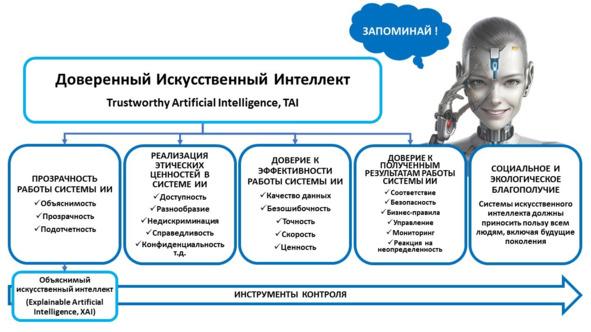
Что такое «доверенный искусственный интеллект»?
Системой доверенного искусственного интеллекта называют прикладную систему искусственного интеллекта, обеспечивающую выполнение возложенных на нее задач с учетом ряда дополнительных требований, учитывающих этические аспекты применения искусственного интеллекта, которая обеспечивает доверие к результатам ее работы, которые, в свою очередь, включают в себя: достоверность (надежность) и интерпретируемость выводов и предлагаемых решений, полученных с помощью системы и проверенных на верифицированных тестовых примерах; безопасность как с точки зрения невозможности причинения вреда пользователям системы на протяжении всего жизненного цикла системы, так и с точки зрения защиты от взлома, несанкционированного доступа и других негативных внешних воздействий, приватность и проверяемость данных, с которыми работают алгоритмы искусственного интеллекта, включая разграничение доступа и другие связанные с этим вопросы.
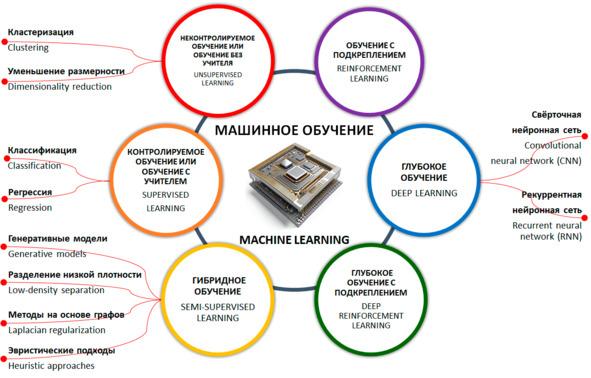
А что же тогда такое «машинное обучение»?
Машинное обучение — это одно из направлений (подмножеств) искусственного интеллекта, благодаря которому воплощается ключевое свойство интеллектуальных компьютерных систем — самообучение на основе анализа и обработки больших разнородных данных. Чем больше объем информации и ее разнообразие, тем проще искусственному интеллекту найти закономерности и тем точнее будет получаемый результат.
Чтобы заинтересовать уважаемого читателя, приведем еще несколько «забавных» примеров.
Слышали ли вы когда-нибудь о «Трансгуманистах»?
С одной стороны, как идея Трансгуманизм (Transhumanism) — это расширение возможностей человека с помощью науки. С другой стороны — это философская концепция и международное движение, приверженцы которого желают стать «постлюдьми» и преодолеть всевозможные физические ограничения, болезни, душевные страдания, старость и смерть благодаря использованию возможностей нано- и био- технологий, искусственного интеллекта и когнитивной науки.
На наш взгляд, идеи «трансгуманизма» очень тесно пересекаются с идеями и концепциями «цифрового человеческого бессмертия».

Несомненно, вы слышали и конечно знаете, кто такой «Data Scientist» — ученый и специалист по работе с данными.
А слышали ли вы когда-нибудь о «датасатанистах»? :-)
Датасатанисты — это определение, придуманное авторами, но отражающее современную действительность (наравне, например, с термином «инфоцыганщина»), которая сформировалась в период популяризации и повсеместной реализации идей искусственного интеллекта в современном информационном обществе. По своей сути датасатанисты — это мошенники и преступники, которые очень умело маскируются под ученых и специалистов в области ИИ и МО, но при этом пользуются чужими заслугами, знаниями и опытом, в своих корыстных целях и целях незаконного обогащения.
А, как вам такой термин — «библеоклазм»?
Библиоклазм — человек, в силу своего трансформированного мировоззрения и чрезмерно раздутого эго, из зависти или какой-либо другой корыстной цели, который стремится уничтожить книги других авторов. Вы не поверите, но таких людей, как «датасатанисты» или «библиоклазмы» сейчас достаточно.
