автордың кітабын онлайн тегін оқу Library of the World's Best Literature, Ancient and Modern, Vol. 7
LIBRARY OF THE
WORLD'S BEST LITERATURE
ANCIENT AND MODERN
CHARLES DUDLEY WARNER
EDITOR
HAMILTON WRIGHT MABIE
LUCIA GILBERT RUNKLE
GEORGE HENRY WARNER
ASSOCIATE EDITORS
Connoisseur Edition
Vol. VII.
NEW YORK
THE INTERNATIONAL SOCIETY
Connoisseur Edition
LIMITED TO FIVE HUNDRED COPIES IN HALF RUSSIA
No. 299
Copyright, 1896, by
R. S. Peale and J. A. Hill
All rights reserved
THE ADVISORY COUNCIL
CRAWFORD H. TOY, A.M., LL.D.,
Professor of Hebrew,
Harvard University, Cambridge, Mass.
THOMAS R. LOUNSBURY, LL.D., L.H.D.,
Professor of English in the Sheffield Scientific School of
Yale University, New Haven, Conn.
WILLIAM M. SLOANE, Ph.D., L.H.D.,
Professor of History and Political Science,
Princeton University, Princeton, N.J.
BRANDER MATTHEWS, A.M., LL.B.,
Professor of Literature,
Columbia University, New York City.
JAMES B. ANGELL, LL.D.,
President of the
University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Mich.
WILLARD FISKE, A.M., Ph.D.,
Late Professor of the Germanic and Scandinavian Languages and Literatures,
Cornell University, Ithaca, N.Y.
EDWARD S. HOLDEN, A.M., LL.D.,
Director of the Lick Observatory, and Astronomer,
University of California, Berkeley, Cal.
ALCÉE FORTIER, Lit.D.,
Professor of the Romance Languages,
Tulane University, New Orleans, La.
WILLIAM P. TRENT, M.A.,
Dean of the Department of Arts and Sciences, and Professor of English and History,
University of the South, Sewanee, Tenn.
PAUL SHOREY, Ph.D.,
Professor of Greek and Latin Literature,
University of Chicago, Chicago, Ill.
WILLIAM T. HARRIS, LL.D.,
United States Commissioner of Education,
Bureau of Education, Washington, D.C.
MAURICE FRANCIS EGAN, A.M., LL.D.,
Professor of Literature in the
Catholic University of America, Washington, D.C.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
VOL. VII
LIVED
PAGE
Henry Cuyler Bunner
1855-1896
2731 Triolet The Love-Letters of Smith ('Short Sixes') The Way to Arcady Chant-RoyalEnvoy
John Bunyan
1628-1688
2747BY EDWIN P. PARKER
The Fight with Apollyon ('Pilgrim's Progress') The Delectable Mountains (same) Christiana and Her Companions Enter the Celestial City (same)Gottfried August Bürger
1747-1794
2767 William and Helen The Wives of WeinsbergEdmund Burke
1729-1797
2779BY E. L. GODKIN
From Speech on 'Conciliation with America' From Speech on 'The Nabob of Arcot's Debts' From Speech on 'The French Revolution'Frances Hodgson Burnett
1849-
2809 At the Pit ('That Lass o' Lowrie's') Frances Burney(Madame D'Arblay)
1752-1840
2817 Evelina's Letter to the Rev. Mr. Villars ('Evelina') A Man of the Ton ('Cecilia') Miss Burney's Friends ('Letters')Robert Burns
1759-1796
2833BY RICHARD HENRY STODDARD
The Cotter's Saturday Night John Anderson, My Jo Man Was Made to Mourn Green Grow the RashesIs There for Honest Poverty
To a Mouse To a Mountain Daisy Tam o' Shanter Bruce to His Men at Bannockburn Highland Mary My Heart's in the Highlands The Banks o' DoonJohn Burroughs
1837-
2867 Sharp Eyes ('Locusts and Wild Honey') WaitingSir Richard F. Burton
1821-1890
2883 The Preternatural in Fiction ('The Book of a Thousand Nights and a Night') A Journey in Disguise ('The Personal Narrative of a Pilgrimage to El Medinah and Meccah') En Route (same)Robert Burton
1577-1640
2904 Conclusions as to Melancholy ('The Anatomy of Melancholy')Horace Bushnell
1802-1876
2909BY THEODORE T. MUNGER
Work and PlayFrom 'The Age of Homespun'
The Founders ('Work and Play') Religious Music (same)Samuel Butler
1612-1680
2927 Hudibras DescribedLord Byron
1788-1824
2935BY CHARLES DUDLEY WARNER
Maid of Athens Translation of a Romaic Song Greece ('The Giaour') The Hellespont and Troy ('The Bride of Abydos') Greece and her Heroes ('The Siege of Corinth') The Isles of Greece ('Don Juan') Greece and the Greeks before the Revolution ('Childe Harold's Pilgrimage') To Rome (same) The Coliseum (same) Chorus of Spirits ('The Deformed Transformed') Venice ('Childe Harold's Pilgrimage') Ode to Venice The East ('The Bride of Abydos') Oriental Royalty ('Don Juan') A Grecian Sunset ('The Curse of Minerva') An Italian Sunset ('Childe Harold's Pilgrimage') Twilight ('Don Juan') An Alpine Storm ('Childe Harold's Pilgrimage') The Ocean (same) The Shipwreck ('Don Juan') Love on the Island ('Don Juan') The Two Butterflies ('The Giaour') To His Sister ('Childe Harold's Pilgrimage') Ode to Napoleon The Battle of Waterloo ('Childe Harold's Pilgrimage') Mazeppa's Ride ('Mazeppa') The Irish Avatàr The Dream She Walks in Beauty ('Hebrew Melodies') Destruction of Sennacherib ('Hebrew Melodies') From 'The Prisoner of Chillon' Prometheus A Summing-Up ('Childe Harold's Pilgrimage') On This Day I Complete my Thirty-sixth Year Fernan Caballero(Cecilia Böhl de Faber)
1796-1877
3001 The Bull-Fight ('La Gaviota') In the Home Circle (same)George W. Cable
1844-
3017 "Posson Jone'" ('Old Creole Days')Caius Julius Cæsar
100-44
b.c. 3037BY J. H. WESTCOTT
Defeat of Ariovistus and the Germans ('The Gallic Wars') On the Manners and Customs of Ancient Gauls and Germans (same) The Two Lieutenants (same) Epigram on TerentiusThomas Henry Hall Caine
1853-
3067 Pete Quilliam's First-Born ('The Manxman')Pedro Calderon
1600-1681
3071BY MAURICE FRANCIS EGAN
The Lovers ('The Secret in Words') Cyprian's Bargain ('The Wonderful Magician') Dreams and Realities ('Such Stuff as Dreams are Made Of') The Dream Called Life (same)John Caldwell Calhoun
1782-1850
3087BY W. P. TRENT
Remarks on the Right of Petition (Speech in the Senate, 1840) State Rights (Speech on the Admission of Michigan, 1837) On the Government of Poland ('A Disquisition on Government') Urging Repeal of the Missouri Compromise (Speech in the Senate, 1850)Callimachus
Third Century
b.c. 3101 Hymn to Jupiter Epitaph Epigram Epitaph on Heracleitus Epitaph The Misanthrope Epitaph upon Himself Epitaph upon CleombrotusCharles Stuart Calverley
1831-1884
3107 From 'An Examination Paper,' 'The Posthumous Papers of the Pickwick Club' Ballad (Imitation of Jean Ingelow) Lovers, and a Reflection (Imitation of Jean Ingelow) Visions Changed Thoughts at a Railway Station "Forever"FULL-PAGE ILLUSTRATIONS
VOLUME VII
PAGE
Persian Manuscript (Colored Plate)
FrontispieceJohn Bunyan (Portrait)
2748Edmund Burke (Portrait)
2780Robert Burns (Portrait)
2834Burns Manuscript (
Facsimile
)
2844"Banks and Braes o' Bonnie Doon" (Etching)
2866Lord Byron (Portrait)
2936"Newstead Abbey" (Etching)
2942"The Bull-Fight" (Photogravure)
3004Julius Cæsar (Portrait)
3038Calderon (Portrait)
3072John Caldwell Calhoun (Portrait)
3088VIGNETTE PORTRAITS
Henry Cuyler Bunner Gottfried August Bürger Frances Burney Sir Richard F. Burton Robert Burton John Burroughs Horace Bushnell Samuel Butler George W. Cable Thomas Henry Hall CaineHENRY CUYLER BUNNER
(1855-1896)

The position which Henry Cuyler Bunner has come to occupy in the literary annals of our time strengthens as the days pass. If the stream of his genius flowed in gentle rivulets, it traveled as far and spread its fruitful influence as wide as many a statelier river. He was above all things a poet. In his prose as in his verse he has revealed the essential qualities of a poet's nature: he dealt with the life which he saw about him in a spirit of broad humanity and with genial sympathy. When he fashioned the tender triolet on the pitcher of mignonette, or sang of the little red box at Vesey Street, he wrote of what he knew; and his stories, even when embroidered with quaint fancies, tread firmly the American soil of the nineteenth century. But Bunner's realism never concerned itself with the record of trivialities for their own sake. When he portrayed the lower phases of city life, it was the humor of that life he caught, and not its sordidness; its kindliness, and not its brutality. His mind was healthy, and since it was a poet's mind, the point upon which it was so nicely balanced was love: love of the trees and flowers, love of his little brothers in wood and field, love of his country home, love of the vast city in its innumerable aspects; above all, love of his wife, his family, and his friends; and all these outgoings of his heart have found touching expression in his verse. Indeed, this attitude of affectionate kinship with the world has colored all his work; it has made his satire sweet-tempered, given his tales their winning grace, and lent to his poetry its abiding power.

Henry C. Bunner
The work upon which Bunner's fame must rest was all produced within a period of less than fifteen years. He was born in 1855 at Oswego, New York. He came to the city of New York when very young, and received his education there. A brief experience of business life sufficed to make his true vocation clear, and at the age of eighteen he began his literary apprenticeship on the Arcadian. When that periodical passed away, Puck was just struggling into existence, and for the English edition, which was started in 1877, Bunner's services were secured. Half of his short life was spent in editorial connection with that paper. To his wisdom and literary abilities is due in large measure the success which has always attended the enterprise. Bunner had an intimate knowledge of American character and understood the foibles of his countrymen; but he was never cynical, and his satire was without hostility. He despised opportune journalism. His editorials were clear and vigorous; free not from partisanship, but from partisan rancor, and they made for honesty and independence. His firm stand against political corruption, socialistic vagaries, the misguided and often criminal efforts of labor agitators, and all the visionary schemes of diseased minds, has contributed to the stability of sound and self-respecting American citizenship.
Bunner's first decided success in story-telling was 'The Midge,' which appeared in 1886. It is a tale of New York life in the interesting old French quarter of South Fifth Avenue. Again, in 'The Story of a New York House,' he displayed the same quick feeling for the spirit of the place, as it was and is. This tale first appeared in the newly founded Scribner's Magazine, to which he has since been a constant contributor. Here some of his best short stories have been published, including the excellent 'Zadoc Pine,' with its healthy presentation of independent manhood in contest with the oppressive exactions of labor organizations. But Bunner was no believer in stories with a tendency; the conditions which lie at the root of great sociological questions he used as artistic material, never as texts. His stories are distinguished by simplicity of motive; each is related with fine unobtrusive humor and with an underlying pathos, never unduly emphasized. The most popular of his collections of tales is that entitled 'Short Sixes,' which, having first appeared in Puck, were published in book form in 1891. A second volume came out three years later. When the shadow of death had already fallen upon Bunner, a new collection of his sketches was in process of publication: 'Jersey Street and Jersey Lane.' In these, as in the still more recent 'Suburban Sage,' is revealed the same fineness of sympathetic observation in town and country that we have come to associate with Bunner's name. Among his prose writings there remains to be mentioned the series from Puck entitled 'Made in France.' These are an application of the methods of Maupassant to American subjects; they display that wonderful facility in reproducing the flavor of another's style which is exhibited in Bunner's verse in a still more eminent degree. His prose style never attained the perfection of literary finish, but it is easy and direct, free from sentimentality and rhetoric; in the simplicity of his conceptions and the delicacy of his treatment lies its chief charm.
Bunner's verse, on the other hand, shows a complete mastery of form. He was a close student of Horace; he tried successfully the most exacting of exotic verse-forms, and enjoyed the distinction of having written the only English example of the difficult Chant-Royal. Graceful vers de société and bits of witty epigram flowed from him without effort. But it was not to this often dangerous facility that Bunner owed his poetic fame. His tenderness, his quick sympathy with nature, his insight into the human heart, above all, the love and longing that filled his soul, have infused into his perfected rhythms the spirit of universal brotherhood that underlies all genuine poetry. His 'Airs from Arcady' (1884) achieved a success unusual for a volume of poems; and the love lyrics and patriotic songs of his later volume, 'Rowen,' maintain the high level of the earlier book. The great mass of his poems is still buried in the back numbers of the magazines, from which the best are to be rescued in a new volume. If his place is not among the greatest of our time, he has produced a sufficient body of fine verse to rescue his name from oblivion and render his memory dear to all who value the legacy of a sincere and genuine poet. He died on May 11th, 1896, at the age of forty-one.
TRIOLET
HENRY CUYLER BUNNER
JOHN BUNYAN
GOTTFRIED AUGUST BÜRGER
EDMUND BURKE
FRANCES HODGSON BURNETT
FRANCES BURNEY (MADAME D'ARBLAY)
ROBERT BURNS
JOHN BURROUGHS
SIR RICHARD F. BURTON
ROBERT BURTON
HORACE BUSHNELL
SAMUEL BUTLER
LORD BYRON
FERNAN CABALLERO
GEORGE W. CABLE
CAIUS JULIUS CÆSAR
THOMAS HENRY HALL CAINE
PEDRO CALDERON
JOHN CALDWELL CALHOUN
CALLIMACHUS
CHARLES STUART CALVERLEY
A pitcher of mignonette, In a tenement's highest casement: Queer sort of flower-pot—yet That pitcher of mignonette Is a garden in heaven set, To the little sick child in the basement— The pitcher of mignonette, In the tenement's highest casement.
Copyrighted by Charles Scribner's Sons.
THE LOVE-LETTERS OF SMITH
From 'Short Sixes'
When the little seamstress had climbed to her room in the story over the top story of the great brick tenement house in which she lived, she was quite tired out. If you do not understand what a story over a top story is, you must remember that there are no limits to human greed, and hardly any to the height of tenement houses. When the man who owned that seven-story tenement found that he could rent another floor, he found no difficulty in persuading the guardians of our building laws to let him clap another story on the roof, like a cabin on the deck of a ship; and in the southeasterly of the four apartments on this floor the little seamstress lived. You could just see the top of her window from the street—the huge cornice that had capped the original front, and that served as her window-sill now, quite hid all the lower part of the story on top of the top story.
The little seamstress was scarcely thirty years old, but she was such an old-fashioned little body in so many of her looks and ways that I had almost spelled her "sempstress," after the fashion of our grandmothers. She had been a comely body, too; and would have been still, if she had not been thin and pale and anxious-eyed.
She was tired out to-night, because she had been working hard all day for a lady who lived far up in the "New Wards" beyond Harlem River, and after the long journey home she had to climb seven flights of tenement-house stairs. She was too tired, both in body and in mind, to cook the two little chops she had brought home. She would save them for breakfast, she thought. So she made herself a cup of tea on the miniature stove, and ate a slice of dry bread with it. It was too much trouble to make toast.
But after dinner she watered her flowers. She was never too tired for that, and the six pots of geraniums that caught the south sun on the top of the cornice did their best to repay her. Then she sat down in her rocking-chair by the window and looked out. Her eyry was high above all the other buildings, and she could look across some low roofs opposite and see the further end of Tompkins Square, with its sparse spring green showing faintly through the dusk. The eternal roar of the city floated up to her and vaguely troubled her. She was a country girl; and although she had lived for ten years in New York, she had never grown used to that ceaseless murmur. To-night she felt the languor of the new season, as well as the heaviness of physical exhaustion. She was almost too tired to go to bed.
She thought of the hard day done and the hard day to be begun after the night spent on the hard little bed. She thought of the peaceful days in the country, when she taught school in the Massachusetts village where she was born. She thought of a hundred small slights that she had to bear from people better fed than bred. She thought of the sweet green fields that she rarely saw nowadays. She thought of the long journey forth and back that must begin and end her morrow's work, and she wondered if her employer would think to offer to pay her fare. Then she pulled herself together. She must think of more agreeable things or she could not sleep. And as the only agreeable things she had to think about were her flowers, she looked at the garden on top of the cornice.
A peculiar gritting noise made her look down, and she saw a cylindrical object that glittered in the twilight, advancing in an irregular and uncertain manner toward her flower-pots. Looking closer, she saw that it was a pewter beer-mug, which somebody in the next apartment was pushing with a two-foot rule. On top of the beer-mug was a piece of paper, and on this paper was written, in a sprawling, half-formed hand:—
porter pleas excuse the libberty And drink it
The seamstress started up in terror and shut the window. She remembered that there was a man in the next apartment. She had seen him on the stairs on Sundays. He seemed a grave, decent person; but—he must be drunk. She sat down on her bed all a tremble. Then she reasoned with herself. The man was drunk, that was all. He probably would not annoy her further. And if he did, she had only to retreat to Mrs. Mulvaney's apartment in the rear, and Mr. Mulvaney, who was a highly respectable man and worked in a boiler-shop, would protect her. So, being a poor woman who had already had occasion to excuse—and refuse—two or three "libberties" of like sort, she made up her mind to go to bed like a reasonable seamstress, and she did. She was rewarded, for when her light was out, she could see in the moonlight that the two-foot rule appeared again with one joint bent back, hitched itself into the mug-handle, and withdrew the mug.
The next day was a hard one for the little seamstress, and she hardly thought of the affair of the night before until the same hour had come around again, and she sat once more by her window. Then she smiled at the remembrance. "Poor fellow," she said in her charitable heart, "I've no doubt he's awfully ashamed of it now. Perhaps he was never tipsy before. Perhaps he didn't know there was a lone woman in here to be frightened."
Just then she heard a gritting sound. She looked down. The pewter pot was in front of her, and the two-foot rule was slowly retiring. On the pot was a piece of paper, and on the paper was—
porter good for the helth it makes meet
This time the little seamstress shut her window with a bang of indignation. The color rose to her pale cheeks. She thought that she would go down to see the janitor at once. Then she remembered the seven flights of stairs; and she resolved to see the janitor in the morning. Then she went to bed, and saw the mug drawn back just as it had been drawn back the night before.
The morning came, but somehow the seamstress did not care to complain to the janitor. She hated to make trouble—and the janitor might think—and—and—well, if the wretch did it again she would speak to him herself, and that would settle it. And so on the next night, which was a Thursday, the little seamstress sat down by her window, resolved to settle the matter. And she had not sat there long, rocking in the creaking little rocking-chair which she had brought with her from her old home, when the pewter pot hove in sight, with a piece of paper on the top. This time the legend read:—
Perhaps you are afrade i will adress you i am not that kind
The seamstress did not quite know whether to laugh or to cry. But she felt that the time had come for speech. She leaned out of her window and addressed the twilight heaven.
"Mr.—Mr.—sir—I—will you please put your head out of the window so that I can speak to you?"
The silence of the other room was undisturbed. The seamstress drew back, blushing. But before she could nerve herself for another attack, a piece of paper appeared on the end of the two-foot rule.
when i Say a thing i mene it i have Sed i would not Adress you and i Will not
What was the little seamstress to do? She stood by the window and thought hard about it. Should she complain to the janitor? But the creature was perfectly respectful. No doubt he meant to be kind. He certainly was kind, to waste these pots of porter on her. She remembered the last time—and the first—that she had drunk porter. It was at home, when she was a young girl, after she had the diphtheria. She remembered how good it was, and how it had given her back her strength. And without one thought of what she was doing, she lifted the pot of porter and took one little reminiscent sip—two little reminiscent sips—and became aware of her utter fall and defeat. She blushed now as she had never blushed before, put the pot down, closed the window, and fled to her bed like a deer to the woods.
And when the porter arrived the next night, bearing the simple appeal—
Dont be afrade of it drink it all
the little seamstress arose and grasped the pot firmly by the handle, and poured its contents over the earth around her largest geranium. She poured the contents out to the last drop, and then she dropped the pot, and ran back and sat on her bed and cried, with her face hid in her hands.
"Now," she said to herself, "you've done it! And you're just as nasty and hard-hearted and suspicious and mean as—as pusley!" And she wept to think of her hardness of heart. "He will never give me a chance to say 'I am sorry,'" she thought. And really, she might have spoken kindly to the poor man, and told him that she was much obliged to him, but that he really must not ask her to drink porter with him.
"But it's all over and done now," she said to herself as she sat at her window on Saturday night. And then she looked at the cornice, and saw the faithful little pewter pot traveling slowly toward her.
She was conquered. This act of Christian forbearance was too much for her kindly spirit. She read the inscription on the paper,
porter is good for Flours but better for Fokes
and she lifted the pot to her lips, which were not half so red as her cheeks, and took a good, hearty, grateful draught.
She sipped in thoughtful silence after this first plunge, and presently she was surprised to find the bottom of the pot in full view. On the table at her side a few pearl buttons were screwed up in a bit of white paper. She untwisted the paper and smoothed it out, and wrote in a tremulous hand—she could write a very neat hand—
Thanks.
This she laid on the top of the pot, and in a moment the bent two-foot rule appeared and drew the mail-carriage home. Then she sat still, enjoying the warm glow of the porter, which seemed to have permeated her entire being with a heat that was not at all like the unpleasant and oppressive heat of the atmosphere, an atmosphere heavy with the spring damp. A gritting on the tin aroused her. A piece of paper lay under her eyes.
fine groing weather Smith
Now it is unlikely that in the whole round and range of conversational commonplaces there was one other greeting that could have induced the seamstress to continue the exchange of communications. But this simple and homely phrase touched her country heart. What did "groing weather" matter to the toilers in this waste of brick and mortar? This stranger must be, like herself, a country-bred soul, longing for the new green and the upturned brown mold of the country fields. She took up the paper, and wrote under the first message:—
Fine
But that seemed curt: "for—" she added; "for" what? She did not know. At last in desperation she put down "potatoes." The piece of paper was withdrawn, and came back with an addition:—
Too mist for potatos
And when the little seamstress had read this, and grasped the fact that "m-i-s-t" represented the writer's pronunciation of "moist," she laughed softly to herself. A man whose mind at such a time was seriously bent upon potatoes was not a man to be feared. She found a half-sheet of note-paper, and wrote:—
I lived in a small village before I came to New York, but I am afraid I do not know much about farming. Are you a farmer?
The answer came:—
have ben most Every thing farmed a Spel in Maine Smith
As she read this, the seamstress heard the church clock strike nine.
"Bless me, is it so late?" she cried, and she hurriedly penciled Good Night, thrust the paper out, and closed the window. But a few minutes later, passing by, she saw yet another bit of paper on the cornice, fluttering in the evening breeze. It said only good nite, and after a moment's hesitation, the little seamstress took it in and gave it shelter.
After this they were the best of friends. Every evening the pot appeared, and while the seamstress drank from it at her window, Mr. Smith drank from its twin at his; and notes were exchanged as rapidly as Mr. Smith's early education permitted. They told each other their histories, and Mr. Smith's was one of travel and variety, which he seemed to consider quite a matter of course. He had followed the sea, he had farmed, he had been a logger and a hunter in the Maine woods. Now he was foreman of an East River lumber-yard, and he was prospering. In a year or two he would have enough laid by to go home to Bucksport and buy a share in a ship-building business. All this dribbled out in the course of a jerky but variegated correspondence, in which autobiographic details were mixed with reflections moral and philosophical.
A few samples will give an idea of Mr. Smith's style:—
i was one trip to van demens land
To which the seamstress replied:—
It must have been very interesting.
But Mr. Smith disposed of this subject very briefly:—
it wornt
Further he vouchsafed:—
i seen a Chinese cook in hong kong could cook flapjacks like your mother
a mishnery that sells Rum is the menest of Gods crechers
a bulfite is not what it is cract up to Be
the dagos are wussen the brutes
i am 6 1-3/4 but my Father was 6 foot 4
The seamstress had taught school one winter, and she could not refrain from making an attempt to reform Mr. Smith's orthography. One evening, in answer to this communication,—
i killd a Bare in Maine 600 lbs waight
she wrote:—
Isn't it generally spelled Bear?
but she gave up the attempt when he responded:—
a bare is a mene animle any way you spel him
The spring wore on, and the summer came, and still the evening drink and the evening correspondence brightened the close of each day for the little seamstress. And the draught of porter put her to sleep each night, giving her a calmer rest than she had ever known during her stay in the noisy city; and it began, moreover, to make a little "meet" for her. And then the thought that she was going to have an hour of pleasant companionship somehow gave her courage to cook and eat her little dinner, however tired she was. The seamstress's cheeks began to blossom with the June roses.
And all this time Mr. Smith kept his vow of silence unbroken, though the seamstress sometimes tempted him with little ejaculations and exclamations to which he might have responded. He was silent and invisible. Only the smoke of his pipe, and the clink of his mug as he set it down on the cornice, told her that a living, material Smith was her correspondent. They never met on the stairs, for their hours of coming and going did not coincide. Once or twice they passed each other in the street—but Mr. Smith looked straight ahead of him about a foot over her head. The little seamstress thought he was a very fine-looking man, with his six feet one and three-quarters and his thick brown beard. Most people would have called him plain.
Once she spoke to him. She was coming home one summer evening, and a gang of corner-loafers stopped her and demanded money to buy beer, as is their custom. Before she had time to be frightened, Mr. Smith appeared,—whence, she knew not,—scattered the gang like chaff, and collaring two of the human hyenas, kicked them, with deliberate, ponderous, alternate kicks, until they writhed in ineffable agony. When he let them crawl away, she turned to him and thanked him warmly, looking very pretty now, with the color in her cheeks. But Mr. Smith answered no word. He stared over her head, grew red in the face, fidgeted nervously, but held his peace until his eyes fell on a rotund Teuton passing by.
"Say, Dutchy!" he roared. The German stood aghast. "I ain't got nothing to write with!" thundered Mr. Smith, looking him in the eye. And then the man of his word passed on his way.
And so the summer went on, and the two correspondents chatted silently from window to window, hid from sight of all the world below by the friendly cornice. And they looked out over the roof and saw the green of Tompkins Square grow darker and dustier as the months went on.
Mr. Smith was given to Sunday trips into the suburbs, and he never came back without a bunch of daisies or black-eyed Susans or, later, asters or golden-rod for the little seamstress. Sometimes, with a sagacity rare in his sex, he brought her a whole plant, with fresh loam for potting.
He gave her also a reel in a bottle, which, he wrote, he had "maid" himself, and some coral, and a dried flying-fish that was something fearful to look upon, with its sword-like fins and its hollow eyes. At first she could not go to sleep with that flying-fish hanging on the wall.
But he surprised the little seamstress very much one cool September evening, when he shoved this letter along the cornice:—

Letter Contents
The little seamstress gazed at this letter a long time. Perhaps she was wondering in what Ready Letter-Writer of the last century Mr. Smith had found his form. Perhaps she was amused at the results of his first attempt at punctuation. Perhaps she was thinking of something else, for there were tears in her eyes and a smile on her small mouth.
But it must have been a long time, and Mr. Smith must have grown nervous, for presently another communication came along the line where the top of the cornice was worn smooth. It read:
If not understood will you mary me
The little seamstress seized a piece of paper and wrote:—
If I say Yes, will you speak to me?
Then she rose and passed it out to him, leaning out of the window, and their faces met.
Copyright of Keppler and Schwarzmann.
THE WAY TO ARCADY
Oh, what's the way to Arcady, To Arcady, to Arcady; Oh, what's the way to Arcady, Where all the leaves are merry?
Oh, what's the way to Arcady? The spring is rustling in the tree— The tree the wind is blowing through— It sets the blossoms flickering white. I knew not skies could burn so blue Nor any breezes blow so light. They blow an old-time way for me, Across the world to Arcady.
Oh, what's the way to Arcady? Sir Poet, with the rusty coat, Quit mocking of the song-bird's note. How have you heart for any tune, You with the wayworn russet shoon? Your scrip, a-swinging by your side, Gapes with a gaunt mouth hungry-wide. I'll brim it well with pieces red, If you will tell the way to tread.
Oh, I am bound for Arcady, And if you but keep pace with me You tread the way to Arcady.
And where away lies Arcady, And how long yet may the journey be?
Ah, that (quoth he) I do not know: Across the clover and the snow— Across the forest, across the flowers— Through summer seconds and winter hours. I've trod the way my whole life long, And know not now where it may be; My guide is but the stir to song, That tells me I cannot go wrong, Or clear or dark the pathway be Upon the road to Arcady.
But how shall I do who cannot sing? I was wont to sing, once on a time— There is never an echo now to ring Remembrance back to the trick of rhyme.
'Tis strange you cannot sing (quoth he), The folk all sing in Arcady.
But how may he find Arcady Who hath nor youth nor melody?
What, know you not, old man (quoth he)— Your hair is white, your face is wise— That Love must kiss that Mortal's eyes Who hopes to see fair Arcady? No gold can buy you entrance, there, But beggared Love may go all bare; No wisdom won with weariness, But Love goes in with Folly's dress; No fame that wit could ever win, But only Love, may lead Love in To Arcady, to Arcady.
Ah, woe is me, through all my days Wisdom and wealth I both have got, And fame and name, and great men's praise; But Love, ah Love! I have it not. There was a time, when life was new— But far away, and half forgot— I only know her eyes were blue; But Love—I fear I knew it not. We did not wed, for lack of gold, And she is dead, and I am old. All things have come since then to me, Save Love, ah Love! and Arcady.
Ah, then I fear we part (quoth he), My way's for Love and Arcady.
But you, you fare alone like me; The gray is likewise in your hair. What love have you to lead you there. To Arcady, to Arcady?
Ah, no, not lonely do I fare: My true companion's Memory. With Love he fills the Spring-time air; With Love he clothes the Winter tree. Oh, past this poor horizon's bound My song goes straight to one who stands— Her face all gladdening at the sound— To lead me to the Spring-green lands, To wander with enlacing hands. The songs within my breast that stir Are all of her, are all of her. My maid is dead long years (quoth he), She waits for me in Arcady.
Oh, yon's the way to Arcady, To Arcady, to Arcady; Oh, yon's the way to Arcady, Where all the leaves are merry.
Copyrighted by Charles Scribner's Sons.
CHANT-ROYAL
I would that all men my hard case might know; How grievously I suffer for no sin: I, Adolphe Culpepper Ferguson, for lo! I of my landlady am lockèd in, For being short on this sad Saturday, Nor having shekels of silver wherewith to pay: She has turned and is departed with my key; Wherefore, not even as other boarders free, I sing (as prisoners to their dungeon stones When for ten days they expiate a spree): Behold the deeds that are done of Mrs. Jones!
One night and one day have I wept my woe; Nor wot I, when the morrow doth begin, If I shall have to write to Briggs & Co., To pray them to advance the requisite tin For ransom of their salesman, that he may Go forth as other boarders go alway— As those I hear now flocking from their tea, Led by the daughter of my landlady Piano-ward. This day, for all my moans, Dry bread and water have been servèd me. Behold the deeds that are done of Mrs. Jones!
Miss Amabel Jones is musical, and so The heart of the young he-boardér doth win, Playing 'The Maiden's Prayer' adagio— That fetcheth him, as fetcheth the banco skin The innocent rustic. For my part, I pray That Badarjewska maid may wait for aye Ere sits she with a lover, as did we Once sit together, Amabel! Can it be That all that arduous wooing not atones For Saturday shortness of trade dollars three? Behold the deeds that are done of Mrs. Jones!
Yea! she forgets the arm was wont to go Around her waist. She wears a buckle, whose pin Galleth the crook of the young man's elbów. I forget not, for I that youth have been. Smith was aforetime the Lothario gay. Yet once, I mind me, Smith was forced to stay Close in his room. Not calm, as I, was he; But his noise brought no pleasaunce, verily. Small ease he got of playing on the bones Or hammering on his stove-pipe, that I see. Behold the deeds that are done of Mrs. Jones!
Thou, for whose fear the figurative crow I eat, accursed be thou and all thy kin! Thee will I show up—yea, up will I show Thy too thick buckwheats, and thy tea too thin. Ay! here I dare thee, ready for the fray: Thou dost not "keep a first-class house," I say! It does not with the advertisements agree. Thou lodgest a Briton with a puggaree, And thou hast harbored Jacobses and Cohns, Also a Mulligan. Thus denounce I thee! Behold the deeds that are done of Mrs. Jones!
ENVOY
Boarders! the worst I have not told to ye: She hath stolen my trousers, that I may not flee Privily by the window. Hence these groans. There is no fleeing in a robe de nuit. Behold the deeds that are done of Mrs. Jones!
Copyrighted by Charles Scribner's Sons.
JOHN BUNYAN
(1628-1688)
BY REV. EDWIN P. PARKER

John Bunyan, son of Thomas Bunnionn Junr and Margaret Bentley, was born 1628, in the quaint old village of Elstow, one mile southwest of Bedford, near the spot where, three hundred years before, his ancestor William Boynon resided. His father was a poor tinker or "braseyer," and his mother's lineage is unknown. He says,—"I never went to school to Aristotle or Plato, but was brought up at my father's house in a very mean condition, among a company of poor countrymen."
He learned to read and write "according to the rate of other poor men's children"; but soon lost "almost utterly" the little he had learned. Shortly after his mother's death, when he was about seventeen years of age, he served as a soldier for several months, probably in the Parliamentary army. Not long afterward he married a woman as poor as himself, by whose gentle influence he was gradually led into the way of those severe spiritual conflicts and "painful exercises of mind" from which he finally came forth, at great cost, victorious. These religious experiences, vividly described in his 'Grace Abounding,' traceable in the course of his chief Pilgrim, and frequently referred to in his discourses, have been too literally interpreted by some, and too much explained away as unreal by others; but present no special difficulty to those who will but consider Bunyan's own explanations.
From boyhood he had lived a roving and non-religious life, although possessing no little tenderness of conscience. He was neither intemperate nor dishonest; he was not a law-breaker; he explicitly and indignantly declares:—"If all the fornicators and adulterers in England were hanged by the neck till they be dead, John Bunyan would still be alive and well!" The particular sins of which he was guilty, so far as he specifies them, were profane swearing, from which he suddenly ceased at a woman's reproof, and certain sports, innocent enough in themselves, which the prevailing Puritan rigor severely condemned. What, then, of that vague and exceeding sinfulness of which he so bitterly accuses and repents himself? It was that vision of sin, however disproportionate, which a deeply wounded and graciously healed spirit often has, in looking back upon the past from that theological standpoint whence all want of conformity to the perfect law of God seems heinous and dreadful.
"A sinner may be comparatively a little sinner, and sensibly a great one. There are two sorts of greatness in sin: greatness by reason of number; greatness by reason of the horrible nature of sin. In the last sense, he that has but one sin, if such an one could be found, may in his own eyes find himself the biggest sinner in the world."
"Visions of God break the heart, because, by the sight the soul then has of His perfections, it sees its own infinite and unspeakable disproportion."
"The best saints are most sensible of their sins, and most apt to make mountains of their molehills."
Such sentences from Bunyan's own writings—and many like them might be quoted—shed more light upon the much-debated question of his "wickedness" than all that his biographers have written.
In John Gifford, pastor of a little Free Church in Bedford, Bunyan found a wise friend, and in 1653 he joined that church. He soon discovered his gifts among the brethren, and in due time was appointed to the office of a gospel minister, in which he labored with indefatigable industry and zeal, and with ever-increasing fame and success, until his death. His hard personal fortunes between the Restoration of 1660 and the Declaration of Indulgence of 1672, including his imprisonment for twelve years in Bedford Gaol; his subsequent imprisonment in 1675-6, when the first part of the 'Pilgrim's Progress' was probably written; and the arduous engagements of his later and comparatively peaceful years,—must be sought in biographies, the latest and perhaps the best of which is that by Rev. John Brown, minister of the Bunyan Church at Bedford. The statute under which Bunyan suffered is the 35th Eliz., Cap. 1, re-enacted with rigor in the 16th Charles II., Cap. 4, 1662; and the spirit of it appears in the indictment preferred against him:—"that he hath devilishly and perniciously abstained from coming to Church to hear Divine service, and is a common upholder of several unlawful meetings and conventicles, to the great disturbance and distraction of the good subjects of this Kingdom," etc., etc.
The story of Bunyan's life up to the time of his imprisonment, and particularly that of his arrests and examinations before the justices, and also the account of his experiences in prison, should be read in his own most graphic narrative, in the 'Grace Abounding,' which is one of the most precious portions of all autobiographic literature. Bunyan was born and bred, he lived and labored, among the common people, with whom his sympathies were strong and tender, and by whom he was regarded with the utmost veneration and affection. He understood them, and they him. For nearly a century they were almost the only readers of his published writings. They came to call him Bishop Bunyan. His native genius, his great human-heartedness and loving-kindness, his burning zeal and indomitable courage, his racy humor and kindling imagination, all vitalized by the spiritual force which came upon him through the encompassing atmosphere of devout Puritanism, were consecrated to the welfare of his fellow-men. His personal friend, Mr. Doe, describes him as "tall in stature, strong-boned, of a ruddy face, with sparkling eyes, nose well set, mouth moderately large, forehead something high, and his habit always plain and modest." His portrait, painted in 1685, shows a vigorous, kindly face, with mustachios and imperial, and abundance of hair falling in long wavy masses about the neck and shoulders,—more Cavalier-like than Roundhead.

JOHN BUNYAN.
Bunyan was a voluminous writer, and his works, many of them posthumous, are said to equal in number the sixty years of his life. But even the devout and sympathetic critic is compelled to acknowledge the justice of that verdict of time which has consigned most of them to a virtual oblivion. The controversial tracts possess no elements of enduring interest. The doctrinal and spiritual discourses are elaborations of a system of religious thought which long ago "had its day and ceased to be." Yet they contain pithy sentences, homely and pat illustrations, and many a paragraph, rugged or tender, in which one recognizes the stamp of his genius, and an intimation of his remarkable power as a preacher. The best of these discourses, 'The Jerusalem Sinner Saved,' 'Come and Welcome to Jesus Christ,' and 'Light for Them that Sit in Darkness,' while they sparkle here and there with things unique and precious to the Bunyan-curious student, would seem dull and tedious to the general though devout reader. In many a passage we feel, to use his phrase, his "heart-pulling power," no less than the force and felicity of his most original images and analogies; but these passages are little oases in a dry and thirsty land. The 'Life and Death of Mr. Badman' vividly presents certain aspects of English provincial life in that day; but they are repulsive, and the entire work is marred by flat moralizings and coarse, often incredible stories.
The 'Holy War,' which Macaulay said would have been our greatest religious allegory if the 'Pilgrim's Progress' had not been written, has ceased to be much read. The conception of the conquest of the human soul by the irresistible operation of divine force is so foreign to modern thought and faith that Bunyan's similitude no longer seems a verisimilitude. The pages abound with quaint, humorous, and lifelike touches;—as where Diabolus stations at Ear-Gate a guard of deaf men under old Mr. Prejudice, and Unbelief is described as "a nimble jack whom they could never lay hold of";—but as compared with the 'Pilgrim's Progress' the allegory is artificial, its elaboration of analogies is ponderous and tedious, and its characters lack solidity and reality.
All these works, however, exhibit a remarkable command of the mother tongue, a shrewd common-sense and mother wit, a fervid spiritual life, and a wonderful knowledge of the English Bible. They may be likened to more or less submerged wrecks kept from sinking into utter neglect by the bond of authorship which connects them with the one incomparable work which floats, unimpaired by time, on the sea of universal appreciation and favor. Bunyan's unique and secure position in English literature was gained by the 'Pilgrim's Progress,' the first part of which was published in 1678, and the second in 1685.
The broader, freer conception of the pilgrimage—as old in literature as the ninetieth Psalm, apt and fond, as innumerable books show, from De Guileville's 'Le Pelerinage de l'Homme' in the fourteenth century to Patrick's 'Parable' three hundred years later—took sudden possession of Bunyan's imagination while he was in prison, and kindled all his finest powers. Then he undertook, poet-wise, to work out this conception, capable of such diversity of illustration, in a form of literature that has ever been especially congenial to the human mind. Unguided save by his own consecrated genius, unaided by other books than his English Bible and Fox's 'Book of Martyrs,' he proceeded with a simplicity of purpose and felicity of expression, and with a fidelity to nature and life, which gave to his unconsciously artistic story the charm of perfect artlessness as well as the semblance of reality. When Bunyan's lack of learning and culture are considered, and also the comparative dryness of his controversial and didactic writings, this efflorescence of a vital spirit of beauty and of an essentially poetic genius in him seems quite inexplicable. The author's rhymed 'Apology for His Book,' which usually prefaces the 'Pilgrim's Progress,' contains many significant hints as to the way in which he was led to
"Make truth spangle, and its rays to shine."
He had no thought of producing a work of literary excellence; but on the other hand he had not, in writing this book, his customary purpose of spiritual edification. Indeed, he put his multiplying thoughts and fancies aside, lest they should interfere with a more serious and important book which he had in hand!
"I only thought to make I knew not what: nor did I undertake Thereby to please my neighbor; no, not I: I did it mine own self to gratify.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Thus I set pen to paper with delight, And quickly had my thoughts in black and white."
The words are exceedingly suggestive. In writing so aimlessly—"I knew not what"—to gratify himself by permitting the allegory into which he had suddenly fallen to take possession of him and carry him whithersoever it would, while he wrote out with delight his teeming fancies, was not Bunyan for the first time exercising his genius in a freedom from all theological and other restraint, and so in a surpassing range and power? The dreamer and poet supplanted the preacher and teacher. He yielded to the simple impulse of his genius, gave his imagination full sweep, and so, as never before or elsewhere, soared and sang in what seemed to many of his Puritan friends a questionable freedom and profane inspiration. And yet his song, or story, was not a creation of mere fancy,—
"It came from my own heart, so to my head, And thence into my fingers tricklèd;"—
and therefore, we add, it finds its way to the heart of mankind.
Hence the spontaneity of the allegory, its ease and freedom of movement, its unlabored development, its natural and vital enfolding of that old pilgrim idea of human life which had so often bloomed in the literature of all climes and ages, but whose consummate flower appeared in the book of this inspired Puritan tinker-preacher. Hence also the dramatic unity and methodic perfectness of the story. Its byways all lead to its highway; its episodes are as vitally related to the main theme as are the ramifications of a tree to its central stem. The great diversities of experience in the true pilgrims are dominated by one supreme motive. As for the others, they appear incidentally to complete the scenes, and make the world and its life manifold and real. The Pilgrim is a most substantial person, and once well on the way, the characters he meets, the difficulties he encounters, the succor he receives, the scenes in which he mingles, are all, however surprising, most natural. The names, and one might almost say the forms and faces, of Pliable, Obstinate, Faithful, Hopeful, Talkative, Mercy, Great-heart, old Honest, Valiant-for-truth, Feeble-mind, Ready-to-halt, Miss Much-afraid, and many another, are familiar to us all. Indeed, the pilgrimage is our own—in many of its phases at least,—and we have met the people whom Bunyan saw in his dream, and are ourselves they whom he describes. When Dean Stanley began his course of lectures on Ecclesiastical History at Oxford, his opening words were those of the passage where the Pilgrim is taken to the House Beautiful to see "the rarities and histories of that place, both ancient and modern"; and at the end of the same course, wishing to sketch the prospects of Christendom, he quoted the words in which, on leaving the House Beautiful, Christian was shown the distant view of the Delectable Mountains.
But for one glance at Pope and Pagan, there is almost nothing to indicate the writer's ecclesiastical standing. But for here and there a marking of time in prosaic passages which have nothing to do with the story, there is nothing to mar the catholicity of its spirit. Romanists and Protestants, Anglicans and Puritans, Calvinists and Arminians,—all communions and sects have edited and circulated it. It is the completest triumph of truth by fiction in all literature. More than any other human book, it is "a religious bond to the whole of English Christendom." The second part is perhaps inferior to the first, but is richer in incident, and some of its characters—Mercy, old Honest, Valiant-for-truth, and Great-heart, for instance—are exquisitely conceived and presented. Here again the reader will do well to carefully peruse the author's rhymed introduction:—
"What Christian left locked up, and went his way, Sweet Christiana opens with her key."
"Go then, my little Book," he says, "and tell young damsels of Mercy, and old men of plain-hearted old Honest. Tell people of Master Fearing, who was a good man, though much down in spirit. Tell them of Feeble-mind, and Ready-to-halt, and Master Despondency and his daughter, who 'softly went but sure.'
"When thou hast told the world of all these things, Then turn about, my Book, and touch these strings, Which, if but touched, will such a music make, They'll make a cripple dance, a giant quake."
This second part introduces some new scenes, as well as characters and experiences, but with the same broad sympathy and humor; and there are closing descriptions not excelled in power and pathos by anything in the earlier pilgrimage.
In his 'Apology' Bunyan says:—
"This book is writ in such a dialect As may the minds of listless men affect."
The idiom of the book is purely English, acquired by a diligent study of the English Bible. It is the simplest, raciest, and most sinewy English to be found in any writer of our language; and Bunyan's amazing use of this Saxon idiom for all the purposes of his story, and the range and freedom of his imaginative genius therein, like certain of Tennyson's 'Idylls,' show it to be an instrument of symphonic capacity and variety. Bunyan's own maxim is a good one:—"Words easy to be understood do often hit the mark, when high and learned ones do only pierce the air."
Of the 'Pilgrim's Progress,' in both its parts, we may say in the words of Milton:—
"These are works that could not be composed by the invocation of Dame Memory and her siren daughters, but by devout prayer to that eternal Spirit who can enrich with all utterance and knowledge, and send out his Seraphim, with the hallowed fire of his altar, to touch and purify the lips of whom he pleases, without reference to station, birth, or education."
Let Bunyan speak for his own book:—
"Wouldst thou be in a dream, and yet not sleep? Or wouldst thou in a moment laugh and weep? Wouldst thou lose thyself and catch no harm, And find thyself again, without a charm? Wouldst read thyself, and read, thou knowst not what, And yet know whether thou art blest or not By reading the same lines? O then come hither! And lay my book, thy head, and heart together."
Bunyan died of fever, in the house of a friend, at London, August 12th, 1688, in the sixty-first year of his age. Three of his four children survived him; the blind daughter, for whom he expressed such affectionate solicitude during his imprisonment, died before him. His second wife, Elisabeth, who pleaded for him with so much dignity and feeling before Judge Hale and other justices, died in 1692. In 1661 a recumbent statue was placed on his tomb in Bunhill Fields, and thirteen years later a noble statue was erected in his honor at Bedford. The church at Elstow is enriched with memorial windows presenting scenes from the 'Holy War' and the 'Pilgrim's Progress,' and the Bunyan Meeting-House in Bedford has bronze doors presenting similar scenes.
The great allegory has been translated into almost every language and dialect under the sun. The successive editions of it are almost innumerable; and no other book save the Bible has had an equally large circulation. The verdict of approval stamped upon it at first by the common people, has been fully recognized and accepted by the learned and cultivated.
THE FIGHT WITH APOLLYON
From the 'Pilgrim's Progress'
But now, in this Valley of Humiliation, poor Christian was hard put to it; for he had gone but a little way before he espied a foul fiend coming over the field to meet him; his name is Apollyon. Then did Christian begin to be afraid, and to cast in his mind whether to go back or to stand his ground: But he considered again that he had no armor for his back, and therefore thought that to turn the back to him might give him the greater advantage with ease to pierce him with his darts. Therefore he resolved to venture and stand his ground; for, thought he, had I no more in mine eye than the saving of my life, 'twould be the best way to stand.
So he went on, and Apollyon met him. Now the monster was hideous to behold: he was clothed with scales like a fish (and they are his pride); he had wings like a dragon, feet like a bear, and out of his belly came fire and smoke; and his mouth was as the mouth of a lion. When he was come up to Christian, he beheld him with a disdainful countenance, and thus began to question with him.
Apollyon—Whence come you? and whither are you bound?
Christian—I am come from the City of Destruction, which is the place of all evil, and am going to the City of Zion.
Apollyon—By this I perceive thou art one of my subjects, for all that country is mine, and I am the prince and god of it. How is it then that thou hast run away from thy King? Were it not that I hope thou mayest do me more service, I would strike thee now at one blow to the ground.
Christian—I was born indeed in your dominions, but your service was hard, and your wages such as a man could not live on, "for the wages of sin is death;" therefore when I was come to years, I did as other considerate persons do—look out, if perhaps I might mend myself.
Apollyon—There is no prince that will thus lightly lose his subjects, neither will I as yet lose thee; but since thou complainest of thy service and wages, be content to go back; what our country will afford, I do here promise to give thee.
Christian—But I have let myself to another, even to the King of Princes, and how can I with fairness go back with thee?
Apollyon—Thou hast done in this according to the proverb, changed a bad for a worse; but it is ordinary for those that have professed themselves his servants, after a while to give him the slip and return again to me: Do thou so too, and all shall be well.
Christian—I have given him my faith, and sworn my allegiance to him: how then can I go back from this, and not be hanged as a traitor?
Apollyon—Thou didst the same to me, and yet I am willing to pass by all, if now thou wilt yet turn again and go back.
Christian—What I promised thee was in my nonage; and besides, I count that the Prince under whose banner now I stand is able to absolve me; yea, and to pardon also what I did as to my compliance with thee: and besides, O thou destroying Apollyon, to speak truth, I like his service, his wages, his servants, his government, his company and country, better than thine; and therefore leave off to persuade me further; I am his servant, and I will follow him.
Apollyon—Consider again when thou art in cool blood, what thou art like to meet with in the way that thou goest. Thou knowest that for the most part his servants come to an ill end, because they are transgressors against me and my ways: How many of them have been put to shameful deaths; and besides, thou countest his service better than mine, whereas he never came yet from the place where he is to deliver any that served him out of our hands; but as for me, how many times, as all the world very well knows, have I delivered, either by power or fraud, those that have faithfully served me, from him and his, though taken by them; and so I will deliver thee.
Christian—His forbearing at present to deliver them is on purpose to try their love, whether they will cleave to him to the end: and as for the ill end thou sayest they come to, that is most glorious in their account;
for,
for present deliverance, they do not much expect it, for they stay for their glory, and then they shall have it, when their Prince comes in his, and the glory of the angels.Apollyon—Thou hast already been unfaithful in thy service to him, and how dost thou think to receive wages of him?
Christian—Wherein, O Apollyon, have I been unfaithful to him?
Apollyon—Thou didst faint at first setting out, when thou wast almost choked in the Gulf of Despond; thou didst attempt wrong ways to be rid of thy burden, whereas thou shouldst have stayed till thy Prince had taken it off; thou didst sinfully sleep and lose thy choice thing; thou wast also almost persuaded to go back at the sight of the lions; and when thou talkest of thy journey, and of what thou hast heard and seen, thou art inwardly desirous of vainglory in all that thou sayest or doest.
Christian—All this is true, and much more which thou hast left out; but the Prince whom I serve and honor is merciful, and ready to forgive; but besides, these infirmities possessed me in thy country, for there I sucked them in, and I have groaned under them, been sorry for them, and have obtained pardon of my Prince.
Apollyon—Then Apollyon broke out into grievous rage, saying, I am an enemy to this Prince; I hate his person, his laws and people: I am come out on purpose to withstand thee.
Christian—Apollyon, beware what you do, for I am in the King's highway, the way of holiness, therefore take heed to yourself.
Apollyon—Then Apollyon straddled quite over the whole breadth of the way, and said, I am void of fear in this matter; prepare thyself to die; for I swear by my infernal den, that thou shalt go no further; here will I spill thy soul.
And with that he threw a flaming dart at his breast, but Christian had a shield in his hand, with which he caught it, and so prevented the danger of that.
Then did Christian draw, for he saw 'twas time to bestir him: and Apollyon as fast made at him, throwing darts as thick as hail; by the which, notwithstanding all that Christian could do to avoid it, Apollyon wounded him in his head, his hand, and foot. This made Christian give a little back; Apollyon therefore followed his work amain, and Christian again took courage, and resisted as manfully as he could. This sore combat lasted for above half a day, even till Christian was almost quite spent; for you must know that Christian, by reason of his wounds, must needs grow weaker and weaker.
Then Apollyon, espying his opportunity, began to gather up close to Christian, and wrestling with him, gave him a dreadful fall; and with that Christian's sword flew out of his hand. Then said Apollyon, I am sure of thee now; and with that he had almost pressed him to death, so that Christian began to despair of life: but as God would have it, while Apollyon was fetching of his last blow, thereby to make a full end of this good man, Christian nimbly stretched out his hand for his sword, and caught it, saying, "Rejoice not against me, O mine enemy! when I fall I shall arise;" and with that gave him a deadly thrust, which made him give back, as one that had received his mortal wound; Christian, perceiving that, made at him again, saying, "Nay, in all these things we are more than conquerors through him that loved us." And with that Apollyon spread forth his dragon's wings, and sped him away, that Christian for a season saw him no more.
In this combat no man can imagine, unless he had seen and heard as I did, what yelling and hideous roaring Apollyon made all the time of the fight; he spake like a dragon; and on the other side, what sighs and groans burst from Christian's heart. I never saw him all the while give so much as one pleasant look, till he perceived he had wounded Apollyon with his two-edged sword; then indeed he did smile, and look upward; but 'twas the dreadfulest sight that ever I saw.
So when the battle was over, Christian said, I will here give thanks to him that hath delivered me out of the mouth of the lion, to him that did help me against Apollyon. And so he did, saying:—
Great Beelzebub, the captain of this fiend, Designed my ruin; therefore to this end He sent him harnessed out: and he with rage That hellish was, did fiercely me engage: But blessed Michael helpèd me, and I By dint of sword did quickly make him fly. Therefore to him let me give lasting praise, And thank and bless his holy name always.
Then there came to him a hand, with some of the leaves of the tree of life, the which Christian took, and applied to the wounds that he had received in the battle, and was healed immediately. He also sat down in that place to eat bread, and to drink of the bottle that was given him a little before; so being refreshed, he addressed himself to his journey, with his sword drawn in his hand; for he said, I know not but some other enemy may be at hand. But he met with no other affront from Apollyon quite through this valley.
THE DELECTABLE MOUNTAINS
From the 'Pilgrim's Progress'
They went then till they came to the Delectable Mountains, which mountains belong to the Lord of that Hill of which we have spoken before; so they went up to the mountains, to behold the gardens and orchards, the vineyards and fountains of water; where also they drank, and washed themselves, and did freely eat of the vineyards. Now there were on the tops of these mountains shepherds feeding their flocks, and they stood by the highway side. The pilgrims therefore went to them, and leaning upon their staves (as is common with weary pilgrims, when they stand to talk with any by the way) they asked, Whose delectable mountains are these? And whose be the sheep that feed upon them?
Shepherds—These mountains are "Immanuel's Land," and they are within sight of his city; and the sheep also are his, and he laid down his life for them.
Christian—Is this the way to the Celestial City?
Shepherds—You are just in your way.
Christian—How far is it thither?
Shepherds—Too far for any but those that shall get thither indeed.
Christian—Is the way safe or dangerous?
Shepherds—Safe for those for whom it is to be safe, "but transgressors shall fall therein."
Christian—Is there in this place any relief for pilgrims that are weary and faint in the way?
Shepherds—The lord of these mountains hath given us a charge "not to be forgetful to entertain strangers"; therefore the good of the place is before you.
I saw also in my dream, that when the shepherds perceived that they were wayfaring men, they also put questions to them (to which they made answer as in other places), as, Whence came you? and, How got you into the way? and, By what means have you so persevered therein? For but few of them that begin to come hither do show their face on these mountains. But when the shepherds heard their answers, being pleased therewith, they looked very lovingly upon them, and said, Welcome to the Delectable Mountains.
The shepherds, I say, whose names were Knowledge, Experience, Watchful, and Sincere, took them by the hand, and had them to their tents, and made them partake of that which was ready at present. They said moreover, We would that ye should stay here a while, to be acquainted with us; and yet more to solace yourselves with the good of these delectable mountains. They then told them that they were content to stay; and so they went to their rest that night, because it was very late.
Then I saw in my dream, that in the morning the shepherds called up Christian and Hopeful to walk with them upon the mountains; so they went forth with them, and walked a while, having a pleasant prospect on every side. Then said the shepherds one to another, Shall we show these pilgrims some wonders? So when they had concluded to do it, they had them first to the top of a hill called Error, which was very steep on the furthest side, and bid them look down to the bottom. So Christian and Hopeful looked down, and saw at the bottom several men dashed all to pieces by a fall that they had from the top. Then said Christian, What meaneth this? The shepherds answered, Have you not heard of them that were made to err, by hearkening to Hymeneus and Philetus, as concerning the faith of the resurrection of the body? They answered, Yes. Then said the shepherds, Those that you see lie dashed in pieces at the bottom of this mountain are they; and they have continued to this day unburied (as you see) for an example to others to take heed how they clamber too high, or how they come too near the brink of this mountain.
Then I saw that they had them to the top of another mountain, and the name of that is Caution, and bid them look afar off; which when they did, they perceived, as they thought, several men walking up and down among the tombs that were there; and they perceived that the men were blind, because they stumbled sometimes upon the tombs, and because they could not get out from among them. Then said Christian, What means this?
The shepherds then answered, Did you not see a little below these mountains a stile, that led into a meadow, on the left hand of this way? They answered, Yes. Then said the shepherds, From that stile there goes a path that leads directly to Doubting Castle, which is kept by Giant Despair; and these men (pointing to them among the tombs) came once on pilgrimages as you do now, even till they came to that same stile; and because the right way was rough in that place, and they chose to go out of it into that meadow, and there were taken by Giant Despair and cast into Doubting Castle; where, after they had been awhile kept in the dungeon, he at last did put out their eyes, and led them among those tombs, where he has left them to wander to this very day, that the saying of the wise man might be fulfilled, "He that wandereth out of the way of understanding shall remain in the congregation of the dead." Then Christian and Hopeful looked upon one another, with tears gushing out, but yet said nothing to the shepherds.
Then I saw in my dream that the shepherds had them to another place, in a bottom, where was a door in the side of a hill, and they opened the door, and bid them look in. They looked in therefore, and saw that within it was very dark and smoky; they also thought that they heard there a rumbling noise as of fire, and a cry as of some tormented, and that they smelt the scent of brimstone. Then said Christian, What means this?
The shepherds told them, This is a by-way to hell, a way that hypocrites go in at; namely, such as sell their
birthright
, with Esau; such as sell their Master, as Judas; such as blaspheme the Gospel, with Alexander; and that lie and dissemble, with Ananias and Sapphira his wife. Then said Hopeful to the shepherds, I perceive that these had on them, even every one, a show of pilgrimage, as we have now: had they not?Shepherds—Yes, and held it a long time too.
Hopeful—How far might they go on in pilgrimage in their day, since they notwithstanding were thus miserably cast away?
Shepherds—Some further, and some not so far as these mountains.
Then said the pilgrims one to another, We had need to cry to the Strong for strength.
Shepherds—Ay, and you will have need to use it when you have it too.
By this time the pilgrims had a desire to go forwards, and the shepherds a desire they should; so they walked together towards the end of the mountains. Then said the shepherds one to another, Let us here show to the pilgrims the gates of the Celestial City, if they have skill to look through our perspective-glass. The pilgrims then lovingly accepted the motion; so they had them to the top of a high hill, called Clear, and gave them their glass to look.
Then they essayed to look, but the remembrance of that last thing that the shepherds had showed them made their hands shake, by means of which impediment they could not look steadily through the glass; yet they thought they saw something like the gate, and also some of the glory of the place.
CHRISTIANA AND HER COMPANIONS ENTER THE CELESTIAL CITY
From the 'Pilgrim's Progress'
Now while they lay here and waited for the good hour, there was a noise in the town that there was a post come from the Celestial City, with matter of great importance to one Christiana, the wife of Christian the pilgrim. So inquiry was made for her, and the house was found out where she was. So the post presented her with a letter, the contents whereof was, Hail, good woman, I bring thee tidings that the Master calleth for thee, and expecteth that thou shouldest stand in his presence in clothes of immortality, within this ten days.
When he had read this letter to her, he gave her therewith a sure token that he was a true messenger, and was come to bid her make haste to be gone. The token was an arrow with a point sharpened with love, let easily into her heart, which by degrees wrought so effectually with her, that at the time appointed she must be gone.
When Christiana saw that her time was come, and that she was the first of this company that was to go over, she called for Mr. Great-heart her guide, and told him how matters were. So he told her he was heartily glad of the news, and could have been glad had the post come for him. Then she bid that he should give advice how all things should be prepared for her journey. So he told her, saying, Thus and thus it must be, and we that survive will accompany you to the river-side.
Then she called for her children and gave them her blessing, and told them that she yet read with comfort the mark that was set in their foreheads, and was glad to see them with her there, and that they had kept their garments so white. Lastly, she bequeathed to the poor that little she had, and commanded her sons and daughters to be ready against the messenger should come for them.
When she had spoken these words to her guide and to her children, she called for Mr. Valiant-for-truth, and said unto him, Sir, you have in all places showed yourself true-hearted; be faithful unto death, and my King will give you a crown of life. I would also entreat you to have an eye to my children, and if at any time you see them faint, speak comfortably to them. For my daughters, my sons' wives, they have been faithful, and a fulfilling of the promise upon them will be their end. But she gave Mr. Stand-fast a ring.
Then she called for old Mr. Honest and said of him, Behold an Israelite indeed, in whom is no guile. Then said he, I wish you a fair day when you set out for Mount Sion, and shall be glad to see that you go over the river dry-shod. But she answered, Come wet, come dry, I long to be gone, for however the weather is in my journey, I shall have time enough when I come there to sit down and rest me and dry me.
Then came in that good man Mr. Ready-to-halt, to see her. So she said to him, Thy travel hither has been with difficulty, but that will make thy rest the sweeter. But watch and be ready, for at an hour when you think not, the messenger may come.
After him came in Mr. Despondency and his daughter Much-afraid, to whom she said, You ought with thankfulness forever to remember your deliverance from the hands of Giant Despair and out of Doubting Castle. The effect of that mercy is, that you are brought with safety hither. Be ye watchful and cast away fear, be sober and hope to the end.
Then she said to Mr. Feeble-mind, Thou wast delivered from the mouth of Giant Slay-good, that thou mightest live in the light of the living for ever, and see thy King with comfort. Only I advise thee to repent thee of thine aptness to fear and doubt of his goodness before he sends for thee, lest thou shouldest, when he comes, be forced to stand before him for that fault with blushing.
Now the day drew on that Christiana must be gone. So the road was full of people to see her take her journey. But behold, all the banks beyond the river were full of horses and chariots, which were come down from above to accompany her to the city gate. So she came forth and entered the river with a beckon of farewell to those who followed her to the river-side. The last words she was heard to say here was, I come, Lord, to be with thee and bless thee.
So her children and friends returned to their place, for that those that waited for Christiana had carried her out of their sight. So she went and called and entered in at the gate with all the ceremonies of joy that her husband Christian had done before her. At her departure her children wept, but Mr. Great-heart and Mr. Valiant played upon the well-tuned cymbal and harp for joy. So all departed to their respective places.
In process of time there came a post to the town again, and his business was with Mr. Ready-to-halt. So he inquired him out, and said to him, I am come to thee in the name of Him whom thou hast loved and followed, though upon crutches; and my message is to tell thee that he expects thee at his table to sup with him in his kingdom the next day after Easter, wherefore prepare thyself for this journey.
Then he also gave him a token that he was a true messenger, saying, "I have broken thy golden bowl, and loosed thy silver cord."
After this Mr. Ready-to-halt called for his fellow pilgrims, and told them saying, I am sent for, and God shall surely visit you also. So he desired Mr. Valiant to make his will. And because he had nothing to bequeath to them that should survive him but his crutches and his good wishes, therefore thus he said, These crutches I bequeath to my son that shall tread in my steps, with a hundred warm wishes that he may prove better than I have done.
Then he thanked Mr. Great-heart for his conduct and kindness, and so addressed himself to his journey. When he came at the brink of the river he said, Now I shall have no more need of these crutches, since yonder are chariots and horses for me to ride on. The last words he was heard to say were, Welcome, life. So he went his way.
After this Mr. Feeble-mind had tidings brought him that the post sounded his horn at his chamber door. Then he came in and told him, saying, I am come to tell thee that thy Master has need of thee, and that in very little time thou must behold his face in brightness. And take this as a token of the truth of my message, "Those that look out at the windows shall be darkened."
Then Mr. Feeble-mind called for his friends, and told them what errand had been brought unto him, and what token he had received of the truth of the message. Then he said, Since I have nothing to bequeath to any, to what purpose should I make a will? As for my feeble mind, that I will leave behind me, for that I have no need of that in the place whither I go. Nor is it worth bestowing upon the poorest pilgrim; wherefore when I am gone, I desire that you, Mr. Valiant, would bury it in a dung-hill. This done, and the day being come in which he was to depart, he entered the river as the rest. His last words were, Hold out faith and patience. So he went over to the other side.
When days had many of them passed away, Mr. Despondency was sent for. For a post was come, and brought this message to him, Trembling man, these are to summon thee to be ready with thy King by the next Lord's day, to shout for joy for thy deliverance from all thy doubtings.
And said the messenger, That my message is true, take this for a proof; so he gave him "The grasshopper to be a burden unto him." Now Mr. Despondency's daughter, whose name was Much-afraid, said when she heard what was done, that she would go with her father. Then Mr. Despondency said to his friends, Myself and my daughter, you know what we have been, and how troublesomely we have behaved ourselves in every company. My will and my daughter's is, that our desponds and slavish fears be by no man ever received from the day of our departure for ever, for I know that after my death they will offer themselves to others. For to be plain with you, they are ghosts, the which we entertained when we first began to be pilgrims, and could never shake them off after; and they will walk about and seek entertainment of the pilgrims, but for our sakes shut ye the doors upon them.
When the time was come for them to depart, they went to the brink of the river. The last words of Mr. Despondency were, Farewell, night; welcome, day. His daughter went through the river singing, but none could understand what she said.
Then it came to pass a while after, that there was a post in the town that inquired for Mr. Honest.... When the day that he was to be gone was come, he addressed himself to go over the river. Now the river at that time overflowed the banks in some places, but Mr. Honest in his lifetime had spoken to one Good-conscience to meet him there, the which he also did, and lent him his hand, and so helped him over. The last words of Mr. Honest were, Grace reigns. So he left the world.
After this it was noised abroad that Mr. Valiant-for-truth was taken with a summons by the same post as the other, and had this for a token that the summons was true, "That his pitcher was broken at the fountain." When he understood it, he called for his friends, and told them of it. Then said he, I am going to my fathers, and though with great difficulty I am got hither, yet now I do not repent me of all the trouble I have been at to arrive where I am. My sword I give to him that shall succeed me in my pilgrimage, and my courage and skill to him that can get it. My marks and scars I carry with me, to be a witness for me that I have fought his battles who now will be my rewarder. When the day that he must go hence was come, many accompanied him to the river-side, into which as he went he said, Death, where is thy sting? And as he went down deeper he said, Grave, where is thy victory? So he passed over, and all the trumpets sounded for him on the other side.
Then there came forth a summons for Mr. Stand-fast (this Mr. Stand-fast was he that the rest of the pilgrims found upon his knees in the enchanted ground), for the post brought it him open in his hands. The contents whereof were, that he must prepare for a change of life, for his Master was not willing that he should be so far from him any longer. At this Mr. Stand-fast was put into a muse. Nay, said the messenger, you need not doubt of the truth of my message, for here is a token of the truth thereof, "Thy wheel is broken at the cistern." Then he called to him Mr. Great-heart, who was their guide, and said unto him, Sir, although it was not my hap to be much in your good company in the days of my pilgrimage, yet since the time I knew you, you have been profitable to me. When I came from home, I left behind me a wife and five small children: let me entreat you at your return (for I know that you will go and return to your Master's house, in hopes that you may yet be a conductor to more of the holy pilgrims) that you send to my family, and let them be acquainted with all that hath and shall happen unto me. Tell them moreover of my happy arrival to this place, and of the present late blessed condition that I am in. Tell them also of Christian and Christiana his wife, and how she and her children came after her husband. Tell them also of what a happy end she made, and whither she is gone. I have little or nothing to send to my family, except it be prayers and tears for them; of which it will suffice if thou acquaint them, if peradventure they may prevail.
When Mr. Stand-fast had thus set things in order, and the time being come for him to haste him away, he also went down to the river. Now there was a great calm at that time in the river; wherefore Mr. Stand-fast, when he was about half-way in, he stood awhile, and talked to his companions that had waited upon him thither. And he said:—
This river has been a terror to many; yea, the thoughts of it also have often frighted me. But now methinks I stand easy; my foot is fixed upon that upon which the feet of the priests that bare the ark of the covenant stood, while Israel went over this Jordan. The waters indeed are to the palate bitter and to the stomach cold, yet the thought of what I am going to and of the conduct that waits for me on the other side, doth lie as a glowing coal at my heart.
I see myself now at the end of my journey; my toilsome days are ended. I am going now to see that Head that was crowned with thorns, and that Face that was spit upon for me.
I have formerly lived by hearsay and faith, but now I go where I shall live by sight, and shall be with him in whose company I delight myself.
I have loved to hear my Lord spoken of, and wherever I have seen the print of his shoe in the earth, there I have coveted to set my foot too.
His name has been to me as a civet-box, yea, sweeter than all perfumes. His voice to me has been most sweet, and his countenance I have more desired than they that have most desired the light of the sun. His Word I did use to gather for my food, and for antidotes against my faintings. He has held me, and I have kept me from mine iniquities; yea, my steps hath he strengthened in his way.
Now while he was thus in discourse, his countenance changed, his strong man bowed under him, and after he had said, Take me, for I come unto thee, he ceased to be seen of them.
But glorious it was to see how the open region was filled with horses and chariots, with trumpeters and pipers, with singers and players on stringed instruments, to welcome the pilgrims as they went up, and followed one another in at the beautiful gate of the city.
GOTTFRIED AUGUST BÜRGER
(1747-1794)

The ballad of 'Lenore,' upon which Bürger's fame chiefly rests, was published in 1773. It constituted one of the articles in that declaration of independence which the young poets of the time were formulating, and it was more than a mere coincidence that in the same year Herder wrote his essay on 'Ossian' and the 'Songs of Ancient Peoples,' and Goethe unfurled the banner of a new time in 'Götz von Berlichingen.' The artificial and sentimental trivialities of the pigtail age were superseded almost at a stroke, and the petty formalism under which the literature of Germany was languishing fell about the powdered wigs of its professional representatives. The new impulse came from England. As in France, Rousseau, preaching the gospel of a return to nature, found his texts in English writers, so in Germany the poets who inaugurated the classic age derived their chief inspiration from the wholesome heart of England. It was Shakespeare that inspired Goethe's 'Götz'; Ossian and the old English and Scotch folk-songs were Herder's theme; and Percy's 'Reliques' stimulated and saved the genius of Bürger. This was the movement which, for lack of a better term, has been called the naturalistic. Literature once more took possession of the whole range of human life and experience, descending from her artificial throne to live with peasant and people. These ardent innovators spurned all ancient rules and conventions, and in the first ecstasy of their new-found freedom and unchastened strength it is no wonder that they went too far. Goethe and Schiller learned betimes the salutary lesson of artistic restraint. Bürger never learned it.