А, как вам такие термины: «искусственная жизнь», «искусственный сверхинтеллект», «нейроморфный искусственный интеллект», «человеко-ориентированный искусственный интеллект», «синтетический интеллект», «распределенный искусственный интеллект», «дружественный искусственный интеллект», «дополненный искусственный интеллект», «композитный искусственный интеллект», «объяснимый искусственный интеллект», «причинно-следственный искусственный интеллект», «символический искусственный интеллект» и многие другие (все они есть в этой книге).
Таких примеров «удивительных» терминов мы можем привести еще не мало. Но в своей работе мы не стали тратить время на «суровую действительность» и сместили акцент на конструктивный и позитивный настрой. Одним словом, мы провели для Вас большую работу и собрали более 2500 терминов и определений по машинному обучению и искусственному интеллекту на основе своего опыта и данных из огромного числа различных источников.
2500 терминов и определений.
Много это или мало?
Наш опыт подсказывает, что для взаимопонимания двум собеседникам достаточно знать десяток или, максимум, два десятка определений. Но, когда дело касается профессиональной деятельности, то может получиться так, что мало знать, даже, несколько десятков терминов.
В этой книге приведены самые актуальные термины и определения, по-нашему мнению, наиболее часто употребляемые, как в повседневной работе, так и профессиональной деятельности специалистами самых разных профессий, интересующихся темой «искусственного интеллекта».
Мы очень старались сделать для вас нужный и полезный «инструмент» для вашей работы.
В заключение хочется добавить и проинформировать уважаемого читателя о том, что эта книга является абсолютно открытым и свободным к распространению документом. В случае, если Вы используете ее в своей практической работе, просим Вас делать ссылку на нее.
Многие из терминов и определений к ним, в этой книге, встречаются в сети Интернет. Они повторяются десятки или сотни раз на различных информационных ресурсах (в основном на зарубежных). Тем не менее, мы поставили перед собой цель — собрать и систематизировать самые актуальные из них в одном месте из самых разных источников, нужные из них перевести на русский язык и/или адаптировать, а какие-то и написать заново, исходя из собственного опыта.
Учитывая вышесказанное, мы не претендуем на авторство или уникальность представленных терминов и определений, но, несомненно, мы внесли свой собственный вклад в систематизацию и адаптацию многих из них.
Книга написана, прежде всего, для вашего удовольствия.
Мы продолжаем работу по улучшению качества и содержания текста этой книги, в том числе дополняем ее новыми знаниями по предметной области. Будем вам благодарны за любые отзывы, предложения и уточнения. Направляйте их, пожалуйста, на aleksander.chesalov@yandex.ru
Приятного Вам чтения и продуктивной работы!
Ваши, Александр Чесалов, Александр Власкин и Матвей Баканач.
16.08.2022. Издание первое.
09.03.2023. Издание второе. Исправленное и дополненное.
01.01.2024. Издание третье. Исправленное и дополненное.

.Чесалов А. Ю. Глоссариум по искусственному интеллекту и информационным технологиям.-М.: Ridero. 2021.-304c. [Электронный ресурс] // Ridero.ru. URL: https://ridero.ru/books/glossarium_po_informacionnym_tekhnologiyam_i_iskusstvennomu_intellektu/
.Чесалов А. Ю. Глоссариум по искусственному интеллекту и информационным технологиям.-М.: Ridero. 2021.-304c. [Электронный ресурс] // Ridero.ru. URL: https://ridero.ru/books/glossarium_po_informacionnym_tekhnologiyam_i_iskusstvennomu_intellektu/
Artificial Intelligence glossary
«A»
A/B Testing is a statistical way of comparing two (or more) techniques, typically an incumbent against a new rival. A/B testing aims to determine not only which technique performs better but also to understand whether the difference is statistically significant. A/B testing usually considers only two techniques using one measurement, but it can be applied to any finite number of techniques and measures[1].
Abductive logic programming (ALP) is a high-level knowledge-representation framework that can be used to solve problems declaratively based on abductive reasoning. It extends normal logic programming by allowing some predicates to be incompletely defined, declared as adducible predicates[2].
Abductive reasoning (also abduction) is a form of logical inference which starts with an observation or set of observations then seeks to find the simplest and most likely explanation. This process, unlike deductive reasoning, yields a plausible conclusion but does not positively verify it. abductive inference, or retroduction[3].
Abstract data type is a mathematical model for data types, where a data type is defined by its behavior (semantics) from the point of view of a user of the data, specifically in terms of possible values, possible operations on data of this type, and the behavior of these operations[4].
Abstraction — the process of removing physical, spatial, or temporal details or attributes in the study of objects or systems in order to more closely attend to other details of interest[5].
Accelerating change is a perceived increase in the rate of technological change throughout history, which may suggest faster and more profound change in the future and may or may not be accompanied by equally profound social and cultural change[6].