Gottfried A. Bürger
Bürger was wholly a child of his time. At the age of twenty-six he wrote 'Lenore,' and his genius never again attained that height. Much may be accomplished in the first outburst of youthful energy; but without the self-control which experience should teach, and without the moral character which is the condition of great achievement, genius rots ere it is ripe; and this was the case with Bürger. We are reminded of Burns. Goethe in his seventy-eighth year said to Eckermann:—"What songs Bürger and Voss have written! Who would say that they are less valuable or less redolent of their native soil than the exquisite songs of Burns?" Like Burns, Bürger was of humble origin; like Burns, he gave passion and impulse the reins and drove to his own destruction; like Burns, he left behind him a body of truly national and popular poetry which is still alive in the mouths of the people.
Bürger was born in the last hour of the year 1747 at Molmerswende. His father was a country clergyman, and he himself was sent to Halle at the age of seventeen to study theology. His wild life there led to his removal to Göttingen, where he took up the study of law. He became a member and afterwards the leader of the famous "Göttinger Dichterbund," and was carried away and for a time rescued from his evil courses by his enthusiasm for Shakespeare and Percy's 'Reliques.' He contributed to the newly established Musenalmanach, and from 1779 until his death in 1794 he was its editor. In 1787 the university conferred an honorary degree upon him, and he was soon afterward made a professor without salary, lecturing on Kantian philosophy and æsthetics. Three times he was married; his days were full of financial struggles and self-wrought misery; there is little in his private life that is creditable to record: a dissolute youth was followed by a misguided manhood, and he died in his forty-seventh year.
It fell to the lot of the young Goethe, then an unknown reviewer, to write for the Frankfurter Gelehrte Anzeigen in November, 1772, a notice of some of Bürger's early poems. "The 'Minnelied' of Mr. Bürger," he says, "is worthy of a better age; and if he has more such happy moments, these efforts of his will be among the most potent influences to render our sentimental poetasters, with their gold-paper Amors and Graces and their elysium of benevolence and philanthropy, utterly forgotten." With such clear vision could Goethe see at the age of twenty-three. But he soon saw also the danger that lay in unbridled freedom. For the best that was in Bürger Goethe retained his admiration to the last, but before he was thirty he felt that their ways had parted. Among the 'Maxims and Reflections' we find this note:—"It is sad to see how an extraordinary man may struggle with his time, with his circumstances, often even with himself, and never prosper. Sad example, Bürger!"
Doubtless German literature owes less to Bürger than English owes to Burns, but it owes much. Bürger revived the ballad form in which so much of the finest German poetry has since been cast. With his lyric gifts and his dramatic power, he infused a life into these splendid poems that has made them a part of the folk-lore of his native land. 'Lenardo und Blandine,' his own favorite, 'Des Pfarrers Tochter von Taubenhain' (The Pastor's Daughter of Taubenhain), 'Das Lied vom braven Mann' (The Song of the Brave Man), 'Die Weiber von Weinsberg' (The Women of Weinsberg), 'Der Kaiser und der Abt' (The Emperor and the Abbot), 'Der Wilde Jäger' (The Wild Huntsman), all belong, like 'Lenore,' to the literary inheritance of the German people. Bürger attempted a translation of the Iliad in iambic blank verse, and a prose translation of 'Macbeth.' To him belongs also the credit of having restored to German literature the long-disused sonnet. His sonnets are among the best in the language, and elicited warm praise from Schiller as "models of their kind." Schiller had written a severe criticism of Bürger's poems, which had inflamed party strife and embittered the last years of Bürger himself; but even Schiller admits that Bürger is as much superior to all his rivals as he is inferior to the ideal he should have striven to attain.
The debt which Bürger owed to English letters was amply repaid. In 'Lenore' he showed Percy's 'Reliques' the compliment of quoting from the ballad of 'Sweet William,' which had supplied him with his theme, the lines:—"Is there any room at your head, Willie, or any room at your feet?" The first literary work of Walter Scott was the translation which he made in 1775 of 'Lenore,' under the title of 'William and Helen'; this was quickly followed by a translation of 'The Wild Huntsman.' Scott's romantic mind received in Bürger's ballads and in Goethe's 'Götz,' which he translated four years later, just the nourishment it craved. It is a curious coincidence that another great romantic writer, Alexandre Dumas, should also have begun his literary career with a translation of 'Lenore.' Bürger was not, however, a man of one poem. He filled two goodly volumes, but the oft-quoted words of his friend Schlegel contain the essential truth:—"'Lenore' will always be Bürger's jewel, the precious ring with which, like the Doge of Venice espousing the sea, he married himself to the folk-song forever."
WILLIAM AND HELEN
Walter Scott's Translation of 'Lenore'
From heavy dreams fair Helen rose, And eyed the dawning red:— "Alas, my love, thou tarriest long! O art thou false or dead?"
With gallant Frederick's princely power He sought the bold crusade; But not a word from Judah's wars Told Helen how he sped.
With Paynim and with Saracen At length a truce was made, And every knight returned to dry The tears his love had shed.
Our gallant host was homeward bound With many a song of joy; Green waved the laurel in each plume, The badge of victory.
And old and young, and sire and son, To meet them crowd the way, With shouts, and mirth, and melody, The debt of love to pay.
Full many a maid her true-love met, And sobbed in his embrace, And fluttering joy in tears and smiles Arrayed full many a face.
Nor joy nor smile for Helen sad; She sought the host in vain; For none could tell her William's fate, If faithless or if slain.
The martial band is past and gone; She rends her raven hair, And in distraction's bitter mood She weeps with wild despair.
"O rise, my child," her mother said, "Nor sorrow thus in vain: A perjured lover's fleeting heart No tears recall again."
"O mother, what is gone, is gone, What's lost forever lorn; Death, death alone can comfort me; O had I ne'er been born!
"O break, my heart, O break at once! Drink my life-blood, Despair! No joy remains on earth for me, For me in heaven no share."
"O enter not in judgment, Lord!" The pious mother prays; Impute not guilt to thy frail child! She knows not what she says.
"O say thy paternoster, child! O turn to God and grace! His will, that turned thy bliss to bale, Can change thy bale to bliss."
"O mother, mother, what is bliss? O mother, what is bale? My William's love was heaven on earth; Without it earth is hell.
"Why should I pray to ruthless Heaven, Since my loved William's slain? I only prayed for William's sake, And all my prayers were vain."
"O take the sacrament, my child, And check these tears that flow; By resignation's humble prayer, O hallowed be thy woe!"
"No sacrament can quench this fire, Or slake this scorching pain; No sacrament can bid the dead Arise and live again.
"O break, my heart, O break at once! Be thou my god, Despair! Heaven's heaviest blow has fallen on me. And vain each fruitless prayer."
"O enter not in judgment, Lord, With thy frail child of clay! She knows not what her tongue has spoke; Impute it not, I pray!
"Forbear, my child, this desperate woe, And turn to God and grace; Well can devotion's heavenly glow Convert thy bale to bliss."
"O mother, mother, what is bliss? O mother, what is bale? Without my William what were heaven, Or with him what were hell?"
Wild she arraigns the eternal doom, Upbraids each sacred Power, Till, spent, she sought her silent room, All in the lonely tower.
She beat her breast, she wrung her hands Till sun and day were o'er, And through the glimmering lattice shone The twinkling of the star.
Then, crash! the heavy drawbridge fell That o'er the moat was hung; And, clatter, clatter, on its boards The hoof of courser rung.
The clank of echoing steel was heard As off the rider bounded; And slowly on the winding stair A heavy footstep sounded.
And hark! and hark! a knock—Tap! tap A rustling stifled noise; Door-latch and tinkling staples ring; At length a whispering voice:
"Awake, awake, arise, my love! How, Helen, dost thou fare? Wak'st thou, or sleep'st? laugh'st thou, or weep'st? Hast thought on me, my fair?"
"My love! my love! so late at night! I waked, I wept for thee. Much have I borne since dawn of morn; Where, William, couldst thou be?"
"We saddle late—from Hungary I rode since darkness fell; And to its bourne we both return Before the matin bell."
"O rest this night within my arms, And warm thee in their fold! Chill howls through hawthorn bush the wind;— My love is deadly cold."
"Let the wind howl through hawthorn bush! This night we must away; The steed is wight, the spur is bright; I cannot stay till day.
"Busk, busk, and boune! Thou mount'st behind Upon my black barb steed: O'er stock and stile, a hundred mile, We haste to bridal bed."
"To-night—to-night a hundred miles! O dearest William, stay! The bell strikes twelve—dark, dismal hour! O wait, my love, till day!"
"Look here, look here—the moon shines clear— Full fast I ween we ride; Mount and away! for ere the day We reach our bridal bed.
"The black barb snorts, the bridle rings, Haste, busk, and boune, and seat thee! The feast is made, the chamber spread, The bridal guests await thee."
Strong love prevailed: she busks, she bounes, She mounts the barb behind, And round her darling William's waist Her lily arms she twined.
And, hurry! hurry! off they rode, And fast as fast might be; Spurned from the courser's thundering heels The flashing pebbles flee.
And on the right, and on the left, Ere they could snatch a view, Fast, fast each mountain, mead, and plain, And cot and castle flew.
"Sit fast—dost fear?—The moon shines clear!— Fleet goes my barb—keep hold! Fear'st thou?"—"O no!" she faintly said; "But why so stern and cold?
"What yonder rings, what yonder sings? Why shrieks the owlet gray?"— "'Tis death-bells' clang, 'tis funeral song, The body to the clay.
"With song and clang, at morrow's dawn, Ye may inter the dead; To-night I ride, with my young bride, To deck our bridal bed.
"Come with thy choir, thou coffined guest, To swell our nuptial song! Come, priest, to bless our marriage feast! Come all, come all along!"
Ceased clang and song; down sunk the bier; The shrouded corpse arose: And hurry! hurry! all the train The thundering steed pursues.
And forward, forward, on they go; High snorts the straining steed; Thick pants the rider's laboring breath As headlong on they speed.
"O William, why this savage haste? And where thy bridal bed?" "'Tis distant far,—low, damp, and chill, And narrow,—trustless maid!"
"No room for me?"—"Enough for both; Speed, speed, my barb, thy course!" O'er thundering bridge, through boiling surge, He drove the furious horse.
Tramp! tramp! along the land they rode, Splash! splash! along the sea; The scourge is wight, the spur is bright, The flashing pebbles flee.
Fled past on right and left how fast Each forest, grove, and bower! On right and left fled past how fast Each city, town, and tower!
"Dost fear? dost fear? The moon shines clear, Dost fear to ride with me? Hurrah! hurrah! the dead can ride!"— "O William, let them be!—
"See there, see there! What yonder swings And creaks 'mid whistling rain?" "Gibbet and steel, th' accursed wheel, A murderer in his chain.
"Hollo! thou felon, follow here: To bridal bed we ride; And thou shalt prance a fetter dance Before me and my bride."
And hurry! hurry! clash, clash, clash! The wasted form descends; And fleet as wind through hazel bush The wild career attends.
Tramp! tramp! along the land they rode, Splash! splash! along the sea; The scourge is red, the spur drops blood, The flashing pebbles flee.
How fled what moonshine faintly showed! How fled what darkness hid! How fled the earth beneath their feet, The heaven above their head!
"Dost fear? dost fear? the moon shines clear And well the dead can ride; Dost, faithful Helen, fear for them?"— "O leave in peace the dead!"
"Barb! barb! methinks I hear the cock; The sand will soon be run; Barb! barb! I smell the morning air; The race is well-nigh done."
Tramp! tramp! along the land they rode, Splash! splash! along the sea; The scourge is red, the spur drops blood, The flashing pebbles flee.
"Hurrah! hurrah! well ride the dead; The bride, the bride is come; And soon we reach the bridal bed, For, Helen, here's my home."
Reluctant on its rusty hinge Revolved an iron door, And by the pale moon's setting beam Were seen a church and tower.
With many a shriek and cry whiz round The birds of midnight, scared; And rustling like autumnal leaves Unhallowed ghosts were heard.
O'er many a tomb and tombstone pale He spurred the fiery horse, Till sudden at an open grave He checked the wondrous course.
The falling gauntlet quits the rein, Down drops the casque of steel, The cuirass leaves his shrinking side, The spur his gory heel.
The eyes desert the naked skull, The mold'ring flesh the bone, Till Helen's lily arms entwine A ghastly skeleton.
The furious barb snorts fire and foam, And with a fearful bound, Dissolves at once in empty air, And leaves her on the ground.
Half seen by fits, by fits half heard, Pale spectres flit along, Wheel round the maid in dismal dance, And howl the funeral song:—
"E'en when the heart's with anguish cleft, Revere the doom of heaven. Her soul is from her body reft; Her spirit be forgiven!"
THE WIVES OF WEINSBERG
Which way to Weinsberg? neighbor, say! 'Tis sure a famous city: It must have cradled, in its day, Full many a maid of noble clay. And matrons wise and witty; And if ever marriage should happen to me, A Weinsberg dame my wife shall be.
King Conrad once, historians say, Fell out with this good city; So down he came, one luckless day,— Horse, foot, dragoons,—in stern array,— And cannon,—more's the pity! Around the walls the artillery roared, And bursting bombs their fury poured.
But naught the little town could scare; Then, red with indignation, He bade the herald straight repair Up to the gates, and thunder there The following proclamation:— "Rascals! when I your town do take, No living thing shall save its neck!"
Now, when the herald's trumpet sent These tidings through the city, To every house a death knell went; Such murder-cries the hot air rent Might move the stones to pity. Then bread grew dear, but good advice Could not be had for any price.
Then, "Woe is me!" "O misery!" What shrieks of lamentation! And "Kyrie Eleison!" cried The pastors, and the flock replied, "Lord! save us from starvation!" "Oh, woe is me, poor Corydon— My neck,—my neck! I'm gone,—I'm gone!"
Yet oft, when counsel, deed, and prayer Had all proved unavailing, When hope hung trembling on a hair, How oft has woman's wit been there!— A refuge never failing; For woman's wit and Papal fraud, Of olden time, were famed abroad.
A youthful dame, praised be her name!— Last night had seen her plighted,— Whether in waking hour or dream, Conceived a rare and novel scheme, Which all the town delighted; Which you, if you think otherwise, Have leave to laugh at and despise.
At midnight hour, when culverin And gun and bomb were sleeping, Before the camp with mournful mien, The loveliest embassy were seen, All kneeling low and weeping. So sweetly, plaintively they prayed, But no reply save this was made:—
"The women have free leave to go, Each with her choicest treasure; But let the knaves their husbands know That unto them the King will show The weight of his displeasure." With these sad terms the lovely train Stole weeping from the camp again.
But when the morning gilt the sky. What happened? Give attention:— The city gates wide open fly, And all the wives come trudging by, Each bearing—need I mention?— Her own dear husband on her back, All snugly seated in a sack!
Full many a sprig of court, the joke Not relishing, protested, And urged the King; but Conrad spoke:— "A monarch's word must not be broke!" And here the matter rested. "Bravo!" he cried, "Ha, ha! Bravo! Our lady guessed it would be so."
He pardoned all, and gave a ball That night at royal quarters. The fiddles squeaked, the trumpets blew, And up and down the dancers flew, Court sprigs with city daughters. The mayor's wife—O rarest sight!— Danced with the shoemaker that night!
Ah, where is Weinsberg, sir, I pray? 'Tis sure a famous city: It must have cradled in its day Full many a maid of noble clay, And matrons wise and witty; And if ever marriage should happen to me, A Weinsberg dame my wife shall be.
Translated by C. T. Brooks: Reprinted from 'Representative German Poems' by the courtesy of Mrs. Charles T. Brooks.
EDMUND BURKE
(1729-1797)
BY E. L. GODKIN

Edmund Burke, born in Dublin, Ireland, in 1729, was the son of a successful attorney, who gave him as good an education as the times and the country afforded. He went to school to an excellent Quaker, and graduated at Trinity College in 1748. He appears to have then gone to London in 1750 to "keep terms," as it was called, at the Middle Temple, with the view of being admitted to the bar, in obedience to his father's desire and ambition. But the desultory habit of mind, the preference for literature and philosophical speculation to connected study, which had marked his career in college, followed him and prevented any serious application to the law. His father's patience was after a while exhausted, and he withdrew Burke's allowance and left him to his own resources.
This was in 1755, but in 1756 he married, and made his first appearance in the literary world by the publication of a book. About these years from 1750 to 1759 little is known. He published two works, one a treatise on the 'Origin of our Ideas of the Sublime and Beautiful,' and the other a 'Vindication of Natural Society,' a satire on Bolingbroke. Stray allusions and anecdotes about other men in the diaries and correspondence of the time show that he frequented the literary coffee-houses, and was gradually making an impression on the authors and wits whom he met there. Besides the two books we have mentioned, he produced some smaller things, such as an 'Essay on the Drama,' and part of an 'Abridgment of the History of England.' But although these helped to secure him admission to the literary set, they did not raise him out of the rank of obscure literary adventurers, who from the Revolution of 1688, and especially after the union with Scotland, began to swarm to London from all parts of the three kingdoms. The first recognition of him as a serious writer was his employment by Dodsley the bookseller, at a salary of $100 a year, to edit the Annual Register, which Dodsley founded in 1769. Considered as a biographical episode, this may fairly be treated as a business man's certificate that Burke was industrious and accurate. As his income from his father was withdrawn or reduced in 1755, there remain four years during which his way of supporting himself is unknown. His published works were certainly not "pot-boilers." He was probably to some extent dependent on his wife's father, Dr. Nugent, an Irish physician who when Burke made his acquaintance lived in Bath, but after his daughter's marriage settled in London, and seems to have frequented and have been acceptable in the same coffee-houses as Burke, and for the same reasons. But Burke was not a man to remain long dependent on any one. These nine years were evidently not spent fruitlessly. They had made him known and brought him to the threshold of public life.
In 1759, political discussion as we understand it—that is, those explorations of the foundations of political society and analyses of social relations which now form our daily intellectual food—was hardly known. The interest in religion as the chief human concern was rapidly declining. The interest in human society as an organism to be studied, and if need be, taken to pieces and put together again, was only just beginning. Montesquieu's great work, 'The Spirit of the Laws,' which demanded for expediency and convenience in legislation the place which modern Europe had long assigned to authority, had only appeared in 1748. Swift's satires had made serious breaches in the wall of convention by which the State, in spite of the convulsions of the seventeenth century, was still surrounded. But the writer whose speculations excited most attention in England was Bolingbroke. The charm of his style and the variety of his interests made him the chief intellectual topic of the London world in Burke's early youth. To write like Bolingbroke was a legitimate ambition for a young man. It is not surprising that Burke felt it, and that his earliest political effort was a satire on Bolingbroke. It attracted the attention of a politician, Gerard Hamilton, and he quickly picked up Burke as his secretary, treated him badly, and was abandoned by him in disgust at the end of six years.
The peculiar condition of the English governmental machine made possible for men of Burke's kind at this period what would not be possible now. The population had vanished from a good many old boroughs, although their representation in Parliament remained, and the selection of the members fell to the lords of the soil. About one hundred and fifty members of the House of Commons were in this way chosen by great landed proprietors, and it is to be said to their credit that they used their power freely to introduce unknown young men of talent into public life. Moreover in many cases, if not in most, small boroughs, however well peopled, were expected to elect the proprietor's nominee. Burke after leaving Hamilton's service was for a short time private secretary to Lord Rockingham, when the latter succeeded Grenville in the Ministry in 1766; but when he went out, Burke obtained a seat in Parliament in 1765 in the manner we have described, for the borough of Wendover, from Lord Verney, who owned it. He made his first successful speech the same year, and was complimented by Pitt. He was already recognized as a man of enormous information, as any one who edited the Annual Register had to be.