Access to information — the ability to obtain information and use it[7].
Access to information constituting a commercial secret — familiarization of certain persons with information constituting a commercial secret, with the consent of its owner or on other legal grounds, provided that this information is kept confidential[8].
Accuracy — the fraction of predictions that a classification model got right. In multi-class classification, accuracy is defined as follows:

In binary classification, accuracy has the following definition:
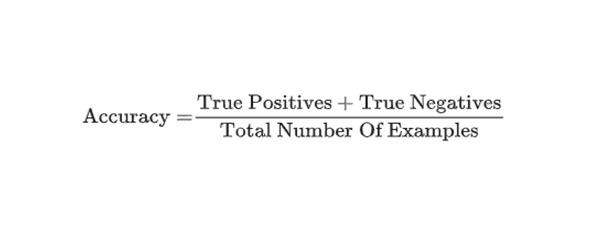
See true positive and true negative. Contrast accuracy with precision and recall[9],[10].
Action in reinforcement learning, is the mechanism by which the agent transitions between states of the environment. The agent chooses the action by using a policy[11].
Action language is a language for specifying state transition systems, and is commonly used to create formal models of the effects of actions on the world. Action languages are commonly used in the artificial intelligence and robotics domains, where they describe how actions affect the states of systems over time, and may be used for automated planning[12].
Action model learning is an area of machine learning concerned with creation and modification of software agent’s knowledge about effects and preconditions of the actions that can be executed within its environment. This knowledge is usually represented in logic-based action description language and used as the input for automated planners[13].
Action selection is a way of characterizing the most basic problem of intelligent systems: what to do next. In artificial intelligence and computational cognitive science, «the action selection problem» is typically associated with intelligent agents and animats — artificial systems that exhibit complex behaviour in an agent environment[14].
Activation function in the context of Artificial Neural Networks, is a function that takes in the weighted sum of all of the inputs from the previous layer and generates an output value to ignite the next layer[15].
Active Learning/Active Learning Strategy is a special case of Semi-Supervised Machine Learning in which a learning agent is able to interactively query an oracle (usually, a human annotator) to obtain labels at new data points. A training approach in which the algorithm chooses some of the data it learns from. Active learning is particularly valuable when labeled examples are scarce or expensive to obtain. Instead of blindly seeking a diverse range of labeled examples, an active learning algorithm selectively seeks the particular range of examples it needs for learning[16],[17],[18].
Adam optimization algorithm it is an extension of stochastic gradient descent which has recently gained wide acceptance for deep learning applications in computer vision and natural language processing[19].
Adaptive algorithm is an algorithm that changes its behavior at the time it is run, based on a priori defined reward mechanism or criterion[20],[21].
Adaptive Gradient Algorithm (AdaGrad) is a sophisticated gradient descent algorithm that rescales the gradients of each parameter, effectively giving each parameter an independent learning rate[22].
Adaptive neuro fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) (also adaptive network-based fuzzy inference system) is a kind of artificial neural network that is based on Takagi–Sugeno fuzzy inference system. The technique was developed in the early 1990s. Since it integrates both neural networks and fuzzy logic principles, it has potential to capture the benefits of both in a single framework. Its inference system corresponds to a set of fuzzy IF–THEN rules that have learning capability to approximate nonlinear functions. Hence, ANFIS is considered to be a universal estimator. For using the ANFIS in a more efficient and optimal way, one can use the best parameters obtained by genetic algorithm[23].
Adaptive system is a system that automatically changes the data of its functioning algorithm and (sometimes) its structure in order to maintain or achieve an optimal state when external conditions change[24].
Additive technologies are technologies for the layer-by-layer creation of three-dimensional objects based on their digital models («twins»), which make it possible to manufacture products of complex geometric shapes and profiles[25].
Admissible heuristic in computer science, specifically in algorithms related to pathfinding, a heuristic function is said to be admissible if it never overestimates the cost of reaching the goal, i.e., the cost it estimates to reach the goal is not higher than the lowest possible cost from the current point in the path[26].
Affective computing (also artificial emotional intelligence or emotion AI) — the study and development of systems and devices that can recognize, interpret, process, and simulate human affects. Affective computing is an interdisciplinary field spanning computer science, psychology, and cognitive science[27].
Agent architecture is a blueprint for software agents and intelligent control systems, depicting the arrangement of components. The architectures implemented by intelligent agents are referred to as cognitive architectures[28].
Agent in reinforcement learning, is the entity that uses a policy to maximize expected return gained from transitioning between states of the environment[29].