Edmund Burke.
A man of such powers and tastes in that day naturally became a pamphleteer. Outside of Parliament there was no other mode of discussing public affairs. The periodical press for purposes of discussion did not exist. During and after the Great Rebellion, the pamphlet had made its appearance as the chief instrument of controversy. Defoe used it freely after the Restoration. Swift made a great hit with it, and probably achieved the first sensational sale with his pamphlet on 'The Conduct of the Allies.' Bolingbroke's 'Patriot King' was a work of the same class. As a rule the pamphlet exposed or refuted somebody, even if it also freely expounded. It was inevitable that Burke should early begin to wield this most powerful of existing weapons. His antagonist was ready for him in the person of George Grenville, the minister who had made way for Burke's friend and patron Lord Rockingham. Grenville showed, as easily as any party newspaper in our own day, that Rockingham and his friends had ruined the country by mismanagement of the war and of the finances. Burke refuted him with a mastery of facts and figures, and a familiarity with the operations of trade and commerce, and a power of exposition and illustration, and a comprehension of the fundamental conditions of national economy, which at once made him famous and a necessary man for the Whigs in the great struggle with the Crown on which they were entering.
The nature of this struggle cannot be better described in brief space than by saying that the King, from his accession to the throne down to the close of the American War, was engaged in a persistent effort to govern through ministers chosen and dismissed, as the German ministers are now, by himself; while the subservience of Parliament was secured by the profuse use of pensions and places. To this attempt, and all the abuses which inevitably grew out of it, the Whigs with Burke as their intellectual head offered a determined resistance, and the conflict was one extraordinarily well calculated to bring his peculiar powers into play.
The leading events in this long struggle were the attempt of the House of Commons to disqualify Wilkes for a seat in the House, to punish reporting their debates as a breach of privilege, and the prosecution of the war against the American colonies. It may be said to have begun at the accession of the King, and to have lasted until the resignation of Lord North after the surrender of Cornwallis, or from 1770 to 1783.
Burke's contributions to it were his pamphlet, 'Thoughts on the Cause of the Present Discontents,' and several speeches in Parliament: the first, like the pamphlet, on the general situation, and others on minor incidents in the struggle. This pamphlet has not only survived the controversy, but has become one of the most famous papers in the political literature of the Anglo-Saxon race. It is a century since every conspicuous figure in the drama passed away; it is seventy years since every trace of the controversy disappeared from English political life; most if not all of the principles for which Burke contended have become commonplaces of English constitutional practice; the discontents of that day have vanished as completely as those of 1630: but Burke's pamphlet still holds a high place in every course of English literature, and is still read and pondered by every student of constitutional history and by every speculator on government and political morals.
In 1774 Parliament was dissolved for the second time since Burke entered it: and there a misfortune overtook him which illustrated in a striking way the practical working of the British Constitution at that period. Lord Verney, to whom he had owed his seat for the borough of Wendover at two elections, had fallen into pecuniary embarrassment and could no longer return him, because compelled to sell his four boroughs. This left Burke high and dry, and he was beginning to tremble for his political future, when he was returned for the great commercial city of Bristol by a popular constituency. The six years during which he sat for Bristol were the most splendid portion of his career. Other portions perhaps contributed as much if not more to his literary or oratorical reputation; but this brought out in very bold relief the great traits of character which will always endear his memory to the lovers of national liberty, and place him high among the framers of great political ideals. In the first place, he propounded boldly to the Bristol electors the theory that he was to be their representative but not their delegate; that his parliamentary action must be governed by his own reason and not by their wishes. In the next, he resolutely sacrificed his seat by opposing his constituents in supporting the removal of the restrictions on Irish trade, of which English merchants reaped the benefit. He would not be a party to what he considered the oppression of his native country, no matter what might be the effect on his political prospects; and in 1780 he was not re-elected.
But the greatest achievement of this period of his history was his share in the controversy over the American War, which was really not more a conflict with the colonies over taxation, than a resolute and obstinate carrying out of the King's principles of government. The colonies were, for the time being, simply resisting pretensions to which the kingdom at home submitted. Burke's speeches on 'American Taxation' (1774), on 'Conciliation with America' (1775), and his 'Letter to the Sheriffs of Bristol' (1777) on the same subject, taken as a sequel to the 'Thoughts on the Present Discontents,' form a body of literature which it is not too much to pronounce not only a history of the dispute with the colonies, but a veritable political manual. He does not confine himself to a minute description of the arguments used in supporting the attempt to coerce America; he furnishes as he goes along principles of legislation applicable almost to any condition of society; illustrations which light up as by a single flash problems of apparently inscrutable darkness; explanations of great political failures; and receipts innumerable for political happiness and success. A single sentence often disposes of half a dozen fallacies firmly imbedded in governmental tradition. His own description of the rhetorical art of Charles Townshend was eminently applicable to himself:—"He knew, better by far than any man I ever was acquainted with, how to bring together within a short time all that was necessary to establish, to illustrate, and to decorate that side of the question which he supported."
This observation suggests the great advantage he derives as a political instructor from the facts that all his political speeches and writings are polemical. The difficulty of keeping exposition from being dry is familiar to everybody who has ever sought to communicate knowledge on any subject. But Burke in every one of his political theses had an antagonist, who was literally as he says himself, a helper: who did the work of an opposing counsel at the bar, in bringing out into prominence all the weak points of Burke's case and all the strong ones of his own; who set in array all the fallacies to be exposed, all the idols to be overthrown, all the doubts to be cleared up. Moreover he was not, like the man who usually figures in controversial dialogues, a sham opponent, but a creature of flesh and blood like Grenville, or the Sheriffs of Bristol, or the King's friends, or the Irish Protestant party, who met Burke with an ardor not inferior to his own. We consequently have, in all his papers and speeches, the very best of which he was capable in thought and expression, for he had not only to watch the city but to meet the enemy in the gate.
After the close of the American War, the remainder of Burke's career was filled with two great subjects, to which he devoted himself with an ardor which occasionally degenerated into fanaticism. One was the government of India by the East India Company, and the other was the French Revolution. Although the East India Company had been long in existence, and had towards the middle of the eighteenth century been rapidly extending its power and influence, comparatively little had been known by the English public of the nature of its operations. Attention had been drawn away from it by the events in America and the long contest with the King in England. By the close of the American War, however, the "Nabobs," as they were called,—or returned English adventurers,—began to make a deep impression on English society by the apparent size of their fortunes and the lavishness of their expenditure. Burke calculated that in his time they had brought home about $200,000,000, with which they bought estates and seats in Parliament and became a very conspicuous element in English public and private life. At the same time, information as to the mode in which their money was made and their government carried on was scanty and hard to acquire. The press had no foreign correspondence; India was six months away, and all the Europeans in it were either servants of the Company, or remained in it on the Company's sufferance. The Whigs finally determined to attempt a grand inquisition into its affairs, and a bill was brought in by Fox, withdrawing the government of India from the Company and vesting it in a commission named in the bill. This was preceded by eleven reports from a Committee of Inquiry. But the bill failed utterly, and brought down the Whig ministry, which did not get into office again in Burke's time. This was followed in 1785, on Burke's instigation, by the impeachment of the most conspicuous of the Company's officers, Warren Hastings. Burke was appointed one of the managers on behalf of the Commons.
No episode in his career is so familiar to the public as his conduct of this trial, owing to Warren Hastings having been the subject of one of the most popular of Macaulay's Essays. None brought out more clearly Burke's great dialectical powers, or so well displayed his mastery of details and his power of orderly exposition. The trial lasted eight years, and was adjourned over from one Parliamentary session to another. These delays were fatal to its success. The public interest in it died out long before the close, as usual in protracted legal prosecutions; the feeling spread that the defendant could not be very guilty when it took so long to prove his crime. Although Burke toiled over the case with extraordinary industry and persistence, and an enthusiasm which never flagged, Hastings was finally acquitted.
But the labors of the prosecution were not wholly vain. It awoke in England an attention to the government of India which never died out, and led to a considerable curtailing of the power of the East India Company, and necessarily of its severity, in dealing with Indian States. The impeachment was preceded by eleven reports on the affairs of India by the Committee of the House of Commons, and the articles of impeachment were nearly as voluminous. Probably no question which has ever come before Parliament has received so thorough an examination. Hardly less important was the report of the Committee of the Commons (which consisted of the managers of the impeachment) on the Lords' journals. This was an elaborate examination of the rules of evidence which govern proceedings in the trial of impeachments, or of persons guilty of malfeasance in office. This has long been a bone of contention between lawyers and statesmen. The Peers in the course of the trial had taken the opinion of the judges frequently, and had followed it in deciding on the admissibility of evidence, a great deal of which was important to the prosecution. The report maintained, and with apparently unanswerable force, that when a legislature sits on offenses against the State, it constitutes a grand inquest which makes its own rules of evidence; and is not and ought not to be tied up by the rules administered in the ordinary law courts, and formed for the most part for the guidance of the unskilled and often uneducated men who compose juries. As a manual for the instruction of legislative committees of inquiry it is therefore still very valuable, if it be not a final authority.
Burke, during and after the Warren Hastings trial, fell into considerable neglect and unpopularity. His zeal in the prosecution had grown as the public interest in it declined, until it approached the point of fanaticism. He took office in the coalition which succeeded the Fox Whigs, and when the French Revolution broke out it found him somewhat broken in nerves, irritated by his failures, and in less cordial relations with some of his old friends and colleagues. He at once arrayed himself fiercely against the Revolution, and broke finally with what might be called the Liberty of all parties and creeds, and stood forth to the world as the foremost champion of authority, prescription, and precedent. Probably none of his writings are so familiar to the general public as those which this crisis produced, such as the 'Thoughts on the French Revolution' and the 'Letters on a Regicide Peace.' They are and will always remain, apart from the splendor of the rhetoric, extremely interesting as the last words spoken by a really great man on behalf of the old order. Old Europe made through him the best possible defense of itself. He told, as no one else could have told it, the story of what customs, precedent, prescription, and established usage had done for its civilization; and he told it nevertheless as one who was the friend of rational progress, and had taken no small part in promoting it. Only one other writer who followed him came near equaling him as a defender of the past, and that was Joseph de Maistre; but he approached the subject mainly from the religious side. To him the old régime was the order of Providence. To Burke it was the best scheme of things that humanity could devise for the advancement and preservation of civilization. In the papers we have mentioned, which were the great literary sensations of Burke's day, everything that could be said for the system of political ethics under which Europe had lived for a thousand years was said with a vigor, incisiveness, and wealth of illustration which must make them for all time and in all countries the arsenal of those who love the ancient ways and dread innovation.
The failure of the proceedings against Warren Hastings, and the strong sympathy with the French Revolution—at least in its beginning—displayed by the Whigs and by most of those with whom Burke had acted in politics, had an unfortunate effect on his temper. He broke off his friendship with Fox and others of his oldest associates and greatest admirers. He became hopeless and out of conceit with the world around him. One might have set down some of this at least to the effect of advancing years and declining health, if such onslaughts on revolutionary ideas as his 'Reflections on the French Revolution' and his 'Letters on a Regicide Peace' did not reveal the continued possession of all the literary qualities which had made the success of his earlier works. Their faults are literally the faults of youth: the brilliancy of the rhetoric, the heat of the invective, the violence of the partisanship, the reluctance to admit the existence of any grievances in France to justify the popular onslaught on the monarchy, the noblesse, and the Church. His one explanation of the crisis and its attendant horrors was the instigation of the spirit of evil. The effect on contemporary opinion was very great, and did much to stimulate the conservative reaction in England which carried on the Napoleonic wars and lasted down to the passage of the Reform Bill in 1832.
There were, however, other causes for the cloud which came over Burke's later years. In spite of his great services to his party and his towering eminence as an orator and writer, he never obtained a seat in the Cabinet. The Paymastership of the Forces, at a salary of $20,000 a year, was the highest reward, either in honor or money, which his party ever bestowed on him. It is true that in those days the Whigs were very particular in reserving high places for men of rank and family. In fact, their government was, from the Revolution of 1688 on, a thorough oligarchy, divided among a few great houses. That they should not have broken through this rule in Burke's case, and admitted to the Cabinet a man to whom they owed so much as they did to him, excited wonder in his own day, and has down to our own time been one of the historical mysteries on which the students of that period love to expend their ingenuity. It is difficult to reconcile this exclusion and neglect of Burke with the unbounded admiration lavished on him by the aristocratic leaders of the party. It is difficult too to account for Burke's quiet acquiescence in what seems to be their ingratitude. There had before his time been no similar instance of party indifference to such claims as he could well make, on such honors and rewards as the party had to bestow.
The most probable explanation of the affair is the one offered by his latest and ablest biographer, Mr. John Morley. Burke had entered public life without property,—probably the most serious mistake, if in his case it can be called a mistake, which an English politician can commit. It is a wise and salutary rule of English public life that a man who seeks a political career shall qualify for it by pecuniary independence. It would be hardly fair in Burke's case to say that he had sought a political career. The greatness of his talents literally forced it on him. He became a statesman and great Parliamentary orator, so to speak, in spite of himself. But he must have early discovered the great barrier to complete success created by his poverty. He may be said to have passed his life in pecuniary embarrassment. This alone might not have shut him out from the Whig official Paradise, for the same thing might have been said of Pitt and Fox: but they had connections; they belonged by birth and association to the Whig class. Burke's relatives were no help or credit to him. In fact, they excited distrust of him. They offended the fastidious aristocrats with whom he associated, and combined with his impecuniousness to make him seem unsuitable for a great place. These aristocrats were very good to him. They lent him money freely, and settled a pension on him, and covered him with social adulation; but they were never willing to put him beside themselves in the government. His latter years therefore had an air of tragedy. He was unpopular with most of those who in his earlier years had adored him, and was the hero of those whom in earlier years he had despised. His only son, of whose capacity he had formed a strange misconception, died young, and he passed his own closing hours, as far as we can judge, with a sense of failure. But he left one of the great names in English history. There is no trace of him in the statute book, but he has, it is safe to say, exercised a profound influence in all succeeding legislation, both in England and America. He has inspired or suggested nearly all the juridical changes which distinguish the England of to-day from the England of the last century, and is probably the only British politician whose speeches and pamphlets, made for immediate results, have given him immortality.
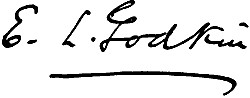
FROM THE SPEECH ON 'CONCILIATION WITH AMERICA'
Sir,—It is not a pleasant consideration; but nothing in the world can read so awful and so instructive a lesson as the conduct of the Ministry in this business, upon the mischief of not having large and liberal ideas in the management of great affairs. Never have the servants of the State looked at the whole of your complicated interests in one connected view. They have taken things by bits and scraps, some at one time and one pretense and some at another, just as they pressed, without any sort of regard to their relations or dependencies. They never had any kind of system, right or wrong; but only invented occasionally some miserable tale for the day, in order meanly to sneak out of difficulties into which they had proudly strutted. And they were put to all these shifts and devices, full of meanness and full of mischief, in order to pilfer piecemeal a repeal of an act which they had not the generous courage, when they found and felt their error, honorably and fairly to disclaim. By such management, by the irresistible operation of feeble counsels, so paltry a sum as Threepence in the eyes of a financier, so insignificant an article as Tea in the eyes of a philosopher, have shaken the pillars of a commercial empire that circled the whole globe.
Do you forget that in the very last year you stood on the precipice of general bankruptcy? Your danger was indeed great. You were distressed in the affairs of the East India Company; and you well know what sort of things are involved in the comprehensive energy of that significant appellation. I am not called upon to enlarge to you on that danger; which you thought proper yourselves to aggravate, and to display to the world with all the parade of indiscreet declamation. The monopoly of the most lucrative trades and the possession of imperial revenues had brought you to the verge of beggary and ruin. Such was your representation—such, in some measure, was your case. The vent of ten millions of pounds of this commodity, now locked up by the operation of an injudicious tax and rotting in the warehouses of the company, would have prevented all this distress, and all that series of desperate measures which you thought yourselves obliged to take in consequence of it. America would have furnished that vent which no other part of the world can furnish but America, where tea is next to a necessary of life and where the demand grows upon the supply. I hope our dear-bought East India Committees have done us at least so much good as to let us know that without a more extensive sale of that article, our East India revenues and acquisitions can have no certain connection with this country. It is through the American trade of tea that your East India conquests are to be prevented from crushing you with their burden. They are ponderous indeed, and they must have that great country to lean upon, or they tumble upon your head. It is the same folly that has lost you at once the benefit of the West and of the East. This folly has thrown open folding-doors to contraband, and will be the means of giving the profits of the trade of your colonies to every nation but yourselves. Never did a people suffer so much for the empty words of a preamble. It must be given up. For on what principles does it stand? This famous revenue stands, at this hour, on all the debate, as a description of revenue not as yet known in all the comprehensive (but too comprehensive!) vocabulary of finance—a preambulary tax. It is indeed a tax of sophistry, a tax of pedantry, a tax of disputation, a tax of war and rebellion, a tax for anything but benefit to the imposers or satisfaction to the subject....
Could anything be a subject of more just alarm to America than to see you go out of the plain high-road of finance, and give up your most certain revenues and your clearest interests, merely for the sake of insulting your colonies? No man ever doubted that the commodity of tea could bear an imposition of threepence. But no commodity will bear threepence, or will bear a penny, when the general feelings of men are irritated; and two millions of people are resolved not to pay. The feelings of the colonies were formerly the feelings of Great Britain. Theirs were formerly the feelings of Mr. Hampden when called upon for the payment of twenty shillings. Would twenty shillings have ruined Mr. Hampden's fortune? No! but the payment of half twenty shillings, on the principle it was demanded, would have made him a slave. It is the weight of that preamble of which you are so fond, and not the weight of the duty, that the Americans are unable and unwilling to bear.
It is then, sir, upon the principle of this measure, and nothing else, that we are at issue. It is a principle of political expediency. Your Act of 1767 asserts that it is expedient to raise a revenue in America; your Act of 1769, which takes away that revenue, contradicts the Act of 1767, and by something much stronger than words asserts that it is not expedient. It is a reflection upon your wisdom to persist in a solemn Parliamentary declaration of the expediency of any object for which at the same time you make no sort of provision. And pray, sir, let not this circumstance escape you,—it is very material: that the preamble of this Act which we wish to repeal is not declaratory of a right, as some gentlemen seem to argue it; it is only a recital of the expediency of a certain exercise of a right supposed already to have been asserted; an exercise you are now contending for by ways and means which you confess, though they were obeyed, to be utterly insufficient for their purpose. You are therefore at this moment in the awkward situation of fighting for a phantom, a quiddity, a thing that wants not only a substance, but even a name; for a thing which is neither abstract right nor profitable enjoyment.
They tell you, sir, that your dignity is tied to it. I know not how it happens, but this dignity of yours is a terrible incumbrance to you; for it has of late been ever at war with your interest, your equity, and every idea of your policy. Show the thing you contend for to be reason; show it to be common-sense; show it to be the means of attaining some useful end: and then I am content to allow it what dignity you please. But what dignity is derived from the perseverance in absurdity, is more than ever I could discern. The honorable gentleman has said well—indeed, in most of his general observations I agree with him—he says that this subject does not stand as it did formerly. Oh, certainly not! Every hour you continue on this ill-chosen ground, your difficulties thicken on you; and therefore my conclusion is, remove from a bad position as quickly as you can. The disgrace and the necessity of yielding, both of them, grow upon you every hour of your delay....
To restore order and repose to an empire so great and so distracted as ours, is, merely in the attempt, an undertaking that would ennoble the flights of the highest genius and obtain pardon for the efforts of the meanest understanding. Struggling a good while with these thoughts, by degrees I felt myself more firm. I derived at length some confidence from what in other circumstances usually produces timidity. I grew less anxious, even from the idea of my own insignificance. For, judging of what you are by what you ought to be, I persuaded myself that you would not reject a reasonable proposition because it had nothing but its reason to recommend it. On the other hand, being totally destitute of all shadow of influence, natural or adventitious, I was very sure that if my proposition were futile or dangerous, if it were weakly conceived or improperly timed, there was nothing exterior to it of power to awe, dazzle, or delude you. You will see it just as it is; and you will treat it just as it deserves.
The proposition is Peace. Not Peace through the medium of War; not Peace to be hunted through the labyrinth of intricate and endless negotiations; not Peace to arise out of universal discord, fomented from principle in all parts of the empire; not Peace to depend on the juridical determination of perplexing questions, or the precise marking of the shadowy boundaries of a complex government. It is simple Peace, sought in its natural course and in its ordinary haunts. It is Peace sought in the spirit of Peace, and laid in principles purely pacific. I propose by removing the ground of the difference, and by restoring the former unsuspecting confidence of the colonies in the mother country, to give permanent satisfaction to your people; and (far from a scheme of ruling by discord) to reconcile them to each other in the same act and by the bond of the very same interest which reconciles them to British government.
My idea is nothing more. Refined policy ever has been the parent of confusion, and ever will be so, as long as the world endures. Plain good intention, which is as easily discovered at the first view as fraud is surely detected at last, is, let me say, of no mean force in the government of mankind. Genuine simplicity of heart is an healing and cementing principle. My plan, therefore, being formed upon the most simple grounds imaginable, may disappoint some people when they hear it. It has nothing to recommend it to the pruriency of curious ears. There is nothing at all new and captivating in it. It has nothing of the splendor of the project which has been lately laid upon your table by the noble lord in the blue ribbon. It does not propose to fill your lobby with squabbling colony agents, who will require the interposition of your mace at every instant to keep the peace amongst them. It does not institute a magnificent auction of finance, where captivated provinces come to general ransom by bidding against each other, until you knock down the hammer, and determine a proportion of payments beyond all the powers of algebra to equalize and settle.
The plan which I shall presume to suggest derives, however, one great advantage from the proposition and registry of that noble lord's project. The idea of conciliation is admissible. First, the House, in accepting the resolution moved by the noble lord, has admitted—notwithstanding the menacing front of our address, notwithstanding our heavy bills of pains and penalties—that we do not think ourselves precluded from all ideas of free grace and bounty.
The House has gone further: it has declared conciliation admissible, previous to any submission on the part of America. It has even shot a good deal beyond that mark, and has admitted that the complaints of our former mode of exerting the right of taxation were not wholly unfounded. That right, thus exerted, is allowed to have something reprehensible in it—something unwise, or something grievous: since in the midst of our heat and resentment we of ourselves have proposed a capital alteration, and in order to get rid of what seemed so very exceptionable have instituted a mode that is altogether new; one that is indeed wholly alien from all the ancient methods and forms of Parliament.
The principle of this proceeding is large enough for my purpose. The means proposed by the noble lord for carrying his ideas into execution, I think indeed are very indifferently suited to the end; and this I shall endeavor to show you before I sit down. But for the present I take my ground on the admitted principle. I mean to give peace. Peace implies reconciliation; and where there has been a material dispute, reconciliation does in a manner always imply concession on the one part or on the other. In this state of things I make no difficulty in affirming that the proposal ought to originate from us. Great and acknowledged force is not impaired, either in effect or in opinion, by an unwillingness to exert itself. The superior power may offer peace with honor and safety. Such an offer from such a power will be attributed to magnanimity. But the concessions of the weak are the concessions of fear. When such a one is disarmed, he is wholly at the mercy of his superior, and he loses forever that time and those chances which, as they happen to all men, are the strength and resources of all inferior power.
The capital leading questions on which you must this day decide are these two: First, whether you ought to concede; and secondly, what your concession ought to be. On the first of these questions we have gained (as I have just taken the liberty of observing to you) some ground. But I am sensible that a good deal more is still to be done. Indeed, sir, to enable us to determine both on the one and the other of these great questions with a firm and precise judgment, I think it may be necessary to consider distinctly the true nature and the peculiar circumstances of the object which we have before us. Because after all our struggle, whether we will or not, we must govern America according to that nature and to those circumstances, and not according to our own imaginations nor according to abstract ideas of right; by no means according to mere general theories of government, the resort to which appears to me, in our present situation, no better than arrant trifling. I shall therefore endeavor, with your leave, to lay before you some of the most material of these circumstances in as full and as clear a manner as I am able to state them.
FROM THE SPEECH ON 'THE NABOB OF ARCOT'S DEBTS'
That you may judge what chance any honorable and useful end of government has for a provision that comes in for the leavings of these gluttonous demands, I must take it on myself to bring before you the real condition of that abused, insulted, racked, and ruined country, though in truth my mind revolts from it; though you will hear it with horror: and I confess I tremble when I think on these awful and confounding dispensations of Providence. I shall first trouble you with a few words as to the cause.
The great fortunes made in India in the beginnings of conquest naturally excited an emulation in all the parts, and through the whole succession, of the company's service. But in the company it gave rise to other sentiments. They did not find the new channels of acquisition flow with equal riches to them. On the contrary, the high flood-tide of private emolument was generally in the lowest ebb of their affairs. They began also to fear that the fortune of war might take away what the fortune of war had given. Wars were accordingly discouraged by repeated injunctions and menaces; and that the servants might not be bribed into them by the native princes, they were strictly forbidden to take any money whatsoever from their hands. But vehement passion is ingenious in resources. The company's servants were not only stimulated but better instructed by the prohibition. They soon fell upon a contrivance which answered their purposes far better than the methods which were forbidden; though in this also they violated an ancient, but they thought an abrogated, order. They reversed their proceedings. Instead of receiving presents, they made loans. Instead of carrying on wars in their own name, they contrived an authority, at once irresistible and irresponsible, in whose name they might ravage at pleasure; and being thus freed from all restraint, they indulged themselves in the most extravagant speculations of plunder. The cabal of creditors who have been the object of the late bountiful grant from His Majesty's ministers, in order to possess themselves, under the name of creditors and assignees, of every country in India as fast as it should be conquered, inspired into the mind of the Nabob of Arcot (then a
dependent
on the company of the humblest order) a scheme of the most wild and desperate ambition that I believe ever was admitted into the thoughts of a man so situated. First, they persuaded him to consider himself as a principal member in the political system of Europe. In the next place they held out to him, and he readily imbibed, the idea of the general empire of Indostan. As a preliminary to this undertaking, they prevailed on him to propose a tripartite division of that vast country—one part to the company; another to the Mahrattas; and the third to himself. To himself he reserved all the southern part of the great peninsula, comprehended under the general name of the Deccan.On this scheme of their servants, the company was to appear in the Carnatic in no other light than as a contractor for the provision of armies and hire of mercenaries, for his use and under his direction. This disposition was to be secured by the Nabob's putting himself under the guarantee of France, and by the means of that rival nation preventing the English forever from assuming an equality, much less a superiority, in the Carnatic. In pursuance of this treasonable project (treasonable on the part of the English), they extinguished the company as a sovereign power in that part of India; they withdrew the company's garrisons out of all the forts and strongholds of the Carnatic; they declined to receive the ambassadors from foreign courts, and remitted them to the Nabob of Arcot; they fell upon, and totally destroyed, the oldest ally of the company, the king of Tanjore, and plundered the country to the amount of near five millions sterling; one after another, in the Nabob's name but with English force, they brought into a miserable servitude all the princes and great independent nobility of a vast country. In proportion to these treasons and violences, which ruined the people, the fund of the Nabob's debt grew and flourished.
Among the victims to this magnificent plan of universal plunder, worthy of the heroic avarice of the projectors, you have all heard (and he has made himself to be well remembered) of an Indian chief called Hyder Ali Khan. This man possessed the western, as the company under the name of the Nabob of Arcot does the eastern, division of the Carnatic. It was among the leading measures in the design of this cabal (according to their own emphatic language) to extirpate this Hyder Ali. They declared the Nabob of Arcot to be his sovereign, and himself to be a rebel, and publicly invested their instrument with the sovereignty of the kingdom of Mysore. But their victim was not of the passive kind. They were soon obliged to conclude a treaty of peace and close alliance with this rebel at the gates of Madras. Both before and since that treaty, every principle of policy pointed out this power as a natural alliance; and on his part it was courted by every sort of amicable office. But the cabinet council of English creditors would not suffer their Nabob of Arcot to sign the treaty, nor even to give to a prince at least his equal the ordinary titles of respect and courtesy. From that time forward, a continued plot was carried on within the divan, black and white, of the Nabob of Arcot, for the destruction of Hyder Ali. As to the outward members of the double, or rather treble, government of Madras, which had signed the treaty, they were always prevented by some over-ruling influence (which they do not describe but which cannot be misunderstood) from performing what justice and interest combined so evidently to enforce.
When at length Hyder Ali found that he had to do with men who either would sign no convention, or whom no treaty and no signature could bind, and who were the determined enemies of human intercourse itself, he decreed to make the country possessed by these incorrigible and predestinated criminals a memorable example to mankind. He resolved, in the gloomy recesses of a mind capacious of such things, to leave the whole Carnatic an everlasting monument of vengeance, and to put perpetual desolation as a barrier between him and those against whom the faith which holds the moral elements of the world together was no protection. He became at length so confident of his force, so collected in his might, that he made no secret whatsoever of his dreadful resolution. Having terminated his disputes with every enemy and every rival, who buried their mutual animosities in their common detestation against the creditors of the Nabob of Arcot, he drew from every quarter whatever a savage ferocity could add to his new rudiments in the arts of destruction; and compounding all the materials of fury, havoc, and desolation into one black cloud, he hung for a while on the declivities of the mountains. Whilst the authors of all these evils were idly and stupidly gazing on this menacing meteor, which blackened all their horizon, it suddenly burst and poured down the whole of its contents upon the plains of the Carnatic. Then ensued a scene of woe, the like of which no eye had seen, no heart conceived, and which no tongue can adequately tell. All the horrors of war before known or heard of were mercy to that new havoc. A storm of universal fire blasted every field, consumed every house, destroyed every temple. The miserable inhabitants, flying from their flaming villages, in part were slaughtered; others, without regard to sex, to age, to the respect of rank, or sacredness of function,—fathers torn from children, husbands from wives,—enveloped in a whirlwind of cavalry, and amidst the goading spears of drivers and the trampling of pursuing horses, were swept into captivity in an unknown and hostile land. Those who were able to evade this tempest fled to the walled cities: but escaping from fire, sword, and exile, they fell into the jaws of famine.
The alms of the settlement in this dreadful exigency were certainly liberal, and all was done by charity that private charity could do: but it was a people in beggary; it was a nation which stretched out its hands for food. For months together these creatures of sufferance,—whose very excess of luxury in their most plenteous days had fallen short of the allowance of our austerest fasts,—silent, patient, resigned, without sedition or disturbance, almost without complaint, perished by an hundred a day in the streets of Madras; every day seventy at least laid their bodies in the streets, or on the glacis of Tanjore, and expired of famine in the granary of India. I was going to awake your justice towards this unhappy part of our fellow-citizens by bringing before you some of the circumstances of this plague of hunger. Of all the calamities which beset and waylay the life of man, this comes the nearest to our heart, and is that wherein the proudest of us all feels himself to be nothing more than he is: but I find myself unable to manage it with decorum; these details are of a species of horror so nauseous and disgusting, they are so degrading to the sufferers and to the hearers, they are so humiliating to human nature itself, that on better thoughts I find it more advisable to throw a pall over this hideous object, and to leave it to your general conceptions.
For eighteen months without intermission this destruction raged from the gates of Madras to the gates of Tanjore; and so completely did these masters in their art, Hyder Ali and his more ferocious son, absolve themselves of their impious vow, that when the British armies traversed, as they did, the Carnatic for hundreds of miles in all directions, through the whole line of their march they did not see one man, not one woman, not one child, not one four-footed beast of any description whatever. One dead uniform silence reigned over the whole region. With the inconsiderable exceptions of the narrow vicinage of some few forts, I wish to be understood as speaking literally;—I mean to produce to you more than three witnesses, above all exception, who will support this assertion in its full extent. That hurricane of war passed through every part of the central provinces of the Carnatic. Six or seven districts to the north and to the south (and those not wholly untouched) escaped the general ravage.
The Carnatic is a country not much inferior in extent to England. Figure to yourself, Mr. Speaker, the land in whose representative chair you sit; figure to yourself the form and fashion of your sweet and cheerful country from Thames to Trent north and south, and from the Irish to the German Sea east and west, emptied and emboweled (may God avert the omen of our crimes!) by so accomplished a desolation. Extend your imagination a little farther, and then suppose your ministers taking a survey of this scene of waste and desolation; what would be your thoughts if you should be informed that they were computing how much had been the amount of the excises, how much the customs, how much the land and malt tax, in order that they should charge (take it in the most favorable light) for public service, upon the relics of the satiated vengeance of relentless enemies, the whole of what England had yielded in the most exuberant seasons of peace and abundance? What would you call it? To call it tyranny sublimed into madness would be too faint an image; yet this very madness is the principle upon which the ministers at your right hand have proceeded in their estimate of the revenues of the Carnatic, when they were providing, not supply for the establishments of its protection, but rewards for the authors of its ruin.
Every day you are fatigued and disgusted with this cant:—"The Carnatic is a country that will soon recover, and become instantly as prosperous as ever." They think they are talking to innocents, who will believe that by sowing of dragons' teeth, men may come up ready grown and ready armed. They who will give themselves the trouble of considering (for it requires no great reach of thought, no very profound knowledge) the manner in which mankind are increased and countries cultivated, will regard all this raving as it ought to be regarded. In order that the people, after a long period of vexation and plunder, may be in a condition to maintain government, government must begin by maintaining them. Here the road to economy lies not through receipt, but through expense; and in that country nature has given no short cut to your object. Men must propagate, like other animals, by the mouth. Never did oppression light the nuptial torch; never did extortion and usury spread out the genial bed. Does any of you think that England, so wasted, would, under such a nursing attendance, so rapidly and cheaply recover? But he is meanly acquainted with either England or India, who does not know that England would a thousand times sooner resume population, fertility, and what ought to be the ultimate secretion from both,—revenue,—than such a country as the Carnatic.
The Carnatic is not by the bounty of nature a fertile soil. The general size of its cattle is proof enough that it is much otherwise. It is some days since I moved that a curious and interesting map kept in the India House should be laid before you. The India House is not yet in readiness to send it; I have therefore brought down my own copy, and there it lies for the use of any gentleman who may think such a matter worthy of his attention. It is indeed a noble map, and of noble things; but it is decisive against the golden dreams and sanguine speculations of avarice run mad. In addition to what you know must be the case in every part of the world (the necessity of a previous provision, seed, stock, capital) that map will show you that the uses of the influences of heaven itself are in that country a work of art. The Carnatic is refreshed by few or no living brooks or running streams, and it has rain only at a season; but its product of rice exacts the use of water subject to perpetual command. This is the national bank of the Carnatic, on which it must have a perpetual credit or it perishes irretrievably. For that reason, in the happier times of India, a number, almost incredible, of reservoirs have been made in chosen places throughout the whole country; they are formed for the greater part of mounds of earth and stones, with sluices of solid masonry; the whole constructed with admirable skill and labor, and maintained at a mighty charge. In the territory contained in that map alone, I have been at the trouble of reckoning the reservoirs, and they amount to upwards of eleven hundred, from the extent of two or three acres to five miles in circuit. From these reservoirs currents are occasionally drawn over the fields, and these water-courses again call for a considerable expense to keep them properly scoured and duly leveled. Taking the district in that map as a measure, there cannot be in the Carnatic and Tanjore fewer than ten thousand of these reservoirs of the larger and middling dimensions, to say nothing of those for domestic services and the uses of religious purification. These are not the enterprises of your power, nor in a style of magnificence suited to the taste of your minister. These are the monuments of real kings, who were the fathers of their people; testators to a posterity which they embrace as their own. These are the grand sepulchres built by ambition; but the ambition of an insatiable benevolence, which, not contented with reigning in the dispensation of happiness during the contracted term of human life, had strained, with all the reachings and graspings of a vivacious mind, to extend the dominion of their bounty beyond the limits of nature, and to perpetuate themselves through generations of generations, the guardians, the protectors, the nourishers of mankind.
Long before the late invasion, the persons who are objects of the grant of public money now before you had so diverted the supply of the pious funds of culture and population that everywhere the reservoirs were fallen into a miserable decay. But after those domestic enemies had provoked the entry of a cruel foreign foe into the country, he did not leave it until his revenge had completed the destruction begun by their avarice. Few, very few indeed, of these magazines of water that are not either totally destroyed, or cut through with such gaps as to require a serious attention and much cost to re-establish them, as the means of present subsistence to the people and of future revenue to the State.
What, sir, would a virtuous and enlightened ministry do on the view of the ruins of such works before them? on the view of such a chasm of desolation as that which yawned in the midst of those countries to the north and south, which still bore some vestiges of cultivation? They would have reduced all their most necessary establishments; they would have suspended the justest payments; they would have employed every shilling derived from the producing, to re-animate the powers of the unproductive, parts. While they were performing this fundamental duty, whilst they were celebrating these mysteries of justice and humanity, they would have told the corps of fictitious creditors whose crimes were their claims, that they must keep an awful distance; that they must silence their inauspicious tongues; that they must hold off their profane, unhallowed paws from this holy work; they would have proclaimed with a voice that should make itself heard, that on every country the first creditor is the plow,—that this original, indefeasible claim supersedes every other demand.
This is what a wise and virtuous ministry would have done and said. This, therefore, is what our minister could never think of saying or doing. A ministry of another kind would first have improved the country, and have thus laid a solid foundation for future opulence and future force. But on this grand point of the restoration of the country, there is not one syllable to be found in the correspondence of our ministers, from the first to the last; they felt nothing for a land desolated by fire, sword, and famine; their sympathies took another direction: they were touched with pity for bribery, so long tormented with a fruitless itching of its palms; their bowels yearned for usury, that had long missed the harvest of its returning months; they felt for peculation, which had been for so many years raking in the dust of an empty treasury; they were melted into compassion for rapine and oppression, licking their dry, parched, unbloody jaws. These were the objects of their solicitude. These were the necessities for which they were studious to provide.
To state the country and its revenues in their real condition, and to provide for those fictitious claims consistently with the support of an army and a civil establishment, would have been impossible; therefore the ministers are silent on that head, and rest themselves on the authority of Lord Macartney, who in a letter to the court of directors written in the year 1781, speculating on what might be the result of a wise management of the countries assigned by the Nabob of Arcot, rates the revenues, as in time of peace, at twelve hundred thousand pounds a year, as he does those of the King of Tanjore (which had not been assigned) at four hundred and fifty. On this Lord Macartney grounds his calculations, and on this they choose to ground theirs. It was on this calculation that the ministry, in direct opposition to the remonstrances of the court of directors, have compelled that miserable enslaved body to put their hands to an order for appropriating the enormous sum of £480,000 annually, as a fund for paying to their rebellious servants a debt contracted in defiance of their clearest and most positive injunctions.
The authority and information of Lord Macartney is held high on this occasion, though it is totally rejected in every other particular of this business. I believe I have the honor of being almost as old an acquaintance as any Lord Macartney has. A constant and unbroken friendship has subsisted between us from a very early period; and I trust he thinks that as I respect his character, and in general admire his conduct, I am one of those who feel no common interest in his reputation. Yet I do not hesitate wholly to disallow the calculation of 1781, without any apprehension that I shall appear to distrust his veracity or his judgment. This peace estimate of revenue was not grounded on the state of the Carnatic as it then, or as it had recently, stood. It was a statement of former and better times. There is no doubt that a period did exist when the large portion of the Carnatic held by the Nabob of Arcot might be fairly reputed to produce a revenue to that, or to a greater amount. But the whole had so melted away by the slow and silent hostilities of oppression and mismanagement, that the revenues, sinking with the prosperity of the country, had fallen to about £800,000 a year even before an enemy's horse had imprinted his hoof on the soil of the Carnatic. From that view, and independently of the decisive effects of the war which ensued, Sir Eyre Coote conceived that years must pass before the country could be restored to its former prosperity and production. It was that state of revenue (namely, the actual state before the war) which the directors have opposed to Lord Macartney's speculation. They refused to take the revenues for more than £800,000. In this they are justified by Lord Macartney himself, who in a subsequent letter informs the court that his sketch is a matter of speculation; it supposes the country restored to its ancient prosperity, and the revenue to be in a course of effective and honest collection. If therefore the ministers have gone wrong, they were not deceived by Lord Macartney: they were deceived by no man. The estimate of the directors is nearly the very estimate furnished by the right honorable gentleman himself, and published to the world in one of the printed reports of his own committee; but as soon as he obtained his power, he chose to abandon his account. No part of his official conduct can be defended on the ground of his Parliamentary information.
FROM THE SPEECH ON 'THE FRENCH REVOLUTION'
When ancient opinions and rules of life are taken away, the loss cannot possibly be estimated. From that moment we have no compass to govern us; nor can we know distinctly to what port we steer. Europe, undoubtedly, taken in a mass, was in a flourishing condition the day on which your revolution was completed. How much of that prosperous state was owing to the spirit of our old manners and opinions is not easy to say; but as such causes cannot be indifferent in their operation, we must presume that on the whole their operation was beneficial.
We are but too apt to consider things in the state in which we find them, without sufficiently adverting to the causes by which they have been produced and possibly may be upheld. Nothing is more certain than that our manners, our civilization, and all the good things which are connected with manners and with civilization, have in this European world of ours depended for ages upon two principles, and were indeed the result of both combined: I mean the spirit of a gentleman and the spirit of religion. The nobility and the clergy, the one by profession, the other by patronage, kept learning in existence even in the midst of arms and confusions, and whilst governments were rather in their causes than formed. Learning paid back what it received to nobility and to priesthood; and paid it with usury, by enlarging their ideas and by furnishing their minds. Happy if they had all continued to know their indissoluble union and their proper place! Happy if learning, not debauched by ambition, had been satisfied to continue the instructor, and not aspired to be the master! Along with its natural protectors and guardians, learning will be cast into the mire and trodden down under the hoofs of a swinish multitude.
If, as I suspect, modern letters owe more than they are always willing to own to ancient manners, so do other interests which we value full as much as they are worth. Even commerce and trade and manufacture, the gods of our economical politicians, are themselves perhaps but creatures; are themselves but effects, which as first causes we choose to worship. They certainly grew under the same shade in which learning flourished. They too may decay with their natural protecting principles. With you, for the present at least, they threaten to disappear together. Where trade and manufactures are wanting to a people, and the spirit of nobility and religion remains, sentiment supplies, and not always ill supplies, their place; but if commerce and the arts should be lost in an experiment to try how well a State may stand without these old fundamental principles, what sort of a thing must be a nation of gross, stupid, ferocious, and at the same time poor and sordid barbarians,—destitute of religion, honor, or manly pride, possessing nothing at present and hoping for nothing hereafter?
I wish you may not be going fast, and by the shortest cut, to that horrible and disgustful situation. Already there appears a poverty of conception, a coarseness and vulgarity, in all the proceedings of the Assembly and of all their instructors. Their liberty is not liberal. Their science is presumptuous ignorance. Their humanity is savage and brutal.
It is not clear whether in England we learned those grand and decorous principles and manners, of which considerable traces yet remain, from you, or whether you took them from us. But to you, I think, we trace them best. You seem to me to be gentis incunabula nostræ. France has always more or less influenced manners in England; and when your fountain is choked up and polluted the stream will not run long, or not run clear, with us or perhaps with any nation. This gives all Europe, in my opinion, but too close and connected a concern in what is done in France. Excuse me therefore if I have dwelt too long on the atrocious spectacle of the 6th of October, 1789, or have given too much scope to the reflections which have arisen in my mind on occasion of the most important of all revolutions, which may be dated from that day,—I mean a revolution in sentiments, manners, and moral opinions. As things now stand, with everything respectable destroyed without us, and an attempt to destroy within us every principle of respect, one is almost forced to apologize for harboring the common feelings of men.
Why do I feel so differently from the Reverend Dr. Price and those of his lay flock who will choose to adopt the sentiments of his discourse? For this plain reason—because it is natural I should; because we are so made as to be affected at such spectacles with melancholy sentiments upon the unstable condition of mortal prosperity, and the tremendous uncertainty of human greatness; because in those natural feelings we learn great lessons; because in events like these our passions instruct our reason; because when kings are hurled from their thrones by the Supreme Director of this great drama, and become the objects of insult to the base and of pity to the good, we behold such disasters in the moral as we should a miracle in the physical order of things. We are alarmed into reflection; our minds (as it has long since been observed) are purified by terror and pity; our weak, unthinking pride is humbled under the dispensations of a mysterious wisdom. Some tears might be drawn from me, if such a spectacle were exhibited on the stage. I should be truly ashamed of finding in myself that superficial, theatric sense of painted distress, whilst I could exult over it in real life. With such a perverted mind, I could never venture to show my face at a tragedy. People would think the tears that Garrick formerly, or that Siddons not long since, have extorted from me, were the tears of hypocrisy; I should know them to be the tears of folly.
Indeed, the theatre is a better school of moral sentiments than churches where the feelings of humanity are thus outraged. Poets, who have to deal with an audience not yet graduated in the school of the rights of men, and who must apply themselves to the moral constitution of the heart, would not dare to produce such a triumph as a matter of exultation. There, where men follow their natural impulses, they would not bear the odious maxims of a Machiavellian policy, whether applied to the attainment of monarchical or democratic tyranny. They would reject them on the modern, as they once did on the ancient stage, where they could not bear even the hypothetical proposition of such wickedness in the mouth of a personated tyrant, though suitable to the character he sustained. No theatric audience in Athens would bear what has been borne in the midst of the real tragedy of this triumphal day: a principal actor weighing, as it were in scales hung in a shop of horrors, so much actual crime against so much contingent advantage, and after putting in and out weights, declaring that the balance was on the side of the advantages. They would not bear to see the crimes of new democracy posted as in a ledger against the crimes of old despotism, and the book-keepers of politics finding democracy still in debt, but by no means unable or unwilling to pay the balance. In the theatre, the first intuitive glance, without any elaborate process of reasoning, will show that this method of political computation would justify every extent of crime. They would see that on these principles, even where the very worst acts were not perpetrated, it was owing rather to the fortune of the conspirators than to their parsimony in the expenditure of treachery and blood. They would soon see that criminal means, once tolerated, are soon preferred. They present a shorter cut to the object than through the highway of the moral virtues. Justifying perfidy and murder for public benefit, public benefit would soon become the pretext, and perfidy and murder the end; until rapacity, malice, revenge, and fear more dreadful than revenge, could satiate their insatiable appetites. Such must be the consequences of losing, in the splendor of these triumphs of the rights of men, all natural sense of wrong and right.
But the reverend pastor exults in this "leading in triumph," because truly Louis the Sixteenth was "an arbitrary monarch"; that is, in other words, neither more nor less than because he was Louis the Sixteenth, and because he had the misfortune to be born King of France, with the prerogatives of which a long line of ancestors, and a long acquiescence of the people, without any act of his, had put him in possession. A misfortune it has indeed turned out to him, that he was born King of France. But misfortune is not crime, nor is indiscretion always the greatest guilt. I shall never think that a prince, the acts of whose whole reign were a series of concessions to his subjects; who was willing to relax his authority, to remit his prerogatives, to call his people to a share of freedom not known, perhaps not desired, by their ancestors: such a prince, though he should be subjected to the common frailties attached to men and to princes, though he should have once thought it necessary to provide force against the desperate designs manifestly carrying on against his person and the remnants of his authority,—though all this should be taken into consideration, I shall be led with great difficulty to think he deserves the cruel and insulting triumph of Paris and of Dr. Price. I tremble for the cause of liberty, from such an example to kings. I tremble for the cause of humanity, in the unpunished outrages of the most wicked of mankind. But there are some people of that low and degenerate fashion of mind that they look up with a sort of complacent awe and admiration to kings who know how to keep firm in their seat, to hold a strict hand over their subjects, to assert their prerogative, and by the awakened vigilance of a severe despotism to guard against the very first approaches of freedom. Against such as these they never elevate their voice. Deserters from principle, listed with fortune, they never see any good in suffering virtue, nor any crime in prosperous usurpation.
If it could have been made clear to me that the King and Queen of France (those I mean who were such before the triumph) were inexorable and cruel tyrants, that they had formed a deliberate scheme for massacring the National Assembly (I think I have seen something like the latter insinuated in certain publications), I should think their captivity just. If this be true, much more ought to have been done; but done, in my opinion, in another manner. The punishment of real tyrants is a noble and awful act of justice; and it has with truth been said to be consolatory to the human mind. But if I were to punish a wicked king, I should regard the dignity in avenging the crime. Justice is grave and decorous, and in its punishments rather seems to submit to a necessity than to make a choice. Had Nero, or Agrippina, or Louis the Eleventh, or Charles the Ninth, been the subject; if Charles the Twelfth of Sweden after the murder of Patkul, or his predecessor Christina after the murder of Monaldeschi, had fallen into your hands, sir, or into mine, I am sure our conduct would have been different.
If the French King, or King of the French (or by whatever name he is known in the new vocabulary of your constitution), has in his own person and that of his Queen really deserved these unavowed but unavenged murderous attempts, and those frequent indignities more cruel than murder, such a person would ill deserve even that subordinate executory trust which I understand is to be placed in him; nor is he fit to be called chief in a nation which he has outraged and oppressed. A worse choice for such an office in a new commonwealth than that of a deposed tyrant could not possibly be made. But to degrade and insult a man as the worst of criminals, and afterwards to trust him in your highest concerns as a faithful, honest, and zealous servant, is not consistent with reasoning, nor prudent in policy, nor safe in practice. Those who could make such an appointment must be guilty of a more flagrant breach of trust than any they have yet committed against the people. As this is the only crime in which your leading politicians could have acted inconsistently, I conclude that there is no sort of ground for these horrid insinuations. I think no better of all the other calumnies.
In England, we give no credit to them. We are generous enemies: we are faithful allies. We spurn from us with disgust and indignation the slanders of those who bring us their anecdotes with the attestation of the flower-de-luce on their shoulder. We have Lord George Gordon fast in Newgate; and neither his being a public proselyte to Judaism, nor his having, in his zeal against Catholic priests and all sorts of ecclesiastics, raised a mob (excuse the term, it is still in use here) which pulled down all our prisons, have preserved to him a liberty of which he did not render himself worthy by a virtuous use of it. We have rebuilt Newgate, and tenanted the mansion. We have prisons almost as strong as the Bastile for those who dare to libel the Queens of France. In this spiritual retreat let the noble libeler remain. Let him there meditate on his Talmud, until he learns a conduct more becoming his birth and parts, and not so disgraceful to the ancient religion to which he has become a proselyte; or until some persons from your side of the water, to please your new Hebrew brethren, shall ransom him. He may then be enabled to purchase, with the old hoards of the synagogue, and a very small poundage on the long compound interest of the thirty pieces of silver (Dr. Price has shown us what miracles compound interest will perform in 1790 years), the lands which are lately discovered to have been usurped by the Gallican Church. Send us your Popish Archbishop of Paris, and we will send you our Protestant Rabbin. We shall treat the person you send us in exchange like a gentleman and an honest man, as he is; but pray let him bring with him the fund of his hospitality, bounty, and charity; and depend upon it, we shall never confiscate a shilling of that honorable and pious fund, nor think of enriching the treasury with the spoils of the poor-box.
To tell you the truth, my dear sir, I think the honor of our nation to be somewhat concerned in the disclaimer of the proceedings of this society of the Old Jewry and the London Tavern. I have no man's proxy. I speak only for myself when I disclaim, as I do with all possible earnestness, all communion with the actors in that triumph, or with the admirers of it. When I assert anything else, as concerning the people of England, I speak from observation, not from authority; but I speak from the experience I have had in a pretty extensive and mixed communication with the inhabitants of this kingdom, of all descriptions and ranks, and after a course of attentive observation begun early in life, and continued for nearly forty years. I have often been astonished, considering that we are divided from you but by a slender dike of about twenty-four miles, and that the mutual intercourse between the two countries has lately been very great, to find how little you seem to know of us. I suspect that this is owing to your forming a judgment of this nation from certain publications which do very erroneously, if they do at all, represent the opinions and dispositions generally prevalent in England. The vanity, restlessness, petulance, and spirit of intrigue of several petty cabals, who attempt to hide their total want of consequence in bustle, and noise, and puffing, and mutual quotation of each other, makes you imagine that our contemptuous neglect of their abilities is a mark of general acquiescence in their opinions. No such thing, I assure you. Because half a dozen grasshoppers under a fern make the field ring with their importunate chink, whilst thousands of great cattle reposed beneath the shadow of the British oak chew the cud and are silent, pray do not imagine that those who make the noise are the only inhabitants of the field; that of course they are many in number; or that after all they are other than the little, shriveled, meagre, hopping, though loud and troublesome, insects of the hour.
FRANCES HODGSON BURNETT
(1849-)

Mrs. Burnett has told the story of her childhood and tried to interpret her own personality in her autobiographical story, 'The One I Knew Best of All.' She has pictured a little English girl in a comfortable Manchester home, leading a humdrum, well-regulated existence, with brothers and sisters, nurse and governess. But an alert imagination added interest to the life of this "Small Person," and from her nursery windows and from the quiet park where she played she watched eagerly for anything of dramatic or picturesque interest. She seized upon the Lancashire dialect often overheard, as upon a game, and practiced it until she gained the facility of use shown in her mining and factory stories. One day the strong and beautiful figure of a young woman, followed by a coarse and abusive father, caught her attention, and years afterward she developed Joan Lowrie from the incident.
When the Hodgson family suffered pecuniary loss, and hoping to better its fortunes came to America, then best known to Frances from the pages of 'Uncle Tom's Cabin,' she was fifteen. A year or two later she began to send her stories to various magazines. In 1867 the first of these appeared. She did not however attain her great popularity until the appearance of 'That Lass o' Lowrie's' in 1877. The thoughtfully drawn group of characters—Derrick the engineer, Grace the young minister, Annie the rector's daughter, and Joan the pit girl,—are dramatic figures, working out their life problems under the eyes and the comments of half-cynical, half-brutalized miners. There is nothing in her history to account for Joan, or for the fact that the strength of vice in her father becomes an equal strength of virtue in her. Abused since her babyhood, doing the work of a man among degrading companionships, she yet remains capable of the noblest self-abnegation. Mrs. Burnett delights in heroes and heroines who are thus loftily at variance with their surroundings. Her stories are romantic in spirit, offering little to the lover of psychologic analysis. Her character-drawing is the product of quick observation and sympathetic intuition. She does not write "tendency" novels, but appeals to simple emotions of love, hate, revenge, or self-immolation, which sometimes, as in the case of her last book, 'A Lady of Quality' (1895), verge on sensationalism. In 1873 Miss Hodgson married Dr. Burnett of Washington. Her longest novel, 'Through One Administration,' is a story of the political and social life of the Capital. 'Little Lord Fauntleroy' (1886) is the best known of a series of stories nominally written for children, but intended to be read by their elders. 'Sara Crewe,' 'Giovanni and the Other,' 'Two Little Pilgrims,' and 'Little Saint Elizabeth' are chronicles of superlunary children. After those before mentioned, 'Esmeralda,' 'Louisiana,' 'A Fair Barbarian,' and 'Haworth's' are her best known stories.
AT THE PIT
From 'That Lass o' Lowrie's'
The next morning Derrick went down to the mine as usual. There were several things he wished to do in these last two days. He had heard that the managers had entered into negotiations with a new engineer, and he wished the man to find no half-done work. The day was bright and frosty, and the sharp, bracing air seemed to clear his brain. He felt more hopeful, and less inclined to view matters darkly.
He remembered afterward that as he stepped into the cage he turned to look at the unpicturesque little town, brightened by the winter's sun; and that as he went down he glanced up at the sky, and marked how intense appeared the bit of blue which was framed in by the mouth of the shaft.
Even in the few hours that had elapsed since the meeting, the rumor of what he had said and done had been bruited about. Some collier had heard it and had told it to his comrades, and so it had gone from one to the other. It had been talked over at the evening and morning meal in divers cottages, and many an anxious hand had warmed into praise of the man who had "had a thowt for th' men."
In the first gallery he entered he found a deputation of men awaiting him,—a group of burly miners with picks and shovels over their shoulders,—and the head of this deputation, a spokesman burlier and generally gruffer than the rest, stopped him.
"Mester," he said, "we chaps 'ud loike to ha' a word wi' yo'."
"All right," was Derrick's reply, "I am ready to listen."
The rest crowded nearer, as if anxious to participate as much as possible, and give their spokesman the support of their presence.
"It is na mich as we ha' getten to say," said the man, "but we're fain to say it. Are na we, mates?"
"Ay, we are, lad," in chorus.
"It's about summat as we'n heerd. Theer wur a chap as towd some on us last neet as yo'd getten th' sack fro' th' managers—or leastways as yo'd turned th' tables on 'em an' gi'en them th' sack yo'rsen. An' we'n heerd as it begun wi' yo're standin' up fur us chaps—axin' fur things as wur wanted i' th' pit to save us fro' runnin' more risk than we need. An' we heerd as yo' spoke up bold, an' argied for us an' stood to what yo' thowt war th' reet thing, an' we set our moinds on tellin' yo' as we'd heerd it an' talked it over, an' we'd loike to say a word o' thanks i' common fur th' pluck yo' showed. Is na that it, mates?"
"Ay, that it is, lad!" responded the chorus.
Suddenly one of the group stepped out and threw down his pick. "An' I'm dom'd, mates," he said, "if here is na a chap as ud loike to shake hands wi' him."
It was the signal for the rest to follow his example. They crowded about their champion, thrusting grimy paws into his hand, grasping it almost enthusiastically.
"Good luck to yo', lad!" said one. "We'n noan smooth soart o' chaps, but we'n stand by what's fair an' plucky. We shall ha' a good word fur thee when tha hast made thy flittin'."
"I'm glad of that, lads," responded Derrick heartily, by no means unmoved by the rough-and-ready spirit of the scene. "I only wish I had had better luck, that's all."
A few hours later the whole of the little town was shaken to its very foundations by something like an earthquake, accompanied by an ominous, booming sound which brought people flocking out of their houses with white faces. Some of them had heard it before—all knew what it meant. From the colliers' cottages poured forth women, shrieking and wailing,—women who bore children in their arms and had older ones dragging at their skirts, and who made their desperate way to the pit with one accord. From houses and workshops there rushed men, who coming out in twos and threes joined each other, and forming a breathless crowd, ran through the streets scarcely daring to speak a word—and all ran toward the pit.
There were scores at its mouth in five minutes; in ten minutes there were hundreds, and above all the clamor rose the cry of women:—
"My mester's down!"
"An' mine!"
"An' mine!"
"Four lads o' mine is down!"
"Three o' mine!"
"My little un's theer—th' youngest—nobbut ten year owd—nobbut ten year owd, poor little chap! an' ony been at work a week!"
"Ay, wenches, God ha' mercy on us aw'—God ha' mercy!" And then more shrieks and wails, in which the terror-stricken children joined.
It was a fearful sight. How many lay dead and dying in the noisome darkness below, God only knew! How many lay mangled and crushed, waiting for their death, Heaven only could tell!
In five minutes after the explosion occurred, a slight figure in clerical garb made its way through the crowd with an air of excited determination.
"Th' parson's feart," was the general comment.
"My men," he said, raising his voice so that all could hear, "can any of you tell me who last saw Fergus Derrick?"
There was a brief pause, and then came a reply from a collier who stood near.
"I coom up out o' th' pit an hour ago," he said, "I wur th' last as coom up, an' it wur on'y chance as browt me. Derrick wur wi' his men i' th' new part o' th' mine. I seed him as I passed through."
Grace's face became a shade or so paler, but he made no more inquiries.
His friend either lay dead below, or was waiting for his doom at that very moment. He stepped a little farther forward.
"Unfortunately for myself, at present," he said, "I have no practical knowledge of the nature of these accidents. Will some of you tell me how long it will be before we can make our first effort to rescue the men who are below?"
Did he mean to volunteer—this young whipper-snapper of a parson? And if he did, could he know what he was doing?
"I ask you," he said, "because I wish to offer myself as a volunteer at once; I think I am stronger than you imagine, and at least my heart will be in the work. I have a friend below—myself," his voice altering its tone and losing its firmness,—"a friend who is worthy the sacrifice of ten such lives as mine, if such a sacrifice could save him."
One or two of the older and more experienced spoke up. Under an hour it would be impossible to make the attempt—it might even be a longer time, but in an hour they might at least make their first effort.
If such was the case, the parson said, the intervening period must be turned to the best account. In that time much could be thought of and done which would assist themselves and benefit the sufferers. He called upon the strongest and most experienced, and almost without their recognizing the prominence of his position, led them on in the work. He even rallied the weeping women and gave them something to do. One was sent for this necessary article and another for that. A couple of boys were dispatched to the next village for extra medical assistance, so that there need be no lack of attention when it was required. He took off his broadcloth and worked with the rest of them until all the necessary preparations were made, and it was considered possible to descend into the mine.
When all was ready, he went to the mouth of the shaft and took his place quietly.
It was a hazardous task they had before them. Death would stare them in the face all through its performance. There was choking after-damp below,—noxious vapors, to breathe which was to die; there was the chance of crushing masses falling from the shaken galleries—and yet these men left their companions one by one, and ranged themselves without saying a word at the curate's side.
"My friends," said Grace, baring his head and raising a feminine hand,—"My friends, we will say a short prayer."
It was only a few words. Then the curate spoke again.
"Ready!" he said.
But just at that moment there stepped out from the anguished crowd a girl, whose face was set and deathly, though there was no touch of fear upon it.
"I ax yo'," she said, "to let me go wi' yo' and do what I con. Lasses, some on yo' speak a word for Joan Lowrie!"
There was a breathless start. The women even stopped their outcry to look at her as she stood apart from them,—a desperate appeal in the very quiet of her gesture as she turned to look about her for some one to speak.
"Lasses," she said again, "some on yo' speak a word for Joan Lowrie!"
There rose a murmur among them then, and the next instant this murmur was a cry.
"Ay," they answered, "we con aw speak fur yo'. Let her go, lads! She's worth two o' th' best on yo'. Nowt fears her. Ay, she mun go, if she will, mun Joan Lowrie! Go, Joan lass, and we'n not forget thee!"
But the men demurred. The finer instinct of some of them shrank from giving a woman a place in such a perilous undertaking—the coarser element in others rebelled against it.
"We'n ha' no wenches," these said, surlily.
Grace stepped forward. He went to Joan Lowrie and touched her gently on the shoulder.
"We cannot think of it," he said. "It is very brave and generous, and—God bless you!—but it cannot be. I could not think of allowing it myself, if the rest would."
"Parson," said Joan, coolly but not roughly, "tha'd ha' hard work to help thysen, if so be as th' lads wur willin'!"
"But," he protested, "it may be death. I could not bear the thought of it. You are a woman. We cannot let you risk your life."
She turned to the volunteers.
"Lads," she cried passionately, "yo' munnot turn me back. I—sin I mun tell yo'—" and she faced them like a queen—"theer's a mon down theer as I'd gi' my heart's blood to save."
They did not know whom she meant, but they demurred no longer.
"Tak' thy place, wench," said the oldest. "If tha mun, tha mun."
She took her seat in the cage by Grace, and when she took it she half turned her face away. But when those above began to lower them, and they found themselves swinging downward into what might be to them a pit of death, she spoke to him.
"Theer's a prayer I'd loike yo' to pray," she said. "Pray that if we mun dee, we may na dee until we ha' done our work."
It was a dreadful work indeed that the rescuers had to do in those black galleries. And Joan was the bravest, quickest, most persistent of all. Paul Grace, following in her wake, found himself obeying her slightest word or gesture. He worked constantly at her side, for he at least had guessed the truth. He knew that they were both engaged in the same quest. When at last they had worked their way—lifting, helping, comforting—to the end of the passage where the collier had said he last saw the master, then for one moment she paused, and her companion with a thrill of pity touched her to attract her attention.
"Let me go first," he said.
"Nay," she answered, "we'n go together."
The gallery was a long and low one, and had been terribly shaken. In some places the props had been torn away, in others they were borne down by the loosened blocks of coal. The dim light of the "Davy" Joan held up showed such a wreck that Grace spoke to her again.
"You must let me go first," he said with gentle firmness. "If one of these blocks should fall—"
Joan interrupted him:—
"If one on 'em should fall, I'm th' one as it had better fall on. There is na mony foak as ud miss Joan Lowrie. Yo' ha' work o' yore own to do."
She stepped into the gallery before he could protest, and he could only follow her. She went before, holding the Davy high, so that its light might be thrown as far forward as possible. Now and then she was forced to stoop to make her way around a bending prop; sometimes there was a falling mass to be surmounted: but she was at the front still when they reached the other end, without finding the object of their search.
"It—he is na there," she said. "Let us try th' next passage," and she turned into it.
It was she who first came upon what they were looking for; but they did not find it in the next passage, or the next, or even the next. It was farther away from the scene of the explosion than they had dared to hope. As they entered a narrow side gallery, Grace heard her utter a low sound, and the next minute she was down upon her knees.
"Theer's a mon here," she said. "It's him as we're lookin' fur."
She held the dim little lantern close to the face,—a still face with closed eyes, and blood upon it. Grace knelt down too, his heart aching with dread.
"Is he—" he began, but could not finish.
Joan Lowrie laid her hand upon the apparently motionless breast and waited almost a minute, and then she lifted her own face, white as the wounded man's—white and solemn, and wet with a sudden rain of tears.
"He is na dead," she said. "We ha' saved him."
She sat down upon the floor of the gallery, and lifting his head, laid it upon her bosom, holding it close, as a mother might hold the head of her child.
"Mester," she said, "gi' me th' brandy flask, and tak' thou thy Davy an' go fur some o' the men to help us get him to th' leet o' day. I'm gone weak at last. I conna do no more. I'll go wi' him to th' top."
When the cage ascended to the mouth again with its last load of sufferers, Joan Lowrie came with it, blinded and dazzled by the golden winter's sunlight as it fell upon her haggard face. She was holding the head of what seemed to be a dead man upon her knee. A great shout of welcome rose up from the bystanders.
She helped them to lay her charge upon a pile of coats and blankets prepared for him, and then she turned to the doctor who had hurried to the spot to see what could be done.
"He is na dead," she said. "Lay yore hond on his heart. It beats yet, Mester,—on'y a little, but it beats."
"No," said the doctor, "he is not dead—yet"; with a breath's pause between the two last words. "If some of you will help me to put him on a stretcher, he may be carried home, and I will go with him. There is just a chance for him, poor fellow, and he must have immediate attention. Where does he live?"
"He must go with me," said Grace. "He is my friend."
So they took him up, and Joan stood a little apart and watched them carry him away,—watched the bearers until they were out of sight, and then turned again and joined the women in their work among the sufferers.
By permission of Charles Scribner's Sons.
FRANCES BURNEY (MADAME D'ARBLAY)
(1752-1840)

There is a suggestion of the 'Ugly Duckling' story in Fanny Burney's early life. The personality of the shy little girl, who was neither especially pretty nor precocious, was rather merged in the half-dozen of gayer brothers and sisters. The first eight years of her life were passed at Lynn Regis in Norfolk; then the family moved to London, where her father continued his career as an important writer on music and a fashionable music-master. Soon after, Mrs. Burney died. All the children but young Fanny were sent away to school. She was to have been educated at home, but received little attention from the learned, kind, but heedless Dr. Burney, who seems to have considered her the dull member of his flock. "Poor Fanny!" he often said, until her sudden fame overwhelmed him with surprise as well as exultation. Only his friend, her beloved "Daddy Crisp" of the letters, appreciated her; himself a disappointed dramatic author, soured by what he felt to be an incomprehensible failure, yet of fine critical talent, with kind and wise suggestions for his favorite Fanny.

Frances Burney
But while her book-education was of the slightest, her social advantages were great. Pleasure-loving Dr. Burney had a delightful faculty of attracting witty and musical friends to enliven his home. Fanny's great unnoticed gift was power of observation. The shy girl who avoided notice herself, found her social pleasure in watching and listening to clever people. Perhaps a Gallic strain—for her mother was of French descent—gave her clear-sightedness. She had a turn for social satire which added humorous discrimination to her judgments. She understood people better than books, and perceived their petty hypocrisies, self-deceptions, and conventional standards, with witty good sense and love of sincerity. Years of this silent note-taking and personal intercourse with brilliant people gave her unusual knowledge of the world.
She was a docile girl, ready always to heed her father and her "Daddy Crisp," ready to obey her kindly stepmother, and try to exchange for practical occupations her pet pastime of scribbling.
But from the time she was ten she had loved to write down her impressions, and the habit was too strong to be more than temporarily renounced. Like many imaginative persons, she was fond of carrying on serial inventions in which repressed fancies found expression. One long story she destroyed; but the characters haunted her, and she began a sequel which became 'Evelina.' In the young, beautiful, virtuous heroine, with her many mortifying experiences and her ultimate triumph, she may have found compensation for a starved vanity of her own.
For a long time she and her sisters enjoyed Evelina's tribulations; then Fanny grew ambitious, and encouraged by her brother, thought of publication. When she tremblingly asked her father's consent, he carelessly countenanced the venture and gave it no second thought. After much negotiation, a publisher offered twenty pounds for the manuscript, and in 1778 the appearance of 'Evelina' ended Fanny Burney's obscurity. For a long time the book was the topic of boundless praise and endless discussion. Every one wondered who could have written the clever story, which was usually attributed to a society man. The great Dr. Johnson was enthusiastic, insisted upon knowing the author, and soon grew very fond of his little Fanny. He introduced her to his friends, and she became the celebrity of a delightful circle. Sir Joshua Reynolds and Burke sat up all night to finish 'Evelina.' The Thrales, Madame Delaney,—who later introduced her at court,—Sheridan, Gibbon, and Sir Walter Scott, were among those who admired her most cordially.
It was a happy time for Fanny, encouraged to believe her talent far greater than it was. She wrote a drama which was read in solemn judgment by her father and "Daddy Crisp," who decided against it as too like 'Les Précieuses Ridicules,' a play she had never read. A second novel, 'Cecilia,' appeared in 1782, and was as successful as its predecessor. Later readers find it less spontaneous, and after it she never resumed her early style except in her journal and correspondence. Her ambition was fully astir. She had every incentive from her family and friends. But the old zest in composition had departed. The self-consciousness which had always tormented her in society seized her now, when she was trying to cater to public taste, and made her change her frank, free, personal expression for a stilted artificial formality of phrase.
Her reputation was now at its height, and she was very happy in her position as society favorite and pride of the father whom she had always passionately admired, when she made the mistake of her life. Urged by her father, she accepted a position at court as Second Keeper of the Queen's Robes. There she spent five pleasureless and worse than profitless years. In her 'Diary and Letters,' the most readable to-day of all her works, she has told the story of wretched discomfort, of stupidly uncongenial companionship, of arduous tasks made worse by the selfish thoughtlessness of her superiors. She has also given our best historical picture of that time; the every-day life at court, the slow agony of King George's increasing insanity. But the drudgery and mean hardships of the place, and the depression of being separated from her family, broke down her health; and after much opposition she was allowed to resign in 1791.
Soon afterwards she astonished her friends by marrying General D'Arblay, a French officer and a gentleman, although very poor. As the pair had an income of only one hundred pounds, this seems a perilously rash act for a woman over forty. Fortunately the match proved a very happy one, and the situation stimulated Madame D'Arblay to renewed authorship. 'Camilla,' her third novel, was sold by subscription, and was a very remunerative piece of work. But from a critical point of view it was a failure; and being written in a heavy pedantic style, is quite deficient in her early charm. With the proceeds she built a modest home, Camilla Cottage. Later the family moved to France, where her husband died and where her only son received his early education. When he was nearly ready for an English university she returned to England, and passed her tranquil age among her friends until she died at eighty-eight.
What Fanny Burney did in all unconsciousness was to establish fiction upon a new basis. She may be said to have created the family novel. Fielding, Smollett, and Sterne had bequeathed their legacy impregnated with objectionable qualities, in spite of strength and charm; they were read rather secretly, and tabooed for women. On the other hand, the followers of Richardson were too didactic to be readable. Fanny Burney proved that entertaining tales, unweighted by heavy moralizing, may be written, adapted to young and old. Her sketches of life were witty, sincere, and vigorous, yet always moral in tone. 'Evelina,' the work of an innocent, frank girl, could be read by any one.
A still greater source of her success was her robust and abounding, though sometimes rather broad and cheap, fun. In her time decent novels were apt to be appallingly serious in tone, and not infrequently stupid; humor in spite of Addison still connoted much coarseness and obtrusive sexuality, and in fiction had to be sought in the novels written for men only. As humor is the deadly foe to sentimentalism and hysterics, the Richardson school were equally averse to it on further grounds. Fanny Burney produced novels fit for women's and family reading, yet full of humor of a masculine vigor—and it must be added, with something of masculine unsensitiveness. There is little fineness to most of it; some is mere horseplay, some is extravagant farce: but it is deep and genuine, it supplied an exigent want, and deserved its welcome. De Morgan says it was like introducing dresses of glaring red and yellow and other crude colors into a country where every one had previously dressed in drab—a great relief, but not art. This is hard measure, however: some of her character-drawing is almost as richly humorous and valid as Jane Austen's own.
Fanny Burney undoubtedly did much to augment the new respect for woman's intellectual ability, and was a stimulus to the brilliant group which succeeded her. Miss Ferrier, Maria Edgeworth, and Jane Austen all owe her something of their inspiration and more of their welcome.
EVELINA'S LETTER TO THE REV. MR. VILLARS
From 'Evelina'
Holborn, June 17th
Yesterday Mr. Smith carried his point of making a party for Vauxhall, consisting of Madame Duval, M. Du Bois, all the Branghtons, Mr. Brown, himself,—and me!—for I find all endeavors vain to escape anything which these people desire I should not.
There were twenty disputes previous to our setting out; first as to the time of our going: Mr. Branghton, his son, and young Brown, were for six o'clock, and all the ladies and Mr. Smith were for eight;—the latter, however, conquered. Then as to the way we should go: some were for a boat, others for a coach, and Mr. Branghton himself was for walking; but the boat at length was decided upon. Indeed, this was the only part of the expedition that was agreeable to me; for the Thames was delightfully pleasant.
The garden is very pretty, but too formal; I should have been better pleased had it consisted less of straight walks, where
"Grove nods at grove, each alley has its brother."
The trees, the numerous lights, and the company in the circle round the orchestra make a most brilliant and gay appearance; and had I been with a party less disagreeable to me, I should have thought it a place formed for animation and pleasure. There was a concert, in the course of which a hautbois concerto was so charmingly played that I could have thought myself upon enchanted ground, had I had spirits more gentle to associate with. The hautbois in the open air is heavenly.
Mr. Smith endeavored to attach himself to me, with such officious assiduity and impertinent freedom that he quite sickened me. Indeed, M. Du Bois was the only man of the party to whom, voluntarily, I ever addressed myself. He is civil and respectful, and I have found nobody else so since I left Howard Grove. His English is very bad; but I prefer it to speaking French myself, which I dare not venture to do. I converse with him frequently, both to disengage myself from others and to oblige Madame Duval, who is always pleased when he is attended to.
As we were walking about the orchestra, I heard a bell ring; and in a moment Mr. Smith, flying up to me, caught my hand, and with a motion too quick to be resisted, ran away with me many yards before I had breath to ask his meaning; though I struggled as well as I could to get from him. At last, however, I insisted upon stopping. "Stopping, ma'am!" cried he, "why, we must run on, or we shall lose the cascade!"
And then again he hurried me away, mixing with a crowd of people, all running with so much velocity that I could not imagine what had raised such an alarm. We were soon followed by the rest of the party; and my surprise and ignorance proved a source of diversion to them all which was not exhausted the whole evening. Young Branghton, in particular, laughed till he could hardly stand.
The scene of the cascade I thought extremely pretty, and the general effect striking and lively.
But this was not the only surprise which was to divert them at my expense; for they led me about the garden purposely to enjoy my first sight of various other deceptions.
About ten o'clock, Mr. Smith having chosen a box in a very conspicuous place, we all went to supper. Much fault was found with everything that was ordered, though not a morsel of anything was left, and the dearness of the provisions, with conjectures upon what profit was made by them, supplied discourse during the whole meal.
When wine and cyder were brought, Mr. Smith said, "Now let's enjoy ourselves; now is the time, or never. Well, ma'am, and how do you like Vauxhall?"
"Like it!" cried young Branghton; "why, how can she help liking it? She has never seen such a place before, that I'll answer for."
"For my part," said Miss Branghton, "I like it because it is not vulgar."
"This must have been a fine treat for you, Miss," said Mr. Branghton; "why, I suppose you was never so happy in all your life before?"
I endeavored to express my satisfaction with some pleasure; yet I believe they were much amazed at my coldness.
"Miss ought to stay in town till the last night," said young Branghton; "and then, it's my belief, she'd say something to it! Why, Lord, it's the best night of any; there's always a riot,—and there the folks run about,—and then there's such squealing and squalling!—and there, all the lamps are broke,—and the women run skimper-scamper—I declare, I would not take five guineas to miss the last night!"
I was very glad when they all grew tired of sitting, and called for the waiter to pay the bill. The Miss Branghtons said they would walk on while the gentlemen settled the account, and asked me to accompany them; which however I declined.
"You girls may do as you please," said Madame Duval, "but as to me, I promise you, I sha'n't go nowhere without the gentlemen."
"No more, I suppose, will my cousin," said Miss Branghton, looking reproachfully towards Mr. Smith.
This reflection, which I feared would flatter his vanity, made me most unfortunately request Madame Duval's permission to attend them. She granted it; and away we went, having promised to meet in the room.
To the room, therefore, I would immediately have gone: but the sisters agreed that they would first have a little pleasure; and they tittered and talked so loud that they attracted universal notice.
"Lord, Polly," said the eldest, "suppose we were to take a turn in the dark walks?"
"Ay, do," answered she; "and then we'll hide ourselves, and then Mr. Brown will think we are lost."
I remonstrated very warmly against this plan, telling them it would endanger our missing the rest of the party all the evening.
"O dear," cried Miss Branghton, "I thought how uneasy Miss would be, without a beau!"
This impertinence I did not think worth answering; and quite by compulsion I followed them down a long alley, in which there was hardly any light.
By the time we came near the end, a large party of gentlemen, apparently very riotous, and who were hallooing, leaning on one another, and laughing immoderately, seemed to rush suddenly from behind some trees, and meeting us face to face, put their arms at their sides and formed a kind of circle, which first stopped our proceeding and then our retreating, for we were presently entirely enclosed. The Miss Branghtons screamed aloud, and I was frightened exceedingly; our screams were answered with bursts of laughter, and for some minutes we were kept prisoners, till at last one of them, rudely seizing hold of me, said I was a pretty little creature.
Terrified to death, I struggled with such vehemence to disengage myself from him that I succeeded, in spite of his efforts to detain me: and immediately, and with a swiftness which fear only could have given me, I flew rather than ran up the walk, hoping to secure my safety by returning to the lights and company we had so foolishly left; but before I could possibly accomplish my purpose, I was met by another party of men, one of whom placed himself directly in my way, calling out, "Whither so fast, my love?"—so that I could only have proceeded by running into his arms.
In a moment both my hands, by different persons, were caught hold of, and one of them, in a most familiar manner, desired when I ran next to accompany me in a race; while the rest of the party stood still and laughed. I was almost distracted with terror, and so breathless with running that I could not speak; till another, advancing, said I was as handsome as an angel, and desired to be of the party. I then just articulated, "For Heaven's sake, gentlemen, let me pass!"
Another, then rushing suddenly forward, exclaimed, "Heaven and earth! what voice is that?"
"The voice of the prettiest little actress I have seen this age," answered one of my persecutors.
"No,—no,—no,—" I panted out, "I am no actress—pray let me go,—pray let me pass—"
"By all that's sacred," cried the same voice, which I then knew for Sir Clement Willoughby's, "'tis herself!"
A MAN OF THE TON
From 'Cecilia'
At the door of the Pantheon they were joined by Mr. Arnott and Sir Robert Floyer, whom Cecilia now saw with added aversion; they entered the great room during the second act of the concert, to which, as no one of the party but herself had any desire to listen, no sort of attention was paid; the ladies entertaining themselves as if no orchestra was in the room, and the gentlemen, with an equal disregard to it, struggling for a place by the fire, about which they continued hovering till the music was over.
Soon after they were seated, Mr. Meadows, sauntering towards them, whispered something to Mrs. Mears, who, immediately rising, introduced him to Cecilia; after which, the place next to her being vacant, he cast himself upon it, and lolling as much at his ease as his situation would permit, began something like a conversation with her.
"Have you been long in town, ma'am?"
"No, sir."
"This is not your first winter?"
"Of being in town, it is."
"Then you have something new to see; oh charming! how I envy you!—Are you pleased with the Pantheon?"
"Very much; I have seen no building at all equal to it."
"You have not been abroad. Traveling is the ruin of all happiness! There's no looking at a building here after seeing Italy."
"Does all happiness, then, depend upon sight of buildings?" said Cecilia, when, turning towards her companion, she perceived him yawning, with such evident inattention to her answer that, not choosing to interrupt his reverie, she turned her head another way.
For some minutes he took no notice of this; and then, as if suddenly recollecting himself, he called out hastily, "I beg your pardon, ma'am, you were saying something?"
"No, sir; nothing worth repeating."
"Oh, pray don't punish me so severely as not to let me hear it!"
Cecilia, though merely not to seem offended at his negligence, was then beginning an answer, when looking at him as she spoke, she perceived that he was biting his nails with so absent an air that he appeared not to know he had asked any question. She therefore broke off, and left him to his cogitation.
Some time after, he addressed her again, saying, "Don't you find this place extremely tiresome, ma'am?"
"Yes, sir," said she half laughing, "it is indeed not very entertaining!"
"Nothing is entertaining," answered he, "for two minutes together. Things are so little different one from another, that there is no making pleasure out of anything. We go the same dull round forever; nothing new, no variety! all the same thing over again! Are you fond of public places, ma'am?"
"Yes, sir, soberly, as Lady Grace says."
"Then I envy you extremely, for you have some amusement always in your own power. How desirable that is!"
"And have you not the same resources?"
"Oh no! I am tired to death! tired of everything! I would give the universe for a disposition less difficult to please. Yet, after all, what is there to give pleasure? When one has seen one thing, one has seen everything. Oh, 'tis heavy work! Don't you find it so, ma'am?"
This speech was ended with so violent a fit of yawning that Cecilia would not trouble herself to answer it: but her silence as before passed unnoticed, exciting neither question nor comment.
A long pause now succeeded, which he broke at last by saying, as he writhed himself about upon his seat, "These forms would be much more agreeable if there were backs to them. 'Tis intolerable to be forced to sit like a schoolboy. The first study of life is ease. There is indeed no other study that pays the trouble of attainment. Don't you think so, ma'am?"
"But may not even that," said Cecilia, "by so much study become labor?"
"I am vastly happy you think so."
"Sir?"
"I beg your pardon, ma'am, but I thought you said—I really beg your pardon, but I was thinking of something else."
"You did very right, sir," said Cecilia, laughing, "for what I said by no means merited any attention."
"Will you do me the favor to repeat it?" cried he, taking out his glass to examine some lady at a distance.
"Oh no," said Cecilia, "that would be trying your patience too severely."
"These glasses shew one nothing but defects," said he; "I am sorry they were ever invented. They are the ruin of all beauty; no complexion can stand them. I believe that solo will never be over! I hate a solo; it sinks, it depresses me intolerably."
"You will presently, sir," said Cecilia, looking at the bill of the concert, "have a full piece; and that I hope will revive you."
"A full piece! oh, insupportable! it stuns, it fatigues, it overpowers me beyond endurance! no taste in it, no delicacy, no room for the smallest feeling."
"Perhaps, then, you are only fond of singing?"
"I should be, if I could hear it; but we are now so miserably off in voices, that I hardly ever attempt to listen to a song, without fancying myself deaf from the feebleness of the performers. I hate everything that requires attention. Nothing gives pleasure that does not force its own way."
"You only, then, like loud voices, and great powers?"
"Oh, worse and worse!—no, nothing is so disgusting to me. All my amazement is that these people think it worth while to give concerts at all—one is sick to death of music."
"Nay," cried Cecilia, "if it gives no pleasure, at least it takes none away; for, far from being any impediment to conversation, I think everybody talks more during the performance than between the acts. And what is there better you could substitute in its place?"
Cecilia, receiving no answer to this question, again looked round to see if she had been heard; when she observed her new acquaintance, with a very thoughtful air, had turned from her to fix his eyes upon the statue of Britannia.
Very soon after, he hastily arose, and seeming entirely to forget that he had spoken to her, very abruptly walked away.
Mr. Gosport, who was advancing to Cecilia and had watched part of this scene, stopped him as he was retreating, and said, "Why, Meadows, how's this? are you caught at last?"
"Oh, worn to death! worn to a thread!" cried he, stretching himself and yawning; "I have been talking with a young lady to entertain her! oh, such heavy work! I would not go through it again for millions!"
"What, have you talked yourself out of breath?"
"No; but the effort! the effort!—Oh, it has unhinged me for a fortnight!—Entertaining a young lady!—one had better be a galley-slave at once!"
"Well, but did she not pay your toils? She is surely a sweet creature."
"Nothing can pay one for such insufferable exertion! though she's well enough, too—better than the common run—but shy, quite too shy; no drawing her out."
"I thought that was to your taste. You commonly hate much volubility. How have I heard you bemoan yourself when attacked by Miss Larolles!"
"Larolles! Oh, distraction! she talks me into a fever in two minutes. But so it is for ever! nothing but extremes to be met with! common girls are too forward, this lady is too reserved—always some fault! always some drawback! nothing ever perfect!"
"Nay, nay," cried Mr. Gosport, "you do not know her; she is perfect enough, in all conscience."
"Better not know her then," answered he, again yawning, "for she cannot be pleasing. Nothing perfect is natural,—I hate everything out of nature."
MISS BURNEY'S FRIENDS
From the 'Letters'
But Dr. Johnson's approbation!—it almost crazed me with agreeable surprise—it gave me such a flight of spirits that I danced a jig to Mr. Crisp, without any preparation, music, or explanation—to his no small amazement and diversion. I left him, however, to make his own comments upon my friskiness, without affording him the smallest assistance.
Susan also writes me word that when my father went last to Streatham, Dr. Johnson was not there, but Mrs. Thrale told him that when he gave her the first volume of 'Evelina,' which she had lent him, he said, "Why, madam, why, what a charming book you lent me!" and eagerly inquired for the rest. He was particularly pleased with the snow-hill scenes, and said that Mr. Smith's vulgar gentility was admirably portrayed; and when Sir Clement joins them, he said there was a shade of character prodigiously well marked. Well may it be said, that the greatest minds are ever the most candid to the inferior set! I think I should love Dr. Johnson for such lenity to a poor mere worm in literature, even if I were not myself the identical grub he has obliged.
Susan has sent me a little note which has really been less pleasant to me, because it has alarmed me for my future concealment. It is from Mrs. Williams, an exceeding pretty poetess, who has the misfortune to be blind, but who has, to make some amends, the honor of residing in the house of Dr. Johnson; for though he lives almost wholly at Streatham, he always keeps his apartments in town, and this lady acts as mistress of his house.
July 25.
"Mrs. Williams sends compliments to Dr. Burney, and begs he will intercede with Miss Burney to do her the favor to lend her the reading of 'Evelina.'"
Though I am frightened at this affair, I am by no means insensible to the honor which I receive from the certainty that Dr. Johnson must have spoken very well of the book, to have induced Mrs. Williams to send to our house for it.
I now come to last Saturday evening, when my beloved father came to Chesington, in full health, charming spirits, and all kindness, openness, and entertainment.
In his way hither he had stopped at Streatham, and he settled with Mrs. Thrale that he would call on her again in his way to town, and carry me with him! and Mrs. Thrale said, "We all long to know her."
I have been in a kind of twitter ever since, for there seems something very formidable in the idea of appearing as an authoress! I ever dreaded it, as it is a title which must raise more expectations than I have any chance of answering. Yet I am highly flattered by her invitation, and highly delighted in the prospect of being introduced to the Streatham society.
She sent me some very serious advice to write for the theatre, as she says I so naturally run into conversations that 'Evelina' absolutely and plainly points out that path to me; and she hinted how much she should be pleased to be "honored with my confidence."
My dear father communicated this intelligence, and a great deal more, with a pleasure that almost surpassed that with which I heard it, and he seems quite eager for me to make another attempt. He desired to take upon himself the communication to my Daddy Crisp; and as it is now in so many hands that it is possible accident might discover it to him, I readily consented.
Sunday evening, as I was going into my father's room, I heard him say, "The variety of characters—the variety of scenes—and the language—why, she has had very little education but what she has given herself—less than any of the others!" and Mr. Crisp exclaimed, "Wonderful!—it's wonderful!"
I now found what was going forward, and therefore deemed it most fitting to decamp.
About an hour after, as I was passing through the hall, I met my daddy [Crisp]. His face was all animation and archness; he doubled his fist at me and would have stopped me, but I ran past him into the parlor.
Before supper, however, I again met him, and he would not suffer me to escape; he caught both my hands and looked as if he would have looked me through, and then exclaimed, "Why, you little hussy—you young devil!—ain't you ashamed to look me in the face, you Evelina, you! Why, what a dance have you led me about it! Young friend, indeed! O you little hussy, what tricks have you served me!"
I was obliged to allow of his running on with these gentle appellations for I know not how long, ere he could sufficiently compose himself, after his great surprise, to ask or hear any particulars; and then he broke out every three instants with exclamations of astonishment at how I had found time to write so much unsuspected, and how and where I had picked up such various materials; and not a few times did he with me, as he had with my father, exclaim "Wonderful!"
He has since made me read him all my letters upon this subject. He said Lowndes would have made an estate had he given me £1000 for it, and that he ought not to have given less! "You have nothing to do now," continued he, "but to take your pen in hand; for your fame and reputation are made, and any bookseller will snap at what you write."
I then told him that I could not but really and unaffectedly regret that the affair was spread to Mrs. Williams and her friends.
"Pho," said he: "if those who are proper judges think it right that it should be known, why should you trouble yourself about it? You have not spread it, there can no imputation of vanity fall to your share, and it cannot come out more to your honor than through such a channel as Mrs. Thrale."
London, August.—I have now to write an account of the most consequential day I have spent since my birth; namely, my Streatham visit.
Our journey to Streatham was the least pleasant part of the day, for the roads were dreadfully dusty, and I was really in the fidgets from thinking what my reception might be, and from fearing they would expect a less awkward and backward kind of person than I was sure they would find.
Mr. Thrale's house is white, and very pleasantly situated in a fine paddock. Mrs. Thrale was strolling about, and came to us as we got out of the chaise.
She then received me, taking both my hands, and with mixed politeness and cordiality welcoming me to Streatham. She led me into the house, and addressed herself almost wholly for a few minutes to my father, as if to give me an assurance she did not mean to regard me as a show, or to distress or frighten me by drawing me out. Afterwards she took me up stairs, and showed me the house, and said she had very much wished to see me at Streatham; and should always think herself much obliged to Dr. Burney for his goodness in bringing me, which she looked upon as a very great favor.
But though we were some time together, and though she was so very civil, she did not hint at my book, and I love her much more than ever for her delicacy in avoiding a subject which she could not but see would have greatly embarrassed me.
When we returned to the music-room, we found Miss Thrale was with my father. Miss Thrale is a very fine girl, about fourteen years of age, but cold and reserved, though full of knowledge and intelligence.
Soon after, Mrs. Thrale took me to the library; she talked a little while upon common topics, and then at last she mentioned 'Evelina.'
"Yesterday at supper," said she, "we talked it all over, and discussed all your characters; but Dr. Johnson's favorite is Mr. Smith. He declares the fine gentleman manqué was never better drawn, and he acted him all the evening, saying 'he was all for the ladies!' He repeated whole scenes by heart. I declare I was astonished at him. Oh, you can't imagine how much he is pleased with the book; he 'could not get rid of the rogue,' he told me. But was it not droll," said she, "that I should recommend it to Dr. Burney? and tease him so innocently to read it?"
I now prevailed upon Mrs. Thrale to let me amuse myself, and she went to dress. I then prowled about to choose some book, and I saw upon the reading-table 'Evelina.' I had just fixed upon a new translation of Cicero's Lælius, when the library door was opened, and Mr. Seward entered. I instantly put away my book because I dreaded being thought studious and affected. He offered his services to find anything for me, and then in the same breath ran on to speak of the book with which I had myself "favored the world"!
The exact words he began with I cannot recollect, for I was actually confounded by the attack; and his abrupt manner of letting me know he was au fait equally astonished and provoked me. How different from the delicacy of Mr. and Mrs. Thrale!
When we were summoned to dinner, Mrs. Thrale made my father and me sit on each side of her. I said that I hoped I did not take Dr. Johnson's place;—for he had not yet appeared.
"No," answered Mrs. Thrale, "he will sit by you, which I am sure will give him great pleasure."
Soon after we were seated, this great man entered. I have so true a veneration for him, that the very sight of him inspires me with delight and reverence, notwithstanding the cruel infirmities to which he is subject; for he has almost perpetual convulsive movements, either of his hands, lips, feet, or knees, and sometimes of all together.
Mrs. Thrale introduced me to him, and he took his place. We had a noble dinner, and a most elegant dessert. Dr. Johnson, in the middle of dinner, asked Mrs. Thrale what was in some little pies that were near him.
"Mutton," answered she, "so I don't ask you to eat any, because I know you despise it!"
"No, madam, no," cried he; "I despise nothing that is good of its sort; but I am too proud now to eat of it. Sitting by Miss Burney makes me very proud to-day!"
"Miss Burney," said Mrs. Thrale, laughing, "you must take great care of your heart if Dr. Johnson attacks it; for I assure you he is not often successless."
"What's that you say, madam?" cried he; "are you making mischief between the young lady and me already?"
A little while after he drank Miss Thrale's health and mine, and then added:—
"'Tis a terrible thing that we cannot wish young ladies well without wishing them to become old women!"
"But some people," said Mr. Seward, "are old and young at the same time, for they wear so well that they never look old."
"No, sir, no," cried the doctor, laughing; "that never yet was: you might as well say they are at the same time tall and short."
ROBERT BURNS
(1759-1796)
BY RICHARD HENRY STODDARD

There have been, there are, and there always will be, poets concerning whose lives it is not necessary that the world should know anything in order to understand their poetry; and there have been, there are, and there always will be, other poets concerning whose lives it is necessary that the world should know all there is to be known, before it can begin to understand their poetry. The difference between these two classes of poets is the difference between a company of accomplished actors, who by virtue of their training and practice are able to project themselves into imaginary characters on the public stage, and the originals of these characters in private personal life; or to put it in other words, the difference between art and nature. It is the privilege of art to dispense with explanations and extenuations; for if it be true to itself it is sufficient in itself, and anything added to it or taken from it is an impertinence or a deformity. When we read 'Hamlet' and 'Lear,' or 'As You Like It' and 'Much Ado About Nothing,' we do not ask ourselves what Shakespeare meant by them,—why some scenes were written in verse and other scenes in prose,—for it is not of Shakespeare that we are thinking as we read, but of his characters, for whom we feel that he is no more responsible than we are, since they move, live, and have their being in a world of their own, above the smoke and stir of this dim spot which men call Earth,—the world of pure, perfect, poetic art. If Shakespeare was conscious of himself when he wrote, he succeeded in concealing himself so thoroughly that it is impossible to discover him in his writing,—as impossible as it is not to discover other poets in their writings; for whatever is absent from the choir of British song, the note of personality is always present there. A low laugh in the gracious mouth of Chaucer, a harsh rebuke on the stern lips of Milton, a modish sneer in the smile of Pope,—it was now a stifled complaint, now an amorous ditty, and now a riotous shout with Burns, who was as much a poet through his personality as through his genius. He put his life into his song; and not to know what his life was, is not to know what his song is,—why it was a consolation to him while he lived, and why after his death it made his—
"One of the few, the immortal names, That were not born to die."
Early in the last half of the eighteenth century a staid and worthy man, named William Burness (as the name Burns was then spelled), a native of Kincardineshire, emigrated to Ayrshire in pursuit of a livelihood. He hired himself as a gardener to the laird of Fairlie, and later to a Mr. Crawford of Doonside, and at length took a lease of seven acres of land on his own account at Alloway on the banks of the Doon. He built a clay cottage there with his own hands, and to this little cottage, in December 1757, he brought a wife, the eldest daughter of a farmer of Carrick. There was a disparity in their ages, for he was about thirty-six and she some eight or nine years younger; and a disparity in their education, for he was an intelligent reader and lover of books, while she, though she had been taught as a child to read the Bible and to repeat the Psalms, was not able to write her name. She had a great respect for her husband, whose occupation was now that of a nurseryman. A little more than a year after their marriage, on the 25th of January, 1759, she bore him a son who was christened Robert, who was followed, as time went on, by brothers and sisters; and before many years were over, what with the guidman, the guidwife, and the bonny bairns, there was not much spare room in the little clay biggin at Alloway.
Poor as they were, the social condition of this Scottish family was superior to the social condition of most English families in the same walk of rustic life; this superiority resulting from certain virtues inherent in the national character,—the virtues of simple appetites and frugal habits, of patience and courage in adversity, and best of all, in affectionate hearts, reverential minds, and a thirst for knowledge which only books could supply. William Burness inherited respect for education from his father, who in his young manhood was instrumental in building a schoolhouse on his farm at Clockenhill. Accordingly, when his son Robert was in his sixth year he sent him to a little school at Alloway Mill, about a mile from his cottage; and not long after he took the lead in hiring a young teacher named Murdoch to instruct him and his younger brother Gilbert at some place near at hand. Their school-books consisted of the Shorter Catechism, the Bible, the spelling-book, and Fisher's 'English Grammar.' Robert was a better scholar than Gilbert, especially in grammar, in which he acquired some proficiency. The only book which he is known to have read outside of his primitive curriculum was a 'Life of Hannibal,' which was loaned him by his teacher. When he was seven the family removed to a small upland farm called Mount Oliphant, about two miles from Alloway, to and from which the boys plodded daily in pursuit of learning. At the end of two years the teacher obtained a better situation in Carrick; the school was broken up, and from that time onward William Burness took upon himself the education of his lads and lassies, whom he treated as if they were men and women, conversing with them on serious topics as they accompanied him in his labors on the farm, and borrowing for their edification, from a Book Society in Ayr, solid works like Derham's 'Physico- and Astro-Theology' and Ray's 'Wisdom of God in the Creation.' This course of heavy reading was lightened by the 'History of Sir William Wallace,' which was loaned to Robert by a blacksmith named Kilpatrick, and which forced a hot flood of Scottish feeling through his boyish veins. His next literary benefactor was a brother of his mother, who while living for a time with the family had learned some arithmetic by their winter evening's candle. He went one day into a bookseller's shop in Ayr to purchase a Ready Reckoner and a Complete Letter-Writer, but procured by mistake in place of the latter a small collection of 'Letters by Eminent Wits,' which proved of more advantage (or disadvantage) to his nephew than to himself, for it inspired the lad with a desire to excel in epistolary writing. Not long after this Robert's early tutor Murdoch returned to Ayr, and lent him Pope's Works; a bookish friend of his father's obtained for him the reading of two volumes of Richardson's 'Pamela' and another friendly soul the reading of Smollett's 'Ferdinand Count Fathom,' and 'Peregrine Pickle.' The book which most delighted him, however, was a collection of English songs called 'The Lark.'