Agglomerative clustering (see hierarchical clustering) is one of the clustering algorithms, first assigns every example to its own cluster, and iteratively merges the closest clusters to create a hierarchical tree[30].
Aggregate is a total created from smaller units. For instance, the population of a county is an aggregate of the populations of the cities, rural areas, etc., that comprise the county. To total data from smaller units into a large unit[31].
Aggregator is a type of software that brings together various types of Web content and provides it in an easily accessible list. Feed aggregators collect things like online articles from newspapers or digital publications, blog postings, videos, podcasts, etc. A feed aggregator is also known as a news aggregator, feed reader, content aggregator or an RSS reader[32].
AI acceleration — acceleration of calculations encountered with AI, specialized AI hardware accelerators are allocated for this purpose (see also artificial intelligence accelerator, hardware acceleration)[33].
AI acceleration is the acceleration of AI-related computations, for this purpose specialized AI hardware accelerators are used[34].
AI accelerator is a class of microprocessor or computer system designed as hardware acceleration for artificial intelligence applications, especially artificial neural networks, machine vision, and machine learning[35].
AI accelerator is a specialized chip that improves the speed and efficiency of training and testing neural networks. However, for semiconductor chips, including most AI accelerators, there is a theoretical minimum power consumption limit. Reducing consumption is possible only with the transition to optical neural networks and optical accelerators for them[36].
AI benchmark is an AI benchmark for evaluating the capabilities, efficiency, performance and for comparing ANNs, machine learning (ML) models, architectures and algorithms when solving various AI problems, special benchmarks are created and standardized, initial marks. For example, Benchmarking Graph Neural Networks — benchmarking (benchmarking) of graph neural networks (GNS, GNN) — usually includes installing a specific benchmark, loading initial datasets, testing ANNs, adding a new dataset and repeating iterations.
AI benchmark is benchmarking of AI systems, to assess the capabilities, efficiency, performance and to compare ANNs, machine learning (ML) models, architectures and algorithms when solving various AI problems, special benchmark tests are created and standardized, benchmarks. For example, Benchmarking Graph Neural Networks — benchmarking (benchmarking) of graph neural networks (GNS, GNN) — usually includes installing a specific benchmark, loading initial datasets, testing ANNs, adding a new dataset and repeating iterations (see also artificial neural network benchmarks).
AI Building and Training Kits — applications and software development kits (SDKs) that abstract platforms, frameworks, analytics libraries, and data analysis appliances, allowing software developers to incorporate AI into new or existing applications.
AI camera is a camera with artificial intelligence, digital cameras of a new generation — allow you to analyze images by recognizing faces, their expression, object contours, textures, gradients, lighting patterns, which is taken into account when processing images; some AI cameras are capable of taking pictures on their own, without human intervention, at moments that the camera finds most interesting, etc. (see also camera, software-defined camera).
AI chipset is a chipset for systems with AI, for example, AI chipset industry is an industry of chipsets for systems with AI, AI chipset market is a market for chipsets for systems with AI.
AI chipset market — chipset market for systems with artificial intelligence (AI), see also AI chipset.
AI chipset market is the market for chipsets for artificial intelligence (AI) systems.
AI cloud services — AI model building tools, APIs, and associated middleware that enable you to build/train, deploy, and consume machine learning models that run on a prebuilt infrastructure as cloud services. These services include automated machine learning, machine vision services, and language analysis services.
AI CPU is a central processing unit for AI tasks, synonymous with AI processor.
AI engineer — AI systems engineer.
AI engineering — transfer of AI technologies from the level of R&D, experiments and prototypes to the engineering and technical level, with the expanded implementation of AI methods and tools in IT systems to solve real production problems of a company, organization. One of the strategic technological trends (trends) that can radically affect the state of the economy, production, finance, the state of the environment and, in general, the quality of life of a person and humanity.
AI hardware (also AI-enabled hardware) — artificial intelligence infrastructure system hardware, AI infrastructure. Explanations in the Glossary are usually brief.
AI hardware is infrastructure hardware or artificial intelligence system, AI infrastructure.
AI industry — for example, commercial AI industry — commercial AI industry, commercial sector of the AI industry.
AI industry trends are promising directions for the development of the AI industry.
AI infrastructure (also AI-defined infrastructure, AI-enabled Infrastructure) — artificial intelligence infrastructure systems, for example, AI infrastructure research — research in the field of AI infrastructures (see also AI, AI hardware).
AI server (artificial intelligence server) — is a server with (based on) AI; a server that provides solving AI problems.