ROBERT BURNS.
Mount Oliphant taxed the industry and endurance of William Burness to the utmost; and what with the sterility of the soil, which was the poorest in the parish, and the loss of cattle by accidents and disease, it was with great difficulty that he managed to support his family. They lived so sparingly that butcher's meat was for years a stranger in the house, and they labored, children and all, from morning to night. Robert, at the age of thirteen, assisted in threshing the crop of corn, and at fifteen he was the principal laborer on the farm, for they could not afford a hired hand. That he was constantly afflicted with a dull headache in the evenings was not to be wondered at; nor that the sight and thought of his gray-haired father, who was turned fifty, should depress his spirits and impart a tinge of gloom to his musings. It was under circumstances like these that he composed his first song, the inspiration of which was a daughter of the blacksmith who had loaned him the 'History of Sir William Wallace.' It was the custom of the country to couple a man and woman together in the labors of harvest; and on this occasion his partner was Nelly Kilpatrick, with whom, boy-like,—for he was in his seventeenth year and she a year younger,—he liked to lurk behind the rest of the hands when they returned from their labors in the evening, and who made his pulse beat furiously when he fingered over her little hand to pick out the cruel nettle-stings and thistles. She sang sweetly, and among her songs there was one which was said to be composed by a small laird's son about one of his father's maids, with whom he was in love; and Robert saw no reason why he should not rhyme as well as he, for the author had no more school-craft than himself. Writing of this song a few years later, he called it puerile and silly; and his verdict as a poetical one was correct. Still, considered as a song, this artless effusion possessed one merit of which he himself was probably not conscious: it was inspired by his feeling and not by his reading, by the warmth and purity of his love of Nelly Kilpatrick, and not by his admiration of any amorous ditty in his collection of English songs. It was a poor thing, but it was certainly his own, and nowhere more so than in its recognition of the womanly personality of its heroine:—
"And then there's something in her gait Gars ony dress look weel."
This touch of nature, which no modish artist would have attempted, marked the hand of one who painted from the life.
William Burness struggled along for twelve years at Mount Oliphant, and then removed to Lochlea, in the parish of Tarbolton. Here he rented a larger farm, the soil of which promised a surer maintenance for himself and the hostages he had given to Fortune. And there these loving hostages began to put away childish things, and to become men and women. They were cheerful, in spite of the frugality which their poverty imposed upon them; and were merry in their simple homely way, singing and dancing among themselves and among their friendly neighbors. Their hearts expanded in the healthy air about them, particularly the heart of Robert, which turned to thoughts of love,—not lightly, as in his boyish fancy for Nelly Kilpatrick, but seriously, as beseemed a man; for he was now in his nineteenth year, and as conscious of what he was to woman as of what woman was to him. A born lover, and a born poet, he discovered himself and his song at Tarbolton. The custom of the country and the time sanctioned a freedom of manners, and a frequency of meeting on the part of rustic amorists, of which he was not slow to avail himself. The love affairs of the Scottish peasantry are thus described by one of his biographers:—"The young farmer or plowman, after his day of exhausting toil, would proceed to the home of his mistress, one, two, three, or more miles distant, there signal her to the door, and then the pair would seat themselves in the barn for an hour or two's conversation." Burns practiced this mode of courtship, which was the only one open to him, and among the only women whom he knew at Tarbolton. "He made no distinction between the farmer's own daughters and those who acted as his servants, the fact after all being that the servants were often themselves the daughters of farmers, and only sent to be the hirelings of others because their services were not needed at home." We should remember this habit of the Scottish peasantry if we wish to understand the early songs of Burns; for they were suggested by it, and vitalized by it, as much as by his impassioned genius. He painted what he saw; he sang what he felt. We have a glimpse of him in one of his winter courtships in 'My Nanie, O'; another and warmer glimpse of him in one of his summer courtships in 'The Rigs o' Barley'; and another and livelier glimpse of him in one of his mocking moods in 'Tibbie, I hae seen the day.' But he was more than the lover which these songs revealed: he was a man of sound understanding and fine, active intelligence, gifted with ready humor and a keen sense of wit. If he had been other than he was, he might and probably would have been elated by his poetic powers, of which he must have been aware; but being what he was, he was content to enjoy them and to exercise them modestly, and at such scanty intervals as his daily duties afforded. He composed his songs as he went about his work, plowing, sowing, reaping; crooning them as he strode along the fields, and correcting them in his head as the hours dragged on, until night came, and he could write them down in his little room by the light of his solitary candle. He had no illusions about himself: he was the son of a poor farmer, who, do what he might, was never prosperous; and poverty was his portion. His apprehension, which was justified by the misfortunes of the family at Mount Oliphant, was confirmed by their dark continuance at Tarbolton, where he saw his honored father, bowed with years of toil, grow older and feebler day by day, dying of consumption before his eyes. The end came on February 13th, 1784; and a day or two afterwards the humble coffin of William Burness, arranged between two leading horses placed after each other, and followed by relations and neighbors on horseback, was borne to Alloway and buried in the old kirkyard.
The funeral over, the family removed to Mossgiel, in the parish of Mauchline, where, at Martinmas, Robert and Gilbert had rented another farm. Having no means of their own, they and their sisters were obliged to rank as creditors of their dead father for the arrears of wages due them as laborers at Lochlea; and it was with these arrears, which they succeeded in wresting from their old landlord or his factor, that they stocked the new farm. The change was a beneficial one for all the family, who were now for the first time in their lives provided with a comfortable dwelling; and everything considered, especially so for their head,—which Robert, who was now in his twenty-sixth year, virtually became. He realized the gravity of the responsibility which rested upon him, and rightly judging that industry alone would not enable him to support it, resolved to work with the brains of others as well as his own hard hands. He read farming books, he calculated crops, he attended markets, but all to no purpose; for like his father before him, however much he may have deserved success, he could not command it. What he could and did command however was the admiration of his fellows, who were quick to perceive and ready to acknowledge his superiority. There was that about him which impressed them,—something in his temperament or talent, in his personality or character, which removed him from the roll of common men. What seemed to distinguish him most was the charm of his conversation, which, remarkable as it was for fluency and force, for originality and brilliancy, was quite as remarkable for good sense and good feeling. Grave or gay, as the occasion suggested and the spirit moved him, he spoke as with authority and was listened to with rapt attention. His company was sought, and go where he would he was everywhere welcomed as a good fellow. He had the art of making friends; and though they were not always of the kind that his well-wishers could have desired, they were the best of their kind in and about Mauchline. What he saw in some of them, other than the pleasure they felt in his society, it is hard to say; but whatever it was, he liked it and the conviviality to which it led,—which, occasionally coarsened by stories that set the table in a roar, was ever and anon refined by songs that filled his eyes with tears. His life was a hard one,—a succession of dull, monotonous, laborious days, haunted by anxiety and harassed by petty, irritating cares,—but he faced it cheerfully, manfully, and wrestled with it triumphantly, for he compelled it to forge the weapons with which he conquered it. He sang like a boy at Lochlea; he wrote like a man at Mossgiel. The first poetical note that he struck there was a personal one, and commemorative of his regard for two rustic rhymers, David Sillar and John Lapraik, to whom he addressed several Epistles,—a form of composition which he found in Ferguson and Ramsay, and of which he was enamored. That he thoroughly enjoyed the impulse which suggested and dictated these Epistles was evident from the spirit with which they were written. In the first of the two, which he addressed to Sillar, he discovered and disclosed for the first time the distinctive individuality of his genius. It was a charming and touching piece of writing; charming as a delineation of his character, and touching as a confession of his creed,—the patient philosophy of the poor. As his social horizon was enlarged, his mental vision was sharpened; and before long, other interests than those which concerned himself and his poetical friends excited his sympathies and stimulated his powers. It was a period of theological squabbles, and he plunged into them at once, partly no doubt because there was a theological strain in his blood, but largely because they furnished opportunities for the riotous exercise of his wit. He paid his disrespects to the fomenters of this holy brawl in 'The Twa Herds,' and he pilloried an old person who was obnoxious to him, in that savage satire on sanctimonious hypocrisy, 'Holy Willy's Prayer.' Always a poet, he was more, much more than a poet. He was a student of man,—of all sorts of men; caring much, as a student, for the baser sort which reveled in Poosie Nansie's dram-shop, and which he celebrated in 'The Jolly Beggars'; but caring more, as a man, for the better sort which languished in huts where poor men lodged, and of which he was the voice of lamentation in 'Man was Made to Mourn.' He was a student of manners, which he painted with a sure hand, his masterpiece being that reverential reproduction of the family life at Lochlea,—'The Cotter's Saturday Night.' He was a student of nature,—his love of which was conspicuous in his poetry, flushing his words with picturesque phrases and flooding his lines with the feeling of outdoor life. He was a student of animal life,—a lover of horses and dogs, observant of their habits and careful of their comfort. He felt for the little mouse which his plowshare turned out of its nest, and he pitied the poor hare which the unskillful fowler could only wound. The commoners of earth and air were dear to him; and the flower beside his path, the gowan wet with dew, was precious in his eyes. His heart was large, his mind was comprehensive, and his temper singularly sweet and sunny.
Such was Robert Burns at Mossgiel, and a very likable person he was. But all the while there was another Robert Burns at Mossgiel, and he was not quite so likable. He had a strange fascination for women, and a strange disregard of the consequences of this fascination. This curious combination of contradictory traits was an unfortunate one, as a young woman of Mauchline was destined to learn. She was the daughter of a mason, and her name was Jean Armour. He met her on a race day at a house of entertainment which must have been popular, since it contained a dancing-hall, admission to which was free, any man being privileged to invite to it any woman whom he fancied and for whose diversion he was willing to disburse a penny to the fiddler. He was accompanied on this occasion by his dog, who insisted on following him into the hall and persisted in keeping at his heels while he danced,—a proof of its fidelity which created considerable amusement, and which its master turned to his personal account by saying he wished he could get any of the lasses to like him as well as his dog. Jean heard his remark, and not long afterwards, as he was passing through the washing-green where she was bleaching clothes (from which she begged him to call off his troublesome follower), she reminded him of it by asking him if he had yet got any of the lasses to like him as well as did his dog? He got one there and then; for from that hour Jean was attached to him and he to Jean. He was reticent about his conquest, concealing it from his closest friends, and even from his dearest foe, the Muse; but however reticent, his conquest was not to be concealed, for Jean one day discovered that she was with child. What he felt when this calamity was made known to him we know not, for he kept his own counsel. What he wished his friends to feel, if they could and would, we may divine from a poem which he wrote about this time,—an address to the rigidly righteous, into whose minds he sought to instill the charity of which he and Jean were sorely in need:—
"Then gently scan your brother man, Still gentler sister woman; Though they may gang a kennin' wrang To step aside is human:
"One point must still be greatly dark, The moving why they do it; And just as lamely can ye mark How far perhaps they rue it."
He wrote a paper which he gave Jean, in the belief that it constituted a marriage between them,—a belief which was perhaps justifiable in the existing condition of Scottish laws of marriage. But he counted without his host; for instead of accepting it as a manly endeavor to shield the reputation of his daughter and divert scandal from his family, the hot-headed father of Jean denounced it and demanded its destruction,—a foolish proceeding to which his foolish daughter consented. Whether its destruction could destroy his obligation need not be curiously considered; it is enough to know that he believed that it did, and that it was a proof of perfidy on the part of Jean. But they should see! She had forsaken him, and he would forsake her. So, the old love being off, he was straightway on with a new one. Of this new love little is known, except that she was, or had been, a servant in the family of one of his friends,—a nurserymaid or something of the sort,—and that she was of Highland parentage. Her name was Mary Campbell. He transferred his affections from Jean to Mary, and his fascination was so strong that she promised to become his wife. They met one Sunday in a sequestered spot on the banks of the Ayr, where, standing on each side of a little brook, they laved their hands in its limpid waters, plighted their troth, and exchanged Bibles,—she giving him her copy, which was a small one, he giving her his copy, which was a large one in two volumes, on the blank leaves of which he had written his name and two quotations from the sacred text, one being the solemn injunction to fidelity in Leviticus:—"And ye shall not swear by my name falsely. I am the Lord." They parted. She returned to her relatives, among whom she died a few months afterward of a malignant fever; he returned to his troubles at Mossgiel. They were not all of his own making. It was not his fault that the farm was an unproductive one; he could not impart fertility to barren acres nor compel the sun to ripen scanty crops. In the hope of bettering his fortunes he resolved to expatriate himself, and entered into negotiations with a man who had an estate in the West Indies, and who agreed to employ him as his factor. He had no money and no means of getting any, except by the publication of his poems, none of which had yet appeared in print. He issued a prospectus for their publication by subscription; and such was the reputation they had made for him through their circulation in manuscript, and the activity of his friends, that the necessary number of subscribers was soon obtained. They were published at Kilmarnock in the summer of 1786, and were read by all classes,—by the plowman as eagerly as by the laird, by the milkmaid in the dairy as eagerly as by her mistress in the parlor,—and wherever they were read they were admired. No poet was ever so quickly recognized as Burns, who captivated his readers by his human quality as well as his genius. They understood him at once. He sung of things which concerned them,—of emotions which they felt, the joys and sorrows of their homely lives, and, singing from his heart, his songs went to their hearts. His fame as a poet spread along the country and came to the knowledge of Dr. Blacklock, a blind poet in Edinburgh, who after hearing Burns's poetry was so impressed by it that he wrote or dictated a letter about it, which he addressed to a correspondent in Kilmarnock, by whom it was placed in the hands of Burns. He was still at Mossgiel, and in a perturbed condition of mind, not knowing whether he could remain there, or whether he would have to go to Jamaica. He resolved at last to do neither, but to go to Edinburgh, which he accordingly did, proceeding thither on a pony borrowed from a friend.
The visit of Burns to Edinburgh was a hazardous experiment from which he might well have shrunk. He was ignorant of the manners of its citizens,—the things which differentiated them as a class from the only class he knew,—but his ignorance did not embarrass him. He was self-possessed; manly in his bearing; modest, but not humble; courteous, but independent. He had no letters of introduction, and needed none, for his poetry had prepared the way for him. It was soon known among the best people in Edinburgh that he was there, and they hastened to make his acquaintance; one of the first to do so being a man of rank, Lord Glencairn. To know him was to know other men of rank, and to be admitted to the brilliant circles in which they moved. Burns's society was sought by the nobility and gentry and by the literary lords of the period, professors, historians, men of letters. They dined him and wined him and listened to him,—listened to him eagerly, for here as elsewhere he distinguished himself by his conversation, the charm of which was so potent that the Duchess of Gordon declared that she was taken off her feet by it. He increased his celebrity in Edinburgh by the publication of a new and enlarged edition of his Poems, which he dedicated to the noblemen and gentlemen of the Caledonian Hunt in a page of manly prose, the proud modesty and the worldly tact of which must have delighted them. "The poetic genius of my country found me," he wrote, "as the prophetic bard Elijah did Elisha, and threw her inspiring mantle over me. She bade me sing the loves, the joys, the rural scenes and rural pleasures of my native soil in my native tongue. I tuned my wild, artless notes as she inspired. She whispered me to come to this ancient metropolis of Caledonia and lay my songs under your honored protection. I now obey her dictates." His mind was not active at this time, for beyond a few trivial verses he wrote nothing worthy of him except a short but characteristic 'Epistle to the Guidwife of Wauchope House.' He spent the winter of 1786 and the spring of 1787 in Edinburgh; and summer being close at hand, he resolved to return for a time to Mossgiel. There were strong reasons for his return, some of which pertained to his impoverished family, whom he was now in a condition to assist, for the new edition of his Poems had proved profitable to himself, and others—for before his departure for Edinburgh, Jean had borne twins, a boy and a girl; and the girl was being cared for at Mossgiel. He returned therefore to his family and his child, and whether he purposed to do so or not, to the mother of his child. It was not a wise thing to do, perhaps, but it was a human thing, and very characteristic of the man, who, whatever else he was not, was very human. And the Armours were very human also, for old Armour received him into his house, and Jean received him into her arms. She was not a prudent young woman, but she was a fond and forgiving one.
The life of Burns during the next twelve months may be briefly described. He returned to Edinburgh, where in his most serious moods he held sessions of thought. It may have been a silent one, but it was not a sweet one; for while he summoned up remembrance of things past, he summoned up apprehensions of things to come. That he had won distinction as a poet was certain; what was not certain was the duration of this distinction. He was famous to-day; he might be forgotten to-morrow. But famous or forgotten, he and those dependent on him must have bread; and since he saw no reasonable prospect of earning it with his head, he must earn it with his hands. They were strong and willing. So he leased a farm at Ellisland in Dumfriesshire, and obtained an appointment from the Board of Excise: then, poet, farmer, and exciseman, he went back to Mauchline and was married to Jean. Leaving her and her child he repaired to Ellisland, where he was obliged to build a cottage for himself. He dug the foundations, collected stone and sand, carted lime, and generally assisted the masons and carpenters. Nor was this all, for he directed at the same time whatever labor the careful cultivation of a farm demanded from its tenant. He was happy at Ellisland,—happier than he had been at Mount Oliphant, where his family had been so sorely pinched by poverty, and much happier than he had been at Mossgiel, where he had wrought so much trouble for himself and others. A good son and a good brother, he was a good husband and a good father. It was in no idle moment that he wrote this stanza, which his conduct now illustrated:—
"To make a happy fireside chime To weans and wife, That's the true pathos and sublime Of human life."
His life was orderly; his wants were few and easily supplied; his mind was active, and his poetical vein more productive than it had been at Edinburgh. The best lyric that he wrote at Ellisland was the one in praise of his wife ('Of a' the airts the wind can blaw—'); the most important poem 'Tam o' Shanter.' Farmer and exciseman, he was very busy,—busier, perhaps, as the last than the first, for while his farming labors might be performed by others, his excise labors could only be performed by himself; the district under his charge covering ten parishes, the inspection of which required his riding about two hundred miles a week. The nature of his duties, and the spirit with which he went through them, may be inferred from a bit of his doggerel:—
"Searching auld wives' barrels, Och, hone, the day! That clarty barm should stain my laurels: But—what'll ye say— These movin' things ca'd wives and weans Wad move the very hearts o' stanes!"
A model exciseman, he was neither a model nor a prosperous farmer, for here as elsewhere, mother earth was an unkind stepmother to him. He struggled on, hoping against hope, from June 1788 to December 1791; then, beaten, worn out, exhausted, he gave up his farm and removed to Dumfries, exchanging his cozy cottage with its outlook of woods and waters for a mean little house in the Wee Vennel, with its inlook of narrow dirty streets and alleys. His life in Dumfries was not what one could wish it might have been for his sake; for though it was not without its hours of happiness, its unhappy days were many, and of a darker kind than he had hitherto encountered. They were monotonous, they were wearisome, they were humiliating. They could not be other than humiliating to a man of his proud, impulsive spirit, who, schooling himself to prudence on account of his wife and children, was not always prudent in his speech. Who indeed could be, unless he were a mean, cowardly creature, in the storm and stress of the great Revolution with which France was then convulsed? His utterances, whatever they may have been, were magnified to his official and social disadvantage, and he was greatly troubled. He felt his disfavor with the people of Dumfries,—as he could not help showing to one of his friends, who, riding into the town on a fine summer evening to attend a county ball, saw him walking alone on the shady side of the principal street, while the other side was crowded with ladies and gentlemen who seemed unwilling to recognize him. This friend dismounted, and joining him, proposed that they should cross the street. "Nay, nay, my young friend," said the poet, "that's all over now." Then, after a pause, he quoted two stanzas from a pathetic ballad by Lady Grizel Bailie:—
"His bonnet stood then fu' fair on his brow, His auld are looked better than mony ane's new; But now he lets 't wear ony way it will hing, And casts himself doure upon the corn bing.
"O were we young now as we ance hae been, We should hae been galloping down on yon green, And linking it owre the lily-white lea— And werena my heart light I wad die."
The light heart of Burns failed him at last,—failed him because, enfeebled by disease and incapacitated from performing his excise duties, his salary, which had never exceeded seventy pounds a year, was reduced to half that beggarly sum; because he was so distressed for money that he was obliged to solicit a loan of a one-pound note from a friend: failed him, poor heart, because it was broken! He took to his bed for the last time on July 21st, 1796, and two days later, surrounded by his little family, he passed away in the thirty-eighth year of his age.

BURNS.
Facsimile of the original of his version of the Scottish song
"Here's a Health to Them that's Awa."
Such was the life of Robert Burns,—the hard, struggling, erring, suffering, manly life, of which his poetry is the imperishable record. He was what his birth, his temperament, his circumstances, his genius made him. He owed but little to books, and the books to which he owed anything were written in his mother tongue. His English reading, which was not extensive, harmed him rather than helped him. No English author taught or could teach him anything. He was not English, but Scottish,—Scottish in his nature and genius, Scottish to his heart's core,—the singer of the Scottish people, their greatest poet, and the greatest poet of his time.
THE COTTER'S SATURDAY NIGHT
My loved, my honored, much respected friend! No mercenary bard his homage pays; With honest pride I scorn each selfish end; My dearest meed, a friend's esteem and praise: To you I sing, in simple Scottish lays, The lowly train in life's sequestered scene; The native feelings strong, the guileless ways; What Aiken in a cottage would have been; Ah! though his worth unknown, far happier there, I ween.
November chill blaws loud wi' angry sugh1; The shortening winter day is near a close; The miry beasts retreating frae the pleugh; The blackening trains o' craws to their repose The toil-worn Cotter frae his labor goes; This night his weekly moil is at an end; Collects his spades, his mattocks, and his hoes, Hoping the morn in ease and rest to spend, And weary, o'er the moor his course does hameward bend.
At length his lonely cot appears in view, Beneath the shelter of an aged tree; The expectant wee-things, toddlin, stacher2 through To meet their Dad, wi' flichterin noise an' glee. His wee bit ingle,3 blinking bonnily, His clean hearthstane, his thriftie wifie's smile, The lisping infant prattling on his knee, Does a' his weary carking cares beguile, An' makes him quite forget his labor an' his toil.
Belyve4 the elder bairns come drapping in, At service out, amang the farmers roun'; Some ca' the pleugh, some herd, some tentie5 rin A cannie errand to a neebor town. Their eldest hope, their Jenny, woman grown, In youthfu' bloom, love sparkling in her e'e, Comes hame, perhaps, to shew a braw new gown, Or deposit her sair-won penny-fee, To help her parents dear, if they in hardship be.
Wi' joy unfeigned brothers and sisters meet, An' each for other's weelfare kindly speirs6: The social hours, swift-winged, unnoticed fleet; Each tells the uncos7 that he sees or hears: The parents, partial, eye their hopeful years; Anticipation forward points the view. The mother, wi' her needle an' her shears, Gars8 auld claes look amaist as weel's the new; The father mixes a' wi' admonition due.
Their masters' an' their mistresses' command, The yonkers a' are warnèd to obey; An' mind their labors wi' an eydent9 hand, An' ne'er, though out o' sight, to jauk10 or play: "An' O! be sure to fear the Lord alway! An' mind your duty duly, morn an' night! Lest in temptation's path ye gang astray, Implore His counsel and assisting might: They never sought in vain that sought the Lord aright!"
But hark! a rap comes gently to the door; Jenny, wha kens the meaning o' the same, Tells how a neebor lad cam o'er the moor, To do some errands, and convoy her hame. The wily mother sees the conscious flame Sparkle in Jenny's e'e, and flush her cheek; With heart-struck anxious care, inquires his name, While Jenny hafflins11 is afraid to speak: Weel pleased, the mother hears it's nae wild, worthless rake.
Wi' kindly welcome Jenny brings him ben,12 A strappan youth; he taks the mother's eye; Blithe Jenny sees the visit's no ill ta'en: The father cracks13 of horses, pleughs, and kye:14 The youngster's artless heart o'erflows wi' joy, But blate15 and laithfu',16 scarce can weel behave; The mother, wi' a woman's wiles, can spy What makes the youth sae bashfu' an' sae grave; Weel pleased to think her bairn's respected like the lave.17
O happy love, where love like this is found! O heartfelt raptures! bliss beyond compare! I've pacèd much this weary mortal round, And sage experience bids me this declare:— "If Heaven a draught of heavenly pleasure spare, One cordial in this melancholy vale, 'Tis when a youthful, loving, modest pair, In other's arms breathe out the tender tale, Beneath the milk-white thorn that scents the evening gale."
Is there in human form, that bears a heart— A wretch! a villain! lost to love and truth! That can, with studied, sly, ensnaring art, Betray sweet Jenny's unsuspecting youth? Curse on his perjured arts! dissembling, smooth! Are honor, virtue, conscience, all exiled? Is there no pity, no relenting ruth, Points to the parents fondling o'er their child? Then paints the ruined maid, and their distraction wild?
But now the supper crowns their simple board, The halesome parritch,18 chief o' Scotia's food: The soupe their only Hawkie19 does afford, That 'yont the hallan20 snugly chows her cood:21 The dame brings forth in complimental mood, To grace the lad, her weel-hained22 kebbuck,23 fell, An' aft he's prest, an' aft he ca's it guid; The frugal wifie, garrulous, will tell, How 'twas a towmond24 auld, sin' lint was i' the bell.25
The cheerfu' supper done, wi' serious face, They round the ingle form a circle wide: The sire turns o'er, wi' patriarchal grace, The big ha' Bible, ance his father's pride; His bonnet rev'rently is laid aside, His lyart haffets26 wearing thin an' bare; Those strains that once did sweet in Zion glide, He wales27 a portion wi' judicious care; And "Let us worship God!" he says, with solemn air.
They chant their artless notes in simple guise, They tune their hearts, by far the noblest aim: Perhaps 'Dundee's' wild warbling measures rise, Or plaintive 'Martyrs,' worthy of the name; Or noble 'Elgin' beets28 the heavenward flame, The sweetest far of Scotia's holy lays: Compared with these, Italian trills are tame; The tickled ears no heartfelt raptures raise; Nae unison hae they with our Creator's praise.
The priest-like father reads the sacred page, How Abram was the friend of God on high; Or Moses bade eternal warfare wage With Amalek's ungracious progeny; Or how the royal bard did groaning lie Beneath the stroke of Heaven's avenging ire; Or Job's pathetic plaint, and wailing cry; Or rapt Isaiah's wild, seraphic fire: Or other holy seers that tune the sacred lyre.
Perhaps the Christian volume is the theme: How guiltless blood for guilty man was shed; How He who bore in heaven the second name Had not on earth whereon to lay his head: How his first followers and servants sped; The precepts sage they wrote to many a land; How he who, lone in Patmos banishèd, Saw in the sun a mighty angel stand; And heard great Bab'lon's doom pronounced by Heaven's command.
Then kneeling down, to Heaven's Eternal King The saint, the father, and the husband prays: Hope "springs exulting on triumphant wing,"29 That thus they all shall meet in future days: There ever bask in uncreated rays, No more to sigh, or shed the bitter tear, Together hymning their Creator's praise, In such society, yet still more dear; While circling time moves round in an eternal sphere.
Compared with this, how poor Religion's pride, In all the pomp of method and of art, When men display to congregations wide Devotion's every grace, except the heart! The Power, incensed, the pageant will desert, The pompous strain, the sacerdotal stole; But haply in some cottage far apart, May hear, well pleased, the language of the soul; And in his Book of Life the inmates poor enroll.
Then homeward all take off their several way; The youngling cottagers retire to rest: The parent pair their secret homage pay, And proffer up to Heaven the warm request That He who stills the raven's clamorous nest, And decks the lily fair in flowery pride, Would, in the way His wisdom sees the best, For them and for their little ones provide; But chiefly in their hearts with grace divine preside.
From scenes like these old Scotia's grandeur springs, That makes her loved at home, revered abroad; Princes and lords are but the breath of kings, "An honest man's the noblest work of God:"30 And certes, in fair virtue's heavenly road, The cottage leaves the palace far behind; What is a lordling's pomp! a cumbrous load, Disguising oft the wretch of human kind, Studied in arts of hell, in wickedness refined!
O Scotia! my dear, my native soil! For whom my warmest wish to Heaven is sent! Long may thy hardy sons of rustic toil Be blest with health, and peace, and sweet content! And oh! may Heaven their simple lives prevent From Luxury's contagion weak and vile! Then, howe'er crowns and coronets be rent, A virtuous populace may rise the while, And stand a wall of fire around their much-loved Isle.
O Thou! who poured the patriotic tide That streamed through Wallace's undaunted heart; Who dared to nobly stem tyrannic pride, Or nobly die, the second glorious part, (The patriot's God peculiarly thou art, His friend, inspirer, guardian, and reward!) O never, never, Scotia's realm desert; But still the patriot, and the patriot bard, In bright succession raise, her ornament and guard!
JOHN ANDERSON, MY JO
Sough.
Stagger.
Fire, or fireplace.
By-and-by.
Careful.
Inquires.
News.
Makes.
Diligent.
Dally.
Half.
Into the spence, or parlor.
Gossips.
Cows.
Bashful.
Sheepish.
Rest.
Porridge.
A white-faced cow.
Wall.
Chews her cud.
Saved.
Cheese.
Twelvemonth.
Flax was in flower.
Gray locks.
Chooses.
Increases.
Pope's 'Windsor Forest.'
Pope's 'Essay on Man.'
John Anderson, my jo, John, When we were first acquent, Your locks were like the raven, Your bonnie brow was brent; But now your brow is bald, John, Your locks are like the snaw; But blessings on your frosty pow, John Anderson, my jo.
John Anderson, my jo, John, We clamb the hill thegither; And mony a canty day, John, We've had wi' ane anither: Now we maun totter down, John, But hand in hand we'll go; And sleep thegither at the foot, John Anderson, my jo.
MAN WAS MADE TO MOURN
A Dirge
When chill November's surly blast Made fields and forests bare, One evening, as I wandered forth Along the banks of Ayr, I spied a man, whose aged step Seemed weary, worn with care; His face was furrowed o'er with years, And hoary was his hair.
"Young stranger, whither wanderest thou?" Began the reverend sage; "Does thirst of wealth thy step constrain, Or youthful pleasure's rage? Or haply, pressed with cares and woes, Too soon thou hast began To wander forth, with me, to mourn The miseries of man!
"The sun that overhangs yon moors, Outspreading far and wide, Where hundreds labor to support A haughty lordling's pride;— I've seen yon weary winter sun Twice forty times return; And every time has added proofs That man was made to mourn.
"O man! while in thy early years, How prodigal of time! Misspending all thy precious hours, Thy glorious youthful prime! Alternate follies take the sway, Licentious passions burn; Which tenfold force gives Nature's law, That man was made to mourn.
"Look not alone on youthful prime, Or manhood's active might; Man then is useful to his kind, Supported is his right: But see him on the edge of life, With cares and sorrows worn, Then age and want—oh ill-matched pair!— Show man was made to mourn.
"A few seem favorites of fate, In Pleasure's lap caressed; Yet think not all the rich and great Are likewise truly blest. But oh! what crowds in every land Are wretched and forlorn! Through weary life this lesson learn, That man was made to mourn.
"Many and sharp the num'rous ills Inwoven with our frame; More pointed still we make ourselves Regret, remorse, and shame! And man, whose heaven-erected face The smiles of love adorn, Man's inhumanity to man Makes countless thousands mourn!
"See yonder poor o'er-labored wight, So abject, mean, and vile, Who begs a brother of the earth To give him leave to toil; And see his lordly fellow-worm The poor petition spurn, Unmindful, though a weeping wife And helpless offspring mourn.
"If I'm designed yon lordling's slave, By Nature's law designed, Why was an independent wish E'er planted in my mind? If not, why am I subject to His cruelty or scorn? Or why has man the will and power To make his fellow mourn?
"Yet let not this too much, my son, Disturb thy youthful breast; This partial view of humankind Is surely not the best! The poor, oppressèd, honest man, Had never, sure, been born, Had there not been some recompense To comfort those that mourn.
"O Death! the poor man's dearest friend— The kindest and the best! Welcome the hour my agèd limbs Are laid with thee at rest! The great, the wealthy, fear thy blow From pomp and pleasure torn; But, oh! a blest relief to those That weary-laden mourn!"
GREEN GROW THE RASHES
There's naught but care on every han', In every hour that passes, O: What signifies the life o' man, An 't werena for the lasses, O?
CHORUS
Green grow the rashes, O! Green grow the rashes, O! The sweetest hours that e'er I spent Were spent amang the lasses, O!
The warly race may riches chase, An' riches still may fly them, O; An' though at last they catch them fast, Their hearts can ne'er enjoy them, O.
But gi'e me a canny hour at e'en, My arms about my dearie, O; An' warly cares, an' warly men, May a' gae tapsalteerie, O!
For you sae douce, ye sneer at this, Ye're nought but senseless asses, O; The wisest man the warl' e'er saw, He dearly loved the lasses, O.
Auld Nature swears the lovely dears Her noblest work she classes, O; Her 'prentice han' she tried on man, An' then she made the lasses, O.
IS THERE FOR HONEST POVERTY
Is there for honest poverty That hangs his head, and a' that? The coward slave, we pass him by, We dare be poor for a' that! For a' that, and a' that, Our toil's obscure, and a' that: The rank is but the guinea's stamp, The man's the gowd for a' that.
What though on hamely fare we dine, Wear hoddin gray, and a' that? Gi'e fools their silks, and knaves their wine, A man's a man for a' that; For a' that, and a' that, Their tinsel show, and a' that— The honest man, though e'er sae poor, Is king o' men for a' that.
Ye see yon birkie,31 ca'd a lord, Wha struts, and stares, and a' that: Though hundreds worship at his word, He's but a coof32 for a' that: For a' that, and a' that, His riband, star, and a' that— The man of independent mind, He looks and laughs at a' that.
A prince can mak' a belted knight, A marquis, duke, and a' that, But an honest man's aboon his might— Guid faith, he mauna fa' that! For a' that, and a' that, Their dignities, and a' that, The pith o' sense and pride o' worth Are higher ranks than a' that.
Then let us pray that come it may— As come it will for a' that— That sense and worth, o'er a' the earth, May bear the gree, and a' that. For a' that, and a' that, It's comin' yet, for a' that,— That man to man, the warld o'er, Shall brothers be for a' that!
TO A MOUSE
Flying before a Plow
Wee, sleekit, cowrin', tim'rous beastie, Oh, what a panic's in thy breastie! Thou needna start awa' sae hasty, Wi' bick'ring brattle!33 I wad be laith to rin and chase thee, Wi' murd'ring pattle!34
I'm truly sorry man's dominion Has broken nature's social union, And justifies that ill opinion Which mak's thee startle At me, thy poor earth-born companion And fellow-mortal!
I doubt na, whiles, but thou may thieve; What then? poor beastie, thou maun live! A daimen icker in a thrave35 'S a sma' request: I'll get a blessin' wi' the lave, And never miss 't!
Thy wee bit housie, too, in ruin! Its silly36 wa's the win's are strewin'! And naething now to big37 a new ane O' foggage38 green! And bleak December's winds ensuin', Baith snell39 and keen!
Thou saw the fields laid bare and waste, And weary winter comin' fast, And cozie here, beneath the blast Thou thought to dwell, Till, crash! the cruel coulter past Out through thy cell.
That wee bit heap o' leaves and stibble Has cost thee mony a weary nibble! Now thou's turned out for a' thy trouble, But house or hauld,40 To thole41 the winter's sleety dribble, And cranreuch42 cauld!
But, Mousie, thou art no thy lane43 In proving foresight may be vain! The best-laid schemes o' mice and men Gang aft agley, And lea'e us naught but grief and pain For promised joy.
Still thou art blest, compared wi' me! The present only toucheth thee; But och! I backward cast my e'e On prospects drear! And forward, though I canna see, I guess and fear.
TO A MOUNTAIN DAISY
On Turning One Down with the Plow
Wee, modest, crimson-tippèd flower, Thou's met me in an evil hour; For I maun crush amang the stoure44 Thy slender stem; To spare thee now is past my power, Thou bonnie gem.
Alas! it's no thy neebor sweet, The bonnie lark, companion meet! Bending thee 'mang the dewy weet, Wi' spreckled breast, When upward-springing, blithe, to greet The purpling east.
Cauld blew the bitter biting north Upon thy early, humble birth, Yet cheerfully thou glinted45 forth Amid the storm, Scarce reared above the parent earth Thy tender form. The flaunting flowers our gardens yield, High shelt'ring woods and wa's maun shield; But thou beneath the random bield46 O' clod or stane, Adorns the histie47 stibble-field, Unseen, alane.
There, in thy scanty mantle clad, Thy snawy bosom sunward spread, Thou lifts thy unassuming head In humble guise; But now the share uptears thy bed, And low thou lies!
Such is the fate of artless maid, Sweet flow'ret of the rural shade! By love's simplicity betrayed, And guileless trust, Till she, like thee, all soiled, is laid Low i' the dust.
Such is the fate of simple bard, On life's rough ocean luckless starred! Unskillful he to note the card Of prudent lore, Till billows rage, and gales blow hard, And whelm him o'er!
Such fate to suffering worth is given, Who long with wants and woes has striven, By human pride or cunning driven To mis'ry's brink, Till wrenched of every stay but Heaven, He, ruined, sink!
Ev'n thou who mourn'st the Daisy's fate, That fate is thine—no distant date; Stern Ruin's plowshare drives, elate, Full on thy bloom, Till crushed beneath the furrow's weight Shall be thy doom!
TAM O' SHANTER
When chapman billies48 leave the street, And drouthy49 neebors neebors meet, As market days are wearing late, An' folk begin to tak' the gate50; While we sit bousing at the nappy,51 An' getting fou and unco happy, We think na on the lang Scots miles, The mosses, waters, slaps,52 and stiles, That lie between us and our hame, Whaur sits our sulky, sullen dame, Gathering her brows like gathering storm, Nursing her wrath to keep it warm.
This truth fand honest Tam o' Shanter, As he frae Ayr ae night did canter (Auld Ayr, wham ne'er a town surpasses, For honest men and bonny lasses). O Tam! hadst thou but been sae wise, As ta'en thy ain wife Kate's advice! She tauld thee weel thou was a skellum,53 A blethering,54 blustering, drunken blellum55; That frae November till October, Ae market-day thou was nae sober; That ilka melder,56 wi' the miller, Thou sat as lang as thou had siller; That every naig was ca'd a shoe on,57 The smith and thee gat roaring fou on; That at the Lord's house, ev'n on Sunday, Thou drank wi' Kirkton Jean58 till Monday. She prophesied that, late or soon, Thou would be found deep drowned in Doon; Or catched wi' warlocks in the mirk, By Alloway's auld haunted kirk.
Ah, gentle dames! it gars me greet,59 To think how mony counsels sweet, How many lengthened sage advices, The husband frae the wife despises!
But to our tale:—Ae market-night, Tam had got planted unco right; Fast by an ingle,60 bleezing finely, Wi' reaming swats,61 that drank divinely; And at his elbow, Souter62 Johnny, His ancient, trusty, drouthy crony: Tam lo'ed him like a vera brither; They had been fou for weeks thegither. The night drave on wi' sangs an' clatter, And aye the ale was growing better; The landlady and Tam grew gracious, Wi' favors, secret, sweet, and precious; The Souter tauld his queerest stories; The landlord's laugh was ready chorus; The storm without might rair63 and rustle. Tam did na mind, the storm a whistle.
Care, mad to see a man sae happy, E'en drowned himself amang the nappy; As bees flee hame wi' lades o' treasure, The minutes winged their way wi' pleasure: Kings may be blest, but Tam was glorious, O'er a' the ills o' life victorious!
But pleasures are like poppies spread, You seize the flower, its bloom is shed! Or like the snowfall in the river, A moment white—then melts for ever; Or like the Borealis race, That flit ere you can point their place; Or like the rainbow's lovely form Evanishing amid the storm.
Nae man can tether time or tide; The hour approaches Tam maun ride: That hour, o' night's black arch the keystane, That dreary hour he mounts his beast in: And sic a night he tak's the road in, As ne'er poor sinner was abroad in. The wind blew as 'twad blawn its last; The rattlin' showers rose on the blast; The speedy gleams the darkness swallowed; Loud, deep, and lang the thunder bellowed: That night, a child might understand, The de'il had business on his hand.
Weel mounted on his gray mare Meg (A better never lifted leg), Tam skelpit64 on through dub and mire, Despising wind, and rain, and fire; Whiles holding fast his guid blue bonnet, Whiles crooning o'er some auld Scots sonnet, Whiles glow'ring round wi' prudent cares, Lest bogles65 catch him unawares; Kirk-Alloway was drawing nigh, Whaur ghaists and houlets66 nightly cry.
By this time he was 'cross the ford, Whaur in the snaw the chapman smoored;67 And past the birks and meikle stane, Whaur drunken Charlie brak's neck-bane; And through the whins, and by the cairn, Whaur hunters fand the murdered bairn; And near the thorn, aboon the well, Whaur Mungo's mither hanged hersel'. Before him Doon pours all his floods; The doubling storm roars through the woods; The lightnings flash from pole to pole; Near and more near the thunders roll; When, glimmering through the groaning trees, Kirk-Alloway seemed in a bleeze; Through ilka bore68 the beams were glancing; And loud resounded mirth and dancing.
Inspiring, bold John Barleycorn! What dangers thou canst mak' us scorn! Wi' tippenny69 we fear nae evil; Wi' usquabae70 we'll face the devil! The swats71 sae reamed72 in Tammie's noddle, Fair play, he cared na de'ils a boddle.73 But Maggie stood right sair astonished, Till, by the heel and hand admonished She ventured forward on the light; And wow! Tam saw an unco sight! Warlocks and witches in a dance; Nae cotillion brent new frae France, But hornpipes, jigs, strathspeys, and reels Put life and mettle in their heels. At winnock-bunker74 in the east, There sat auld Nick, in shape o' beast;— A towzie tyke,75 black, grim, and large; To gi'e them music was his charge: He screwed the pipes and gart them skirl,76 Till roof and rafters a' did dirl!77 Coffins stood round, like open presses, That shawed the dead in their last dresses; And by some devilish cantrip78 slight, Each in its cauld hand held a light, By which heroic Tam was able To note upon the haly table A murderer's banes in gibbet airns;79 Twa span-lang, wee unchristened bairns; A thief new-cutted frae a rape, Wi' his last gasp his gab80 did gape; Five tomahawks, wi' bluid red-rusted; Five scimitars wi' murder crusted; A garter which a babe had strangled; A knife a father's throat had mangled, Whom his ain son o' life bereft— The gray hairs yet stack to the heft: Wi' mair o' horrible and awfu', Which ev'n to name wad be unlawfu'.
As Tammie glow'red,81 amazed and curious, The mirth and fun grew fast and furious: The piper loud and louder blew; The dancers quick and quicker flew; They reeled, they set, they crossed, they cleekit,82 Till ilka carlin83 swat and reekit,84 And coost85 her duddies86 to the wark, And linket87 at it in her sark!88
Now Tam, O Tam! had they been queans A' plump and strapping, in their teens; Their sarks, instead o' creeshie flannen,89 Been snaw-white seventeen-hunder linen90, Thir breeks91 o' mine, my only pair, That ance were plush, o' guid blue hair, I wad hae gi'en them off my hurdies, For ane blink o' the bonnie burdies!
But withered beldams old and droll, Rigwoodie92 hags wad spean93 a foal, Lowping and flinging on a crummock,94 I wonder didna turn thy stomach.
But Tam kenned what was what fu' brawlie: "There was ae winsome wench and walie,"95 That night inlisted in the core (Lang after kenned on Carrick shore! For mony a beast to dead she shot, And perished mony a bonnie boat, And shook baith meikle corn and bear,96 And kept the country-side in fear), Her cutty sark,97 o' Paisley harn,98 That while a lassie she had worn, In longitude though sorely scanty, It was her best, and she was vauntie.99 Ah! little kenned thy reverend grannie, That sark she coft100 for her wee Nannie, Wi' twa pund Scots ('twas a' her riches), Wad ever graced a dance of witches! But here my muse her wing maun cour101; Sic flights are far beyond her power: To sing how Nannie lap and flang (A souple jade she was and strang), And how Tam stood like ane bewitched, And thought his very een enriched; Even Satan glow'red and fidged fu' fain, And hotched and blew wi' might and main: Till first ae caper, syne anither, Tam tints102 his reason a'thegither, And roars out, "Weel done, Cutty-sark!" And in an instant all was dark; And scarcely had he Maggie rallied, When out the hellish legion sallied.
As bees bizz out wi' angry fyke,103 When plundering hords assail their byke104; As open pussie's mortal foes When, pop! she starts before their nose; As eager runs the market-crowd, When "Catch the thief!" resounds aloud; So Maggie runs, the witches follow, Wi' mony an eldritch105 screech and hollow.
Ah, Tam! ah, Tam, thou'll get thy fairin'! In hell they'll roast thee like a herrin'! In vain thy Kate awaits thy comin'! Kate soon will be a woefu' woman! Now, do thy speedy utmost, Meg, And win the keystane of the brig; There at them thou thy tail may toss,— A running stream they dare na cross. But ere the keystane she could make, The fient a tail she had to shake!
For Nannie, far before the rest, Hard upon noble Maggie prest, And flew at Tam wi' furious ettle; But little wist she Maggie's mettle— Ae spring brought off her master hale, But left behind her ain grey tail: The carlin claught her by the rump, And left poor Maggie scarce a stump!
Now, wha this tale o' truth shall read, Ilk man and mother's son, take heed: Whene'er to drink you are inclined, Or cutty sarks run in your mind, Think, ye may buy the joys o'er dear— Remember Tam o' Shanter's mare.
BRUCE TO HIS MEN AT BANNOCKBURN
Spirited fellow.
Fool.
Hurrying run.
The plow-spade.
An ear of corn in twenty-four sheaves—that is, in a thrave.
Frail.
Build.
Aftermath.
Bitter.
Holding.
Endure.
Crevice.
Alone.
Dust.
Peeped.
Shelter.
Barren.
Fellows.
Thirsty.
Road.
Ale.
[51]
Gates or openings through a hedge.
Good-for-nothing fellow.
Nonsensical.
Chattering fellow.
Grain sent to the mill to be ground; i.e., that every time he carried the corn to the mill he sat to drink with the miller.
Nag that required shoeing.
Jean Kennedy, a public-house keeper at Kirkoswald.
Makes me weep.
Fire.
Foaming ale.
Shoemaker.
Roar.
Rode carelessly.
Ghosts, bogies.
Owls.
Was smothered.
Crevice, or hole.
Twopenny ale.
Whisky.
Drink.
Frothed, mounted.
A small old coin.
Window-seat.
Shaggy dog.
Made them scream.
Shake.
Spell.
Irons.
Mouth.
Stared.
Caught hold of each other.
Old hag.
Reeked with heat.
Cast off.
Clothes.
Tripped.
Chemise.
Greasy flannel.
Manufacturers' term for linen woven in a reed of 1700 divisions.
Breeches.
Gallows-worthy.
Wean.
A crutch—a stick with a crook.
Quoted from Allan Ramsay.
Barley.
Short shift or shirt.
Very coarse linen.
Proud.
Bought.
Cower—sink.
Loses.
Fuss.
[103]
Hive.
[104]
Unearthly.
Scots wha hae wi' Wallace bled, Scots wham Bruce has aften led; Welcome to your gory bed, Or to victorie!
Now's the day, and now's the hour; See the front o' battle lour: See approach proud Edward's pow'r— Chains and slaverie!
Wha will be a traitor-knave? Wha can fill a coward's grave? Wha sae base as be a slave? Let him turn and flee!
Wha for Scotland's king and law Freedom's sword will strongly draw, Freemen stand, or freemen fa', Let him follow me!
By oppression's woes and pains! By our sons in servile chains! We will drain our dearest veins, But they shall be free!
Lay the proud usurpers low! Tyrants fall in every foe! Liberty's in every blow!— Let us do or die!
HIGHLAND MARY
Ye banks and braes and streams around The castle o' Montgomery, Green be your woods, and fair your flowers, Your waters never drumlie! There Simmer first unfald her robes, And there the langest tarry; For there I took the last fareweel O' my sweet Highland Mary.
How sweetly bloomed the gay green birk, How rich the hawthorn's blossom! As underneath their fragrant shade, I clasped her to my bosom! The golden hours, on angel wings, Flew o'er me and my dearie; For dear to me as light and life Was my sweet Highland Mary.
Wi' mony a vow and locked embrace Our parting was fu' tender; And, pledging aft to meet again, We tore oursel's asunder; But oh! fell Death's untimely frost, That nipt my flower sae early! Now green's the sod and cauld's the clay That wraps my Highland Mary!
Oh pale, pale now those rosy lips, I aft hae kissed so fondly! And closed for aye the sparkling glance, That dwelt on me sae kindly; And moldering now in silent dust That heart that lo'ed me dearly! But still within my bosom's core Shall live my Highland Mary.
MY HEART'S IN THE HIGHLANDS
My heart's in the Highlands, my heart is not here; My heart's in the Highlands, a-chasing the deer; Chasing the wild deer, and following the roe— My heart's in the Highlands wherever I go. Farewell to the Highlands, farewell to the North! The birthplace of valor, the country of worth; Wherever I wander, wherever I rove, The hills of the Highlands for ever I love.
Farewell to the mountains high covered with snow! Farewell to the straths and green valleys below! Farewell to the forests and wild-hanging woods! Farewell to the torrents and loud-pouring floods! My heart's in the Highlands, my heart is not here, My heart's in the Highlands a-chasing the deer; Chasing the wild deer, and following the roe— My heart's in the Highlands wherever I go.
THE BANKS O' DOON
Ye banks and braes o' bonnie Doon, How can ye bloom sae fresh and fair? How can ye chant, ye little birds, And I sae weary fu' o' care? Thou'll break my heart, thou warbling bird, That wantons through the flowering thorn; Thou minds me o' departed joys, Departed—never to return!
Oft ha'e I roved by bonnie Doon, To see the rose and woodbine twine; And ilka bird sang o' its luve, And fondly sae did I o' mine. Wi' lightsome heart I pu'd a rose, Fu' sweet upon its thorny tree; And my fause lover stole my rose, But ah! he left the thorn wi' me.