AI shopper is a non-human economic entity that receives goods or services in exchange for payment. Examples include virtual personal assistants, smart appliances, connected cars, and IoT-enabled factory equipment. These AIs act on behalf of a human or organization client.
AI supercomputer is a supercomputer for artificial intelligence tasks, a supercomputer for AI, characterized by a focus on working with large amounts of data (see also artificial intelligence, supercomputer).
AI term is a term from the field of AI (from terminology, AI vocabulary), for example, in AI terms — in terms of AI (in AI language) (see also AI terminology).
AI term is a term from the field of AI (from terminology, AI vocabulary), for example, in AI terms — in terms of AI (in AI language).
AI terminology (artificial intelligence terminology) is a set of special terms related to the field of AI (see also AI term).
AI terminology is the terminology of artificial intelligence, a set of technical terms related to the field of AI.
AI TRiSM is the management of an AI model to ensure trust, fairness, efficiency, security, and data protection[37].
AI vendor is a supplier of AI tools (systems, solutions).
AI vendor is a supplier of AI tools (systems, solutions).
AI winter (Winter of artificial intelligence) is a period of reduced interest in the subject area, reduced research funding. The term was coined by analogy with the idea of nuclear winter. The field of artificial intelligence has gone through several cycles of hype, followed by disappointment and criticism, followed by a strong cooling off of interest, and then followed by renewed interest years or decades later[38],[39].
AI workstation is a workstation (PC) with (based on) AI; AI RS, a specialized computer for solving technical or scientific problems, AI tasks; usually connected to a LAN with multi-user operating systems, intended primarily for the individual work of one specialist.
AI workstation is a workstation (PC) with means (based on) AI; AI PC, a specialized desktop PC for solving technical or scientific problems, AI tasks; usually connected to a LAN with multi-user operating systems, intended primarily for the individual work of one specialist.
AI-based management system — the process of creating policies, allocating decision-making rights and ensuring organizational responsibility for risk and investment decisions for an application, as well as using artificial intelligence methods.
AI-based systems are information processing technologies that include models and algorithms that provide the ability to learn and perform cognitive tasks, with results in the form of predictive assessment and decision making in a material and virtual environment. AI systems are designed to work with some degree of autonomy through modeling and representation of knowledge, as well as the use of data and the calculation of correlations. AI-based systems can use various methodologies, in particular: machine learning, including deep learning and reinforcement learning; automated reasoning, including planning, dispatching, knowledge representation and reasoning, search and optimization. AI-based systems can be used in cyber-physical systems, including equipment control systems via the Internet, robotic equipment, social robotics and human-machine interface systems that combine the functions of control, recognition, processing of data collected by sensors, as well as the operation of actuators in the environment of functioning of AI systems[40].
AI-complete. In the field of artificial intelligence, the most difficult problems are informally known as AI-complete or AI-hard, implying that the difficulty of these computational problems is equivalent to that of solving the central artificial intelligence problem — making computers as intelligent as people, or strong AI. To call a problem AI-complete reflects an attitude that it would not be solved by a simple specific algorithm[41].
AI-enabled — using AI and equipped with AI, for example, AI-enabled tools — tools with AI (see also AI-enabled device).
AI-enabled device is a device supported by an artificial intelligence (AI) system, such as an intelligent robot.
AI-enabled device is a device supported by an artificial intelligence (AI) system, such as an intelligent robot (see also AI-enabled healthcare device)[42].
AI-enabled healthcare device is an AI-enabled device for healthcare (medical care), see also AI-enabled device.
AI-enabled healthcare device is an AI-enabled healthcare device[43].
AI-enabled is hardware or software that uses AI-enabled AI, such as AI-enabled tools.
AI-optimized — optimized for AI tasks; AI-optimized chip, for example, an AI-optimized chip is a chip optimized for AI tasks (see also artificial intelligence).
AI-optimized is one that is optimized for AI tasks or optimized using AI tools, for example, an AI-optimized chip is a chip that is optimized for AI tasks.
AlexNet — the name of a neural network that won the ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge in 2012. It is named after Alex Krizhevsky, then a computer science PhD student at Stanford University. See ImageNet.[44]
Algorithm — an exact prescription for the execution in a certain order of a system of operations for solving any problem from some given class (set) of problems. The term «algorithm» comes from the name of the Uzbek mathematician Musa Al-Khorezmi, who in the 9th century proposed the simplest arithmetic algorithms. In mathematics and cybernetics, a class of problems of a certain type is considered solved when an algorithm is established to solve it. Finding algorithms is a natural human goal in solving various classes of problems[45].
Algorithmic Assessment is a technical evaluation that helps identify and address potential risks and unintended consequences of AI systems across your business, to engender trust and build supportive systems around AI decision making[46].
AlphaGo is the first computer program that defeated a professional player on the board game Go in October 2015. Later in October 2017, AlphaGo’s team released its new version named AlphaGo Zero which is stronger than any previous human-champion defeating versions. Go is played on 19 by 19 board which allows for 10171 possible layouts (chess 1050 configurations). It is estimated that there are 1080 atoms in the universe[47].
Physical media is the physical material that is used to store or transmit information in a data transmission[48].
Ambient intelligence (AmI) represents the future vision of intelligent computing where explicit input and output devices will not be required; instead, sensors and processors will be embedded into everyday devices and the environment will adapt to the user’s needs and desires seamlessly. AmI systems, will use the contextual information gathered through these embedded sensors and apply Artificial Intelligence (AI) techniques to interpret and anticipate the users’ needs. The technology will be designed to be human centric and easy to use[49].
Analogical Reasoning — solving problems by using analogies, by comparing to past experiences[50].
Analysis of algorithms (AofA) — the determination of the computational complexity of algorithms, that is the amount of time, storage and/or other resources necessary to execute them. Usually, this involves determining a function that relates the length of an algorithm’s input to the number of steps it takes (its time complexity) or the number of storage locations it uses (its space complexity)[51].
Annotation is a metadatum attached to a piece of data, typically provided by a human annotator[52].
Anokhin’s theory of functional systems is a functional system consists of a certain number of nodal mechanisms, each of which takes its place and has a certain specific purpose. The first of these is afferent synthesis, in which four obligatory components are distinguished: dominant motivation, situational and triggering afferentation, and memory. The interaction of these components leads to the decision-making process[53].
Anomaly detection — the process of identifying outliers. For example, if the mean for a certain feature is 100 with a standard deviation of 10, then anomaly detection should flag a value of 200 as suspicious[54],[55].
Anonymization — the process in which data is de-identified as part of a mechanism to submit data for machine learning[56].
Answer set programming (ASP) is a form of declarative programming oriented towards difficult (primarily NP-hard) search problems. It is based on the stable model (answer set) semantics of logic programming. In ASP, search problems are reduced to computing stable models, and answer set solvers — programs for generating stable models — are used to perform search[57].
Antivirus software is a program or set of programs that are designed to prevent, search for, detect, and remove software viruses, and other malicious software like worms, trojans, adware, and more[58].
Anytime algorithm is an algorithm that can return a valid solution to a problem even if it is interrupted before it ends[59].
API-AS-a-service (AaaS) combines the API economy and software renting and provides application programming interfaces as a service[60].
Application programming interface (API) is a set of subroutine definitions, communication protocols, and tools for building software. In general terms, it is a set of clearly defined methods of communication among various components. A good API makes it easier to develop a computer program by providing all the building blocks, which are then put together by the programmer. An API may be for a web-based system, operating system, database system, computer hardware, or software library[61].
Application security is the process of making apps more secure by finding, fixing, and enhancing the security of apps. Much of this happens during the development phase, but it includes tools and methods to protect apps once they are deployed. This is becoming more important as hackers increasingly target applications with their attacks[62].
Application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC) is a specialized integrated circuit for solving a specific problem[63].
Approximate string matching (also fuzzy string searching) — the technique of finding strings that match a pattern approximately (rather than exactly). The problem of approximate string matching is typically divided into two sub-problems: finding approximate substring matches inside a given string and finding dictionary strings that match the pattern approximately[64].
Approximation error — the discrepancy between an exact value and some approximation to it[65].
Architectural description group (Architectural view) is a representation of the system as a whole in terms of a related set of interests[66],[67].
Architectural frameworks are high-level descriptions of an organization as a system; they capture the structure of its main components at varied levels, the interrelationships among these components, and the principles that guide their evolution[68].
Architecture of a computer is a conceptual structure of a computer that determines the processing of information and includes methods for converting information into data and the principles of interaction between hardware and software[69].
Architecture of a computing system is the configuration, composition and principles of interaction (including data exchange) of the elements of a computing system[70].
Architecture of a system is the fundamental organization of a system, embodied in its elements, their relationships with each other and with the environment, as well as the principles that guide its design and evolution[71].
Archival Information Collection (AIC) is information whose content is an aggregation of other archive information packages. The digital preservation function preserves the capability to regenerate the DIPs (Dissemination Information Packages) as needed over time[72].
Archival Storage is a source for data that is not needed for an organization’s everyday operations, but may have to be accessed occasionally. By utilizing an archival storage, organizations can leverage to secondary sources, while still maintaining the protection of the data. Utilizing archival storage sources reduces primary storage costs required and allows an organization to maintain data that may be required for regulatory or other requirements[73].