"THE BANKS AND BRAES O' BONNIE DOON."
Oft hae I roved by bonnie Doon, To see the rose and woodbine twine; And ilka bird sang o' his luve. And fondly sae did I o' mine.
Etching from a Photograph.
JOHN BURROUGHS
(1837-)

John Burroughs was born in Roxbury, New York, April 3d, 1837, and like many other American youths who later in life became distinguished, he went to school winters and worked on the farm in summer. He grew up among people who neither read books nor cared for them, and he considers this circumstance best suited to his development. Early intercourse with literary men would, he believes, have dwarfed his original faculty.
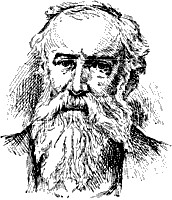
John Burroughs
He began to write essays at the age of fourteen, but these early literary efforts give little hint of his later work, of that faculty for seeing, and commenting on all that he saw in nature, which became his chief characteristic. He was especially fond of essays; one of his first purchases with his own money was a full set of Dr. Johnson, and for a whole year he lived on 'The Idler' and 'The Rambler' and tried to imitate their ponderous prose. His first contributions to literature, modeled on these essays, were promptly returned. By chance he picked up a volume of Emerson, the master who was to revolutionize his whole manner of thinking; and as he had fed on Dr. Johnson he fed on the 'Essays and Miscellanies,' until a paper he wrote at nineteen on 'Expressions' was accepted by the editor of the Atlantic, with a lurking doubt whether it had not come to him on false pretenses, as it was very much like an early essay of Emerson.
Mr. Burroughs ascribes to Emerson, who stimulated his religious nature, his improved literary expression; while Whitman was to him a great humanizing power, and Matthew Arnold taught him clear thinking and clean writing. He had passed through these different influences by the time he was twenty-one or twenty-two; had taught for a while; and from 1863 to 1873 was vault-keeper and afterwards chief of the organization division of the Bureau of National Banks, in the Treasury Department. For several years afterward he was a special national bank examiner.
The literary quality of his writings from the first captivates the reader. He has the interpretive power which makes us see what he sees and invites us to share his enjoyment in his strange adventures. The stories of the wary trout and the pastoral bee, the ways of sylvan folk, their quarrels and their love-making, are so many character sketches on paper, showing a most intimate acquaintance with nature.
He is a born naturalist. He tells us that from childhood he was familiar with the homely facts of the barn, the cattle and the horses, the sugar-making and the work of the corn-field, the hay-field, the threshing, the planting, the burning of fallows. He "loved nature in those material examples and subtle expressions, with a love passing all the books in the world." But he also loved and knew books, and this other love gives to his works their literary charm.
His account of a bird, a flower, or an open-air incident, however painstaking and minute the record, teems with literary memories. The sight of the Scotch hills recalls Shakespeare's line,
"The tufty mountains where lie the nibbling sheep."
The plane-tree vocal with birds' voices recalls Tennyson,—"The pillared dusk of sounding sycamores"; he hears the English chaffinch, and remembers with keen delight that Drayton calls it "the throstle with sharp thrills," and Ben Jonson "the lusty throstle." After much wondering, he finds out why Shakespeare wrote
"The murmuring surge That on the unnumbered idle pebbles chafes,"
his own experience being that sea-shores are sandy; but the pebbled cliffs of Folkestone, with not a grain of sand on the chalk foundation, justified the poet.
This lover of nature loves not only the beautiful things he sees, but he loves what they suggest, what they remind him of, what they bid him aspire to. Like Wordsworth, he "looks on the hills with tenderness, and makes deep friendship with the streams and groves." He notes what he divines by observation. And what an observer he is! He discovers that the bobolink goes south in the night. He scraped an acquaintance with a yellow rumpled warbler who, taking the reflection of the clouds and blue sky in a pond for a short cut to the tropics, tried to cross it; with the result of his clinging for a day and night to a twig that hung down in the water.
Burroughs has found that whatever bait you use in a trout stream,—grasshopper, grub, or fly,—there is one thing you must always put on your hook; namely, your heart. It is a morsel they love above everything else. He tells us that man has sharper eyes than a dog, a fox, or any of the wild creatures except the birds, but not so sharp an ear or a nose; he says that a certain quality of youth is indispensable in the angler, a certain unworldliness and readiness to invest in an enterprise that does not pay in current coin. He says that nature loves to enter a door another hand has opened: a mountain view never looks better than when one has been warmed up by the capture of a big trout. Like certain wary game, she is best taken by seeming to pass her by, intent on other matters. What he does not find out for himself, people tell him. From a hedge-cutter he learns that some of the birds take an earth-bath and some a water-bath, while a few take both; a farmer boy confided to him that the reason we never see any small turtles is because for two or three years the young turtles bury themselves in the ground and keep hidden from observation. From a Maine farmer he heard that both male and female hawks take part in incubation. A barefooted New Jersey boy told him that "lampers" die as soon as they have built their nests and laid their eggs. How apt he is in similes! The pastoral fields of Scotland are "stall-fed," and the hill-sides "wrinkled and dimpled, like the forms of fatted sheep."
And what other bird-lover has such charming fancies about birds, in whom he finds a hundred human significances? "The song of the bobolink," he says, "expresses hilarity; the sparrow sings faith, the bluebird love, the catbirds pride, the white-eyed fly-catchers self-consciousness, that of the hermit thrush spiritual serenity, while there is something military in the call of the robin." Mr. Burroughs has been compared with Thoreau, but he seems closer to White of Selborne, whom he has commemorated in one of his most charming essays. Like White, he is a literary man who is a born naturalist in close intimacy with his brute neighbors and "rural nature's varied shows." In both, the moral element is back of nature and the source of her value and charm. Never nature for her own sake, but for the sake of the soul that is above all and over all. Like White, too, though by nature solitary, Burroughs is on cordial terms with his kind. He is an accurate observer, and he takes Bryant to task for giving an odor to the yellow violet, and Coleridge for making a lark perch on the stalk of a foxglove. He gloats over a felicitous expression, like Arnold's "blond meadow-sweet" and Tennyson's "little speedwell's darling blue"; though in commenting on another poet he waives the question of accuracy, and says "his happy literary talent makes up for the poverty of his observation."
And again as with White, he walks through life slowly and in a ruminating fashion, as though he had leisure to linger with the impression of the moment. Incident he uses with reserve, but with picturesque effects; figures do not dominate his landscape but humanize it.
As a critic Mr. Burroughs most fully reveals his personality. In his sketches of nature we see what he sees; in his critiques, what he feels and thinks. The cry of discovery he made when 'Leaves of Grass' fell into his hands found response in England and was re-echoed in this country till Burroughs's strange delight in Whitman seemed no longer strange, but an accepted fact in the history of poetry. The essay on Emerson, his master, shows the same discriminating mind. But as a revelation of both author and subject there are few more delightful papers than Burroughs's essay on Thoreau. In manner it is as pungent and as racy as Thoreau's writings, and as epigrammatic as Emerson's; and his defense of Thoreau against the English reviewer who dubbed him a "skulker" has the sound of the trumpet and the martial tread of soldiers marching to battle.
SHARP EYES
From 'Locusts and Wild Honey'
Noting how one eye seconds and reinforces the other, I have often amused myself by wondering what the effect would be if one could go on opening eye after eye, to the number, say, of a dozen or more. What would he see? Perhaps not the invisible—not the odors of flowers or the fever germs in the air—not the infinitely small of the microscope or the infinitely distant of the telescope. This would require not so much more eyes as an eye constructed with more and different lenses; but would he not see with augmented power within the natural limits of vision? At any rate, some persons seem to have opened more eyes than others, they see with such force and distinctness; their vision penetrates the tangle and obscurity where that of others fails, like a spent or impotent bullet. How many eyes did Gilbert White open? how many did Henry Thoreau? how many did Audubon? how many does the hunter, matching his sight against the keen and alert senses of a deer, or a moose, or a fox, or a wolf? Not outward eyes, but inward. We open another eye whenever we see beyond the first general features or outlines of things—whenever we grasp the special details and characteristic markings that this mask covers. Science confers new powers of vision. Whenever you have learned to discriminate the birds, or the plants, or the geological features of a country, it is as if new and keener eyes were added.
Of course one must not only see sharply, but read aright what he sees. The facts in the life of nature that are transpiring about us are like written words that the observer is to arrange into sentences. Or, the writing is a cipher and he must furnish the key. A female oriole was one day observed very much preoccupied under a shed where the refuse from the horse stable was thrown. She hopped about among the barn fowls, scolding them sharply when they came too near her. The stable, dark and cavernous, was just beyond. The bird, not finding what she wanted outside, boldly ventured into the stable, and was presently captured by the farmer. What did she want? was the query. What but a horse-hair for her nest, which was in an apple-tree near by? and she was so bent on having one that I have no doubt she would have tweaked one out of the horse's tail had he been in the stable. Later in the season I examined her nest, and found it sewed through and through with several long horse-hairs, so that the bird persisted in her search till the hair was found.
Little dramas and tragedies and comedies, little characteristic scenes, are always being enacted in the lives of the birds, if our eyes are sharp enough to see them. Some clever observer saw this little comedy played among some English sparrows, and wrote an account of it in his newspaper. It is too good not to be true: A male bird brought to his box a large, fine goose-feather, which is a great find for a sparrow and much coveted. After he had deposited his prize and chattered his gratulations over it, he went away in quest of his mate. His next-door neighbor, a female bird, seeing her chance, quickly slipped in and seized the feather,—and here the wit of the bird came out, for instead of carrying it into her own box she flew with it to a near tree and hid it in a fork of the branches, then went home, and when her neighbor returned with his mate, was innocently employed about her own affairs. The proud male, finding his feather gone, came out of his box in a high state of excitement, and with wrath in his manner and accusation on his tongue, rushed into the cot of the female. Not finding his goods and chattels there as he had expected, he stormed around awhile, abusing everybody in general and his neighbor in particular, and then went away as if to repair the loss. As soon as he was out of sight, the shrewd thief went and brought the feather home and lined her own domicile with it....
The bluebird is a home bird, and I am never tired of recurring to him. His coming or reappearance in the spring marks a new chapter in the progress of the season; things are never quite the same after one has heard that note. The past spring the males came about a week in advance of the females. A fine male lingered about my grounds and orchard all that time, apparently awaiting the arrival of his mate. He called and warbled every day, as if he felt sure she was within earshot and could be hurried up. Now he warbled half angrily or upbraidingly; then coaxingly; then cheerily and confidently, the next moment in a plaintive and far-away manner. He would half open his wings, and twinkle them caressingly as if beckoning his mate to his heart. One morning she had come, but was shy and reserved. The fond male flew to a knot-hole in an old apple-tree and coaxed her to his side. I heard a fine confidential warble—the old, old story. But the female flew to a near tree and uttered her plaintive, homesick note. The male went and got some dry grass or bark in his beak and flew again to the hole in the old tree, and promised unremitting devotion; but the other said "Nay," and flew away in the distance. When he saw her going, or rather heard her distant note, he dropped his stuff and cried out in a tone that said plainly enough, "Wait a minute: one word, please!" and flew swiftly in pursuit. He won her before long, however, and early in April the pair were established in one of the four or five boxes I had put up for them, but not until they had changed their minds several times. As soon as the first brood had flown, and while they were yet under their parents' care, they began to nest in one of the other boxes, the female as usual doing all the work and the male all the complimenting. A source of occasional great distress to the mother-bird was a white cat that sometimes followed me about. The cat had never been known to catch a bird, but she had a way of watching them that was very embarrassing to the bird. Whenever she appeared, the mother bluebird set up that pitiful melodious plaint. One morning the cat was standing by me, when the bird came with her beak loaded with building material, and alighted above me to survey the place before going into the box. When she saw the cat she was greatly disturbed, and in her agitation could not keep her hold upon all her material. Straw after straw came eddying down, till not half her original burden remained. After the cat had gone away the bird's alarm subsided; till presently, seeing the coast clear, she flew quickly to the box and pitched in her remaining straws with the greatest precipitation, and without going in to arrange them as was her wont, flew away in evident relief.
In the cavity of an apple-tree but a few yards off, and much nearer the house than they usually build, a pair of high-holes, or golden-shafted woodpeckers, took up their abode. A knot-hole which led to the decayed interior was enlarged, the live wood being cut away as clean as a squirrel would have done it. The inside preparations I could not witness, but day after day as I passed near I heard the bird hammering away, evidently beating down obstructions and shaping and enlarging the cavity. The chips were not brought out, but were used rather to floor the interior. The woodpeckers are not nest-builders, but rather nest-carvers.
The time seemed very short before the voices of the young were heard in the heart of the old tree,—at first feebly, but waxing stronger day by day, until they could be heard many rods distant. When I put my hand upon the trunk of the tree they would set up an eager, expectant chattering; but if I climbed up it toward the opening, they soon detected the unusual sound and would hush quickly, only now and then uttering a warning note. Long before they were fully fledged they clambered up to the orifice to receive their food. As but one could stand in the opening at a time, there was a good deal of elbowing and struggling for this position. It was a very desirable one, aside from the advantages it had when food was served; it looked out upon the great shining world, into which the young birds seemed never tired of gazing. The fresh air must have been a consideration also, for the interior of a high-hole's dwelling is not sweet. When the parent birds came with food, the young one in the opening did not get it all; but after he had received a portion, either on his own motion or on a hint from the old one, he would give place to the one behind him. Still, one bird evidently outstripped his fellows, and in the race of life was two or three days in advance of them. His voice was the loudest and his head oftenest at the window. But I noticed that when he had kept the position too long, the others evidently made it uncomfortable in his rear, and after "fidgeting" about awhile he would be compelled to "back down." But retaliation was then easy, and I fear his mates spent few easy moments at the outlook. They would close their eyes and slide back into the cavity as if the world had suddenly lost all its charms for them.
This bird was of course the first to leave the nest. For two days before that event he kept his position in the opening most of the time, and sent forth his strong voice incessantly. The old ones abstained from feeding him almost entirely, no doubt to encourage his exit. As I stood looking at him one afternoon and noticing his progress, he suddenly reached a resolution,—seconded, I have no doubt, from the rear,—and launched forth upon his untried wings. They served him well, and carried him about fifty yards up-hill the first heat. The second day after, the next in size and spirit left in the same manner; then another, till only one remained. The parent birds ceased their visits to him, and for one day he called and called till our ears were tired of the sound. His was the faintest heart of all: then he had none to encourage him from behind. He left the nest and clung to the outer hole of the tree, and yelped and piped for an hour longer; then he committed himself to his wings and went his way like the rest.
A young farmer in the western part of New York sends me ... some interesting observations about the cuckoo. He says a large gooseberry-bush, standing in the border of an old hedge-row in the midst of the open fields, and not far from his house, was occupied by a pair of cuckoos for two seasons in succession; and after an interval of a year, for two seasons more. This gave him a good chance to observe them. He says the mother-bird lays a single egg and sits upon it a number of days before laying the second, so that he has seen one young bird nearly grown, a second just hatched, and a whole egg all in the nest at once. "So far as I have seen, this is the settled practice,—the young leaving the nest one at a time, to the number of six or eight. The young have quite the look of the young of the dove in many respects. When nearly grown they are covered with long blue pin-feathers as long as darning needles, without a bit of plumage on them. They part on the back and hang down on each side by their own weight. With its curious feathers and misshapen body the young bird is anything but handsome. They never open their mouths when approached, as many young birds do, but sit perfectly still, hardly moving when touched." He also notes the unnatural indifference of the mother-bird when her nest and young are approached. She makes no sound, but sits quietly on a near branch in apparent perfect unconcern.
These observations, together with the fact that the egg of the cuckoo is occasionally found in the nest of other birds, raise the inquiry whether our bird is slowly relapsing into the habit of the European species, which always foists its egg upon other birds; or whether on the other hand it be not mending its manners in this respect. It has but little to unlearn or forget in the one case, but great progress to make in the other. How far is its rudimentary nest—a mere platform of coarse twigs and dry stalks of weeds—from the deep, compact, finely woven and finely modeled nest of the goldfinch or
kingbird
, and what a gulf between its indifference toward its young and their solicitude! Its irregular manner of laying also seems better suited to a parasite like our cow-bird, or the European cuckoo, than to a regular nest-builder.This observer, like most sharp-eyed persons, sees plenty of interesting things as he goes about his work. He one day saw a white swallow, which is of rare occurrence. He saw a bird, a sparrow, he thinks, fly against the side of a horse and fill his beak with hair from the loosened coat of the animal. He saw a shrike pursue a chickadee, when the latter escaped by taking refuge in a small hole in a tree. One day in early spring he saw two hen-hawks that were circling and screaming high in air, approach each other, extend a claw, and grasping them together, fall toward the earth flapping and struggling as if they were tied together; on nearing the ground they separated and soared aloft again. He supposed that it was not a passage of war but of love, and that the hawks were toying fondly with each other.
When the air is damp and heavy, swallows frequently hawk for insects about cattle and moving herds in the field. My farmer describes how they attended him one foggy day, as he was mowing in the meadow with a mowing-machine. It had been foggy for two days, and the swallows were very hungry and the insects stupid and inert. When the sound of his machine was heard, the swallows appeared and attended him like a brood of hungry chickens. He says there was a continual rush of purple wings over the "cutter-bar," and just where it was causing the grass to tremble and fall. Without his assistance the swallows would have gone hungry yet another day.
Of the hen-hawk he has observed that both the male and female take part in incubation. "I was rather surprised," he says, "on one occasion, to see how quickly they change places on the nest. The nest was in a tall beech, and the leaves were not yet fully out. I could see the head and neck of the hawk over the edge of the nest, when I saw the other hawk coming down through the air at full speed. I expected he would alight near by, but instead of that he struck directly upon the nest, his mate getting out of the way barely in time to avoid being hit; it seemed almost as if he had knocked her off the nest. I hardly see how they can make such a rush on the nest without danger to the eggs."
The kingbird will worry the hawk as a whiffet dog will worry a bear. It is by his persistence and audacity, not by any injury he is capable of dealing his great antagonist. The kingbird seldom more than dogs the hawk, keeping above and between his wings and making a great ado; but my correspondent says he once "saw a
kingbird
riding on a hawk's back. The hawk flew as fast as possible, and the kingbird sat upon his shoulders in triumph until they had passed out of sight,"—tweaking his feathers, no doubt, and threatening to scalp him the next moment.That near relative of the
kingbird
, the great crested fly-catcher, has one well-known peculiarity: he appears never to consider his nest finished until it contains a cast-off snake-skin. My alert correspondent one day saw him eagerly catch up an onion skin and make off with it, either deceived by it or else thinking it a good substitute for the coveted material.One day in May, walking in the woods, I came upon a nest of whippoorwill, or rather its eggs,—for it builds no nest,—two elliptical whitish spotted eggs lying upon the dry leaves. My foot was within a yard of the mother-bird before she flew. I wondered what a sharp eye would detect curious or characteristic in the ways of the bird, so I came to the place many times and had a look. It was always a task to separate the bird from her surroundings, though I stood within a few feet of her, and knew exactly where to look. One had to bear on with his eye, as it were, and refuse to be baffled. The sticks and leaves, and bits of black or dark-brown bark, were all exactly copied in the bird's plumage. And then she did sit so close and simulate so well a shapeless decaying piece of wood or bark! Twice I brought a companion, and guiding his eye to the spot, noted how difficult it was for him to make out there, in full view upon the dry leaves, any semblance to a bird. When the bird returned after being disturbed, she would alight within a few inches of her eggs and then, after a moment's pause, hobble awkwardly upon them.
After the young had appeared, all the wit of the bird came into play. I was on hand the next day, I think. The mother-bird sprang up when I was within a pace of her, and in doing so fanned the leaves with her wings till they sprang up too; as the leaves started the young started, and, being of the same color, to tell which was the leaf and which the bird was a trying task to any eye. I came the next day, when the same tactics were repeated. Once a leaf fell upon one of the young birds and nearly hid it. The young are covered with a reddish down like a young partridge, and soon follow their mother about. When disturbed they gave but one leap, then settled down, perfectly motionless and stupid, with eyes closed. The parent bird, on these occasions, made frantic efforts to decoy me away from her young. She would fly a few paces and fall upon her breast, and a spasm like that of death would run through her tremulous outstretched wings and prostrate body. She kept a sharp eye out the meanwhile to see if the ruse took, and if it did not she was quickly cured, and moving about to some other point tried to draw my attention as before. When followed she always alighted upon the ground, dropping down in a sudden peculiar way. The second or third day both old and young had disappeared.
The whippoorwill walks as awkwardly as a swallow, which is as awkward as a man in a bag, and yet she manages to lead her young about the woods. The latter, I think, move by leaps and sudden spurts, their protective coloring shielding them most effectively. Wilson once came upon the mother-bird and her brood in the woods, and though they were at his very feet, was so baffled by the concealment of the young that he was about to give up the search, much disappointed, when he perceived something "like a slight moldiness among the withered leaves, and, on stooping down, discovered it to be a young whippoorwill, seemingly asleep." Wilson's description of the young is very accurate, as its downy covering does look precisely like a "slight moldiness." Returning a few moments afterward to the spot to get a pencil he had forgotten, he could find neither old nor young.
It takes an eye to see a partridge in the woods, motionless upon the leaves; this sense needs to be as sharp as that of smell in hounds and pointers, and yet I know an unkempt youth that seldom fails to see the bird and shoot it before it takes wing. I think he sees it as soon as it sees him, and before it suspects itself seen. What a training to the eye is hunting! To pick out the game from its surroundings, the grouse from the leaves, the gray squirrel from the mossy oak limb it hugs so closely, the red fox from the ruddy or brown or gray field, the rabbit from the stubble, or the white hare from the snow, requires the best powers of this sense. A woodchuck motionless in the fields or upon a rock looks very much like a large stone or bowlder, yet a keen eye knows the difference at a glance, a quarter of a mile away.
A man has a sharper eye than a dog, or a fox, or than any of the wild creatures; but not so sharp an ear or nose. But in the birds he finds his match. How quickly the old turkey discovers the hawk, a mere speck against the sky, and how quickly the hawk discovers you if you happen to be secreted in the bushes, or behind the fence near which he alights! One advantage the bird surely has; and that is, owing to the form, structure, and position of the eye, it has a much larger field of vision—indeed, can probably see in nearly every direction at the same instant, behind as well as before. Man's field of vision embraces less than half a circle horizontally, and still less vertically; his brow and brain prevent him from seeing within many degrees of the zenith without a movement of the head; the bird, on the other hand, takes in nearly the whole sphere at a glance.
I find I see, almost without effort, nearly every bird within sight in the field or wood I pass through (a flit of the wing, a flirt of the tail, are enough, though the flickering leaves do all conspire to hide them), and that with like ease the birds see me, though unquestionably the chances are immensely in their favor. The eye sees what it has the means of seeing, truly. You must have the bird in your heart before you can find it in the bush. The eye must have purpose and aim. No one ever yet found the walking-fern who did not have the walking-fern in his mind. A person whose eye is full of Indian relics picks them up in every field he walks through.
One season I was interested in the tree-frogs, especially the tiny pipers that one hears about the woods and brushy fields—the hylas of the swamps become a denizen of trees; I had never seen him in this new rôle. But this season having them in mind, or rather being ripe for them, I several times came across them. One Sunday, walking amid some bushes, I captured two. They leaped before me as doubtless they had done many times before, but though not looking for or thinking of them, yet they were quickly recognized, because the eye had been commissioned to find them. On another occasion, not long afterward, I was hurriedly loading my gun in the October woods in hopes of overtaking a gray squirrel that was fast escaping through the treetops, when one of these Lilliput frogs, the color of the fast-yellowing leaves, leaped near me. I saw him only out of the corner of my eye, and yet bagged him, because I had already made him my own.
Nevertheless, the habit of observation is the habit of clear and decisive gazing; not by a first casual glance, but by a steady, deliberate aim of the eye are the rare and characteristic things discovered. You must look intently and hold your eye firmly to the spot, to see more than do the rank and file of mankind. The sharpshooter picks out his man and knows him with fatal certainty from a stump, or a rock, or a cap on a pole. The phrenologists do well to locate not only form, color, weight, etc., in the region of the eye, but a faculty which they call individuality—that which separates, discriminates, and sees in every object its essential character. This is just as necessary to the naturalist as to the artist or the poet. The sharp eye notes specific points and differences,—it seizes upon and preserves the individuality of the thing.
We think we have looked at a thing sharply until we are asked for its specific features. I thought I knew exactly the form of the leaf of the tulip-tree, until one day a lady asked me to draw the outlines of one. A good observer is quick to take a hint and to follow it up. Most of the facts of nature, especially in the life of the birds and animals, are well screened. We do not see the play, because we do not look intently enough.
Birds, I say, have wonderfully keen eyes. Throw a fresh bone or a piece of meat upon the snow in winter, and see how soon the crows will discover it and be on hand. If it be near the house or barn, the crow that first discovers it will alight near it, to make sure that he is not deceived; then he will go away and soon return with a companion. The two alight a few yards from the bone, and after some delay, during which the vicinity is sharply scrutinized, one of the crows advances boldly to within a few feet of the coveted prize. Here he pauses, and if no trick is discovered, and the meat be indeed meat, he seizes it and makes off.
One midwinter I cleared away the snow under an apple-tree near the house, and scattered some corn there. I had not seen a bluejay for weeks, yet that very day they found my corn, and after that they came daily and partook of it, holding the kernels under their feet upon the limbs of the trees and pecking them vigorously.
Of course the woodpecker and his kind have sharp eyes. Still I was surprised to see how quickly Downy found out some bones that were placed in a convenient place under the shed to be pounded up for the hens. In going out to the barn I often disturbed him making a meal off the bits of meat that still adhered to them.
"Look intently enough at anything," said a poet to me one day, "and you will see something that would otherwise escape you." I thought of the remark as I sat on a stump in the opening of the woods one spring day. I saw a small hawk approaching; he flew to a tall tulip-tree and alighted on a large limb near the top. He eyed me and I eyed him. Then the bird disclosed a trait that was new to me; he hopped along the limb to a small cavity near the trunk, when he thrust in his head and pulled out some small object and fell to eating it. After he had partaken of it some minutes he put the remainder back in his larder and flew away. I had seen something like feathers eddying slowly down as the hawk ate, and on approaching the spot found the feathers of a sparrow here and there clinging to the bushes beneath the tree. The hawk then—commonly called the chicken hawk—is as provident as a mouse or squirrel, and lays by a store against a time of need; but I should not have discovered the fact had I not held my eye to him.
An observer of the birds is attracted by any unusual sound or commotion among them. In May and June, when other birds are most vocal, the jay is a silent bird; he goes sneaking about the orchards and the groves as silent as a pickpocket; he is robbing birds'-nests and he is very anxious that nothing should be said about it, but in the fall none so quick and loud to cry "Thief, thief" as he. One December morning a troop of them discovered a little screech-owl secreted in the hollow trunk of an old apple-tree near my house. How they found the owl out is a mystery, since it never ventures forth in the light of day; but they did, and proclaimed the fact with great emphasis. I suspect the bluebirds first told them, for these birds are constantly peeping into holes and crannies, both spring and fall. Some unsuspecting bird probably entered the cavity, prospecting for a place for next year's nest, or else looking out a likely place to pass a cold night, when it has rushed with very important news. A boy who should unwittingly venture into a bear's den when Bruin was at home could not be more astonished and alarmed than a bluebird would be on finding itself in the cavity of a decayed tree with an owl. At any rate, the bluebirds joined the jays, in calling the attention of all whom it might concern to the fact that a culprit of some sort was hiding from the light of day in the old apple-tree. I heard the notes of warning and alarm and approached to within eyeshot. The bluebirds were cautious, and hovered about uttering their peculiar twittering calls; but the jays were bolder, and took turns looking in at the cavity and deriding the poor shrinking owl. A jay would alight in the entrance of the hole, and flirt and peer and attitudinize, and then fly away crying "Thief, thief, thief," at the top of his voice.
I climbed up and peered into the opening, and could just descry the owl clinging to the inside of the tree. I reached in and took him out, giving little heed to the threatening snapping of his beak. He was as red as a fox and as yellow-eyed as a cat. He made no effort to escape, but planted his claws in my forefinger and clung there with a grip that soon grew uncomfortable. I placed him in the loft of an out-house in hopes of getting better acquainted with him. By day he was a very willing prisoner, scarcely moving at all even when approached and touched with the hand, but looking out upon the world with half-closed sleepy eyes. But at night what a change; how alert, how wild, how active! He was like another bird; he darted about with wild fearful eyes, and regarded me like a cornered cat. I opened the window, and swiftly, but as silently as a shadow, he glided out into the congenial darkness, and perhaps ere this has revenged himself upon the sleeping jay or bluebird that first betrayed his hiding-place.
Copyrighted by Houghton, Mifflin and Company, Boston.
WAITING
Serene, I fold my hands and wait, Nor care for wind, or tide, or sea; I rave no more 'gainst time or fate, For lo! my own shall come to me.
I stay my haste, I make delays, For what avails this eager pace? I stand amid the eternal ways, And what is mine shall know my face.
Asleep, awake, by night or day, The friends I seek are seeking me; No wind can drive my bark astray, Nor change the tide of destiny.
What matter if I stand alone? I wait with joy the coming years; My heart shall reap where it has sown, And garner up its fruit of tears.
The waters know their own, and draw The brook that springs in yonder height; So flows the good with equal law Unto the soul of pure delight.
The stars come nightly to the sky; The tidal wave unto the sea; Nor time, nor space, nor deep, nor high, Can keep my own away from me.
Republished by courtesy of John Burroughs.
SIR RICHARD F. BURTON
(1821-1890)

It has sometimes been said that the roving propensities of Sir Richard Burton are attributable to a slight infusion of gipsy blood; but if this pedigree were to be assumed for all instinctively nomadic Englishmen, it would make family trees as farcical in general as they often are now. At any rate, Burton early showed a love for travel which circumstances strengthened. Although born in Hertfordshire, England, he spent much of his boyhood on the Continent, where he was educated under tutors. He returned for a course at Oxford, after which, at twenty-one, he entered the Indian service. For nineteen years he was in the Bombay army corps, the first ten in active service, principally in the Sindh Survey, on Sir Charles Napier's staff. He also served in the Crimea as Chief of Staff to General Blatsom, and was chief organizer of the irregular cavalry. For nearly twenty-six years he was in the English consular service in Africa, Asia, South America, and Europe.