Area under curve (AUC) — the area under a curve between two points is calculated by performing the definite integral. In the context of a receiver operating characteristic for a binary classifier, the AUC represents the classifier’s accuracy[74].
Area Under the ROC curve is the probability that a classifier will be more confident that a randomly chosen positive example is actually positive than that a randomly chosen negative example is positive[75].
Argumentation framework is a way to deal with contentious information and draw conclusions from it. In an abstract argumentation framework, entry-level information is a set of abstract arguments that, for instance, represent data or a proposition. Conflicts between arguments are represented by a binary relation on the set of arguments[76].
Artifact is one of many kinds of tangible by-products produced during the development of software. Some artifacts (e.g., use cases, class diagrams, and other Unified Modeling Language (UML) models, requirements and design documents) help describe the function, architecture, and design of software. Other artifacts are concerned with the process of development itself — such as project plans, business cases, and risk assessments[77].
Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) as opposed to narrow intelligence, also known as complete, strong, super intelligence, Human Level Machine Intelligence, indicates the ability of a machine that can successfully perform any tasks in an intellectual way as the human being. Artificial superintelligence is a term referring to the time when the capability of computers will surpass humans[78],[79].
Artificial Intelligence (AI) — (machine intelligence) refers to systems that display intelligent behavior by analyzing their environment and taking actions — with some degree of autonomy — to achieve specific goals. AI-based systems can be purely software-based, acting in the virtual world (e.g., voice assistants, image analysis software, search engines, speech and face recognition systems) or AI can be embedded in hardware devices (e.g., advanced robots, autonomous cars, drones, or Internet of Things applications). The term AI was first coined by John McCarthy in 1956[80].
Artificial Intelligence Automation Platforms — platforms that enable the automation and scaling of production-ready AI. Artificial Intelligence Platforms involves the use of machines to perform the tasks that are performed by human beings. The platforms simulate the cognitive function that human minds perform such as problem-solving, learning, reasoning, social intelligence as well as general intelligence. Top Artificial Intelligence Platforms: Google AI Platform, TensorFlow, Microsoft Azure, Rainbird, Infosys Nia, Wipro HOLMES, Dialogflow, Premonition, Ayasdi, MindMeld, Meya, KAI, Vital A.I, Wit, Receptiviti, Watson Studio, Lumiata, Infrrd[81].
Artificial intelligence engine (also AI engine, AIE) is an artificial intelligence engine, a hardware and software solution for increasing the speed and efficiency of artificial intelligence system tools.
Artificial Intelligence for IT Operations (AIOps) is an emerging IT practice that applies artificial intelligence to IT operations to help organizations intelligently manage infrastructure, networks, and applications for performance, resilience, capacity, uptime, and, in some cases, security. By shifting traditional, threshold-based alerts and manual processes to systems that take advantage of AI and machine learning, AIOps enables organizations to better monitor IT assets and anticipate negative incidents and impacts before they take hold. AIOps is a term coined by Gartner in 2016 as an industry category for machine learning analytics technology that enhances IT operations analytics covering operational tasks include automation, performance monitoring and event correlations, among others. Gartner define an AIOps Platform thus: «An AIOps platform combines big data and machine learning functionality to support all primary IT operations functions through the scalable ingestion and analysis of the ever-increasing volume, variety and velocity of data generated by IT. The platform enables the concurrent use of multiple data sources, data collection methods, and analytical and presentation technologies»[82],[83],[84].
Artificial Intelligence Markup Language (AIML) is an XML dialect for creating natural language software agents[85].
Artificial Intelligence of the Commonsense knowledge is one of the areas of development of artificial intelligence, which is engaged in modeling the ability of a person to analyze various life situations and be guided in his actions by common sense[86].
Artificial Intelligence Open Library is a set of algorithms designed to develop technological solutions based on artificial intelligence, described using programming languages and posted on the Internet[87].
Artificial intelligence system (AIS) is a programmed or digital mathematical model (implemented using computer computing systems) of human intellectual capabilities, the main purpose of which is to search, analyze and synthesize large amounts of data from the world around us in order to obtain new knowledge about it and solve them. basis of various vital tasks. The discipline «Artificial Intelligence Systems» includes consideration of the main issues of modern theory and practice of building intelligent systems.
Artificial intelligence technologies — technologies based on the use of artificial intelligence, including computer vision, natural language processing, speech recognition and synthesis, intelligent decision support and advanced methods of artificial intelligence[88].