Richard Burton
In 1852, when upon leave, Captain Burton accomplished one of his most striking feats. Disguised as an Afghan Moslem, he went on a pilgrimage to Mecca and Medina, in the hope of finding out "something of the great eastern wilderness marked 'Ruba el Khala' (the Empty Abode) on our maps." For months he successfully braved the imminent danger of detection and death. Conspicuous among his explorations is his trip of 1856, when with Speke he discovered the lake regions of Central Africa. The bitter Speke controversy which followed, dividing geographers for a time into two contending factions, deprived Burton of the glory which he merited and drew upon him much unfriendly criticism.
He had the true ardor of the discoverer. In 'First Footsteps in Eastern Africa' he shows his unhesitating bravery again, when penetrating the mysterious, almost mythical walled city of Harar. After many dangers and exhausting experiences he sees the goal at last. "The spectacle, materially speaking, was a disappointment," he says. "Nothing conspicuous appeared but two gray minarets of rude shape. Many would grudge exposing their lives to win so paltry a prize. But of all that have attempted, none ever succeeded in entering that pile of stones."
Richard Burton carefully worded his varied experiences, and has left about fifty valuable and interesting volumes. Among the best known are 'Sindh,' 'The Lake Regions of Central Africa,' 'Two Trips to Gorilla Land,' and 'Ultima Thule.' With his knowledge of thirty-five languages and dialects he gained an intimate acquaintance with the people among whom he lived, and was enabled to furnish the world much novel information in his strong, straightforward style.
Perhaps his most noteworthy literary achievement was his fine translation of the 'Arabian Nights,' which appeared in 1885. Of this his wife wrote:—
"This grand Arabian work I consider my husband's Magnum Opus.... We were our own printers and our own publishers, and we made, between September 1885 and November 1888, sixteen thousand guineas—six thousand of which went for publishing and ten thousand into our own pockets, and it came just in time to give my husband the comforts and luxuries and freedom that gilded the five last years of his life. When he died there were four florins left, which I put into the poor-box."
This capable soldier and author was very inadequately recompensed. As a soldier, his bravery and long service brought him only the rank of Captain. In the civil service he was given only second-class consulates. The French Geographical Society, and also the Royal Geographical Society of England, each awarded him a gold medal, but the latter employed him upon only one expedition. At the age of sixty-five he was knighted. He had no other honors. This lack of recognition was undoubtedly a mortification, although toward the end of his career he writes philosophically:—
"The press are calling me 'the neglected Englishman,' and I want to express to them the feelings of pride and gratitude with which I have seen the exertions of my brethren of the press to procure for me a tardy justice. The public is a fountain of honor which amply suffices all my aspirations; it is the more honorable as it will not allow a long career to be ignored because of catechisms or creed."
He comforted himself, no doubt, with the belief that his outspoken skepticism was the cause of this lack of advancement, and that he was in some sort a martyr to freedom of thought; but one may be excused for discrediting this in the face of so many contrary instances. Capable men are too scarce to throw aside for such things in this century. The real and sufficient reason was his equally outspoken criticism of his superior officers in every department. A subordinate may and often does know more than his masters; but if he wishes the luxury of advertising the fact, he must pay for it with their ill-will and his own practical suppression.
Lady Burton was also an author; her 'Inner Life in Syria' and 'Arabia, Egypt, and India' are bright and entertaining. But her most important work is the 'Life of Sir Richard F. Burton,' published in 1892, two years after her husband's death. This unorganized mass of interesting material, in spite of carelessness and many faults of style and taste, shows her a ready observer, with a clever and graphic way of stating her impressions.
THE PRETERNATURAL IN FICTION
From the Essay on 'The Book of a Thousand Nights and a
Night'
"As the active world is inferior to the rational soul," says Bacon, with his normal sound sense, "so Fiction gives to Mankind what History denies, and in some measure satisfies the Mind with Shadows when it cannot enjoy the Substance. And as real History gives us not the success of things according to the deserts of vice and virtue, Fiction corrects it and presents us with the fates and fortunes of persons rewarded and punished according to merit." But I would say still more. History paints or attempts to paint life as it is, a mighty maze with or without a plan; Fiction shows or would show us life as it should be, wisely ordered and laid down on fixed lines. Thus Fiction is not the mere handmaid of History: she has a household of her own, and she claims to be the triumph of Art, which, as Goethe remarked, is "Art because it is not Nature." Fancy, la folle du logis, is "that kind and gentle portress who holds the gate of Hope wide open, in opposition to Reason, the surly and scrupulous guard." As Palmerin of England says, and says well:—"For that the report of noble deeds doth urge the courageous mind to equal those who bear most commendation of their approved valiancy; this is the fair fruit of Imagination and of ancient histories." And last, but not least, the faculty of Fancy takes count of the cravings of man's nature for the marvelous, the impossible, and of his higher aspirations for the Ideal, the Perfect; she realizes the wild dreams and visions of his generous youth, and portrays for him a portion of that "other and better world," with whose expectation he would console his age.
The imaginative varnish of 'The Nights' serves admirably as a foil to the absolute realism of the picture in general. We enjoy being carried away from trivial and commonplace characters, scenes, and incidents; from the matter-of-fact surroundings of a workaday world, a life of eating and drinking, sleeping and waking, fighting and loving, into a society and a mise-en-scène which we suspect can exist and which we know do not. Every man, at some turn or term of his life, has longed for supernatural powers and a glimpse of Wonderland. Here he is in the midst of it. Here he sees mighty spirits summoned to work the human mite's will, however whimsical; who can transport him in an eye-twinkling whithersoever he wishes; who can ruin cities and build palaces of gold and silver, gems and jacinths; who can serve up delicate viands and delicious drinks in priceless chargers and impossible cups, and bring the choicest fruits from farthest Orient: here he finds magas and magicians who can make kings of his friends, slay armies of his foes, and bring any number of beloveds to his arms.
And from this outraging probability and outstripping possibility arises not a little of that strange fascination exercised for nearly two centuries upon the life and literature of Europe by 'The Nights,' even in their mutilated and garbled form. The reader surrenders himself to the spell, feeling almost inclined to inquire, "And why may it not be true?" His brain is dazed and dazzled by the splendors which flash before it, by the sudden procession of Jinns and Jinniyahs, demons and fairies, some hideous, others preternaturally beautiful; by good wizards and evil sorcerers, whose powers are unlimited for weal and for woe; by mermen and mermaids, flying horses, talking animals, and reasoning elephants; by magic rings and their slaves, and by talismanic couches which rival the carpet of Solomon. Hence, as one remarks, these Fairy Tales have pleased and still continue to please almost all ages, all ranks, and all different capacities.
Dr. Hawkesworth observes that these Fairy Tales find favor "because even their machinery, wild and wonderful as it is, has its laws; and the magicians and enchanters perform nothing but what was naturally to be expected from such beings, after we had once granted them existence." Mr. Heron "rather supposes the very contrary is the truth of the fact. It is surely the strangeness, the unknown nature, the anomalous character of the supernatural agents here employed, that makes them to operate so powerfully on our hopes, fears, curiosities, sympathies, and in short, on all the feelings of our hearts. We see men and women who possess qualities to recommend them to our favor, subjected to the influence of beings whose good or ill will, power or weakness, attention or neglect, are regulated by motives and circumstances which we cannot comprehend: and hence we naturally tremble for their fate with the same anxious concern as we should for a friend wandering in a dark night amidst torrents and precipices; or preparing to land on a strange island, while he knew not whether he should be received on the shore by cannibals waiting to tear him piecemeal and devour him, or by gentle beings disposed to cherish him with fond hospitality."
Both writers have expressed themselves well; but meseems each has secured, as often happens, a fragment of the truth and holds it to be the whole Truth. Granted that such spiritual creatures as Jinns walk the earth, we are pleased to find them so very human, as wise and as foolish in word and deed as ourselves; similarly we admire in a landscape natural forms like those of Staffa or the Palisades, which favor the works of architecture. Again, supposing such preternaturalisms to be around and amongst us, the wilder and more capricious they prove, the more our attention is excited and our forecasts are baffled, to be set right in the end. But this is not all. The grand source of pleasure in fairy tales is the natural desire to learn more of the Wonderland which is known to many as a word and nothing more, like Central Africa before the last half-century; thus the interest is that of the "personal narrative" of a grand exploration, to one who delights in travels. The pleasure must be greatest where faith is strongest; for instance, amongst imaginative races like the Kelts, and especially Orientals, who imbibe supernaturalism with their mothers' milk. "I am persuaded," writes Mr. Bayle St. John, "that the great scheme of preternatural energy, so fully developed in 'The Thousand and One Nights,' is believed in by the majority of the inhabitants of all the religious professions both in Syria and Egypt." He might have added, "by every reasoning being from prince to peasant, from Mullah to Badawi, between Marocco and Outer Ind."...
Dr. Johnson thus sums up his notice of 'The Tempest':—"Whatever might have been the intention of their author, these tales are made instrumental to the production of many characters, diversified with boundless invention, and preserved with profound skill in nature, extensive knowledge of opinions, and accurate observation of life. Here are exhibited princes, courtiers, and sailors, all speaking in their real characters. There is the agency of airy spirits and of earthy goblins, the operations of magic, the tumults of a storm, the adventures on a desert island, the native effusion of untaught affection, the punishment of guilt, and the final happiness of those for whom our passions and reason are equally interested."
We can fairly say this much and far more for our Tales. Viewed as a tout ensemble in full and complete form, they are a drama of Eastern life, and a Dance of Death made sublime by faith and the highest emotions, by the certainty of expiation and the fullness of atoning equity, where virtue is victorious, vice is vanquished, and the ways of Allah are justified to man. They are a panorama which remains ken-speckle upon the mental retina. They form a phantasmagoria in which archangels and angels, devils and goblins, men of air, of fire, of water, naturally mingle with men of earth; where flying horses and talking fishes are utterly
realistic;
where King and Prince meet fisherman and pauper, lamia and cannibal; where citizen jostles Badawi, eunuch meets knight; the Kazi hob-nobs with the thief; the pure and pious sit down to the same tray with the pander and the procuress; where the professional religionist, the learned Koranist, and the strictest moralist consort with the wicked magician, the scoffer, and the debauchee-poet like Abu Nowas; where the courtier jests with the boor, and where the sweep is bedded with the noble lady. And the characters are "finished and quickened by a few touches swift and sure as the glance of sunbeams." The whole is a kaleidoscope where everything falls into picture; gorgeous palaces and pavilions; grisly underground caves and deadly wolds; gardens fairer than those of the Hesperid; seas dashing with clashing billows upon enchanted mountains; valleys of the Shadow of Death; air-voyages and promenades in the abysses of ocean; the duello, the battle, and the siege; the wooing of maidens and the marriage-rite. All the splendor and squalor, the beauty and baseness, the glamor and grotesqueness, the magic and the mournfulness, the bravery and baseness of Oriental life are here: its pictures of the three great Arab passions—love, war, and fancy—entitle it to be called 'Blood, Musk, and Hashish.' And still more, the genius of the story-teller quickens the dry bones of history, and by adding Fiction to Fact revives the dead past; the Caliphs and the Caliphate return to Baghdad and Cairo, whilst Asmodeus kindly removes the terrace-roof of every tenement and allows our curious glances to take in the whole interior. This is perhaps the best proof of their power. Finally the picture-gallery opens with a series of weird and striking adventures, and shows as a tail-piece an idyllic scene of love and wedlock, in halls before reeking with lust and blood.A JOURNEY IN DISGUISE
From 'The Personal Narrative of a Pilgrimage to El Medinah and Meccah'
The thoroughbred wanderer's idiosyncrasy I presume to be a composition of what phrenologists call "inhabitiveness" and "locality," equally and largely developed. After a long and toilsome march, weary of the way, he drops into the nearest place of rest to become the most domestic of men. For a while he smokes the "pipe of permanence" with an infinite zest; he delights in various siestas during the day, relishing withal a long sleep at night; he enjoys dining at a fixed dinner hour, and wonders at the demoralization of the mind which cannot find means of excitement in chit-chat or small talk, in a novel or a newspaper. But soon the passive fit has passed away; again a paroxysm of ennui coming on by slow degrees, Viator loses appetite, he walks about his room all night, he yawns at conversations, and a book acts upon him as a narcotic. The man wants to wander, and he must do so or he shall die.
After about a month most pleasantly spent at Alexandria, I perceived the approach of the enemy, and as nothing hampered my incomings and outgoings, I surrendered. The world was "all before me," and there was pleasant excitement in plunging single-handed into its chilling depths. My Alexandrian Shaykh, whose heart fell victim to a new "jubbeh" which I had given in exchange for his tattered zaabut, offered me in consideration of a certain monthly stipend the affections of a brother and religious refreshment, proposing to send his wife back to her papa, and to accompany me in the capacity of private chaplain to the other side of Kaf. I politely accepted the "brüderschaft," but many reasons induced me to decline his society and services. In the first place, he spoke the detestable Egyptian jargon. Secondly, it was but prudent to lose the "spoor" between Alexandria and Suez. And thirdly, my "brother" had shifting eyes (symptoms of fickleness), close together (indices of cunning); a flat-crowned head and large ill-fitting lips, signs which led me to think lightly of his honesty, firmness, and courage. Phrenology and physiognomy, be it observed, disappoint you often among civilized people, the proper action of whose brains and features is impeded by the external pressure of education, accident, example, habit, necessity, and what not. But they are tolerably safe guides when groping your way through the mind of man in his natural state, a being of impulse in that chrysalis stage of mental development which is rather instinct than reason. But before my departure there was much to be done.
The land of the Pharaohs is becoming civilized, and unpleasantly so: nothing can be more uncomfortable than its present middle state between barbarism and the reverse. The prohibition against carrying arms is rigid as in Italy; all "violence" is violently denounced; and beheading being deemed cruel, the most atrocious crimes, as well as those small political offenses which in the days of the Mamelukes would have led to a beyship or a bowstring, receive fourfold punishment by deportation to Faizoghli, the local Cayenne. If you order your peasant to be flogged, his friends gather in threatening hundreds at your gates; when you curse your boatman, he complains to your consul; the dragomans afflict you with strange wild notions about honesty; a government order prevents you from using vituperative language to the "natives" in general; and the very donkey-boys are becoming cognizant of the right of man to remain unbastinadoed. Still the old leaven remains behind; here, as elsewhere in "morning-land," you cannot hold your own without employing your fists. The passport system, now dying out of Europe, has sprung up, or rather revived, in Egypt with peculiar vigor. Its good effects claim for it our respect; still we cannot but lament its inconvenience. We, I mean real Easterns. As strangers—even those whose beards have whitened in the land—know absolutely nothing of what unfortunate natives must endure, I am tempted to subjoin a short sketch of my adventures in search of a Tezkireh at Alexandria.
Through ignorance which might have cost me dear but for my friend Larking's weight with the local authorities, I had neglected to provide myself with a passport in England; and it was not without difficulty, involving much unclean dressing and an unlimited expenditure of broken English, that I obtained from the consul at Alexandria a certificate declaring me to be an Indo-British subject named Abdullah, by profession a doctor, aged thirty, and not distinguished—at least so the frequent blanks seemed to denote—by any remarkable conformation of eyes, nose, or cheek. For this I disbursed a dollar. And here let me record the indignation with which I did it. That mighty Britain—the mistress of the seas—the ruler of one-sixth of mankind—should charge five shillings to pay for the shadow of her protecting wing! That I cannot speak my modernized "civis sum Romanus" without putting my hand into my pocket, in order that these officers of the Great Queen may not take too ruinously from a revenue of fifty-six millions! Oh the meanness of our magnificence! the littleness of our greatness!
My new passport would not carry me without the Zabit or Police Magistrate's counter-signature, said the consul. Next day I went to the Zabit, who referred me to the Muhafiz (Governor) of Alexandria, at whose gate I had the honor of squatting at least three hours, till a more compassionate clerk vouchsafed the information that the proper place to apply to was the Diwan Kharijiyeh (the Foreign Office). Thus a second day was utterly lost. On the morning of the third I started as directed for the place, which crowns the Headland of Figs. It is a huge and couthless shell of building in parallelogrammic form, containing all kinds of public offices in glorious confusion, looking with their glaring whitewashed faces upon a central court, where a few leafless wind-wrung trees seem struggling for the breath of life in an eternal atmosphere of clay, dust, and sun-blaze.
The first person I addressed was a Kawwas or police officer, who, coiled comfortably up in a bit of shade fitting his person like a robe, was in full enjoyment of the Asiatic "Kaif." Having presented the consular certificate and briefly stated the nature of my business, I ventured to inquire what was the right course to pursue for a visá.
They have little respect for Dervishes, it appears, at Alexandria! "M'adri" (Don't know), growled the man of authority, without moving anything but the quantity of tongue necessary for articulation.
Now there are three ways of treating Asiatic officials,—by bribe, by bullying, or by bothering them with a dogged perseverance into attending to you and your concerns. The latter is the peculiar province of the poor; moreover, this time I resolved for other reasons to be patient. I repeated my question in almost the same words. "Ruh!" (Be off) was what I obtained for all reply. By this time the questioned went so far as to open his eyes. Still I stood twirling the paper in my hands, and looking very humble and very persevering, till a loud "Ruh ya Kalb!" (Go, O dog!) converted into a responsive curse the little speech I was preparing about the brotherhood of El-Islam and the mutual duties obligatory on true believers. I then turned away slowly and fiercely, for the next thing might have been a cut with the Kurbaj [bastinado], and by the hammer of Thor! British flesh and blood could never have stood that.
After which satisfactory scene,—for satisfactory it was in one sense, proving the complete fitness of the Dervish's dress,—I tried a dozen other promiscuous sources of information,—policemen, grooms, scribes, donkey-boys, and idlers in general. At length, wearied of patience, I offered a soldier some pinches of tobacco and promised him an Oriental sixpence if he would manage the business for me. The man was interested by the tobacco and the pence; he took my hand, and inquiring the while he went along, led me from place to place till, mounting a grand staircase, I stood in the presence of Abbas Effendi, the governor's Naib or deputy.
It was a little whey-faced black-bearded Turk, coiled up in the usual conglomerate posture upon a calico-covered divan, at the end of a long bare large-windowed room. Without deigning even to nod the head which hung over his shoulder with transcendent listlessness and affectation of pride, in answer to my salams and benedictions, he eyed me with wicked eyes and faintly ejaculated "Minent?" Then hearing that I was a Dervish and doctor,—he must be an Osmanli Voltairian, that little Turk,—the official snorted a contemptuous snort. He condescendingly added, however, that the proper source to seek was "Taht," which, meaning simply "below," conveyed rather imperfect information in a topographical point of view to a stranger. At length however my soldier guide found out that a room in the custom-house bore the honorable appellation of "Foreign Office." Accordingly I went there, and after sitting at least a couple of hours at the bolted door in the noonday sun, was told, with a fury which made me think I had sinned, that the officer in whose charge the department was had been presented with an olive-branch in the morning, and consequently that business was not to be done that day. The angry-faced official communicated the intelligence to a large group of Anadolian, Caramanian, Bosniac, and Roumelian Turks,—sturdy, undersized, broad-shouldered, bare-legged, splay-footed, horny-fisted, dark-browed, honest-looking mountaineers, who were lounging about with long pistols and yataghans stuck in their broad sashes, head-gear composed of immense tarbooshes with proportionate turbans coiled round them, and two or three suits of substantial clothes—even at this season of the year—upon their shoulders.
Like myself they had waited some hours, but they were not patient under disappointment: they bluntly told the angry official that he and his master were a pair of idlers, and the curses that rumbled and gurgled in their hairy throats as they strode towards the door sounded like the growling of wild beasts.
Thus was another day truly Orientally lost. On the morrow however I obtained permission, in the character of Dr. Abdullah, to visit any part of Egypt I pleased, and to retain possession of my dagger and pistols.
And now I must explain what induced me to take so much trouble about a passport. The home reader naturally inquires, Why not travel under your English name?
For this reason. In the generality of barbarous countries you must either proceed, like Bruce, preserving the "dignity of manhood" and carrying matters with a high hand, or you must worm your way by timidity and subservience; in fact, by becoming an animal too contemptible for man to let or injure. But to pass through the Holy Land you must either be a born believer, or have become one; in the former case you may demean yourself as you please, in the latter a path is ready prepared for you. My spirit could not bend to own myself a Burma, a renegade—to be pointed at and shunned and catechized, an object of suspicion to the many and of contempt to all. Moreover, it would have obstructed the aim of my wanderings. The convert is always watched with Argus eyes, and men do not willingly give information to a "new Moslem," especially a Frank: they suspect his conversion to be a feigned or a forced one, look upon him as a spy, and let him see as little of life as possible. Firmly as was my heart set upon traveling in Arabia, by Heaven! I would have given up the dear project rather than purchase a doubtful and partial success at such a price. Consequently I had no choice but to appear as a born believer, and part of my birthright in that respectable character was toil and trouble in obtaining a tezkirah.
Then I had to provide myself with certain necessaries for the way. These were not numerous. The silver-mounted dressing-case is here supplied by a rag containing a miswak, a bit of soap, and a comb—wooden, for bone and tortoise-shell are not, religiously speaking, correct. Equally simple was my wardrobe: a change or two of clothing. The only article of canteen description was a zemzemiyah, a goatskin water-bag, which communicates to its contents, especially when new, a ferruginous aspect and a wholesome though hardly an attractive flavor of tanno-gelatine. This was a necessary; to drink out of a tumbler, possibly fresh from pig-eating lips, would have entailed a certain loss of reputation. For bedding and furniture I had a coarse Persian rug—which, besides being couch, acts as chair, table, and oratory,—a cotton-stuffed chintz-covered pillow, a blanket in case of cold, and a sheet, which does duty for tent and mosquito curtains in nights of heat. As shade is a convenience not always procurable, another necessary was a huge cotton umbrella of Eastern make, brightly yellow, suggesting the idea of an overgrown marigold. I had also a substantial housewife, the gift of a kind friend: it was a roll of canvas, carefully soiled, and garnished with needles and thread, cobblers' wax, buttons, and other such articles. These things were most useful in lands where tailors abound not; besides which, the sight of a man darning his coat or patching his slippers teems with pleasing ideas of humility. A dagger, a brass inkstand and penholder stuck in the belt, and a mighty rosary, which on occasion might have been converted into a weapon of offense, completed my equipment. I must not omit to mention the proper method of carrying money, which in these lands should never be intrusted to box or bag. A common cotton purse secured in a breast pocket (for Egypt now abounds in that civilized animal the pickpocket) contained silver pieces and small change. My gold, of which I carried twenty-five sovereigns, and papers, were committed to a substantial leathern belt of Maghrabi manufacture, made to be strapped round the waist under the dress. This is the Asiatic method of concealing valuables, and a more civilized one than ours in the last century, when Roderick Random and his companion "sewed their money between the lining and the waistband of their breeches, except some loose silver for immediate expense on the road." The great inconvenience of the belt is its weight, especially where dollars must be carried, as in Arabia, causing chafes and inconvenience at night. Moreover it can scarcely be called safe. In dangerous countries wary travelers will adopt surer precautions.
A pair of common native khurjin or saddle-bags contained my wardrobe, the "bed," readily rolled up into a bundle; and for a medicine chest I bought a pea-green box with red and yellow flowers, capable of standing falls from a camel twice a day.
The next step was to find out when the local steamer would start for Cairo, and accordingly I betook myself to the Transit Office. No vessel was advertised; I was directed to call every evening till satisfied. At last the fortunate event took place: a "weekly departure," which by-the-by had occurred once every fortnight or so, was in order for the next day. I hurried to the office, but did not reach it till past noon—the hour of idleness. A little dark gentleman, so formed and dressed as exactly to resemble a liver-and-tan bull-terrier, who with his heels on the table was dozing, cigar in mouth, over the last Galignani, positively refused after a time,—for at first he would not speak at all,—to let me take my passage till three in the afternoon. I inquired when the boat started, upon which he referred me, as I had spoken bad Italian, to the advertisement. I pleaded inability to read or write, whereupon he testily cried "Alle nove! alle nove!" (At nine! at nine!) Still appearing uncertain, I drove him out of his chair, when he rose with a curse and read "8 a.m." An unhappy Eastern, depending upon what he said, would have been precisely one hour too late.
Thus were we lapsing into the real good old Indian style of doing business. Thus Indicus orders his first clerk to execute some commission; the senior, having "work" upon his hands, sends a junior; the junior finds the sun hot, and passes on the word to a "peon"; the peon charges a porter with the errand; and the porter quietly sits or dozes in his place, trusting that fate will bring him out of the scrape, but firmly resolved, though the shattered globe fall, not to stir an inch.
The reader, I must again express a hope, will pardon the egotism of these descriptions: my object is to show him how business is carried on in these hot countries—business generally. For had I, instead of being Abdullah the Dervish, been a rich native merchant, it would have been the same. How many complaints of similar treatment have I heard in different parts of the Eastern world! and how little can one realize them without having actually experienced the evil! For the future I shall never see a "nigger" squatting away half a dozen mortal hours in a broiling sun, patiently waiting for something or for some one, without a lively remembrance of my own cooling of the calces at the custom-house of Alexandria.
At length, about the end of May, all was ready. Not without a feeling of regret I left my little room among the white myrtle blossoms and the oleander flowers. I kissed with humble ostentation my kind host's hand in presence of his servants, bade adieu to my patients, who now amounted to about fifty, shaking hands with all meekly and with religious equality of attention, and, mounted in a "trap" which looked like a cross between a wheel-barrow and dog-cart, drawn by a kicking, jibbing, and biting mule, I set out for the steamer.
EN ROUTE
From 'A Pilgrimage to El Medinah and Meccah'
At 3 p.m. we left El Zaribah, traveling towards the S.W., and a wondrously picturesque scene met the eye. Crowds hurried along, habited in the pilgrim garb, whose whiteness contrasted strangely with their black skins, their newly shaven heads glistening in the sun, and their long black hair streaming in the wind. The rocks rang with shouts of "Labbayk! Labbayk!" At a pass we fell in with the Wahhabis, accompanying the Baghdad caravan, screaming "Here am I"; and guided by a large loud kettle-drum, they followed in double file the camel of a standard-bearer, whose green flag bore in huge white letters the formula of the Moslem creed. They were wild-looking mountaineers, dark and fierce, with hair twisted into thin dalik or plaits: each was armed with a long spear, a matchlock, or a dagger. They were seated upon coarse wooden saddles, without cushions or stirrups, a fine saddle-cloth alone denoting a chief. The women emulated the men; they either guided their own dromedaries, or sitting in pillion, they clung to their husbands; veils they disdained, and their countenances certainly belonged not to a "soft sex." These Wahhabis were by no means pleasant companions. Most of them were followed by spare dromedaries, either unladen or carrying water-skins, fodder, fuel, and other necessaries for the march. The beasts delighted in dashing furiously through our file, which, being colligated, was thrown each time into the greatest confusion. And whenever we were observed smoking, we were cursed aloud for infidels and idolaters.
Looking back at El Zaribah, soon after our departure, I saw a heavy nimbus settle upon the hilltops, a sheet of rain being stretched between it and the plain. The low grumbling of thunder sounded joyfully in our ears. We hoped for a shower, but were disappointed by a dust-storm, which ended with a few heavy drops. There arose a report that the Bedouins had attacked a party of Meccans with stones,—classical Arabian missiles,—and the news caused men to look exceeding grave.
At 5 p.m. we entered the wide bed of the fiumara, down which we were to travel all night. Here the country falls rapidly towards the sea, as the increasing heat of the air, the direction of the
water-courses
, and signs of violence in the torrent-bed show. The fiumara varies in breadth from 150 feet to three-quarters of a mile; its course, I was told, is towards the southwest, and it enters the sea near Jeddah. The channel is a coarse sand, with here and there masses of sheet rock and patches of thin vegetation.At about half-past 5 p.m. we entered a suspicious-looking place. On the right was a stony buttress, along whose base the stream, when there is one, flows; and to this depression was our road limited by the rocks and thorn-trees, which filled the other half of the channel. The left side was a precipice, grim and barren, but not so abrupt as its brother. Opposite us the way seemed barred by piles of hills, crest rising above crest into the far blue distance. Day still smiled upon the upper peaks, but the lower slopes and the fiumara bed were already curtained with gray sombre shade.
A damp seemed to fall upon our spirits as we approached this Valley Perilous. I remarked with wonder that the voices of the women and children sank into silence, and the loud Labbaykas of the pilgrims were gradually stilled. Whilst still speculating upon the cause of this phenomenon, it became apparent. A small curl of smoke, like a lady's ringlet, on the summit of the right-hand precipice, caught my eye, and simultaneous with the echoing crack of the matchlock a high-trotting dromedary in front of me rolled over upon the sands. A bullet had split his heart, throwing his rider a goodly somerset of five or six yards.
Ensued terrible confusion; women screamed, children shrieked, and men vociferated, each one striving with might and main to urge his animal out of the place of death. But the road being narrow, they only managed to jam the vehicles in a solid immovable mass. At every matchlock shot a shudder ran through the huge body, as when the surgeon's scalpel touches some more sensitive nerve. The irregular horsemen, perfectly useless, galloped up and down over the stones, shouting to and ordering one another. The Pacha of the army had his carpet spread at the foot of the left-hand precipice, and debated over his pipe with the officers what ought to be done. No good genius whispered "Crown the heights."
Then it was that the conduct of the Wahhabis found favor in my eyes. They came up, galloping their camels,—
"Torrents less rapid and less rash.—"
with their elf-locks tossing in the wind, and their flaring matches casting a strange lurid light over their features. Taking up a position, one body began to fire upon the Utaybah robbers, whilst two or three hundred, dismounting, swarmed up the hill under the guidance of the Sherif Zayd. I had remarked this nobleman at El Medinah as a model specimen of the pure Arab. Like all Sherifs, he is celebrated for bravery, and has killed many with his own hand. When urged at El Zaribah to ride into Meccah, he swore that he would not leave the caravan till in sight of the walls; and fortunately for the pilgrims, he kept his word. Presently the firing was heard far in our rear—the robbers having fled; the head of the column advanced, and the dense body of the pilgrims opened out. Our forced halt was now exchanged for a flight. It required much management to steer our desert-craft clear of danger; but Shaykh Masud was equal to the occasion. That many were lost was evident by the boxes and baggage that strewed the shingles. I had no means of ascertaining the number of men killed and wounded: reports were contradictory, and exaggeration unanimous. The robbers were said to be 150 in number; their object was plunder, and they would eat the shot camels. But their principal ambition was the boast "We, the Utaybah, on such and such a night stopped the Sultan's mahmal one whole hour in the pass."
At the beginning of the skirmish I had primed my pistols, and sat with them ready for use. But soon seeing that there was nothing to be done, and wishing to make an impression,—nowhere does Bobadil now "go down" but in the East,—I called aloud for my supper. Shaykh Nur, exanimate with fear, could not move. The boy Mohammed ejaculated only an "Oh, sir!" and the people around exclaimed in disgust, "By Allah! he eats!" Shaykh Abdullah, the Meccan, being a man of spirit, was amused by the spectacle. "Are these Afghan manners, Effendim?" he inquired from the shugduf behind me. "Yes," I replied aloud, "in my country we always dine before an attack of robbers, because that gentry is in the habit of sending men to bed supperless." The Shaykh laughed aloud, but those around him looked offended. I thought the bravado this time mal placé; but a little event which took place on my way to Jeddah proved that it was not quite a failure.
As we advanced our escort took care to fire every large dry asclepias, to disperse the shades which buried us. Again the scene became wondrous wild:—
"Full many a waste I've wander'd o'er, Clomb many a crag, cross'd many a shore, But, by my halidome, A scene so rude, so wild as this, Yet so sublime in barrenness, Ne'er did my wandering footsteps press, Where'er I chanced to roam."
On either side were ribbed precipices, dark, angry, and towering above, till their summits mingled with the glooms of night; and between them formidable looked the chasm, down which our host hurried with shouts and discharges of matchlocks. The torch-smoke and the night-fires of flaming asclepias formed a canopy, sable above and livid red below, which hung over our heads like a sheet, and divided the cliffs into two equal parts. Here the fire flashed fiercely from a tall thorn, that crackled and shot up showers of sparks into the air; there it died away in lurid gleams, which lit up a truly Stygian scene. As usual, however, the picturesque had its inconveniences. There was no path. Rocks, stone-banks, and trees obstructed our passage. The camels, now blind in darkness, then dazzled by a flood of light, stumbled frequently; in some places slipping down a steep descent, in others sliding over a sheet of mud. There were furious quarrels and fierce language between camel-men and their hirers, and threats to fellow-travelers; in fact, we were united in discord. I passed that night crying "Hai! Hai!" switching the camel, and fruitlessly endeavoring to fustigate Masud's nephew, who resolutely slept upon the water-bags. During the hours of darkness we made four or five halts, when we boiled coffee and smoked pipes, but man and beasts were beginning to suffer from a deadly fatigue.
Dawn found us still traveling down the fiumara, which here is about one hundred yards broad. The granite hills on both sides were less precipitous, and the borders of the torrent-bed became natural quays of stiff clay, which showed a water-mark of from twelve to fifteen feet in height. In many parts the bed was muddy, and the moist places, as usual, caused accidents. I happened to be looking back at Shaykh Abdullah, who was then riding in old Ali bin Ya Sin's fine shugduf; suddenly the camel's four legs disappeared from under him, his right side flattening the ground, and the two riders were pitched severally out of the smashed vehicle. Abdullah started up furious, and abused the Bedouins, who were absent, with great zest. "Feed these Arabs," he exclaimed, quoting a Turkish proverb, "and they will fire at Heaven!" But I observed that, when Shaykh Masud came up, the citizen was only gruff.
We then turned northward, and sighted El Mazik, more generally known as Wady Laymun, the Valley of Limes. On the right bank of the fiumara stood the Meccan Sherif's state pavilion, green and gold: it was surrounded by his attendants, and prepared to receive the Pacha of the caravan. We advanced half a mile, and encamped temporarily in a hill-girt bulge of the fiumara bed. At 8 a.m. we had traveled about twenty-four miles from El Zaribah, and the direction of our present station was S. W. 50°.
Shaykh Masud allowed us only four hours' halt; he wished to precede the main body. After breaking our fast joyously upon limes, pomegranates, and fresh dates, we sallied forth to admire the beauties of the place. We are once more on classic ground, the ground of the ancient Arab poets:—
"Deserted is the village—waste the halting place and home At Mina; o'er Rijam and Ghul wild beasts unheeded roam; On Rayyan hill the channel lines have left a naked trace, Time-worn, as primal Writ that dints the mountains flinty face;"—
and this wady, celebrated for the purity of its air, has from remote ages been a favorite resort of the Meccans. Nothing can be more soothing to the brain than the dark-green foliage of the limes and pomegranates; and from the base of the southern hill bursts a bubbling stream, whose
"Chiare, fresche e dolci acque"
flow through the garden, filling them with the most delicious of melodies, and the gladdest sound which nature in these regions knows.
Exactly at noon Masud seized the halter of the foremost camel, and we started down the fiumara. Troops of Bedouin girls looked over the orchard walls laughingly, and children came out to offer us fresh fruit and sweet water. At 2 p.m., traveling southwest, we arrived at a point where the torrent-bed turns to the right, and quitting it, we climbed with difficulty over a steep ridge of granite. Before three o'clock we entered a hill-girt plain, which my companions called "Sola." In some places were clumps of trees, and scattered villages warned us that we were approaching a city. Far to the left rose the blue peaks of Taif, and the mountain road, a white thread upon the nearer heights, was pointed out to me. Here I first saw the tree, or rather shrub, which bears the balm of Gilead, erst so celebrated for its tonic and stomachic properties. I told Shaykh to break off a twig, which he did heedlessly. The act was witnessed by our party with a roar of laughter, and the astounded Shaykh was warned that he had become subject to an atoning sacrifice. Of course he denounced me as the instigator, and I could not fairly refuse assistance. The tree has of late years been carefully described by many botanists; I will only say that the bark resembled in color a cherry-stick pipe, the inside was a light yellow, and the juice made my fingers stick together.
At 4 p.m. we came to a steep and rocky pass, up which we toiled with difficulty. The face of the country was rising once more, and again presented the aspect of numerous small basins divided and surrounded by hills. As we jogged on we were passed by the cavalcade of no less a personage than the Sherif of Meccah. Abd el Muttalib bin Ghalib is a dark, beardless old man with African features, derived from his mother. He was plainly dressed in white garments and a white muslin turban, which made him look jet-black; he rode an ambling mule, and the only emblem of his dignity was the large green satin umbrella borne by an attendant on foot. Scattered around him were about forty matchlock-men, mostly slaves. At long intervals, after their father, came his four sons, Riza Bey, Abdullah, Ali, and Ahmed, the latter still a child. The three elder brothers rode splendid dromedaries at speed; they were young men of light complexion, with the true Meccan cast of features, showily dressed in bright-colored silks, and armed, to denote their rank, with sword and gold-hilted dagger.
We halted as evening approached, and strained our eyes, but all in vain, to catch sight of Meccah, which lies in a winding valley. By Shaykh Abdullah's direction I recited, after the usual devotions, the following prayer. The reader is forewarned that it is difficult to preserve the flowers of Oriental rhetoric in a European tongue.
"O Allah! verily this is thy safeguard (Amn) and thy Sanctuary (Haram)! Into it whoso entereth becometh safe (Amin). So deny (Harrim) my flesh and blood, my bones and skin, to hell-fire. O Allah! Save me from thy wrath on the day when thy servants shall be raised from the dead. I conjure thee by this that thou art Allah, besides whom is none (thou only), the merciful, the compassionate. And have mercy upon our lord Mohammed, and upon the progeny of our lord Mohammed, and upon his followers, one and all!" This was concluded with the "Talbiyat," and with an especial prayer for myself.
We again mounted, and night completed our disappointment. About 1 a.m. I was aroused by general excitement. "Meccah! Meccah!" cried some voices. "The Sanctuary! O the Sanctuary!" exclaimed others; and all burst into loud "Labbayk," not unfrequently broken by sobs. I looked out from my litter, and saw by the light of the southern stars the dim outlines of a large city, a shade darker than the surrounding plain. We were passing over the last ridge by a "winding path" flanked on both sides by watch-towers, which command the "Darb el Maala," or road leading from the north into Meccah. Thence we passed into the Maabidah (northern suburb), where the Sherif's palace is built. After this, on the left hand, came the deserted abode of the Sherif bin Aun, now said to be a "haunted house."106 Opposite to it lies the Jannat el Maala, the holy cemetery of Meccah. Thence, turning to the right, we entered the Sulaymaniyah or Afghan quarter. Here the boy Mohammed, being an inhabitant of the Shamiyah or Syrian ward, thought proper to display some apprehension. These two are on bad terms; children never meet without exchanging volleys of stones, and men fight furiously with quarter-staves. Sometimes, despite the terrors of religion, the knife and sabre are drawn. But these hostilities have their code. If a citizen be killed, there is a subscription for blood-money. An inhabitant of one quarter, passing singly through another, becomes a guest; once beyond the walls, he is likely to be beaten to insensibility by his hospitable foes.
At the Sulaymaniyah we turned off the main road into a by-way, and ascended by narrow lanes the rough heights of Jebel Hindi, upon which stands a small whitewashed and crenellated building called a "fort." Thence descending, we threaded dark streets, in places crowded with rude cots and dusky figures, and finally at 2 a.m. we found ourselves at the door of the boy Mohammed's house.
We arrived on the morning of Sunday the 7th Zu'l Hijjah (11th September, 1853), and had one day before the beginning of the pilgrimage to repose and visit the Haram. From El Medinah to Meccah the distance, according to my calculation, was 248 English miles, which was accomplished in eleven marches.
ROBERT BURTON
(1577-1640)
I cannot conceive what made the accurate Niebuhr fall into the strange error that "apparitions are unknown in Arabia." Arabs fear to sleep alone, to enter the bath at night, to pass by cemeteries during dark, and to sit amongst ruins, simply for fear of apparitions. And Arabia, together with Persia, has supplied half the Western World—Southern Europe—with its ghost stories and tales of angels, demons, and fairies. To quote Milton, the land is struck "with superstition as with a planet."