Artificial life (Alife, A-Life) is a field of study wherein researchers examine systems related to natural life, its processes, and its evolution, through the use of simulations with computer models, robotics, and biochemistry. The discipline was named by Christopher Langton, an American theoretical biologist, in 1986. In 1987 Langton organized the first conference on the field, in Los Alamos, New Mexico. There are three main kinds of alife, named for their approaches: soft, from software; hard, from hardware; and wet, from biochemistry. Artificial life researchers study traditional biology by trying to recreate aspects of biological phenomena[89].
Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI), also known as weak or applied intelligence, represents most of the current artificial intelligent systems which usually focus on a specific task. Narrow AIs are mostly much better than humans at the task they were made for: for example, look at face recognition, chess computers, calculus, and translation. The definition of artificial narrow intelligence is in contrast to that of strong AI or artificial general intelligence, which aims at providing a system with consciousness or the ability to solve any problems. Virtual assistants and AlphaGo are examples of artificial narrow intelligence systems[90].
Artificial Neural Network (ANN) is a computational model in machine learning, which is inspired by the biological structures and functions of the mammalian brain. Such a model consists of multiple units called artificial neurons which build connections between each other to pass information. The advantage of such a model is that it progressively «learns» the tasks from the given data without specific programing for a single task[91].
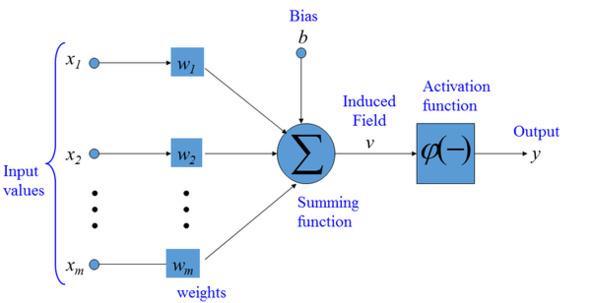
Artificial neuron is a mathematical function conceived as a model of biological neurons, a neural network. The difference between an artificial neuron and a biological neuron is shown in the figure. Artificial neurons are the elementary units of an artificial neural network. An artificial neuron receives one or more inputs (representing excitatory postsynaptic potentials and inhibitory postsynaptic potentials on nerve dendrites) and sums them to produce an output signal (or activation, representing the action potential of the neuron that is transmitted down its axon). Typically, each input is weighted separately, and the sum is passed through a non-linear function known as an activation function or transfer function. Transfer functions are usually sigmoid, but they can also take the form of other non-linear functions, piecewise linear functions, or step functions. They are also often monotonically increasing, continuous, differentiable, and bounded[92],[93].
Artificial Superintelligence (ASI) is a term referring to the time when the capability of computers will surpass humans. «Artificial intelligence,» which has been much used since the 1970s, refers to the ability of computers to mimic human thought. Artificial superintelligence goes a step beyond and posits a world in which a computer’s cognitive ability is superior to a human’s[94].
Assistive intelligence is AI-based systems that help make decisions or perform actions.
Association for the Advancement of Artificial Intelligence (AAAI) is an international, nonprofit, scientific society devoted to promote research in, and responsible use of, artificial intelligence. AAAI also aims to increase public understanding of artificial intelligence (AI), improve the teaching and training of AI practitioners, and provide guidance for research planners and funders concerning the importance and potential of current AI developments and future directions[95].
Association is another type of unsupervised learning method that uses different rules to find relationships between variables in a given dataset. These methods are frequently used for market basket analysis and recommendation engines, along the lines of «Customers Who Bought This Item Also Bought» recommendations[96].
Association Rule Learning is a rule-based Machine Learning method for discovering interesting relations between variables in large data sets[97].
Asymptotic computational complexity in computational complexity theory, asymptotic computational complexity is the usage of asymptotic analysis for the estimation of computational complexity of algorithms and computational problems, commonly associated with the usage of the big O notation[98].
Asynchronous inter-chip protocols are protocols for data exchange in low-speed devices; instead of frames, individual characters are used to control the exchange of data[99].
Attention mechanism is one of the key innovations in the field of neural machine translation. Attention allowed neural machine translation models to outperform classical machine translation systems based on phrase translation. The main bottleneck in sequence-to-sequence learning is that the entire content of the original sequence needs to be compressed into a vector of a fixed size. The attention mechanism facilitates this task by allowing the decoder to look back at the hidden states of the original sequence, which are then provided as a weighted average as additional input to the decoder[100].
Attributional calculus (AC) is a logic and representation system defined by Ryszard S. Michalski. It combines elements of predicate logic, propositional calculus, and multi-valued logic. Attributional calculus provides a formal language for natural induction, an inductive learning process whose results are in forms natural to people
